flat tire JEEP YJ 1995 Service And Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: YJ, Model: JEEP YJ 1995Pages: 2158, PDF Size: 81.9 MB
Page 7 of 2158
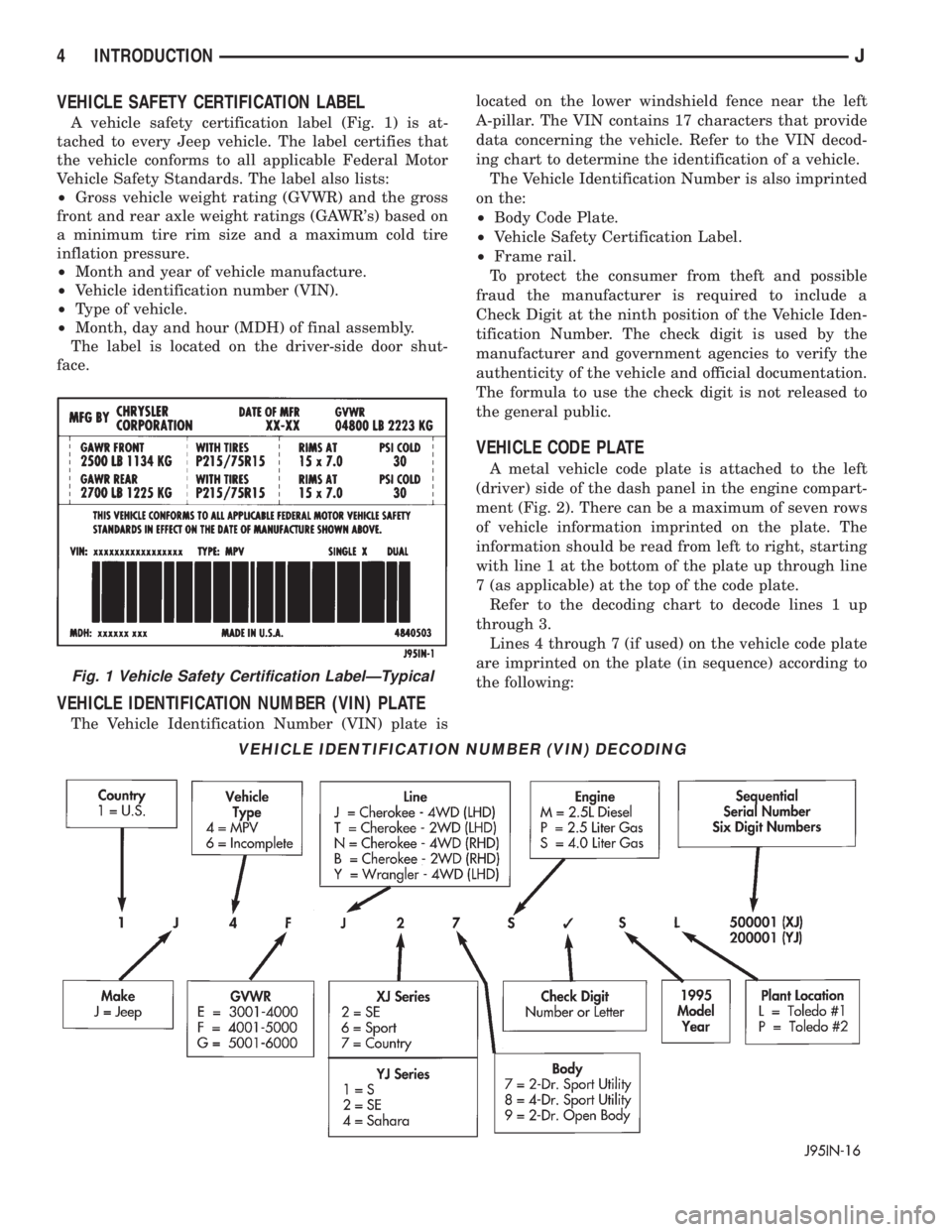
VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION LABEL
A vehicle safety certification label (Fig. 1) is at-
tached to every Jeep vehicle. The label certifies that
the vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal Motor
Vehicle Safety Standards. The label also lists:
²Gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) and the gross
front and rear axle weight ratings (GAWR's) based on
a minimum tire rim size and a maximum cold tire
inflation pressure.
²Month and year of vehicle manufacture.
²Vehicle identification number (VIN).
²Type of vehicle.
²Month, day and hour (MDH) of final assembly.
The label is located on the driver-side door shut-
face.
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) PLATE
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) plate islocated on the lower windshield fence near the left
A-pillar. The VIN contains 17 characters that provide
data concerning the vehicle. Refer to the VIN decod-
ing chart to determine the identification of a vehicle.
The Vehicle Identification Number is also imprinted
on the:
²Body Code Plate.
²Vehicle Safety Certification Label.
²Frame rail.
To protect the consumer from theft and possible
fraud the manufacturer is required to include a
Check Digit at the ninth position of the Vehicle Iden-
tification Number. The check digit is used by the
manufacturer and government agencies to verify the
authenticity of the vehicle and official documentation.
The formula to use the check digit is not released to
the general public.
VEHICLE CODE PLATE
A metal vehicle code plate is attached to the left
(driver) side of the dash panel in the engine compart-
ment (Fig. 2). There can be a maximum of seven rows
of vehicle information imprinted on the plate. The
information should be read from left to right, starting
with line 1 at the bottom of the plate up through line
7 (as applicable) at the top of the code plate.
Refer to the decoding chart to decode lines 1 up
through 3.
Lines 4 through 7 (if used) on the vehicle code plate
are imprinted on the plate (in sequence) according to
the following:
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) DECODING
Fig. 1 Vehicle Safety Certification LabelÐTypical
4 INTRODUCTIONJ
Page 32 of 2158

4WD YJ VEHICLES
(1) Raise the rear of the vehicle off the ground and
install tow dollies under rear wheels.
CAUTION: Use tow chains with T-hooks for con-
necting to the disabled vehicle's frame rails. Never
use J-hooks.
(2) Attach the T-hooks to the slots in the front end
of each frame rail (Fig. 7).
(3) Position each safety chain over the top of each
front spring and inboard of each front spring shackle.
(4) Double wrap each chain.
(5) Position the sling crossbar under the front
bumper.
(6) Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position to
unlock the steering wheel.
(7) Shift the transfer case to NEUTRAL.
TOWING WHEN KEYS ARE NOT AVAILABLE
When the vehicle is locked and keys are not avail-
able, use a flat bed hauler. A Wheel-lift or Sling-type
device can be used provided all the wheels are lifted
off the ground using tow dollies (Fig. 8).
EMERGENCY TOW HOOKS
WARNING: REMAIN AT A SAFE DISTANCE FROM A
VEHICLE THAT IS BEING TOWED VIA ITS TOW
HOOKS. THE TOW STRAPS/CHAINS COULD BREAK
AND CAUSE SERIOUS INJURY.
Some Jeep vehicles are equipped with front and
rear emergency tow hooks (Fig. 9). The tow hooks
should be used forEMERGENCYpurposes only.CAUTION: DO NOT use emergency tow hooks for
tow truck hook-up or highway towing.
FLAT TOWING (4 TIRES/WHEELS ON
SURFACE)
Tow a vehicle in this manner only when all four
wheels will freely rotate. Prepare the vehicle accord-
ing to the following procedures.
2WD VEHICLES
(1) Mark the drive shaft and the axle drive pinion
gear shaft yoke for installation alignment reference.
(2) Remove the drive shaft. Install a protective cov-
ering over the drive shaft U-joints to retain them as-
sembled and protected.
Fig. 7 Sling-Type, Front-End Towing (YJ Vehicles)
Fig. 8 Sling-Type, Front-End Towing With Rear
Wheels On A Tow Dolly
Fig. 9 Emergency Front Tow HooksÐXJ & YJ
Vehicles
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 13
Page 51 of 2158
(2) Note any indication of drum/rotor overheating,
wheel dragging or the vehicle pulling to one side
when the brakes are applied.
(3) Evaluate any performance complaints received
from the owner/operator.
(4) Repair the brake system as necessary. Refer to
Group, 5 Brakes for additional information and ser-
vice procedures.
TIRES
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The general condition of the tires and the inflation
pressures should be inspected at the same time the
engine oil is changed and the oil filter is replaced.
In addition, the tires/wheels should be rotated at
the intervals described in the Maintenance Schedules
section of this group.
INSPECTION
Inspect the tires for excessive wear, damage, etc.
Test the tires for the recommended inflation pres-sure. Refer to the tire inflation pressure decal located
on the inside of the glove box door, and also to Group
22, Tires And Wheels.
ROTATION
Refer to Group 22, Tires And Wheels for the recom-
mended method of tire/wheel rotation for a Jeep ve-
hicle.
BODY COMPONENTS
LUBRICATION REQUIREMENTS
All Jeep operating mechanisms and linkages
should be lubricated when necessary. The door
weatherstrip seals should be lubricated to prolong
their life as well as to improve door sealing.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
All applicable exterior and interior vehicle operat-
ing mechanisms should be:
²Inspected
²Cleaned
²Pivot/sliding contact areas on the mechanisms
should then be lubricated.
Multi-purpose NLGI GC-LB MOPAR Multi-Mileage
Lubricant or an equivalent, should be used to lubri-
cate the mechanisms. The door weatherstrip seals
should be lubricated with silicone lubricant spray.
Refer to the Body Lubricant Specifications chart be-
low for additional lubricant applications.
LUBRICATION
All pivoting and sliding contact areas, should be lu-
bricated periodically to ensure quiet, easy operation
and to protect against wear and corrosion. Areas in-
clude:
²Seat tracks.
²Door hinges/latches/strikers.
²Liftgate/tailgate/hood hinges (Fig. 11).
(1) As required, lubricate the body components
with the specified lubricants.
(2) Apply silicone lubricant to a cloth and wipe it
on door seals to avoid over-spray that can soil pas-
senger clothing.
(3) Before applying lubricant, the component
should be wiped clean. After lubrication, any excess
lubricant should be removed.
(4) The door lock cylinders should be lubricated 2
times each year (preferably autumn and spring):
²Spray a small amount of lock cylinder lubricant di-
rectly into the lock cylinder.
²Apply a small amount to the key and insert it into
the lock cylinder.
²Rotate it to the locked position and then back to
the unlocked position several times.
²Remove the key. Wipe the lubricant from it with a
clean cloth to avoid soiling of clothing.
Fig. 9 Park Brake Equalizer (XJ)ÐTypical
Fig. 10 Park Brake Equalizer (YJ)ÐTypical
0 - 32 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 134 of 2158

BEARING AND SEAL INSTALLATION
Do not install the original axle shaft seal. Al-
ways install a new seal.
(1) Wipe the bore in the axle shaft tube clean.
(2) If the original bearing is not reusable, install a
new bearing. Place the axle shaft bearing on the pilot
of Bearing Installer C-4198 and Handle C-4171.
CAUTION: DO NOT use the new axle shaft seal to
position or seat the bearing in the axle shaft bore.
(3) Insert the bearing into the tube. Ensure that
the bearing is not cocked and is seated firmly against
the tube shoulder.
(4) Install the new axle shaft seal (Fig. 6) with In-
staller C-4198 and Handle C-4171. The flat side of
the installation tool must face the seal.
(5) When the tool contacts the end of the tube
(face), the seal will be at the correct position and
depth.
AXLE SHAFT INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the bearing bore and seal lip. Insert
the axle shaft and engage the splines with the side
gear. Use care to prevent the shaft splines from dam-
aging the axle shaft seal lip.
(2) Insert the C-clip lock in the recessed groove(Fig. 4). Push the axle shaft outward to seat the C-
clip lock.
(3) Insert the pinion gear mate shaft in the case.
Install through the thrust washers and pinion gears.
Align the hole in the shaft with the lock screw hole.
Install the lock screw with Loctiteton the threads.
Tighten the screw to 11 Nzm (8 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig.
3).
(4) Clean the cover and apply a bead of sealant.
Refer to the Drain and Refill in this section.
(5) Install the brake drum and wheel and tire.
(6) Raise or lower the hoist until the vehicle is
level.
(7) Remove the fill hole plug. Fill the differential
housing with lubricant. Refer to the Specifications
chart for the type and the quantity. Install the fill
hole plug.
(8) Lower the vehicle and test the brakes and axle
for correct operation.
PINION SEAL REPLACEMENT
CAUTION: The following procedures must be used
so the correct pinion bearing preload torque is re-
tained. If this procedure is not followed completely,
it may result in premature failure of the rear axle.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Mark the U-joint, pinion yoke, and pinion shaft
for reference.
(3) Disconnect the drive shaft from the pinion
yoke. Secure the drive shaft in an upright position to
prevent damage to the rear U-joint.
(4) Remove the rear wheels and brake drums to
prevent any drag. The drag can cause a possible false
bearing preload torque measurement.
(5) Use a Newton-meter or an inch-pound torque
wrench to measure the pinion bearing preload. Ro-
tate the pinion shaft several times with the torque
wrench. Note the indicated torque as the wrench is
moved through several revolutions.
This measurement is very important because
the bearing preload torque must be carefully
re-adjusted after the new seal is installed.
(6) Retain the yoke with Wrench C-3281. Remove
the pinion shaft nut and Belleville washer.
(7) Make reference marks and remove the yoke
with a puller.
(8) Lower the rear of the vehicle to prevent lubri-
cant leakage.
(9) Remove the pinion shaft seal with Puller
C-748. Clean the seal contact surface in the housing
bore.
Fig. 5 Axle Shaft Bearing Removal
Fig. 6 Axle Shaft Seal Installation
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 33
Page 156 of 2158

SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Brake Drag............................... 6
Brake Fade.............................. 6
Brake Fluid Contamination................... 7
Brake Noise.............................. 7
Brake Pull............................... 6
Brake Warning Light Operation................ 5
Brakes Do Not Hold After Driving Through Deep
Water Puddles........................... 7
Component Inspection...................... 5
Contaminated Brakelining.................... 7
Diagnosing Parking Brake Malfunctions.......... 8
Diagnosis Procedures....................... 4
General Information........................ 4Hard Pedal or High Pedal Effort............... 6
Low Pedal............................... 5
Master Cylinder/Power Booster Test............ 8
Pedal Falls Away.......................... 5
Pedal Pulsation (Non-ABS Brakes Only)......... 6
Power Booster Check Valve Test............... 9
Power Booster Vacuum Test.................. 9
Preliminary Brake Check..................... 4
Rear Brake Grab.......................... 7
Road Testing............................. 5
Spongy Pedal............................. 5
Wheel and Tire Problems.................... 7
GENERAL INFORMATION
The diagnosis information in this section covers
service brake components which include:
²disc brake calipers
²disc brakeshoes
²drum brake wheel cylinders
²drum brakeshoes and brake drums
²drum brake support plates
²parking brake mechanism
²master cylinder/combination valve
²vacuum power brake booster
²brake pedal and brakelight switch
²brake warning light
DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURES
Service brake diagnosis involves determining if a
problem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic or vac-
uum operated component. A preliminary brake check,
followed by road testing and component inspection
are needed to determine a problem cause.
Road testing will either verify proper brake opera-
tion or confirm the existence of a problem. Compo-
nent inspection will, in most cases, identify the
actual part responsible for a problem.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary brake
check. This involves inspecting fluid level, parking
brake action, wheel and tire condition, checking for
obvious leaks or component damage and testing
brake pedal response. A road test will confirm or
deny the existence of a problem. The final diagnosis
procedure involves road test analysis and a visual in-
spection of brake components.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) If amber ABS light is illuminated, refer to ABS
Brake System Diagnosis. If red warning light is illu-
minated, or if neither warning light is illuminated,
continue with brake check.(2) Inspect condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, tramp and a condition simi-
lar to grab.
(3) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn, or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(4) Inspect brake fluid level:
(a) If vehicle has one-piece master cylinder, fluid
level should be within 6 mm (1/4 in.) of reservoir
rim.
(b) If vehicle has nylon reservoir with single
filler cap, correct level is to FULL mark on side of
reservoir. Acceptable level is between FULL and
ADD marks.
(c) Remember that fluid level in the reservoir
compartments will decrease in proportion to nor-
mal lining wear. However, if fluid level is abnor-
mally low, look for leaks at calipers, wheel
cylinders, brakelines and master cylinder.
(5) Inspect brake fluid condition:
(a) Fluid should be free of foreign material.Note
that brake fluid tends to darken over time.
This is normal and should not be mistaken for
contamination. If fluid is clear of foreign ma-
terial, it is OK.
(b) If fluid is highly discolored, or appears to con-
tain foreign material, drain out a sample with a
clean suction gun. Pour sample in a glass container
and note condition described in step (c).
(c) If fluid separates into layers, obviously con-
tains oil, or a substance other than brake fluid,
system seals and cups will have to be replaced and
hydraulic system flushed.
(6) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and foot pedal or
5 - 4 SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSISJ
Page 160 of 2158

produce a condition similar to grab as the tire loses
and recovers traction.
Flat-spotted tires can cause vibration and wheel
tramp and generate shudder during brake operation.
A tire with internal damage such as a severe bruise
or ply separation can cause vibration and pull. The
pull will be magnified when braking.
DIAGNOSING PARKING BRAKE MALFUNCTIONS
Adjustment Mechanism
Parking brake adjustment is controlled by a ca-
ble tensioner mechanism. The cable tensioner,
once adjusted at the factory, will not need further
attention under normal circumstances. There are
only two instances when adjustment is required.
The first is when a new tensioner, or cables have
been installed. And the second, is when the ten-
sioner and cables are disconnected for access to
other brake components.
Parking Brake Switch And Warning Light Illumination
The parking brake switch on the lever, or foot
pedal, is in circuit with the red warning light. The
switch will illuminate the red light only when the
parking brakes are applied. If the light remains on
after parking brake release, the switch or wires are
faulty, or cable tensioner adjustment is incorrect.
If the red light comes on while the vehicle is in mo-
tion and brake pedal height decreases, a fault has oc-
curred in the front or rear brake hydraulic system.
Parking Brake problem Causes
In most cases, the actual cause of an improperly
functioning parking brake (too loose/too tight/wont
hold), can be traced to a drum brake component.
The leading cause of improper parking brake
operation, is excessive clearance between the
brakeshoes and the drum surface. Excessive
clearance is a result of: lining and/or drum
wear; oversize drums; or inoperative shoe ad-
juster components.
Excessive parking brake lever travel (sometimes de-
scribed as a loose lever or too loose condition), is the re-
sult of worn brakeshoes/drums, improper brakeshoe
adjustment, or incorrectly assembled brake parts.
A ``too loose'' condition can also be caused by inop-
erative brakeshoe adjusters. If the adjusters are mis-
assembled, they will not function. In addition, since
the adjuster mechanism only works during reverse
stops, it is important that complete stops be made.
The adjuster mechanism does not operate when roll-
ing stops are made in reverse. The vehicle must be
brought to a complete halt before the adjuster lever
will turn the adjuster screw.
A condition where the parking brakes do not hold, will
most probably be due to a wheel brake component.
Items to look for when diagnosing a parking brake
problem, are:
²rear brakeshoe wear or adjuster problem
²rear brake drum wear
²brake drums machined beyond allowable diameter
(oversize)
²parking brake front cable not secured to lever
²parking brake rear cable seized
²parking brake strut reversed
²parking brake strut not seated in both shoes
²parking brake lever not seated in secondary shoe
²parking brake lever or brakeshoe bind on support
plate
²brakeshoes reversed
²adjuster screws seized
²adjuster screws reversed
²holddown or return springs misassembled or lack
tension
²wheel cylinder pistons seized
Brake drums that are machined oversize are diffi-
cult to identify without inspection. If oversize drums
are suspected, diameter of the braking surface will
have to be checked with an accurate drum gauge.
Oversize drums will cause low brake pedal and lack
of parking brake holding ability.
Improper parking brake strut and lever installation
will result in unsatisfactory parking brake operation.
Intermixing the adjuster screws will cause drag, bind
and pull along with poor parking brake operation.
Parking brake adjustment and parts replacement pro-
cedures are described in the Parking Brake section.
MASTER CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER TEST
(1) Start engine and check booster vacuum hose
connections. Hissing noise indicates vacuum leak.
Correct any vacuum leak before proceeding.
(2) Stop engine and shift transmission into Neu-
tral.
(3) Pump brake pedal until all vacuum reserve in
booster is depleted.
(4) Press and hold brake pedal under light foot
pressure.
(a) If pedal holds firm, proceed to step (5).
(b) If pedal does not hold firm and falls away,
master cylinder is faulty due to internal leakage.
Overhaul or replace cylinder.
(5) Start engine and note pedal action.
(a) If pedal falls away slightly under light foot
pressure then holds firm, proceed to step (6).
(b) If no pedal action is discernible, or hard pedal
is noted, power booster or vacuum check valve is
faulty. Install known good check valve and repeat
steps (2) through (5).
(6) Rebuild booster vacuum reserve as follows: Re-
lease brake pedal. Increase engine speed to 1500
rpm, close throttle and immediately turn off ignition.
5 - 8 SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSISJ
Page 466 of 2158
SERVICE PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Back-Up/Rear Turn Signal/Tail Lamp Bulb
ReplacementÐXJ....................... 12
Center High Mounted Stop Lamp (CHMSL)ÐXJ . . 12
Daytime Running Lights (Canada Only)ÐXJ..... 15
Drl Module ReplacementÐXJ................ 15
Fog Lamp ReplacementÐXJ.................. 9
Fog Lamp Switch ReplacementÐXJ........... 10
Fog LampsÐXJ........................... 7
Front Park/Turn Signal Lamp Bulb
ReplacementÐXJ........................ 9
Headlamp Alignment PreparationÐXJ........... 6
Headlamp AlignmentÐXJ.................... 6
Headlamp Bulb ReplacementÐXJ.............. 7Headlamp Delay Function Trouble DiagnosisÐXJ . 14
Headlamp Delay Module ReplacementÐXJ...... 14
Headlamp SwitchÐXJ...................... 10
Headlamp/Fog Lamp Adjustment Using Alignment
ScreenÐXJ............................. 7
License Plate LampÐXJ.................... 12
Multi-Function Switch Service ProceduresÐXJ.... 11
Sentinel Headlamp Delay ModuleÐXJ.......... 14
Side Marker Lamp Bulb ReplacementÐXJ....... 10
Underhood Lamp Bulb ReplacementÐXJ....... 13
Underhood Lamp ReplacementÐXJ........... 13
Underhood Lamp Service InformationÐXJ....... 12
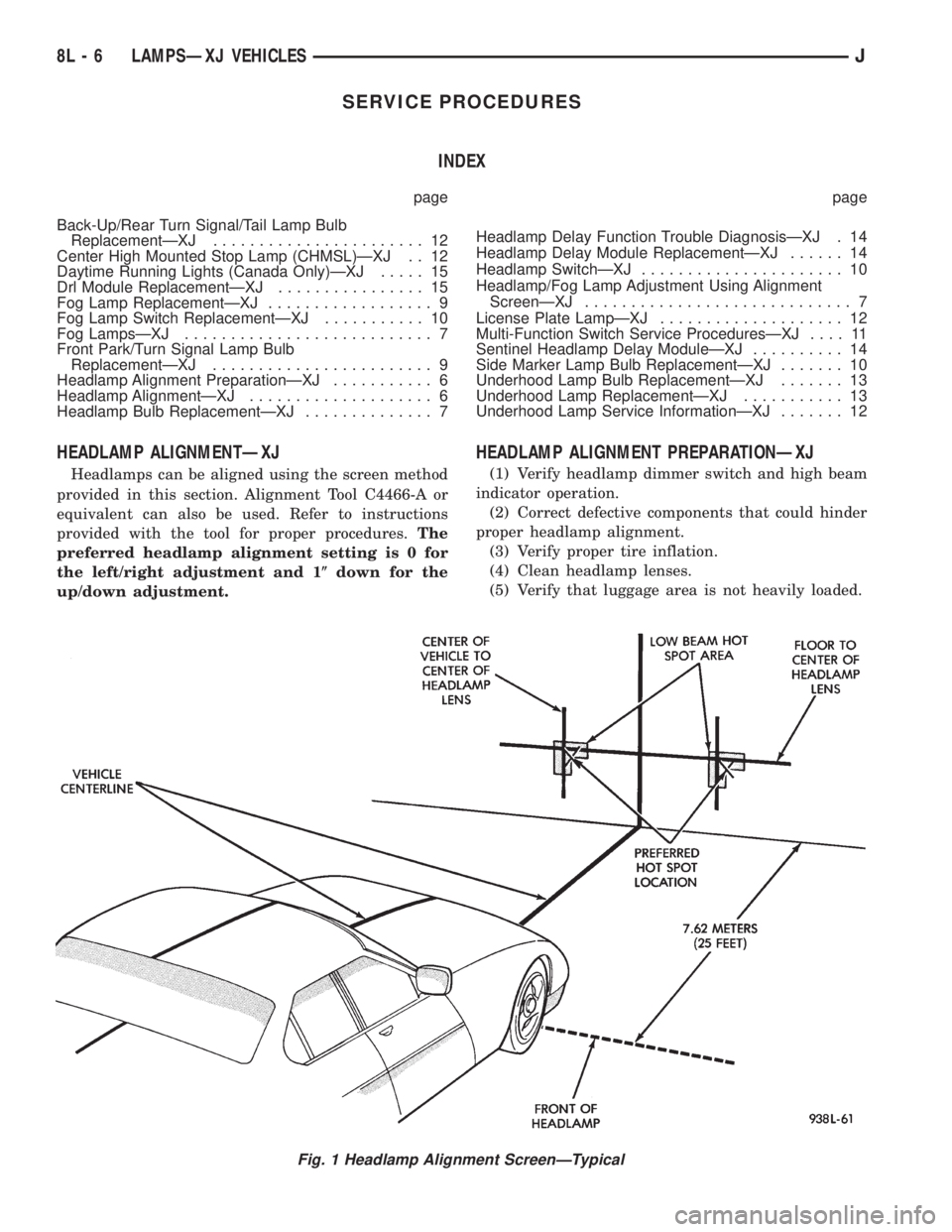
HEADLAMP ALIGNMENTÐXJ
Headlamps can be aligned using the screen method
provided in this section. Alignment Tool C4466-A or
equivalent can also be used. Refer to instructions
provided with the tool for proper procedures.The
preferred headlamp alignment setting is 0 for
the left/right adjustment and 1(down for the
up/down adjustment.
HEADLAMP ALIGNMENT PREPARATIONÐXJ
(1) Verify headlamp dimmer switch and high beam
indicator operation.
(2) Correct defective components that could hinder
proper headlamp alignment.
(3) Verify proper tire inflation.
(4) Clean headlamp lenses.
(5) Verify that luggage area is not heavily loaded.
Fig. 1 Headlamp Alignment ScreenÐTypical
8L - 6 LAMPSÐXJ VEHICLESJ
Page 482 of 2158
SERVICE PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Back-Up/Rear Turn Signal/Tail Lamp Bulb
ReplacementÐYJ....................... 28
Center High Mounted Stop Lamp (CHMSL)ÐYJ . . 28
Daytime Running Lights (Canada Only)ÐYJ..... 30
Drl Module ReplacementÐYJ................ 30
Fog Lamp ReplacementÐYJ................. 25
Fog Lamp Switch ReplacementÐYJ........... 26
Fog LampsÐYJ.......................... 23
Front Park/Turn Signal Lamp Bulb ReplacementÐ
YJ ................................... 25
Headlamp Alignment PreparationÐYJ.......... 22Headlamp AlignmentÐYJ................... 22
Headlamp Bulb ReplacementÐYJ............. 23
Headlamp Dimmer Switch ReplacementÐYJ..... 26
Headlamp SwitchÐYJ...................... 26
Headlamp/Fog Lamp Adjustment Using Alignment
ScreenÐYJ............................ 23
Side Marker Lamp Bulb ReplacementÐYJ....... 25
Underhood Lamp Bulb ReplacementÐYJ....... 29
Underhood Lamp ReplacementÐYJ........... 29
Underhood Lamp Service InformationÐYJ....... 28
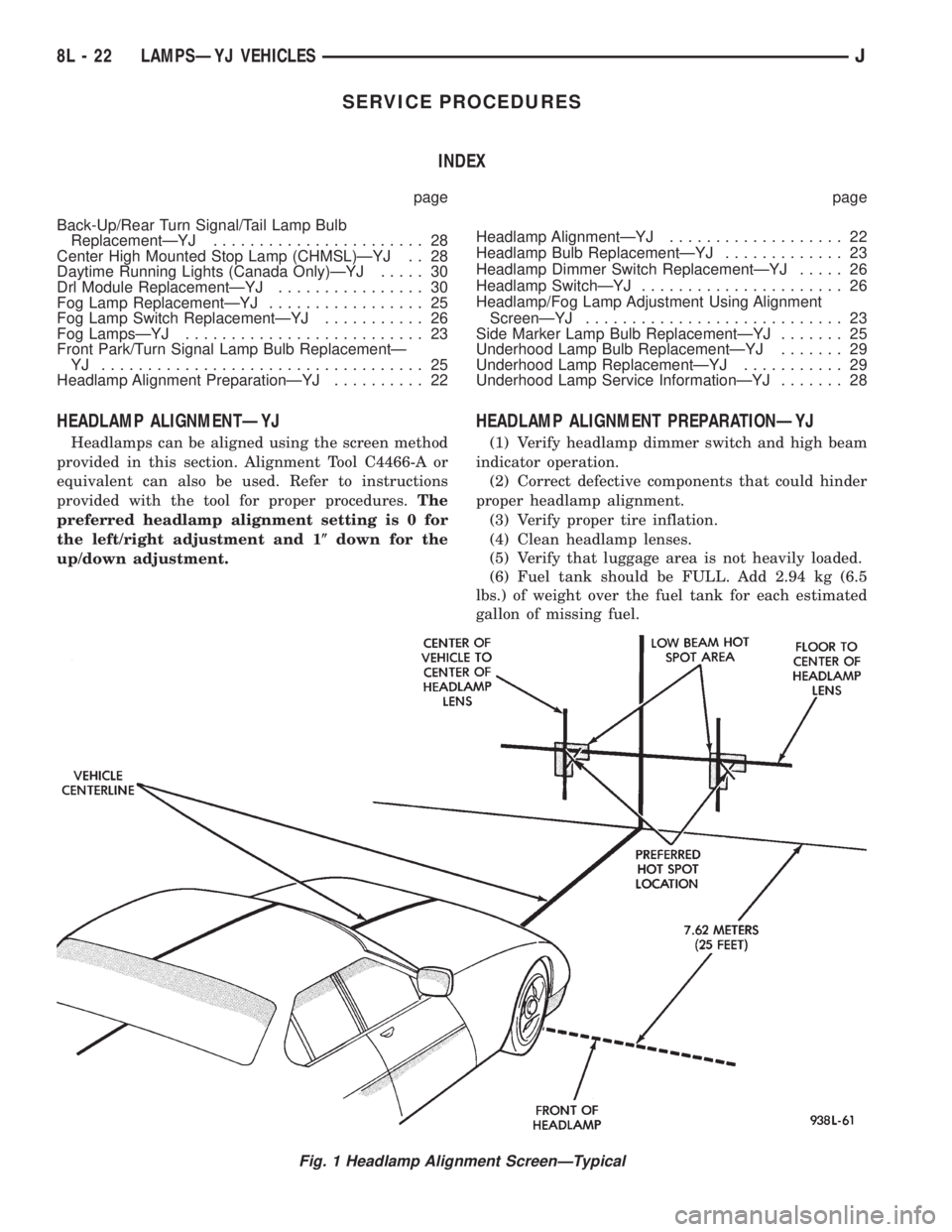
HEADLAMP ALIGNMENTÐYJ
Headlamps can be aligned using the screen method
provided in this section. Alignment Tool C4466-A or
equivalent can also be used. Refer to instructions
provided with the tool for proper procedures.The
preferred headlamp alignment setting is 0 for
the left/right adjustment and 1(down for the
up/down adjustment.
HEADLAMP ALIGNMENT PREPARATIONÐYJ
(1) Verify headlamp dimmer switch and high beam
indicator operation.
(2) Correct defective components that could hinder
proper headlamp alignment.
(3) Verify proper tire inflation.
(4) Clean headlamp lenses.
(5) Verify that luggage area is not heavily loaded.
(6) Fuel tank should be FULL. Add 2.94 kg (6.5
lbs.) of weight over the fuel tank for each estimated
gallon of missing fuel.
Fig. 1 Headlamp Alignment ScreenÐTypical
8L - 22 LAMPSÐYJ VEHICLESJ
Page 1282 of 2158

CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 50É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 1).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
MEASURING WITH PLASTIGAGE
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage, or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedures for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) The total clearance of the main bearings can
only be determined by removing the weight of the
crankshaft. This can be accomplished by either of two
methods:
METHOD - 1 (PREFERRED)ÐShim the bear-
ings adjacent to the bearing to be checked. This will
remove the clearance between upper bearing shell
and the crankshaft. Place a minimum of 0.254 mm
(0.010 inch) shim between the bearing shell and the
adjacent bearing cap. Tighten the bolts to 18 Nzm (13
ft. lbs.) torque.²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.1 main bear-
ing; shim No.2 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.2 main bear-
ing; shim No.1 and No.3 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.3 main bear-
ing; shim No.2 and No.4 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.4 main bear-
ing; shim No.3 and No.5 main bearing.
²2.5L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.5 main bear-
ing; shim No.4 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.5 main bear-
ing; shim No.4 and No.6 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.6 main bear-
ing; shim No.5 and No.7 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.7 main bear-
ing; shim No.6 main bearing.
Remove all shims before assembling engine.
METHOD - 2 (ALTERNATIVE)ÐThe weight of
the crankshaft is supported by a jack under the coun-
terweight adjacent to the bearing being checked.
(3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing cap shell (Fig. 2). Position the
Plastigage approximately 6.35 mm (1/4 inch) off cen-
ter and away from the oil holes. In addition, suspect
areas can be checked by placing the Plastigage in
that area. Tighten the bearing cap bolts of the bear-
ing being checked to 108 Nzm (80 ft. lbs.) torque.DO
NOT rotate the crankshaft or the Plastigage
may be smeared, giving inaccurate results.
(4) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage with the scale provided on
the package (Fig. 3). Plastigage generally comes in 2
scales (one scale is in inches and the other is a met-
ric scale). Locate the band closest to the same width.
This band shows the amount of clearance. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken
(refer to Engine Specifications).
(5) Plastigage is available in a variety of clearance
ranges. The 0.025-0.076 mm (0.001-0.003 inch) range
is usually the most appropriate for checking engine
bearing clearances.
Fig. 1 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
Fig. 2 Placement of Plastigage in Bearing Shell
JENGINES 9 - 3
Page 1283 of 2158

CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine connecting rod bearing clearances can be
determined by use of Plastigage, or equivalent. The
following is the recommended procedures for the use
of Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire width
of the bearing cap shell (Fig. 2). Position the Plastigage
approximately 6.35 mm (1/4 inch) off center and away
from the oil holes. In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspect area.
(3) The crankshaft must be turned until the connect-
ing rod to be checked starts moving toward the top of
the engine. Only then should the rod cap with Plasti-
gage in place be assembled. Tighten the rod cap nut to
45 Nzm (33 ft. lbs.) torque.DO NOT rotate the crank-
shaft or the Plastigage may be smeared, giving in-
accurate results.
(4) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage with the scale provided on
the package (Fig. 3). Plastigage generally comes in 2
scales (one scale is in inches and the other is a met-
ric scale). Locate the band closest to the same width.
This band shows the amount of clearance. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken
(refer to Engine Specifications).
(5) Plastigage is available in a variety of clearance
ranges. The 0.025-0.076 mm (0.001-0.003 inch) range
is usually the most appropriate for checking engine
bearing clearances.
REPAIR DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole.
This brings the hole back to its original thread
size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
SERVICE ENGINE ASSEMBLY (SHORT BLOCK)
A service replacement engine assembly (short
block) may be installed whenever the original cylin-
der block is defective or damaged beyond repair. It
consists of the cylinder block, crankshaft, piston and
rod assemblies. If needed, the camshaft must be pro-
cured separately and installed before the engine is
installed in the vehicle.
A short block is identified with the letter ``S'' stamped
on the same machined surface where the build date
code is stamped for complete engine assemblies.
Installation includes the transfer of components
from the defective or damaged original engine. Fol-
low the appropriate procedures for cleaning, inspec-
tion and torque tightening.
HYDROSTATIC LOCK
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(refer to Group 14, Fuel System).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and in-
take manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure in
the cylinder head. Remove the plugs from the engine.
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (i.e. coolant,
fuel, oil, etc.).
(7) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt engine oil into the cylinders to lubricate
the walls. This will prevent damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil (refer to Group 0, Lubrica-
tion and Maintenance).
(15) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
Fig. 3 Clearance Measurement
9 - 4 ENGINESJ