steering wheel LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996Pages: 455, PDF Size: 6.44 MB
Page 56 of 455

MAINTENANCE
13
MAINTENANCE REV: 05/992.When pure diesel is emitted, retighten drain
plug.
3.Disconnect fuel inlet pipe at sedimenter. Raise
and support pipe above level of fuel tank to
prevent fuel draining from tank.
4.Support sedimenter bowl, unscrew bolt and
remove bowl.
5.Remove sedimenter element.
6.Clean all components in kerosene.
7.Fit new seals.
8.Fit element into sedimenter bowl.
9.Secure bowl to sedimenter head.
10.Fit fuel inlet pipe to sedimenter.
11.Slacken drain plug and when pure diesel is
emitted, retighten plug.
12.If necessary, prime the system.
See FUEL SYSTEM, Adjustment, Priming
the fuel system
CHECK CONDITION OF ENGINE MOUNTING
RUBBERS
CHECK SECURITY OF TOWING BRACKET
FITTINGSCARRY OUT ROAD OR ROLLER TEST
WARNING: Two wheel roller tests MUST
NOT be carried out.
For details of dynamometer testing.
See
INTRODUCTION, Information, Dynamometer
testing
Check the following components:
1.Engine for excessive noise.
2.Clutch for slip, judder or spin/drag.
3.Gear selection/noise - high/low range.
4.Steering for abnormal noise/effort.
5.Steering for free play.
6.All instruments, gauges and warning indicators.
7.Heater and air conditioning systems.
8.Heated rear screen.
9.Shock absorbers - ride irregularities.
10.Foot brake, on emergency stop, pulling to one
side, binding and pedal effort.
11.Handbrake operation.
12.Seat reclining and latching.
13.Fully extend seat belt, check operation of
retraction and latching. Inertia belts lock when
snatched or vehicle on slope.
14.Road wheel balance.
15.Transmissions for vibrations.
16.Body noises, squeaks and rattles.
17.Excessive exhaust smoke.
18.Engine idle speed.
19.Endorse service record.
20.Report any unusual features of vehicle condition
and additional work required.
ENDORSE SERVICE RECORD
Page 209 of 455

FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
1
REPAIR REV: 05/99 FRONT AXLE ASSEMBLY
Service repair no - 54.10.01
Remove
WARNING: Remove and refit of axle
requires a further two persons to steady
axle when lowering or repositioning axle.
1.Support chassis front.
2.Remove road wheels.
3.Support axle weight with hydraulic jack.
4.Remove radius arms to chassis frame nuts.
5.Disconnect steering damper from track rod.
Using a extractor remove track rod links from
swivel pin arms.
6.Remove four nuts and bolts securing radius
arms to axle bracket.
7.Remove radius arms.
8.Remove bolts securing brake hose brackets .
Refit bolts to prevent oil leakage.
9.Remove bolts from brake calipers and tie to one
side.
10.Remove nuts and washers securing shock
absorbers to axle.
11.Disconnect drag link from swivel pin housing
arm.
12.Remove two nuts and bolts securing panhard
rod to axle bracket. Lift rod clear of axle.
13.Mark for reassembly drive shaft flanges.
Remove four nuts and bolts, tie propeller shaft to
one side.
14.Release axle ventilation pipe banjo and lower
axle assembly. Remove road springs.
15.Disconnect anti-roll bar link
See FRONT
SUSPENSION, Repair, Anti-roll bar ball
.
16.Remove axle assembly.
Refit
17.Position axle under vehicle, supporting left side
of axle, and fit anti-roll bar links
See FRONT
SUSPENSION, Repair, Anti-roll bar links
.
18.Fit propeller shaft. Tighten bolts to
47 Nm (35
lbf/ft).
19.Fit panhard rod to axle bracket. Tighten bolts to
88 Nm (65 lbf/ft).
20.Fit drag link to swivel pin arm. Tighten fixings to
40 Nm (30 lbf/ft).
21.Fit shock absorbers to axle.
22.Fit brake calipers. Tighten bolts to
82 Nm (60
lbf/ft).
23.Tighten upper swivel pin bolts to78 Nm (58
lbf/ft).
24.Fit radius arms to axle brackets. Tighten bolts to
197 Nm (145 lbf/ft).
25.Fit steering damper to track rod.
26.Fit radius arms to chassis side member. Tighten
fixings to
197 Nm (145 lbf/ft).
27.Tighten track rod end to40 Nm (30 lbf/ft)and fit
new split pin.
28.Remove chassis supports, fit road wheels and
tighten to correct torque:
Alloy wheels -
130 Nm (96 lbf/ft)
Steel wheels -100 Nm (80 lbf/ft)
Heavy duty wheels -170 Nm (125 lbf/ft)
Page 218 of 455
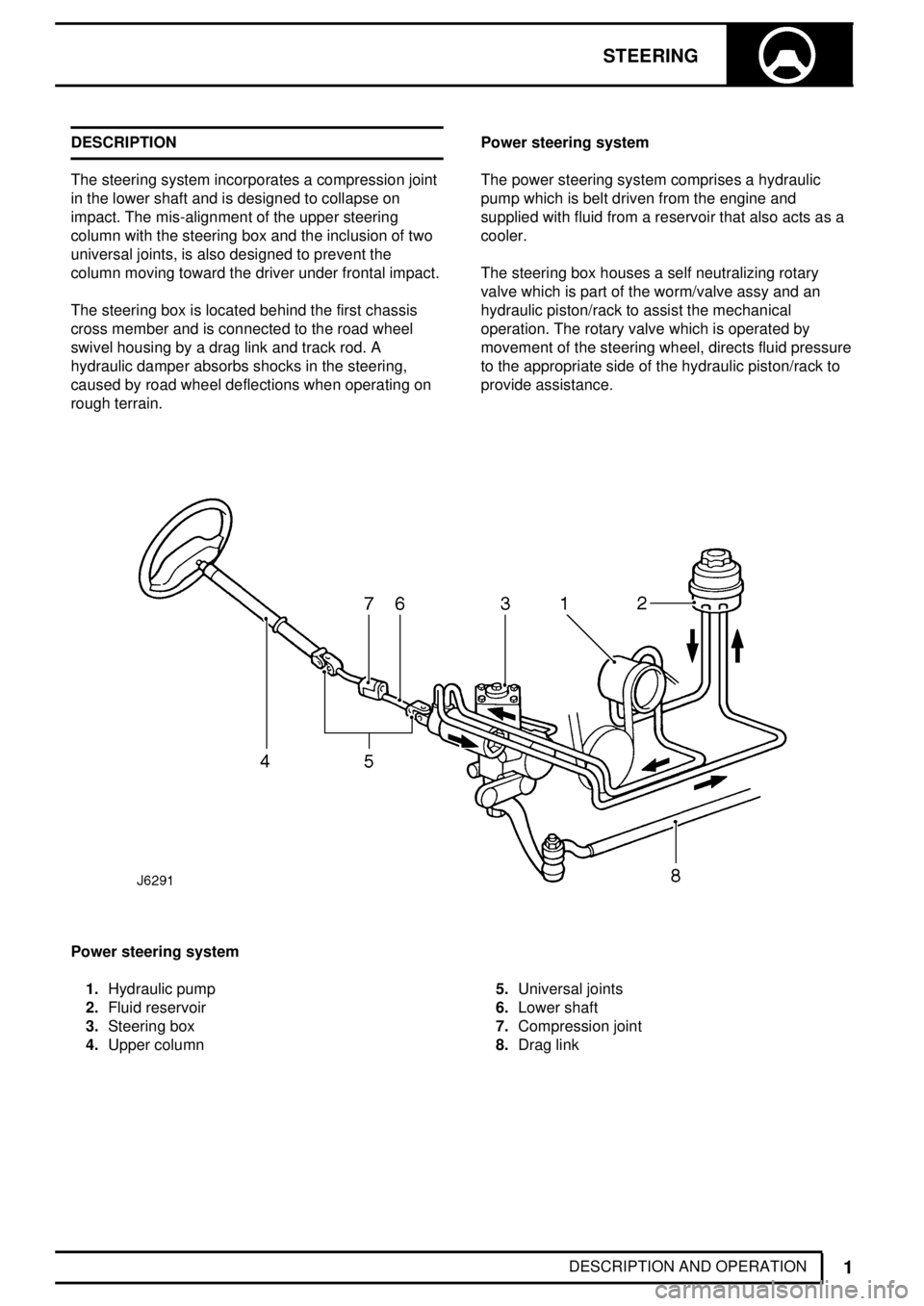
STEERING
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
The steering system incorporates a compression joint
in the lower shaft and is designed to collapse on
impact. The mis-alignment of the upper steering
column with the steering box and the inclusion of two
universal joints, is also designed to prevent the
column moving toward the driver under frontal impact.
The steering box is located behind the first chassis
cross member and is connected to the road wheel
swivel housing by a drag link and track rod. A
hydraulic damper absorbs shocks in the steering,
caused by road wheel deflections when operating on
rough terrain.Power steering system
The power steering system comprises a hydraulic
pump which is belt driven from the engine and
supplied with fluid from a reservoir that also acts as a
cooler.
The steering box houses a self neutralizing rotary
valve which is part of the worm/valve assy and an
hydraulic piston/rack to assist the mechanical
operation. The rotary valve which is operated by
movement of the steering wheel, directs fluid pressure
to the appropriate side of the hydraulic piston/rack to
provide assistance.
Power steering system
1.Hydraulic pump
2.Fluid reservoir
3.Steering box
4.Upper column5.Universal joints
6.Lower shaft
7.Compression joint
8.Drag link
Page 220 of 455

STEERING
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Rotary valve operation
Rotary valve at neutral
The rotary valve assembly comprises a worm (1),
valve sleeve (2), input shaft (4) and torsion bar (5).
The valve sleeve is retained inside the worm by a trim
screw (3), and incorporates valve ports in its inner
bore. The input shaft is attached to the steering wheel
via a steering shaft and steering column and
incorporates valve ports in its outer diameter to align
with those in the sleeve.
The torsion bar, which is secured to the worm and
input shaft with pins (6) at each end, holds the valve
ports in neutral alignment when there is no demand
for assistance.No demand for assistance (Valve at neutral)
When there is no demand for assistance the torsion
bar holds the input shaft and sleeve valve ports in
neutral relationship to one another, allowing equal
pump pressure (A) to both sides of the piston/rack (9).
Any excess fluid flow from the pump returns to the
reservoir via (B).
Page 221 of 455

57STEERING
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Rotary valve misaligned
Demand for assistance (Valve misaligned)
When the steering wheel and input shaft is turned,
steering resistance transmitted to the worm causes
the torsion bar to be twisted and the valve ports to be
misaligned for a right or left turn. The misalignment of
the valve ports directs all fluid pressure A to one side
of the piston only and allows displaced fluid B on the
other side.
When demanding maximum assistance, any
excessive fluid output from the pump due to high
pump speed, will circulate through the regulator valve
located in the pump unit, causing the temperature of
the fluid and the pump to rise rapidly.CAUTION: To avoid excessive fluid
temperatures which could damage the oil
seals, the steering must not be held on full
lock for more than 30 seconds in one minute.
Only when the steering wheel, and the demand for
assistance, is released, will the torsion bar return the
valve to neutral, allowing the fluid to circulate through
the reservoir where it is cooled.
In the unlikely event of mechanical failure of the
torsion bar, a coarse splined connection (7) between
the input shaft and worm, ensures steering control is
maintained sufficient to allow the vehicle to be
recovered.
Page 222 of 455

STEERING
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Pump and regulator valve operation
The pump which is belt driven from the engine is an
eccentric roller type and also houses the pressure
regulator and flow control valve. The pressure is
controlled by a spring loaded ball valve (3) which is
housed inside the flow control valve piston (4).
No demand for assistance High flow through box -
Low pressure
With no demand for assistance the rotary valve in the
steering box acts as a pressure relief valve, allowing
fluid (A) to flow freely through the steering box and
back to the reservoir and pump inlet (B).
No demand for assistance
1.Reservoir
2.Pump
3.Pressure control ball valve and spring
4.Flow control valve and spring
5.Press fit plug (ball bearing)
6.Restrictor
The ball plug (5) is pressed into the valve (4)
during manufacture and determines the opening
pressure of pressure relief valve (3).No flow, through box - High pressure
When the steering is turned, the rotary valve
effectively stops all fluid flow through the steering box,
thus causing an increase in pressure (A). This
increase in pressure is felt in the flow control valve
spring chamber where, at a pre-determined pressure
the relief valve (3) will open and allow the pressure to
escape. The fall in pressure in the flow control spring
chamber, allows the flow control valve to move to the
right, which in turn allows pump output (A) to escape
directly into the pump inlet (B).
Assistance demanded
As soon as the steering wheel is released after
making a turn, the system reverts to the condition
seen in J6292 and the road wheels are returned to the
straight ahead position by the mechanical steering
geometry.
In the event of any hydraulic failure, steering control,
though heavy, will be maintained through the
mechanical components in the steering box.
Page 223 of 455

STEERING
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS INSUFFICIENT POWER ASSISTANCE
1.Is fluid level correct?
YES - go to 3.
NO - Fill/bleed sytem
2.Is problem a leak?
YES - Diagnose
See Power Steering Fluid
Leaks
.
NO - continue
3.Is drive belt tension correct?
YES - go to 5.
NO - Is drive belt worn or contaminated with oil?
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Auxiliary drive
belt
.
4.Is problem resolved?
YES - end
NO - continue
5.Carry out pressure test at idle and 1000 rev/min.
See Power Steering System - Test.
6.Is correct pressure achieved?
YES - steering box defective
Not at any speed go to 9.
Not at idle go to 7.
7.Is idle speed correct?
YES-Goto8.
NO - Correct idle speed -
See ENGINE TUNING
DATA, Information, 300 Tdi Engine
.
8.Is problem resolved?
YES - end
NO - go to 9.
9.Bypass steering box using adaptor tap
LRT-57-001
10.Is correct pressure obtained?
YES - defective steering box
NO - defective steering pump
CAUTION: Do not hold steering wheel on
full lock for more than 30 seconds in any
one minute to avoid overheating fluid and
possibly damaging seals.
NOTE: 1. Excessive pressure in the
system is almost always caused by a
faulty relief valve in the PAS pump.
NOTE: 2. Insufficient pressure in the
system is usually caused by low fluid level
or PAS pump drive belt slip, or one of the
following: PAS system leaks, faulty PAS pump
relief valve, fault in steering box valve and worm
assembly, leak at piston in steering box, worn
components in PAS pump or box.
Page 224 of 455
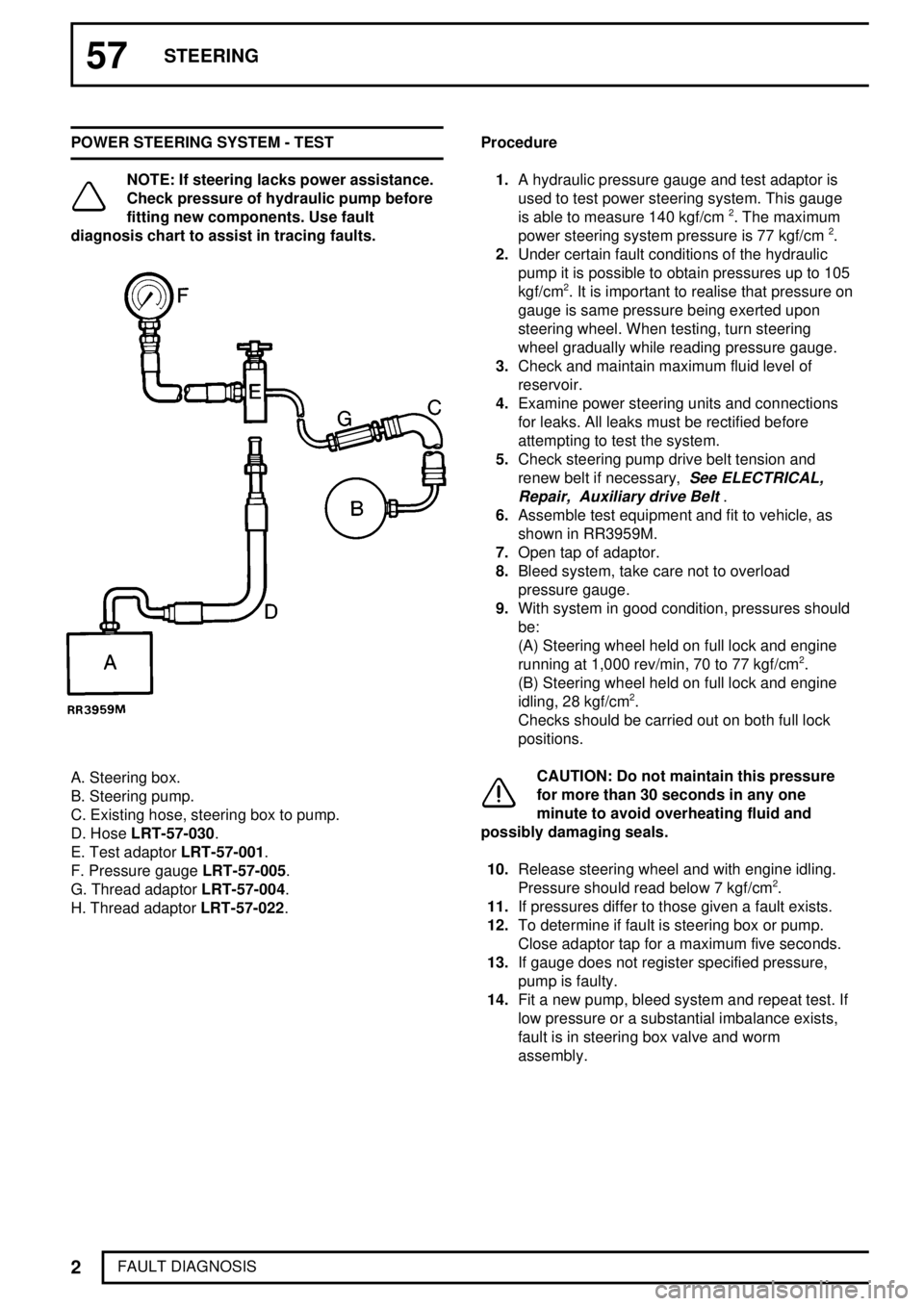
57STEERING
2
FAULT DIAGNOSIS POWER STEERING SYSTEM - TEST
NOTE: If steering lacks power assistance.
Check pressure of hydraulic pump before
fitting new components. Use fault
diagnosis chart to assist in tracing faults.
A. Steering box.
B. Steering pump.
C. Existing hose, steering box to pump.
D. HoseLRT-57-030.
E. Test adaptorLRT-57-001.
F. Pressure gaugeLRT-57-005.
G. Thread adaptorLRT-57-004.
H. Thread adaptorLRT-57-022.Procedure
1.A hydraulic pressure gauge and test adaptor is
used to test power steering system. This gauge
is able to measure 140 kgf/cm
2. The maximum
power steering system pressure is 77 kgf/cm2.
2.Under certain fault conditions of the hydraulic
pump it is possible to obtain pressures up to 105
kgf/cm
2. It is important to realise that pressure on
gauge is same pressure being exerted upon
steering wheel. When testing, turn steering
wheel gradually while reading pressure gauge.
3.Check and maintain maximum fluid level of
reservoir.
4.Examine power steering units and connections
for leaks. All leaks must be rectified before
attempting to test the system.
5.Check steering pump drive belt tension and
renew belt if necessary,
See ELECTRICAL,
Repair, Auxiliary drive Belt
.
6.Assemble test equipment and fit to vehicle, as
shown in RR3959M.
7.Open tap of adaptor.
8.Bleed system, take care not to overload
pressure gauge.
9.With system in good condition, pressures should
be:
(A) Steering wheel held on full lock and engine
running at 1,000 rev/min, 70 to 77 kgf/cm
2.
(B) Steering wheel held on full lock and engine
idling, 28 kgf/cm
2.
Checks should be carried out on both full lock
positions.
CAUTION: Do not maintain this pressure
for more than 30 seconds in any one
minute to avoid overheating fluid and
possibly damaging seals.
10.Release steering wheel and with engine idling.
Pressure should read below 7 kgf/cm
2.
11.If pressures differ to those given a fault exists.
12.To determine if fault is steering box or pump.
Close adaptor tap for a maximum five seconds.
13.If gauge does not register specified pressure,
pump is faulty.
14.Fit a new pump, bleed system and repeat test. If
low pressure or a substantial imbalance exists,
fault is in steering box valve and worm
assembly.
Page 225 of 455

STEERING
3
FAULT DIAGNOSIS STEERING DAMPER
The power steering system, as well as reducing the
effort required to manoeuvre the vehicle when
parking, also helps to dampen any deflections of the
road wheels, being transmitted back to the steering
wheel.
When operating the vehicle off road, the road wheels
are often deflected by ruts and boulders causing the
steering wheel to turn left and right. This phenomenon
is known as 'steering kickback'. To subdue the effects
of 'steering kickback', a hydraulic damper is fitted in
the steering linkage between the track rod and the
differential casing. The damper, which offers the same
resistance in extension and compression, is sealed for
life.
Steering damper check
Check the condition operation of the hydraulic
steering damper as follows:
Check procedure
1.Inspect damper for casing damage or leaks.
2.Clamp one end of the damper horizontally in a
vice using soft jaws. Compress and extend the
unit by hand. Resistance should be equal in both
directions.
3.If it is felt that the unit is outside acceptable
limits, fit a new steering damperSTEERING FAULTS
Symptom:-
Excessive kickback through steering wheel - when
driven on rough terrain.
1.Is the steering damper in good working order?
See Steering Damper.
NO - Renew unit
See Repair, Steering
Damper
.
YES - Continue.
2.Is there any looseness or free play in the
steering ball joints and linkage?
YES -
See Steering Linkage Inspect.
NO - Continue.
3.Is there any looseness or worn bushes in front
suspension?
YES -
See FRONT SUSPENSION, Repair,
Radius Arm
.
NOTE: When replacing suspension bushes
ALL bushes and fixings must be replaced.
NO - Continue.
4.Is the steering exceptionally light/sensitive when
driven on good road surface?
YES - See fault symptom -Steering
excessively light/sensitive and freeplay at
steering wheel.
NO - Suspect axle swivel resistance.
5.Check the resistance of the axle swivels
See
FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE, Overhaul,
Front Stub Axle, Constant Velocity Joint and
Swivel Pin Housing
.
Page 226 of 455

57STEERING
4
FAULT DIAGNOSIS Symptom:-
Fluid leaks from steering box seals.
CAUTION: The steering wheel must not be
held on full lock for more than 30 seconds
in one minute, as this may overheat the
fluid and cause damage to the oil seals.
1.Check fluid level
See Repair, Power Steering
Fluid Reservoir
.
Check fluid pressure
See Power Steering
System - Test
.
2.Is pressure high?
YES - Renew pump
See Repair, Power
steering Pump
.
If oil seal leaks persist after renewing the pump
See Overhaul, Power Steering Box.
NO -
See Overhaul, Power Steering Box.
Symptom:-
Insufficient power assistance - castor return
action normal.
1.Are tyres correct type and pressure?
NO -
See GENERAL SPECIFICATION DATA,
Information, Wheels and Tyres
.
YES - Continue.
2.Is fluid level correct?
NO - Check fluid level
See Repair, Power
Steering Fluid Reservoir
.
YES - Check system for air locks
See Repair,
Power Steering System - Bleed
.
3.Is pressure correct?
NO - Check fluid pressure
See Power Steering
System - Test
.
If pressure is not correct after bleeding the
system, renew pump
See Repair, Power
Steering Pump
.
YES -
See Overhaul, Power Steering Box.Symptom:-
Steering heavy - stiff, poor castor return action.
1.Are tyres correct type and pressure?
NO -
See INTRODUCTION, Information,
Wheels and Tyres
.
YES - Check universal joints for seizure and
correct alignment
See Repair, Lower Steering
Shaft and Universal Joints
.
Check power steering box adjustments
See
Overhaul, Power Steering Box
.
2.Is the power assistance satisfactory?
NO - See fault symptomInsufficient
assistance, (castor return action normal).
YES - Disconnect drag link from drop arm and
check steering column and box for stiffness
See
Repair, Drag Link and Drag Link Ends
.
3.Is the steering stiff with the drag link
disconnected?
NO - Check steering ball joints for seizure and
axle swivels lubrication and resistance
See
Repair, Drag Link and Drag Link Ends
,See
FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE, Overhaul,
Front Stub Axle, Constant Velocity Joint and
Swivel Pin Housing
.
YES - Disconnect the lower steering shaft and
check the column and box for stiffness
See
Repair, Lower Steering Shaft and Universal
Joints
.
4.Is the steering column stiff to turn when
disconnected from the box?
NO - Remove and overhaul box
See Overhaul,
Power Steering Box
.
YES - Adjust steering column
See Stiff
Steering Checklist
.