air condition LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 327 of 1672
EMISSION CONTROL - TD5
17-1-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The EGR modulator is located on a plate fixed to the inner wing on the RH side of the engine. The modulator is
attached to the plate by two through-studs, each with two nuts which secure the modulator assembly to a rubber
mounting which helps to reduce noise. The modulator must be mounted in the vertical orientation with the two vacuum
ports uppermost.
The modulator operation is controlled by a signal from the ECM which determines the required amount of EGR
needed in response to inputs relating to air flow and engine operating and ambient conditions. The modulator has a
black two-pin connector at its base to connect it to the ECM through the engine harness.
Each modulator features three ports:
lThe top port of the EGR modulator is identified by a white band and connects to a 'T'-piece in the vacuum line
via a small-bore brown plastic hose. On type 2 systems the brown hose is connected in parallel with the vacuum
source to the ILT modulator.
The other two ports on the 'T'-piece connects vacuum line hoses of black vinyl tubing between the vacuum pump
and the brake-servo assembly attached to the bulkhead. The vacuum pump end of the vacuum line tubing
terminates in a rubber elbow, which gives a vacuum tight seal on the suction port of the vacuum pump. The
brake-servo end of the vacuum line tubing terminates with a non-return valve in a plastic housing which plugs
into the front face of the brake-servo housing.
lThe middle port of the EGR modulator is identified by a blue band and connects to the suction port on the EGR
valve through a small-bore blue plastic hose.
lThe lower port of the EGR modulator is identified by a green band and connects to atmosphere through an in-
line filter via a small-bore green plastic hose. On type 2 models a 3 way connector is fitted to vent both modulators
through a single filter. The other port of the in-line filter vents directly to atmosphere.
The blue and brown vacuum hoses are protected by corrugated plastic sheaths. The ends of the hoses are fitted with
rubber boots to ensure vacuum tight seals at the component ports.
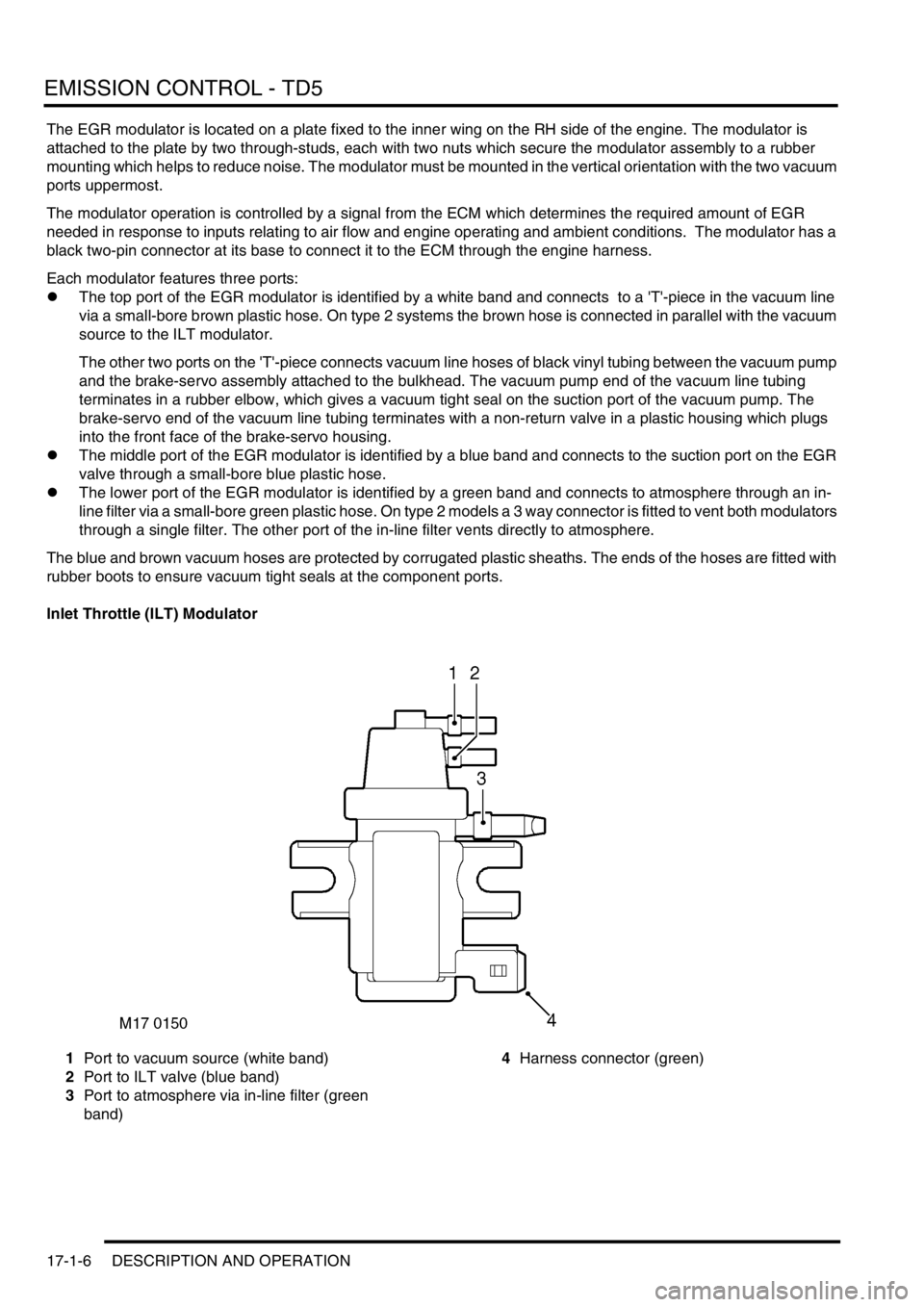
Inlet Throttle (ILT) Modulator
1Port to vacuum source (white band)
2Port to ILT valve (blue band)
3Port to atmosphere via in-line filter (green
band)4Harness connector (green)
Page 328 of 1672
EMISSION CONTROL - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-1-7
The ILT modulator is located on a plate fixed to the inner wing on the RH side of the engine below the EGR modulator.
The modulator is attached to the plate by two through-studs, each with two nuts which secure the modulator assembly
to a rubber mounting which helps to reduce noise. The modulator must be mounted in the vertical orientation with the
two vacuum ports uppermost.
The modulator operation is controlled by a signal from the ECM which determines the required ratio of exhaust gas
to fresh inlet air needed in response to inputs relating to air flow and engine operating and ambient conditions. The
modulator has a green two-pin connector at its base to connect it to the ECM through the engine harness.
The ILT valve modulator features three ports:
lThe top port is identified by a white band and connects to a 'T'-piece in the vacuum line via a small-bore brown
plastic hose where it is connected in parallel with the vacuum source line to the EGR valve modulator. The two
other ports on the 'T'-piece connect vacuum line hoses of black vinyl tubing between the vacuum pump attached
to the alternator and the brake-servo assembly attached to the bulkhead.
lThe middle port is identified by a blue band and connects to the suction port on the ILT valve through a small-
bore blue plastic hose.
lThe lower port is identified by a green band and connects to atmosphere through an in-line filter via a green
plastic hose and a three-way connector positioned in-line between the modulators and the filter. The ILT
modulator hose is connected opposite to the two parallel ports at the three-way connector which connect the vent
lines to the EGR valve modulator and the in-line filter. The other port of the in-line filter vents directly to
atmosphere.
The blue and brown vacuum hoses are protected by corrugated plastic sheaths. The ends of the hoses are fitted with
rubber boots to ensure vacuum tight seals at the component ports.
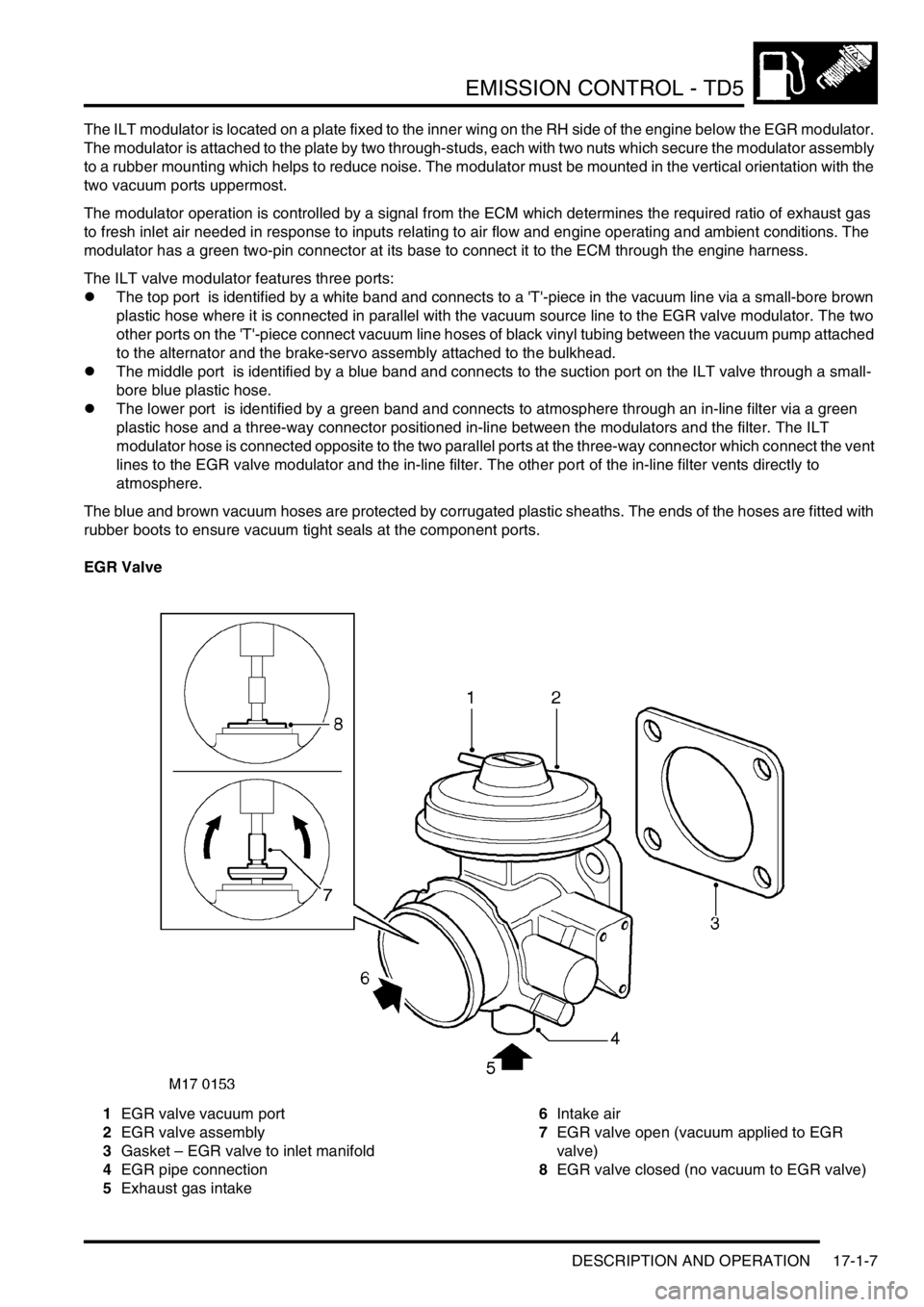
EGR Valve
1EGR valve vacuum port
2EGR valve assembly
3Gasket – EGR valve to inlet manifold
4EGR pipe connection
5Exhaust gas intake6Intake air
7EGR valve open (vacuum applied to EGR
valve)
8EGR valve closed (no vacuum to EGR valve)
Page 331 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - TD5
17-1-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
EGR systems
There are two types of exhaust gas recirculation system used with the Td5 engine dependent on legislation and
market requirements, these are type 1 and type 2.
Type 1 EGR system is fitted to all Td5's built up to the introduction of 2002 MY, except for Japanese specification
vehicles.
Type 2 EGR system is fitted to all Japanese specification vehicles and was introduced into European markets for 2002
MY to meet EU3 emission requirements. An additional feature introduced at 2002 MY is the EGR cooler, which is
bolted to the front of the cylinder head.
EGR system - type 1
This EGR system features a single modulator which is electrically controlled to modulate a vacuum source to the EGR
valve. The controlled vacuum opens and closes the valve by the amount required to ensure the optimal proportion of
exhaust gas is allowed through to the inlet manifold to be combined with the fresh air intake. Control feedback is
achieved by monitoring the mass of fresh air flowing through the mass air flow sensor.
The modulator operation is controlled by a signal from the ECM which determines the required amount of EGR
needed in response to inputs relating to air flow and engine operating and ambient conditions. The ECM is low-side
driven, sinking current returned from the vacuum modulator for switching operating condition.
The exhaust gases are routed from the exhaust manifold through a shaped metal pipe which connects to the
underside of the EGR valve. The pipe is held securely in position to the front of the cylinder head using a clamp
bracket. The EGR pipe is attached to a mating port at the front end of the exhaust manifold using two Allen screws
and at the EGR valve assembly by a metal band clamp. The two Allen screws fixing the EGR pipe to the exhaust
manifold should be replaced every time the EGR pipe is removed. Extreme care should be exercised when
removing and refitting the EGR pipe to avoid damage.
When a vacuum is applied to the EGR suction port, it causes a spindle with sealing disc (EGR valve) to be raised,
thus opening the port at the EGR pipe to allow the recirculated exhaust gas to pass through into the inlet manifold.
The valve is spring loaded so that when the vacuum is removed from the suction port the valve returns to its rest
position to tightly close the exhaust gas port.
By controlling the quantity of recirculated exhaust gas available in the inlet manifold, the optimum mix for the prevailing
engine operating conditions can be maintained, which ensures the intake gas to the combustion chambers will have
burning rate properties which will reduce the NO
x emissions to an acceptable level. Normally, full recirculation is only
applicable when the NO
x emissions are most prevalent.
EGR system - type 2
This system features twin modulators mounted one above the other on a metal plate located on the inner wing at the
RH side of the engine. The modulators are electrically controlled by the engine management system and are used to
modulate a vacuum source to the EGR valve and a supplementary Inlet Throttle (ILT) valve; the two valves are
controlled to operate in tandem. The ILT valve vacuum pot is mounted adjacent to the EGR valve housing and has a
linkage which connects to a butterfly valve mounted in front of the EGR valve at the air intake manifold.
The modulator operations are electrically controlled by signals from the engine management system which
determines the required volume of exhaust gas needed in response to inputs relating to air flow, engine operating
conditions and ambient parameters such as temperature and altitude. The engine management ECM switches on the
circuit by completing the path to ground, operating the vacuum modulators.
Pre EU3 models: The exhaust gases are routed from the exhaust manifold through a shaped metal pipe which
connects to the underside of the EGR valve. The pipe is held securely in position to the front of the engine cylinder
head using a metal clamp bracket. The EGR pipe is attached to a mating port at the front end of the exhaust manifold
using two Allen screws and at the EGR valve assembly by a metal band clamp. The two Allen screws fixing the EGR
pipe to the exhaust manifold should be replaced every time the EGR pipe is removed. Extreme care should be
exercised when removing and refitting the EGR pipe to avoid damage.
Page 332 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-1-11
EU3 models: The exhaust gases are routed from the exhaust manifold through the EGR cooler to the underside of
the EGR valve. The EGR cooler is bolted to the front of the engine cylinder head. An EGR pipe connects the EGR
cooler to the exhaust manifold and is secured by two Allen screws. The two Allen screws fixing the EGR pipe to the
exhaust manifold should be replaced every time the EGR pipe is removed. A second pipe connects the EGR cooler
to the EGR valve; this pipe is secured to the EGR valve by a clip, and to the cooler by two Allen screws.Extreme care
should be exercised when removing and refitting the EGR pipe to avoid damage. When refitting the EGR
cooler, always tighten the pipe connections BEFORE tightening the bolts securing the cooler to the cylinder
head.
When a vacuum is applied to the EGR suction port, it causes a spindle with sealing disc (EGR valve) to be raised,
opening the port at the EGR pipe to allow the recirculated exhaust gas to pass through into the inlet manifold. The
valve is spring loaded so that when the vacuum is removed from the suction port, the valve returns to its rest position
to tightly close the exhaust gas port.
A vacuum is simultaneously applied to the inlet throttle (ILT) valve suction port which causes the butterfly valve in the
inlet manifold to close by means of a spindle and lever mechanism. Closing the butterfly valve limits the supply of
fresh intercooled air entering the inlet manifold and causes a depression within the inlet manifold to create a greater
suction at the open port to the EGR delivery pipe. In this condition a greater mass of recirculated exhaust gas is drawn
into the inlet manifold for use in the combustion process. When the vacuum is released from the ILT valve suction port
a spring returns the butterfly valve to its fully open position.
By controlling the quantities of recirculated exhaust gas and fresh intake air available in the inlet manifold, the
optimum mix for the prevailing engine operating conditions can be maintained which ensures the intake gas to the
combustion chambers will have burning rate properties which will reduce the NO
x emissions to an acceptable level.
Normally, full recirculation is only applicable when the NO
x emissions are most prevalent.
Page 346 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-9
Emission Control Systems
Engine design has evolved in order to minimise the emission of harmful by-products. Emission control systems are
fitted to Land Rover vehicles which are designed to maintain the emission levels within the legal limits pertaining for
the specified market.
Despite the utilisation of specialised emission control equipment, it is still necessary to ensure that the engine is
correctly maintained and is in good mechanical order so that it operates at its optimal condition. In particular, ignition
timing has an effect on the production of HC and NO
x emissions, with the harmful emissions rising as the ignition
timing is advanced.
CAUTION: In many countries it is against the law for a vehicle owner or an unauthorised dealer to modify or
tamper with emission control equipment. In some cases, the vehicle owner and/or the dealer may even be
liable for prosecution.
The engine management ECM is fundamental for controlling the emission control systems. In addition to controlling
normal operation, the system complies with On Board Diagnostic (OBD) system strategies. The system monitors and
reports on faults detected with ignition, fuelling and exhaust systems which cause an excessive increase in tailpipe
emissions. This includes component failures, engine misfire, catalyst damage, catalyst efficiency, fuel evaporative
loss and exhaust leaks.
When an emission relevant fault is determined, the fault condition is stored in the ECM memory. For NAS vehicles,
the MIL warning light on the instrument pack will be illuminated when the fault is confirmed. Confirmation of a fault
condition occurs if the fault is still found to be present during the driving cycle subsequent to the one when the fault
was first detected.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
The following types of supplementary control system are used to reduce harmful emissions released into the
atmosphere from the vehicle:
1Crankcase emission control – also known as blow-by gas emissions from the engine crankcase.
2Exhaust emission control – to limit the undesirable by-products of combustion.
3Fuel vapour evaporative loss control – to restrict the emission of fuel through evaporation from the fuel
system.
4Fuel leak detection system (NAS only) – there are two types of system which may be used to check the
evaporative emission system for the presence of leaks from the fuel tank to purge valve.
aVacuum leak detection test – checks for leaks down to 1 mm (0.04 in.) in diameter.
bPositive pressure leak detection test – utilises a leak detection pump to check for leaks down to 0.5 mm (0.02
in.) in diameter.
5Secondary air injection system (NAS only) – to reduce emissions experienced during cold starting.
Crankcase emission control system
The concentration of hydrocarbons in the crankcase of an engine is much greater than that in the vehicle's exhaust
system. In order to prevent the emission of these hydrocarbons into the atmosphere, crankcase emission control
systems are employed and are a standard legal requirement.
The crankcase ventilation system is an integral part of the air supply to the engine combustion chambers and it is
often overlooked when diagnosing problems associated with engine performance. A blocked ventilation pipe or filter
or excessive air leak into the inlet system through a damaged pipe or a leaking gasket can affect the air:fuel mixture,
performance and efficiency of the engine. Periodically check the ventilation hoses are not cracked and that they are
securely fitted to form airtight connections at their relevant ports.
The purpose of the crankcase ventilation system is to ensure that any noxious gas generated in the engine crankcase
is rendered harmless by complete burning of the fuel in the combustion chamber. Burning the crankcase vapours in
a controlled manner decreases the HC pollutants that could be emitted and helps to prevent the development of
sludge in the engine oil as well as increasing fuel economy.
Page 347 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
A spiral oil separator is located in the stub pipe to the ventilation hose on the right hand cylinder head rocker cover,
where oil is separated and returned to the cylinder head. The rubber ventilation hose from the right hand rocker cover
is routed to a port on the right hand side of the inlet manifold plenum chamber where the returned gases mix with the
fresh inlet air passing through the throttle butterfly valve. The stub pipe on the left hand rocker cover does not contain
an oil separator, and the ventilation hose is routed to the throttle body housing at the air inlet side of the butterfly valve.
The ventilation hoses are attached to the stub pipe by metal band clamps.
Exhaust emission control system
The fuel injection system provides accurately metered quantities of fuel to the combustion chambers to ensure the
most efficient air to fuel ratio under all operating conditions. A further improvement to combustion is made by
measuring the oxygen content of the exhaust gases to enable the quantity of fuel injected to be varied in accordance
with the prevailing engine operation and ambient conditions; any unsatisfactory composition of the exhaust gas is
then corrected by adjustments made to the fuelling by the ECM.
The main components of the exhaust emission system are two catalytic converters which are an integral part of the
front exhaust pipe assembly. The catalytic converters are included in the system to reduce the emission to
atmosphere of carbon monoxide (CO), oxides of nitrogen (NO
x) and hydrocarbons (HC). The active constituents of
the catalytic converters are platinum (Pt), palladium (PD) and rhodium (Rh). Catalytic converters for NAS low
emission vehicles (LEVs) from 2000MY have active constituents of palladium and rhodium only. The correct
functioning of the converters is dependent upon close control of the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas entering
the catalyst.
The two catalytic converters are shaped differently to allow sufficient clearance between the body and transmission,
but they remain functionally identical since they have the same volume and use the same active constituents.
The basic control loop comprises the engine (controlled system), the heated oxygen sensors (measuring elements),
the engine management ECM (control) and the injectors and ignition (actuators). Other factors also influence the
calculations of the ECM, such as air flow, air intake temperature and throttle position. Additionally, special driving
conditions are compensated for, such as starting, acceleration, deceleration, overrun and full load.
The reliability of the ignition system is critical for efficient catalytic converter operation, since misfiring will lead to
irreparable damage of the catalytic converter due to the overheating that occurs when unburned combustion gases
are burnt inside it.
CAUTION: If the engine is misfiring, it should be shut down immediately and the cause rectified. Failure to do
so will result in irreparable damage to the catalytic converter.
CAUTION: Ensure the exhaust system is free from leaks. Exhaust gas leaks upstream of the catalytic
converter could cause internal damage to the catalytic converter.
CAUTION: Serious damage to the engine may occur if a lower octane number fuel than recommended is used.
Serious damage to the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors will occur if leaded fuel is used.
Air : fuel ratio
The theoretical ideal air:fuel ratio to ensure complete combustion and minimise emissions in a spark-ignition engine
is 14.7:1 and is referred to as the stoichiometric ratio.
The excess air factor is denoted by the Lambda symbol
λ, and is used to indicate how far the air:fuel mixture ratio
deviates from the theoretical optimum during any particular operating condition.
lWhen
λ = 1, the air to fuel ratio corresponds to the theoretical optimum of 14.7:1 and is the desired condition for
minimising emissions.
lWhen
λ > 1, (i.e. λ = 1.05 to λ = 1.3) there is excess air available (lean mixture) and lower fuel consumption can
be attained at the cost of reduced performance. For mixtures above
λ = 1.3, the mixture ceases to be ignitable.
lWhen
λ < 1, (i.e. λ = 0.85 to λ = 0.95) there is an air deficiency (rich mixture) and maximum output is available,
but fuel economy is impaired.
The engine management system used with V8 engines operates in a narrower control range about the stoichiometric
ideal between
λ = 0.97 to 1.03 using closed-loop control techniques. When the engine is warmed up and operating
under normal conditions, it is essential to maintain
λ close to the ideal (λ = 1) to ensure the effective treatment of
exhaust gases by the three-way catalytic converters installed in the downpipes from each exhaust manifold.
Page 352 of 1672
EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-15
Evaporative emission control system
The evaporation emission control (EVAP) system is used to reduce the level of hydrocarbons emitted into the
atmosphere from the fuel system. The system comprises an EVAP canister which stores the hydrocarbons from the
fuel tank, pressure valves, vent lines and a purge control solenoid valve.
Fuel vapour is stored in the canister until it is ready to be purged to the inlet manifold under the control of the Engine
Control Module (ECM).
A two-way valve is included in the vent line between the fuel tank and the EVAP canister in all markets except NAS.
A fuel vapour separator is fitted next to the fuel filler neck, the construction is different between NAS and ROW
vehicles; the liquid vapour separator (LVS) on NAS vehicles is an L-shaped metal tube and for all other markets it is
an integral part of the moulded plastic filler neck.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
NAS vehicles have stainless steel filler necks whilst all other markets use moulded plastic filler necks. On NAS fillers,
a valve closes the roll-over valve (ROV) vent line when the fuel filler cap is removed; for all other markets a pressure
relief valve is fitted into the ROV vent line.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Four ROV's are fitted to the fuel tank, for NAS vehicles the valves are fitted inside the fuel tank and for ROW vehicles
the ROV's are welded external to the fuel tank. Nylon vent lines from the ROV's connect to the liquid vapour separator
allowing vapour to pass to the EVAP canister via the LVS. To prevent the canister from being overloaded (particularly
in hot ambient conditions) and to prevent wastage of fuel, the vapour is allowed to condense within the LVS and flow
back through the ROVs into the tank.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Pressure / vacuum relief valves are incorporated into the fuel filler cap which operate in the event of an evaporation
system failure (e.g. blockage in the evaporation system line to atmosphere). The cap relieves fuel tank pressure to
atmosphere at approximately 1.8 to 2.0 psi (12 to 14 kPa) and opens in the opposite direction at approximately – 0.7
psi (- 5kPa) vacuum. All plastic bodied fuel fillers are fitted with a tank overpressure relief valve.
A vent line flow restrictor (anti-trickle valve) is fitted to the filler pipe in the line between the tank and the canister on
NAS vehicles. The purpose of the anti-trickle valve is to preserve the vapour space in the tank by blocking the vent
line during the fuel filling process. The valve is operated by the action of inserting the filler gun, so that when the fuel
in the tank reaches the level of the filling breather, flow cut off occurs due to fuel filling the filler pipe.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
The breather ports from the EVAP canister are located high up in the engine bay (CVS unit on NAS vehicles with
vacuum type, fuel evaporation leak detection capability; via an air filter on NAS vehicles with positive pressure type,
fuel evaporation leak detection capability; snorkel tubes on ROW vehicles), to prevent water ingress during vehicle
wading.
The ECM connectors and pins which are pertinent to evaporative emission control are listed in the following table:
Connector / Pin No. Function Signal type Control
C0635-23 Main relay output Output drive Switch to ground
C0635-24 Leak detection pump motor (NAS vehicles
with positive pressure type EVAP system
leak detection only)Output drive Switch to ground
C0636-3 Purge valve drive Output signal PWM 12 - 0V
C0636-6 Fuel tank pressure sensor (NAS vehicles
with vacuum type EVAP system leak
detection only)Ground 0V
C0636-30 Canister vent solenoid (CVS) valve (NAS
vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system
leak detection only) / Fuel leak detection
pump (NAS vehicles with positive pressure
type EVAP system leak detection only)Output drive Switch to ground
Page 353 of 1672
EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Fuel leak detection system (vacuum type) – NAS only
The advanced evaporative loss control system equipped with a vacuum type, fuel evaporation leak detection
capability is similar to the standard evaporative loss system, but also includes additional components to enable the
engine control module (ECM) to perform a fuel evaporation leak detection test. The system includes an EVAPs
canister and purge valve, and in addition, a canister vent solenoid (CVS) valve and a fuel tank pressure sensor.
The function of the CVS valve is to block the atmospheric vent side of the EVAP canister under the control of the ECM
so that an evaporation system leak check can be performed. The test is carried out when the vehicle is stationary and
the engine is running at idle speed. The system test uses the natural rate of fuel evaporation and engine manifold
depression. Failure of the leak check will result in illumination of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL).
The fuel evaporation leak detection is part of the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) strategy and it is able to determine
vapour leaks from holes or breaks greater than 1 mm (0.04 in.) in diameter. Any fuel evaporation system leaks which
occur between the output of the purge valve and the connection to the inlet manifold cannot be determined using this
test, but these will be detected through the fuelling adaption diagnostics.
Fuel leak detection system (positive pressure type) – NAS only
The evaporative loss control system equipped with a positive pressure type, fuel evaporation leak detection capability
is similar to the vacuum type, but it is capable of detecting smaller leaks by placing the evaporation system under the
influence of positive air pressure. The system includes an EVAPs canister and purge valve, and in addition, a leak
detection pump comprising a motor and solenoid valve.
The solenoid valve contained in the leak detection pump assembly performs a similar function to the CVS valve
utilised on the vacuum type pressure test. The solenoid valve is used to block the atmospheric vent side of the EVAP
canister under the control of the ECM so that an EVAP system leak check can be performed. At the same time,
pressurised air from the pump is allowed past the valve into the EVAP system to set up a positive pressure. The test
is carried out at the end of a drive cycle when the vehicle is stationary and the ignition is switched off. The test is
delayed for a brief period (approximately 10 seconds) after the engine is switched off to allow any slosh in the fuel
tank to stabilise. Component validity checks and pressure signal reference checking takes a further 10 seconds before
the pressurised air is introduced into the EVAP system.
During reference checking, the purge valve is closed and the leak detection pump solenoid valve is not energised,
while the leak detection pump is operated. The pressurised air is bypassed through a restrictor which corresponds to
a 0.5 mm (0.02 in) leak while the current consumption of the leak detection pump motor is monitored.
The system test uses the leak detection pump to force air into the EVAP system when the purge valve and solenoid
valves are both closed (solenoid valve energised), to put the evaporation lines, components and fuel tank under the
influence of positive air pressure. Air is drawn into the pump through an air filter which is located in the engine
compartment.
The fuel leak detection pump current consumption is monitored by the ECM while the EVAP system is under pressure,
and compared to the current noted during the reference check. A drop in the current drawn by the leak detection pump
motor, indicates that air is being lost through holes or leaks in the system which are greater than the reference value
of 0.5 mm (0.02 in). An increase in the current drawn by the leak detection pump motor, indicates that the EVAP
system is well sealed and that there are no leaks present which are greater than 0.5 mm (0.02 in).
The presence of leakage points indicates the likelihood of hydrocarbon emissions to atmosphere from the
evaporation system outside of test conditions and the necessity for rectification work to be conducted to seal the
system. Failure of the leak check will result in illumination of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL).
C0637-9 Fuel tank pressure sensor (NAS vehicles
with vacuum type EVAP system leak
detection only)Output reference 5V
C0637-12 Analogue fuel level (NAS vehicles with
positive pressure type EVAP system leak
detection only)Input Analogue 0 - 5V
C0637-14 Fuel tank pressure sensor (NAS vehicles
with vacuum type EVAP system leak
detection only)Input signal Analogue 0 - 5V
C0637-20 MIL "ON" Output drive Switch to ground Connector / Pin No. Function Signal type Control
Page 356 of 1672
EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-19
For NAS vehicles with positive pressure, EVAP system leak detection capability, the atmosphere vent line from the
EVAP canister connects to a port on the fuel leak detection pump via a short, large bore hose which is secured to the
component ports by crimped metal clips at each end. A large bore plastic hose from the top of the leak detection pump
is routed to the RH side of the engine bay where it connects to an air filter canister. Under normal operating conditions
(when the fuel leak detection solenoid valve is not energised), the EVAP canister is able to take in clean air via the
air filter, through the pipework and past the open solenoid valve to allow normal purge operation to take place and
release any build up of EVAP system pressure to atmosphere.
The EVAP system pipes are clipped at various points along the pipe runs and tied together with tie straps at suitable
points along the runs.
The NAS and ROW EVAP canisters are of similar appearance, but use charcoal of different consistency. The ROW
vehicles use granular charcoal of 11 bwc (butane working capacity) and NAS vehicles use pelletised charcoal with a
higher absorption capacity of 15 bwc. All canisters are of rectangular shape and have capacities of 1.8 litres (3 1/8
imp. pts) with purge foam retention.
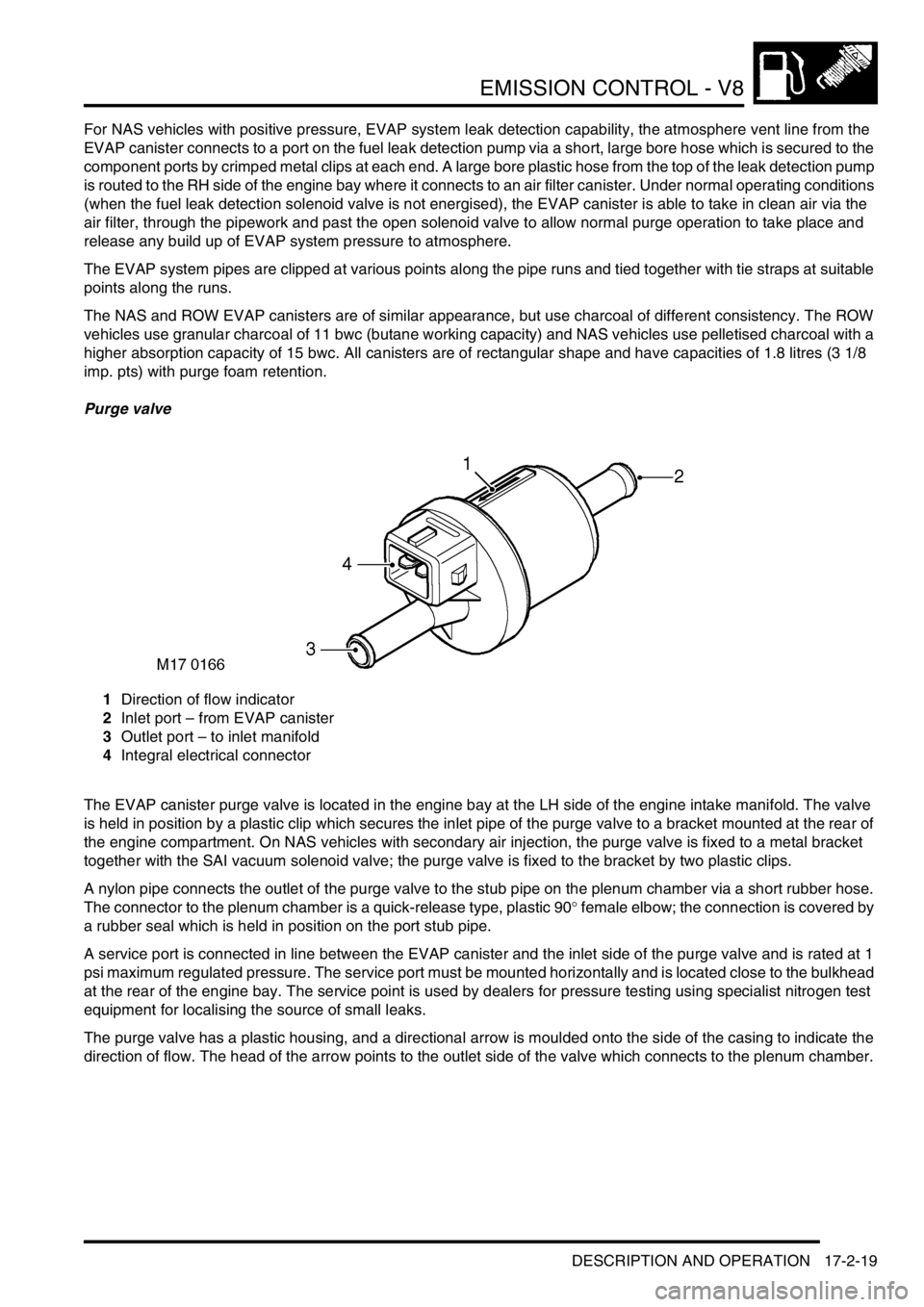
Purge valve
1Direction of flow indicator
2Inlet port – from EVAP canister
3Outlet port – to inlet manifold
4Integral electrical connector
The EVAP canister purge valve is located in the engine bay at the LH side of the engine intake manifold. The valve
is held in position by a plastic clip which secures the inlet pipe of the purge valve to a bracket mounted at the rear of
the engine compartment. On NAS vehicles with secondary air injection, the purge valve is fixed to a metal bracket
together with the SAI vacuum solenoid valve; the purge valve is fixed to the bracket by two plastic clips.
A nylon pipe connects the outlet of the purge valve to the stub pipe on the plenum chamber via a short rubber hose.
The connector to the plenum chamber is a quick-release type, plastic 90
° female elbow; the connection is covered by
a rubber seal which is held in position on the port stub pipe.
A service port is connected in line between the EVAP canister and the inlet side of the purge valve and is rated at 1
psi maximum regulated pressure. The service port must be mounted horizontally and is located close to the bulkhead
at the rear of the engine bay. The service point is used by dealers for pressure testing using specialist nitrogen test
equipment for localising the source of small leaks.
The purge valve has a plastic housing, and a directional arrow is moulded onto the side of the casing to indicate the
direction of flow. The head of the arrow points to the outlet side of the valve which connects to the plenum chamber.
Page 357 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Purge valve operation is controlled by the engine control module (ECM). The purge valve has a two-pin electrical
connector which links to the ECM via the engine harness. Pin-1 of the connector is the power supply source from fuse
2 in the engine compartment fusebox, and pin-2 of the connector is the switched earth from the ECM (pulse width
modulated (PWM) signal) which is used to control the purge valve operation time. Note that the harness connector
for the purge valve is black, and must not be confused with the connector for the Secondary Air Injection
vacuum solenoid valve which is grey.
When the purge valve is earthed by the ECM, the valve opens to allow hydrocarbons stored in the EVAP canister to
be purged to the engine inlet manifold for combustion.
If the purge valve breaks or becomes stuck in the open or closed position, the EVAP system will cease to function
and there are no default measures available. The ECM will store the fault in memory and illuminate the MIL warning
lamp if the correct monitoring conditions have been achieved (i.e. valve status unchanged for 45 seconds after engine
has been running for 15 minutes). If the purge valve is stuck in the open position, a rich air:fuel mixture is likely to
result at the intake manifold, this could cause the engine to misfire and the fuelling adaptions will change.
The following failure modes are possible:
lSticking valve
lValve blocked
lConnector or harness wiring fault (open or short circuit)
lValve stuck open
If the purge valve malfunctions, the following fault codes may be stored in the ECM diagnostic memory, which can be
retrieved using 'Testbook':
P-code Description
P0440Purge valve not sealing
P0444Purge valve open circuit
P0445Purge valve short circuit to ground
P0443Purge valve short circuit to battery voltage