ECO mode LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 9 of 1672

CONTENTS
6CONTENTS
EGR systems .................................................................................................................................. 17-1-10
REPAIRS
Modulator - EGR ........................................................................................................................... 17-1-13
Inlet Throttle (ILT) Modulator .......................................................................................................... 17-1-13
Valve - EGR - Pre EU3 models ...................................................................................................... 17-1-14
Valve - EGR - EU3 models ............................................................................................................. 17-1-15
EMISSION CONTROL - V8 ....................................................................... 17-2-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Crankcase emission control system ............................................................................................... 17-2-1
Exhaust emission control ................................................................................................................ 17-2-2
Evaporative emission system component layout ............................................................................ 17-2-3
Evaporative emission system (with positive pressure leak detection) component layout (NAS only) 17-2-4
Evaporative emission system control diagram ............................................................................... 17-2-5
Secondary air injection system component layout.......................................................................... 17-2-6
Secondary air injection system control diagram ............................................................................. 17-2-8
Emission Control Systems .............................................................................................................. 17-2-9
Crankcase emission control system ............................................................................................... 17-2-9
Exhaust emission control system ................................................................................................... 17-2-10
Evaporative emission control system ............................................................................................. 17-2-15
Secondary air injection system ....................................................................................................... 17-2-26
Crankcase emission control operation............................................................................................ 17-2-33
Exhaust emission control operation ................................................................................................ 17-2-34
Evaporative emission control operation .......................................................................................... 17-2-38
Secondary air injection system ....................................................................................................... 17-2-42
REPAIRS
Canister - EVAP ............................................................................................................................ 17-2-43
Canister - EVAP - Models with Fuel Leak Detection Pump - up to 03MY ...................................... 17-2-43
Canister - EVAP - Models with Fuel Leak Detection Pump - from 03MY ....................................... 17-2-44
Valve - purge control ..................................................................................................................... 17-2-46
Solenoid - evap canister vent solenoid (CVS) valve ..................................................................... 17-2-46
Sensor - heated oxygen (HO2S) - pre-catalytic converter .............................................................. 17-2-47
Sensor - heated oxygen (HO2S) - post-catalytic converter ............................................................ 17-2-48
Control Valve - Secondary Air Injection (SAI) ............................................................................... 17-2-49
Reservoir - Vacuum - Secondary Air Injection (SAI) - up to 03MY ................................................. 17-2-49
Reservoir - vacuum - Secondary Air Injection (SAI) - from 03MY .................................................. 17-2-50
Pump - Air - Secondary Air Injection (SAI) ..................................................................................... 17-2-50
Air Manifold - LH - Secondary Air Injection (SAI) ........................................................................... 17-2-51
Air Manifold - RH - Secondary Air Injection (SAI) .......................................................................... 17-2-51
Solenoid - Vacuum - Secondary Air Injection (SAI) ...................................................................... 17-2-52
Pipe - Secondary Air Injection (SAI) .............................................................................................. 17-2-52
Pump - Fuel Leak Detection - up to 03MY...................................................................................... 17-2-54
Pump - fuel leak detection - from 03MY ......................................................................................... 17-2-54
Filter - fuel leak detection pump - up to 03MY ................................................................................ 17-2-55
Filter - fuel leak detection pump - from 03MY ................................................................................. 17-2-55
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - Td5 ................................................ 18-1-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Engine management component location - passenger compartment ............................................ 18-1-2
Engine management component location - engine compartment .................................................. 18-1-3
Engine management block diagram ............................................................................................... 18-1-4
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 18-1-6
Page 24 of 1672

CONTENTS
CONTENTS 21
PAINTING ................................................................................................ 77-5-1
PROCEDURES
Panel preparation............................................................................................................................ 77-5-1
Paint preparation............................................................................................................................. 77-5-2
HEATING AND VENTILATION................................................................. 80-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Heating and ventilation component layout ...................................................................................... 80-1
Fuel burning heater component layout ........................................................................................... 80-2
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 80-3
Operation ........................................................................................................................................ 80-13
REPAIRS
Heater control and fan switch ....................................................................................................... 80-15
Cables - heater control .................................................................................................................. 80-15
Servo - recirculation flap ............................................................................................................... 80-17
Switch - recirculation control ......................................................................................................... 80-18
Servo - air distribution control ........................................................................................................ 80-19
Servo - air temperature control ....................................................................................................... 80-20
Plenum Air Intake ........................................................................................................................... 80-20
Heater assembly - models without air conditioning ......................................................................... 80-21
Heater assembly - models with air conditioning .............................................................................. 80-23
Blower assembly ............................................................................................................................ 80-25
Motor - blower ............................................................................................................................. 80-26
Resistor pack - power resistor A/C ............................................................................................... 80-27
Heater matrix ................................................................................................................................ 80-28
Pipe - Heater - Feed ...................................................................................................................... 80-29
Pipe - Heater - Return .................................................................................................................... 80-29
Fuel burning heater - (FBH) - Td5................................................................................................... 80-30
AIR CONDITIONING ................................................................................. 82-1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
A/C refrigerant system component layout ....................................................................................... 82-1
A/C control system component layout ............................................................................................ 82-2
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 82-3
Operation ........................................................................................................................................ 82-18
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Rear A/C refrigerant system component layout .............................................................................. 82-23
Rear A/C distribution and control component layout ....................................................................... 82-24
Description ...................................................................................................................................... 82-25
Operation ........................................................................................................................................ 82-27
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY, RECYCLING AND RECHARGING
Refrigerant recovery, recycling and recharging .............................................................................. 82-29
REPAIRS
Compressor - diesel ........................................................................................................................ 82-31
Compressor - V8 ............................................................................................................................. 82-32
Fan - condenser ............................................................................................................................ 82-33
Page 33 of 1672
INTRODUCTION
01-4
HRW Heated Rear Window
HSLA High Strength Low Alloy
ht/HT High tension
IACV Idle Air Control Valve
IAT Intake Air Temperature
ICE In-Car Entertainment
i.dia. Internal diameter
IDM Intelligent Driver Module
IF Intermediate Frequency
in
3Cubic inch
ILT Inlet Throttle
IPW Injector Pulse Width
ISO International Organisation for
Standardisation
ITS Inflatable Tubular Structure
k Thousand
kg Kilogramme
kg/h Kilogrammes per hour
km Kilometre
km/h Kilometres per hour
kPa KiloPascal
KS Knock Sensor
lb(s) Pounds
lbf Pounds force
lbf.in Pounds force inches
lbf/in
2Pounds per square inch
lbf.ft Pounds force feet
λLambda
lc Low compression
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
LEV Low Emission Vehicle
LH Left-Hand
LHD Left-Hand Drive
LSM Light Switch Module
LVS Liquid Vapour Separator
mMetre
µMicro
MAF Mass Air Flow
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure
MET Mechanical, Electrical and Trim
MFU Multi-Function Unit
MFL Multi-Function Logic
max. Maximum
MEMS Modular Engine Management
System
MIG Metal/Inert Gas
MIL Malfunction Indicator Lamp
MPa MegaPascal
MOSFET Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field
Effect Transistor
min. Minimum
- Minus (tolerance)
' Minute (angle)
mm Millimetre
mph Miles per hour MPi Multi-Point injection
MV Motorised Valve
MY Model Year
NAS North American Specification
(-) Negative (electrical)
Nm Newton metre
No. Number
NO
2Nitrogen Dioxide
NO
xOxides of Nitrogen
NTC Negative Temperature
Coefficient
NRV Non Return Valve
OBD On Board Diagnostics
OBM On Board Monitoring
o.dia. Outside diameter
OAT Organic Acid Technology
ORM Off-road Mode
ΩOhm
PAS Power Assisted Steering
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PCV Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PDC Parking Distance Control
PDOP Position Dilation Of Precision
PI Programme Information
PPS Pulse Per Second
PS Programme Service
psi Pounds per square inch
pts. Pints
% Percentage
+ Plus (tolerance) or Positive
(electrical)
±Plus or minus (tolerance)
PTC Positive Temperature Coefficient
PTFE Polytetrafluorethylene
PVC Polyvinyl chloride
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
RDS Radio Data Service
rRadius
:Ratio
ref Reference
REG Regionalisation
RES Rover Engineering Standards
rev/min Revolutions per minute
RF Radio Frequency
RGB Red / Green / Blue
RH Right-Hand
RHD Right-Hand Drive
ROM Read Only Memory
RON Research Octane Number
ROV Roll Over Valve
ROW Rest Of World
SAE Society of Automotive Engineers
SAI Secondary Air Injection
" Second (angle)
SLABS Self Levelling and Anti-Lock
Brake System
SLS Self Levelling Suspension
SOHC Single Overhead Camshaft
Page 36 of 1672

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-1
GENERAL INFORMATION
General Precautions
Dangerous substances
Modern vehicles contain many materials and liquids
which if not handled with care can be hazardous to
both personal health and the environment.
WARNING: Many liquids and other substances
used in motor vehicles are poisonous and should
under no circumstances be consumed and
should, as far as possible, be kept from contact
with the skin. These liquids and substances
include acid, anti-freeze, asbestos, brake fluid,
fuel, windscreen washer additives, lubricants,
refrigerants and various adhesives.
Always read carefully the instructions printed on
labels or stamped on components and obey them
implicitly. Such instructions are included for
reasons of your health and personal safety.
Never disregard them.
Synthetic rubber
Many 'O' rings, seals, hoses, flexible pipes and other
similar items which appear to be natural rubber, are
in fact, made of synthetic materials called
Fluoroelastomers. Under normal operating
conditions this material is safe and does not present
a health hazard. However, if the material is damaged
by fire or excessive heating, it can break down and
produce highly corrosive Hydrofluoric acid.
Contact with Hydrofluoric acid can cause serious
burns on contact with skin. If skin contact does occur:
lRemove any contaminated clothing
immediately.
lIrrigate effected area of skin with a copious
amount of cold water or limewater for 15 to 60
minutes.
lObtain medical assistance immediately.
Should any material be in a burnt or overheated
condition, handle with extreme caution and wear
protective clothing (seamless industrial gloves,
protective apron etc.).
Decontaminate and dispose of gloves immediately
after use.Lubricating oils
Avoid excessive skin contact with used lubricating
oils and always adhere to the health protection
precautions.
WARNING: Avoid excessive skin contact with
used engine oil. Used engine oil contains
potentially harmful contaminants which may
cause skin cancer or other serious skin
disorders.
WARNING: Avoid excessive skin contact with
mineral oil. Mineral oils remove the natural fats
from the skin, leading to dryness, irritation and
dermatitis.
Health protection precautions
The following precautions should be observed at all
times.
lWear protective clothing, including impervious
gloves where practicable.
lAvoid prolonged and repeated contact with oils,
particularly used engine oils.
lDo not put oily rags in pockets.
lAvoid contaminating clothes (particularly those
next to the skin) with oil.
lOveralls must be cleaned regularly. Discard
heavily soiled clothing and oil impregnated
footwear.
lFirst aid treatment should be obtained
immediately for open cuts and wounds.
lApply barrier creams before each work period to
help prevent lubricating oil from contaminating
the skin.
lWash with soap and water to ensure all oil is
removed (proprietary skin cleansers and nail
brushes will help).
lUse moisturisers after cleaning; preparations
containing lanolin help replace the skin's natural
oils which have been removed.
lDo not use petrol/gasoline, kerosene, diesel
fuel, oil, thinners or solvents for cleaning skin.
lWhere practicable, degrease components prior
to handling.
lIf skin disorders develop, obtain medical advice
without delay.
lWear eye protection (e.g. goggles or face
shield) if there is a risk of eye contamination.
Eye wash facilities should be provided in close
vicinity of the work area.
Page 151 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
12-1-12 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The Td5 diesel engine is a 2.5 litre, 5 cylinder, in-line direct injection unit having 2 valves per cylinder, operated by a
single overhead camshaft. The engine emissions, on pre EU3 models, comply with ECD2 (European Commission
Directive) and on EU3 models, comply with ECD3 legislative requirements. Both models employ electronic engine
management control, positive crankcase ventilation and exhaust gas recirculation to limit the emission of pollutants.
The unit is water cooled and turbo-charged and is controlled by an electronic engine management system.
The engine is a monobloc cast iron construction with an aluminium stiffening plate fitted to the bottom of the cylinder
block to improve lower structure rigidity. The cylinder head and sump are cast aluminium. An acoustic cover is fitted
over the upper engine to reduce engine generated noise.
The engine utilises the following features:
lElectronic Unit Injectors (EUI's) controlled by an Engine Management System for precise fuel delivery under
all prevailing operating conditions.
lTurbocharging which delivers compressed air to the combustion chambers via an intercooler for improved
power output.
lFuel Cooler
lOil Cooler
lCentrifuge Oil Filter
lHydraulic Lash Adjusters with independent finger followers
Cylinder block components
The cylinder block components are described below:
Cylinder Block
The cylinders and crankcase are contained in a single cast iron construction. The cylinders are direct bored and
plateau honed with lubrication oil supplied via lubrication jets for piston and gudgeon pin lubrication and cooling. It is
not possible to rebore the cylinder block if the cylinders become worn or damaged. Three metal core plugs are fitted
to the three centre cylinders on the right hand side of the cylinder block.
Lubrication oil is distributed throughout the block via the main oil gallery to critical moving parts through channels
bored in the block which divert oil to the main and big-end bearings via oil holes machined into the crankshaft. Oil is
also supplied from the cylinder block main gallery to the five lubrication jets which cool and lubricate the piston and
gudgeon pins. Plugs are used to seal both ends of the main oil gallery at front and rear of the engine block. An oil
cooler is fitted to the LH side of the engine block; ports in the oil cooler assembly mate with ports in the cylinder block
to facilitate coolant flow. Oil is diverted through the oil cooler, centrifuge filter and full-flow filter before supplying the
main oil gallery. A tapping in the oil filter housing provides a lubrication source for the turbocharger bearings and an
oil pressure switch is included in a tapping in the oil cooler housing which determines whether sufficient oil pressure
is available to provide engine lubrication and cooling.
Cylinder cooling is achieved by water circulating through chambers in the engine block casting. A threaded coolant
jacket plug is located at the front RH side of the cylinder block.
Cast mounting brackets are bolted to both sides of the engine block for mounting the engine to the chassis on the LH
and RH hydramount studs.
The gearbox bolts directly to the engine block; a gearbox shim plate is located between the adjoining faces of the
gearbox and the flywheel side of the engine block and is fixed to the rear of the engine block by two bolts. Two hollow
metal dowels locate the rear of the cylinder block to the gearbox shim plate. The gearbox casing provides the
mounting for the starter motor.
A port is included at the rear left hand side of the cylinder block which connects to the turbocharger oil drain pipe to
return lubrication oil to the sump.
A plug sealing the lubrication cross-drilling gallery is located at the front right hand side of the cylinder block and plugs
for the main lubrication gallery is included at the front and rear of the cylinder block.
Page 160 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-1-21
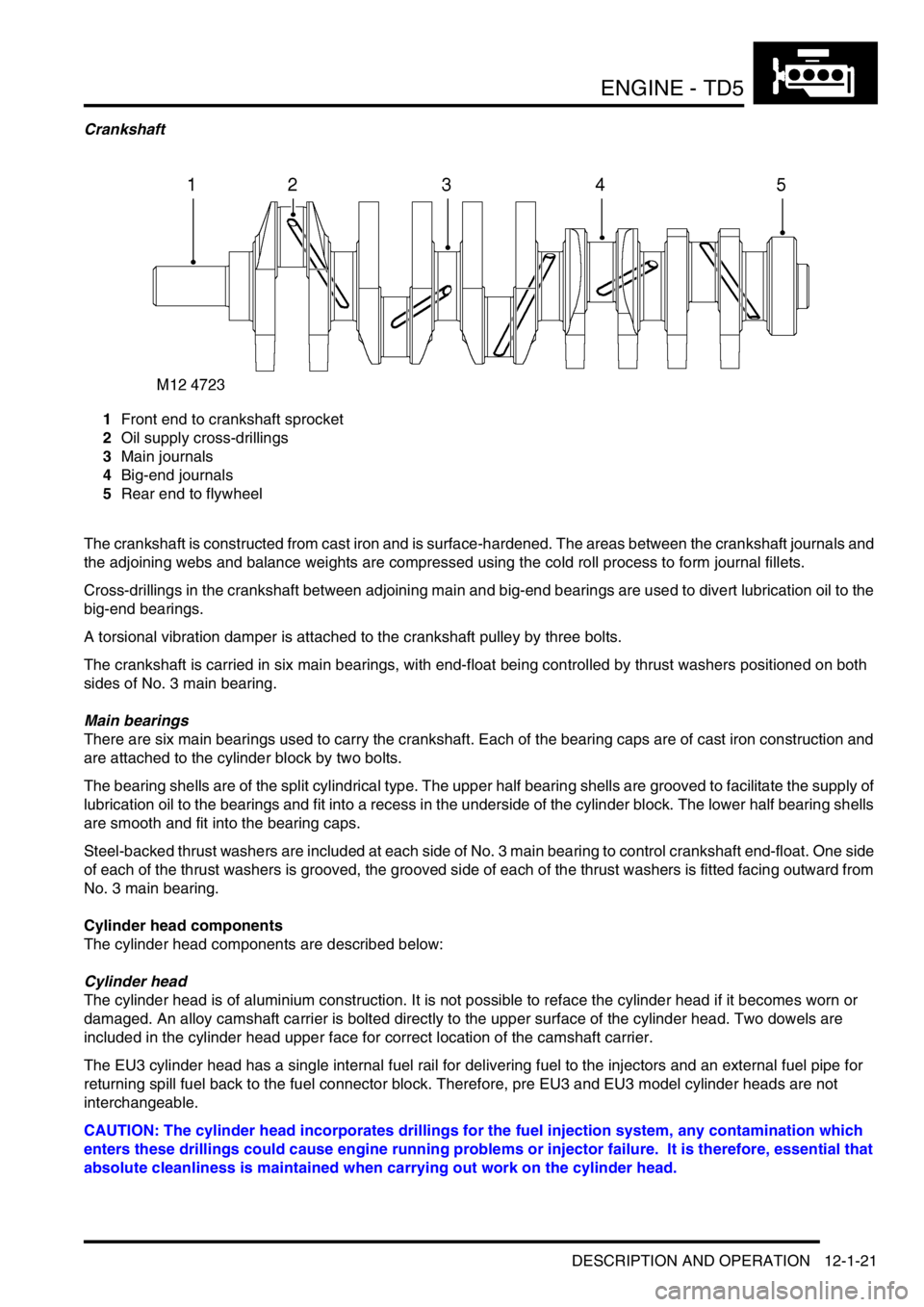
Crankshaft
1Front end to crankshaft sprocket
2Oil supply cross-drillings
3Main journals
4Big-end journals
5Rear end to flywheel
The crankshaft is constructed from cast iron and is surface-hardened. The areas between the crankshaft journals and
the adjoining webs and balance weights are compressed using the cold roll process to form journal fillets.
Cross-drillings in the crankshaft between adjoining main and big-end bearings are used to divert lubrication oil to the
big-end bearings.
A torsional vibration damper is attached to the crankshaft pulley by three bolts.
The crankshaft is carried in six main bearings, with end-float being controlled by thrust washers positioned on both
sides of No. 3 main bearing.
Main bearings
There are six main bearings used to carry the crankshaft. Each of the bearing caps are of cast iron construction and
are attached to the cylinder block by two bolts.
The bearing shells are of the split cylindrical type. The upper half bearing shells are grooved to facilitate the supply of
lubrication oil to the bearings and fit into a recess in the underside of the cylinder block. The lower half bearing shells
are smooth and fit into the bearing caps.
Steel-backed thrust washers are included at each side of No. 3 main bearing to control crankshaft end-float. One side
of each of the thrust washers is grooved, the grooved side of each of the thrust washers is fitted facing outward from
No. 3 main bearing.
Cylinder head components
The cylinder head components are described below:
Cylinder head
The cylinder head is of aluminium construction. It is not possible to reface the cylinder head if it becomes worn or
damaged. An alloy camshaft carrier is bolted directly to the upper surface of the cylinder head. Two dowels are
included in the cylinder head upper face for correct location of the camshaft carrier.
The EU3 cylinder head has a single internal fuel rail for delivering fuel to the injectors and an external fuel pipe for
returning spill fuel back to the fuel connector block. Therefore, pre EU3 and EU3 model cylinder heads are not
interchangeable.
CAUTION: The cylinder head incorporates drillings for the fuel injection system, any contamination which
enters these drillings could cause engine running problems or injector failure. It is therefore, essential that
absolute cleanliness is maintained when carrying out work on the cylinder head.
Page 257 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
12-2-14 REPAIRS
Gasket - cylinder head - LH
$% 12.29.02
Remove
1.Remove inlet manifold gasket.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Gasket - inlet
manifold - lower.
2.Noting their fitted order, disconnect ht leads
from spark plugs.
3.Remove bolt securing engine harness to rear
of cylinder head.
4. LH drive models: Remove brake servo heat
shield.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Heat shield -
brake servo - Without Secondary Air
Injection.
5.Remove 8 bolts securing exhaust manifold to
cylinder head, release manifold and collect 2
gaskets.6.Progressively remove 4 bolts securing the
rocker shaft and remove rocker shaft.
7.Remove push rods. Store push rods in their
fitted order.
8. Models with SAI: Remove 2 air injection
adapters from cylinder head and discard.
9.In the sequence shown, remove 10 bolts
securing the cylinder head to block. Discard the
bolts.
Page 259 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
12-2-16 REPAIRS
17. LH drive models: Fit brake servo heat shield.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Heat shield -
brake servo - Without Secondary Air
Injection.
18.Fit engine harness bolt and tighten to 22 Nm
(16 lbf.ft).
19.Connect ht leads to spark plugs in their correct
fitted order.
20.Fit inlet manifold gasket.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Gasket - inlet
manifold - lower.
Gasket - cylinder head - RH
$% 12.29.03
Remove
1.Remove inlet manifold gasket.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Gasket - inlet
manifold - lower.
2.Remove bolt securing auxiliary drive belt
tensioner and remove tensioner.
3.Remove 4 bolts securing alternator mounting
bracket and remove bracket.
4.Noting their fitted order, disconnect ht leads
from spark plugs.
5.Remove bolt securing engine earth lead.
Page 260 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
REPAIRS 12-2-17
6. RH drive models: Remove brake servo heat
shield.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Heat shield -
brake servo - Without Secondary Air
Injection.
7.Remove 8 bolts securing exhaust manifold to
cylinder head, release manifold and collect 2
gaskets.
8.Progressively remove 4 bolts securing the
rocker shaft and remove rocker shaft.
9.Remove push rods. Store push rods in their
fitted order. 10. Models with SAI: Remove 2 air injection
adapters and discard.
11.In the sequence shown, remove 10 bolts
securing the cylinder head to block. Discard the
bolts.
12.Remove cylinder head.
CAUTION: Support both ends of cylinder
head on blocks of wood.
13.Remove cylinder head gasket.
Page 261 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
12-2-18 REPAIRS
Refit
1.Clean mating faces of cylinder block and head
using suitable gasket removal spray and a
plastic scraper, ensure that bolt holes in block
are clean and dry. Clean mating faces of
cylinder head and exhaust manifold.
CAUTION: Do not use a metal scraper or
machined surfaces may be damaged.
2.Check head and block faces for warping and
pitting. If out of specification, renew head.
3.Fit cylinder head gasket with the word 'TOP'
uppermost.
CAUTION: Gaskets must be fitted dry.
4.Carefully fit cylinder head and locate on
dowels.
5.Lightly lubricate new cylinder head bolt threads
with clean engine oil.
6.Noting that bolts 1, 3 and 5 are longer than the
remainder, fit bolts and tighten in the sequence
shown to 20 Nm (15 lbf.ft) then 90
°, and finally
a further 90
°.
CAUTION: Do not tighten bolts 180
° in one
operation.
7. Models with SAI: Fit new air injection adapters
and tighten to 33 Nm (24 lbf.ft).
8.Clean push rods.
9.Lubricate ends of push rods with clean engine
oil.
10.Fit push rods in their removed order.
11.Clean bases of rocker pillars and mating faces
on cylinder head.
12.Clean contact surfaces on rockers, valves and
push rods.
13.Lubricate contact surfaces and rocker shaft
with clean engine oil.
14.Fit rocker shaft assembly and engage push
rods.
15.Fit rocker shaft bolts and progressively tighten
to 40 Nm (30 lbf.ft). 16.Position alternator mounting bracket, fit bolts
and tighten to 40 Nm (30 lbf.ft).
17.Position auxiliary drive belt tensioner, fit bolt
and tighten to 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
18.Connect ht leads to spark plugs in their fitted
order.
19. Using new gaskets, fit exhaust manifold to
cylinder head. Fit bolts and using sequence
shown, tighten initially to 15 Nm (11 lbf.ft), then
finally tighten to 36 Nm (28 lbf.ft).
20. RH drive models: Fit brake servo heat shield.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Heat shield -
brake servo - Without Secondary Air
Injection.
21.Position engine earth lead, fit bolt and tighten to
22 Nm (16 lbf.ft).
22.Fit inlet manifold gasket.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Gasket - inlet
manifold - lower.