brake fluid LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 135 of 1529

MAINTENANCE
10-12 PROCEDURES
Fluid reservoirs
Check/top-up — Brake/Clutch reservoir
1.Check fluid level in brake/clutch fluid reservoirs.
2.Clean area around filler cap, remove cap.
3.Top-up if necessary to correct level on reservoir
using recommended fluid.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS,
LUBRICANTS AND SEALANTS, Fluids.
4.Fit filler cap.
Check/top-up — PAS/ACE reservoirs
1.Check fluid level in PAS and ACE fluid
reservoirs.
2.Clean area around filler cap, remove cap.
3.Top-up if necessary to correct level on reservoir
using recommended fluid.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS,
LUBRICANTS AND SEALANTS, Fluids.
4.Fit filler cap.Check/top-up — Washer reservoir
1.Check fluid level in windscreen washer
reservoir.
2.Clean area around filler cap, remove cap.
3.Top-up if necessary to correct level on reservoir
using recommended fluid.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS,
LUBRICANTS AND SEALANTS, Fluids.
4.Fit filler cap.
Page 141 of 1529

MAINTENANCE
10-18 PROCEDURES
Automatic gearbox
WARNING: Avoid excessive skin contact with
mineral oil. Mineral oils remove the natural fats
from the skin, leading to dryness, irritation and
dermatitis.
Replace oil filter
1.Replace oil filter.
+ AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22
- 24, REPAIRS, Filter - oil.
Replace oil
1. Ensure that gearbox is cool. Apply
handbrake and securely chock front and rear
wheels.
2.Place a suitable container beneath gearbox.
3.Clean area around oil filler/level and drain
plugs.
4.Remove oil drain plug, remove and discard
sealing washer.
5.Allow oil to drain.
6.Fit new sealing washer to oil drain plug.
7.Fit automatic gearbox drain plug and tighten to
15 Nm (11 lbf.ft).
8.Remove oil filler/level plug, remove and discard
sealing washer.
9.Fill gearbox with recommended oil to bottom of
oil level/filler plug hole.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS,
LUBRICANTS AND SEALANTS,
Lubrication.
10.Select 'P' (Park).
11.Ensure handbrake is applied.
12.Start engine and allow it to idle.
13.Apply footbrake. 14.Move selector lever through all gear positions,
while continuing to fill the gearbox. Select 'P'
(Park).
15.With engine idling, continue filling gearbox until
a 2 mm bead of oil runs from oil filler/level plug
hole.
16.Fit new sealing washer to automatic gearbox
filler/level plug, fit plug and tighten to 30 Nm (22
l b f . f t ) .
17.Stop engine.
18.Remove all traces of oil from gearbox casing.
Page 147 of 1529
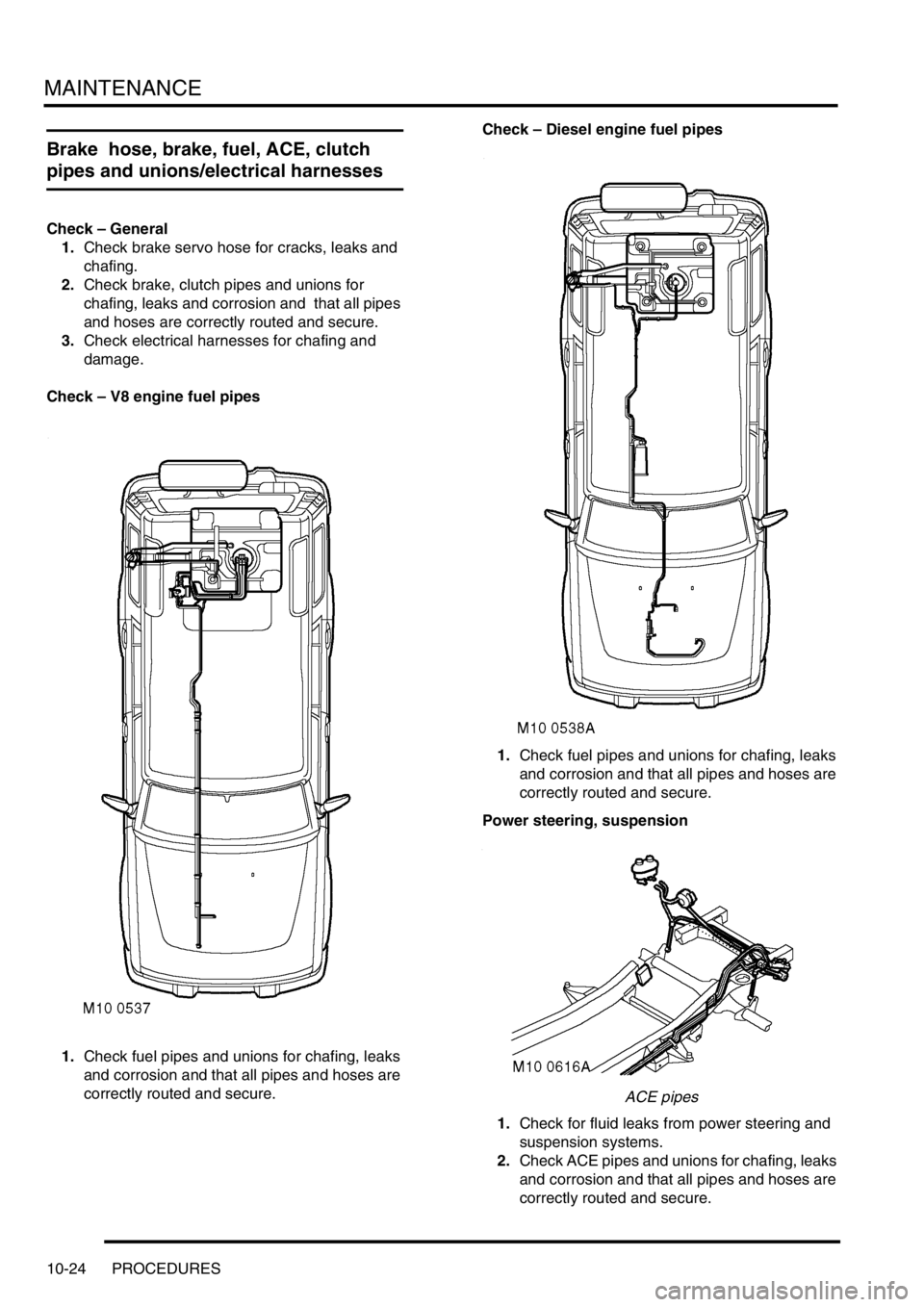
MAINTENANCE
10-24 PROCEDURES
Brake hose, brake, fuel, ACE, clutch
pipes and unions/electrical harnesses
Check – General
1.Check brake servo hose for cracks, leaks and
chafing.
2.Check brake, clutch pipes and unions for
chafing, leaks and corrosion and that all pipes
and hoses are correctly routed and secure.
3.Check electrical harnesses for chafing and
damage.
Check – V8 engine fuel pipes
1.Check fuel pipes and unions for chafing, leaks
and corrosion and that all pipes and hoses are
correctly routed and secure. Check – Diesel engine fuel pipes
1.Check fuel pipes and unions for chafing, leaks
and corrosion and that all pipes and hoses are
correctly routed and secure.
Power steering, suspension
ACE pipes
1.Check for fluid leaks from power steering and
suspension systems.
2.Check ACE pipes and unions for chafing, leaks
and corrosion and that all pipes and hoses are
correctly routed and secure.
Page 154 of 1529

MAINTENANCE
PROCEDURES 10-31
Road/roller test
WARNING: Roller test must be restricted to 3
mph (5 km/h). If 2 wheel rolling road is to be used,
disconnect propeller shaft from the transfer box
output shaft driving the axle which is NOT on the
rolling road.
Testing
1. 2 wheel rolling road: Engage differential lock
using a 10 mm open ended spanner on flats
machined on differential lock selector
shaft.Switch on ignition and check that the
differential lock, electronic brake
distribution and hill descent warning lamps
are illuminated.
2.Check for correct operation of starter switch,
ensure engine starts correctly; leave the engine
running.
3.Check for correct operation of starter switch,
ensure engine starts correctly; leave the engine
running.
4.With vehicle stationary, turn steering from lock
to lock. Check for smooth operation and ensure
there is no undue noise from power steering
pump or drive belt.
5.Depress clutch and select all gears in turn,
check for smooth, notch free engagement.6. Check all vehicle systems for correct
operation.
7.Check for unusual engine, gearbox and
suspension noises.
8.Check braking system operation.
9.Check for smooth gear engagement.
10.Check engine performance.
11.Check operation of all instruments and warning
devices where practicable.
12.Where possible, check for correct operation of
hill descent control (HDC) mechanism. This
should not be carried out if excessive journey
time is required.
13.After road/roller test, carry out a final inspection
of vehicle, with vehicle on a ramp.
14.Check all fluid levels and top-up if necessary.
15. 2 wheel rolling road: Ensure differential lock is
disengaged and propeller shaft is connected on
completion of test. Switch on ignition and
check that differential lock, electronic brake
distribution and hill descent warning lamps
are extinguished.
Page 460 of 1529

CLUTCH - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 33-2-5
1Brake/clutch reservoir
2Fluid supply pipe
3Hydraulic feed pipe
4Master cylinder
5Piston
6Clutch pedal
7Primary driveshaft
8Engine crankshaft
9Drive plate
10Flywheel
11Ring gear12Cover - Pressure plate
13Leaf spring
14Retractor clip
15Diaphragm
16Release bearing
17Ball spigot
18Release bearing sleeve
19Release lever
20Slave cylinder
21Piston
22Bleed nipple
Page 461 of 1529

CLUTCH - V8
33-2-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The clutch system is a conventional diaphragm type clutch operated by a hydraulic cylinder. The clutch requires no
adjustment to compensate for wear.
Hydraulic clutch
The hydraulic clutch comprises a master cylinder, slave cylinder and a hydraulic reservoir, which is also shared with
the braking system. The master and slave cylinders are connected to each other hydraulically by plastic and metal
pipes. The plastic section of the pipe allows ease of pipe routing and also absorbs engine movements and vibrations.
The master cylinder comprises a body with a central bore. Two ports in the body connect the bore to the hydraulic
feed pipe to the slave cylinder and the brake/clutch fluid reservoir. A piston is fitted in the bore and has an external
rod which is attached to the clutch pedal with a pin. Two coiled springs on the clutch pedal reduce the effort required
to depress the pedal.
The master cylinder is mounted on the bulkhead in the engine compartment and secured with two bolts. The cylinder
is connected to the shared brake/clutch reservoir on the brake servo by a braided connecting hose.
The slave cylinder is located on the left hand side of the gearbox housing and secured with two bolts. A heat shield
protects the underside of the cylinder from heat generated from the exhaust system. The slave cylinder comprises a
cylinder with a piston and a rod. A port in the cylinder body provides the attachment for the hydraulic feed pipe from
the master cylinder. A second port is fitted with a bleed nipple for removing air from the hydraulic system after
servicing. The piston rod locates on a clutch release lever located in the gearbox housing. The rod is positively
retained on the release lever with a clip.
Clutch mechanism
The clutch mechanism comprises a flywheel, drive plate, pressure plate, release lever and a release bearing. The
clutch mechanism is fully enclosed at the rear of the engine by the gearbox housing.
A clutch release bearing sleeve is attached in the gearbox housing with two bolts and located on two dowels. A spigot
with a ball end is formed on the release bearing sleeve and provides a mounting and pivot point for the clutch release
lever. A dished pivot washer is located on the ball of the spigot. When the release lever is located on the ball, the pivot
washer seats against the rear face of the release lever. A spring clip is located on the lever and the pivot washer and
secures the lever on the spigot. A small bolt retains the spring clip in position.
The release lever is forked at its inner end and locates on the clutch release bearing carrier. The outer end of the
release lever has a nylon seat which locates the slave cylinder piston rod. A second nylon seat, positioned centrally
on the release lever, locates on the ball spigot of the release bearing sleeve and allows the release lever to pivot freely
around the ball.
The clutch release bearing locates on the clutch release lever and the release bearing sleeve. The bearing is retained
on a carrier which has two flats to prevent the carrier rotating on the release lever. A clip retains the release lever on
the carrier. The bearing and carrier are not serviceable individually.
Flywheel
The flywheel is bolted to a flange on the rear of the crankshaft with six bolts. A dowel on the crankshaft flange ensures
that the flywheel is correctly located. A ring gear is fitted on the outside diameter of the flywheel and seats against a
flange. The ring gear is an interference fit on the flywheel and is installed by heating the ring and cooling the flywheel.
The ring gear is a serviceable item and can be replaced if damaged or worn.
The operating face of the flywheel is machined to provide a smooth surface for the drive plate to engage on. Three
dowels and six threaded holes provide for the location and attachment of the pressure plate. The flywheel is balanced
to ensure that it does not produce vibration when rotating. A machined slot, with a series of holes within the slot, is
located on the engine side of the flywheel. The slot accommodates the tip of the crankshaft position sensor which is
used by the Engine Control Module (ECM) for engine management.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
Page 466 of 1529
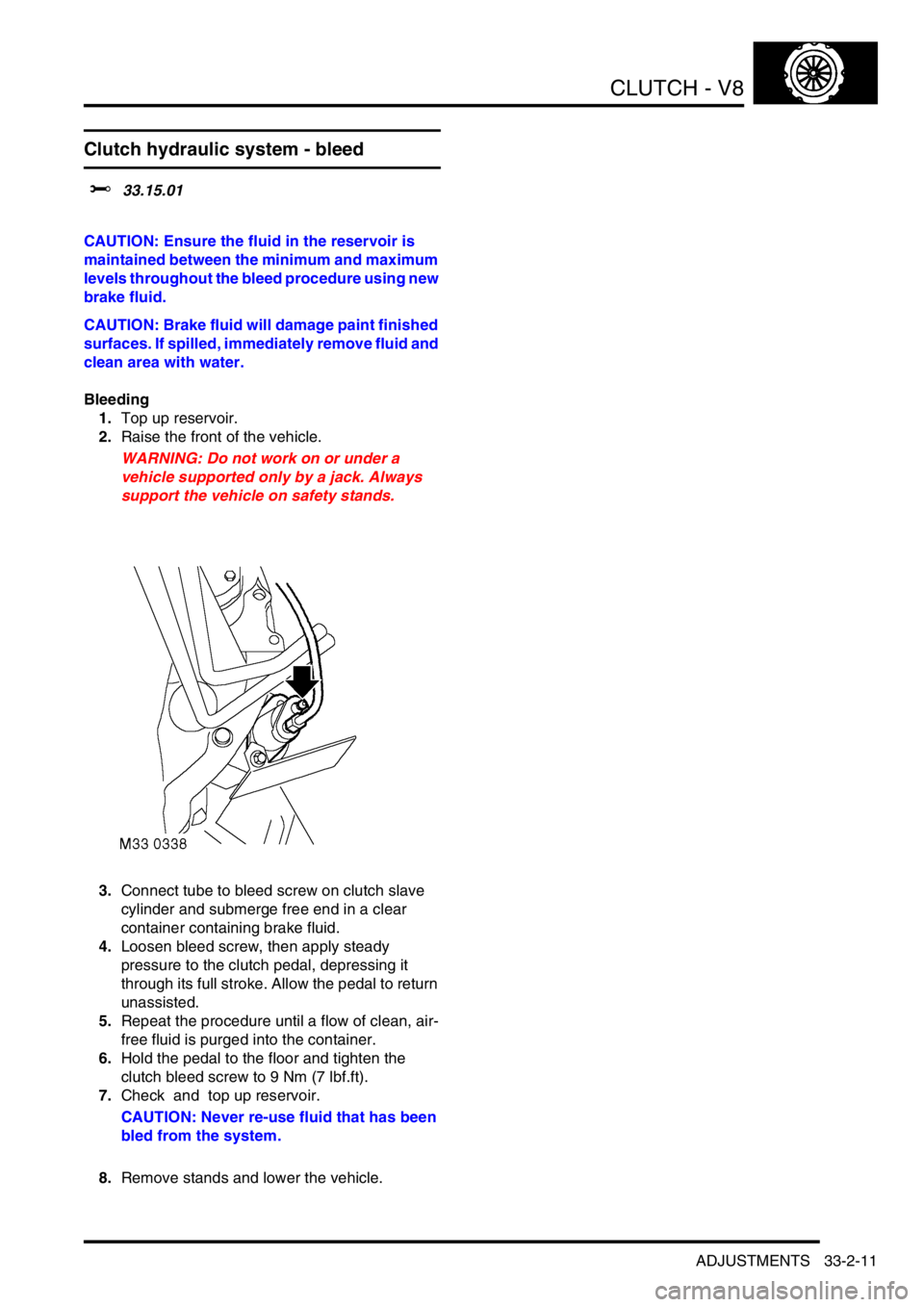
CLUTCH - V8
ADJUSTMENTS 33-2-11
ADJUST ME NTS
Clutch hydraulic system - bleed
$% 33.15.01
CAUTION: Ensure the fluid in the reservoir is
maintained between the minimum and maximum
levels throughout the bleed procedure using new
brake fluid.
CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage paint finished
surfaces. If spilled, immediately remove fluid and
clean area with water.
Bleeding
1.Top up reservoir.
2.Raise the front of the vehicle.
WARNING: Do not work on or under a
vehicle supported only by a jack. Always
support the vehicle on safety stands.
3.Connect tube to bleed screw on clutch slave
cylinder and submerge free end in a clear
container containing brake fluid.
4.Loosen bleed screw, then apply steady
pressure to the clutch pedal, depressing it
through its full stroke. Allow the pedal to return
unassisted.
5.Repeat the procedure until a flow of clean, air-
free fluid is purged into the container.
6.Hold the pedal to the floor and tighten the
clutch bleed screw to 9 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
7.Check and top up reservoir.
CAUTION: Never re-use fluid that has been
bled from the system.
8.Remove stands and lower the vehicle.
Page 469 of 1529

CLUTCH - V8
33-2-14 REPAIRS
Master cylinder
$% 33.20.01
CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage paint finished
surfaces. If spilled, immediately remove fluid and
clean area with water.
Remove
1.Raise front of vehicle.
WARNING: Do not work on or under a
vehicle supported only by a jack. Always
support the vehicle on safety stands.
2.Release spring clip securing clutch pedal
clevis pin and remove pin from push rod and
clutch pedal.
3.Position container to catch spillage. Disconnect
hydraulic pipe from clutch master cylinder.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open
connections to prevent contamination.
4.Release clip and remove connecting hose from
clutch master cylinder.
5.Remove 2 bolts securing clutch master
cylinder to pedal box and remove clutch master
cylinder. Refit
1.Clean master cylinder and pedal box mating
faces.
2.Position clutch master cylinder to pedal box, fit
bolts and tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
3.Position clevis pin to push-rod and clutch pedal
and secure with spring clip.
4.Fit connecting hose to brake master cylinder
and tighten clip.
5.Position hydraulic pipe and tighten union to 18
Nm (13 lbf.ft).
6.Bleed clutch.
+ CLUTCH - V8, ADJUSTMENTS,
Clutch hydraulic system - bleed.
7.Remove stand(s) and lower vehicle.
Page 604 of 1529

AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22 - 24
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 44-7
The gearbox consists of a torque converter housing, an intermediate plate, a gearbox housing and a rear extension
housing, bolted together in series. The rear of the gearbox is supported by a rubber mounting installed between a
mounting bracket on the gearbox and the LH chassis rail. A heat shield is installed on the mounting to protect it from
the exhaust.
Sectioned view of gearbox
1Lock-up clutch
2Impeller
3Turbine
4Forward drive clutch
5Reverse drive clutch
6Brake clutch
7Brake clutch
8Brake clutch
9Epicyclic gear set10Epicyclic gear set
11Clutch
12Brake clutch
13Output shaft
14Freewheel (one way clutch)
15Freewheel (one way clutch)
16Freewheel (one way clutch)
17Stator and one way clutch
Torque converter housing
The torque converter housing attaches the gearbox to the engine and contains the torque converter. Different torque
converter housings are used to accommodate the difference between the V8 and Td5 engine interfaces. The torque
converter is connected to the engine drive plate and transmits the drive from the engine to the gearbox input shaft.
When engaged, a hydraulic lock-up clutch in the torque converter prevents slippage, to give a direct drive from the
engine to the gearbox for improved driving response.
Intermediate plate
The intermediate plate supports the gearbox input shaft and provides the interface between the transmission fluid
pump and the lubrication circuit. The pump attaches to the front of the intermediate plate and is driven by the impeller
in the torque converter. The pump pressurises transmission fluid drawn from the sump on the gearbox housing. The
pressurised fluid then circulates through the torque converter and gearbox housing components for cooling,
lubrication and gear shift purposes. Ports around the outer periphery of the intermediate plate provide the inlet and
outlet connections to the fluid cooler and a pressure take-off point for servicing.
Page 607 of 1529

AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22 - 24
44-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The lock-up and brake clutches are operated by pressurised transmission fluid from the valve block in the sump. A
manual valve and four solenoid valves, also known as Motorised Valves (MV), control the supply of pressurised
transmission fluid from the valve block:
lThe manual valve controls the supply in P, R, N and D.
lSolenoid valves MV 1 and MV 2 control the supplies that operate the brake clutches for shift control.
lSolenoid valve MV 3 controls the supply that operates the lock-up clutch.
lSolenoid valve MV 4 modulates the pressure of the supplies to the brake clutches, to control shift quality.
Operation of the manual valve is controlled by the selector lever assembly. In the gearbox, a selector shaft engages
with the manual valve. The selector shaft is connected to the selector lever assembly via the selector cable and a
selector lever on the left side of the gearbox. The selector shaft also operates a mechanism that locks the output shaft
when P is selected.
Operation of the solenoid valves is controlled by the EAT ECU.
An output shaft speed sensor in the gearbox housing outputs a signal to the EAT ECU. The EAT ECU compares
output shaft speed with engine speed to determine the engaged gear, and output shaft speed with vehicle speed to
confirm the range selected on the transfer box.
A bayonet lock electrical connector in the gearbox casing, to the rear of the selector lever, connects the solenoid
valves and the output shaft speed sensor to the vehicle wiring.
A pressed steel sump encloses the valve block and collects transmission fluid draining from the gearbox housing. A
suction pipe and filter on the underside of the valve block connect to the inlet side of the fluid pump. A magnet is
installed in the sump to collect any magnetic particles that may be present. A level plug and a drain plug are installed
in the sump for servicing.
Rear extension housing
The rear extension housing provides the interface between the gearbox housing and the transfer box. A splined
extension shaft, secured to the gearbox output shaft by a bolt, transmits the drive from the gearbox to the transfer
box. A seal in the rear of the housing prevents leakage past the extension shaft. A breather pipe, attached to the left
side of the rear extension housing, ventilates the interior of the gearbox and rear extension housings to atmosphere.
The open end of the breather pipe is located in the engine compartment at the right front corner of the engine sump
on gearboxes fitted to early vehicles and is clipped to the top of the gearbox on later vehicles.
Gearbox power flows
The following Figures show the power flow through the gearbox for each forward gear when D is selected, and for
reverse. The key to the Item numbers on the Figures, and in parenthesis in the accompanying text, can be found on
the 'Sectioned view of gearbox' Figure, above.
1st Gear (D selected)
Clutches (4) and (11) are engaged. The front planet gear carrier of gear set (9) locks against the gearbox housing
through freewheel (15) when the engine powers the vehicle, and freewheels when the vehicle is coasting. Gear set
(10) rotates as a solid unit with the front planet gear carrier. In 1st gear hold brake clutch (8) is applied to provide
overrun braking.