automatic transmission LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 15 of 1529

CONTENTS
12 CONTENTS
AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22 - 24 ................................................ 44-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Automatic gearbox component layout ............................................................................................ 44-1
Control schematic ........................................................................................................................... 44-2
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 44-4
Operation ........................................................................................................................................ 44-17
ADJUSTMENTS
Cable - selector ............................................................................................................................. 44-21
Stall test .......................................................................................................................................... 44-21
REPAIRS
Cable and lever assembly - selector .............................................................................................. 44-23
Selector indicator .......................................................................................................................... 44-24
Switch - starter inhibitor ................................................................................................................. 44-25
Seal - selector shaft ........................................................................................................................ 44-26
Gearbox - convertor and transfer gearbox - Diesel ....................................................................... 44-27
Gearbox - convertor and transfer gearbox - V8 ............................................................................ 44-32
Torque converter and oil seal ......................................................................................................... 44-37
Housing - torque converter ............................................................................................................ 44-38
Gasket - intermediate plate ............................................................................................................ 44-39
Intermediate plate .......................................................................................................................... 44-41
Pump - fluid .................................................................................................................................... 44-43
Seal - rear extension housing ......................................................................................................... 44-44
Gasket - rear extension housing. .................................................................................................. 44-45
Parking pawl assembly. ................................................................................................................ 44-46
Gasket - oil sump ........................................................................................................................... 44-47
Filter - oil ........................................................................................................................................ 44-48
Cooler - fluid - Td5 .......................................................................................................................... 44-49
Cooler - fluid - V8 ........................................................................................................................... 44-50
Valve body assembly ..................................................................................................................... 44-51
Seal - valve body ........................................................................................................................... 44-53
Pressure regulator ......................................................................................................................... 44-54
Lock-up solenoid valve (MV 3) ...................................................................................................... 44-55
Solenoids - shift control valves
(MV 1 & 2) 44-56
Harness - solenoid valves .............................................................................................................. 44-57
Electronic control unit - automatic transmission ............................................................................. 44-58
PROPELLER SHAFTS ............................................................................. 47-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Propeller shaft component layout ................................................................................................... 47-1
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 47-2
REPAIRS
Propeller shaft - front ..................................................................................................................... 47-5
Propeller shaft - rear ...................................................................................................................... 47-5
Bush - spigot - rear propeller shaft ................................................................................................ 47-6
Flexible coupling ............................................................................................................................ 47-7
OVERHAUL
Propeller shaft................................................................................................................................. 47-9
Page 34 of 1529
INTRODUCTION
01-3
Abbreviations and Symbols
A Amperes
AAP Ambient Air Pressure
ABDC After Bottom Dead Centre
ABS Anti-Lock Brake System
ac Alternating current
A/C Air Conditioning
ACE Active Cornering Enhancement
ACEA Association of Constructors of
European Automobiles
AFR Air Fuel Ratio
AP Ambient Pressure
ASC Anti-shunt Control
ATC Air Temperature Control
ATDC After Top Dead Centre
BBDC Before Bottom Dead Centre
BBUS Battery Backed Up Sounder
BCU Body Control Unit
BDC Bottom Dead Centre
bhp Brake Horse Power
BP Boost Pressure
BPP Brake Pedal Position
BS British Standard
BTDC Before Top Dead Centre
C Celsius
CAN Controller Area Network
CD Compact Disc
CDC Centre Differential Control
CDL Central Door Locking
CD - ROM Compact Disc - Read Only
Memory
CFC Chlorofluorocarbon
CHMSL Centre High Mounted Stop Lamp
CKP Crankshaft Position
CLV Calculated Load Value
cm Centimetre
cm
2Square centimetre
cm3Cubic centimetre
CMP Camshaft Position
CPP Clutch Pedal Position
CO Carbon Monoxide
CO
2Carbon Dioxide
CR Common Rail
CVS Canister Vent Solenoid
deg. Degree, angle or temperature
dia. Diameter
DIN Deutsche Industrie Normen
(German Industrial Standards)
dc Direct current
DCV Directional Control Valve
DOHC Double Overhead Camshaft
DTI Dial Test Indicator
DFM Dual Mass Flywheel
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
EACV Electronic Air Control Valve EAT Electronic Automatic
Transmission
EBD Electronic Brake pressure
Distribution
ECD European Community Directive
ECM Engine Control Module
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature
ECU Electronic Control Unit
EDC Electronic Diesel Control
EEPROM Electronic Erasable
Programmable Read Only
Memory
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EKA Emergency Key Access
EN European Norm
EOBD European On Board Diagnostics
ETC Electronic Traction Control
EUI Electronic Unit Injector
EVAP Evaporative Emission
EVR Electronic Vacuum Regulator
F Fahrenheit
FBH Fuel Burning Heater
FIP Fuel Injection Pump
FTC Fast Throttle Control
g Gramme or Gravity
hHour
hc High compression
HC Hydro Carbons
HDC Hill Descent Control
HDPE High Density Polyethylene
HFS Heated Front Screen
Hg Mercury
HO2S Heated Oxygen Sensor
HMW High Molecular Weight
HRW Heated Rear Window
ht/HT High tension
IACV Idle Air Control Valve
IAT Intake Air Temperature
ICE In-Car Entertainment
i.dia. Internal diameter
IDM Intelligent Driver Module
in3Cubic inch
ILT Inlet Throttle
ISO International Organisation for
Standardisation
k Thousand
kg Kilogramme
km Kilometre
km/h Kilometres per hour
kPa KiloPascal
KS Knock Sensor
lLitre
lbf.in Pounds force inches
lbf/in
2Pounds per square inch
lbf.ft Pounds force feet
Page 89 of 1529

IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS
05-2
Vehicle identification number - except NAS and
Canada
Example: SALLTGM87WA600172Vehicle identification number - NAS and Canada
Example: SALTY124OWA600180
Paint and trim colour codes
Paint code (F): a 3 digit code identifying the original
paint colour is stamped on the VIN plate. Refer to
Parts Catalogue for full list of colour codes.
Trim code (G): a code identifying the original trim
type and colour is stamped on the VIN plate. Refer to
the relevant Parts Catalogue for coding details
SALManufacturer's identifier (Land Rover UK)
LTMarque/Model
LT = Discovery
GClass
A = Japan
G = 100 inch
MBody Style
B = 5 door models
8Engine
1 = 4.0 V8 LC Cat
2 = 4.0 V8 HC Cat
3 = 4.0 LC Non Cat
8 = TD5 engine EGR/Cat
9 = TD5 engine EGR/ Non Cat
7Transmission and Steering
3 = RHD automatic gearbox
4 = LHD automatic gearbox
7 = RHD manual gearbox
8 = LHD manual gearbox
WModel Year
W = 1998 Model year
X = 1999 Model year
Y = 2000 Model year
1 = 2001 Model year
2 = 2002 Model year
3 = 2003 Model year
AAssembly plant
A = Solihull
F = KD build
6 figures= Serial number
SALManufacturer's identifier (Land Rover UK)
TMarque/Model
T = Discovery
YClass
Y = 100 inch USA/Canada
N = 100 inch California
1Body Style
1 = 4 door Station Wagon
2Engine
2 = 4.0 V8 HC Cat
4Transmission and Steering
4 = LHD automatic gearbox
OCheck digit
WModel Year
W = 1998 Model year
X = 1999 Model year
Y = 2000 Model year
1 = 2001 Model year
2 = 2002 Model year
3 = 2003 Model year
AAssembly plant
A = Solihull
6 figures= Serial number
Page 93 of 1529

TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
06-2
Engine Td5
TORQUE DESCRIPTION METRIC IMPERIAL
ACE pump bolts25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
A/C compressor bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Alternator support bracket to cylinder head bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Alternator/vacuum pump oil feed pipe union 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Camshaft cover to camshaft carrier bolts 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Camshaft sprocket to camshaft bolts 37 Nm (27 lbf.ft)
Centrifuge cover bolts 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Centrifuge oil drain pipe to sump bolts (or nuts) 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Centrifuge to oil drain pipe bolts 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Centrifuge to oil cooler housing bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
CKP sensor bolt10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Coolant pipe bolt50 Nm (37 lbf.ft)
Connecting rod bolts, then a further 80°20 Nm (15 lbf.ft)
Crankshaft pulley bolt 460 Nm (340 lbf.ft)
Crankshaft pulley TV damper bolts 80 Nm (59 lbf.ft)
Crankshaft rear oil seal housing bolts 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Cylinder head bolts initial tighten 30 Nm (22 lbf.ft)
Cylinder head bolts final tighten, then a further 90°, then a further 180° and finally a
further 45°65 Nm (48 lbf.ft)
Dipstick tube to camshaft carrier bolt 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Drive plate (automatic transmission) to crankshaft bolts 115 Nm (85 lbf.ft)
EGR pipe clamp to cylinder head bolt - if fitted 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
EGR pipe Allen screws 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Engine mounting (front) to cylinder block bolts 48 Nm (35 lbf.ft)
Engine mounting (front) to chassis nuts 85 Nm (63 lbf.ft)
Engine mounting bracket (rear, LH & RH) to gearbox bolts 85 Nm (63 lbf.ft)
Engine mounting bracket (rear, LH & RH) nuts 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft)
Flywheel to crankshaft (manual transmission) bolts, then a further 90°40 Nm (30 lbf.ft)
Front crossmember bolts 26 Nm (20 lbf.ft)
Fuel connector block bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Fuel cooler to inlet manifold bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Gearbox housing to engine bolts 50 Nm (37 lbf.ft)
Heater pipe to cylinder head bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Main bearing cap bolts then a further 90°33 Nm (24 lbf.ft)
Oil cooler housing to cylinder block bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Oil cooler pipe clip bolts 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Oil filter adaptor housing to oil cooler housing bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Oil pick-up strainer Torx screws + 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Oil pressure switch 15 Nm (11 lbf.ft)
Oil pump drive sprocket bolt + 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Oil pump pressure relief valve plug + 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Oil pump and stiffener assembly to cylinder block bolts 13 Nm (10 lbf.ft)
Oil sump to cylinder block bolts 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Oil sump to gearbox bell housing bolts 13 Nm (10 lbf.ft)
PAS pump bracket bolts 27 Nm (20 lbf.ft)
PAS pump pulley bolts 27 Nm (20 lbf.ft)
Rocker arm adjusting screw locknuts 16 Nm (12 lbf.ft)
Page 94 of 1529

TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
06-3
+ Apply sealant, Part No. STC 50552 to threads
Rocker shaft bolts 32 Nm (24 lbf. ft)
Timing chain adjustable guide bolt 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Timing chain cover bolts 27 Nm (20 lbf.ft)
Timing chain cover to cylinder block stud 7 Nm (5.2 lbf.ft)
Timing chain fixed guide Allen screw + 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Timing chain cover to cylinder head nut and bolt 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Timing chain fixed guide (M6) bolt 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Timing chain fixed guide (M10) bolt 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft)
Timing chain lubrication jet bolt 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Timing chain tensioner 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft)
Torque converter to drive plate (automatic transmission) bolts 50 Nm (37 lbf.ft)
Turbocharger heatshield bolts 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Turbocharger oil feed pipe banjo bolt 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft)
Turbocharger to exhaust manifold nuts 30 Nm (22 lbf.ft)
Vacuum pump oil feed pipe to cylinder head union 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft)
Viscous fan nut45 Nm (33 lbf.ft)
Fuel spill return pipe unions - if fitted 20 Nm (15 lbf.ft)TORQUE DESCRIPTION METRIC IMPERIAL
Page 114 of 1529
LIFTING AND TOWING
08-1
LIFTING AND TOWING
LIFTING
The following instructions must be carried out before
raising the vehicle off the ground.
lUse a solid level ground surface.
lApply hand brake.
lSelect 'P' (Automatic gearbox) or 1st gear
(Manual gearbox) in main gearbox.
lSelect Low range in transfer gearbox.
To avoid damage occurring to the under body
components of the vehicle the following jacking
procedures must be adhered to.
DO NOT POSITION JACKS OR AXLE STANDS
UNDER THE FOLLOWING COMPONENTS:
lBody structure
lBumpers
lFuel lines
lBrake lines
lFront radius arms
lPanhard rod
lSteering linkage
lRear trailing arms
lFuel tank
lEngine sump
lGearbox bell housing
Vehicle jack
The jack provided with the vehicle is only intended for
use in an emergency, for changing a tyre. DO NOT
use the jack for any other purpose. Refer to Owner's
Handbook for vehicle jack location points and
procedure. Never work under a vehicle supported
solely by the vehicle jack.
Hydraulic jack
A hydraulic jack with a minimum 1500 kg, 3,300 lbs
load capacity must be used. Do not commence
work on the underside of the vehicle until
suitable axle stands have been positioned under
the axle.
WARNING: Always chock the wheels when
jacking. The hand brake acts on the
transmission, not the rear wheels, and may be
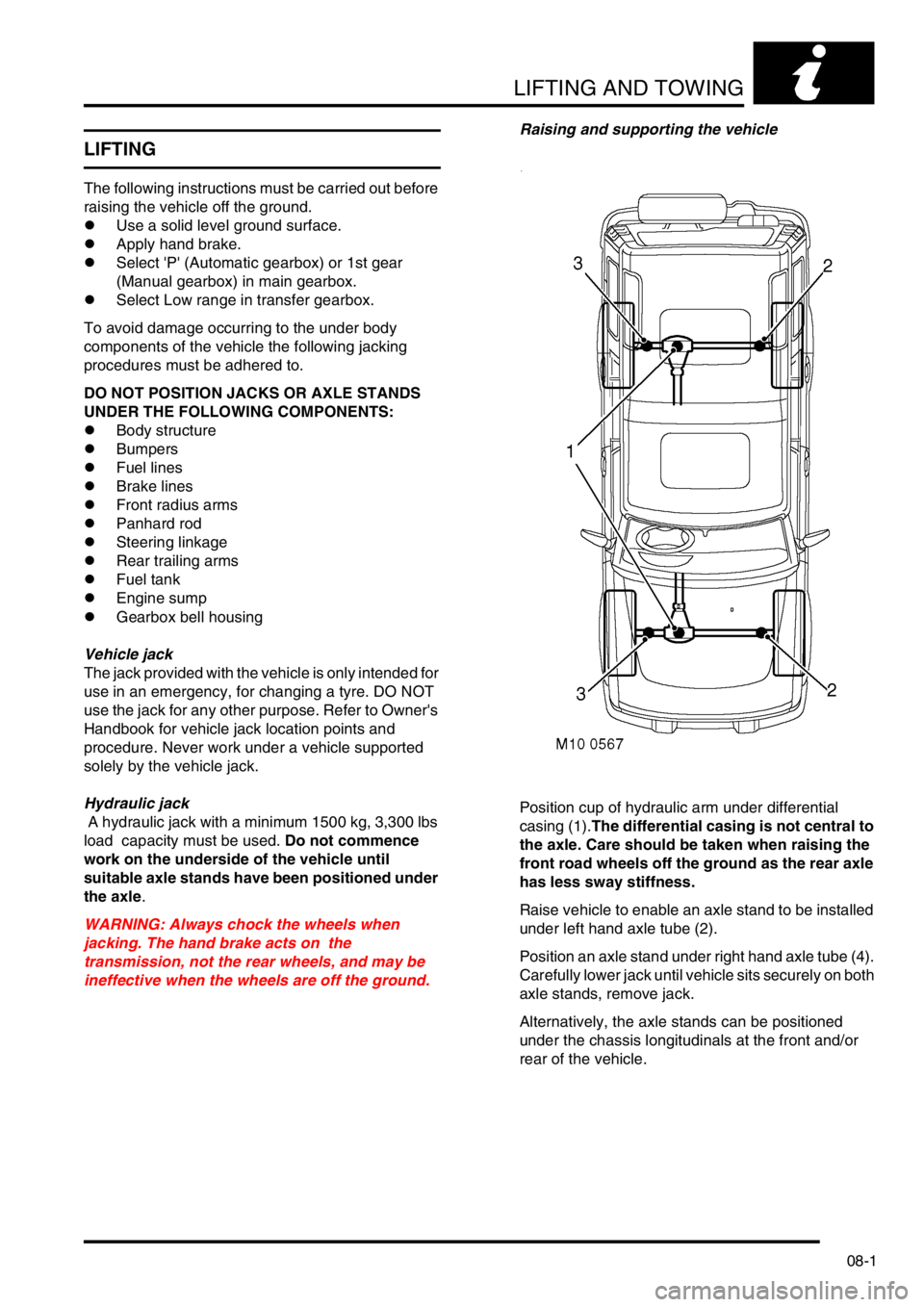
ineffective when the wheels are off the ground.Raising and supporting the vehicle
Position cup of hydraulic arm under differential
casing (1).The differential casing is not central to
the axle. Care should be taken when raising the
front road wheels off the ground as the rear axle
has less sway stiffness.
Raise vehicle to enable an axle stand to be installed
under left hand axle tube (2).
Position an axle stand under right hand axle tube (4).
Carefully lower jack until vehicle sits securely on both
axle stands, remove jack.
Alternatively, the axle stands can be positioned
under the chassis longitudinals at the front and/or
rear of the vehicle.
Page 327 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-28 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Throttle Position (TP) sensor (C0175)
The TP sensor is located on the throttle body assembly in the engine compartment. The ECM is able to determine the
position of the throttle plate and the rate of change of its angle. The ECM processes the signal received from the TP
sensor.
The TP sensor consists of a resistance track and a sliding contact connected to the throttle plate assembly. As the
throttle is opened and closed the sliding contact moves along the resistance track to change the output voltage of the
sensor. The ECM determines throttle plate position by processing this output voltage. The connection of the sensor
to the throttle plate assembly is via a shaft.
The ECM is able to determine the closed throttle position, this enables the TP sensor to be fitted without the need for
prior adjustment. The TP sensor signal has input into the ECM's fuelling strategy and also to determine closed throttle
position for idle speed control. The TP sensor also supplies the ECM with information to enable the overrun fuel cut
off strategy to be implemented. When the ECM receives closed throttle information from the TP sensor it closes the
injectors for the duration of the closed throttle time.
The TP sensor signal is also used by the Electronic Automatic Transmission (EAT) ECU to determine the correct point
for gear shifts and acceleration kickdown. The ECM also supplies the SLABS ECU with this TP sensor information as
a PWM signal.
Input/Output
The TP sensor has electrical input and output. Input is a 5 volt supply via pin 10 of connector C0636 of the ECM. The
signal output is via pin 24 of connector C0636 and is a varying voltage, less than 0.5V (closed throttle) and greater
than 4.5V (wide open throttle) depending on throttle plate position. The TP sensor earth is via pin 25 of connector
C0636 of the ECM, this acts as a screen to protect the integrity of the TP sensor signal.
The connector and sensor terminals are gold plated for corrosion and temperature resistance, care must be exercised
while probing the connector and sensor terminals.
If the TP sensor signal fails, the ECM uses a default value derived from engine load and speed.
The TP sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lSignal out of parameters.
lBlocked air filter (load monitoring, ratio of the TP sensor to air flow).
lRestriction in air inlet (load monitoring, ratio of the TP sensor to air flow).
lVacuum leak
Page 350 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-51
Conditions
The ECM calculates ignition timing using input from the following:
lCKP sensor.
lKnock sensors (KS).
lMAF sensor.
lTP sensor (idle only).
lECT sensor.
Function
At engine start up, the ECM sets ignition timing dependent on ECT information and starting rev/min from the CKP. As
the running characteristics of the engine change, the ignition timing changes. The ECM compares the CKP signal to
stored values in its memory, and if necessary advances or retards the spark via the ignition coils.
Ignition timing is used by the ECM for knock control.
Knock control
The ECM uses active knock control to prevent possible engine damage due to pre-ignition. This is achieved by
converting engine block noise into a suitable electrical signal that can be processed by the ECM. A major contributing
factor to engine 'knock' is fuel quality, the ECM can function satisfactorily on 91 RON fuel as well as the 95 RON fuel
that it is calibrated for.
Conditions
The ECM knock control system operates as follows:
lHot running engine.
l91 or 95 RON fuel.
Function
The ECM knock control uses two sensors located one between the centre two cylinders of each bank. The knock
sensors consist of piezo ceramic crystals that oscillate to create a voltage signal. During pre-ignition, the frequency
of crystal oscillation increases which alters the signal output to the ECM.
If the knock sensors detect pre-ignition in any of the cylinders, the ECM retards the ignition timing by 3° for that
particular cylinder. If this action stops the engine knock, the ignition timing is restored to its previous figure in
increments of 0.75°. If this action does not stop engine knock then the ECM retards the ignition timing a further 3° up
to a maximum of -15° and then restores it by 0.75° and so on until the engine knock is eliminated.
The ECM also counteracts engine knock at high intake air temperatures by retarding the ignition as above. The ECM
uses the IAT signal to determine air temperature.
Idle speed control
The ECM regulates the engine speed at idling. The ECM uses the idle air control valve (IACV) to compensate for the
idle speed drop that occurs when the engine is placed under greater load than usual. When the throttle is in the rest
position i.e. it has not been pressed, the majority of intake air that the engine consumes comes from the idle air control
valve.
IACV control idle speed
Conditions in which the ECM operates the IACV control idle speed is as follows:
lIf any automatic transmission gears other than P or N are selected.
lIf air conditioning is switched on.
lIf cooling fans are switched on.
lAny electrical loads activated by the driver.
Function
The idle air control valve utilises two coils that use opposing pulse width modulated (PWM) signals to control the
position of a rotary valve. If one of the circuits that supplies the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining
signal preventing the idle air control valve from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the idle
air control valve assumes a default idle position at which the engine idle speed is raised to 1200 rev/min with no load
placed on the engine.
Page 351 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-52 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Evaporative emission control
Due to increasing legislation, all new vehicles must be able to limit evaporative emissions (fuel vapour) from the fuel
tank.
The ECM controls the emission control system using the following components:
lEVAP canister.
lPurge valve.
lCanister vent solenoid (CVS) valve – (NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability
only)
lFuel tank pressure sensor – (NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability only)
lFuel leak detection pump – (NAS vehicles with positive pressure type EVAP system leak detection capability
only)
lInterconnecting pipe work.
Refer to Emissions section for operating conditions of evaporative emission systems.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Evaporative Emission Control
Operation.
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) - North American Specification vehicles only
The ECM monitors performance of the engine for misfires, catalyst efficiency, exhaust leaks and evaporative control
loss. If a fault occurs, the ECM stores the relevant fault code and warns the driver of component failure by illuminating
the Malfunction Indicator Light in the instrument pack.
On vehicles fitted with automatic gearbox, the ECM combines with the Electronic Automatic Transmission (EAT) ECU
to provide the OBD strategy.
Conditions
If the OBD function of the ECM flags a fault during its operation, it falls into one of the following categories:
lmin = minimum value of the signal exceeded.
lmax = maximum value of the signal exceeded.
lsignal = signal not present.
lplaus = an implausible condition has been diagnosed.
Function
All of the ECM's internal diagnostic fault paths are monitored by the OBD system. Specific faults have their own
numeric code relating to certain sensors or actuators etc. These specific faults fall into two types, error codes (E xxx)
or cycle codes (Z xxx). E codes represent instantaneous faults and Z codes relate to codes generated after completion
of a drive cycle.
If an emission relevant fault occurs on a drive cycle, the ECM stores a temporary fault code, if the fault does not occur
on subsequent drive cycles the fault code stays as a temporary fault code. If the fault recurs on subsequent drive
cycles the ECM stores the fault code as a permanent code, and depending on which component has failed the ECM
will illuminate the MIL.
Immobilisation system
The ECM and the body control unit (BCU) security system comprise the immobilisation system.
The ECM and the BCU combine to prevent the engine from running unless the appropriate security criteria are met.
The ECM and the BCU are a matched pair, if either one is replaced for any reason, the system will not operate unless
the replaced unit is correctly matched to its original specification. TestBook must be used to reconfigure the
immobilisation system.
Conditions
The ECM operates immobilisation in three states:
l'New'.
l'Secure'.
l'No Code'.
Page 352 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-53
Function
With the ECM operating in the 'New' state, TestBook is required to instruct the ECM to learn the new BCU code. If the
ECM is in delivery state (i.e. direct from the supplier), it will not run the vehicle and will store a new ECM fault code
when it is fitted. This code must be cleared after instructing the ECM to learn the BCU code using TestBook.
When the ECM is in the 'Secure' state, no further action is required as the ECM has successfully learned the BCU
code. A 'Secure' ECM can not be configured to a 'No Code' state.
If the vehicle is fitted with an ECM with a valid code, the engine will start and the MIL will go out.
However, if the ECM has an invalid BCU security code the engine will crank, start, and then immediately stall. The
status of the security system can only be interrogated using TestBook.
TestBook is able to retrieve the following immobilisation fault codes:
Misfire detection
Due to increasing legislation, all new vehicles must be able to detect two specific levels of misfire.
Conditions
The ECM is able to carry out misfire detection as part of the OBD system using the following component parts:
lFlywheel reluctor adaptation.
lCalculation of engine roughness.
lDetection of excess emissions misfire.
lDetection of catalyst damaging misfire.
Function
The flywheel/ reluctor ring is divided into four segments 90° wide. The ECM misfire detection system uses information
generated by the CKP to determine crankshaft speed and position. If a misfire occurs, there will be an instantaneous
slight decrease in engine speed. The ECM misfire detection system is able to compare the length of time each 90°
segment takes and is therefore able to pinpoint the source of the misfire.
For the ECM misfire detection system to be calibrated for the tolerances of the reluctor tooth positions, the flywheel/
reluctor ring must be 'adapted' as follows:
l1800 - 3000 rev/min = speed range 1.
l3000 - 3800 rev/min = speed range 2.
l3800 - 4600 rev/min = speed range 3.
l4600 - 5400 rev/min = speed range 4.
The ECM carries out flywheel/ reluctor ring adaptions across all the above speed ranges and can be monitored by
TestBook. The test should be carried out as follows:
lEngine at normal operating temperature.
lSelect second gear (for both automatic and manual transmission vehicles).
lAccelerate until engine rev limiter is operational.
lRelease throttle smoothly to allow engine to decelerate throughout the speed ranges.
lRepeat process as necessary until all adaptations are complete.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1666 Engine anti-theft signal circuit malfunction BCU serial link frame/ bit timing error
P1667 Engine anti-theft signal circuit low Serial link short circuit to earth
P1668 Engine anti-theft signal circuit high Serial link open circuit
P1672 Engine anti-theft signal circuit wrong code
receivedSecure ECM, received incorrect code
P1673 Engine anti-theft signal new engine control
module not configuredNew ECM fitted
P1674 Engine anti-theft signal No code ECM, valid code received