differential LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 1053 of 1672

BRAKES
70-8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
During the initial movement of the piston, the valve, assisted by the valve spring, moves with the piston and closes
the vacuum port to isolate the chambers at the rear of the diaphragms from the vacuum source. Further movement
of the input push rod causes the piston to move away from the valve and open the air inlet port. This allows a restricted
flow of filtered ambient air through the air inlet port, which creates a servo pressure in the chambers at the rear of the
diaphragms. Force from the resultant pressure differential across the diaphragms is transmitted through the valve
body to the output push rod, augmenting the pressure being applied by the brake pedal. The force produced by the
diaphragms, in proportion to the input force, i.e. the boost ratio, is 5.6 : 1. The boost ratio remains constant, as the
input force from the brake pedal increases, until the limit of assistance is reached when servo pressure is equal to
ambient pressure.
Brakes held on
When the brake pedal effort is constant, opposing pressures cause the reaction disc to extrude onto the ratio disc,
which moves the piston against the valve to close the air inlet port. This prevents any further increase in servo
pressure and maintains a constant output force to the master cylinder assembly.
Brakes released
When the brake pedal is released, the input rod spring moves the input rod and piston rearwards within the valve body
to close the air inlet port and open the vacuum port. The air from the chambers at the rear of the diaphragms is then
evacuated, through the vacuum port and the chambers at the front of the diaphragms, to restore a partial vacuum in
all four chambers. Simultaneously, the return spring moves the valve body, diaphragms, output rod and input rod
rearwards to return them to their brakes off position.
Page 1063 of 1672
BRAKES
70-18 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The SLABS ECU continually calculates vehicle speed using the wheel speed inputs from all four ABS sensors. The
calculated vehicle speed is then used as a reference against which individual wheel speeds are monitored for
unacceptable acceleration or deceleration. The ABS sensor inputs are also used by the SLABS ECU to detect vehicle
deceleration rate, vehicle cornering rate and rough terrain.
The engaged forward gear and (on manual gearbox models) the clutch status are computed from the engine data
input, the engine speed input and vehicle speed. Reverse gear status is provided by an input from the reverse lamp
switch (manual gearbox models) or the BCU (automatic gearbox models). On automatic models, the BCU also
provides the neutral selected input.
In addition to controlling the brake related functions, the SLABS ECU:
lControls the operation of the self levelling suspension (SLS) system (where fitted).
+ REAR SUSPENSION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
lOn V8 models, outputs a rough road signal to the ECM when traversing rough terrain.
lOutputs a vehicle speed signal.
The vehicle speed signal is output to the following systems (where fitted):
lActive Cornering Enhancement.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - ACE.
lAir conditioning.
+ AIR CONDITIONING, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
lCruise control.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
lEngine management.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
lIn-car entertainment.
+ IN CAR ENTERTAINMENT, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
lInstrument pack.
+ INSTRUMENTS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
ABS sensors
The ABS sensors supply the SLABS ECU with a sinusoidal speed signal from each wheel. An inductive sensor,
installed in the hub bearing of each wheel, senses off a 60 tooth exciter ring integrated into the inner race of the hub
bearing. Each ABS sensor has a fly-lead connecting it to the vehicle wiring.
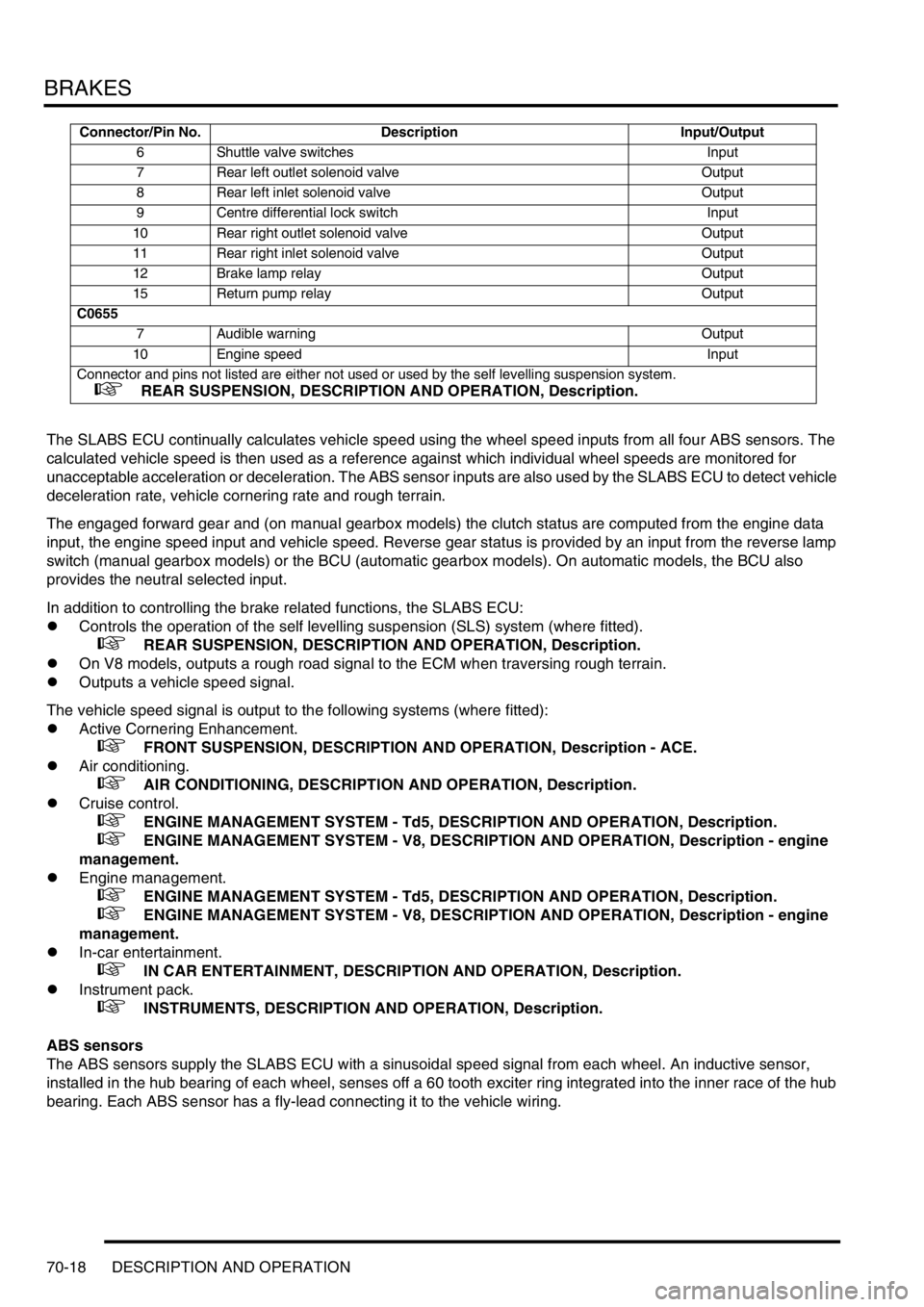
6 Shuttle valve switches Input
7 Rear left outlet solenoid valve Output
8 Rear left inlet solenoid valve Output
9 Centre differential lock switch Input
10 Rear right outlet solenoid valve Output
11 Rear right inlet solenoid valve Output
12 Brake lamp relay Output
15 Return pump relay Output
C0655
7 Audible warning Output
10 Engine speed Input
Connector and pins not listed are either not used or used by the self levelling suspension system.
+ REAR SUSPENSION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Connector/Pin No. Description Input/Output
Page 1066 of 1672

BRAKES
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 70-21
ETC
The ETC function uses brake intervention to prevent wheel spin and maintain even torque distribution to the wheels.
ETC is automatically enabled while the brakes are off at speeds up to 62.5 mph (100 km/h), and operates the brakes
either individually or in axle pairs:
lAt speeds up to 31.3 mph (50 km/h), ETC uses individual brake intervention to maintain even torque distribution
between wheels on the same axle.
lVehicles up to 03 model year – At speeds between 0 and 62.5 mph (0 and 100 km/h), ETC also uses brake
intervention in axle pairs to maintain even torque distribution between the front and rear axles. In effect, this mode
of operation replaces the centre differential lock of the transfer box which, although still incorporated, is non
operational under normal driving conditions.
+ TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description. If the centre differential
lock is in the locked condition, the SLABS ECU illuminates the ABS and ETC warning lamps and inhibits the ETC
function (the ABS, EBD and HDC functions are retained, but at degraded performance levels).
lVehicles from 03 model year (with differential lock fitted) – At speeds between 0 and 62.5 mph (0 and 100
km/h), ETC uses brake intervention in axle pairs to maintain even torque distribution between the front and rear
axles. If the centre differential lock is in the locked condition, the differential lock warning lamp in the instrument
pack is illuminated. The ABS, EBD, ETC and HDC functions are retained, but with revised parameters to suit the
locked differential.
While the ETC function is enabled, if the SLABS ECU detects a wheel accelerating faster than the average, indicating
loss of traction, it operates the ABS modulator in the active braking mode. Depending on the vehicle speed, active
braking is employed for either the brake of the affected wheel or for both brakes on the affected axle, until all four
wheels are driven at approximately the same speed again. During active braking the SLABS ECU also illuminates the
ETC warning lamp, for a minimum of 2 seconds or for the duration that ETC is active. ETC operation is desensitised
during 'hard' cornering.
HDC
HDC uses brake intervention to provide a controlled descent ability in off road conditions when engine braking is
insufficient to maintain a comfortable speed. This allows the driver to leave HDC selected and to control the vehicle's
descent speed, down to the system's minimum target speed, using only the accelerator pedal. The HDC function is
selected on/off by a switch on the fascia. When selected on, HDC is enabled in all forward gears and reverse provided:
lVehicle speed is below 31.3 mph (50 km/h).
lThe transfer box is in low range.
lOn manual gearbox vehicles, the clutch is engaged.
When HDC is enabled, the HDC information warning lamp illuminates. If HDC is selected outside the above
conditions, the HDC information warning lamp flashes and the audible warning sounds continuously.
When HDC is enabled, the SLABS ECU calculates a target speed from the throttle position element of the engine data
input, and compares this with actual speed. If the actual speed is higher than the target speed, the SLABS ECU
operates the ABS modulator in the active braking mode to slow the vehicle down to the target speed. While the braking
force is being applied, the SLABS ECU also energizes the brake lamp relay to put the brake lamps on. Active braking
is discontinued while vehicle speed is below the target speed or if the foot brakes are applied. Applying the foot brakes
during active braking may result in a pulse through the brake pedal, which is normal.
During active braking, the brakes are operated predominantly on the wheels of the leading axle, but if that is not
sufficient to achieve the required deceleration the brakes of the trailing axle are also applied. The deceleration rate is
dependent on the speed differential between initial vehicle speed and the target speed. The deceleration rates are
relatively low at higher speed differentials, then progressively increase as vehicle speed approaches the target speed.
Anti-lock braking is also enabled during active braking, but at very low speeds some wheel lock can occur.
The target speed increases as the accelerator pedal is pressed, from a programmed minimum with the accelerator
pedal released, up to a maximum of 31.3 mph (50 km/h). For any given accelerator pedal position, while travelling
uphill or on level ground the target speed is always greater than the corresponding vehicle speed, which allows the
vehicle to be driven normally without HDC intervention. However, when travelling downhill, the gravitational effect on
the vehicle means that for any given accelerator pedal position the target speed is less than the corresponding vehicle
speed, and HDC intervenes to limit vehicle speed to the target speed.
Page 1349 of 1672

HEATING AND VENTILATION
80-8DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Control panel
The controls for heating and ventilation are installed on a control panel in the centre of the fascia, below the radio.
Three rotary knobs control the LH and RH outlet temperatures and distribution. A slider switch controls blower speed.
A latching pushswitch controls the selection of fresh/recirculated air; an amber LED in the switch illuminates when
recirculated air is selected.
Graphics on the panel and the controls indicate the function and operating positions of the controls.
Outlet vent
The outlet vent promotes the free flow of heating and ventilation air through the cabin. The outlet vent is installed in
the RH rear quarter body panel and vents cabin air into the sheltered area between the rear quarter body panel and
the outer body side panel. The vent consists of a grille covered by soft rubber flaps and is effectively a non-return
valve. The flap opens and closes automatically depending on the differential between cabin and outside air pressures.
FBH system (diesel models only)
The FBH system is an auxiliary heating system that compensates for the relatively low coolant temperatures inherent
in the diesel engine. At low ambient temperatures, the FBH system heats the coolant supply to the heater assembly,
and maintains it within the temperature range required for good in-car heating performance. Operation is fully
automatic, with no intervention required by the driver.
The system consists of an air temperature sensor, a FBH fuel pump and a FBH unit. Fuel for the FBH system is taken
from the fuel tank, through a line attached to the fuel tank's fuel pump, and supplied via the FBH fuel pump to the FBH
unit. The connection on the fuel tank's fuel pump incorporates a tube which extends down into the tank. At the FBH
unit connection, the fuel line incorporates a self-sealing, quick disconnect coupling. In the FBH unit, the fuel delivered
by the FBH fuel pump is burned and the resultant heat output is used to heat the coolant. An ECU integrated into the
FBH unit controls the operation of the system at one of two heat output levels, 2.5 kW at part load and 5 kW at full load
Ambient temperature sensor
The ambient temperature sensor controls a power supply from the alternator to the FBH unit. The sensor is installed
on the RH support strut of the bonnet closing panel and contains a temperature sensitive switch that is closed at
temperatures below 5
°C (41 °F) and open at temperatures of 5 °C (41 °F) and above.
Page 1628 of 1672

INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-1
INS TRUMENTS DESCRIPTION AND OPERAT ION
Instrument pack
1Hill descent control information warning lamp
2Overspeed warning lamp
3Brake system warning lamp
4Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
5Tachometer
6Direction indicator warning lamp
7Main beam warning lamp
8Direction indicator warning lamp
9Speedometer
10SRS warning lamp
11Off road mode warning lamp
12Glow plug warning lamp
13Trailer warning lamp
14Water in fuel filter warning lamp
15Transmission high temperature warning lamp
16Seat belt warning lamp17Fuel tank level gauge
18Low fuel level warning lamp
19LCD odometer/trip meter
20Anti-theft status warning lamp
21ABS warning lamp
22Gearbox manual/sport mode warning lamp
23Alternator charge warning lamp
24ACE warning lamp
25Oil pressure warning lamp
26SLS warning lamp
27Hill descent control warning lamp
28Engine coolant temperature gauge
29High coolant temperature warning lamp
30Traction control warning lamp
31Differential lock warning lamp
32Transfer box neutral warning lamp
Page 1629 of 1672

INSTRUMENTS
88-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Instrument component location - Engine
compartment / underneath vehicle
1ECM (diesel models)
2Alternator
3Glow plugs
4Transmission temperature sensor
5Water in fuel filter sensor
6Fuel tank sender unit
7Differential lock switch – vehicles up to 03
model year8Differential lock switches – vehicles from 03
model year (where fitted)
9Parking brake switch
10Brake fluid level switch
11Oil pressure switch
Page 1631 of 1672

INSTRUMENTS
88-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Instrument block diagram
1Instrument pack
2ECM
3Brake fluid level switch
4Parking brake switch
5Oil pressure switch
6Alternator
7Fuel tank sender unit
8Water in fuel filter sensor
9Transmission temperature sensor
10Differential lock switch - vehicles up to 03
model year or Differential lock switches -
vehicles from 03 model year11Audible warning speaker
12SRS DCU
13SLABS ECU
14BCU
15ACE ECU
16EAT ECU
17Diagnostic connector
18Serial communications link
Page 1632 of 1672

INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-5
Description
General
The instrument pack consists of four analogue dials, four warning lamp packs and a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
odometer.
The four dials are used to indicate:
lRoad speed.
lEngine speed.
lFuel tank level.
lEngine coolant temperature.
The dials are driven by a microprocessor from information received from the serial communication link. Information
input is received as either:
lDigital.
lAnalogue.
lPulse train.
lPulse Width Modulation (PWM).
The LCD provides information for:
lOdometer.
lTrip distance.
lSelected gear (on vehicles fitted with an automatic gearbox).
A trip reset button is provided to zero the trip display, this button also allows the selection of "miles" or "kilometres"
for the display. A photocell controls the illumination of the LCD, maintaining contrast of the display during ambient light
changes.
Within the four warning lamp packs there are 28 lamps. A long life bulb illuminates the high beam warning lamp and
the rest of the warning lamps are illuminated by Light Emitting Diodes (LED's). All warning lamp legends are invisible
until lit. When lit the symbols are illuminated on a black background.
The warning lamps illuminate in one of four colours. The colour indicates the level of importance to the driver, as
follows:
lRed = warning.
lAmber = caution.
lGreen = system operative.
lBlue = main beam operative.
The first warning lamp pack is located in the top left-hand side of the instrument pack and contains the following
warning lamps:
lTraction control warning lamp.
lTransfer box in neutral warning lamp.
lDifferential lock warning lamp
lOverspeed warning lamp (activated for gulf market only).
lBrake system warning lamp.
lHill Descent Control (HDC) information warning lamp.
lMalfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)/ SERVICE ENGINE SOON warning lamp.
The second warning lamp pack is located in the centre of the instrument pack and contains the following warning
lamps:
lDirection indicator warning lamps.
lHigh beam warning lamp.
lAnti-lock brake system warning lamp.
Page 1650 of 1672

INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-23
Differential lock warning lamp (If fitted)
The differential lock is a device used for rolling road testing only on vehicles up to 03 model year. On vehicles from
03 model year, the differential is a driver selectable option which can also be used for off road driving. Refer to the
service procedures for details of rolling road testing on vehicles up to and from 03 model year.
CAUTION: Engage the differential lock when testing the vehicle on a two wheel rolling road. The propeller
shaft connecting the axle not on the rolling road must also be removed.
Differential lock warning lamp – vehicles up to 03 model year
The differential lock warning lamp within the instrument pack utilises a red LED and a clear legend. When the
differential lock is engaged, using the lever on the side of the transfer box, the differential lock switch is operated and
the warning lamp is switched on providing the driver with a visible warning.
When the differential lock is engaged, the warning lamp will be illuminated continuously when the ignition switch is in
position II.
Differential lock warning lamp – vehicles from 03 model year
The differential lock warning lamp is located in the top left hand corner of the instrument pack and uses an amber LED
and a clear legend. When the differential lock is engaged, the warning lamp illuminates when the ignition is on to
provide a visual indication to the driver that the differential lock is engaged. The instrument pack, simultaneously emits
three audible warning chimes as a confirmation.
When the differential lock is disengaged, the warning lamp is extinguished and the instrument pack simultaneously
emits three audible warning chimes as a confirmation.
All vehicles
The power input for the LED is supplied by the instrument pack via fuse 13 in the engine compartment fusebox. The
differential lock switch or switches provide(s) the earth path illuminating the warning lamp.
The voltage on the differential lock switch or switches to instrument pack earth path produces the following warning
lamp functions:
l< 1.8 volts = warning lamp on.
l> 7.7 volts = warning lamp off.