ESP LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999Pages: 667, PDF Size: 8.76 MB
Page 13 of 667

01INTRODUCTION
6
INFORMATION 3.Position an axle stand under right hand axle
tube, carefully lower jack until axle sits securely
on both axle stands, remove trolley jack.
4.Before commencing work on underside of
vehicle re-check security of vehicle on stands.
5.Reverse procedure when removing vehicle from
stands.
Raise rear of vehicle
1.Position cup of hydraulic arm under differential
casing.
2.Raise vehicle to enable axle stands to be
installed under left and right hand axle tubes.
3.Lower jack until axle sits securely on axle
stands, remove trolley jack.
4.Before commencing work on underside of
vehicle re-check security of vehicle on stands.
5.Reverse procedure when removing vehicle from
stands.
HYDRAULIC VEHICLE RAMP (FOUR POST)
Use only a’drive on’type ramp which supports vehicle
on its road wheels. If a’wheel-free’condition is
required, use a’drive on’ramp incorporating a
’wheel-free’system providing support beneath axle
casings. Alternatively, place vehicle on a firm, flat floor
and support on axle stands.
TWO POST VEHICLE RAMPS
The manufacturer of LAND ROVER VEHICLES
DOES NOT recommend using ’Two Post’ ramps
that employ four adjustable support arms. These
are NOT considered safe for Land Rover vehicles.
If vehicle is installed on a Two Post ramp
responsibility for safety of vehicle and personnel
performing service operations is in the hands of
the Service Provider.DYNAMOMETER TESTING
The front and rear axles cannot be driven
independently.
WARNING: DO NOT attempt to drive
individual wheels with vehicle supported
on floor jacks or stands.
Four wheel dynamometers
Provided that front and rear dynamometer rollers are
rotating at identical speeds and that normal workshop
safety standards are applied, there is no speed
restriction during testing except any that may apply to
the tyres.
Two wheel dynamometers
IMPORTANT: Use a four wheel dynamometer for
brake testing if possible.
If brake testing on a single axle rig is necessary it
must be carried out with propeller shaft to rear axle
removed, AND neutral selected in BOTH main
gearbox and transfer gearbox. When checking brakes,
run engine at idle speed to maintain servo vacuum.
If checking engine performance, the transfer box must
be in high range and propeller shaft to stationary axle
must be removed.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 33 of 667

04GENERAL SPECIFICATION DATA
10
INFORMATION VEHICLE WEIGHTS AND PAYLOAD
When loading a vehicle to its maximum (Gross Vehicle Weight), consideration must be taken of the unladen
vehicle weight and the distribution of the payload to ensure that axle loadings do not exceed the permitted
maximum values.
It is the customer’s responsibility to limit the vehicle’s payload in an appropriate manner such that neither
maximum axle loads nor Gross Vehicle Weight are exceeded.
Maximum EEC kerb weight and distribution - all optional equipment
VEHICLE AXLE WEIGHTS
90 models Station Wagon Utility
Front axle 1200 Kg (2645 lb)......................................................................... 1200 Kg (2645 lb)
Rear axle 1500 kg (3307 lb).......................................................................... 1500 Kg (3307 lb)
Gross vehicle weight 2550 Kg (5291 lb)........................................................ 2400 Kg (5622 lb)
110 models Station Wagon Utility
Front axle 1200 Kg (2645 lb)......................................................................... 1200 Kg (2645 lb)
Rear axle 1750 Kg (3858 lb).......................................................................... 1850 Kg (4078 lb)
Gross vehicle weight 2950 Kg (6503 lb)........................................................ 3050 Kg (6724 lb)
130 modelsUtility
Front axle1580 Kg (3483 lb) .....................................................................................................................
Rear axle2200 Kg (4850 lb) ......................................................................................................................
Gross vehicle weight 3500 Kg (7716 lb)....................................................................................................
NOTE: Axle weights are not accumulative. The individual maximum axle weights and gross vehicle
weight must not be exceeded.
EEC VEHICLE KERB WEIGHTS
90 models Standard Heavy Duty
Soft top: 1770 Kg (3402 lb)............................................................................ 1993 Kg (4393 lb)
Pick-up: 1770 Kg (3402 lb)............................................................................ 1993 Kg (4393 lb)
Hard top: 1815 Kg (4001 lb).......................................................................... 1987 Kg (4380 lb)
Station wagon: 1870 Kg - 1885 Kg................................................................. 1989 Kg - 1998 Kg
(4122 lb - 4155 lb) (4385 lb - 4404 lb)
110 models
Soft top: 1885 Kg - 2080 Kg............................................................................ (4155 lb - 4585 lb)
High capacity pick-up: 1920 Kg - 2122 Kg...................................................... (4232 lb - 4678 lb)
Hard top: 1920 Kg - 2110 Kg.......................................................................... (4232 lb - 4651 lb)
Station wagon: 2055 Kg - 2229 Kg................................................................. (4530 lb - 4914 lb)
130 models
Crew cab and high capacity pick-up: 2177 Kg - 2286 Kg...........................................................................
(4667 lb - 5039 lb)
EEC kerb weight = Unladen weight + Full fuel tank + 75 Kg (165 lb).
ProCarManuals.com
Page 44 of 667

GENERAL FITTING REMINDERS
1
INFORMATION GENERAL FITTING REMINDERS
WORKSHOP SAFETY IS YOUR RESPONSIBILITY!
The suggestions, cautions and warnings in the
section are intended to serve as reminders for
trained and experienced mechanics. This manual
is not a definitive guide to automotive mechanics
or workshop safety.
Shop equipment, shop environment, and the use
and disposal of solvents, fluids, and chemicals
are subject to government regulations which are
intended to provide a level of safety. It is your
responsibility to know and comply with such
regulations.
PRECAUTIONS AGAINST DAMAGE
1.Always fit covers to protect fenders before
commencing work in engine compartment.
2.Cover seats and carpets, wear clean overalls
and wash hands or wear gloves before working
inside vehicle.
3.Avoid spilling hydraulic fluid or battery acid on
paint work. Wash off with water immediately if
this occurs. Use Polythene sheets to protect
carpets and seats.
4.Always use a recommended Service Tool where
specified.
5.Protect temporarily exposed screw threads by
replacing nuts or fitting plastic caps.SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.Whenever possible, use a lift when working
beneath vehicle, in preference to jacking. Chock
wheels as well as applying parking brake.
WARNING: Do not use a pit when
removing fuel system components.
2.Never rely on a jack alone to support vehicle.
Use axle stands carefully placed at jacking
points to provide rigid support.
3.Ensure that a suitable form of fire extinguisher is
conveniently located.
4.Check that any lifting equipment used has
adequate capacity and is fully serviceable.
5.Disconnect battery.
WARNING: Do not disconnect any pipes in
air conditioning system, unless trained
and instructed to do so. A refrigerant is
used which can cause blindness if allowed to
contact eyes.
6.Ensure that adequate ventilation is provided
when volatile degreasing agents are being used.
7.Do not apply heat in an attempt to free stiff
fixings; as well as causing damage to protective
coatings, there is a risk of damage to electronic
equipment and brake linings from stray heat.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 113 of 667

12ENGINE
28
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Inlet and exhaust valves
The inlet and exhaust valves are mounted directly above the engine block cylinders.
Each valve is a forged and ground solid one-piece head and stem which is hardened by heat treatment. The
stems are chrome-plated then ground for improved heat transfer, wear resistance and smooth operation. It is not
possible to recut the valve’s face angle, but the valves can be lapped to their seats using grinding paste.
The valve springs are made from spring steel and are of the parallel single-coil type. The bottom end of the spring
rests on the flange of a spring seal which has a centre bore that locates on a recess ground into the lower valve
stem. The top end of the spring is held in place by a spring cap which is held in position at the top end of the valve
stem by split taper collets. The taper collets have grooves on the internal bore that locate in grooves ground into
the upper stems of the valves.
The valve seats and valve guides are sintered and are an interference fit into the cylinder head. The valve seats
and guides are non-serviceable.
Finger followers and lash adjusters
1.Valve stem
2.Finger follower
3.Lash adjuster plunger4.Oil supply hole
5.Lash adjuster body
The valves are operated through finger followers and lash adjusters, actuated by the camshaft lobes. When the
camshaft lobe presses down on the top of a finger follower roller mechanism, the respective valve is forced down
opening the inlet or exhaust port.
The lash adjuster body contains a plunger and two chambers for oil feed and pressurised oil. Pressurised oil is
supplied to the lash adjusters via the oil galleries in the cylinder head and through a hole in the side of the lash
adjuster body. The oil passes into a feed chamber in the lash adjuster then through to a separate pressure
chamber via a one way ball valve. Oil flow from the pressure chamber is determined by the amount of clearance
between the lash adjuster outer body and the centre plunger, oil escapes up the side of the plunger every time the
lash adjuster is operated, the downward pressure on the plunger forcing a corresponding amount of oil in the lash
adjuster body to be displaced. When the downward pressure from the camshaft and finger follower is removed
(i.e. after the trailing flank of the camshaft lobe has passed), oil pressure forces the lash adjuster’s plunger up
again. This pressure is not sufficient to effect the valve operation, but eliminates the clearance between the finger
follower and top of the valve stem.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 173 of 667
12ENGINE
14
OVERHAUL Valve springs - Inspection
1.Check free length of valve springs:
Free length =47.0±0.25 mm (1.85±0.011 in)
CAUTION: Valve springs must be replaced
as a set, if springs are to be refitted, keep
them in their fitted order.
Valves and valve guides - Inspection
1.Clean carbon from valves, check valves for
burning, pitting or cracking; replace as
necessary.
2.Clean carbon from valve seat inserts, remove all
loose particles on completion.
3.Check valve seat inserts for pitting and burning.
CAUTION: It is not permissible to recut or
replace valve seat inserts.
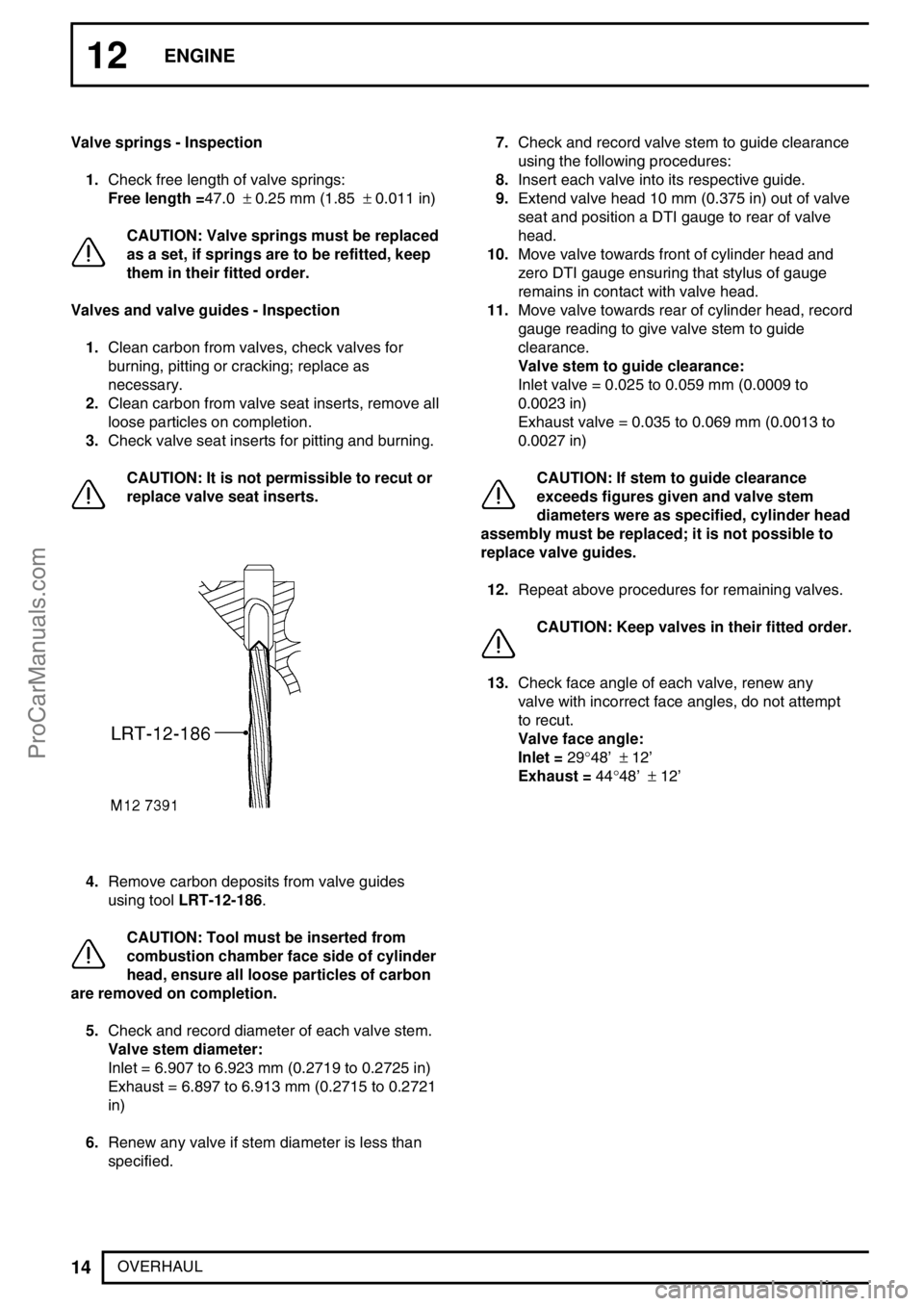
4.Remove carbon deposits from valve guides
using toolLRT-12-186.
CAUTION: Tool must be inserted from
combustion chamber face side of cylinder
head, ensure all loose particles of carbon
are removed on completion.
5.Check and record diameter of each valve stem.
Valve stem diameter:
Inlet = 6.907 to 6.923 mm (0.2719 to 0.2725 in)
Exhaust = 6.897 to 6.913 mm (0.2715 to 0.2721
in)
6.Renew any valve if stem diameter is less than
specified.7.Check and record valve stem to guide clearance
using the following procedures:
8.Insert each valve into its respective guide.
9.Extend valve head 10 mm (0.375 in) out of valve
seat and position a DTI gauge to rear of valve
head.
10.Move valve towards front of cylinder head and
zero DTI gauge ensuring that stylus of gauge
remains in contact with valve head.
11.Move valve towards rear of cylinder head, record
gauge reading to give valve stem to guide
clearance.
Valve stem to guide clearance:
Inlet valve = 0.025 to 0.059 mm (0.0009 to
0.0023 in)
Exhaust valve = 0.035 to 0.069 mm (0.0013 to
0.0027 in)
CAUTION: If stem to guide clearance
exceeds figures given and valve stem
diameters were as specified, cylinder head
assembly must be replaced; it is not possible to
replace valve guides.
12.Repeat above procedures for remaining valves.
CAUTION: Keep valves in their fitted order.
13.Check face angle of each valve, renew any
valve with incorrect face angles, do not attempt
to recut.
Valve face angle:
Inlet =29°48’±12’
Exhaust =44°48’±12’
ProCarManuals.com
Page 174 of 667
ENGINE
15
OVERHAUL Valves - Lapping-in
1.Lap each valve to its seat using grinding paste.
2.Apply Prussian Blue to valve seat, insert valve
into guide and press it firmly, without rotating on
to seat.
3.Remove valve and check that a continuous,
even line of Prussian Blue has been transferred
on to valve face.
NOTE: Line does not have to be across
whole width of valve face.
4.Remove all traces of grinding paste on
completion.
5.Check valve head stand-down.See this
Section.
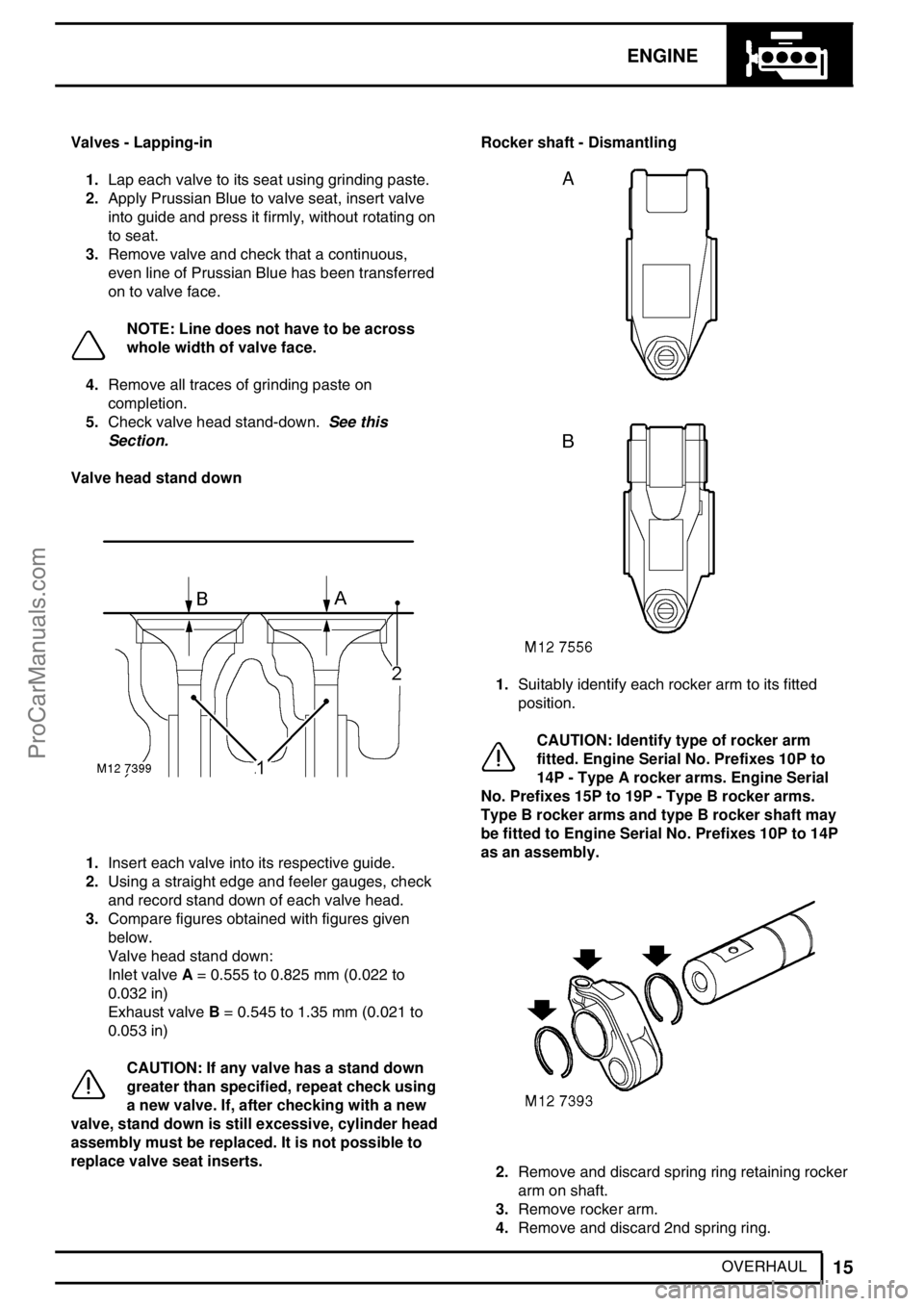
Valve head stand down
1.Insert each valve into its respective guide.
2.Using a straight edge and feeler gauges, check
and record stand down of each valve head.
3.Compare figures obtained with figures given
below.
Valve head stand down:
Inlet valveA= 0.555 to 0.825 mm (0.022 to
0.032 in)
Exhaust valveB= 0.545 to 1.35 mm (0.021 to
0.053 in)
CAUTION: If any valve has a stand down
greater than specified, repeat check using
a new valve. If, after checking with a new
valve, stand down is still excessive, cylinder head
assembly must be replaced. It is not possible to
replace valve seat inserts.Rocker shaft - Dismantling
1.Suitably identify each rocker arm to its fitted
position.
CAUTION: Identify type of rocker arm
fitted. Engine Serial No. Prefixes 10P to
14P - Type A rocker arms. Engine Serial
No. Prefixes 15P to 19P - Type B rocker arms.
Type B rocker arms and type B rocker shaft may
be fitted to Engine Serial No. Prefixes 10P to 14P
as an assembly.
2.Remove and discard spring ring retaining rocker
arm on shaft.
3.Remove rocker arm.
4.Remove and discard 2nd spring ring.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 191 of 667

12ENGINE
32
OVERHAUL
8.Carefully move connecting rod to one side of
journal and using feeler gauges, measure
end-float of connecting rod on journal:
Connecting rod end-float =0.2 to 0.5 mm
(0.008 to 0.021 in).
CAUTION: If end-float exceeds limits
given, replace connecting rod and repeat
end-float check - See pistons, connecting
rods and cylinder bores.
9.Repeat above procedures for remaining big-end
bearings.
10.Fit oil pump.See this Section.PISTONS, CONNECTING RODS AND CYLINDER
BORES
Service repair no - 12.17.02.01
Remove
1.Remove cylinder head gasket.See this
Section.
2.Remove connecting rod bearings.See this
Section.
3.Remove ridge of carbon from top of cylinder
bore.
4.Suitably identify each piston and connecting rod
assembly to its respective cylinder bore.
5.Carefully push connecting rod to top of cylinder
bore taking care that connecting rod does not
contact oil squirt jet or cylinder wall, remove
each piston and connecting rod assembly in
turn.
6.Using a suitable expander, remove and discard
piston rings from pistons.
7.Using a squared off end of an old piston ring,
clean carbon from ring grooves.
8.Clean carbon from piston crown and skirt.
CAUTION: Do not use abrasives on
graphited area of piston skirt, do not use a
wire brush or scraper on any part of the
pistons.
9.Secure connecting rod in a soft jawed vice.
10.Suitably identify each piston to its connecting rod
and fitted position of piston on rod.
11.Using suitable circlip pliers, remove and discard
2 circlips securing gudgeon pin.
12.Push gudgeon pin out of piston and connecting
rod; remove piston.
13.Suitably identify each gudgeon pin to its
respective piston.
14.Repeat above procedures for each piston.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 194 of 667
ENGINE
35
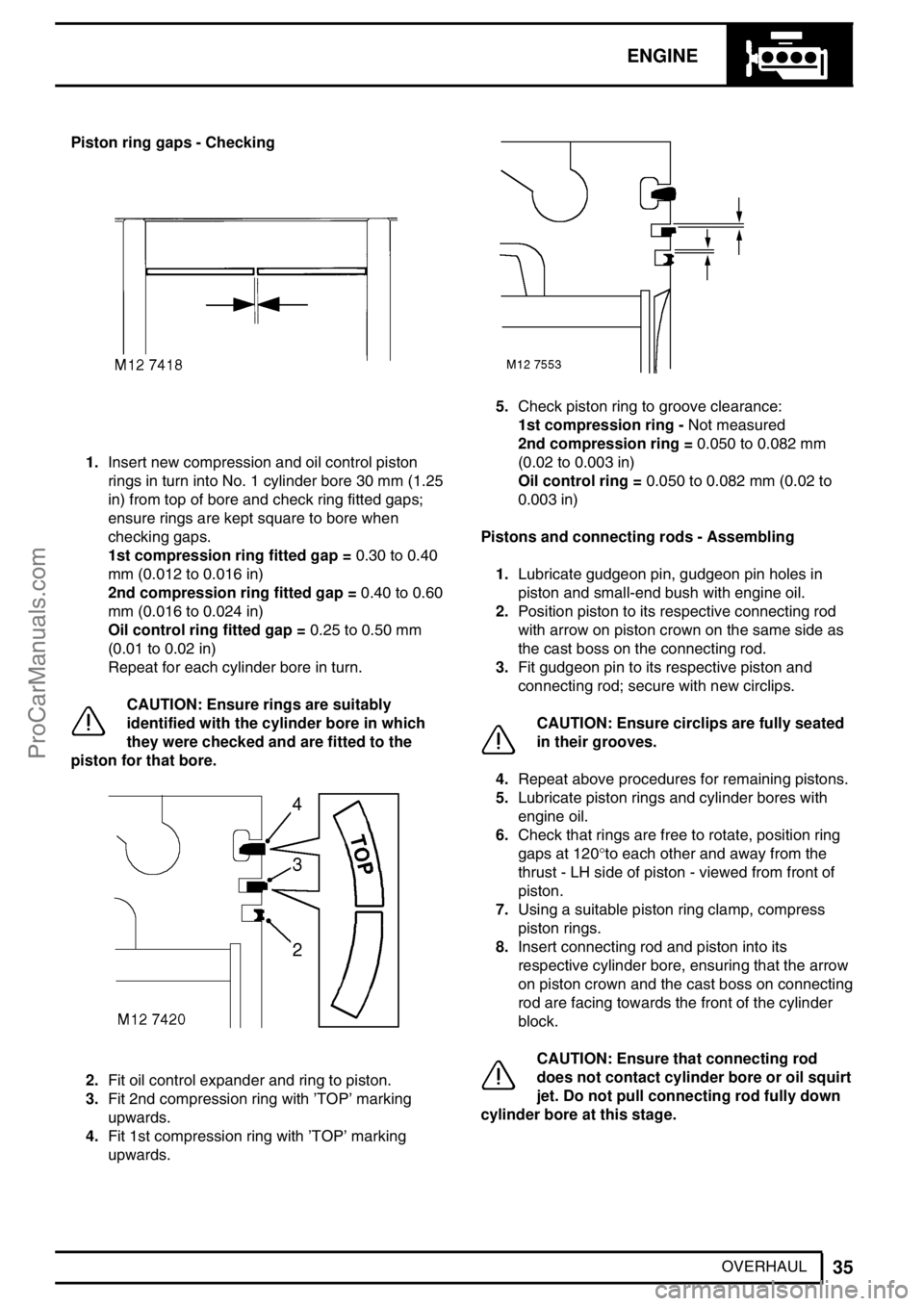
OVERHAUL Piston ring gaps - Checking
1.Insert new compression and oil control piston
rings in turn into No. 1 cylinder bore 30 mm (1.25
in) from top of bore and check ring fitted gaps;
ensure rings are kept square to bore when
checking gaps.
1st compression ring fitted gap =0.30 to 0.40
mm (0.012 to 0.016 in)
2nd compression ring fitted gap =0.40 to 0.60
mm (0.016 to 0.024 in)
Oil control ring fitted gap =0.25 to 0.50 mm
(0.01 to 0.02 in)
Repeat for each cylinder bore in turn.
CAUTION: Ensure rings are suitably
identified with the cylinder bore in which
they were checked and are fitted to the
piston for that bore.
2.Fit oil control expander and ring to piston.
3.Fit 2nd compression ring with’TOP’marking
upwards.
4.Fit 1st compression ring with’TOP’marking
upwards.
5.Check piston ring to groove clearance:
1st compression ring -Not measured
2nd compression ring =0.050 to 0.082 mm
(0.02 to 0.003 in)
Oil control ring =0.050 to 0.082 mm (0.02 to
0.003 in)
Pistons and connecting rods - Assembling
1.Lubricate gudgeon pin, gudgeon pin holes in
piston and small-end bush with engine oil.
2.Position piston to its respective connecting rod
with arrow on piston crown on the same side as
the cast boss on the connecting rod.
3.Fit gudgeon pin to its respective piston and
connecting rod; secure with new circlips.
CAUTION: Ensure circlips are fully seated
in their grooves.
4.Repeat above procedures for remaining pistons.
5.Lubricate piston rings and cylinder bores with
engine oil.
6.Check that rings are free to rotate, position ring
gaps at 120°to each other and away from the
thrust - LH side of piston - viewed from front of
piston.
7.Using a suitable piston ring clamp, compress
piston rings.
8.Insert connecting rod and piston into its
respective cylinder bore, ensuring that the arrow
on piston crown and the cast boss on connecting
rod are facing towards the front of the cylinder
block.
CAUTION: Ensure that connecting rod
does not contact cylinder bore or oil squirt
jet. Do not pull connecting rod fully down
cylinder bore at this stage.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 207 of 667

17EMISSION CONTROL
6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS
Engine design has evolved in order to minimise the emission of harmful by-products. Emission control systems
fitted to Land Rover vehicles are designed to maintain the emission levels within the legal limits pertaining for the
specified market.
Despite the utilisation of specialised emission control equipment, it is still necessary to ensure that the engine is
correctly maintained and is in good mechanical order, so that it operates at its optimum condition.
In addition to emissions improvements through engine design and the application of electronic engine
management systems, special emission control systems are used to limit the pollutant levels developed under
certain conditions. Two main types of additional emission control system are utilised with the Td5 engine to reduce
levels of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. These are as follows:
Crankcase emission control - Also known as blow-by gas emissions from the engine crankcase.
Exhaust gas recirculation - To reduce NO
2emissions.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 210 of 667

EMISSION CONTROL
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION EGR MODULATOR
1.Port to vacuum source (white band)
2.Port to EGR valve (blue band)3.Port to atmosphere via in-line filter (green band)
4.Harness connector
The EGR modulator is located on a plate fixed to the inner RH front wing. The modulator is attached to the plate
by two studs, each with two nuts which secure the assembly to a rubber mounting, which helps reduce noise. The
modulator must be mounted vertically with the two vacuum ports uppermost.
Modulator operation is controlled by a signal from the ECM which determines the required amount of EGR needed
in response to inputs relating to air flow, engine operation, and ambient conditions. The modulator has a two pin
connector at its base to connect it to the ECM via the engine harness.
The modulator features three ports:
The top port is identified by a white band and connects to a T-piece in the vacuum line via a small bore light
brown plastic hose. The two other ports on the T-piece connect to the vacuum line hoses of black vinyl tubing
between the vacuum pump and the brake servo assembly attached to the bulkhead. The vacuum pump end of
the tubing terminates in a rubber elbow, which gives a vacuum tight seal on the suction port of the vacuum
pump. The brake servo end of the tubing terminates with a non-return valve in a plastic housing which plugs
into the front face of the brake servo housing.
The middle port is identified by a blue band, and connects to the suction port on the EGR valve through a small
bore blue plastic hose.
The lower port is identified by a green band and connects to atmosphere through an in-line filter via a small
bore green plastic hose.
The blue and brown vacuum hoses are protected by corrugated plastic sheaths. The ends of the hoses are fitted
with rubber boots to ensure vacuum tight seals at the component ports.
ProCarManuals.com