axle JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 55 of 1803

SPECIFICATIONS
PROPELLER SHAFT
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Front Shaft - Companion
Flange Bolts30 22 -
Rear Shaft - Yoke Nuts 18 13 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
PROPELLER SHAFT - FRONT
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission and transfer case into Neu-
tral.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Mark companion flanges and C/V joints at the
front and rear of the propeller shaft for installation
reference.
(4) Remove bolts from the front and rear C/V
joints.
(5) Push propeller shaft forward to clear transfer
case companion flange (Fig. 8).
(6) Remove the shaft from the front axle compan-
ion flange.
(7) Tilt the front of the shaft down and pull shaft
forward and remove from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install propeller shaft between companion
flanges.
(2) Align marks on the companion flanges with the
marks on the C/V joints.
(3) Install front C/V joint bolts and tighten to 30
N´m (22 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install rear C/V joint bolts and tighten to 30
N´m (22 ft. lbs.).
(5) Lower vehicle.
Inclinometer 7663
Fig. 8 TRANSFER CASE COMPANION FLANGE
1 - FLANGE BOLT
2 - COMPANION FLANGE
3 - 6 PROPELLER SHAFTKJ
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 56 of 1803

PROPELLER SHAFT - REAR
REMOVAL
(1) Shift the transmission/transfer case into Neu-
tral.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Mark a reference line across the pinion yoke
and propeller shaft for installation.
(4) Remove U-joint strap bolts at the pinion shaft
yoke.
(5) Pry open clamp holding the dust boot to propel-
ler shaft yoke (Fig. 9), if equipped.
(6) Slide slip yoke off of the transmission/transfer
case output shaft and remove the propeller shaft
(Fig. 10).
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide slip yoke on the transmission/transfer
case output shaft.
(2) Align reference marks on the pinion yoke and
propeller shaft.
(3) Install U-joint straps and tighten strap bolts to
18 N´m (13 ft. lbs.).
(4) Tighten dust boot clamp if equipped with
Clamp C-4975A (Fig. 11).
(5) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
Fig. 9 DUST BOOT CLAMP
1 - SLINGER
2 - BOOT
3-AWL
4 - TRANSFER CASE
Fig. 10 REAR PROPELLER SHAFT
1 - CLAMP
2 - YOKE
3 - PROPELLER SHAFT
4 - AXLE YOKE
5 - CLAMP
6 - OUTPUT SHAFT
7 - BOOT
Fig. 11 CRIMPING BOOT CLAMP
1 - CLAMP TOOL
2 - SLINGER
3 - BOOT
4 - CLAMPS
KJPROPELLER SHAFT 3 - 7
Page 60 of 1803

(5) Remove lower clevis bolt (Fig. 2).
(6) Seperate lower ball joint from the lower control
arm (Fig. 3).
(7) Pull out on the steering knuckle and push the
half shaft out of the knuckle.
(8) With a pry bar remove the half shaft from the
axle.
NOTE: The right side has a splined axle shaft that
will stay in the axle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coat of wheel bearing grease on
the female splines of the inner C/V joint.(2) Install half shaft on the axle shaft spline and
push firmly to engage the snap ring. Pull on the half
shaft to verify snap has engaged.
(3) Clean hub bearing bore and apply a light coat
of wheel bearing grease.
(4) Pull out on the steering knuckle and push the
half shaft through the knuckle.
(5) Install lower ball joint into the lower control
arm and tighten pinch bolt.
(6) Align clevis with knuckle. Install and tighten
lower clevis bolt.
(7) Install stabilizer link.
(8) Install half shaft hub nut.
(9) Install wheel and tire assembly.
(10) Remove support and lower vehicle.
SPECIFICATIONS
HALF SHAFT
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Half Shaft Nut 136 100 -
Fig. 3 LOWER CONTROL ARM
1 - FRONT CAM BOLT
2 - OUTER TIE ROD END
3 - LOWER BALL JOINT NUT
4 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
5 - REAR CAM BOLTFig. 2 CLEVIS BRACKET
1 - UPPER BOLT
2 - CLEVIS BRACKET
3 - LOWER BOLT
KJHALF SHAFT 3 - 11
HALF SHAFT (Continued)
Page 68 of 1803
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AXLE..........20
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................24
ADJUSTMENTS........................25
SPECIFICATIONS - FRONT AXLE...........33
SPECIAL TOOLS
FRONT AXLE........................34
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................38
AXLE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................38INSTALLATION.........................38
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................39
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL.............................40
DISASSEMBLY.........................41
ASSEMBLY............................41
INSTALLATION.........................42
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................44
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................46
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA
DESCRIPTION
The 186FIA (Model 30) axle consists of an alumu-
num center section with an axle tube extending from
one side. The tube is pressed into the differential
housing. The integral type housing, hypoid gear
design has the centerline of the pinion set below the
centerline of the ring gear.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The differ-
ential pinion mate shaft is retained with a roll-pin. Dif-
ferential bearing preload and ring gear backlash is
adjusted by the use of shims (select thickness). The
shims are located between the differential bearing cups
and the axle housing. Pinion bearing preload is set and
maintained by the use of a collapsible spacer.
The power is transferred from the axle through two
constant velocity (C/V) drive shafts to the wheel hubs.
The differential cover provides a means for inspec-
tion and service without removing the axle from the
vehicle. The cover has a vent tube used to relieve
internal pressure caused by vaporization and inter-
nal expansion.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the transfer case through
the front propeller shaft. The front propeller shaft is con-
nected to the pinion gear which rotates the differential
through the gear mesh with the ring gear bolted to thedifferential case. The engine power is transmitted to the
axle shafts through the pinion mate and side gears. The
side gears are splined to the axle shafts.
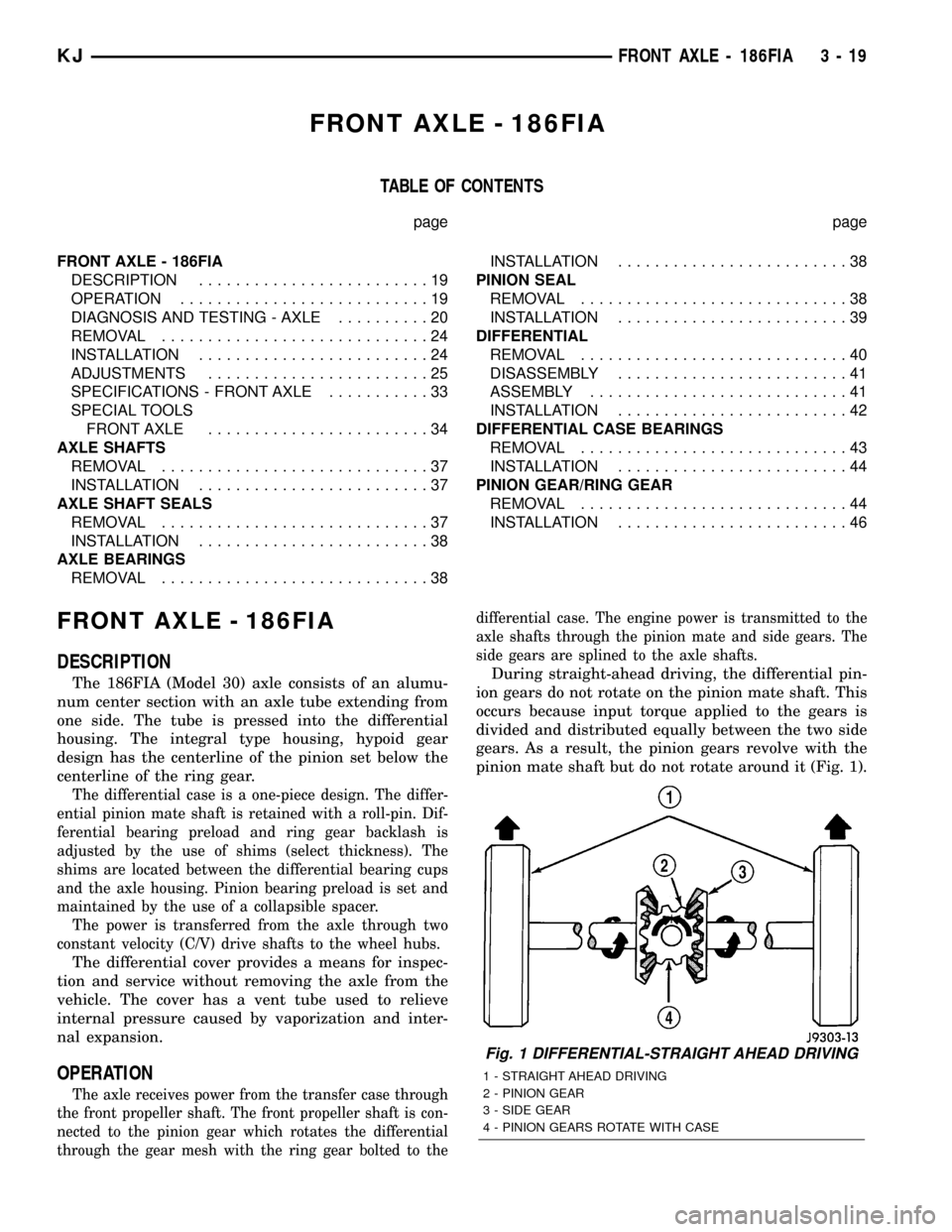
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the
pinion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 DIFFERENTIAL-STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING
1 - STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING
2 - PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
KJFRONT AXLE - 186FIA 3 - 19
Page 69 of 1803

When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. The difference must be compensated
for to prevent the tires from scuffing and skidding
through turns. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
2). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
pinion gears is not divided equally. The pinion gears
now rotate around the pinion mate shaft in opposite
directions. This allows the side gear and axle shaft
attached to the outside wheel to rotate at a faster
speed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AXLE
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
Fig. 2 DIFFERENTIAL-ON TURNS
1 - PINION GEARS ROTATE ON PINION SHAFT
3 - 20 FRONT AXLE - 186FIAKJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA (Continued)
Page 70 of 1803
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
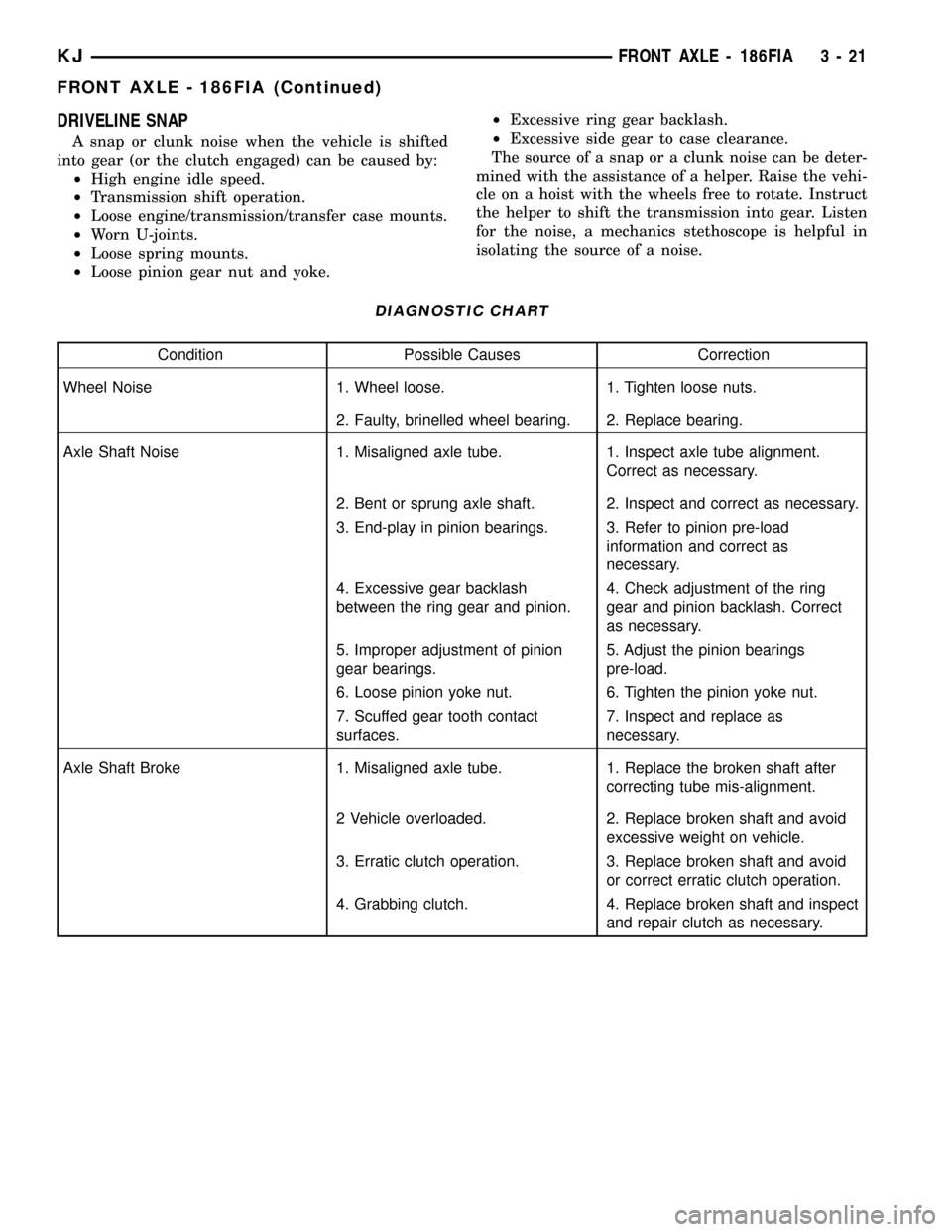
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load
information and correct as
necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash
between the ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring
gear and pinion backlash. Correct
as necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion
gear bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings
pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact
surfaces.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
KJFRONT AXLE - 186FIA 3 - 21
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA (Continued)
Page 71 of 1803
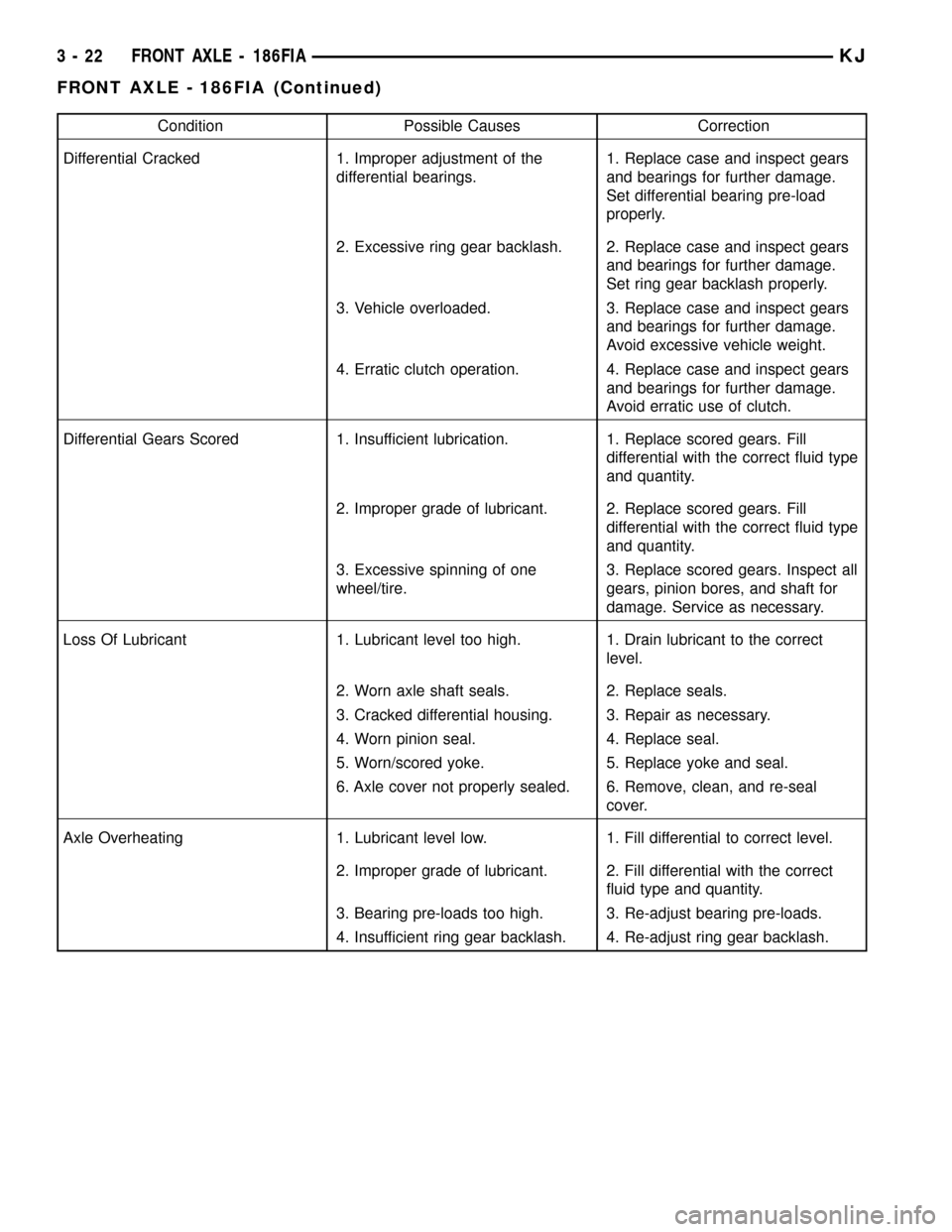
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
3 - 22 FRONT AXLE - 186FIAKJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA (Continued)
Page 72 of 1803
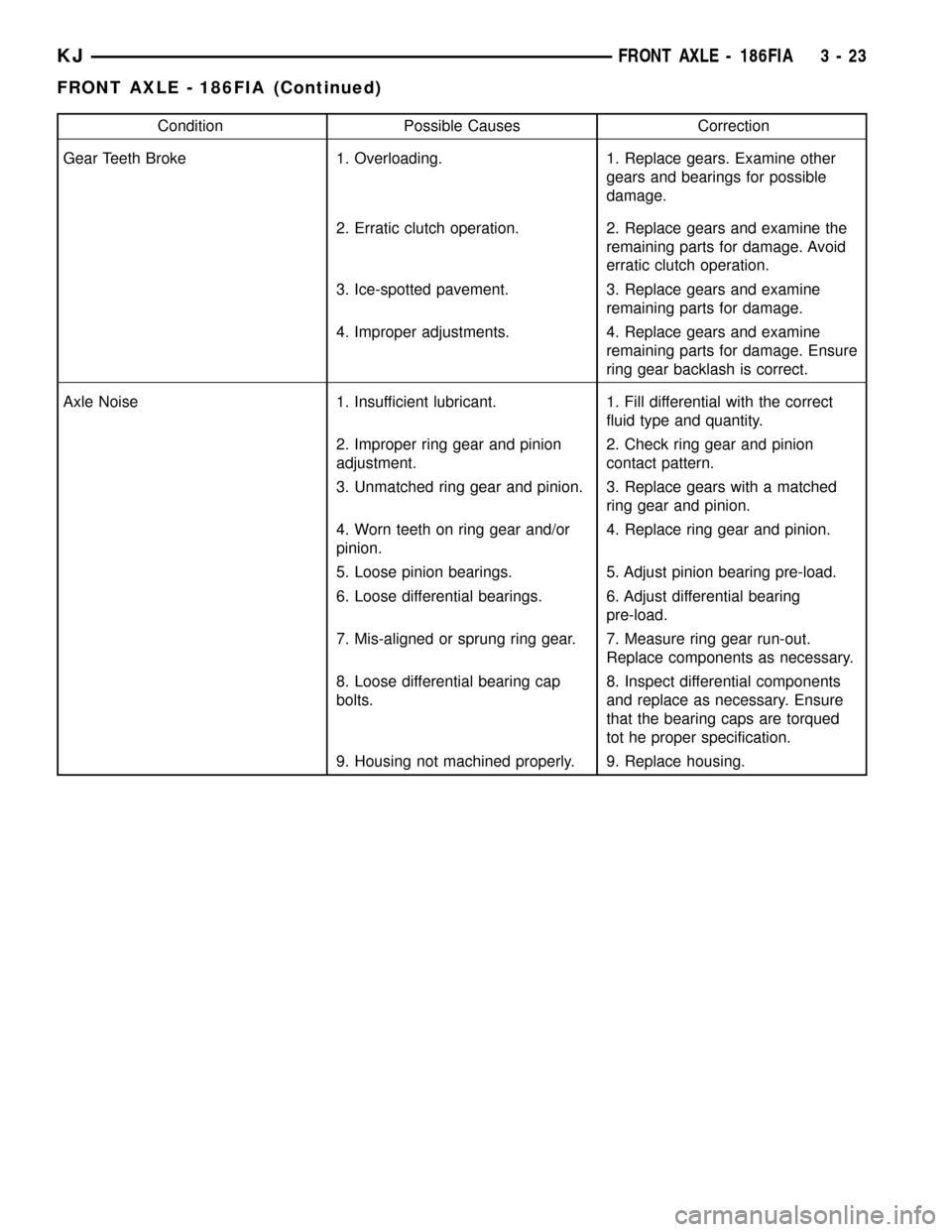
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
KJFRONT AXLE - 186FIA 3 - 23
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA (Continued)
Page 73 of 1803

REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove half shaft hub nuts.
(4) Remove lower control arms. Refer to 2 suspen-
sion for procedure.
(5) Remove half shafts.
(6) Remove skid plate.
(7) Remove differential drain plug (Fig. 3) and
drain fluid.
(8) Remove differential vent hose (Fig. 4) from
cover.
(9) Remove propeller shaft from pinion flange.
(10) Support axle with a lift/jack.
(11) Remove bolt from left front axle bracket frame
mount (Fig. 5).
(12) Remove bolts from right axle bracket frame
mounts (Fig. 6).
(13) Remove bolt from left rear axle bracket frame
mount (Fig. 7).
(14) Lower axle from vehicle.
(15) Remove brackets from axle if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install left rear bracket to axle and tighten to
61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install right bracket to axle and tighten to 88
N´m (65 ft. lbs.).(3) Install left front bracket to axle and tighten to
61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(4) Raise axle up and align brackets with frame
mounts.
(5) Install frame mount bolts and tighten to 88
N´m (65 ft. lbs.).
(6) Install propeller shaft.
(7) Install half shafts.
Fig. 3 DRAIN PLUG
1 - LEFT FRONT AXLE BRACKET
2 - DRAIN PLUG
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 4 DIFFERENTIAL COVER
1 - COVER
2 - VENT TUBE
Fig. 5 LEFT FRONT AXLE BRACKET
1 - LEFT FRONT AXLE BRACKET
2 - BRACKET BOLT
3 - 24 FRONT AXLE - 186FIAKJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA (Continued)
Page 74 of 1803

(8) Install lower control arms, refer to 2 Suspen-
sion for procedures.
(9) Install new half shaft hub nuts and tighten to
136 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install axle vent hose.
(11) Fill differential with gear lubricant.
(12) Install skid plate.
(13) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(14) Remove support and lower vehicle.
(15) Check vehicle alignment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched onto each gear (Fig. 8). A plus
(+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is etched
into the face of the pinion gear. This number is the
amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth varies
from the standard depth setting of a pinion etched
with a (0). The standard setting from the center line
of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion is 92.1
mm (3.625 in.). The standard depth provides the best
gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to Backlash and
Contact Pattern Analysis paragraph in this section
for additional information.
Fig. 6 RIGHT AXLE BRACKET
1 - RIGHT AXLE BRACKET
2 - FRONT BRACKET BOLT
3 - REAR BRACKET BOLT
Fig. 7 LEFT REAR AXLE BRACKET
1 - LEFT REAR AXLE BRACKET
2 - BRACKET BOLT
Fig. 8 PINION GEAR ID NUMBERS
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - DRIVE PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
KJFRONT AXLE - 186FIA 3 - 25
FRONT AXLE - 186FIA (Continued)