fuel type LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 480 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-23
Should the IAT sensor fail, the ECM defaults to an assumed air temperature of 45 °C (113 °F).
The IAT sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle battery supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lIncreased sensor resistance.
lDamaged sensor element.
In the event of an IAT sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lAdaptive fuelling disabled.
lIdle speed adaption disabled.
lCatalyst monitoring affected due to exhaust temperature model.
lIdle speed actuator test disabled.
lWarm up ignition angle affected.
lCondenser fan hot restart inhibited.
There are two types of IAT sensor diagnostic checks:
lThe IAT sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold – the engine has to have been running for longer than
180 seconds, and idle speed control must have been operational for longer than 10 seconds. No fuel cut off is
active. The IAT sensor signal must be less than -35
°C (-31°F) for longer than 200 ms.
lThe IAT sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold – the ECM has to be powered up (engine does not
need to be running), and the signal must be greater than 140
°C (284°F) for longer than 200 ms.
If the IAT sensor fails the following fault codes will be produced and can be retrieved by TestBook:
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0112 Intake air temperature circuit low input Intake air temperature signal less than minimum
threshold, after time for exhaust to warm up
P0113 Intake air temperature circuit high input Intake air temperature signal greater than maximum
threshold
Page 487 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-30 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
There are eight fuel injectors one per cylinder that the ECM operates sequentially. All the injectors are fed from a
common fuel rail as part of the returnless fuel system. Fuel pressure is maintained at a constant 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in2) by
a regulator that is integral with the fuel pump.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Input/Output
All eight fuel injectors are supplied with battery voltage via fuse number 1 located in engine compartment fuse box.
The ECM controls the individual earth path for each injector via its own pin at connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
This facility allows the ECM to control the fuel injectors so that sequential fuel injection can take place.
Typical hot engine injector pulse width values:
lIdle = 2.5 ms.
lPeak torque (3000 rev/min) = 7 ms The ECM controls injector earth as follows:
lCylinder No 1 - pin 41 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 2 - pin 1 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 3 - pin 27 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 4 - pin 40 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 5 - pin 2 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 6 - pin 15 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 7 - pin 14 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 8 - pin 28 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
Individual injectors can be measured for resistance using a multimeter. An acceptable injector resistance is as follows:
l14.5
± 0.7 ohms at 20 °C (68 °F).
The fuel injectors can fail in the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lInjector actuator open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBlocked injector.
lRestricted injector.
lLow fuel pressure.
In the event of fuel injector signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lRough running.
lDifficult starting.
lEngine misfire.
lPossible catalyst damage.
lHigh emissions.
lAdaptive fuelling disabled.
lAdaptive idle speed control disabled.
The ECM performs three types of fuel injector diagnostic check:
lOutput short circuit to earth
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage
lOutput open circuit
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0201 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 1 Injector 1 open circuit
P0261 Cylinder 1 injector circuit low Injector 1 short circuit to earth
P0262 Cylinder 1 injector circuit high Injector 1 short circuit to battery supply
P0301 Cylinder 1 misfire detected Injector 1 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0202 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 2 Injector 2 open circuit
P0264 Cylinder 2 injector circuit low Injector 2 short circuit to earth
P0265 Cylinder 2 injector circuit high Injector 2 short circuit to battery supply
Page 491 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-34 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Input/Output
The input value for the relay windings is battery voltage, the input value for the switching contacts comes from fuse
10 in the engine compartment fuse box. The output control of the switching contacts is direct to the fuel pump motor,
and the relay windings are controlled by pin number 18 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
At ignition 'on' (position II) the fuel pump relay contacts remain open until the ECM supplies an earth path for the relay
windings via pin number 18 of connector C0635 of the ECM. At this point, the relay windings are energised, drawing
the relay contacts closed. This allows voltage from fuse 10 in the passenger compartment fuse box to pass directly
to the fuel pump.
The fuel pump relay can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lRelay drive open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lComponent failure.
In the event of a fuel pump relay failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine stalls or will not start.
lNo fuel pressure at the fuel injectors.
The ECM performs three types of diagnostic test to confirm the fuel pump relay integrity:
lOutput short circuit to earth
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage
lOutput open circuit
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Evaporative emissions
Refer to Emissions section for description of the evaporative emissions system components.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Evaporative emission control system.
Secondary air injection (NAS only)
Refer to Emissions section for description of the secondary air injection system components.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Secondary air injection system.
Fuel tank pressure sensor (NAS only)
Refer to Fuel Delivery section for description of the fuel system components.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Refer to Emissions section for description of the fuel tank pressure sensor.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Evaporative emission control system.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1230 Fuel pump relay malfunction Fuel pump relay open circuit - not the fuel pump
P1231 Fuel pump relay circuit low Fuel pump relay short circuit to battery supply - not the
fuel pump
P1232 Fuel pump relay circuit high Fuel pump relay short circuit to earth - not the fuel pump
Page 503 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-46 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Idle speed control
The ECM regulates the engine speed at idling. The ECM uses the idle air control valve (IACV) to compensate for the
idle speed drop that occurs when the engine is placed under greater load than usual. When the throttle is in the rest
position i.e. it has not been pressed, the majority of intake air that the engine consumes comes from the idle air control
valve.
IACV control idle speed
Conditions in which the ECM operates the IACV control idle speed is as follows:
lIf any automatic transmission gears other than P or N are selected.
lIf air conditioning is switched on.
lIf cooling fans are switched on.
lAny electrical loads activated by the driver.
Function
The idle air control valve utilises two coils that use opposing pulse width modulated (PWM) signals to control the
position of a rotary valve. If one of the circuits that supplies the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining
signal preventing the idle air control valve from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the idle
air control valve assumes a default idle position at which the engine idle speed is raised to 1200 rev/min with no load
placed on the engine.
Evaporative emission control
Due to increasing legislation, all new vehicles must be able to limit evaporative emissions (fuel vapour) from the fuel
tank.
The ECM controls the emission control system using the following components:
lEVAP canister.
lPurge valve.
lCanister vent solenoid (CVS) valve – (NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability
only)
lFuel tank pressure sensor – (NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability only)
lFuel leak detection pump – (NAS vehicles with positive pressure type EVAP system leak detection capability
only)
lInterconnecting pipe work.
Refer to Emissions section for operating conditions of evaporative emission systems.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Evaporative emission control operation.
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) - North American Specification vehicles only
The ECM monitors performance of the engine for misfires, catalyst efficiency, exhaust leaks and evaporative control
loss. If a fault occurs, the ECM stores the relevant fault code and warns the driver of component failure by illuminating
the Malfunction Indicator Light in the instrument pack.
On vehicles fitted with automatic gearbox, the ECM combines with the Electronic Automatic Transmission (EAT) ECU
to provide the OBD strategy.
Conditions
If the OBD function of the ECM flags a fault during its operation, it falls into one of the following categories:
lmin = minimum value of the signal exceeded.
lmax = maximum value of the signal exceeded.
lsignal = signal not present.
lplaus = an implausible condition has been diagnosed.
Page 508 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-51
Should a malfunction of the rough road signal occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved
by TestBook:
Hill Descent Control (HDC) signal
The ECM transmits throttle angle, engine torque, engine identification (Td5 or V8), and transmission type (automatic
or manual) data to the SLABS ECU to support the Hill Descent Control system. The information is transmitted via a
0 – 12V pulse width modulated (PWM) signal at a frequency of 179.27 Hz.
Function
The HDC signal output from the ECM is via pin 29 of connector C0636. The ECM generates a PWM signal that varies
in pulse width in accordance with changing throttle angle or engine torque. The throttle angle data is transmitted on
pulses 1, 3, 5 and 37. The engine torque data is transmitted on pulses 2,4,6 and 38. The engine and transmission
information is transmitted on pulse 39. A synchronising pulse is transmitted after every 39th pulse.
The HDC signal can fail in the following ways:
lHarness or connector damage
A HDC signal failure may be evident from the following:
lHDC / ABS warning light on
lHDC inoperative
lAudible warning
Should a malfunction of the HDC signal occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
Low fuel level signal
When the fuel level in the fuel tank becomes low enough to illuminate the low fuel level warning lamp in the instrument
cluster, the instrument cluster generates a low fuel level signal. If the low fuel level signal is present during the ECM
misfire detection function the ECM can use it to check for a 'false misfire'.
Conditions
The fuel sender generates the low fuel level signal when the fuel sender resistance is greater than 158
± 8 ohms.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1590 ABS rough road signal circuit malfunction Hardware is OK, but SLABS ECU is sending an error
signal
P1591 ABS rough road signal circuit low Signal from SLABS ECU short circuit to earth
P1592 ABS rough road signal circuit high Signal from SLABS ECU short circuit to vehicle battery
supply
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1663 Throttle angle/Torque signal circuit malfunction SLABS HDC link open circuit
P1664 Throttle angle/Torque signal circuit low SLABS HDC link short circuit to ground
P1665 Throttle angle/Torque signal circuit high SLABS HDC link short circuit to battery voltage
Page 550 of 1672

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-1-5
The fuel pump is a 'self priming', wet type, two stage pump which is immersed in fuel in the tank and operates at all
times when the ignition switch is in position II. If the engine is not started, the ECU will 'time-out' after three minutes
and de-energise the fuel pump relay. The pump receives a feed from the battery via fuse 10 in the engine
compartment fusebox and the fuel pump relay. The relay is energised by the ECM when the ignition switch is moved
to position II.
The fuel pump assembly is retained with a locking ring and sealed with a rubber seal. The locking ring requires a
special tool for removal and refitment. An access panel for the fuel pump is located in the loadspace floor below the
carpet. The access panel is sealed to the floor with a rubber seal and retained by six self-tapping screws. A four pin
electrical connector is located on the top cover and provides power feed and earth for the fuel pump and also inputs
and outputs for the fuel gauge sender operation.
The fuel gauge sender is integral with the fuel pump. The sender is submerged in the fuel and is operated by a float
which moves with the fuel level in the tank.
Fuel pump
The fuel pump assembly comprises a top cover which locates the electrical connector, fuel burning heater connection
and four fuel pipe couplings. The top cover is attached to a plastic cup shaped housing and retained on three sliding
clips. Two coil springs are located between the cover and the housing and ensure that the fuel pump remains seated
positively at the bottom of the tank when installed.
The housing locates the two stage fuel pump and also the fuel gauge sender unit. The lower part of the housing is the
swirl pot which maintains a constant level of fuel at the fuel pick-up. A coarse filter is located in the base of the housing
and prevents the ingress of contaminants into the pump and the fuel system from the fuel being drawn into the pump.
A fine filter is located in the intake to the low pressure stage to protect the pump from contaminants. Flexible pipes
connect the couplings on the top cover to the pump.
A non-return valve is located in the base of the housing. When the fuel tank is full, fuel pressure keeps the valve lifted
from its seat allowing fuel to flow into the swirl pot. As the tank level reduces, the fuel pressure in the tank reduces
causing the valve to close. When the valve is closed fuel is retained in the swirl pot, ensuring that the swirl pot remains
full and maintains a constant supply to the fuel pump.
The two stage pump comprises a high and a low pressure stage. The low pressure stage draws fuel from the swirl
pot through the filter. The low pressure stage pumps fluid at a pressure of 0.75 bar (10.9 lbf.in
2) and a flow of 30 litres/
hour (8 US Gallons/hour) to the fuel filter. A proportion of the fuel from the low pressure stage also passes, via a
restrictor, through a jet pump which keeps fuel circulating in the swirl pot. The high pressure stage draws the low
pressure fuel from the fuel filter and pressurises it to a pressure of 4.0 bar (58 lbf.in
2). The pressurised fuel is then
passed from the pump to the injectors at a flow of 180 litres/hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour). A fuel pressure regulator is
located at the rear of the engine and ensures that the delivery pressure remains at 4.0 bar (58 lbf.in
2) by controlling
the amount of fuel returning to the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a maximum current draw of 15 Amps at 12.5 V and is protected by a 20 Amp fuse in the engine
compartment fusebox.
Page 554 of 1672
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-1-9
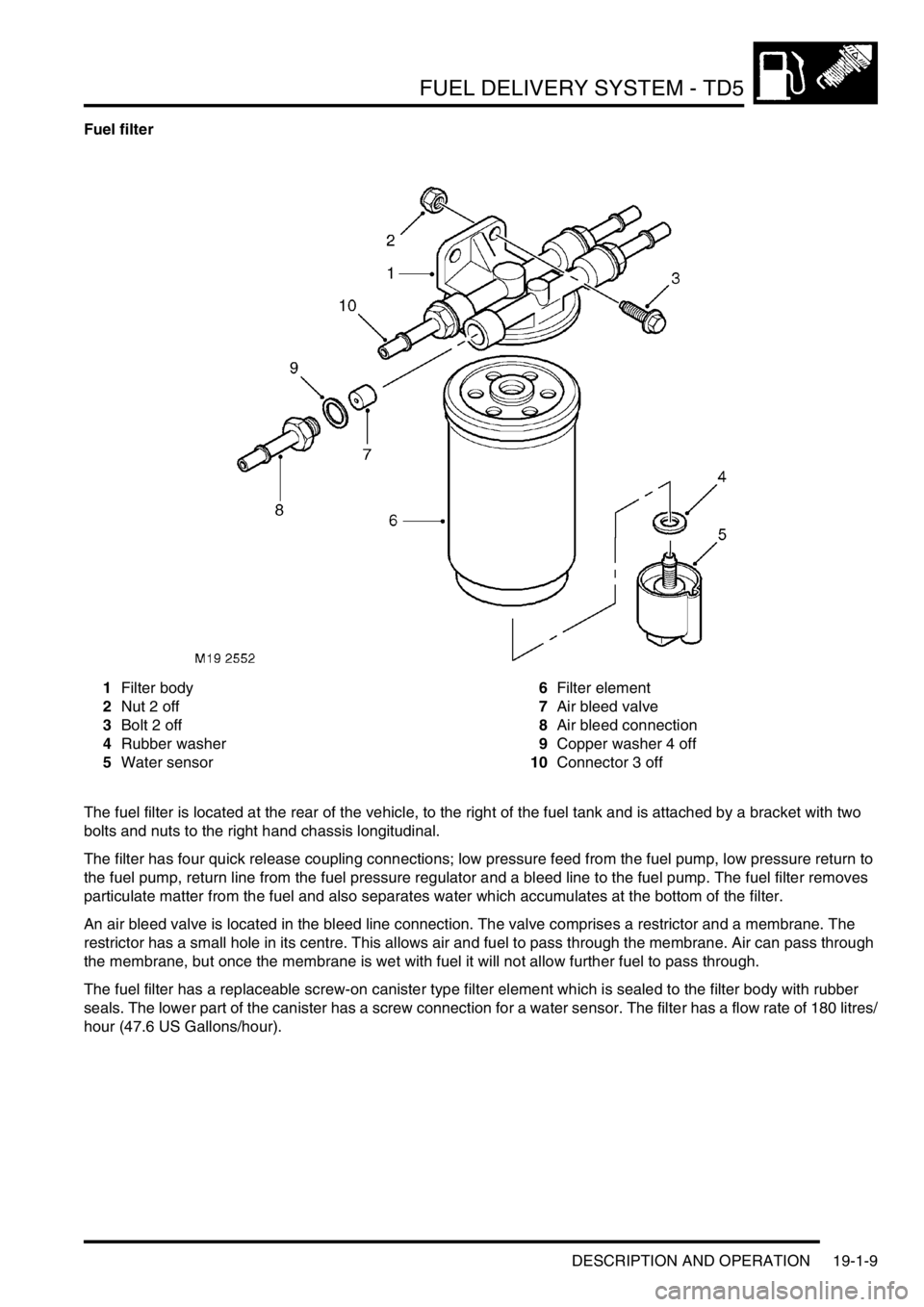
Fuel filter
1Filter body
2Nut 2 off
3Bolt 2 off
4Rubber washer
5Water sensor6Filter element
7Air bleed valve
8Air bleed connection
9Copper washer 4 off
10Connector 3 off
The fuel filter is located at the rear of the vehicle, to the right of the fuel tank and is attached by a bracket with two
bolts and nuts to the right hand chassis longitudinal.
The filter has four quick release coupling connections; low pressure feed from the fuel pump, low pressure return to
the fuel pump, return line from the fuel pressure regulator and a bleed line to the fuel pump. The fuel filter removes
particulate matter from the fuel and also separates water which accumulates at the bottom of the filter.
An air bleed valve is located in the bleed line connection. The valve comprises a restrictor and a membrane. The
restrictor has a small hole in its centre. This allows air and fuel to pass through the membrane. Air can pass through
the membrane, but once the membrane is wet with fuel it will not allow further fuel to pass through.
The fuel filter has a replaceable screw-on canister type filter element which is sealed to the filter body with rubber
seals. The lower part of the canister has a screw connection for a water sensor. The filter has a flow rate of 180 litres/
hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour).
Page 568 of 1672
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-2-3
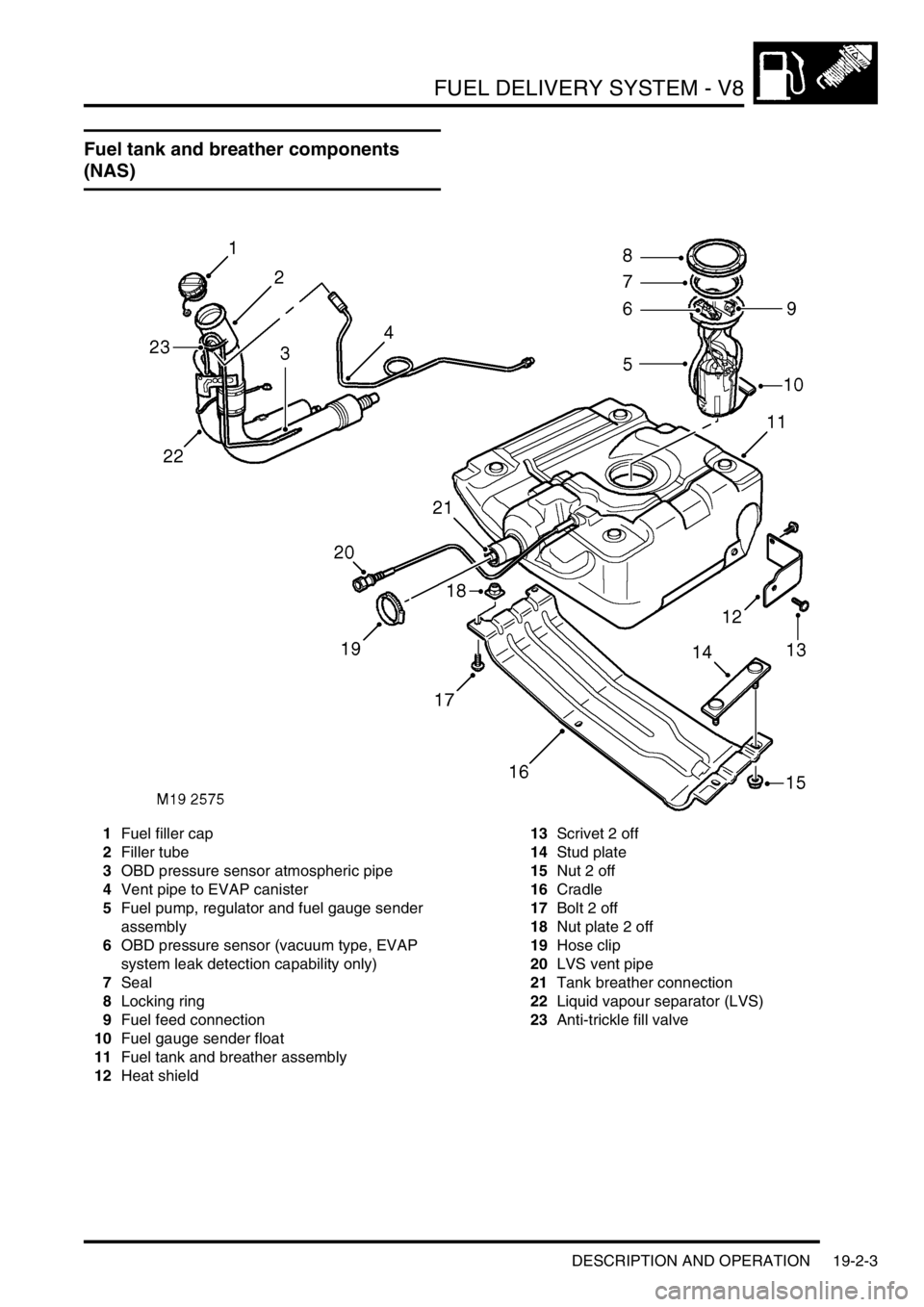
Fuel tank and breather components
(NAS)
1Fuel filler cap
2Filler tube
3OBD pressure sensor atmospheric pipe
4Vent pipe to EVAP canister
5Fuel pump, regulator and fuel gauge sender
assembly
6OBD pressure sensor (vacuum type, EVAP
system leak detection capability only)
7Seal
8Locking ring
9Fuel feed connection
10Fuel gauge sender float
11Fuel tank and breather assembly
12Heat shield13Scrivet 2 off
14Stud plate
15Nut 2 off
16Cradle
17Bolt 2 off
18Nut plate 2 off
19Hose clip
20LVS vent pipe
21Tank breather connection
22Liquid vapour separator (LVS)
23Anti-trickle fill valve
Page 570 of 1672

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-2-5
NAS markets: A fabricated filler tube, made from stainless steel, connects the filler to the tank via a flexible rubber
hose. The filler tube is connected at it's top end behind the filler flap.
On all vehicles that use unleaded fuel, the filler neck is fitted with an inhibitor. The inhibitor is a tapered nozzle in the
mouth of the filler neck which will only allow the use of a standard unleaded fuel filler gun. A spring loaded flap valve
prevents the incorrect fuel from being trickle filled from an incorrect filler gun.
Fuel tank breather system (all markets except NAS)
The filler tube incorporates a tank vent which allows air and fuel vapour displaced from the tank when filling to vent to
atmosphere via the filler neck. A relief valve in the vent line to the EVAP canister prevents vapour escaping through
the canister during filling. This prevents the customer overfilling the tank and maintains the correct fuel cut-off level.
The filler tube also incorporates an integral Liquid Vapour Separator (LVS). During normal driving excess fuel vapour
is passed via the vent line into the EVAP canister. To prevent the canister from being overloaded with fuel vapour,
especially in hot climates, the vapour is given the opportunity to condense in the LVS. Fuel which condenses in the
LVS flows back into the tank through the ROV's.
A breather spout within the tank controls the tank 'full' height. When fuel covers the spout it prevents fuel vapour and
air from escaping from the tank. This causes the fuel to 'back-up' in the filler tube and shuts off the filler gun. The
position of the spout ensures that when the filler gun shuts off, a vapour space of approximately 10% of the tanks total
capacity remains. This vapour space ensures that Roll Over Valves (ROV's) are always above the fuel level and the
vapour can escape and allow the tank to breathe.
The pressure relief valve fitted in the vent line to the EVAP canister prevents the customer trickle filling the tank.
Trickle filling greatly reduces the vapour space in the tank which in turn affects the tank's ability to breathe properly,
reducing engine performance and safety. When filling the tank, the pressures created are too low to open the pressure
relief valve, preventing the customer from trickle filling the tank. Vapour pressures created during driving are higher
and will open the valve allowing vapour to vent to the EVAP canister.
Four ROV's are welded onto the top surface of the tank. Each ROV is connected by a tube to the main vent line to
the EVAP canister. The ROV's allow fuel vapour to pass through them during normal vehicle operation. In the event
of the vehicle being overturned the valves shut-off, sealing the tank and preventing fuel from spilling from the vent line.
Fuel tank breather system (NAS)
The filler tube incorporates a tank vent which allows air and fuel vapour displaced from the tank when filling to vent to
atmosphere via the filler neck. A filler cap operated valve within the fuel filler neck prevents vapour escaping through
the EVAP canister during filling. This prevents the customer overfilling the tank and maintains the correct fuel cut-off
level.
The filler tube also has an 'L' shaped, stainless steel Liquid Vapour Separator (LVS). During normal driving excess
fuel vapour is passed via the vent line into the EVAP canister. To prevent the canister from being overloaded with fuel
vapour, especially in hot climates, the vapour is given the opportunity to condense in the LVS. Fuel which condenses
in the LVS flows back into the tank via the LVS vent line and through the Roll Over Valves (ROV's).
For NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability, a small tube is located alongside the filler
tube and terminates near to the filler neck. The tube is connected to the On Board Diagnostics (OBD) pressure sensor
in the fuel pump and provides the sensor with a reading of atmospheric pressure to compare against the tank
pressure.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Emission Control Systems.
A breather spout within the tank controls the tank 'full' height. When fuel covers the spout it prevents fuel vapour and
air from escaping from the tank. This causes the fuel to 'back-up' in the filler tube and shuts off the filler gun. The
position of the spout ensures that when the filler gun shuts off, a vapour space of approximately 10% of the tanks total
capacity remains. This vapour space ensures that the ROV's are always above the fuel level and the vapour can
escape to the LVS and allow the tank to breathe.
Page 571 of 1672
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8
19-2-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The filler cap operated valve closes the vent line to the EVAP canister to prevent the customer trickle filling the tank.
Trickle filling greatly reduces the vapour space in the tank which in turn affects the tank's ability to breathe properly,
reducing engine performance and safety. When filling the tank, the removal of the filler cap closes the valve and the
vent line preventing the customer from trickle filling the tank. When the cap is installed the valve is opened by the cap
allowing vapour to vent to the EVAP canister.
The four ROV's are welded inside the top surface of the tank. Each ROV is connected internally in the tank by a tube
to the LVS. The ROV's allow fuel vapour to pass through them during normal vehicle operation. In the event of the
vehicle being overturned the valves shut-off, sealing the tank and preventing fuel from spilling from the vent line into
the LVS.
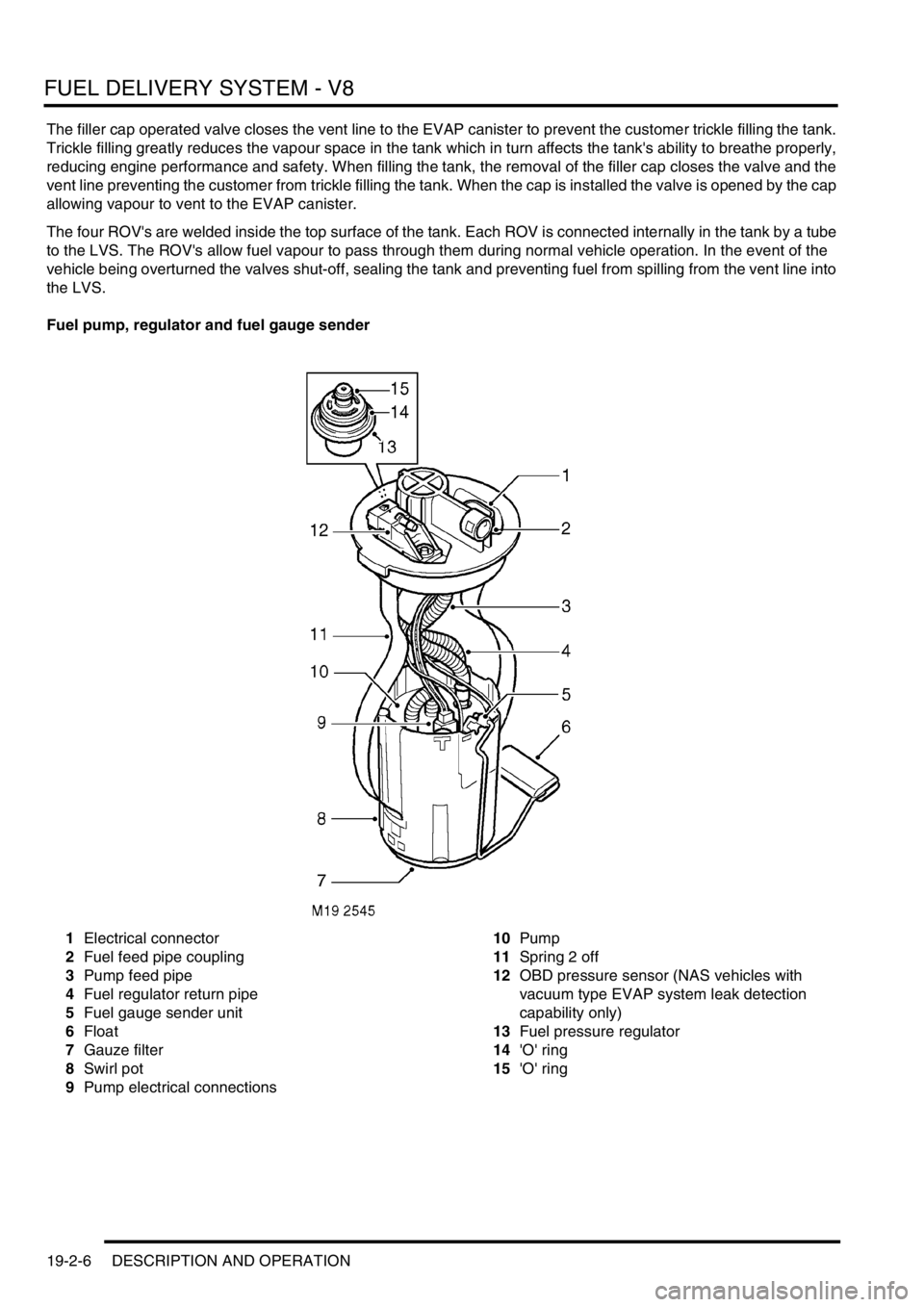
Fuel pump, regulator and fuel gauge sender
1Electrical connector
2Fuel feed pipe coupling
3Pump feed pipe
4Fuel regulator return pipe
5Fuel gauge sender unit
6Float
7Gauze filter
8Swirl pot
9Pump electrical connections10Pump
11Spring 2 off
12OBD pressure sensor (NAS vehicles with
vacuum type EVAP system leak detection
capability only)
13Fuel pressure regulator
14'O' ring
15'O' ring