eco JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 190 of 1803

FLUID RESERVOIR
REMOVAL
(1) Install prop rod on brake pedal to keep pres-
sure on the brake system.
(2) Remove reservoir cap and siphon fluid into
drain container.
(3) Remove the electrical connector from the fluid
level switch in the reservoir.
(4) Remove the reservoir mounting bolt.
(5) Remove the reservoir from the master cylinder
by pulling upwards.
(6) Remove old grommets from cylinder body.
INSTALLATION
(1) Fill and bleed master cylinder on bench before
installation in vehicle.
CAUTION: Do not use any type of tool to install the
grommets. Tools may cut, or tear the grommets cre-
ating a leak problem after installation. Install the
grommets using finger pressure only.
(2) Lubricate new grommets with clean brake fluid
and Install new grommets in cylinder body. Use fin-
ger pressure to install and seat grommets.
(3) Start reservoir in grommets. Then rock reser-
voir back and forth while pressing downward to seat
it in grommets.
(4) Install the mounting bolt for the reservoir to
the master cylinder.
(5) Reconnect the electrical connector to the fluid
reservoir level switch.(6) Remove the prop rod from the vehicle.
(7) Fill and bleed base brake system,(Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
FLUID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brakes hydraulic unit and all hydraulic
fluid hoses.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - MASTER
CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL
Always clean the master cylinder reservoir and cap
before adding fluid. This will prevent dirt from fall-
ing in the reservoir and contaminating the brake
fluid.
The reservoir has a ADD and a FULL mark on the
side (Fig. 42) fill to the FULL mark.
Fig. 41 MASTER CYLINDER
1 - FLUID RESERVOIR
2 - BOOSTER
3 - FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
4 - MASTER CYLINDER
5 - FLUID LEVEL MARKS
Fig. 42 TYPICAL - MASTER CYLINDER FLUID
LEVEL
1 - FLUID LEVEL MARKS
2 - RESERVOIR
5 - 26 BRAKES - BASEKJ
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 191 of 1803

SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications and SAE J1703 standards.
No other type of brake fluid is recommended or
approved for usage in the vehicle brake system. Use
only Mopar brake fluid or an equivalent from a
tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container will absorb moisture from the air
and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
DRUM
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE DRUM
The maximum allowable diameter of the drum
braking surface is indicated on the drum outer edge.
Generally, a drum can be machined to a maximum of
1.52 mm (0.060 in.) oversize. Always replace the
drum if machining would cause drum diameter to
exceed the size limit indicated on the drum.
BRAKE DRUM RUNOUT
Measure drum diameter and runout with an accu-
rate gauge. The most accurate method of measure-
ment involves mounting the drum in a brake lathe
and checking variation and runout with a dial indi-
cator.
Variations in drum diameter should not exceed
0.076 mm (0.003 in.). Drum runout should not exceed
0.20 mm (0.008 in.) out of round. Machine the drum
if runout or variation exceed these values. Replace
the drum if machining causes the drum to exceed the
maximum allowable diameter.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - BRAKE DRUM
MACHINING
The brake drums can be machined on a drum lathe
when necessary. Initial machining cuts should be lim-
ited to 0.12 - 0.20 mm (0.005 - 0.008 in.) at a time as
heavier feed rates can produce taper and surface
variation. Final finish cuts of 0.025 to 0.038 mm(0.001 to 0.0015 in.) are recommended and will gen-
erally provide the best surface finish.
Be sure the drum is securely mounted in the lathe
before machining operations. A damper strap should
always be used around the drum to reduce vibration
and avoid chatter marks.
The maximum allowable diameter of the drum
braking surface is stamped or cast into the drum
outer edge.
CAUTION: Replace the drum if machining will cause
the drum to exceed the maximum allowable diame-
ter.
SUPPORT PLATE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 198 RBI AXLE
(1) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(2) Remove the brake drum.
(3) Remove the brake shoes.
(4) Remove parking brake cable from parking
brake lever.
(5) Compress parking brake cable retainer tabs.
Then push retainer and cable through and out of
support plate.
(6) Disconnect brake line at wheel cylinder.
(7) Remove wheel cylinder from support plate,(Re-
fer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
WHEEL CYLINDERS - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the four bolts attaching the support
plate to axle and remove the support plate with the
axle, bearing and seal.
(9) Remove axle shaft,(Refer to 3 - DIFFEREN-
TIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR AXLE/AXLE SHAFTS -
REMOVAL).
REMOVAL - 8 1/4 AXLE
(1) Remove the wheel and tire assembly.
(2) Remove the brake drum.
(3) Install the brake pedal prop rod.
(4) Remove the brake shoes (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/BRAKE PADS/SHOES
- REMOVAL).
(5) Remove parking brake cable from parking
brake lever.
(6) Compress parking brake cable retainer tabs.
Then push retainer and cable through and out of
support plate.
(7) Disconnect the brake line at wheel cylinder.
(8) Remove the wheel cylinder from the support
plate,(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHAN-
ICAL/WHEEL CYLINDERS - REMOVAL).
KJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 27
FLUID (Continued)
Page 193 of 1803

INSPECTION
Inspect the cylinder bore. Light discoloration and
dark stains in the bore are normal and will not
impair cylinder operation.
The cylinder bore can be lightly polished but only
with crocus cloth. Replace the cylinder if the bore is
scored, pitted or heavily corroded. Honing the bore to
restore the surface is not recommended.
Inspect the cylinder pistons. The piston surfaces
should be smooth and free of scratches, scoring and
corrosion. Replace the pistons if worn, scored, or cor-
roded. Do not attempt to restore the surface by sand-
ing or polishing.Discard the old piston cups and the spring and
expander. These parts are not reusable. The original
dust boots may be reused but only if they are in good
condition.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate wheel cylinder bore, pistons, piston
cups and spring and expander with clean brake fluid.
(2) Install first piston in cylinder bore. Then
install first cup in bore and against piston.Be sure
lip of piston cup is facing inward (toward
spring and expander) and flat side is against
piston.
(3) Install spring and expander followed by
remaining piston cup and piston.
(4) Install boots on each end of cylinder and insert
push rods in boots.
(5) Install cylinder bleed screw.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install cylinder mounting bolts and tighten to
20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 44).
(2) Connect brake line to cylinder and tighten to
14 N´m (124 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the brake shoe return springs.
(4) Remove the brake pedal prop rod.
(5) Install the brake drum.
(6) Install the wheel and tire assembly (Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(7) Bleed base brake system (Refer to 5 - BRAKES
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
PARKING BRAKE
DESCRIPTION
The parking brake is a hand lever and cable oper-
ated system used to apply the rear brakes.
OPERATION
A hand operated lever in the passenger compart-
ment is the main application device. The front cable
is connected between the hand lever and the rear
cables with an equalizer.
The rear cables are connected to the actuating
lever on each primary brake shoe. The levers are
attached to the brake shoes by a pin either pressed
into, or welded to the lever. A clip is used to secure
the pin in the brake shoe. The pin allows each lever
to pivot independently of the brake shoe.
To apply the parking brakes, the hand lever is
pulled upward. This pulls the rear brake shoe actu-
ating levers forward, by means tensioner and cables.
As the actuating lever is pulled forward, the parking
brake strut (which is connected to both shoes), exerts
Fig. 44 WHEEL CYLINDER
1 - WHEEL CYLINDER
2 - SUPPORT PLATE
Fig. 45 Wheel Cylinder Components±Typical
1 - SPRING
2 - CYLINDER
3 - PISTON CLIP
4 - BOOT
5 - PUSH ROD
6 - PISTON
7 - BLEED SCREW
8 - CUP EXPANDERS
KJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 29
WHEEL CYLINDERS (Continued)
Page 194 of 1803

a linear force against the secondary brake shoe. This
action presses the secondary shoe into contact with
the drum. Once the secondary shoe contacts the
drum, force is exerted through the strut. This force is
transferred through the strut to the primary brake
shoe causing it to pivot into the drum as well.
A gear type ratcheting mechanism is used to hold
the lever in an applied position. Parking brake
release is accomplished by the hand lever release
button.
A parking brake switch is mounted on the parking
brake lever and is actuated by movement of the
lever. The switch, which is in circuit with the red
warning light in the dash, will illuminate the warn-
ing light whenever the parking brakes are applied.
Parking brake is self-adjusting when the lever is
pulled. The cable tensioner, once adjusted at the fac-
tory, should not need further adjustment under nor-
mal circumstances.
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - LOCK OUT
NOTE: The parking brake is self-adjusting, It can
not be adjusted.
(1) Remove the center floor console (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - REMOVAL).
(2) Pull up on the spring until the tab on the lever
passes the tab on the cable guide and install a punch
in the hole on the side then release (Fig. 46).(3) The park brake system is now locked out to
perform necessary repairs.
CABLES
REMOVAL
(1) Lock out the parking brake cables (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE - ADJUSTMENTS) (Fig.
46).
(2) Remove the rear seat (Refer to 23 - BODY/
SEATS/SEAT - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the cable saddle bracket (Fig. 47).
(4) Disconnect the two cables from the front mount
(Fig. 48).
(5) Pull the carpet forward far enough in the rear
to gain access to the two parking brake cables thru
the floor (Fig. 47).
(6) Push the cables thru the floor with the grom-
mets.
(7) Remove the primary brake shoe hold down
spring and separate the shoes to gain access, Then
disconnect the cable from lever on brake shoe.
(8) Remove cables from backing plates by using a
screw driver to break off the tangs on the cable or a
proper sized box end wrench over the tangs.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the cables into the support plate.
(2) Reconnect the cable to the lever on the brake
shoe, Install the primary brake shoe hold down
spring and the shoes.
Fig. 46 LOCK OUT CABLES
1 - PARKING BRAKE HANDLE
2 - PUNCH
3 - CABLE GUIDE
4 - CABLE
Fig. 47 MOUNTING BRACKETS
1 - MOUNTING SADDLE BRACKET
2 - PARK BRAKE CABLES
3 - CARPET
5 - 30 BRAKES - BASEKJ
PARKING BRAKE (Continued)
Page 195 of 1803

(3) Push the cables thru the floor and seat the
grommets.
(4) Reconnect the two cables to the front mount.
(5) Install the cable saddle bracket (Fig. 47).
(6) Lay the carpet back down in the rear.
(7) Install the rear seat (Refer to 23 - BODY/
SEATS/SEAT - INSTALLATION).
(8) Remove the lock out device on the lever.
(9) Test the parking brake.
LEVER
REMOVAL
The center floor console must be removed to service
the parking brake lever,(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERI-
OR/FLOOR CONSOLE - REMOVAL) .
(1) Lock out the parking brakes (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE - ADJUSTMENTS).
(2) Disengage the front cables from the equalizer
(Fig. 49).
(3) Disconnect the parking brake lamp switch wire
(Fig. 49).
(4) Remove the parking brake lever assembly
mounting bolts (Fig. 50).
(5) Remove the lever assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the parking brake lever assembly.
(2) Install the parking brake lever assembly to the
mounting bolts. Tighten (Fig. 50).
Install the center floor console, (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLA-
TION).
(3) Engage the front cables to the equalizer (Fig.
49).(4) Reconnect the parking brake lamp switch wire
(Fig. 49).
(5) If installing a new parking brake lever remove
the pin that come on the lever when shipped.
(6) If you are reinstalling the original park brake
lever remove the lock out device at this time.
(7) Test the parking brake lever. (Fig. 50).
Fig. 48 CABLE FRONT MOUNT
1 - RETAINER CLIPS
2 - CABLES
Fig. 49 PARKING BRAKE LEVER
1 - PARK BRAKE LEVER ASSEMBLY
2 - EQUALIZER
Fig. 50 LEVER MOUNT
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - PARK BRAKE LEVER ASSEMBLY
3 - CABLE
KJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 31
CABLES (Continued)
Page 196 of 1803

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................32
OPERATION...........................32
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKING SYSTEM....................33
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ABS BRAKE
BLEEDING...........................33
SPECIFICATIONS.......................33
ELECTRICAL
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
REMOVAL.............................36
INSTALLATION.........................36
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
ANTILOCK BRAKING SYSTEM
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching 20 to 30 percent of
actual vehicle speed during braking. Periods of high
wheel slip occur when brake stops involve high pedal
pressure and rate of vehicle deceleration.
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB ignition ter-
minal when the ignition switch is turned to Run posi-
tion. The CAB performs a system initialization
procedure at this point. Initialization consists of a
static and dynamic self check of system electrical
components.
The static check occurs after the ignition switch is
turned to Run position. The dynamic check occurs
when vehicle road speed reaches approximately 30
kph (18 mph). During the dynamic check, the CAB
briefly cycles the pump and solenoids to verify oper-
ation.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ELECTRONIC BRAKE DISTRIBUTION
The electronic brake distribution (EBD) functions
like a rear proportioning valve. The EBD system usesthe ABS system to control the slip of the rear wheels
in partial braking range. The braking force of the
rear wheels is controlled electronically by using the
inlet and outlet valves located in the HCU.
OPERATION
ANTILOCK BRAKING SYSTEM
During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
During antilock braking fluid pressure is modu-
lated according to wheel speed, degree of slip and
rate of deceleration. A sensor at each wheel converts
wheel speed into electrical signals. These signals are
transmitted to the CAB for processing and determi-
nation of wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a high slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program. Two solenoid valves are used
in each antilock control channel. The valves are all
located within the HCU valve body and work in pairs
to either increase, hold, or decrease apply pressure as
needed in the individual control channels. The sole-
noid valves are not static during antilock braking.
They are cycled continuously to modulate pressure.
Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be mea-
sured in milliseconds.
ELECTRONIC BRAKE DISTRIBUTION
Upon entry into EBD the inlet valve for the rear
brake circuit is switched on so that the fluid supply
from the master cylinder is shut off. In order to
decrease the rear brake pressure the outlet valve for
5 - 32 BRAKES - ABSKJ
Page 197 of 1803
the rear brake circuit is pulsed. This allows fluid to
enter the low pressure accumulator (LPA) in the
HCU resulting in a drop in fluid pressure to the rear
brakes. In order to increase the rear brake pressure
the outlet valve is switched off and the inlet valve is
pulsed. This increases the pressure to the rear
brakes. This will continue until the required slip dif-
ference is obtained. At the end of EBD braking (no
brake application) the fluid in the LPA drains back to
the master cylinder by switching on the outlet valve
and draining through the inlet valve check valve. At
the same time the inlet valve is switched on to pre-
vent a hydraulic short circiut in case of another
brake application.The EBD will remain functional
during many ABS fault modes. If the red and amber
warning lamps are illuminated the EBD may have a
fault.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKING SYSTEM
The ABS brake system performs several self-tests
every time the ignition switch is turned on and the
vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the systems
input and output circuits to verify the system is oper-
ating correctly. If the on board diagnostic system
senses that a circuit is malfunctioning the system
will set a trouble code in its memory.
NOTE: An audible noise may be heard during the
self-test. This noise should be considered normal.NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the ABS system. For additional informa-
tion refer to the Electrical, Electronic Control Mod-
ules section. For test procedures refer to the
Chassis Diagnostic Manual.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ABS BRAKE
BLEEDING
ABS system bleeding requires conventional bleed-
ing methods plus use of the DRB scan tool. The pro-
cedure involves performing a base brake bleeding,
followed by use of the scan tool to cycle and bleed the
HCU pump and solenoids. A second base brake bleed-
ing procedure is then required to remove any air
remaining in the system.
(1) Perform base brake bleeding,(Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR (Refer to
5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Connect scan tool to the Data Link Connector.
(3) Select ANTILOCK BRAKES, followed by MIS-
CELLANEOUS, then ABS BRAKES. Follow the
instructions displayed. When scan tool displays TEST
COMPLETE, disconnect scan tool and proceed.
(4) Perform base brake bleeding a second time,(Re-
fer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Hydraulic Control
Unit/Controller Antilock
Brakes Mounting Nuts14.1 Ð 125
Hydraulic Control
Unit/Controller Antilock
Brakes Brake Lines20.3 Ð 180
Controller Antilock Brakes
Mounting Screws1.8 Ð 16
Wheel Speed Sensors
Front Mounting Bolt12 Ð 132
Wheel Speed Sensor
Rear Mounting Bolt9Ð80
KJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 33
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)
Page 198 of 1803

ELECTRICAL
DESCRIPTION
Three wheel speed sensors are used. The front sen-
sors are mounted to the steering knuckles. The rear
sensor is mounted at the top of the rear axle differ-
ential carrier. Tone wheels are mounted to the out-
board ends of the front axle shafts. The gear type
tone wheel serves as the trigger mechanism for each
sensor.
OPERATION
The sensors convert wheel speed into a small digi-
tal signal. The CAB sends 12 volts to the sensors.
The sensor has an internal magneto resistance
bridge that alters the voltage and amperage of the
signal circuit. This voltage and amperage is changed
by magnetic induction when the toothed tone wheel
passes the wheel speed sensor. This digital signal is
sent to the CAB. The CAB measures the voltage and
amperage of the digital signal for each wheel.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the front wheel speed sensor wire
connector that is located on the inboard side of the
respective wheel house.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(4) Remove the caliper adapter. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - REMOVAL).
CAUTION: Never allow the disc brake caliper to
hang from the brake hose. Damage to the brake
hose with result. Provide a suitable support to hang
the caliper securely.
(5) Remove the disc brake rotor. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
REMOVAL).
(6) Remove the wheel speed sensor mounting bolt
to the hub (Fig. 1).
(7) Remove the wheel speed sensor wire from the
hub/bearing (Fig. 1).
(8) Remove the wheel speed sensor wire hold down
from the knuckle (Fig. 1).
(9) Remove the wheel speed sensor wire thru the
wheel well.
(10) Remove the wheel speed sensor from the vehi-
cle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the wheel speed sensor to the vehicle.
(2) Install the wheel speed sensor wire thru the
wheel well.
(3) Install the wheel speed sensor wire to the hub/
bearing.
(4) Install the wheel speed sensor wire hold down
to the knuckle.
(5) Install the wheel speed sensor mounting bolt to
the hub. Tighten the mounting bolt to 14 N´m (10
ft.lbs.).
(6) Install the disc brake rotor (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Install the disc brake caliper adapter. (Refer to
5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the tire and wheel assembly (Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(9) Reconnect the front wheel speed sensor wire
connector to the inboard side of the wheel house
being worked on.
Fig. 1 FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR WIRE
2 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
3 - ROTOR
4 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR WIRE HOLD DOWN
5 - 34 BRAKES - ABSKJ
Page 206 of 1803

WARNING
WARNING:: EXERCISE CARE WHEN SERVICING
CLUTCH COMPONENTS. FACTORY INSTALLED
CLUTCH DISCS DO NOT CONTAIN ASBESTOS
FIBERS. DUST AND DIRT ON CLUTCH PARTS MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM AFTERMAR-
KET COMPONENTS. BREATHING EXCESSIVE CON-
CENTRATIONS OF THESE FIBERS CAN CAUSE
SERIOUS BODILY HARM. WEAR A RESPIRATOR
DURING SERVICE AND NEVER CLEAN CLUTCH
COMPONENTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR WITH
A DRY BRUSH. EITHER CLEAN THE COMPONENTS
WITH A WATER DAMPENED RAGS OR USE A VAC-
UUM CLEANER SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR
REMOVING ASBESTOS FIBERS AND DUST. DO NOT
CREATE DUST BY SANDING A CLUTCH DISC.
REPLACE THE DISC IF THE FRICTION MATERIAL IS
DAMAGED OR CONTAMINATED. DISPOSE OF ALL
DUST AND DIRT CONTAINING ASBESTOS FIBERS
IN SEALED BAGS OR CONTAINERS. THIS WILL
HELP MINIMIZE EXPOSURE TO YOURSELF AND TO
OTHERS. FOLLOW ALL RECOMMENDED SAFETY
PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY THE OCCUPATIONAL
SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION (OSHA)
AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY AGENCY
(EPA), FOR THE HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF
PRODUCTS CONTAINING ASBESTOS.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH
Drive the vehicle at normal speeds. Shift the trans-
mission through all gear ranges and observe clutch
action. If the clutch chatters, grabs, slips or does not
release properly, remove and inspect the clutch com-
ponents. If the problem is noise or hard shifting, fur-
ther diagnosis may be needed as the transmission or
another driveline component may be at fault.
NOTE: Vehicles equipped with a Dual Mass Fly-
wheel may produce a rattle when the engine is shut
off. This noise is considered normal.
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION
Fluid contamination is a frequent cause of clutch
malfunctions. Oil, water or clutch fluid on the clutch
disc and pressure plate surfaces will cause chatter,
slip and grab. Inspect components for oil, hydraulic
fluid or water/road splash contamination.
Oil contamination indicates a leak at either the
rear main seal or transmission input shaft. Clutch
fluid leaks are usually from damaged slave cylinder
push rod seals. Heat buildup caused by slippage
between the pressure plate, disc and flywheel can
bake the oil residue onto the components. The glaze-
like residue ranges in color from amber to black.Road splash contamination is dirt/water entering
the clutch housing due to loose bolts, housing cracks.
Driving through deep water puddles can force water/
road splash into the housing through such openings.
IMPROPER RELEASE OR CLUTCH ENGAGEMENT
Clutch release or engagement problems are caused
by wear or damage clutch components. A visual
inspection of the release components will usually
reveal the problem part.
Release problems can result in hard shifting and
noise. Look for leaks at the clutch cylinders and
interconnecting line and loose slave cylinder bolts.
Also worn/loose release fork, pivot stud, clutch disc,
pressure plate or release bearing.
Engagement problems can result in slip, chatter/
shudder and noisy operation. The causes may be
clutch disc contamination, wear, distortion or fly-
wheel damage. Visually inspect to determine the
actual cause of the problem.
CLUTCH MISALIGNMENT
Clutch components must be in proper alignment
with the crankshaft and transmission input shaft.
Misalignment caused by excessive runout or warpage
of any clutch component will cause grab, chatter and
improper clutch release.
PRESSURE PLATE AND DISC RUNOUT
Check the clutch disc before installation. Axial
(face) runout of anewdisc should not exceed 0.50
mm (0.020 in.). Measure runout about 6 mm (1/4 in.)
from the outer edge of the disc facing. Obtain
another disc if runout is excessive.
Check condition of the clutch before installation. A
warped cover or diaphragm spring will cause grab
and incomplete release or engagement. Be careful
when handling the cover and disc. Impact can distort
the cover, diaphragm spring, release fingers and the
hub of the clutch disc.
Use an alignment tool when positioning the disc on
the flywheel. The tool prevents accidental misalign-
ment which could result in cover distortion and disc
damage.
A frequent cause of clutch cover distortion (and
consequent misalignment) is improper bolt tighten-
ing.
FLYWHEEL RUNOUT
Check flywheel runout whenever misalignment is
suspected. Flywheel runout should not exceed 0.08
mm (0.003 in.). Measure runout at the outer edge of
the flywheel face with a dial indicator. Mount the
indicator on a stud installed in place of one of the fly-
wheel bolts.
6 - 2 CLUTCHKJ
CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 207 of 1803
Common causes of runout are:
²heat warpage
²improper machining
²incorrect bolt tightening
²improper seating on crankshaft flange shoulder
²foreign material on crankshaft flange
Flywheel machining is not recommended. The fly-
wheel clutch surface is machined to a unique contour
and machining will negate this feature. Minor fly-
wheel scoring can be cleaned up by hand with 180
grit emery or with surface grinding equipment.
Remove only enough material to reduce scoring
(approximately 0.001 - 0.003 in.). Heavy stock
removal isnot recommended.Replace the flywheel
if scoring is severe and deeper than 0.076 mm (0.003
in.). Excessive stock removal can result in flywheel
cracking or warpage after installation; it can alsoweaken the flywheel and interfere with proper clutch
release.
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
flywheel. Dirt and grease on the flange surface may
cock the flywheel causing excessive runout. Use new
bolts when remounting a flywheel and secure the
bolts with Mopar Lock And Seal or equivalent.
Tighten flywheel bolts to specified torque only. Over-
tightening can distort the flywheel hub causing
runout.
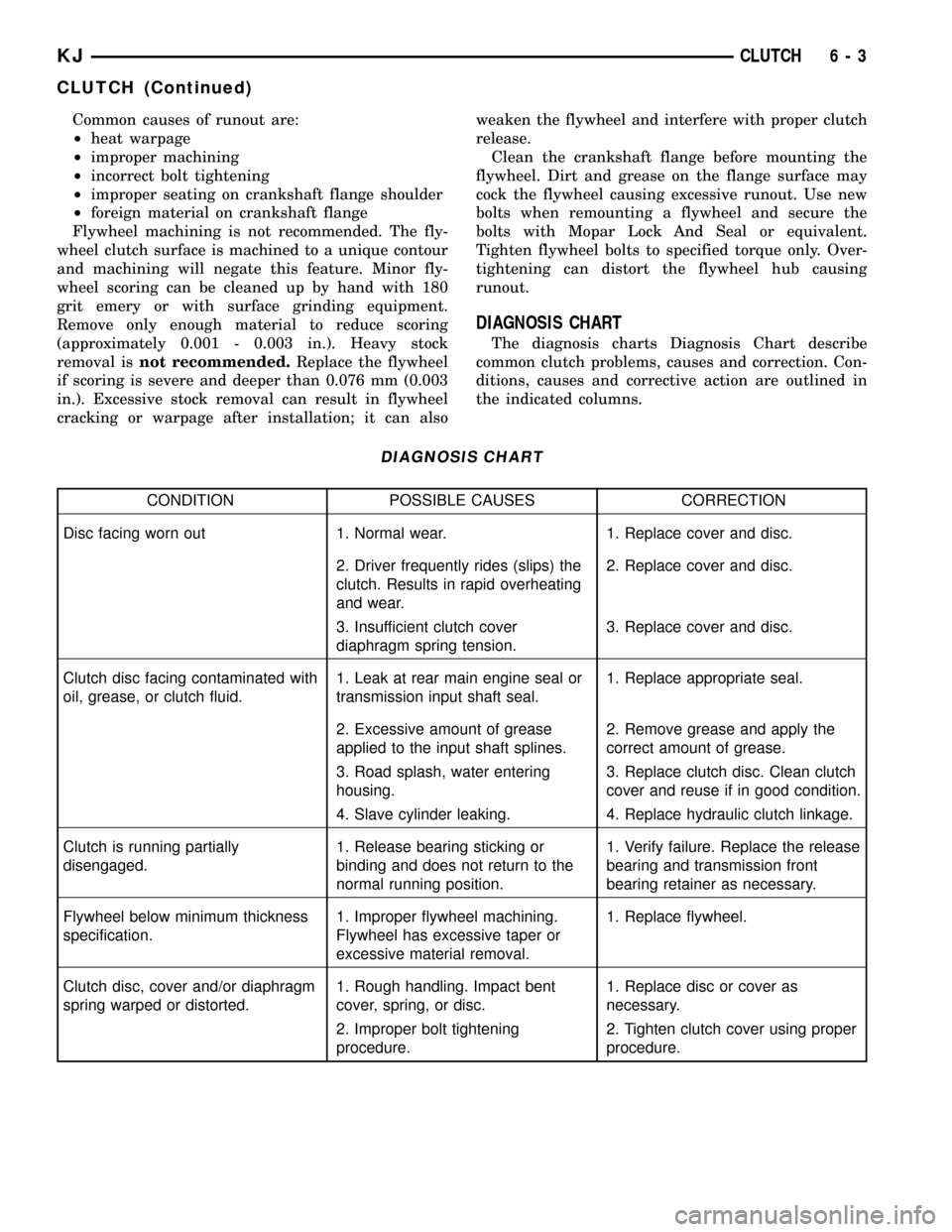
DIAGNOSIS CHART
The diagnosis charts Diagnosis Chart describe
common clutch problems, causes and correction. Con-
ditions, causes and corrective action are outlined in
the indicated columns.
DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Disc facing worn out 1. Normal wear. 1. Replace cover and disc.
2. Driver frequently rides (slips) the
clutch. Results in rapid overheating
and wear.2. Replace cover and disc.
3. Insufficient clutch cover
diaphragm spring tension.3. Replace cover and disc.
Clutch disc facing contaminated with
oil, grease, or clutch fluid.1. Leak at rear main engine seal or
transmission input shaft seal.1. Replace appropriate seal.
2. Excessive amount of grease
applied to the input shaft splines.2. Remove grease and apply the
correct amount of grease.
3. Road splash, water entering
housing.3. Replace clutch disc. Clean clutch
cover and reuse if in good condition.
4. Slave cylinder leaking. 4. Replace hydraulic clutch linkage.
Clutch is running partially
disengaged.1. Release bearing sticking or
binding and does not return to the
normal running position.1. Verify failure. Replace the release
bearing and transmission front
bearing retainer as necessary.
Flywheel below minimum thickness
specification.1. Improper flywheel machining.
Flywheel has excessive taper or
excessive material removal.1. Replace flywheel.
Clutch disc, cover and/or diaphragm
spring warped or distorted.1. Rough handling. Impact bent
cover, spring, or disc.1. Replace disc or cover as
necessary.
2. Improper bolt tightening
procedure.2. Tighten clutch cover using proper
procedure.
KJCLUTCH 6 - 3
CLUTCH (Continued)