high beam JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 445 of 1803

front of the vehicle. In certain markets where
required, a headlamp leveling actuator motor is
included on each headlamp.
²Park Lamps- The park lamps include the front
park lamps and front side marker lamps that are
integral to the front lamp units mounted at each end
of the bumper fascia at the front of the vehicle, as
well as the rear park lamps and rear side marker
lamps that are integral to the rear lamp units
mounted to the back of the quarter panel on each
side of the tailgate at the rear of the vehicle. The
park lamps include a license plate lamp or lamps,
depending upon the requirements of the market for
which the vehicle is manufactured. Vehicles with a
license plate tub located near the left end of the rear
bumper fascia have a single lamp, while vehicles
with a license plate module located on the spare tire
carrier have two license plate lamps. In certain mar-
kets where required, a front position lamp that is
integral to each headlamp unit is illuminated instead
of the front park lamps and front side marker lamps
in the park lamps circuit; and, a rectangular, red
reflector is located on the rear bumper fascia just
inboard and below each rear lamp unit.
²Rear Fog Lamps- Rear fog lamps are avail-
able only in certain markets where they are required
equipment. The rear fog lamps are integral to the
rear lamp units mounted to the back of the quarter
panel on each side of the tailgate at the rear of the
vehicle.
²Turn Signal Lamps- The turn signal lamps
include the front turn signal and front side marker
lamps that are integral to the front lamp units
mounted at each end of the bumper fascia at the
front of the vehicle, as well as rear turn signal lamps
that are integral to the rear lamp units mounted to
the back of the quarter panel on each side of the tail-
gate at the rear of the vehicle. In certain markets
where required, a repeater lamp unit mounted to
each front fender just behind the front wheel opening
is illuminated instead of the front side marker lamp
in each turn signal lamp circuit.
Other components of the exterior lighting system
for this model include:
²Combination Flasher- An electronic combina-
tion flasher is integral to the hazard warning switch
in the center of the instrument panel.
²Backup Lamp Switch- Vehicles equipped with
a manual transmission have a plunger-type backup
lamp switch located on the transmission housing. ATransmission Range Sensor (TRS) integral to the
solenoid pack on the valve body of the optional elec-
tronic automatic transmission performs the backup
lamp switch function on models that are so equipped.
²Brake Lamp Switch- A plunger-type brake
lamp switch is located on the steering column sup-
port bracket under the instrument panel and actu-
ated by the brake pedal arm.
²Body Control Module- The Body Control
Module (BCM) is located on the Junction Block (JB)
under the driver side outboard end of the instrument
panel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/BODY CONTROL MODULE
- DESCRIPTION).
²Daytime Running Lamp Relay- Vehicles
manufactured for sale in Canada use a solid state
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL) relay installed in the
Junction Block (JB) instead of the conventional high
beam relay.
²Front Fog Lamp Relay- Vehicles equipped
with the optional front fog lamps have a front fog
lamp relay located in the Junction Block (JB).
²Hazard Switch- The hazard switch is located
near the center of the instrument panel and includes
the integral electronic combination flasher circuitry
for the hazard warning system and the turn signal
system.
²Headlamp Leveling Motor- A headlamp lev-
eling actuator motor is located on the back of each
headlamp housing of vehicles manufactured for cer-
tain markets where this equipment is required.
²Headlamp Leveling Switch- A thumbwheel
actuated headlamp leveling switch is mounted in the
driver side inboard instrument panel trim bezel of
vehicles manufactured for certain markets where this
equipment is required.
²High Beam Relay- A high beam relay is
located in the Junction Block (JB) of all vehicles
except those that are manufactured for sale in Can-
ada. Canadian vehicles have a solid state Daytime
Running Lamps (DRL) relay in the JB instead of the
high beam relay.
²Low Beam Relay- A low beam relay is located
in the Junction Block (JB) of all vehicles.
²Multi-Function Switch- The multi-function
switch is located on the top of the steering column,
just below the steering wheel. The multi-function
switch includes a left (lighting) control stalk and a
right (wiper) control stalk. The left control stalk is
dedicated to providing almost all of the driver con-
1 - HEADLAMP UNIT (2)
2 - REPEATER LAMP UNIT (2)
3 - FRONT POSITION LAMP (2)
4 - FRONT LAMP UNIT (2)
5 - FRONT FOG LAMP (2)6 - CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP UNIT
7 - REAR LAMP UNIT
8 - LICENSE PLATE LAMP UNIT
8L - 4 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORKJ
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 446 of 1803

trols for both the exterior and interior lighting sys-
tems.
²Park Lamp Relay- A park lamp relay is
located in the Junction Block (JB) of all vehicles.
²Rear Fog Lamp Relay- Vehicles manufac-
tured for certain markets where rear fog lamps are
required equipment have a rear fog lamp relay
located in the Junction Block (JB).
²Trailer Tow Adapter- Vehicles equipped with
a factory-installed trailer towing package have an
adapter provided that adapts the factory-installed
heavy duty 7-way trailer tow connector to a conven-
tional 4-way light duty connector.
²Trailer Tow Connector- Vehicles equipped
with a factory-installed trailer towing package have a
heavy duty 7-way trailer tow connector installed in a
bracket on the trailer hitch receiver.
²Trailer Tow Relays- Vehicles equipped with a
factory-installed trailer towing package have a con-
nector bank containing four relays located behind the
right quarter trim panel and over the right rear
wheel housing. The four relays are used to supply
fused ignition switch output (run), brake lamps, right
turn signal, and left turn signal outputs to a trailer
through the trailer tow wiring and connectors.
Hard wired circuitry connects the exterior lighting
system components to the electrical system of the
vehicle. These hard wired circuits are integral to sev-
eral wire harnesses, which are routed throughout the
vehicle and retained by many different methods.
These circuits may be connected to each other, to the
vehicle electrical system and to the exterior lighting
system components through the use of a combination
of soldered splices, splice block connectors, and many
different types of wire harness terminal connectors
and insulators. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
further details on wire harness routing and reten-
tion, as well as pin-out and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
OPERATION
Following are paragraphs that briefly describe the
operation of each of the major exterior lighting sys-
tems. The hard wired circuits and components of the
exterior lighting systems may be diagnosed and
tested using conventional diagnostic tools and proce-
dures. However, conventional diagnostic methods
may not prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the Body
Control Module (BCM), the ElectroMechanical
Instrument Cluster (EMIC), the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM), or the Programmable Communica-
tions Interface (PCI) data bus network. The most
reliable, efficient, and accurate means to diagnose
the BCM, the EMIC, the PCM, and the PCI data busnetwork inputs and outputs related to the various
exterior lighting systems requires the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information.
BACKUP LAMPS
The backup (or reverse) lamps have a path to
ground at all times through their connection to the
rear lighting wire harness from a take out of the rear
body wire harness with an eyelet terminal connector
that is secured by a ground screw to the base of the
right D-pillar behind the quarter trim panel. The
backup lamps receive battery current from a fused
ignition switch output (run) fuse in the Junction
Block (JB) on the back-up lamp feed circuit only
when the backup lamp switch (manual transmission),
or backup lamp switch circuit of the Transmission
Range Sensor (TRS - electronic automatic transmis-
sion) is closed by the gearshift mechanism within the
transmission.
BRAKE LAMPS
The brake (or stop) lamps have a path to ground at
all times through their connection to the rear light-
ing wire harness from a take out of the rear body
wire harness with an eyelet terminal connector that
is secured by a screw to the base of the right D-pillar
behind the quarter trim panel. The Center High
Mounted Stop Lamp (CHMSL) has a path to ground
at all times through its connection to the rear body
wire harness from a take out of the rear body wire
harness with an eyelet terminal connector that is
secured by a ground screw to the driver side D-pillar
(left side D-pillar for left-hand drive, right side D-pil-
lar for right-hand drive) behind the quarter trim
panel. The brake lamps and CHMSL receive battery
current from a fused B(+) fuse in the Junction Block
(JB) on the brake lamp switch output circuit only
when the brake lamp switch circuit of the brake
lamp switch is closed by the brake pedal arm.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMPS
Vehicles manufactured for sale in Canada illumi-
nate the high beam filament at a reduced intensity
when the engine is running and the exterior lamps
are turned off. This feature is enabled by the Body
Control Module (BCM) and a solid state Daytime
Running Lamps (DRL) relay, which is installed in the
Junction Block (JB) and the high beam relay is omit-
ted. When the BCM monitors an engine speed signal
of greater than 450 RPM and the status of the exte-
rior lighting switch input from the multi-function
switch is Off, the BCM duty cycles the DRL relay to
produce illumination of the headlamp high beam fil-
aments at a reduced intensity. The BCM also pro-
vides normal headlamp high beam operation through
the DRL relay on vehicles so equipped. When the
KJLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 5
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 447 of 1803

DRL relay is energized, it provides battery current
from a fused B(+) fuse in the JB to the headlamp
high beam filament through the DRL relay output
circuit.
FRONT FOG LAMPS
Vehicles equipped with optional front fog lamps
have a premium Body Control Module (BCM), a front
fog lamp relay installed in the Junction Block (JB),
and a front fog lamp switch integral to the left (light-
ing) control stalk of the multi-function switch. The
front fog lamps have a path to ground at all times
through their connection to the front fascia wire har-
ness from two take outs of the headlamp and dash
wire harness with eyelet terminal connectors that
are secured by ground screws to the left inner fender
shield in the engine compartment. The BCM controls
front fog lamp operation by monitoring the exterior
lighting switch input from the multi-function switch,
then energizing or de-energizing the front fog lamp
relay control coil; and, by sending the appropriate
electronic message to the instrument cluster over the
Programmable Communications Interface (PCI) data
bus to turn the front fog lamp indicator on or off.
When the front fog lamp relay is energized, it pro-
vides battery current from a fused B(+) fuse in the
JB to the front fog lamps through the front fog lamp
relay output circuit. The BCM provides a battery
saver (load shedding) feature for the front fog lamps,
which will turn these lamps off if they are left on for
more than about eight minutes with the ignition
switch in the Off position. In certain markets where
required, the front fog lamps are also turned off by
the BCM whenever the headlamp high beams are
selected. Each front fog lamp includes an integral
adjustment screw to be used for static aiming the fog
lamp beams.
HAZARD WARNING LAMPS
With the hazard switch in the On position, the
hazard warning system is activated causing the haz-
ard switch button illumination lamp, the right and
left turn signal indicators, and the right and left turn
signal lamps to flash on and off. When the hazard
warning system is activated, the circuitry within the
hazard switch and electronic combination flasher
unit will repeatedly energize and de-energize two
internal relays that switch battery current from a
fused B(+) fuse in the Junction Block (JB) to the
right side and left side turn signal indicators, and
turn signal lamps through the right and left turn sig-
nal circuits. The flashing of the hazard switch button
illumination lamp is performed internally by the haz-
ard switch and combination flasher unit circuit
board. The hazard warning lamps can also be ener-
gized by the Body Control Module (BCM) through ahazard lamp control circuit input to the hazard
switch and combination flasher unit.
HEADLAMPS
The headlamp system includes the Body Control
Module (BCM), a low beam relay installed in the
Junction Block (JB), a high beam relay installed in
the JB (except Canada), a solid state Daytime Run-
ning Lamps (DRL) relay installed in the JB (Canada
only), and the exterior lighting (headlamp and dim-
mer) switches integral to the left (lighting) control
stalk of the multi-function switch. The headlamp
bulbs have a path to ground at all times through
their connection to the grille opening reinforcement
wire harness from two take outs of the headlamp and
dash wire harness with eyelet terminal connectors
that are secured by ground screws to the left inner
fender shield in the engine compartment. The BCM
controls the headlamp operation by monitoring the
exterior lighting switch inputs from the multi-func-
tion switch, then energizing or de-energizing the con-
trol coils of the low beam relay, the high beam relay,
or the solid state circuitry of the DRL relay; and, by
sending the appropriate electronic message to the
instrument cluster over the Programmable Commu-
nications Interface (PCI) data bus to turn the high
beam indicator on or off. When each respective relay
is energized, it provides battery current from a fused
B(+) fuse in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
through a relay (low beam, high beam, or DRL) out-
put circuit and four separate fuses in the JB through
individual fused right and left, low and high beam
output circuits to the appropriate headlamp bulb fil-
aments. The BCM provides a battery saver (load
shedding) feature for the headlamps, which will turn
these lamps off if they are left on for more than
about eight minutes with the ignition switch in the
Off position; and, a headlamp delay feature with a
DRBIIItscan tool programmable delay interval.
Each headlamp includes an integral adjustment
screw to be used for static aiming of the headlamp
beams.
HEADLAMP LEVELING
In certain markets where required, a headlamp
leveling system is provided on the vehicle. The head-
lamp leveling system includes unique headlamp units
equipped with a headlamp leveling actuator motor,
and a rotary thumbwheel actuated headlamp leveling
switch on the instrument panel. The headlamp level-
ing system allows the headlamp beams to be
adjusted to one of four vertical positions to compen-
sate for changes in inclination caused by the loading
of the vehicle suspension. The actuator motors are
mechanically connected through an integral pushrod
to an adjustable headlamp reflector. The headlamp
8L - 6 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORKJ
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 450 of 1803
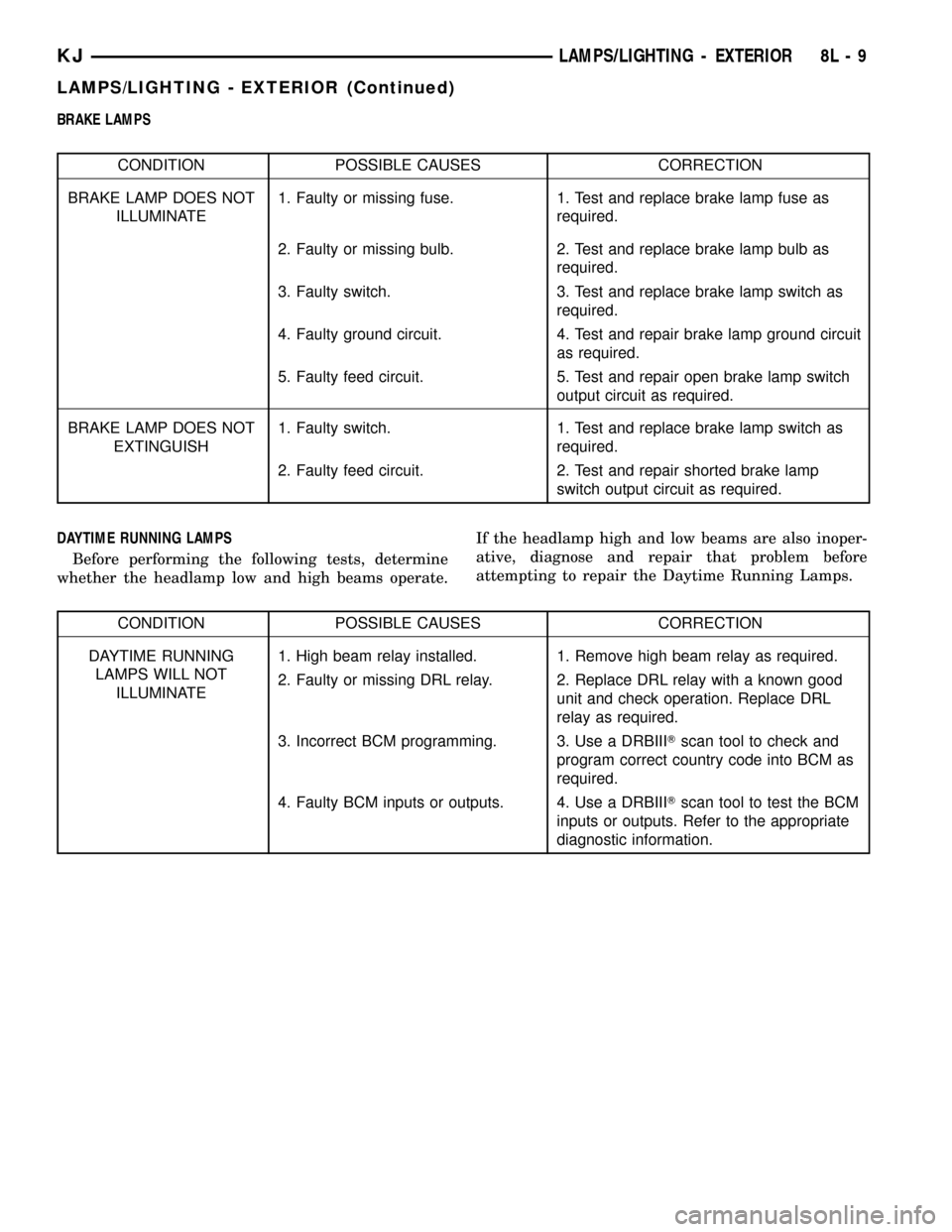
BRAKE LAMPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BRAKE LAMP DOES NOT
ILLUMINATE1. Faulty or missing fuse. 1. Test and replace brake lamp fuse as
required.
2. Faulty or missing bulb. 2. Test and replace brake lamp bulb as
required.
3. Faulty switch. 3. Test and replace brake lamp switch as
required.
4. Faulty ground circuit. 4. Test and repair brake lamp ground circuit
as required.
5. Faulty feed circuit. 5. Test and repair open brake lamp switch
output circuit as required.
BRAKE LAMP DOES NOT
EXTINGUISH1. Faulty switch. 1. Test and replace brake lamp switch as
required.
2. Faulty feed circuit. 2. Test and repair shorted brake lamp
switch output circuit as required.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMPS
Before performing the following tests, determine
whether the headlamp low and high beams operate.If the headlamp high and low beams are also inoper-
ative, diagnose and repair that problem before
attempting to repair the Daytime Running Lamps.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DAYTIME RUNNING
LAMPS WILL NOT
ILLUMINATE1. High beam relay installed. 1. Remove high beam relay as required.
2. Faulty or missing DRL relay. 2. Replace DRL relay with a known good
unit and check operation. Replace DRL
relay as required.
3. Incorrect BCM programming. 3. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to check and
program correct country code into BCM as
required.
4. Faulty BCM inputs or outputs. 4. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to test the BCM
inputs or outputs. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
KJLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 9
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 452 of 1803
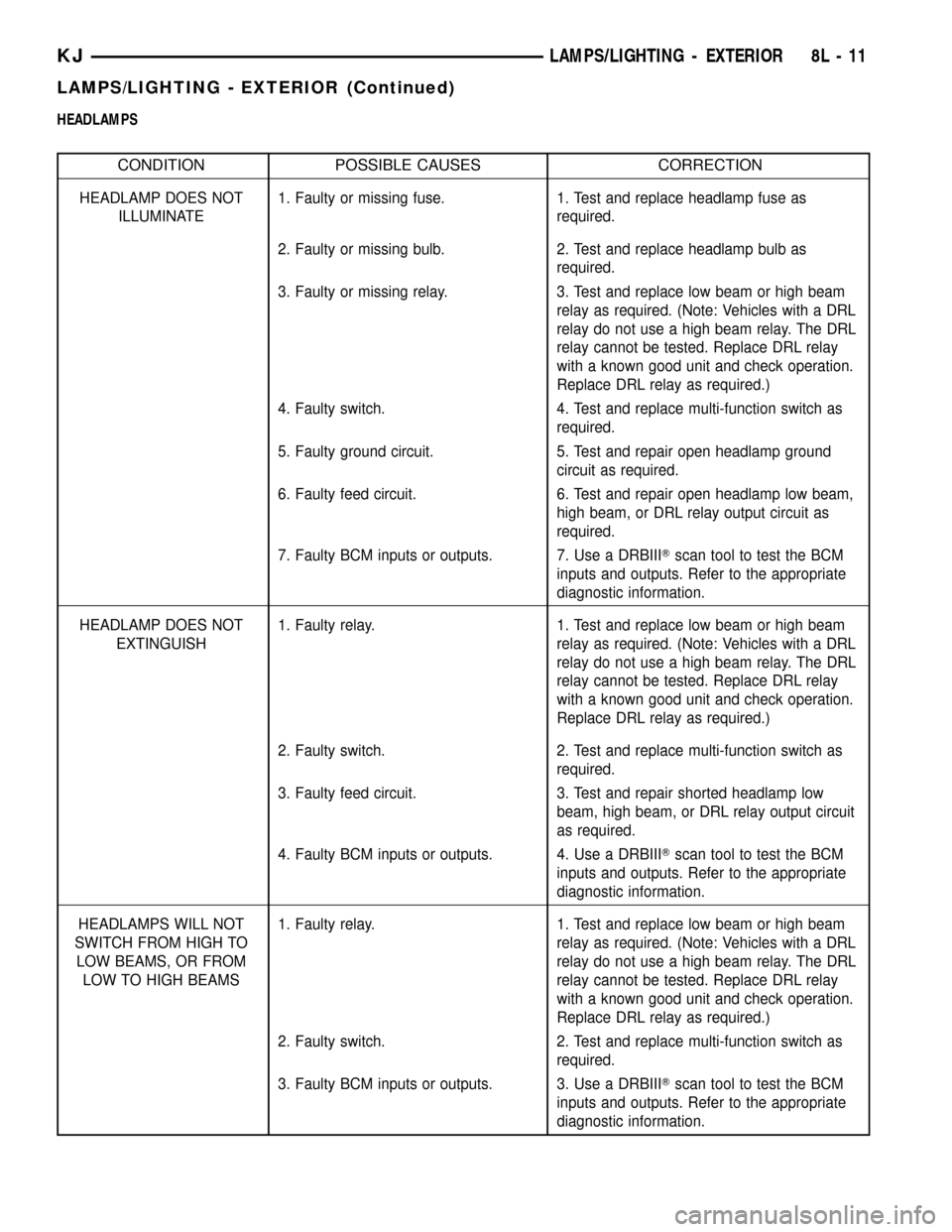
HEADLAMPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HEADLAMP DOES NOT
ILLUMINATE1. Faulty or missing fuse. 1. Test and replace headlamp fuse as
required.
2. Faulty or missing bulb. 2. Test and replace headlamp bulb as
required.
3. Faulty or missing relay. 3. Test and replace low beam or high beam
relay as required. (Note: Vehicles with a DRL
relay do not use a high beam relay. The DRL
relay cannot be tested. Replace DRL relay
with a known good unit and check operation.
Replace DRL relay as required.)
4. Faulty switch. 4. Test and replace multi-function switch as
required.
5. Faulty ground circuit. 5. Test and repair open headlamp ground
circuit as required.
6. Faulty feed circuit. 6. Test and repair open headlamp low beam,
high beam, or DRL relay output circuit as
required.
7. Faulty BCM inputs or outputs. 7. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to test the BCM
inputs and outputs. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
HEADLAMP DOES NOT
EXTINGUISH1. Faulty relay. 1. Test and replace low beam or high beam
relay as required. (Note: Vehicles with a DRL
relay do not use a high beam relay. The DRL
relay cannot be tested. Replace DRL relay
with a known good unit and check operation.
Replace DRL relay as required.)
2. Faulty switch. 2. Test and replace multi-function switch as
required.
3. Faulty feed circuit. 3. Test and repair shorted headlamp low
beam, high beam, or DRL relay output circuit
as required.
4. Faulty BCM inputs or outputs. 4. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to test the BCM
inputs and outputs. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
HEADLAMPS WILL NOT
SWITCH FROM HIGH TO
LOW BEAMS, OR FROM
LOW TO HIGH BEAMS1. Faulty relay. 1. Test and replace low beam or high beam
relay as required. (Note: Vehicles with a DRL
relay do not use a high beam relay. The DRL
relay cannot be tested. Replace DRL relay
with a known good unit and check operation.
Replace DRL relay as required.)
2. Faulty switch. 2. Test and replace multi-function switch as
required.
3. Faulty BCM inputs or outputs. 3. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to test the BCM
inputs and outputs. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
KJLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 11
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 461 of 1803

stant battery voltage is supplied to the flasher so that it
can perform the hazard warning function, and ignition
switched battery voltage is supplied for the turn signal
function. The Integrated Circuit (IC) within the combi-
nation flasher contains the logic that controls the
flasher operation and the flash rate. The IC receives
separate sense ground inputs from the multi-function
switch for the right and left turn signals, and from the
hazard switch contacts or the BCM for the hazard
warning signals. A special design feature of the combi-
nation flasher allows it to9sense9that a turn signal cir-
cuit or bulb is not operating, and provide the driver an
indication of the condition by flashing the remaining
bulbs in the affected circuit at a higher rate (120 flash-
es-per-minute or higher). Conventional flashers either
continue flashing at their typical rate (heavy-duty type),
or discontinue flashing the affected circuit entirely
(standard-duty type).
Because of the active electronic elements within
the combination flasher, it cannot be tested with con-
ventional automotive electrical test equipment. If the
combination flasher is believed to be faulty, test the
turn signal and hazard warning system. Then
replace the hazard switch with a known good unit to
confirm system operation.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMP
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The Daytime Running Lamp (DRL) relay (Fig. 8) is
a solid state relay that is used only on vehicles man-
ufactured for sale in Canada. The DRL relay features
a die cast aluminum housing with integral cooling
fins that act as a heat sink for the solid state DRL
circuitry. Four male spade terminals extend from the
base of the relay through a potting material that
encloses and protects the DRL circuitry. Although the
DRL relay has four terminals that are laid out in a
footprint that is similar to that of a conventional
International Standards Organization (ISO) relay, a
standard ISO relay should never be installed in place
of the DRL relay. The DRL relay is installed in the
Junction Block (JB) on the driver side outboard end
of the instrument panel. Vehicles equipped with this
relay do not have a headlamp high beam relay
installed in the JB.
The DRL relay cannot be adjusted or repaired and,
if faulty or damaged, the unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The Daytime Running Lamp (DRL) relay is a solid
state relay that controls the flow of battery current
to the high beam filaments of both headlamp bulbs
based upon a duty cycled control input received from
the Body Control Module (BCM) of vehicles equipped
with the DRL feature. By cycling the DRL relay out-
put, the BCM controls the illumination intensity of
the high beam filaments. The DRL relay terminals
are connected to the vehicle electrical system through
a connector receptacle in the Junction Block (JB).
The inputs and outputs of the DRL relay include:
²Battery Current Input- The DRL relay
receives battery current on a fused B(+) circuit from
a fuse in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
²Ground Input- The DRL relay receives a path
to ground through a splice block located in the
instrument panel wire harness with an eyelet termi-
nal connector that is secured by a nut to a ground
stud on the driver side instrument panel end bracket
near the Junction Block (JB).
²Control Input- The DRL relay control input is
received from the BCM and/or the momentary optical
horn (flash-to-pass) output of the multi-function
switch through a high beam relay control circuit.
²Control Output- The DRL relay supplies bat-
tery current output to the headlamp high beam fila-
ments through the high beam relay output circuit.
Because of active electronic elements within the
DRL relay, it cannot be tested with conventional
automotive electrical test equipment. If the DRL
relay is believed to be faulty, replace the relay with a
known good unit to confirm system operation.
Fig. 8 Daytime Running Lamp Relay
1 - DRL RELAY
2 - HEAT SINK
3 - POTTING MATERIAL
4 - TERMINAL (4)
8L - 20 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORKJ
COMBINATION FLASHER (Continued)
Page 462 of 1803

REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the end cap from the driver side out-
board end of the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL END CAP - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the Daytime Running Lamp (DRL)
relay by grasping it firmly and pulling it straight out
from the receptacle in the Junction Block (JB) (Fig.
9).
INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Position the Daytime Running Lamp (DRL)
relay to the proper receptacle in the Junction Block
(JB) (Fig. 9).
(2) Align the DRL relay terminals with the termi-
nal cavities in the JB receptacle.
(3) Push firmly and evenly on the top of the DRL
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the JB receptacle.
(4) Reinstall the end cap onto the driver side out-
board end of the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL END CAP - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
FRONT FOG LAMP BULB
REMOVAL
(1) Turn the front wheels full lock in the direction
of the fog lamp bulb that is to be changed.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Reach into the front wheel opening to unsnap
and lift the cover over the access hole at the front of
the front wheelhouse splash shield (Fig. 10).
(4) Reach through the access hole and firmly grasp
the socket on the back of the front fog lamp unit
housing.
(5) Rotate the socket on the back of the front fog
lamp unit housing counterclockwise about 30
degrees.
CAUTION: Do not contaminate the bulb glass by
touching it with your fingers or by allowing it to
contact other oily surfaces. Shortened bulb life will
result.
Fig. 9 Junction Block - Outboard Side (RHD Shown
- Rotate 180É for LHD)
1 - JB/BCM CONNECTOR
2 - HIGH BEAM RELAY
3 - DRL RELAY
KJLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 21
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMP RELAY (Continued)
Page 467 of 1803
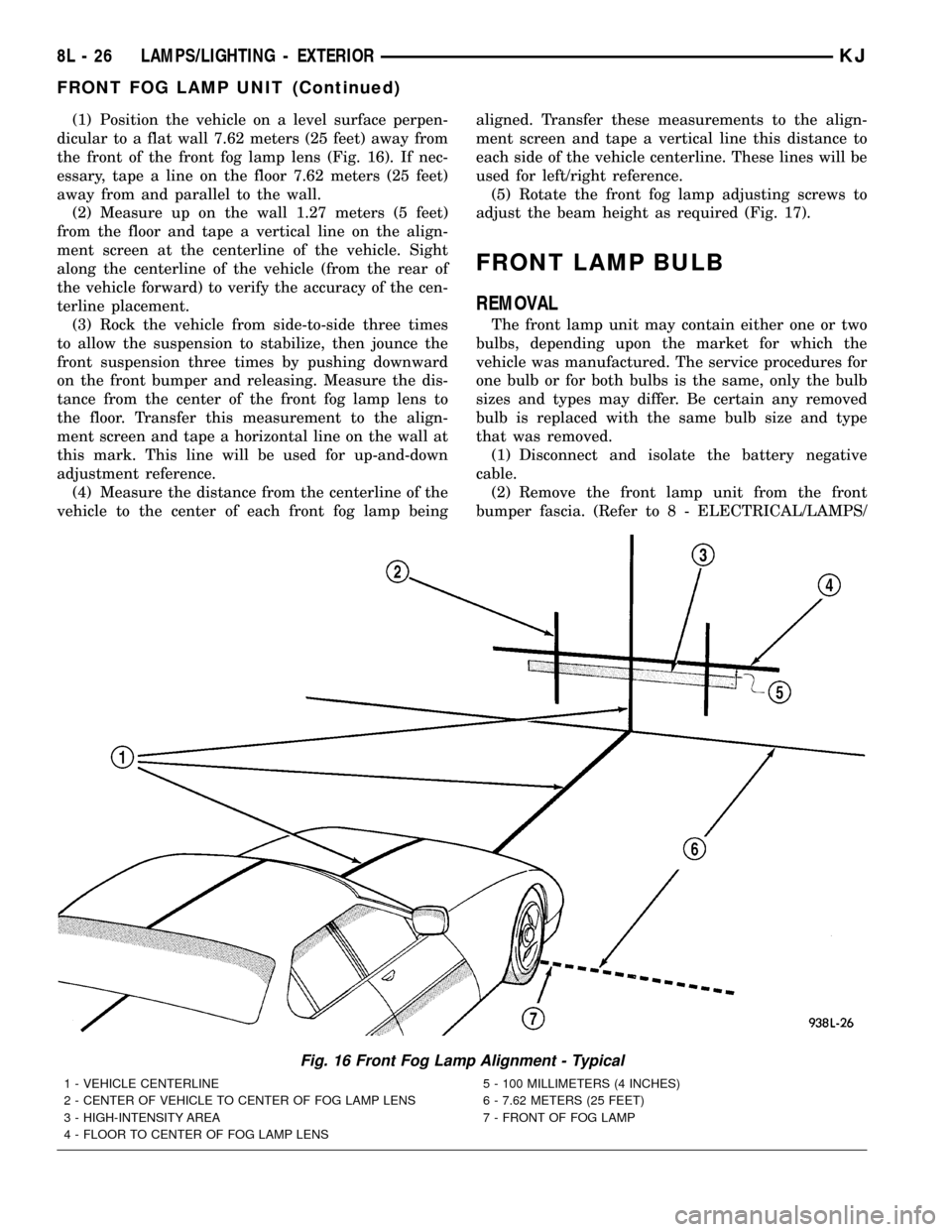
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface perpen-
dicular to a flat wall 7.62 meters (25 feet) away from
the front of the front fog lamp lens (Fig. 16). If nec-
essary, tape a line on the floor 7.62 meters (25 feet)
away from and parallel to the wall.
(2) Measure up on the wall 1.27 meters (5 feet)
from the floor and tape a vertical line on the align-
ment screen at the centerline of the vehicle. Sight
along the centerline of the vehicle (from the rear of
the vehicle forward) to verify the accuracy of the cen-
terline placement.
(3) Rock the vehicle from side-to-side three times
to allow the suspension to stabilize, then jounce the
front suspension three times by pushing downward
on the front bumper and releasing. Measure the dis-
tance from the center of the front fog lamp lens to
the floor. Transfer this measurement to the align-
ment screen and tape a horizontal line on the wall at
this mark. This line will be used for up-and-down
adjustment reference.
(4) Measure the distance from the centerline of the
vehicle to the center of each front fog lamp beingaligned. Transfer these measurements to the align-
ment screen and tape a vertical line this distance to
each side of the vehicle centerline. These lines will be
used for left/right reference.
(5) Rotate the front fog lamp adjusting screws to
adjust the beam height as required (Fig. 17).
FRONT LAMP BULB
REMOVAL
The front lamp unit may contain either one or two
bulbs, depending upon the market for which the
vehicle was manufactured. The service procedures for
one bulb or for both bulbs is the same, only the bulb
sizes and types may differ. Be certain any removed
bulb is replaced with the same bulb size and type
that was removed.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the front lamp unit from the front
bumper fascia. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/
Fig. 16 Front Fog Lamp Alignment - Typical
1 - VEHICLE CENTERLINE
2 - CENTER OF VEHICLE TO CENTER OF FOG LAMP LENS
3 - HIGH-INTENSITY AREA
4 - FLOOR TO CENTER OF FOG LAMP LENS5 - 100 MILLIMETERS (4 INCHES)
6 - 7.62 METERS (25 FEET)
7 - FRONT OF FOG LAMP
8L - 26 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORKJ
FRONT FOG LAMP UNIT (Continued)
Page 474 of 1803

(3) Pinch the two hooked ends of the wire head-
lamp bulb retainer clip together and engage them
into the slots in the flange of the reflector (Fig. 26).
(4) Position the center opening of the boot seal
over the base of the headlamp bulb and pull it down-
ward until the seal is fully engaged over the bulb
base (Fig. 25).
(5) Position the outer circumference of the boot
seal over the flange on the back of the headlamp unit
housing and pull it downward until the seal is fully
engaged over the flange.
(6) Reinstall the headlamp unit onto the grille
opening reinforcement. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/HEADLAMP UNIT
- INSTALLATION).
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(8) Confirm proper headlamp unit alignment.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING -
EXTERIOR/HEADLAMP UNIT - ADJUSTMENTS).
HEADLAMP HIGH BEAM
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The headlamp high beam relay is located in the
Junction Block (JB) on the driver side outboard end
of the instrument panel in the passenger compart-
ment of the vehicle. The headlamp high beam relay
is omitted from vehicles manufactured for sale in
Canada, which have a Daytime Running Lamp (DRL)
solid state relay installed in the JB that also per-forms the function of the headlamp high beam relay.
The headlamp high beam relay is a conventional
International Standards Organization (ISO) micro
relay (Fig. 28). Relays conforming to the ISO specifi-
cations have common physical dimensions, current
capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal functions.
The relay is contained within a small, rectangular,
molded plastic housing and is connected to all of the
required inputs and outputs by five integral male
spade-type terminals that extend from the bottom of
the relay base.
The headlamp high beam relay cannot be adjusted
or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the unit must
be replaced.
OPERATION
The headlamp high beam relay is an electrome-
chanical switch that uses a low current input from
the Body Control Module (BCM) to control a high
current output to the headlamp high beam filaments.
The movable common feed contact point is held
against the fixed normally closed contact point by
spring pressure. When the relay coil is energized, an
electromagnetic field is produced by the coil wind-
ings. This electromagnetic field draws the movable
relay contact point away from the fixed normally
closed contact point, and holds it against the fixed
normally open contact point. When the relay coil is
de-energized, spring pressure returns the movable
contact point back against the fixed normally closed
contact point. A resistor is connected in parallel with
the relay coil in the relay, and helps to dissipate volt-
age spikes and electromagnetic interference that can
be generated as the electromagnetic field of the relay
coil collapses.
The headlamp high beam relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a con-
nector receptacle in the Junction Block (JB). The
inputs and outputs of the headlamp high beam relay
include:
²Common Feed Terminal- The common feed
terminal (30) receives battery current at all times
from a fuse in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
through a fused B(+) circuit.
²Coil Ground Terminal- The coil ground termi-
nal (85) receives battery current at all times from a
fuse in the PDC through a fused B(+) circuit.
²Coil Battery Terminal- The coil battery ter-
minal (86) is connected to a control output of the
Body Control Module (BCM) and to the momentary
optical horn (flash-to-pass) output of the multi-func-
tion switch through a high beam relay control circuit.
The BCM and/or the multi-function switch controls
headlamp high beam operation by controlling a
ground path through this circuit.
Fig. 28 ISO Micro Relay
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
KJLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 33
HEADLAMP BULB (Continued)
Page 475 of 1803

²Normally Open Terminal- The normally open
terminal (87) is connected to the headlamp high
beam filaments through the high beam relay output
circuit and provides battery current to the headlamp
high beams whenever the relay is energized.
²Normally Closed Terminal- The normally
closed terminal (87A) is not connected in this appli-
cation.
The headlamp high beam relay can be diagnosed
using conventional diagnostic tools and methods.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEADLAMP HIGH
BEAM RELAY
The headlamp high beam relay (Fig. 29) is located
in the Junction Block (JB) on the driver side out-
board end of the instrument panel. Refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Remove the headlamp high beam relay from
the JB. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHT-
ING - EXTERIOR/HEADLAMP HIGH BEAM RELAY
- REMOVAL).
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 8 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, reinstall the relay and use a DRBIIItscan tool to perform further testing. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the end cap from the driver side out-
board end of the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL END CAP - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the headlamp high beam relay by
grasping it firmly and pulling it straight out from the
receptacle in the Junction Block (JB) (Fig. 30).
Fig. 29 ISO Micro Relay
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
8L - 34 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORKJ
HEADLAMP HIGH BEAM RELAY (Continued)