check engine LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999Pages: 667, PDF Size: 8.76 MB
Page 195 of 667
12ENGINE
36
OVERHAUL 9.Check that the cut-out in piston skirt is
positioned above the oil squirt jet.
10.Repeat for other pistons in turn ensuring that
pistons and connecting rods are fitted in cylinder
bores from which they were removed.
11.Fit connecting rod bearings.See this Section.
CAUTION: If new pistons, connecting rods
or crankshaft have been fitted, it will be
necessary to select correct thickness of
cylinder head gasket.See this Section.CRANKSHAFT
Service repair no - 12.21.33.01
Remove
1.Remove timing chain and sprockets.See this
Section.
2.Remove crankshaft rear oil seal.See this
Section.
3.Remove connecting rod bearings.See this
Section.
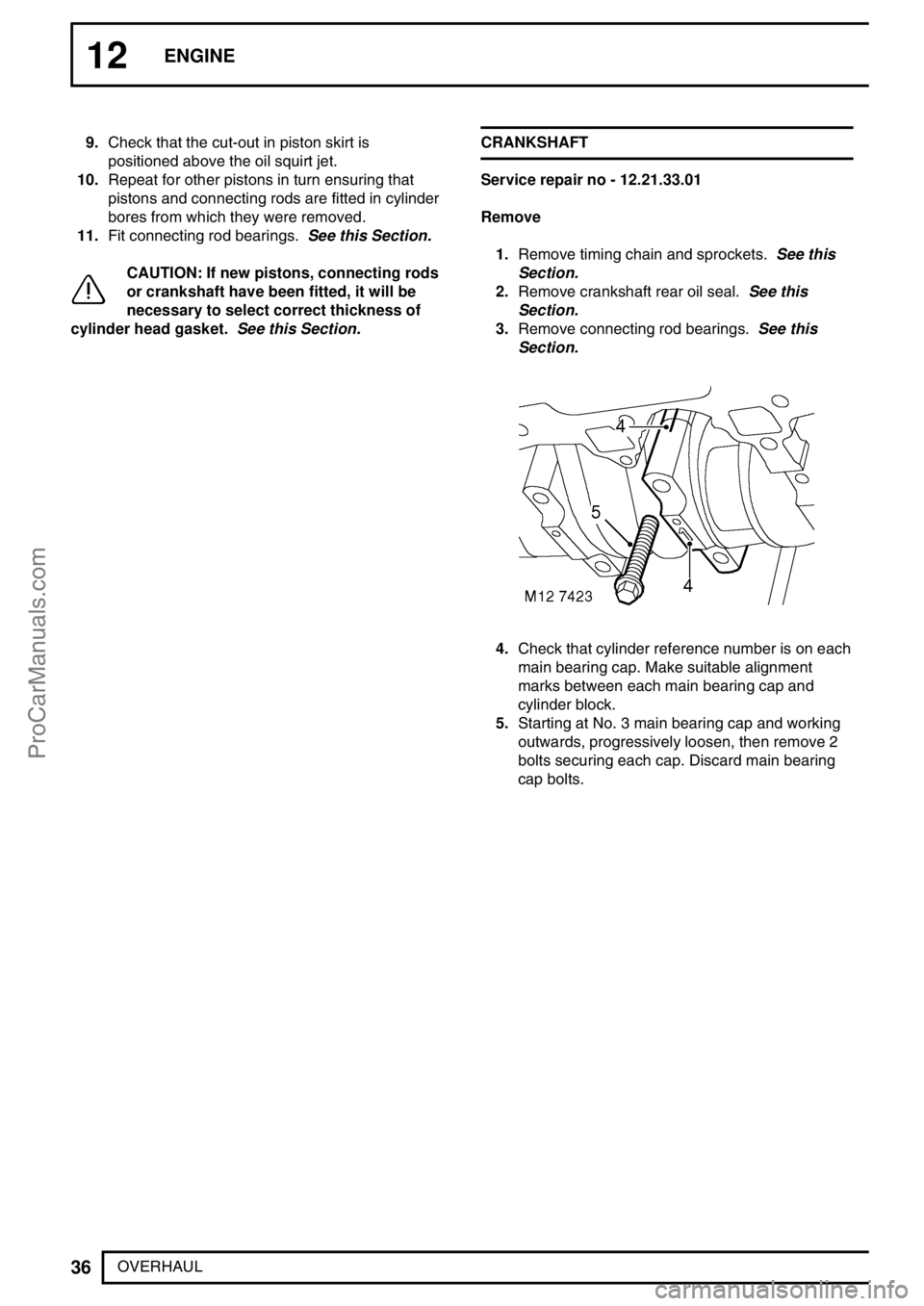
4.Check that cylinder reference number is on each
main bearing cap. Make suitable alignment
marks between each main bearing cap and
cylinder block.
5.Starting at No. 3 main bearing cap and working
outwards, progressively loosen, then remove 2
bolts securing each cap. Discard main bearing
cap bolts.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 196 of 667
ENGINE
37
OVERHAUL
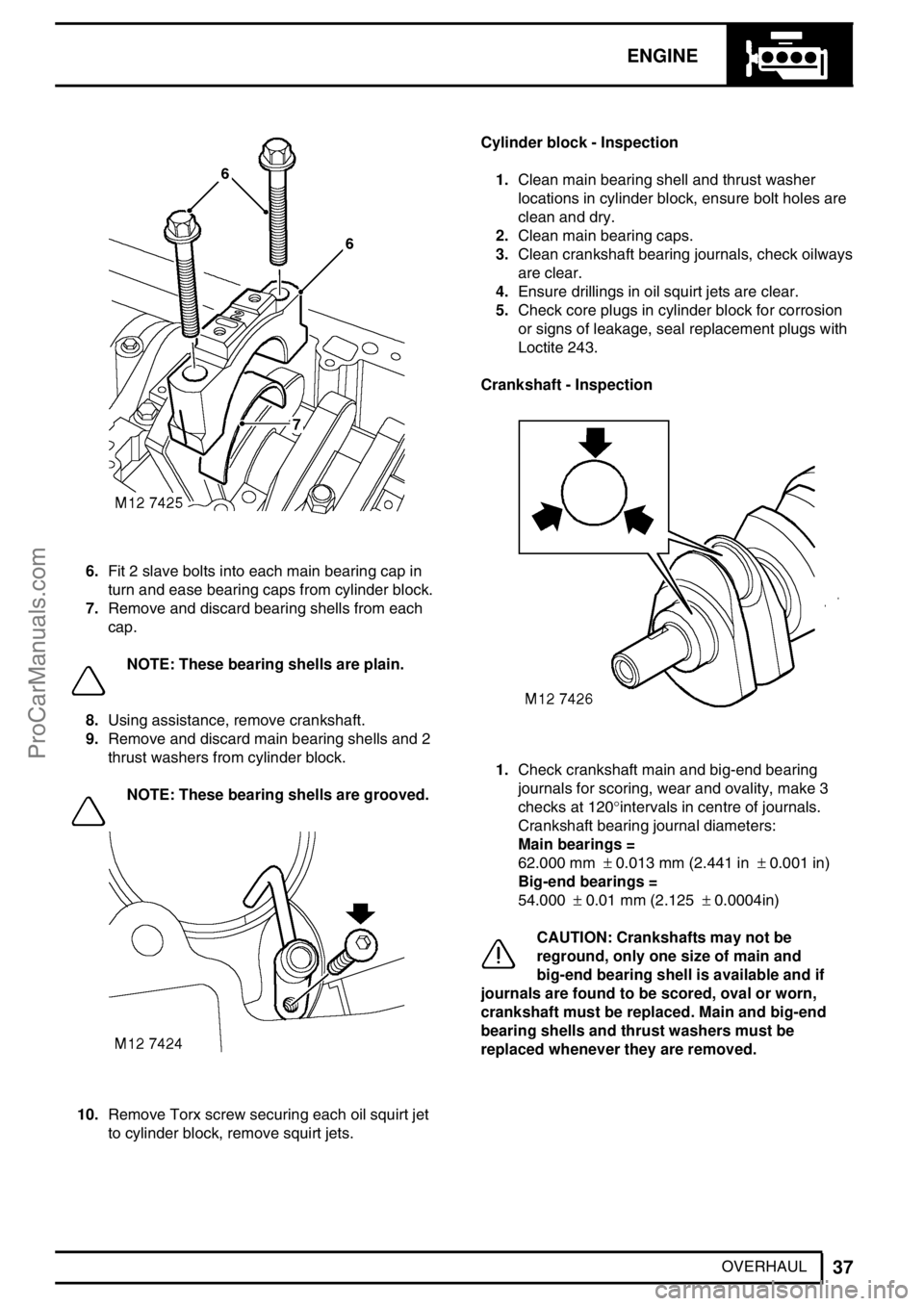
6.Fit 2 slave bolts into each main bearing cap in
turn and ease bearing caps from cylinder block.
7.Remove and discard bearing shells from each
cap.
NOTE: These bearing shells are plain.
8.Using assistance, remove crankshaft.
9.Remove and discard main bearing shells and 2
thrust washers from cylinder block.
NOTE: These bearing shells are grooved.
10.Remove Torx screw securing each oil squirt jet
to cylinder block, remove squirt jets.Cylinder block - Inspection
1.Clean main bearing shell and thrust washer
locations in cylinder block, ensure bolt holes are
clean and dry.
2.Clean main bearing caps.
3.Clean crankshaft bearing journals, check oilways
are clear.
4.Ensure drillings in oil squirt jets are clear.
5.Check core plugs in cylinder block for corrosion
or signs of leakage, seal replacement plugs with
Loctite 243.
Crankshaft - Inspection
1.Check crankshaft main and big-end bearing
journals for scoring, wear and ovality, make 3
checks at 120°intervals in centre of journals.
Crankshaft bearing journal diameters:
Main bearings =
62.000 mm±0.013 mm (2.441 in±0.001 in)
Big-end bearings =
54.000±0.01 mm (2.125±0.0004in)
CAUTION: Crankshafts may not be
reground, only one size of main and
big-end bearing shell is available and if
journals are found to be scored, oval or worn,
crankshaft must be replaced. Main and big-end
bearing shells and thrust washers must be
replaced whenever they are removed.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 197 of 667

12ENGINE
38
OVERHAUL Crankshaft spigot bush
1.Check crankshaft spigot bush for wear, replace if
necessary using the following procedures:
2.Secure crankshaft in a suitably padded vice.
3.Tap a thread in spigot bush to accommodate a
suitable impulse extractor.
4.Fit impulse extractor to spigot bush.
5.Remove spigot bush.
6.Clean spigot bush recess in crankshaft.
7.Fit new spigot bush to crankshaft using a
suitable mandrel.
Crankshaft - Refit
1.Fit oil squirt jets, fit Torx screws and tighten to8
Nm (6 lbf.ft).
2.Lubricate new, grooved, main bearing shells with
engine oil and fit to cylinder block.
3.Lubricate new thrust washers with engine oil and
fit, grooved side facing outwards, to recess in
each side of cylinder block No. 3 main bearing.
4.Lubricate crankshaft journals with engine oil and
using assistance, position crankshaft in cylinder
block.
5.Lubricate new, plain, main bearing shells with
engine oil and fit to main bearing caps.
6.Fit main bearing caps in their original fitted
positions ensuring that reference marks are
aligned.
7.Fit and lightly tighten new main bearing cap
bolts.
CAUTION: Do not lubricate bolt threads.
8.Starting with No. 3 main bearing cap and
working outwards, tighten main bearing cap bolts
to:
Stage 1 -33 Nm (24 lbf.ft)
Stage 2 -Further 90
°
CAUTION: Do not carry out stages 1 and 2
in one operation.
9.Check that crankshaft rotates smoothly.
10.Assemble a magnetic base DTI to front of
cylinder block with stylus of gauge on end of
crankshaft.
11.Using suitably padded levers, move crankshaft
rearwards and zero DTI.
12.Move crankshaft forwards and note crankshaft
end-float reading on gauge.
Crankshaft end-float =0.02 to 0.25 mm (0.001
to 0.011 in)
CAUTION: Oversize thrust washers are not
available, if end-float exceeds figure given,
crankshaft must be replaced.
13.Remove DTI.
14.Fit connecting rod bearings.See this Section.
15.Fit timing chain and sprockets.See this
Section.
16.Fit crankshaft rear oil seal.See this Section.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 208 of 667

EMISSION CONTROL
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL
All internal combustion engines generate oil vapour and smoke in the crankcase as a result of high crankcase
temperatures and piston ring and valve stem blow-by. A closed crankcase ventilation system is used to vent
crankcase gases back to the air induction system and so reduce the emission of hydrocarbons.
Gases from the crankcase are drawn into the inlet manifold to be burnt in the combustion chambers with the fresh
air/fuel mixture. The system provides effective emission control under all engine operating conditions.
Crankcase gases are drawn through the breather port in the top of the camshaft cover and routed through the
breather hose and breather valve on the flexible air intake duct to be drawn into the turbocharger intake for
delivery to the air inlet manifold via the intercooler.
An oil separator plate is included in the camshaft cover which removes the heavy particles of oil before the
crankcase gas leaves via the camshaft cover port. The rocker cover features circular chambers which promote
swirl in the oil mist emanating from the cylinder head and camshaft carrier. As the mist passes through the series
of chambers between the rocker cover and oil separator plate, oil particles are thrown against the separator walls
where they condense and fall back into the cylinder head via two air inlet holes located at each end of the rocker
cover.
The breather valve is a pressure depression limiting valve which progressively closes as engine speed increases,
thereby limiting the depression in the crankcase. The valve is of moulded plastic construction and has a port on
the underside which plugs into a port in the flexible air duct. A port on the side of the breather valve connects to
the camshaft cover port by means of a breather hose which is constructed from a heavy duty braided rubber hose
which is held in place by hose clips. A corrugated plastic sleeve is used to give further protection to the breather
hose. The breather valve is orientation sensitive, and’TOP’is marked on the upper surface to ensure it is
mounted correctly.
It is important that the system is air tight. Hose connections to ports should be checked and the condition of the
breather hose should be periodically inspected to ensure it is in good condition.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 239 of 667

18ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
16
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION On Defender models, at wide open throttle, track 2 returns a signal of 0.28V and track 1 returns a signal of 4.7V to
the ECM. The ECM calculates the sum of these two figures which totals 5.0V.
The ECM uses this strategy to error check the TP sensor signal and ensure that the requested throttle position is
applied. The third potentiometer track measures the tolerance of tracks 1 and 2 and provides an improved
functionality check of the pedal angle.
NOTE: Three track TP sensors cannot be fitted as replacements on vehicles previously fitted with
two track TP sensors. Replacement ECM’s are configured for two track TP sensors and can be
fitted to all Td5 models. When replacement ECM’s are fitted to vehicles using three track TP
sensors, TestBook must be used to configure the ECM for three track TP sensor use.
If the TP sensor fails, the ECM will illuminate the MIL and the engine will operate at normal idle speed only.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 252 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
1
REPAIR ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
Service repair no - 18.30.03
Remove
1.Release fixings and remove battery cover.
2.Disconnect battery negative lead.
3.Remove RH seat cushion, release clip and
remove ECM access panel.
4.Remove 3 bolts, release ECM and disconnect 2
multiplugs. Remove ECM.
Refit
5.Position new ECM and connect multiplugs.
6.Fit ECM and tighten bolts.
7.Fit access panel and RH seat cushion.
8.Reconnect battery negative lead.
9.Fit battery cover and secure with fixings.SENSOR - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
(ECT)
Service repair no - 18.30.10
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Remove spring clip and disconnect ECT sensor
multiplug.
3.Position cloth around ECT sensor to absorb
coolant spillage.
4.Remove ECT sensor.
5.Remove sealing washer and discard.
Refit
6.Clean sealing washer, sensor threads and
sensor location.
7.Coat sensor threads with Loctite 577 and fit new
sealing washer.
8.Fit ECT sensor and tighten to20 Nm (14 lbf.ft).
9.Fit spring clip to multiplug and connect multiplug
to ECT sensor.
10.Top up cooling system.
11.Run engine to normal operating temperature.
Check for leaks around ECT sensor.
12.Reconnect battery negative lead.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 268 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
1
ADJUSTMENT HEATER PLUG TEST
Service repair no - 19.90.20.01
Check
1. Test out of engine
2.Remove heater plug.See Repair.
3.UsingLRT-12-511,connect RED lead to battery
’+’positive and the BLACK lead to battery’-’
negative.
4.Position heater plug into tester and retain with
spring loaded bar.
5.Connect YELLOW lead to heater plug terminal.
6.Press red button on tester and note ammeter
reading. Keep button depressed, heater plug tip
should start to glow after 5 seconds
CAUTION: The heater plug tip must glow
first, if it fails to do so, replace heater plug.
7.The ammeter reading should show an initial
current draw of 25 amps, which should fall to 12
amps after 20 seconds.
8.Refit heater plug.See Repair.FUEL SYSTEM - BLEED
Service repair no - 19.50.07
Fuel Purging Procedure
1.If the vehicle runs out of fuel, or the fuel level is
so low that the fuel system draws air into the fuel
rail, the fuel rail will need to be purged before the
engine will start. This can be achieved by
following a set procedure. The process does not
require the use of any specialist equipment and
can be performed by the driver of the vehicle.
The process is as follows:
2.Switch off ignition and wait 15 seconds.
3.Turn ignition key to position 2 and wait 3
minutes, (this ensures that the fuel system
purges all the air from the fuel rail within the
cylinder head).
4.Depress the throttle pedal to more than 90% of
its total travel, (to the throttle stop).
5.Crank the engine keeping the throttle pedal
depressed.
NOTE: This operation is controlled by the
ECM and it is important that the purging
operation is not carried out on a vehicle
that has not run out of fuel. If it is carried out
unnecessarily it can lead to the engine flooding
and failing to start.
This operation will be cancelled:
6.As soon as engine speed exceeds 600 rev/min.
7.The driver allows the throttle pedal to close to a
position less than 90% of its travel.
8.The ignition key is released from the start
position.
NOTE: The engine must not be cranked for
more than 30 seconds in any one period.
9.Repeat the above procedure if the engine fails to
start.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 302 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
1
ADJUSTMENT DRAIN AND REFILL
Service repair no - 26.10.01
WARNING: Hot coolant
Drain
1.Remove engine acoustic cover.
2.Visually check engine and cooling system for
signs of coolant leaks.
3.Examine hoses for signs of cracking, distortion
and security of connections.
4.Position drain tray to collect coolant.
5.Remove expansion tank filler cap.
6.Loosen clip screws securing air inlet hose to
intercooler and inlet manifold, release and
remove hose.
7.Release clip and disconnect bottom hose from
radiator.
8.Allow cooling system to drain.
9.Disconnect bottom hose from radiator.Refill
1.Flush system with water under low pressure.
2.Do not use water under high pressure as it could
damage the radiator.
3.Connect bottom hose to radiator and secure
hose with clip.
4.Prepare coolant to required concentration.
5.Position heater temperature control to maximum
hot position.
6.Remove bleed screw from top hose.
7.Fill system slowly through coolant expansion
tank until a steady flow of coolant is emitted from
the bleed hole in top hose.
8.Fit bleed screw to top hose.
9.Continue filling system until coolant level
reaches’MAX’mark on expansion tank.
10.Fit expansion tank filler cap.
11.Position air intake hose and tighten clip screws.
12.Start and run engine until normal running
temperature is reached.
13.If fitted, DO NOT operate air conditioning.
14.Switch off engine and allow to cool.
15.Check for leaks and top-up coolant to’MAX’
mark on expansion tank.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 510 of 667

PANEL REPAIRS
1
INFORMATION BODY REPAIRS
Body shells are of riveted, bolted and welded
construction and are bolted to the chassis frame.
It is essential that design dimensions and strength are
restored in accident rectification. It is important that
neither structural weakness nor excessive local
stiffness are introduced into the vehicle during body or
chassis repair.
Repairs usually involve a combination of operations
ranging from straightening procedures to renewal of
either individual panels or panel assemblies. The
repairer will determine the repair method and this
decision will take into account a balance of economics
between labour and material costs and the availability
of repair facilities in both equipment and skills. It may
also involve considerations of vehicles down-time,
replacement vehicle availability and repair turn-around
time.
It is expected that a repairer will select the best and
most economic repair method possible, making use of
the facilities available. The instructions given are
intended to assist a skilled body repairer by expanding
approved procedures for panel replacement with the
objective of restoring the vehicle to a safe running
condition and effecting a repair which is visually
acceptable and which, even to the experienced eye,
does not advertise the fact that it has been damaged.
This does not necessarily mean that the repaired
vehicle will be identical in all respects with original
factory build. Repair facilities cannot always duplicate
methods of construction used during production.
The panel repairs shown in this section are all based
on a 110 Station Wagon. Therefore all illustrations
and text relate only to this model. Although certain
areas of the vehicle, such as the front end, are
relevant to all models.
Operations covered in this Manual do not include
reference to testing the vehicle after repair. It is
essential that work is inspected and suspension
geometry checked after completion and if necessary a
road test of the vehicle is carried out, particularly
where safety related items are concerned.Where major units have been disconnected or
removed, it is necessary to ensure that fluid levels are
checked and topped up when necessary. It is also
necessary to ensure that the repaired vehicle is in a
roadworthy condition in respect of tyre pressures,
lights, washer fluid etc.
Body repairs often involve the removal of mechanical
and electrical units as well as associated wiring.
Where this is necessary use the relevant section in
this manual.
Taking into consideration the differences in body
styles, steering and suspension systems as well as
engine and suspension layouts, the location of the
following components as applicable to a particular
vehicle is critical:
Front suspension upper damper
mountings.
Front suspension or sub frame mountings.
Engine mountings on RH and LH chassis
longitudinals.
Rear suspension upper damper mountings.
Rear suspension mountings or lower
pivots.
Steering rack mountings.
Additional points which can be used to check
alignment and assembly are:
Inner holes in crossmember - side - main
floor.
Holes in valance front assembly.
Body to chassis mounting holes.
Holes in rear floor.
Holes in rear lower panels or extension
rear floor.
Fuel tank mountings.
Apertures for windscreen, backlight, bonnet and doors
can be checked by offering up an undamaged
component as a gauge and also by measuring known
dimensions.See BODY DIMENSIONS section.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 534 of 667

PANEL REPAIRS
9
SEALING AND CORROSION PROTECTION Stone Chip Resistant Paint/Primer
Re-treat all areas protected with factory-applied
anti-chip primer with suitable approved material in
repair.
Inspections during Maintenance Servicing
It is a requirement of the Land Rover Corrosion
Warranty that the vehicle body is checked for
corrosion by an authorised Land Rover dealer at least
once a year, to ensure that the factory-applied
protection remains effective.
Service Job Sheets include the following operations to
check bodywork for corrosion:
With the vehicle on a lift, carry out visual
check of underbody sealer for damage.
With the vehicle lowered, inspect exterior
paintwork for damage and body panels for
corrosion.
NOTE: Wash the vehicle and ensure that it
is free from deposits prior to inspection. It
is part of the owner’s responsibility to
ensure that the vehicle is kept free of
accumulations of mud which could accelerate the
onset of corrosion. The Dealer MUST wash the
vehicle prior to inspection of bodywork if the
customer has offered it in a dirty condition, and
pay special attention to areas where access is
difficult.
NOTE: The checks described above are
intended to be visual only. It is not
intended that the operator should remove
trim panels, finishers, rubbing strips or sound
deadening materials when checking the vehicle
for corrosion and paint damage.
With the vehicle on a lift, and using an inspection or
spot lamp, visually check for the following:
Corrosion damage and damaged
paintwork, condition of underbody sealer
on front and rear lower panels, sills and
wheel arches.
Damage to underbody sealer on main floor
and chassis members. Corrosion in areas
adjacent to suspension mountings and fuel
tank fixings.
NOTE: The presence of small blisters in
PVC underbody sealer is acceptable,
providing they do not expose bare metal.
Special attention must be paid to signs of damage
caused to panels or corrosion material by incorrect
jack positioning.
It is essential to follow the correct jacking and lifting
procedures.See GENERAL INFORMATION DATA,
Information section.
With the vehicle lowered, visually check for evidence
of damage and corrosion on all painted areas, in
particular the following:
Front edge of bonnet.
Visible flanges in engine compartment and
boot.
Lower body and door panels.
Where bodywork damage or evidence of corrosion is
found during inspection, rectify this as soon as is
practicable, both to minimise the extent of the damage
and to ensure the long term effectiveness of the
factory-applied corrosion protection treatment. Where
the cost of rectification work is the owner’s
responsibility, the Dealer must advise the owner and
endorse the relevant documentation accordingly.
Where corrosion has become evident and is
emanating from beneath a removable component
(e.g. trim panel, window glass, seat etc.), remove the
component as required to permit effective rectification.
ProCarManuals.com