oil LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 1499 of 1672

BODY CONTROL UNIT
86-3-30 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Fog lamps
The BCU operates the rear fog lamps and the front fog lamps (where fitted) via the IDM. The BCU front fog lamp
operation can be programmed to operate under one of three set conditions. The BCU will ensure the logical conditions
are satisfied for the lamps to operate under the set conditions.
Front fog lamps
Front fog lamp operation is monitored by the BCU, which allows only the front fog lamps to operate when the side
lamps or headlamps are on. When the side lamps, headlamps or ignition switch is turned off, the BCU also switches
off the fog lamps. When the side or headlamps are switched on again, the front fog lamps will remain off unless the
front fog lamp switch is pressed to resume operation. If the rear fog guard lamps are selected on, switching off the
front fog lamps will also switch off the rear fog guard lamps.
When the fog lamp switch is operated, an earth path is completed and the BCU allows the fog lights to be switched
on providing the logical preconditions have been satisfied. The BCU then supplies a voltage supply to the fog lamp
relay, to illuminate the fog lamps.
The front fog lamps option can be programmed in one of three states dependent on market/ customer requirements,
these are:
lOption 1– not fitted.
lOption 2 – main beam no effect.
lOption 3 – off with main beam.
The BCU checks the status of the following inputs to determine the logic action for providing an output to the front fog
lamp relay:
lIgnition state.
lMain beam state.
lSide lamps.
lDipped beam.
lFront fogs selected (press button, not latched).
If the ignition state is crank the state of the front fog relay is memorised and the relay is switched off. Pressing the
front fog switch during cranking will not be recognised. When the ignition state returns to Ignition after cranking, the
memorised front fog relay state is restored. If the ignition is turned off, the front fog relay is turned off.
For option 3 configuration, if the main beam is turned on the state of the front fog relay is memorised and the relay is
switched off. Pressing the front fog switch while main beam is on will not be recognised. When the Main beam state
returns to OFF, the memorised front fog relay state is restored.
In the event of a communications link failure while the front fog relay is on, the front fog relay will be switched off.
Rear fog lamps
The rear fog lamps operation is monitored by the BCU, which only allows the rear fog lamps to operate when the side
lamps or the headlamps are on. When the side lamps, headlamps or ignition is switched off, the rear fog lamps are
also switched off. When the side lamps or headlamps are switched on again, the rear fog lamps will not switch on
again unless reselected by operating the rear fog lamps switch. If front fog lamps are fitted, the rear fog lamps will be
switched off if the front fog lamps are switched off.
A supply voltage to the rear fog lamps relay is provided from a fuse in the passenger compartment fuse box, then
through two electronic switches in the IDM. With the lighting switch in the side lamp or headlamp position, an earth
path from the coil of the rear fog lamps relay completes the circuit through the two switches in the IDM to switch the
rear fog lamps on when the BCU receives a request signal from the rear fog lamps switch to turn the circuit on.
Page 1501 of 1672

BODY CONTROL UNIT
86-3-32 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Odometer update
The BCU can be programmed for one of two options:
lOption 1 – no odometer error warning.
lOption 2 – odometer error warning.
In order to provide an LCD flash request to the instrument pack via the communications link, the following inputs are
checked:
lIgnition state.
lInstrument pack odometer value (via the communications link).
lBCU odometer value.
The function is only active when the ignition state is on. The maximum allowed value is 999,999 miles (1,608,999
km).If the instrument pack odometer value is greater than the maximum allowed value, the maximum value is
assumed. The BCU odometer value is stored in EEPROM. If 16 identical values of the instrument pack odometer
reading is received consecutively, the instrument pack odometer value is compared with the BCU odometer value. If
the consecutive readings from the instrument pack differ, the BCU odometer value is incremented accordingly. If the
BCU odometer value is less than the instrument pack odometer value by up to 10 km, the BCU odometer value is set
equal to the instrument pack odometer value.
If the odometer warning option is enabled, and the contents of the instrument pack odometer value buffer is identical
to, or greater than BCU odometer value
± 10 km, the BCU sends an LED flash request to the instrument pack.
In the event of a communications link failure, this function will be unable to operate.
Gear position indicator illumination
On automatic gearbox models, two variations of illumination for the gear position indicators on the selector lever can
be programmed into the BCU. In option 1, illumination is provided when the ignition is on. In option 2, illumination is
enabled when the ignition is on and the side lamps are off.
Starter relay
The BCU checks the status of the following inputs and internal BCU conditions to determine whether or not to provide
an output to enable the starter relay:
lAutostart inhibit (vehicles with automatic gearbox only).
lSecurity start inhibit (immobilisation check).
lEngine running (link to instrument pack).
lEEPROM locked (internal check).
lIDM and BCU matched.
When the BCU receives a crank signal from the ignition switch, an earth path is completed to the starter relay coil,
provided that the security system has been de-activated. If the ECM has not received a valid unlock/ remobilise signal,
the starter relay will be disengaged and the engine stopped. The BCU also receives an engine running signal from
the instrument pack, so that if the ignition key is turned to the crank position while the engine is running, the starter
motor relay will not be engaged.
If the logic conditions are correct to allow starter operation, the completion of the earth path from the starter relay coil
to the BCU energises the coil and the relay contacts close to supply battery power to the starter motor.
When the ignition switch is released from the crank position, the power supply feed from the ignition switch to the
starter relay coil is interrupted and the relay contacts open to prevent further battery feed to the starter motor.
If a communications link failure is experienced, the BCU will be prevented from detecting the 'engine running'
condition and the BCU will default to assume that the engine is not running.
Page 1503 of 1672

BODY CONTROL UNIT
86-3-34 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The ignition key interlock option can be programmed in one of three states dependent on market/ customer
requirements, these are:
lOption 1– not fitted.
lOption 2 – normal operation.
lOption 3 – inhibit transfer box.
The BCU checks the status of the following inputs to determine the logic action for operating the ignition key interlock
solenoid:
lTransfer box neutral selected.
lGearbox state.
lTransit mode.
When the transit mode is on, the ignition key interlock solenoid is off.
Transfer box interlock (where fitted)
The transfer box interlock is controlled by the IDM to prevent transfer box shifter operation unless certain
preconditions have been satisfied.
The transfer box interlock prevents the transfer box being shifted from High or Low to neutral with the ignition key
removed from the ignition switch. When the BCU senses that the ignition key is removed from the ignition switch, it
signals the IDM via the serial data bus. The IDM then provides an earth path for the coil of the transfer box relay,
energising the relay coil and closing the relay contacts to provide a voltage supply to the transfer box interlock
solenoid.
A diode is included in the supply line to the solenoid to prevent residual current causing the solenoid to stick in the
energised position.
The transfer box solenoid interlock option can be programmed in one of three states dependent on market/ customer
requirements, these are:
lOption 1– not fitted.
lOption 2 – normal operation.
lOption 3 – inhibit transfer box.
The BCU checks the status of the following inputs to determine the logic action for employing the transfer box interlock
solenoid (transfer box solenoid enable):
lIgnition state.
lGearbox state.
In the event of a communications link failure occurring while the transfer box enable is on, the output will be switched
off.
Gear position switch
On automatic gearbox models, the BCU provides an output which supplies power to the automatic gearbox gear
position switch. The BCU checks for the following inputs before it supplies power:
lIgnition on.
lAuxiliary.
When the ignition is on, the feed to the gear position switch is on. When the ignition is off and auxiliary is off for more
than 30 seconds, feed to the gear position switch is off.
+ AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22 - 24, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Page 1512 of 1672

ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-4-3
1Theft deterrent LED
2Receiver
3Volumetric sensors
4Central door locking switch
5Body Control Unit (BCU)
6Bonnet activated alarm switch
7Vehicle horn
8Alarm sounder
9Fuel cut off switch
10Fuel flap release switch
11Door latch switches, drivers door key lock/
unlock switches
12Battery Backed Up Sounder (BBUS)
13Passive remobilisation exciter coil
Page 1520 of 1672

ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-4-11
Central door locking switches
A momentary action switch mounted on the fascia allows for central door locking/unlocking from within the vehicle.
The switch is mounted adjacent to the clock.
Input/Output
The input from the central door locking/unlocking switch to the BCU is either zero volts or an open circuit. Zero volts
indicates the switch is closed. An open circuit indicates that the switch is open. When the BCU sees an open circuit,
it pulls the input high internally.
The central door locking/unlocking switch has a dedicated signal input to the BCU. This allows the BCU to identify
the lock/ unlock request.
TestBook provides the ability to monitor the real time state of the central door locking/ unlocking switch.
Handset and receiver
The handset is incorporated in the key. It uses coded radio frequency signals to lock, unlock and super lock the vehicle
remotely with a range of up to 10 metres (33 ft). The handset also mobilises the vehicle by transmitting a
remobilisation signal when the handset is within range of the passive remobilisation exciter coil.
The receiver is located in front of the rear sunroof beneath the headlining. Signals transmitted by the handset are
distributed to the BCU via the receiver.
Input/Output
The BCU supplies the receiver with a 12 volts power supply. On receiving a valid signal from the handset, the receiver
transmits a 1000 baud signal to the BCU to allow locking/unlocking of the vehicle.
TestBook provides the ability to monitor the real time state of the remote receiver.
Page 1521 of 1672

ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
86-4-12 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Passive remobilisation exciter coil
The passive remobilisation exciter coil consists of a coil around the steering column lock. The coil energises to create
a magnetic field when the ignition is switched to position II.
This coil activates the handset initiating the mobilisation of the vehicle.
Input/Output
The input to the passive remobilisation exciter coil from the BCU is a 12 volts 125 kHz sinewave. The passive
remobilisation exciter coil also receives an ignition controlled power supply via fuse 20 (15 amperes) located in the
engine compartment fuse box. On receiving these signals, a magnetic field is generated which activates the handset
to produce a remobilisation signal. This remobilisation signal is transmitted to the remote receiver and onto the BCU
to allow the engine to start.
Page 1529 of 1672

ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
86-4-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Mislock
Mislock alerts the driver that a failed attempt has been made to lock the vehicle because of the doors or the bonnet
not being fully closed.
There are six audible configurations for mislock:
lNo audible warning.
lAlarm sounder.
lVehicle horn.
lAlarm sounder and vehicle horn.
lBBUS.
lAlarm sounder, vehicle horn and BBUS.
When a failed attempt has been made to lock the vehicle, the audible warning device is switched on for 50 ms and
off for 200 ms. The BCU allows the audible warning device to operate 3 times.
Passive immobilisation
Passive immobilisation prevents the vehicle from being started unless the authorised key is used to start the vehicle.
There are only two configurations for passive immobilisation:
lpassive immobilisation not active
lpassive immobilisation active
When the ignition is switched off, the vehicle remains mobilised for up to a maximum of 5 minutes. If however the
driver's door is opened, after 2 minutes 30 seconds, the vehicle remains in a mobilised state for a further 30 seconds.
When the timer in the BCU has expired, the vehicle is immobilised.
Once the ignition is switched on, the BCU transmits a coded signal to the ECM. If the coded signal does not
correspond to the programmed code in the ECM, the ECM is inhibited and the BCU inhibits the starting circuit.
In order for passive immobilisation to occur, the following conditions must be met:
lDriver's door closed.
lFuel cut-off switch not tripped.
lKey not inserted in ignition.
Passive remobilisation
Whenever the vehicle is immobilised, passive remobilisation of the engine occurs when the ignition is switched on,
allowing the vehicle to be started.
There are three configurations for passive remobilisation:
lPassive immobilisation not active.
lPassive immobilisation active.
lEKA with super locking on receiving good passive remobilisation exciter coil signal.
The BCU controls the passive remobilisation exciter coil (located around the ignition barrel) to generate a magnetic
field which causes the handset to transmit a remobilisation signal. The BCU receives the signal and allows the vehicle
to be started. If a valid signal from the handset is not received within one minute of the ignition being switched to
position II, the BCU stops the passive coil from generating the magnetic field.
Page 1530 of 1672

ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-4-21
Emergency key access
If the handset fails to operate, the engine can be remobilised by using the key to enter a unique four digit Emergency
Key Access (EKA) code.
There are three configurations for emergency key access:
lEKA not active (no immobiliser fitted).
lEKA active.
lEKA with super locking on receiving good passive remobilisation exciter coil signal.
The code is recorded on the security information card and is entered as follows:
1Using the key, turn the driver's door lock to the UNLOCK position and hold in this position for at least 5 seconds.
An audible warning is then emitted to indicate that the body control unit is ready to accept the code. Return the
key to the centre position. It is now possible to use the key to enter the separate numerical values of the four
digits that make up the EKA code.
2Enter the first digit of the code. If the first digit is 4, turn the key to the UNLOCK position 4 times. Ensure the
key is fully returned to the centre position after each turn of the key.
3Enter the second digit of the code. If the second digit is 3, turn the key to the LOCK position 3 times. Ensure
the key is fully returned to the centre position after each turn of the key.
4Enter the third digit of the code. If the third digit is 2, turn the key to the UNLOCK position twice. Ensure the key
is fully returned to the centre position after each turn of the key.
5Enter the fourth digit of the code. If the fourth digit is 1, turn the key to the LOCK position once. Ensure the key
is fully returned to the centre position after each turn of the key.
6Finally, turn the key to the UNLOCK position and back to the centre position, a double bleep will indicate that
the code has been entered correctly. A single bleep indicates that the code has been entered incorrectly.
Then, before opening the door, wait 5 minutes for the alarm and immobiliser to be de-activated. During the 5
minute wait for the alarm and immobiliser to be de-activated, the alarm indicator LED in the instrument pack
continues to flash (one flash every 2 seconds). DO NOT OPEN THE DOOR OR ATTEMPT TO ENTER THE
CAR until the full delay period has elapsed.
When the 5 minute wait has elapsed, the alarm indicator LED stops flashing. Immediately open the door, insert
the key in the ignition switch and turn the switch to position II. If the ignition switch is not turned to position II
within 30 seconds of the end of the 5 minute wait, the engine is automatically immobilised again.
The EKA code will not be recognised if there is an interval of 10 seconds or more between key turns or if the key is
held turned for 5 seconds or more during the procedure.
In some system configurations a successful EKA code entry is indicated by the audible warning device pulsing twice
for a period of 50 ms on, 200 ms off. The theft deterrent LED is switched on for 1 second, all doors unlock, the alarm
disarms and the vehicle is remobilised allowing the engine to start.
If an incorrect code is entered, an audible warning is emitted and the procedure must be repeated. Up to a maximum
of 10 attempts to enter the code is possible. After 10 attempts, the BCU will not allow any further codes to be entered
for a period of 10 minutes.
Single point entry
Single point entry (SPE) allows the driver to unlock the driver's door while leaving all other doors locked.
There are two configurations for single point entry:
lSPE not active.
lSPE active.
To use SPE, press the unlock button on the handset once. Depressing the unlock button a second time in the space
of one minute unlocks the remaining doors. SPE is also possible by turning the key in the driver's door lock to the
unlock position once. Turning the key to the unlock position again within one minute unlocks the remaining doors.
In order for SPE to operate, the following conditions must be met:
lThe ignition is off.
lAll doors are locked.
Page 1538 of 1672
ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN
REPAIR 86-4-29
Coil - passive immobilisation
$% 86.77.35
Remove
1.Remove steering column nacelle.
+ STEERING, REPAIRS, Nacelle -
steering column.
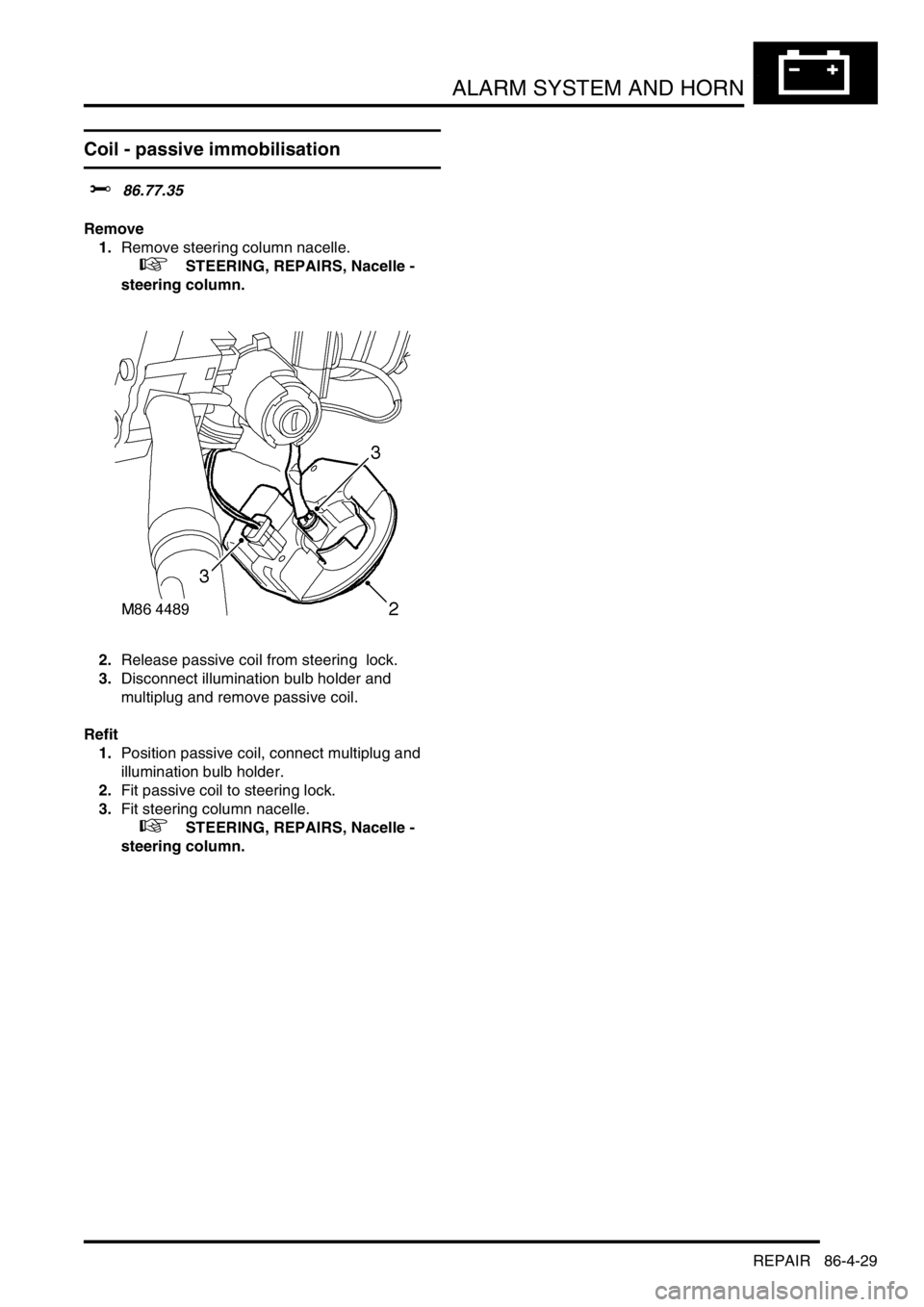
2.Release passive coil from steering lock.
3.Disconnect illumination bulb holder and
multiplug and remove passive coil.
Refit
1.Position passive coil, connect multiplug and
illumination bulb holder.
2.Fit passive coil to steering lock.
3.Fit steering column nacelle.
+ STEERING, REPAIRS, Nacelle -
steering column.
Page 1546 of 1672

WINDOWS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-5-7
Rear window lift relay
The rear window lift relay is a normally open relay that provides power to the rear window system. It is controlled by
the IDM. The IDM receives a rear window enable signal from the BCU to allow operation during the ignition switched-
off timeout period.
Both the rear window lift relay and the IDM are located in the passenger compartment fusebox. The IDM is integral
to the passenger compartment fusebox.
The rear window lift relay receives voltage from fuse 13 (30A) in the passenger compartment fusebox. The IDM
controls the earth side of the relay coil.
TestBook cannot monitor the status of the rear window lift relay.