Heating JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 1654 of 1803

DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT
The two refrigerant system service ports are used
to charge, recover/recycle, evacuate, and test the air
conditioning refrigerant system. Unique service port
coupler sizes are used on the R-134a system, to
ensure that the refrigerant system is not accidentally
contaminated by the use of the wrong refrigerant
(R-12), or refrigerant system service equipment.
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
The heater and optional air conditioner are blend-
air type systems. In a blend-air system, a blend door
controls the amount of unconditioned air (or cooled
air from the evaporator on models with air condition-
ing) that is allowed to flow through, or around, the
heater core. A temperature control knob on the A/C
Heater control panel determines the discharge air
temperature by controlling an electric actuator,
which moves the blend door. This allows an almost
immediate control of the output air temperature of
the system.
The mode control knob on the heater-only or A/C
Heater control panel is used to direct the conditioned
air to the selected system outlets. Both mode control
switches use engine vacuum to control the mode
doors, which are operated by vacuum actuators.
On all vehicles, the outside air intake can be shut
off by selecting the Recirculation Mode with the
mode control knob. This will operate a vacuum actu-
ated recirculation door that closes off the outside
fresh air intake and recirculates the air that is
already inside the vehicle.
The optional air conditioner for all models is
designed for the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant.
The air conditioning system has an evaporator to cool
and dehumidify the incoming air prior to blending it
with the heated air. This air conditioning system
uses a fixed orifice tube in the liquid line near the
condenser outlet tube to meter refrigerant flow to the
evaporator coil. To maintain minimum evaporator
temperature and prevent evaporator freezing, the
A/C low pressure switch on the accumulator cycles
the compressor clutch.
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
PORT
The high pressure service port is located on the
refrigerant line, near the discharge port of the com-
pressor. The low pressure service port is located on
the liquid line at the side of the engine compartment,
near the condensor.Each of the service ports has a threaded plastic
protective cap installed over it from the factory. After
servicing the refrigerant system, always reinstall
both of the service port caps.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to provide
the passenger compartment with low temperature
and low humidity air. The evaporator, located in the
HVAC housing on the dash panel below the instru-
ment panel, is cooled to temperatures near the freez-
ing point. As warm damp air passes through the
cooled evaporator, the air transfers its heat to the
refrigerant in the evaporator and the moisture in the
air condenses on the evaporator fins. During periods
of high heat and humidity, an air conditioning sys-
tem will be more effective in the Recirculation Mode.
With the system in the Recirculation Mode, only air
from the passenger compartment passes through the
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, the air conditioning system performance
levels improve.
Humidity has an important bearing on the temper-
ature of the air delivered to the interior of the vehi-
cle. It is important to understand the effect that
humidity has on the performance of the air condition-
ing system. When humidity is high, the evaporator
has to perform a double duty. It must lower the air
temperature, and it must lower the temperature of
the moisture in the air that condenses on the evapo-
rator fins. Condensing the moisture in the air trans-
fers heat energy into the evaporator fins and tubing.
This reduces the amount of heat the evaporator can
absorb from the air. High humidity greatly reduces
the ability of the evaporator to lower the temperature
of the air.
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Remov-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from the
air conditioning system on humid days. A perfor-
mance test is the best way to determine whether the
system is performing up to standard. This test also
provides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the air conditioning system.
Before proceeding, (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION). The air temperature in
the test room and in the vehicle must be a minimum
of 21É C (70É F) for this test.
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1655 of 1803

(1) Connect a tachometer a manifold gauge set or
A/C recycling/charging station.
(2) Set the A/C Heater mode control switch knob in
the Recirculation Mode position, the temperature
control knob in the full cool position, and the blower
motor switch knob in the highest speed position.
(3) Start the engine and hold the idle at 1,000 rpm
with the compressor clutch engaged.
(4) The engine should be at operating temperature.
The doors and windows must be closed.
(5) Insert a thermometer in the driver side center
A/C (panel) outlet. Operate the engine for five min-
utes.
(6) The compressor clutch may cycle, depending
upon the ambient temperature and humidity. If the
clutch cycles, unplug the a/c low pressure switch wire
harness connector. (Fig. 2). Place a jumper wire
across the terminals of the a/c low pressure switch
wire harness connector.
(7) With the compressor clutch engaged, record the
discharge air temperature and the compressor dis-
charge pressure.
(8) Compare the discharge air temperature to the
Performance Temperature and Pressure chart. If the
discharge air temperature is high, (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM LEAKS) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECIFICATIONS -
CHARGE CAPACITY).
Performance Temperature and Pressure
Ambient Air
Temperature21É C
(70É F)27É C
(80É F)32É C
(90É F)38É C
(100É F)43É C
(110É F)
Air Temperature at
Center Panel Outlet7É C
(45É F)7É C
(45É F)13É C
(55É F)13É C
(55É F)18É C
(64É F)
Compressor Inlet
Pressure at Service
Port (low Side)138 to 207 kPa
(20 to 30 psi)172 to 241
kPa
(25 to 35 psi)207 to 276
kPa
(30 to 40 psi)241 to 310
kPa
(35 to 45 psi)276 to 345 kPa
(40 to 50 psi)
Condensor Out
Pressuree at Service
POrt (High Side)1034 to 1724
kPa
(150 to 250
psi)1379 to 2068
kPa
(200 to 300
psi)1724 to 2413
kPa
(250 to 350
psi)1999 to 2689
kPa
(290 to 390
psi)2413 to 2965
kPa
(350 to 430 psi)
(9) Compare the compressor discharge pressure to
the Performance Temperature and Pressure chart. If
the compressor discharge pressure is high, see the
Pressure Diagnosis chart.
Fig. 2 A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH - TYPICAL
1 - A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
2 - ACCUMULATOR
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 3
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1656 of 1803
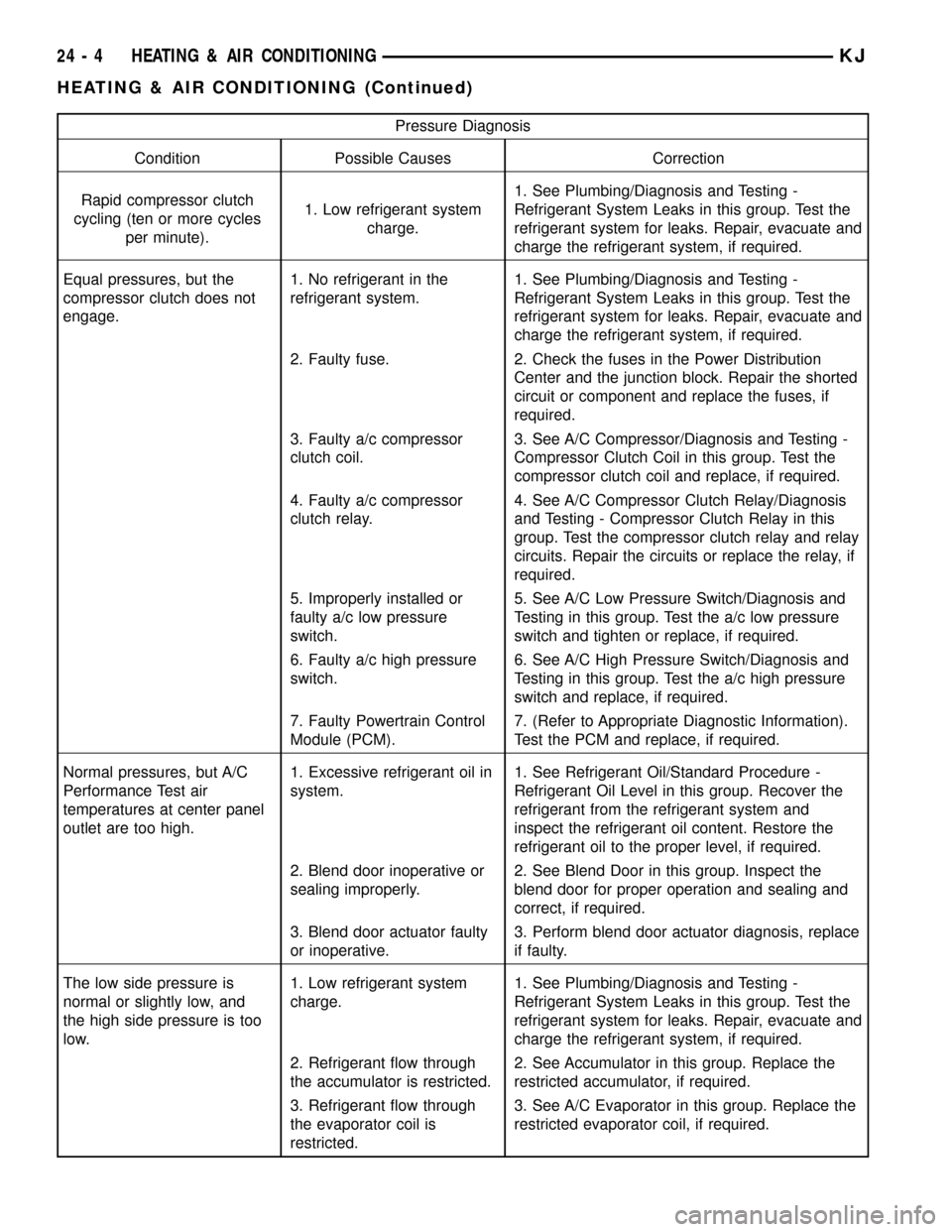
Pressure Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Rapid compressor clutch
cycling (ten or more cycles
per minute).1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
Equal pressures, but the
compressor clutch does not
engage.1. No refrigerant in the
refrigerant system.1. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
2. Faulty fuse. 2. Check the fuses in the Power Distribution
Center and the junction block. Repair the shorted
circuit or component and replace the fuses, if
required.
3. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch coil.3. See A/C Compressor/Diagnosis and Testing -
Compressor Clutch Coil in this group. Test the
compressor clutch coil and replace, if required.
4. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch relay.4. See A/C Compressor Clutch Relay/Diagnosis
and Testing - Compressor Clutch Relay in this
group. Test the compressor clutch relay and relay
circuits. Repair the circuits or replace the relay, if
required.
5. Improperly installed or
faulty a/c low pressure
switch.5. See A/C Low Pressure Switch/Diagnosis and
Testing in this group. Test the a/c low pressure
switch and tighten or replace, if required.
6. Faulty a/c high pressure
switch.6. See A/C High Pressure Switch/Diagnosis and
Testing in this group. Test the a/c high pressure
switch and replace, if required.
7. Faulty Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).7. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information).
Test the PCM and replace, if required.
Normal pressures, but A/C
Performance Test air
temperatures at center panel
outlet are too high.1. Excessive refrigerant oil in
system.1. See Refrigerant Oil/Standard Procedure -
Refrigerant Oil Level in this group. Recover the
refrigerant from the refrigerant system and
inspect the refrigerant oil content. Restore the
refrigerant oil to the proper level, if required.
2. Blend door inoperative or
sealing improperly.2. See Blend Door in this group. Inspect the
blend door for proper operation and sealing and
correct, if required.
3. Blend door actuator faulty
or inoperative.3. Perform blend door actuator diagnosis, replace
if faulty.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly low, and
the high side pressure is too
low.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
2. Refrigerant flow through
the accumulator is restricted.2. See Accumulator in this group. Replace the
restricted accumulator, if required.
3. Refrigerant flow through
the evaporator coil is
restricted.3. See A/C Evaporator in this group. Replace the
restricted evaporator coil, if required.
24 - 4 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1657 of 1803
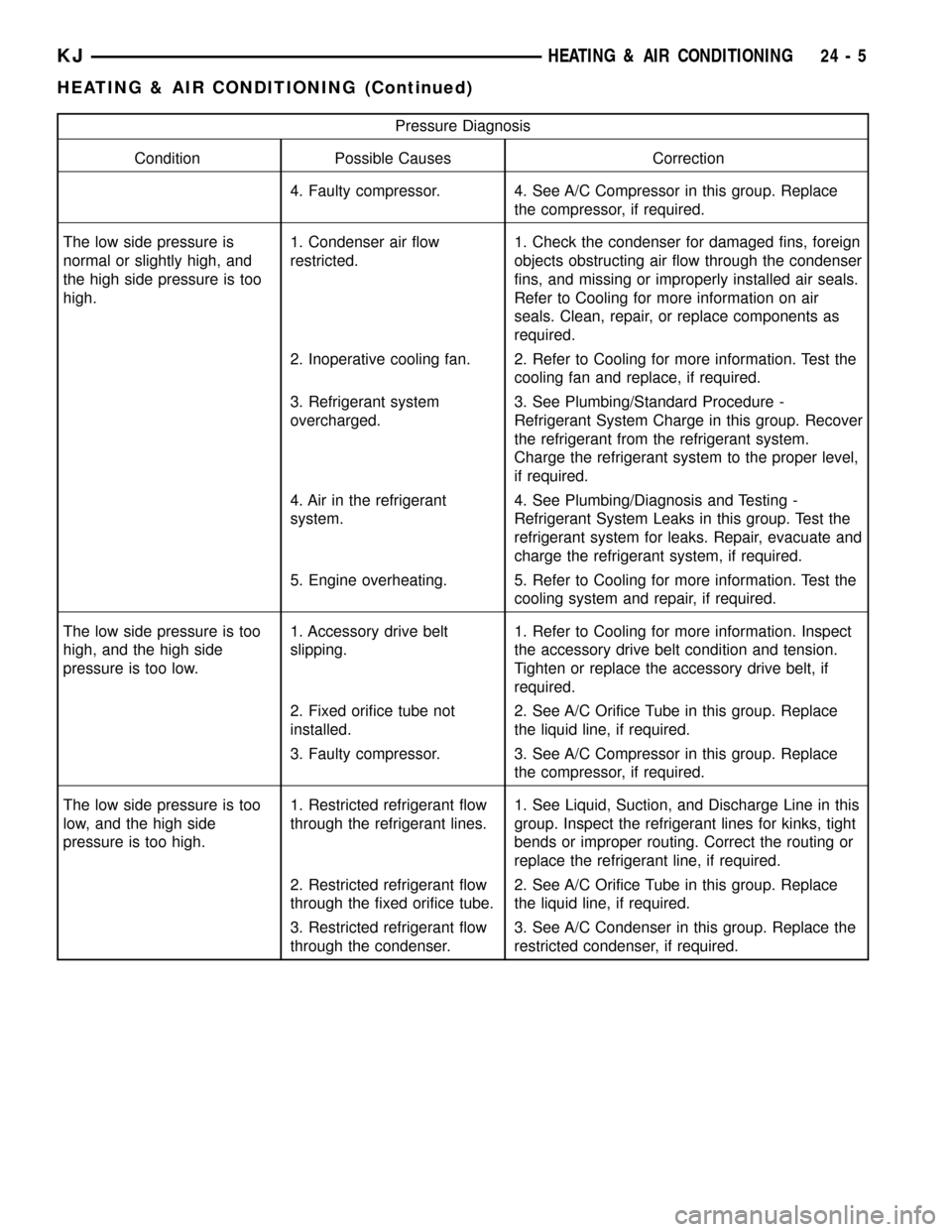
Pressure Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
4. Faulty compressor. 4. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly high, and
the high side pressure is too
high.1. Condenser air flow
restricted.1. Check the condenser for damaged fins, foreign
objects obstructing air flow through the condenser
fins, and missing or improperly installed air seals.
Refer to Cooling for more information on air
seals. Clean, repair, or replace components as
required.
2. Inoperative cooling fan. 2. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling fan and replace, if required.
3. Refrigerant system
overcharged.3. See Plumbing/Standard Procedure -
Refrigerant System Charge in this group. Recover
the refrigerant from the refrigerant system.
Charge the refrigerant system to the proper level,
if required.
4. Air in the refrigerant
system.4. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
5. Engine overheating. 5. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling system and repair, if required.
The low side pressure is too
high, and the high side
pressure is too low.1. Accessory drive belt
slipping.1. Refer to Cooling for more information. Inspect
the accessory drive belt condition and tension.
Tighten or replace the accessory drive belt, if
required.
2. Fixed orifice tube not
installed.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Faulty compressor. 3. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid, Suction, and Discharge Line in this
group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for kinks, tight
bends or improper routing. Correct the routing or
replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the fixed orifice tube.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 5
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1658 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures to check the radiator coolant
level, serpentine drive belt tension, radiator air flow
and the radiator fan operation. Also be certain that
the accessory vacuum supply line is connected at the
engine intake manifold.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT
Engine coolant is delivered to the heater core
through two heater hoses. With the engine idling atnormal operating temperature, set the temperature
control knob in the full hot position, the mode control
switch knob in the floor heat position, and the blower
motor switch knob in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged at the HVAC housing floor
outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the
Temperature Reference chart.
Temperature Reference
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet52.2É C
(126É F)56.1É C
(133É F)59.4É C
(139É F)62.2É C
(144É F)
If the floor outlet air temperature is too low, refer
to Cooling to check the engine coolant temperature
specifications. Both of the heater hoses should be hot
to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should
be slightly cooler than the coolant supply heater
hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the sup-
ply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. Refer to Cooling
for the procedures.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible loca-
tions or causes of obstructed coolant flow:
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²A plugged heater core.
If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is still
low, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS Possible locations or
causes of insufficient heat:
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²A blend door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob on theA/C Heater control panel, the following could require
service:
²The A/C Heater control.
²The blend door actuator.
²The blend door.
²Improper engine coolant temperature.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM SYSTEM
Vacuum control is used to operate the mode doors
in the heater-only and a/c heater housings. Testing of
the heater-only and A/C Heater mode control switch
operation will determine if the vacuum, electrical,
and mechanical controls are functioning. However, it
is possible that a vacuum control system that oper-
ates perfectly at engine idle (high engine vacuum)
may not function properly at high engine speeds or
loads (low engine vacuum). This can be caused by
leaks in the vacuum system, or a faulty vacuum
check valve.
A vacuum system test will help to identify the
source of poor vacuum system performance or vac-
uum system leaks. Before starting this test, stop the
engine and make certain that the problem is not a
disconnected vacuum supply tube at the engine
intake manifold vacuum tap or at the vacuum reser-
voir.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1659 of 1803

Use an adjustable vacuum test set (Special Tool
C-3707-B) and a suitable vacuum pump to test the
HVAC vacuum control system. With a finger placed
over the end of the vacuum test hose probe (Fig. 3),
adjust the bleed valve on the test set gauge to obtain
a vacuum of exactly 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.). Release and
block the end of the probe several times to verify that
the vacuum reading returns to the exact 27 kPa (8
in. Hg.) setting. Otherwise, a false reading will be
obtained during testing.
VACUUM CHECK VALVE
(1) Remove the vacuum check valve. The valve is
located in the vacuum supply tube (black) at the
HVAC system vacuum tee.
(2) Connect the test set vacuum supply hose to the
A/C Heater Control side of the valve. When con-
nected to this side of the check valve, no vacuum
should pass and the test set gauge should return to
the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting. If OK, go to Step 3. If
not OK, replace the faulty valve.
(3) Connect the test set vacuum supply hose to the
engine vacuum side of the valve. When connected to
this side of the check valve, vacuum should flow
through the valve without restriction. If not OK,
replace the faulty valve.
A/C HEATER CONTROLS
(1) Connect the test set vacuum probe to the
HVAC vacuum supply (black) tube at the tee in the
engine compartment. Position the test set gauge so
that it can be viewed from the passenger compart-
ment.(2) Place the A/C Heater Mode Control switch
knob in each mode position, one position at a time,
and pause after each selection. The test set gauge
should return to the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting
shortly after each selection is made. If not OK, a
component or vacuum line in the vacuum circuit of
the selected mode has a leak. See the procedure in
Locating Vacuum Leaks.
CAUTION: Do not use lubricant on the switch ports
or in the holes in the plug, as lubricant will ruin the
vacuum valve in the switch. A drop of clean water
in the connector plug holes will help the connector
slide onto the switch ports.
LOCATING VACUUM LEAKS
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect the vacuum harness connector from
the back of the HVAC control head(Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C
HEATER CONTROL - REMOVAL).
(2) Connect the test set vacuum hose probe to each
port in the HVAC housing half of the vacuum har-
ness connector, one port at a time, and pause after
each connection. The test set gauge should return to
the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting shortly after each con-
nection is made. If OK, replace the faulty A/C Heater
Control. If not OK, go to Step 3.
(3) Determine the vacuum line color of the vacuum
circuit that is leaking. To determine the vacuum line
colors, refer to the Vacuum Circuits chart (Fig. 4).
(4) Disconnect and plug the vacuum line from the
component (fitting, actuator, valve, switch, or reser-
voir) on the other end of the leaking circuit. Instru-
ment panel disassembly or removal may be necessary
to gain access to some components. See the appropri-
ate service procedures.
Fig. 3 ADJUST VACUUM TEST BLEED VALVE
1 - VACUUM PUMP TOOL C-4289
2 - VACUUM TEST SET C-3707
3 - BLEED VALVE
4 - PROBE
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 7
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1660 of 1803
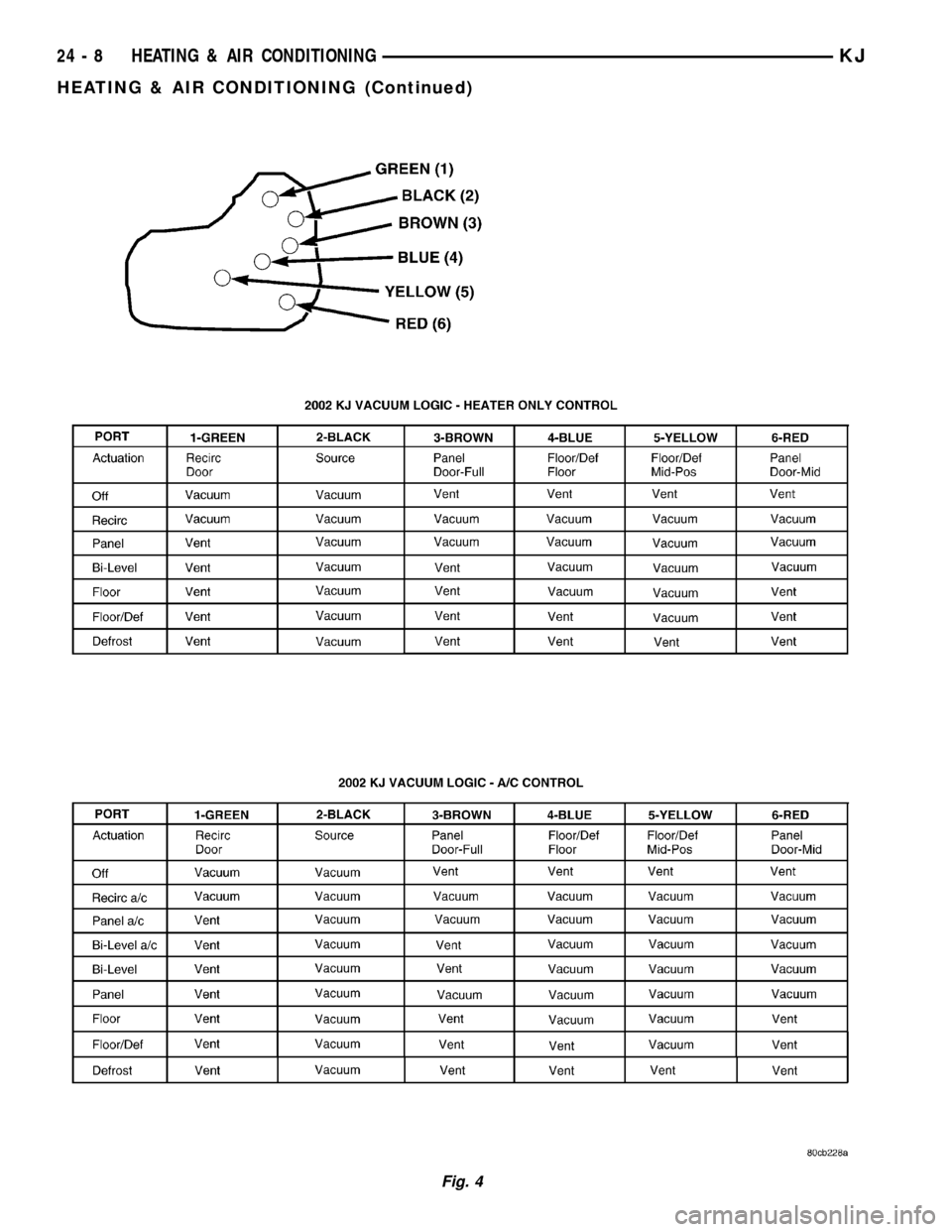
Fig. 4
24 - 8 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1661 of 1803
(5) Connect the test set hose or probe to the open
end of the leaking circuit. The test set gauge should
return to the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting shortly after
each connection is made. If OK, replace the faulty
disconnected component. If not OK, go to Step 6.
(6)
To locate a leak in a vacuum line, leave one end
of the line plugged and connect the test set hose or
probe to the other end of the line. Run your fingers
slowly along the line while watching the test set gauge.
The vacuum reading will fluctuate when your fingers
contact the source of the leak. To repair the vacuum
line, cut out the leaking section of the line. Then, insert
the loose ends of the line into a suitable length of 3 mil-
limeter (0.125 inch) inside diameter rubber hose.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable and iso-
late it.
(2) Locate the diode in the harness, and remove
the protective covering.
(3) Remove the diode from the harness, pay atten-
tion to the current flow direction (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove the insulation from the wires in the
harness. Only remove enough insulation to solder in
the new diode.
(5) Install the new diode in the harness, making
sure current flow is correct. If necessary refer to the
appropriate wiring diagram for current flow.
(6) Solder the connection together using rosin core
type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.
(7) Tape the diode to the harness using electrical
tape making, sure the diode is completely sealed
from the elements.
(8) Re-connect the battery negative cable, and test
affected systems.
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE
Item Description Notes
Vehicle KJ- Liberty
System R134a w/ fixed
orifice tube
Compressor Sanden PXF-18 SP-10 PAG oil
Freeze±up
ControlA/C low
pressure switchaccumulator
mounted
Low psi Control opens < 25 psi
- resets > 43
psi
High psi Control switch - opens
> 450-490 psi -
resets <
270-330 psidischarge line
Control Head manual type
Mode Door vacuum
Blend Door electric
Recirculation
Doorvacuum
Blower Motor hardwired to
control headresistor block
Cooling Fan viscous for
cooling, single
speed electric
for A/C
Clutch Electro-
mechanical
Control relay PCM
Draw 2 - 3.7 amps @
12V 0.5V @ 70É F
Gap 0.0169- 0.0319
DRB IIIT
Reads TPS, RPM, A/C
switch test
Actuators clutch and fan
relay
Fig. 5 DIODE IDENTIFICATION
1 - CURRENT FLOW
2 - BAND AROUND DIODE INDICATES CURRENT FLOW
3 - DIODE AS SHOWN IN THE DIAGRAMS
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 9
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1662 of 1803
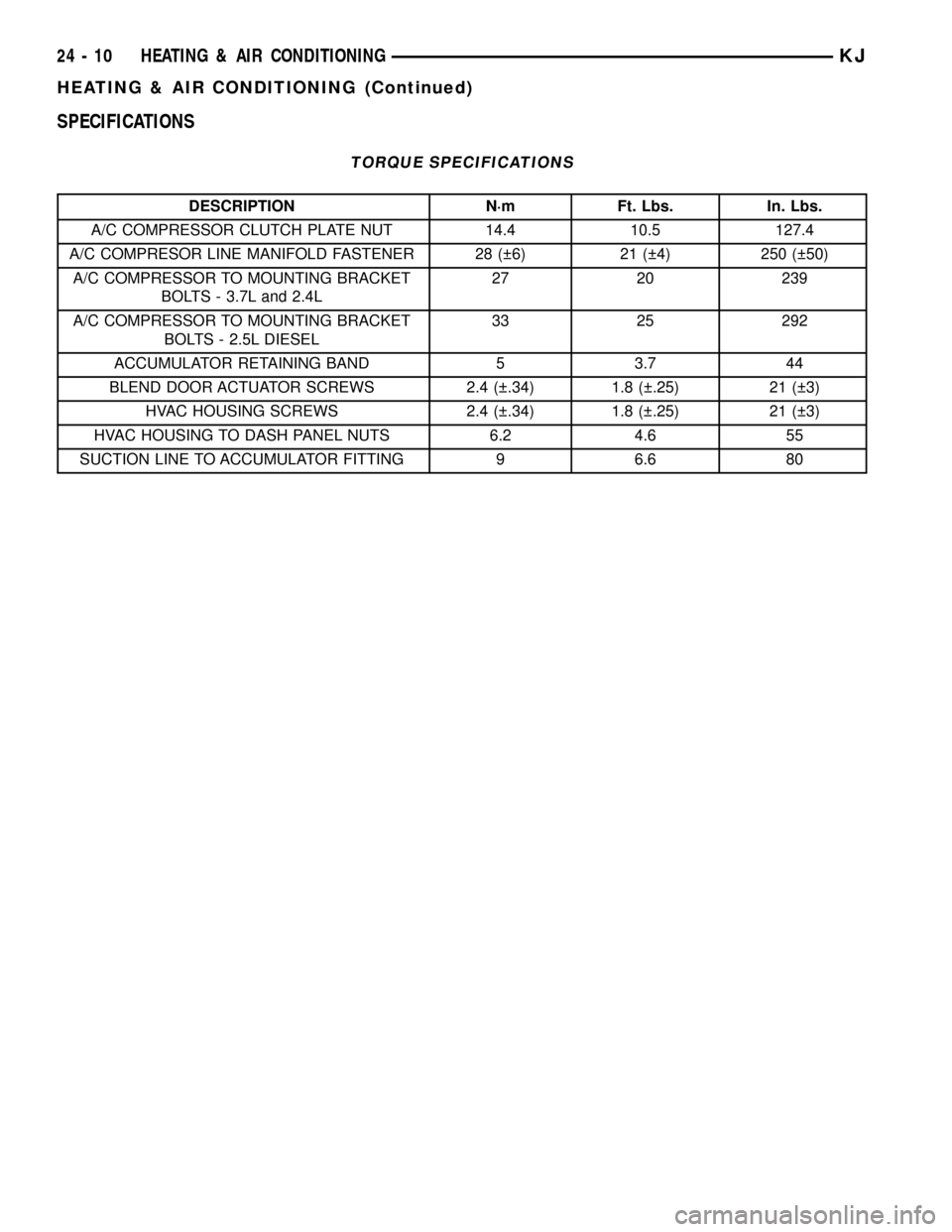
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH PLATE NUT 14.4 10.5 127.4
A/C COMPRESOR LINE MANIFOLD FASTENER 28 ( 6) 21 ( 4) 250 ( 50)
A/C COMPRESSOR TO MOUNTING BRACKET
BOLTS - 3.7L and 2.4L27 20 239
A/C COMPRESSOR TO MOUNTING BRACKET
BOLTS - 2.5L DIESEL33 25 292
ACCUMULATOR RETAINING BAND 5 3.7 44
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR SCREWS 2.4 ( .34) 1.8 ( .25) 21 ( 3)
HVAC HOUSING SCREWS 2.4 ( .34) 1.8 ( .25) 21 ( 3)
HVAC HOUSING TO DASH PANEL NUTS 6.2 4.6 55
SUCTION LINE TO ACCUMULATOR FITTING 9 6.6 80
24 - 10 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1667 of 1803

CAUTION: If the snap ring is not fully seated in the
groove it will vibrate out, resulting in a clutch fail-
ure and severe damage to the front housing of the
compressor.
(6) Install the original clutch shims on the com-
pressor shaft.
(7) Install the clutch plate. Install the shaft hex
nut and tighten to 15±20 N´m (11±15 ft. lbs.).
(8) Check the clutch air gap with a feeler gauge
(Fig. 9). If the air gap does not meet the specification,
add or subtract shims as required. The air gap spec-
ification is 0.41 to 0.79 millimeter (0.016 to 0.031
inch).NOTE: The air gap is determined by the spacer
shims. When installing an original, or a new clutch
assembly, try the original shims first. When install-
ing a new clutch onto a compressor that previously
did not have a clutch, use a 1.0, 0.50, and 0.13 mil-
limeter (0.040, 0.020, and 0.005 inch) shims from the
new clutch hardware package that is provided with
the new clutch.
(9) To complete the procedure, (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch relay is a International
Standards Organization (ISO) micro-relay. The termi-
nal designations and functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the micro-relay
terminal orientation (footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the relay case dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The compressor clutch relay is located in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine compart-
ment. Refer to the PDC label for relay identification
and location.
OPERATION
The compressor clutch relay is a electromechanical
device that switches battery current to the compres-
sor clutch coil when the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) grounds the coil side of the relay. The PCM
responds to inputs from the A/C Heater mode control
switch, the A/C low pressure switch, and the A/C
high pressure switch. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
The compressor clutch relay cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH RELAY
RELAY TEST
The compressor clutch relay (Fig. 10) is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
PDC label for relay identification and location.
Remove the relay from the PDC to perform the fol-
lowing tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
Fig. 8 CLUTCH PULLEY INSTALL
1 - ROTOR BEARING ASSEMBLY
2 - INSTALLER
Fig. 9 CHECK CLUTCH AIR GAP
1 - FEELER GAUGE
KJCONTROLS 24 - 15
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)