wiring LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 414 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-21
The EUI's earth paths are as follows:
lEUI 1 via pin 25 of the ECM connector C0158.
lEUI 2 via pin 26 of the ECM connector C0158.
lEUI 3 via pin 27 of the ECM connector C0158.
lEUI 4 via pin 24 of the ECM connector C0158.
lEUI 5 via pin 1 of the ECM connector C0158.
The EUI can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
lConnector water ingress.
lConnector failure due to excess heat.
In the event of a fuel injector failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine misfire.
lIdle faults.
lReduced engine performance.
lReduced fuel economy.
lDifficult cold start.
lDifficult hot start.
lExcess smoke.
Page 424 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-31
The purpose of the glow plugs is:
lAssist cold engine start.
lReduce exhaust emissions at low engine load/speed.
The main part of the glow plug is a tubular heating element that protrudes into the combustion chamber of the engine.
The heating element contains a spiral filament that is encased in magnesium oxide powder. At the tip of the tubular
heating element is the heater coil. Behind the heater coil and connected in series is a control coil. The control coil
regulates the heater coil to ensure that it does not overheat and cause a possible failure. The glow plug circuit has its
own control relay located in the engine compartment fuse box.
Pre-heat is the length of time the glow plugs operate prior to engine cranking. The ECM controls the pre-heat time of
the glow plugs based on battery voltage and coolant temperature information via the glow plug relay.
Post-heat is the length of time the glow plugs operate after the engine starts. The ECM controls the post-heat time
based on ECT information. If the ECT fails the ECM will operate pre/post-heat time strategies with default values from
its memory. The engine will be difficult to start.
Input/Output
The glow plugs receive voltage from the glow plug relay that is controlled by the ECM. The ECM provides the earth
path for the relay coil closing the relay contacts and supplying the glow plugs with battery voltage. The supply voltage
heats the coils to approximately 1000
°C (1832 °F). The glow plug circuit is wired in parallel, the body of each glow
plug is screwed directly into the engine block which provides each glow plug with an earth path.
The glow plugs can fail in the following ways:
lHeater coil open circuit.
lControl coil open circuit.
lPoor earth quality.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
lRelay windings open circuit.
lIncorrect relay fitted.
In the event of a glow plug failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDifficult starting.
lExcessive smoke emissions after engine start.
Page 427 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-34 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
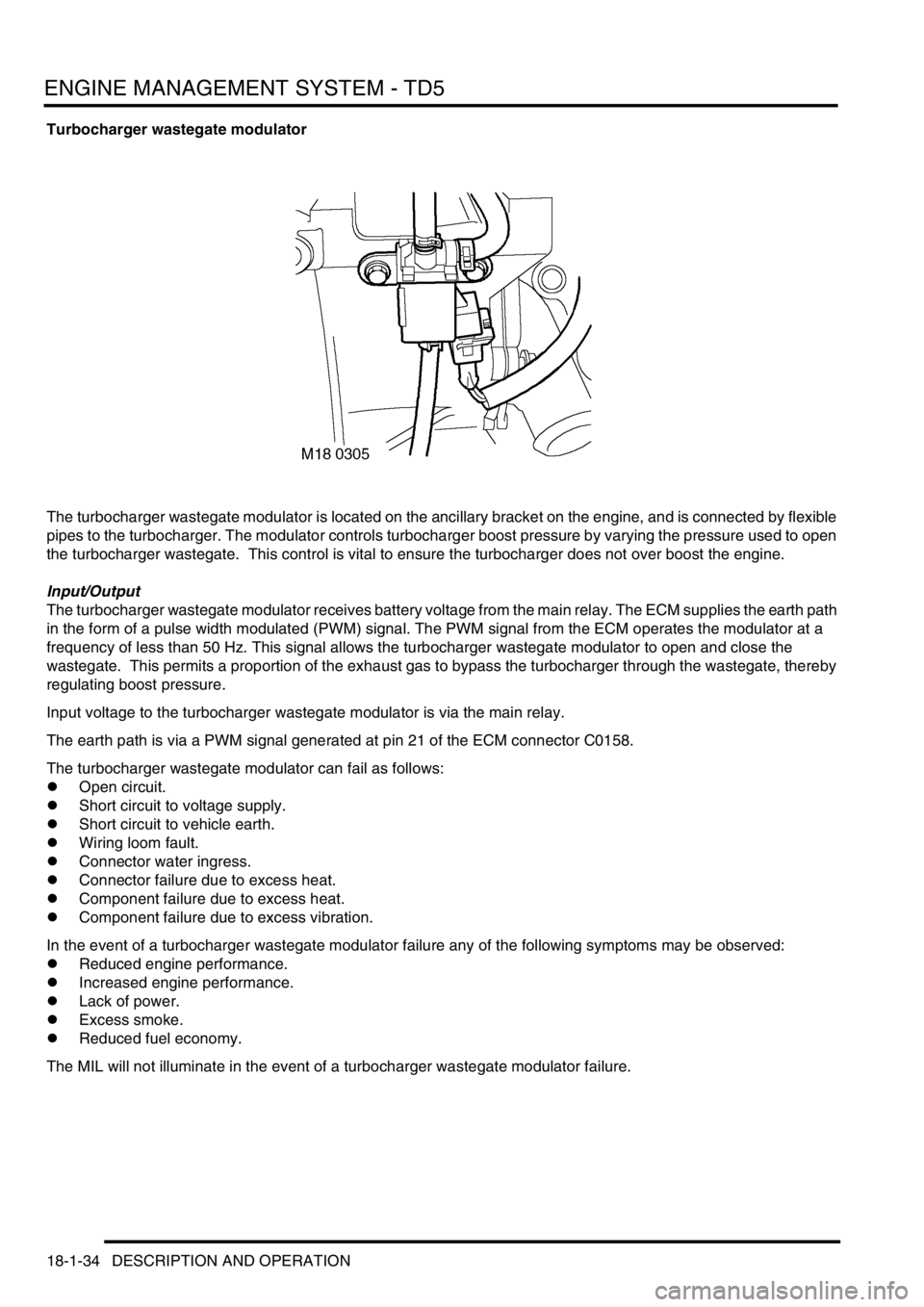
Turbocharger wastegate modulator
The turbocharger wastegate modulator is located on the ancillary bracket on the engine, and is connected by flexible
pipes to the turbocharger. The modulator controls turbocharger boost pressure by varying the pressure used to open
the turbocharger wastegate. This control is vital to ensure the turbocharger does not over boost the engine.
Input/Output
The turbocharger wastegate modulator receives battery voltage from the main relay. The ECM supplies the earth path
in the form of a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal. The PWM signal from the ECM operates the modulator at a
frequency of less than 50 Hz. This signal allows the turbocharger wastegate modulator to open and close the
wastegate. This permits a proportion of the exhaust gas to bypass the turbocharger through the wastegate, thereby
regulating boost pressure.
Input voltage to the turbocharger wastegate modulator is via the main relay.
The earth path is via a PWM signal generated at pin 21 of the ECM connector C0158.
The turbocharger wastegate modulator can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
lConnector water ingress.
lConnector failure due to excess heat.
lComponent failure due to excess heat.
lComponent failure due to excess vibration.
In the event of a turbocharger wastegate modulator failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lReduced engine performance.
lIncreased engine performance.
lLack of power.
lExcess smoke.
lReduced fuel economy.
The MIL will not illuminate in the event of a turbocharger wastegate modulator failure.
Page 428 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-35
Cruise control master switch
The cruise control master switch is located on the dashboard. When the driver activates the switch it requests the
cruise control system to be active. The switch acts as a latching switch, on the first operation of the switch the cruise
control system is activated, when the switch is pressed again the cruise control system is de-activated. The cruise
control warning lamp is part of the switch and illuminates when the switch is activated.
Input/Output
Input to the cruise control master switch is 12 volts via the main relay. When the switch is pressed the circuit is
completed by the ECM providing an earth path for the relay via pin 15 of connector C0658 of the ECM.
The cruise control master switch can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
In the event of a cruise control master switch failure cruise control does not operate.
Page 429 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-36 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Cruise control set/accelerate (SET+) switch
The cruise control SET+ switch is located on the vehicle steering wheel. The switch is a momentary switch and when
pressed by the driver reacts as follows:
lRequests the cruise control to become active and set at the current road speed if not already set.
lIf the cruise control is already set, pressing the switch increases the road speed at 1 mph (1.6 km/h) intervals.
The cruise control SET+ switch will only become active and operate under the following conditions:
lThe vehicle speed must be above 22 mph (35 km/h).
lThe cruise control master switch must be 'on'.
lThe brake pedal must not be pressed.
lThe automatic transmission must be in 'drive'.
lThe clutch pedal must not be pressed.
lThe suspend switch has not been operated.
Input/Output
Input to the cruise control SET+ switch is 12 volts via the main relay. When the switch is pressed the circuit is
completed by the ECM providing an earth path for the relay via pin 11 of connector C0658 of the ECM.
The cruise control SET+ switch can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault In the event of a cruise control SET+ switch failure cruise control does not operate.
Cruise control resume/suspend (RES) switch
The cruise control RES switch is located on the vehicle steering wheel. The switch is a momentary switch and when
pressed by the driver reacts as follows:
lRequests the cruise control to be suspended if it has already been set.
lRequests that cruise control is resumed at the previously set road speed.
The cruise control RES switch will only become active and operate under the following conditions:
lThe vehicle speed must be above 22 mph (35 km/h).
lThe cruise control master switch must be 'on'.
lThe brake pedal must not be pressed.
lThe automatic transmission must be in 'drive'.
lThe clutch pedal must not be pressed.
Page 430 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-37
Input/Output
Input to the cruise control RES switch is 12 volts via the main relay. When the switch is pressed the circuit is completed
by the ECM providing an earth path for the relay via pin 17 of connector C0658 of the ECM.
The cruise control RES switch can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
In the event of a cruise control RES switch failure cruise control resume/ suspend operation does not operate.
Page 433 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-40 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Controller Area Network (CAN) system
The CAN system is a high speed serial interface between the ECM and the Electronic Automatic Transmission (EAT)
ECU. The CAN system uses a data bus to transmit information messages between the ECM and the EAT ECU.
Because there are only two components in this CAN system, one will transmit information messages and the other
will receive information messages, and vice-versa.
The CAN system is used by the EAT ECU and the ECM for the following:
lGearshift torque control information.
lEAT OBD information.
lMIL request.
lVehicle speed signal.
lEngine temperature.
lEngine torque and speed.
lGear selected.
lGear change information.
The CAN system uses a twisted pair of wires to form the data bus to minimise electrical interference. This method of
serial interface is very reliable and very fast. The information messages are structured so that each of the receivers
(ECM or EAT ECU) is able to interpret and react to the messages sent.
The CAN data bus is connected directly between pin 32 of connector C0158 of the ECM and pin 44 of connector
C0193 at the EAT ECU, and pin 35 of connector C0158 of the ECM and pin 16 of connector C0193 at the EAT ECU.
The CAN system can fail in the following ways:
lCAN data bus wiring open circuit.
lCAN data bus wiring short circuit.
In the event of a CAN data bus failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEAT defaults to reverse and 4th gear if the vehicle is moving, 3rd gear if the vehicle is stationary.
lHarsh gearshifts.
lSport and manual warning lamps flash alternately.
Vehicle Speed Signal (VSS)
The VSS is an integral part of the ECM's overall adaptive strategy. The ECM receives the signal direct from the
SLABS ECU. The SLABS ECU is not connected to the controller area network (CAN) so therefore is hard wired.
Vehicles fitted with automatic transmission have two vehicle speed input signals to the ECM. One signal is from the
SLABS ECU and the other is from the automatic transmission ECU. The ECU compares these speed signals.
The ECM also receives transfer gearbox information. This allows the ECM to take in to account the vehicle being
driven using low range gearing and compensate as necessary. The signals generated by the SLABS ECU for manual
transmission, and by the EAT ECU for automatic transmission are received by the ECM in the form of a PWM signal.
The frequency of this signal changes in accordance with road speed.
The input signal for the SLABS is measured via pin 13 of connector C0658 of the ECM. The SLABS ECU generates
a PWM signal switching between 0 and 12 volts at a frequency of 8000 pulses per mile.
For vehicles with automatic transmission the input signal for the EAT ECU is measured via pins 32 and 35 of
connector C0158 of the ECM. These pin numbers provide a bi-directional communications link using the CAN data
bus.
Page 434 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-41
In the case of a VSS failure on vehicles with automatic transmissions the ECM applies default values derived from
the EAT ECU. There is no default value for manual transmission vehicle.
The VSS can fail in the following ways:
lWiring short circuit to vehicle supply.
lWiring short circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring open circuit.
In the event of a VSS failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lVehicle speed limiting disabled (manual transmission only).
lHill Descent Control (HDC) warning lamp on and audible warning.
Cruise control
All markets have a common cruise control system. The cruise control system, when activated, regulates vehicle
speed. The ECM controls the cruise control system.
Cruise control activation
Cruise control is a passive system, and must be activated by the driver. Cruise control is activated by switching on
the cruise control master switch located on the instrument panel. A LED in the switch illuminates indicating cruise
control is available. The driver must accelerate the vehicle to the desired speed using the accelerator pedal. When
the desired speed is reached, cruise control can be activated by pressing the SET+ switch.
Cruise control will only activate if the following conditions are met:
lVehicle speed is above 22 mph (35 km/h).
lThe brake pedal is not pressed.
lThe clutch pedal is not pressed (manual transmission only).
lThe transmission is not in Park, Reverse or Neutral (automatic transmission only).
The ECM receives the set signal and determines the vehicle speed provided by the SLABS ECU. The ECM then
maintains current road speed.
Cruise control cancellation
Cancelling cruise control enables the driver to regain control of the vehicle speed by using the accelerator pedal.
Cruise control is cancelled if any of the following conditions occur:
lThe brake pedal is pressed.
lThe RES switch is pressed.
lThe clutch pedal is pressed (manual transmission only).
lThe cruise control master switch is switched off.
lThe transmission is placed in Park, Neutral, or Reverse (automatic transmission only).
The ECM cancels cruise control operation and returns it to the control of the accelerator pedal.
The set speed will be stored in the ECM unless:
lThe cruise control master switch is switched off.
lThe ignition is switched off.
If cruise control is deactivated using either of the above methods, the set speed will be erased from the memory of
the ECM.
Page 478 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-21
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
The MAF sensor utilises a “hot film” element contained in the air intake duct to monitor the mass of the air flow being
drawn into the engine. The MAF sensor contains two sensing elements, one element is controlled at ambient
temperature (e.g. 25
°C (77°F)), while the other is heated to 200°C (360°F) above the ambient temperature (e.g. 225°C
(437
°F)).
When the intake air passes the heated element, it cools it down, so lowering the resistance of the hot film element. In
order to maintain the same temperature, the circuit to the heated element has to supply more current. The change in
current causes a corresponding change in potential difference to be detected in the monitoring circuit. This change is
supplied to the ECM as a voltage between 0 and 5V, where it is processed by the ECM's internal mapping to interpret
the data as a measure of the mass of air flow.
The measured air mass flow is used by the ECM to determine the fuel quantity to be injected in order to maintain the
stoiciometric air:fuel mixture for optimum engine performance and low emissions.
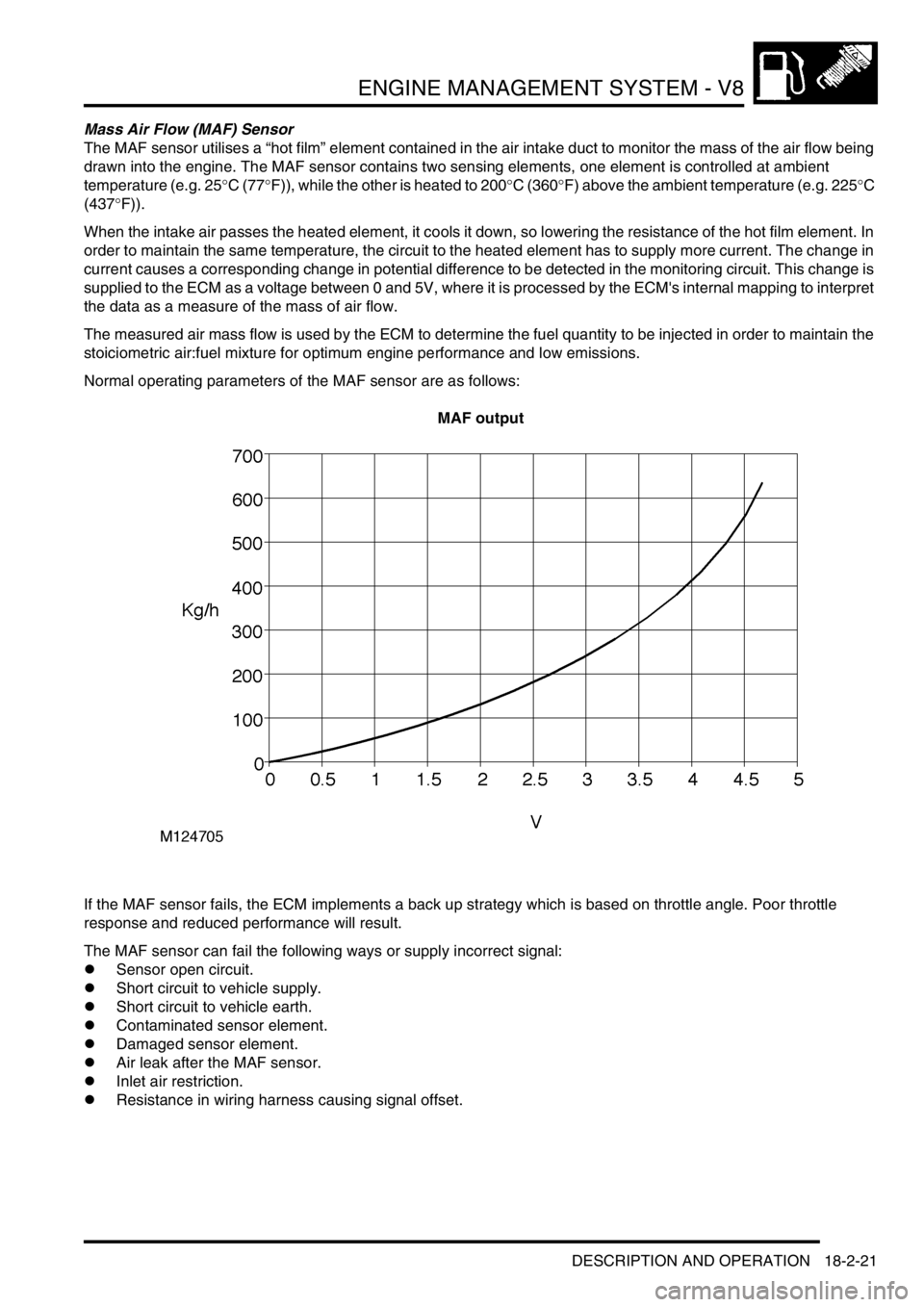
Normal operating parameters of the MAF sensor are as follows:
MAF output
If the MAF sensor fails, the ECM implements a back up strategy which is based on throttle angle. Poor throttle
response and reduced performance will result.
The MAF sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lContaminated sensor element.
lDamaged sensor element.
lAir leak after the MAF sensor.
lInlet air restriction.
lResistance in wiring harness causing signal offset.
Page 485 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-28 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The HO2S can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lSensor disconnected.
lStoichiometric ratio outside the correct operating band.
lContamination from leaded fuel.
lAir leak into the exhaust system.
lWiring loom damage.
lSensors fitted incorrectly or cross wired.
In the event of a HO
2S signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDefault to open loop fuelling on defective bank.
lIf the sensors are crossed over (LH bank to RH bank), the engine will run normally after initial start up, but
performance will become progressively worse as the sensors go towards maximum rich for one bank of cylinders
and maximum lean for the other. The ECM will eventually default into open loop fuelling.
lHigh CO reading.
lExcess emissions.
lStrong hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) smell until the ECM defaults to open loop fuelling. .
lMIL illuminated (NAS market only).
A number of diagnostic tests are performed by the ECM with regards to the HO
2sensors:
lHO
2 sensor and system diagnostics
lHO
2 sensor heater diagnostics
lHO
2 sensor switching period (ageing) diagnostics
lRear HO
2 sensor adaption diagnostic (NAS only)
lCatalyst monitoring diagnostic
For further details of the heated oxygen sensors and exhaust emission control, refer to the V8 Emission Control
section of this manual.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Exhaust emission control system.
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1129 O
2 sensors swapped bank to bank (sensor 1) Front sensors transposed
P0130 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 1, sensor 1) Front sensor LH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band
P0132 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 1, sensor 1) Front sensor LH bank short circuit to battery supply
P0134 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 1,
sensor 1)Front sensor LH bank open circuit
P0150 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 2, sensor 1) Front sensor RH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band
P0152 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 2, sensor 1) Front sensor RH bank short circuit to battery supply
P0154 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 2,
sensor 1)Front sensor RH bank open circuit
P0136 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band (NAS only)
P0137 O
2 sensor circuit low voltage (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank short circuit to earth (NAS only)
P0138 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank short circuit to battery supply
(NAS only)
P0140 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 1,
sensor 2)Rear sensor LH bank open circuit (NAS only)
P0156 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 2, sensor 2) Rear sensor RH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band (NAS only)
P0157 O
2 sensor circuit low voltage (bank 2, sensor 2) Rear sensor RH bank short circuit to earth (NAS only)