removal JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 1385 of 1803

OPERATION
Fuel is picked up in the fuel tank by the fuel pump
module. This module is located on the bottom of the
fuel tank.
A fuel return system is provided within the fuel
pump module using check valves. A separate fuel
return line from the engine to the tank is not used.
The fuel pressure regulator and the main fuel filter
are not combined. They are separate items.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock
ring/gasket, ORVR components. Refer to 25, Emis-
sion Control System for ORVR information.
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap. A one-way check valve is installed into the
tanks fuel fill fitting.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system and ORVR system. This
is designed to reduce the emission of fuel vapors into
the atmosphere. The description and function of the
Evaporative Control System is found in 25, Emission
Control Systems.
Both fuel filters (mounted to front of fuel tank, and
inside the bottom fuel pump module) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. The bottom section of the fuel
pump module (with included filter) should only be
replaced if a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
Also, the fuel filter mounted to the front of the fuel
tank should only be replaced if a diagnostic proce-
dure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Quick Connect Fittings for procedures. On some
engines, air cleaner housing removal may be neces-
sary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 2).
(4) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.The DRBtIII Scan
Tool along with the PEP module, the 500 psi
pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-test
port adapter may also be used in place of the
fuel pressure gauge.
The fittings on both tools must be in good
condition and free from any small leaks before
performing the proceeding test.
(5) Start engine and bring to normal operating
temperature.
(6) Observe test gauge. Normal operating pressure
should be 339 kPa +/±34 kPa (49.2 psi +/±5 psi).
(7) Shut engine off.
Fig. 2 CONNECTING ADAPTER TOOLÐTYPICAL
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 3
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1386 of 1803

(8) Pressure should not fall below30 psi for five
minutes.
(9) If pressure falls below 30 psi, it must be deter-
mined if a fuel injector, the check valve within the
fuel pump module, or a fuel tube/line is leaking.
(10) Again, start engine and bring to normal oper-
ating temperature.
(11) Shut engine off.
(12)Testing for fuel injector or fuel rail leak-
age:Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor
Tool between the fuel rail and the test port ªTº on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a fuel injector or the fuel rail is leaking.
(13)Testing for fuel pump check valve, filter,
regulator check valve or fuel tube/line leakage:
Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor Tool
between the vehicle fuel line and test port ªTº on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a leak may be found at a fuel tube/line. If no
leaks are found at fuel tubes or lines, one of the
check valves in either the electric fuel pump, fuel fil-
ter or fuel pressure regulator may be leaking.
Note: A quick loss of pressure usually indicates a
defective check valve in the pressure regulator. A
slow loss of pressure usually indicates a defective
check valve in the bottom of the fuel pump module.
The check valves are not serviced separately. Also,
the electric fuel pump is not serviced separately.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE
Use following procedure if the fuel injector
rail is, or is not equipped with a fuel pressure
test port.
(1) Remove fuel fill cap.
(2) Remove fuel pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.(3) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(4) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(5) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
CAUTION: Steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 must be performed to
relieve high pressure fuel from within fuel rail. Do
not attempt to use following steps to relieve this
pressure as excessive fuel will be forced into a cyl-
inder chamber.
(6) Unplug connector from any fuel injector.
(7) Attach one end of a jumper wire with alligator
clips (18 gauge or smaller) to either injector terminal.
(8) Connect other end of jumper wire to positive
side of battery.
(9) Connect one end of a second jumper wire to
remaining injector terminal.
CAUTION: Powering an injector for more than a few
seconds will permanently damage the injector.
(10) Momentarily touch other end of jumper wire
to negative terminal of battery for no more than a
few seconds.
(11) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(12) Disconnect quick-connect fitting at fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(14) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRBtscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1388 of 1803
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL SYSTEMFLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The flow management valve is a part of the ORVR
system. This plastic valve is placed inline between
the fuel tank vent fitting and the EVAP canister. It is
located on top of the fuel tank (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The flow management valve (Fig. 1) is one of the com-
ponents used in the ORVR system. The valve meters
the flow of fuel vapors to the EVAP canister during
vehicle run and refueling. Pressure from the tank dur-
ing refueling opens the main port valve and allows
vapors to enter the EVAP canister. During vehicle run,
the vapors are metered through an orifice to the EVAP
canister. It is also used as a liquid separator to keep liq-
uid fuel out of the EVAP canister.
REMOVAL
The flow management valve is located on top of the
fuel tank (Fig. 1).
(1) Four cargo holdown clamps are located inside
the vehicle on the floor of the rear cargo area.
Remove the 2 rearward mounted clamps by drilling
out the clamp rivets.
(2) Fold carpeting forward to gain access to fuel
pump module access plate (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 ACCESS PLATE
1 - FLOORPAN AT REAR
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE ACCESS PLATE
3 - NUTS (4)
4 - OPENING TO PUMP MODULE
ADAPTERS, FUEL PRESSURE TESTÐ6539 AND/OR
6631
TEST KIT, FUEL PRESSUREÐ5069
TEST KIT, FUEL
14 - 6 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1389 of 1803

(3) Remove 4 fuel pump module access plate nuts
(Fig. 3).
(4) While applying heat from a heat gun, carefully
pry up fuel pump module access plate. Take care not
to bend plate.
(5) Disconnect flow management valve hose clamp
and hose (Fig. 4) at pump module fitting. Also discon-
nect small recirculation line at top half of manage-
ment valve.
(6) Raise vehicle.
(7) Disconnect opposite end of flow management
valve hose at EVAP canister (Fig. 1).
(8) Remove valve and 2 hoses as an assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Attach 2 large hoses and 1 small line to flow
management valve. Position this assembly to top of
fuel tank.
(3) Connect valve hose at EVAP canister.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Attach valve hose and clamp to top of fuel
pump module.
(6) Apply silicone sealant to bottom of fuel pump
module metal access plate.(7) Install fuel pump module metal access plate
and 4 nuts. Tighten nuts to 3 N´m (26 in. lbs.)
torque.
(8) Position carpet and install 2 new cargo clamp
rivets.
FUEL FILTER
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pressure regulator and fuel filter are not
combined on this vehicle. The main fuel filter is
attached to the front of the fuel tank (Fig. 1) and is a
serviceable/replaceable item. Also refer to Inlet Filter
and Fuel Pressure Regulator.
REMOVAL
The main fuel filter is attached to the front of fuel
tank (Fig. 1). Three fuel lines are used at filter.
Fuel tank removal will not be necessary for
fuel filter removal. Access is from rear cargo
area.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY BE UNDER A
CONSTANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF). BEFORE SERVICING MOST FUEL SYSTEM
COMPONENTS, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL SYS-
TEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Release fuel system pressure.
(2) Four cargo holdown clamps are located inside
vehicle on floor of rear cargo area. Two of these four
clamps must be removed. Remove 2 rearward
mounted clamps by drilling out clamp rivets.
(3) Fold carpeting forward to gain access to fuel
pump module access plate (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove 4 fuel pump module access plate nuts
(Fig. 5).
(5) While applying heat from a heat gun, carefully
pry up metal fuel pump module access plate. Take
care not to bend plate.
(6) Clean top of fuel pump module area around
fuel line connection points.
(7) Disconnect 2 fuel lines at fuel pump module
(Fig. 6) by pressing on tabs at side of fitting.
(8) Raise vehicle.
(9) Place drain pan under fuel filter.
(10) A third fuel line is attached to bottom of filter
(Fig. 7). The disconnection point for this 3rd line is
approximately 1 foot towards front of vehicle. Clean
fuel line connection point before disconnection. Dis-
connect by pressing on tabs at side of fitting.
(11) Disconnect 3rd fuel line from body retention
clip. Place a small screwdriver into side of clip and
twist for removal.
Fig. 4 TOP OF FUEL PUMP MODULE
1 - LOCK RING
2 - ALIGNMENT NOTCH
3 - FUEL FILTER FITTINGS (2)
4 - ORVR SYSTEM HOSE AND CLAMP
5 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
7 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
8 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
9 - FUEL PUMP MODULE (UPPER SECTION)
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 7
FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE (Continued)
Page 1391 of 1803
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module has 4 different circuits
(wires). Two of these circuits are used for the fuel
gauge sending unit for fuel gauge operation, and for
certain OBD II emission requirements. The other 2
wires are used for electric fuel pump operation.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant current
source of approximately 32 milliamps is supplied to
the resistor track on the fuel gauge sending unit.
This is fed directly from the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM).NOTE: For diagnostic purposes, this
12V power source can only be verified with the
circuit opened (fuel pump module electrical
connector unplugged). With the connectors
plugged, output voltages will vary from about
0.6 volts at FULL, to about 8.6 volts at EMPTY
(about 8.6 volts at EMPTY for Jeep models, and
about 7.0 volts at EMPTY for Dodge Truck mod-
els).The resistor track is used to vary the voltage
(resistance) depending on fuel tank float level. As
fuel level increases, the float and arm move up,
which decreases voltage. As fuel level decreases, the
float and arm move down, which increases voltage.
The varied voltage signal is returned back to the
PCM through the sensor return circuit.
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the PCM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the PCM, the PCM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.
For OBD II Emission Monitor Requirements:
The PCM will monitor the voltage output sent from
the resistor track on the sending unit to indicate fuel
level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent the
OBD II system from recording/setting false misfire
and fuel system monitor diagnostic trouble codes.
The feature is activated if the fuel level in the tank
is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated
capacity. If equipped with a Leak Detection Pump
(EVAP system monitor), this feature will also be acti-
vated if the fuel level in the tank is more than
approximately 85 percent of its rated capacity.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL LEVEL
SENDING UNIT
The fuel level sending unit contains a variable
resistor (track). As the float moves up or down, elec-
trical resistance will change. Refer to Instrument
Panel and Gauges for Fuel Gauge testing. To test the
gauge sending unit only, it must be removed from
vehicle. The unit is a separate part of the lower fuel
pump module section. Refer to Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation for procedures (remove only the
upper section of the fuel pump module). Measure the
resistance across the sending unit terminals. With
float in up position, resistance should be 20 ohms (+/-
5%). With float in down position, resistance should be
270 ohms (+/- 5%).
REMOVAL
The fuel level sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of the lower sec-
tion of the fuel pump module. The lower section of
the fuel pump module is located within the fuel tank.
(1) Remove lower section of fuel pump module
from fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/
Installation.
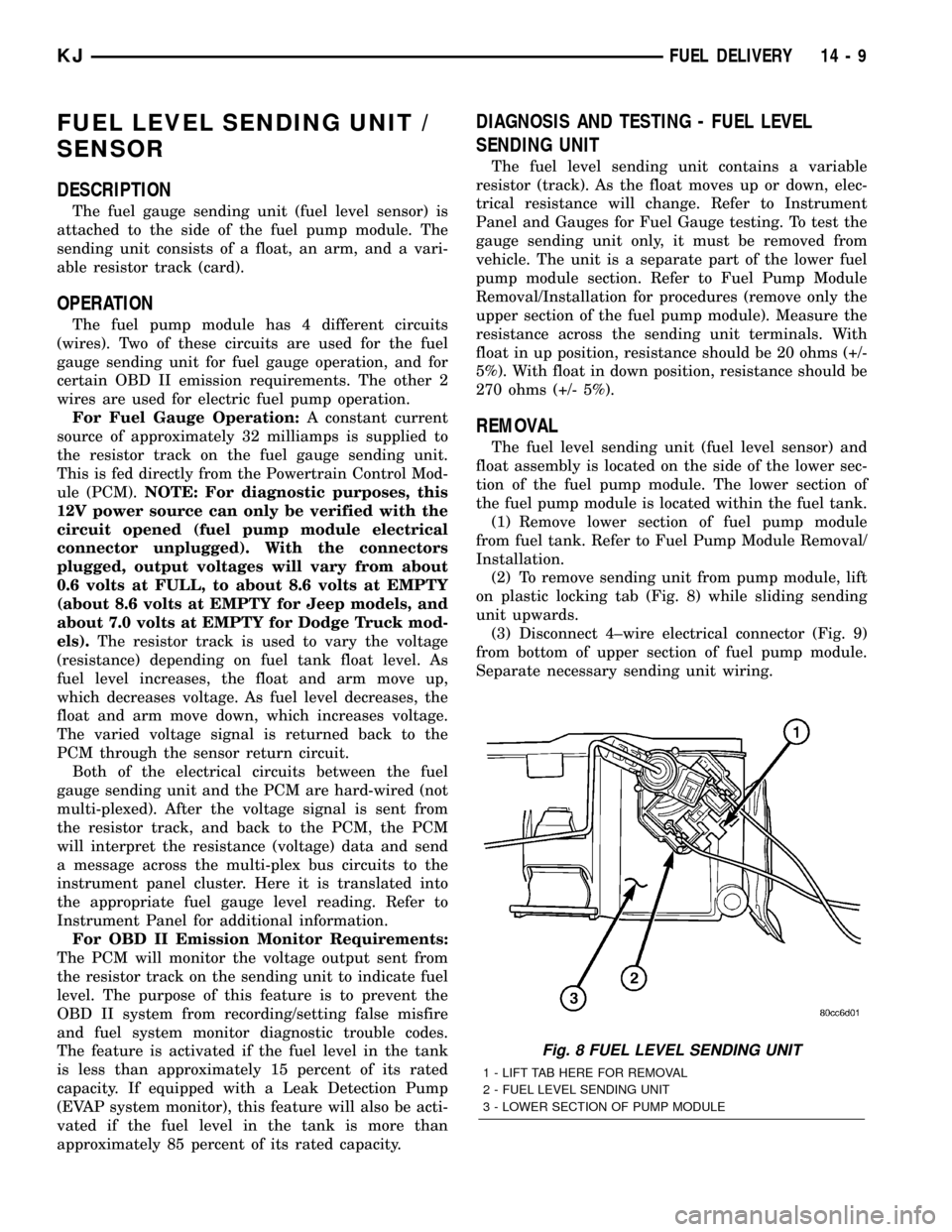
(2) To remove sending unit from pump module, lift
on plastic locking tab (Fig. 8) while sliding sending
unit upwards.
(3) Disconnect 4±wire electrical connector (Fig. 9)
from bottom of upper section of fuel pump module.
Separate necessary sending unit wiring.
Fig. 8 FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT
1 - LIFT TAB HERE FOR REMOVAL
2 - FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT
3 - LOWER SECTION OF PUMP MODULE
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 9
Page 1392 of 1803

INSTALLATION
(1) Connect necessary wiring into electrical con-
nectors. Connect 4±wire connector to upper section of
pump module.
(2) Position sending unit to pump module. Slide
and snap into place.
(3) Install lower section of fuel pump module.
Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation.
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION
Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY BE UNDER A
CONSTANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF). BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM
HOSES, FITTINGS, LINES, OR MOST COMPO-
NENTS, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on fuel injected vehicles are of a special
rolled edge construction. This construction is used to
prevent the edge of the clamp from cutting into the
hose. Only these rolled edge type clamps may be
used in this system. All other types of clamps may
cut into the hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components, lines and
tubes. These are: a single-tab type, a two-tab type or
a plastic retainer ring type. Some are equipped with
safety latch clips. Some may require the use of a spe-
cial tool for disconnection and removal. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings Removal/Installation for more
information.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, clips)
of quick-connect fittings are not serviced sepa-
rately, but new plastic spacers are available for
some types. If service parts are not available, do
not attempt to repair the damaged fitting or fuel line
(tube). If repair is necessary, replace the complete
fuel line (tube) assembly.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
Also refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps.
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components, lines and
tubes. These are: a single-tab type, a two-tab type or
a plastic retainer ring type. Safety latch clips are
used on certain components/lines. Certain fittings
may require use of a special tool for disconnection.
DISCONNECTING
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSE,
FITTING OR LINE, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST
BE RELEASED. REFER TO FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
Fig. 9 FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR/SENDING
UNIT ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
1 - UPPER SECTION OF PUMP MODULE
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
3 - FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - 4-WIRE ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
14 - 10 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1393 of 1803
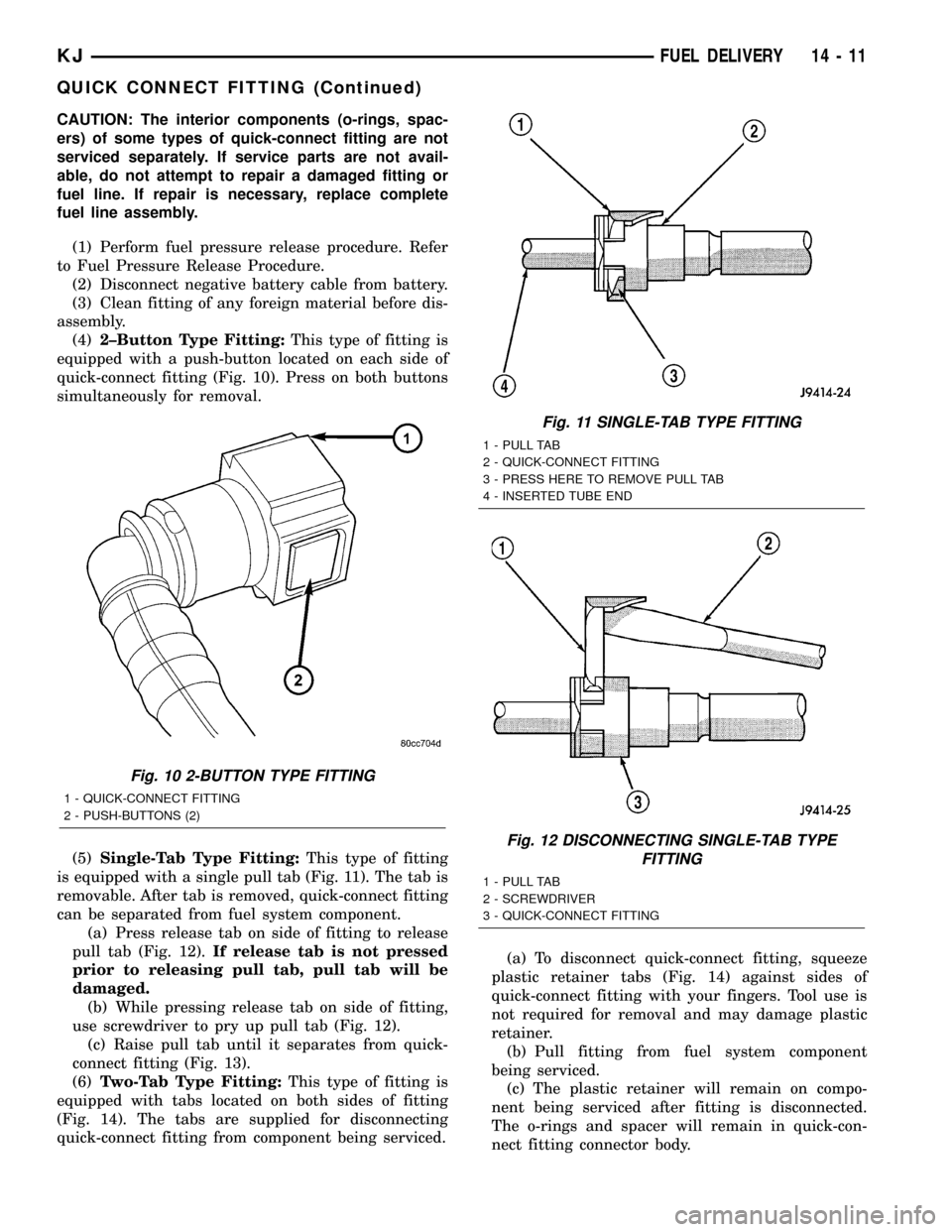

CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, spac-
ers) of some types of quick-connect fitting are not
serviced separately. If service parts are not avail-
able, do not attempt to repair a damaged fitting or
fuel line. If repair is necessary, replace complete
fuel line assembly.
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4)2±Button Type Fitting:This type of fitting is
equipped with a push-button located on each side of
quick-connect fitting (Fig. 10). Press on both buttons
simultaneously for removal.
(5)Single-Tab Type Fitting:This type of fitting
is equipped with a single pull tab (Fig. 11). The tab is
removable. After tab is removed, quick-connect fitting
can be separated from fuel system component.
(a) Press release tab on side of fitting to release
pull tab (Fig. 12).If release tab is not pressed
prior to releasing pull tab, pull tab will be
damaged.
(b) While pressing release tab on side of fitting,
use screwdriver to pry up pull tab (Fig. 12).
(c) Raise pull tab until it separates from quick-
connect fitting (Fig. 13).
(6)Two-Tab Type Fitting:This type of fitting is
equipped with tabs located on both sides of fitting
(Fig. 14). The tabs are supplied for disconnecting
quick-connect fitting from component being serviced.(a) To disconnect quick-connect fitting, squeeze
plastic retainer tabs (Fig. 14) against sides of
quick-connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is
not required for removal and may damage plastic
retainer.
(b) Pull fitting from fuel system component
being serviced.
(c) The plastic retainer will remain on compo-
nent being serviced after fitting is disconnected.
The o-rings and spacer will remain in quick-con-
nect fitting connector body.
Fig. 10 2-BUTTON TYPE FITTING
1 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
2 - PUSH-BUTTONS (2)
Fig. 11 SINGLE-TAB TYPE FITTING
1 - PULL TAB
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
3 - PRESS HERE TO REMOVE PULL TAB
4 - INSERTED TUBE END
Fig. 12 DISCONNECTING SINGLE-TAB TYPE
FITTING
1 - PULL TAB
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 11
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
Page 1394 of 1803

(7)Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting:This
type of fitting can be identified by the use of a full-
round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 15) usually black in
color.
(a) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-
nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 15). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plas-
tic retainer ring must be pressed squarely
into fitting body. If this retainer is cocked
during removal, it may be difficult to discon-
nect fitting. Use an open-end wrench on
shoulder of plastic retainer ring to aid in dis-
connection.
Fig. 13 REMOVING PULL TAB
1 - FUEL TUBE OR FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT
2 - PULL TAB
3 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
4 - FUEL TUBE STOP
Fig. 14 TYPICAL 2±TAB TYPE FITTING
1 - TAB(S)
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
Fig. 15 PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
1 - FUEL TUBE
2 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 - PUSH
4 - PLASTIC RETAINER
5 - PUSH
6 - PUSH
7 - PUSH
8 - PUSH
Fig. 16 LATCH CLIP-TYPE 1
1 - TETHER STRAP
2 - FUEL LINE
3 - SCREWDRIVER
4 - LATCH CLIP
5 - FUEL RAIL
14 - 12 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
Page 1395 of 1803

(b) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(c) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage.
Replace as necessary.
(8)Latch Clips:Depending on vehicle model and
engine, 2 different types of safety latch clips are used
(Fig. 16) or (Fig. 17). Type-1 is tethered to fuel line
and type-2 is not. A special tool will be necessary todisconnect fuel line after latch clip is removed. The
latch clip may be used on certain fuel line/fuel rail
connection, or to join fuel lines together.
(a) Type 1: Pry up on latch clip with a screw-
driver (Fig. 16).
(b) Type 2: Separate and unlatch 2 small arms
on end of clip (Fig. 17) and swing away from fuel
line.
(c) Slide latch clip toward fuel rail while lifting
with screwdriver.
(d) Insert special fuel line removal tool (Snap-On
number FIH 9055-1 or equivalent) into fuel line
(Fig. 18). Use tool to release locking fingers in end
of line.
(e) With special tool still inserted, pull fuel line
from fuel rail.
(f) After disconnection, locking fingers will
remain within quick-connect fitting at end of fuel
line.
(9) Disconnect quick-connect fitting from fuel sys-
tem component being serviced.
CONNECTING
(1) Inspect quick-connect fitting body and fuel sys-
tem component for damage. Replace as necessary.
(2) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(3) Insert quick-connect fitting into fuel tube or
fuel system component until built-on stop on fuel
tube or component rests against back of fitting.
(4) Continue pushing until a click is felt.
(5) Single-tab type fitting: Push new tab down
until it locks into place in quick-connect fitting.
(6) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(7) Latch Clip Equipped: Install latch clip (snaps
into position).If latch clip will not fit, this indi-
cates fuel line is not properly installed to fuel
rail (or other fuel line). Recheck fuel line con-
nection.
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pressure regulator is located on the bot-
tom of the upper section of the fuel pump module.
The fuel filteris not combinedinto the pressure
regulator on this model.
Fig. 17 LATCH CLIP-TYPE 2
1 - LATCH CLIP
Fig. 18 FUEL LINE DISCONNECTION USING
SPECIAL TOOL
1 - SPECIAL FUEL LINE TOOL
2 - FUEL LINE
3 - FUEL RAIL
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 13
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
Page 1396 of 1803

OPERATION
The fuel pressure regulator is a mechanical device
that is not controlled by engine vacuum or the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM).
The regulator is calibrated to maintain fuel system
operating pressure of approximately 339 kPa +/- 34
kPa (49.2 psi +/- 5 psi) at the fuel injectors. It con-
tains a diaphragm, calibrated springs and a fuel
return valve.
The main fuel filteris not combinedwithin the
fuel pressure regulator as in other Jeeptmodels.
Three different fuel filters are used: 1. a serviceable,
separate, externally mounted, main fuel filter; 2. a
non-serviceable primary filter located on the bottom
of the electric fuel pump; 3. a non-serviceable second-
ary filter attached to the side of the fuel pump mod-
ule.
Fuel Flow:Fuel migrates into the fuel pump mod-
ule reservoir through a one-way check valve located
on the bottom of the module. This check valve pre-
vents the reservoir from running empty such as
when going up or down hills with a low amount of
fuel in the tank. A primary fuel filter (sock) is located
at the bottom of the electric fuel pump. Fuel is drawn
in through this filter, and up to the electric fuel
pump. High pressure fuel (unregulated) is supplied
from the electric fuel pump through a high-pressure
line to one of 3 fittings on the main fuel filter. If fuel
pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds approxi-
mately 49 psi, an internal diaphragm within the reg-
ulator closes, and excess fuel is routed through a
second fitting on the main fuel filter, and back into
the fuel tank (the fuel pressure regulator is installed
into the return side of the system). Pressure regu-
lated fuel is then delivered from the third fitting on
the fuel filter, up to and through the fuel rail, and on
to the fuel injectors.
A secondary fuel filter is attached to the side of the
fuel pump module. High-pressure from the electric
fuel pump causes a siphoning action across a passage
connected to this filter, and fuel is drawn into the
fuel pump module reservoir. This is used to help keep
the module reservoir full of fuel.
The fuel pressure regulator also acts as a check
valve to maintain some fuel pressure when the
engine is not operating. This will help to start the
engine. A second check valve is located at the outlet
of the fuel pump module housing.Refer to Fuel
Pump - Description and Operation for more
information. Also refer to the Fuel Pressure
Leak Down Test, and the Fuel Pump Pressure
Tests.
A separate fuel return line from the engine is not
used with this system.
REMOVAL
The fuel pressure regulator is located in the fuel
tank. It is attached to the bottom of the upper sec-
tion of the fuel pump module with a quick-connect
fitting (Fig. 19). The fuel pump module is supplied in
2 sections (upper and lower). To replace the pressure
regulator, the bottom section of the fuel pump mod-
ule must be replaced.
(1) Remove upper and lower sections of fuel pump
module from fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation.
(2) Replace lower section of fuel pump module
(includes fuel pressure regulator).
INSTALLATION
The fuel pressure regulator is located in the fuel
tank. It is attached to the bottom of the upper sec-
tion of the fuel pump module with a quick-connect
fitting. The fuel pump module is supplied in 2 sec-
tions (upper and lower). To replace the pressure reg-
ulator, the bottom section of the fuel pump module
must be replaced.
(1) Replace lower section of fuel pump module
(includes fuel pressure regulator).
(2) Install upper and lower sections of fuel pump
module to fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Pump Module
Installation.
Fig. 19 FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR/SENDING
UNIT ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
1 - UPPER SECTION OF PUMP MODULE
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
3 - FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - 4-WIRE ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
14 - 14 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR (Continued)