ABS LAND ROVER FREELANDER 2001 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: FREELANDER, Model: LAND ROVER FREELANDER 2001Pages: 1007, PDF Size: 23.47 MB
Page 9 of 1007
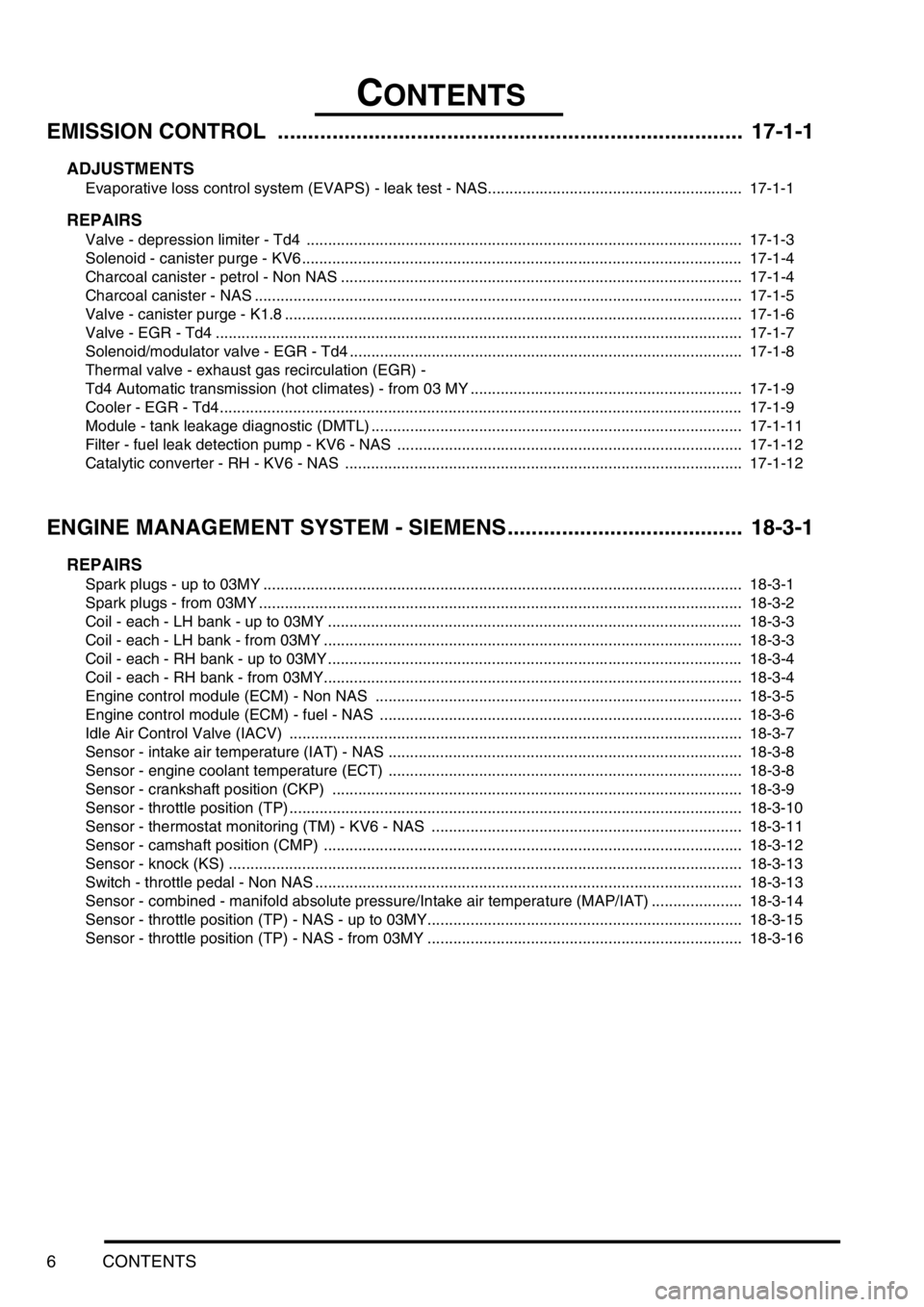
CONTENTS
6CONTENTS
EMISSION CONTROL ............................................................................. 17-1-1
ADJUSTMENTS
Evaporative loss control system (EVAPS) - leak test - NAS........................................................... 17-1-1
REPAIRS
Valve - depression limiter - Td4 ..................................................................................................... 17-1-3
Solenoid - canister purge - KV6 ...................................................................................................... 17-1-4
Charcoal canister - petrol - Non NAS ............................................................................................. 17-1-4
Charcoal canister - NAS ................................................................................................................. 17-1-5
Valve - canister purge - K1.8 .......................................................................................................... 17-1-6
Valve - EGR - Td4 .......................................................................................................................... 17-1-7
Solenoid/modulator valve - EGR - Td4 ........................................................................................... 17-1-8
Thermal valve - exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) -
Td4 Automatic transmission (hot climates) - from 03 MY ............................................................... 17-1-9
Cooler - EGR - Td4 ......................................................................................................................... 17-1-9
Module - tank leakage diagnostic (DMTL) ...................................................................................... 17-1-11
Filter - fuel leak detection pump - KV6 - NAS ................................................................................ 17-1-12
Catalytic converter - RH - KV6 - NAS ............................................................................................ 17-1-12
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - SIEMENS....................................... 18-3-1
REPAIRS
Spark plugs - up to 03MY ............................................................................................................... 18-3-1
Spark plugs - from 03MY ................................................................................................................ 18-3-2
Coil - each - LH bank - up to 03MY ................................................................................................ 18-3-3
Coil - each - LH bank - from 03MY ................................................................................................. 18-3-3
Coil - each - RH bank - up to 03MY ................................................................................................ 18-3-4
Coil - each - RH bank - from 03MY................................................................................................. 18-3-4
Engine control module (ECM) - Non NAS ..................................................................................... 18-3-5
Engine control module (ECM) - fuel - NAS .................................................................................... 18-3-6
Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) ......................................................................................................... 18-3-7
Sensor - intake air temperature (IAT) - NAS .................................................................................. 18-3-8
Sensor - engine coolant temperature (ECT) .................................................................................. 18-3-8
Sensor - crankshaft position (CKP) ............................................................................................... 18-3-9
Sensor - throttle position (TP) ......................................................................................................... 18-3-10
Sensor - thermostat monitoring (TM) - KV6 - NAS ........................................................................ 18-3-11
Sensor - camshaft position (CMP) ................................................................................................. 18-3-12
Sensor - knock (KS) ....................................................................................................................... 18-3-13
Switch - throttle pedal - Non NAS ................................................................................................... 18-3-13
Sensor - combined - manifold absolute pressure/Intake air temperature (MAP/IAT) ..................... 18-3-14
Sensor - throttle position (TP) - NAS - up to 03MY......................................................................... 18-3-15
Sensor - throttle position (TP) - NAS - from 03MY ......................................................................... 18-3-16
Page 28 of 1007
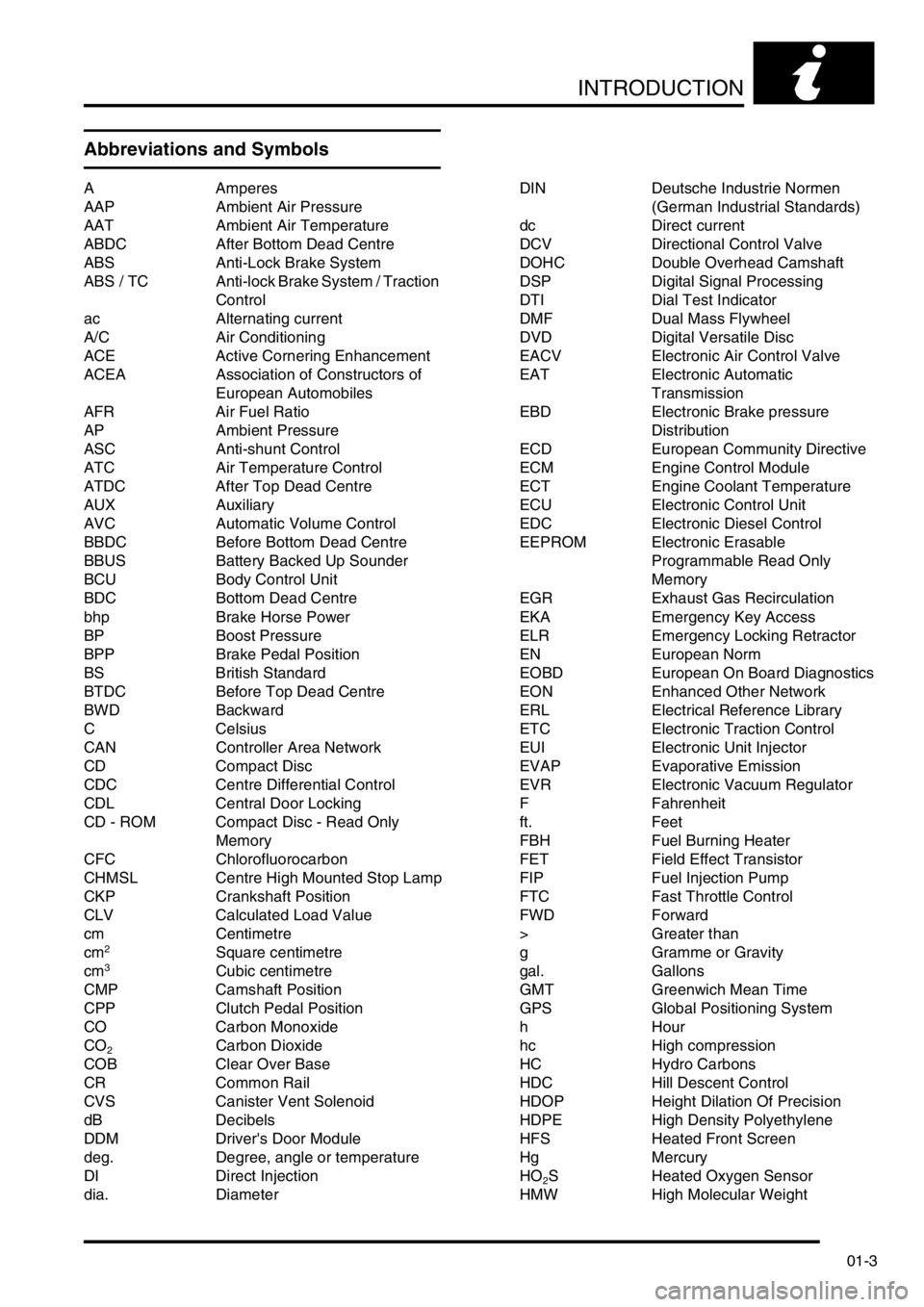
INTRODUCTION
01-3
Abbreviations and Symbols
A Amperes
AAP Ambient Air Pressure
AAT Ambient Air Temperature
ABDC After Bottom Dead Centre
ABS Anti-Lock Brake System
ABS / TC Anti-lock Brake System / Traction
Control
ac Alternating current
A/C Air Conditioning
ACE Active Cornering Enhancement
ACEA Association of Constructors of
European Automobiles
AFR Air Fuel Ratio
AP Ambient Pressure
ASC Anti-shunt Control
ATC Air Temperature Control
ATDC After Top Dead Centre
AUX Auxiliary
AVC Automatic Volume Control
BBDC Before Bottom Dead Centre
BBUS Battery Backed Up Sounder
BCU Body Control Unit
BDC Bottom Dead Centre
bhp Brake Horse Power
BP Boost Pressure
BPP Brake Pedal Position
BS British Standard
BTDC Before Top Dead Centre
BWD Backward
C Celsius
CAN Controller Area Network
CD Compact Disc
CDC Centre Differential Control
CDL Central Door Locking
CD - ROM Compact Disc - Read Only
Memory
CFC Chlorofluorocarbon
CHMSL Centre High Mounted Stop Lamp
CKP Crankshaft Position
CLV Calculated Load Value
cm Centimetre
cm
2Square centimetre
cm3Cubic centimetre
CMP Camshaft Position
CPP Clutch Pedal Position
CO Carbon Monoxide
CO
2Carbon Dioxide
COB Clear Over Base
CR Common Rail
CVS Canister Vent Solenoid
dB Decibels
DDM Driver's Door Module
deg. Degree, angle or temperature
DI Direct Injection
dia. DiameterDIN Deutsche Industrie Normen
(German Industrial Standards)
dc Direct current
DCV Directional Control Valve
DOHC Double Overhead Camshaft
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DTI Dial Test Indicator
DMF Dual Mass Flywheel
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
EACV Electronic Air Control Valve
EAT Electronic Automatic
Transmission
EBD Electronic Brake pressure
Distribution
ECD European Community Directive
ECM Engine Control Module
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature
ECU Electronic Control Unit
EDC Electronic Diesel Control
EEPROM Electronic Erasable
Programmable Read Only
Memory
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EKA Emergency Key Access
ELR Emergency Locking Retractor
EN European Norm
EOBD European On Board Diagnostics
EON Enhanced Other Network
ERL Electrical Reference Library
ETC Electronic Traction Control
EUI Electronic Unit Injector
EVAP Evaporative Emission
EVR Electronic Vacuum Regulator
F Fahrenheit
ft. Feet
FBH Fuel Burning Heater
FET Field Effect Transistor
FIP Fuel Injection Pump
FTC Fast Throttle Control
FWD Forward
> Greater than
g Gramme or Gravity
gal. Gallons
GMT Greenwich Mean Time
GPS Global Positioning System
hHour
hc High compression
HC Hydro Carbons
HDC Hill Descent Control
HDOP Height Dilation Of Precision
HDPE High Density Polyethylene
HFS Heated Front Screen
Hg Mercury
HO
2S Heated Oxygen Sensor
HMW High Molecular Weight
Page 29 of 1007
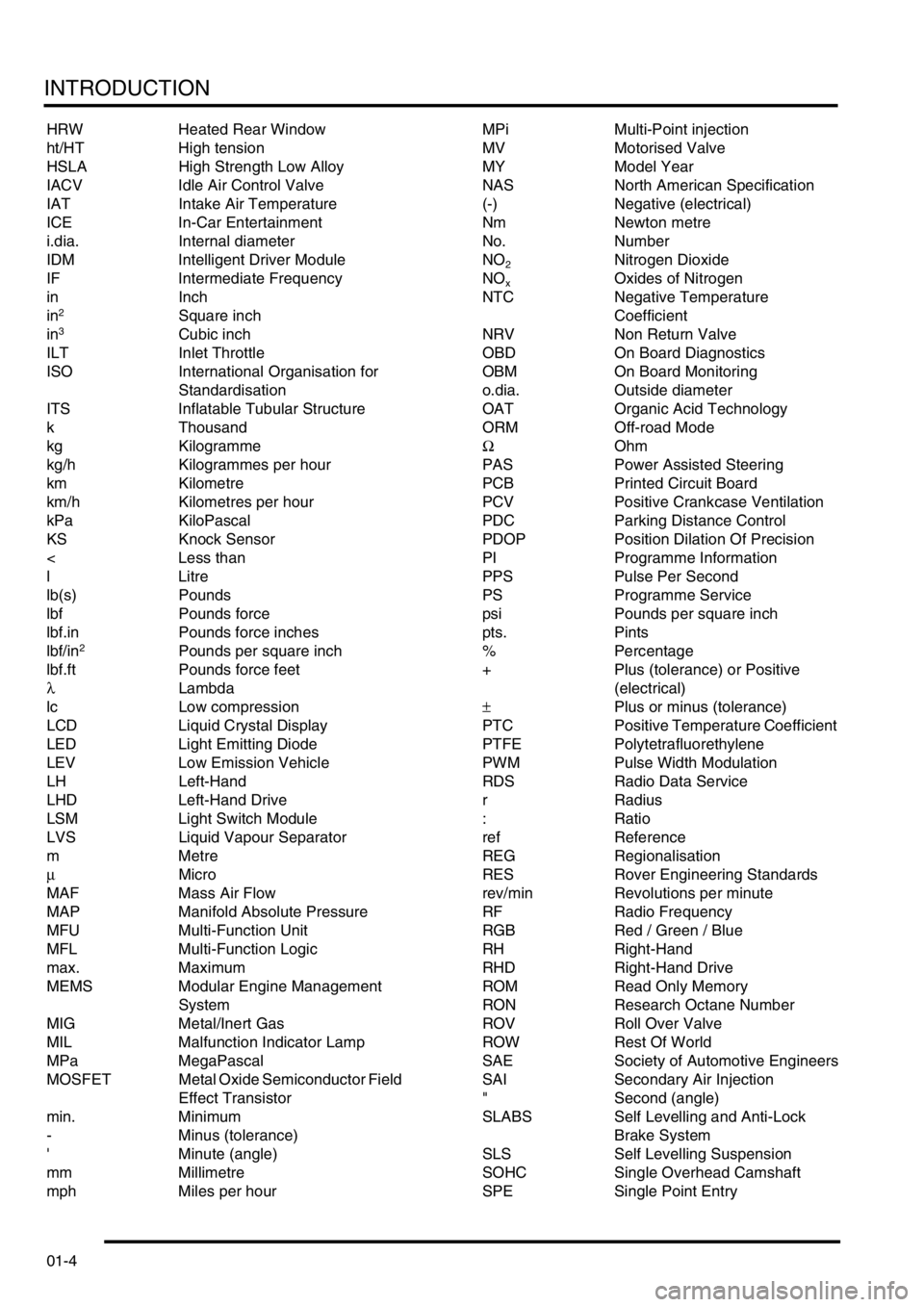
INTRODUCTION
01-4
HRW Heated Rear Window
ht/HT High tension
HSLA High Strength Low Alloy
IACV Idle Air Control Valve
IAT Intake Air Temperature
ICE In-Car Entertainment
i.dia. Internal diameter
IDM Intelligent Driver Module
IF Intermediate Frequency
in Inch
in
2Square inch
in3Cubic inch
ILT Inlet Throttle
ISO International Organisation for
Standardisation
ITS Inflatable Tubular Structure
k Thousand
kg Kilogramme
kg/h Kilogrammes per hour
km Kilometre
km/h Kilometres per hour
kPa KiloPascal
KS Knock Sensor
lb(s) Pounds
lbf Pounds force
lbf.in Pounds force inches
lbf/in
2Pounds per square inch
lbf.ft Pounds force feet
λLambda
lc Low compression
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
LEV Low Emission Vehicle
LH Left-Hand
LHD Left-Hand Drive
LSM Light Switch Module
LVS Liquid Vapour Separator
mMetre
µMicro
MAF Mass Air Flow
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure
MFU Multi-Function Unit
MFL Multi-Function Logic
max. Maximum
MEMS Modular Engine Management
System
MIG Metal/Inert Gas
MIL Malfunction Indicator Lamp
MPa MegaPascal
MOSFET Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field
Effect Transistor
min. Minimum
- Minus (tolerance)
' Minute (angle)
mm Millimetre
mph Miles per hour MPi Multi-Point injection
MV Motorised Valve
MY Model Year
NAS North American Specification
(-) Negative (electrical)
Nm Newton metre
No. Number
NO
2Nitrogen Dioxide
NO
xOxides of Nitrogen
NTC Negative Temperature
Coefficient
NRV Non Return Valve
OBD On Board Diagnostics
OBM On Board Monitoring
o.dia. Outside diameter
OAT Organic Acid Technology
ORM Off-road Mode
ΩOhm
PAS Power Assisted Steering
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PCV Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PDC Parking Distance Control
PDOP Position Dilation Of Precision
PI Programme Information
PPS Pulse Per Second
PS Programme Service
psi Pounds per square inch
pts. Pints
% Percentage
+ Plus (tolerance) or Positive
(electrical)
±Plus or minus (tolerance)
PTC Positive Temperature Coefficient
PTFE Polytetrafluorethylene
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
RDS Radio Data Service
rRadius
:Ratio
ref Reference
REG Regionalisation
RES Rover Engineering Standards
rev/min Revolutions per minute
RF Radio Frequency
RGB Red / Green / Blue
RH Right-Hand
RHD Right-Hand Drive
ROM Read Only Memory
RON Research Octane Number
ROV Roll Over Valve
ROW Rest Of World
SAE Society of Automotive Engineers
SAI Secondary Air Injection
" Second (angle)
SLABS Self Levelling and Anti-Lock
Brake System
SLS Self Levelling Suspension
SOHC Single Overhead Camshaft
SPE Single Point Entry
Page 30 of 1007
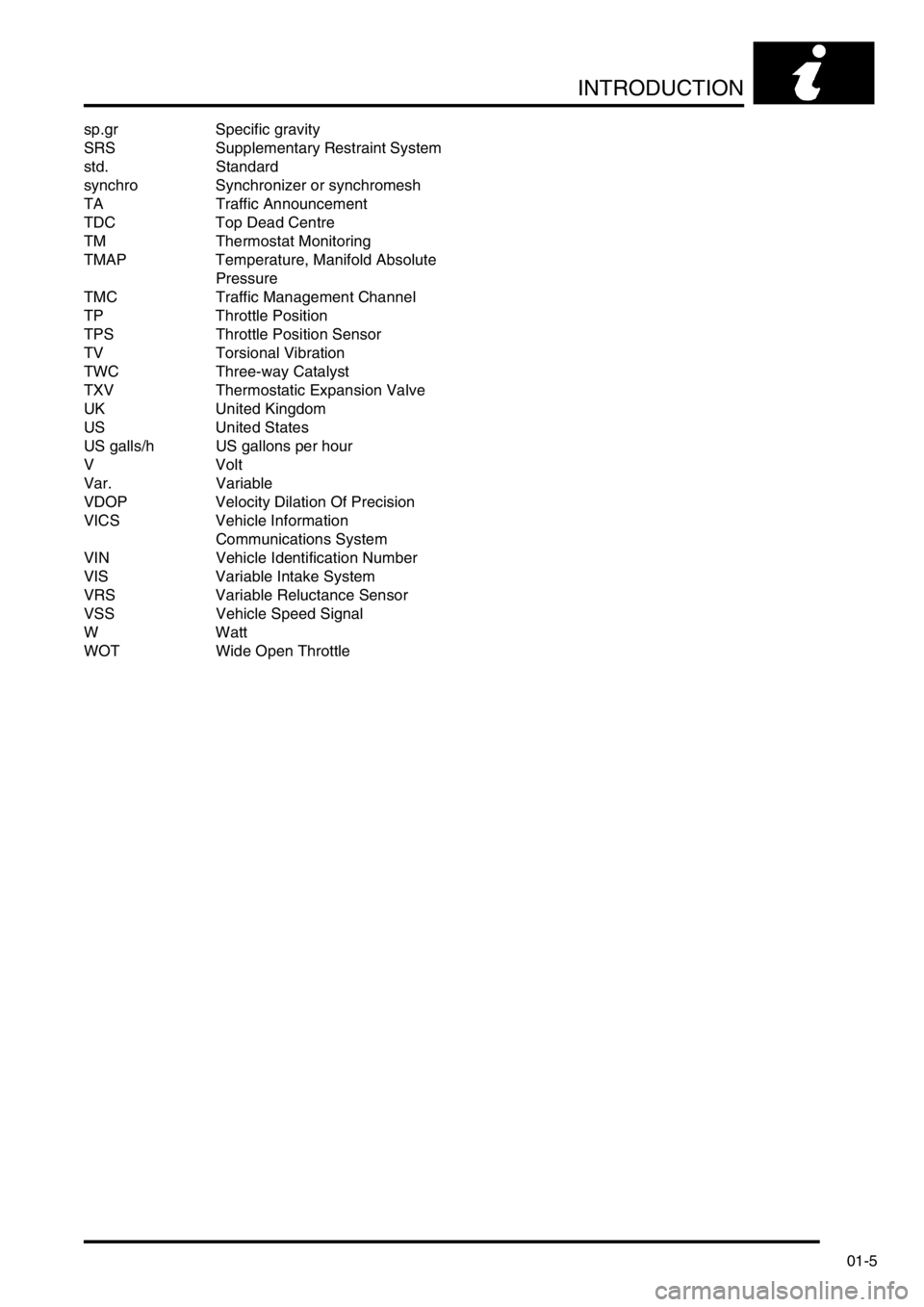
INTRODUCTION
01-5
sp.gr Specific gravity
SRS Supplementary Restraint System
std. Standard
synchro Synchronizer or synchromesh
TA Traffic Announcement
TDC Top Dead Centre
TM Thermostat Monitoring
TMAP Temperature, Manifold Absolute
Pressure
TMC Traffic Management Channel
TP Throttle Position
TPS Throttle Position Sensor
TV Torsional Vibration
TWC Three-way Catalyst
TXV Thermostatic Expansion Valve
UK United Kingdom
US United States
US galls/h US gallons per hour
V Volt
Var. Variable
VDOP Velocity Dilation Of Precision
VICS Vehicle Information
Communications System
VIN Vehicle Identification Number
VIS Variable Intake System
VRS Variable Reluctance Sensor
VSS Vehicle Speed Signal
WWatt
WOT Wide Open Throttle
Page 34 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-3
Brake hydraulics
Observe the following recommendations when
working on the brake system:
lAlways use two spanners when loosening or
tightening brake pipe or hose connections.
lEnsure that hoses run in a natural curve and are
not kinked or twisted.
lFit brake pipes securely in their retaining clips
and ensure that the pipe run cannot contact a
potential chafing point.
lContainers used for hydraulic brake fluid must
be kept absolutely clean.
lDo not store hydraulic brake fluid in an unsealed
container, it will absorb water and in this
condition would be dangerous to use due to a
lowering of its boiling point.
lDo not allow hydraulic brake fluid to be
contaminated with mineral oil, or put new
hydraulic brake fluid in a container which has
previously contained mineral oil.
lDo not re-use hydraulic brake fluid previously
removed from the system.
lAlways use clean brake fluid or a recommended
alternative to clean hydraulic components.
lFit a blanking cap to a hydraulic union and a
plug to its socket, immediately after
disconnection of pipes and hoses to prevent the
ingress of dirt.
lAbsolute cleanliness must be observed when
working with hydraulic components.
lIt is imperative that the correct brake fittings are
used and that threads of components are
compatible.
Cooling system caps and plugs
Extreme care is necessary when removing engine
cooling system expansion tank caps and coolant
drain or bleed screws when the engine is hot, and
especially if it is overheated.
To avoid the possibility of scalding allow the engine
to cool before attempting coolant cap or plug
removal.
Environmental Precautions
General
This section provides general information which can
help to reduce adverse environmental impacts
incurred through the activities carried out in
workshops.
Emissions to air
Many of the activities that are carried out in
workshops emit gases and fumes which contribute to
global warming, depletion of the ozone layer and/or
the formation of photo-chemical smog at ground
level. By considering and controlling how the
workshop activities are carried out, these gases and
fumes can be minimised, thus reducing the damage
to the environment.
Exhaust fumes
Running car engines is an essential part of workshop
activities and exhaust fumes need to be ventilated to
atmosphere. However, the amount of time engines
are running and the position of the vehicle should be
carefully considered at all times, to reduce the
release of poisonous gases and minimise the
inconvenience to people living nearby.
Solvents
Some of the cleaning agents used are solvent based
and will evaporate to atmosphere if used carelessly,
or if cans are left unsealed. All solvent containers
should be firmly closed when not needed and solvent
should be used sparingly. Suitable alternative
materials may be available to replace some of the
commonly used solvents. Similarly, many paints are
solvent based and the spray should be minimised to
reduce solvent emissions.
Refrigerant
It is illegal to release any refrigerants into the
atmosphere. Discharge and replacement of these
materials from air conditioning units should only be
carried out using the correct equipment.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
Engines –
ldon't leave engines running unnecessarily;
lminimise testing times and check where the
exhaust fumes are being blown.
Page 35 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-4
Materials –
lkeep lids on containers of solvents;
lonly use the minimum quantity;
lconsider alternative materials;
lminimise over-spray when painting.
Gases –
luse the correct equipment for collecting
refrigerants;
ldon't burn rubbish on site.
Discharges to water
Most sites will have two systems for discharging
water: storm drains and foul drains. Storm drains
should only receive clean water, foul drains will take
dirty water.
The foul drain will accept many of the normal waste
waters such as washing water, detergents and
domestic type wastes, but oil, petrol, solvent, acids,
hydraulic oil, antifreeze and other such substances
should never be poured down the drain. If in any
doubt, speak to the local Water Company first.
Every precaution must be taken to prevent spillage of
oil, fuel, solvents etc. reaching the drains. All
handling of such materials must take place well away
from the drains and preferably in an area with a kerb
or wall around it, to prevent discharge into the drain.
If a spillage occurs, it should be soaked up
immediately. Having a spill kit available will make this
easier.
Additional precautions
Check whether the surface water drains are
connected to an oil/water separator, this could
reduce the pollution if an incident was to occur. Oil/
water separators require regular maintenance to
ensure effectiveness.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
Disposal –
lnever pour anything down a drain without first
checking that it is environmentally safe to do so,
and that it does not contravene any local
regulations or bye-laws;
lhave oil traps emptied regularly.
Spillage prevention –
lstore liquids in a walled area;
lmake sure the taps on liquid containers are
secure and cannot be accidentally turned on;
lprotect bulk storage tanks from vandalism by
locking the valves;
ltransfer liquids from one container to another in
an area away from open drains;
lensure lids are replaced securely on containers;
lhave spill kits available near to points of storage
and handling of liquids.Spill kits
Special materials are available to absorb a number of
different substances. They can be in granular form,
ready to use and bought in convenient containers for
storage. Disposal of used spill-absorbing material is
dealt with in the 'Waste Management' section.
Land contamination
Oils, fuels and solvents etc. can contaminate any soil
that they are allowed to contact. Such materials
should never be disposed of by pouring onto soil and
every precaution must be taken to prevent spillage
reaching soil. Waste materials stored on open
ground could also leak, or have polluting substances
washed off them that would contaminate the land.
Always store these materials in suitable skips or
other similarly robust containers.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
ldon't pour or spill anything onto the soil or bare
ground;
ldon't store waste materials on bare ground, see
'Spillage prevention' list.
Legal compliance
Some sites may have a discharge consent for
effluent discharge to the foul drain for a car wash etc.
It is important to know what materials are allowed in
the drain and to check the results of any monitoring
carried out by the Water Company.
Where paint spraying operations are carried out it
may be necessary to apply to the Local Authority for
an air emissions licence to operate the plant. If such
a licence is in operation, additional precautions will
be necessary to comply with the requirements, and
the results of any air quality monitoring must be
checked regularly.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
lknow what legal consents and licences apply to
the operations;
lcheck that the emissions and discharges
comply with legal requirements.
Page 37 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-6
Waste Management
One of the major ways that pollution can be reduced
is by the careful handling, storage and disposal of all
waste materials that occur on sites. Legislation
makes it illegal to dispose of waste materials other
than to licensed waste carriers and disposal sites.
This means that it is necessary to not only know what
the waste materials are, but also to have the
necessary documentation and licenses.
Handling and storage of waste
Ensure that waste materials are not poured down the
drain or onto soils. They should be stored in such a
way as to prevent the escape of material to land,
water or air.
They must also be segregated into different types of
waste e.g. oil, metals, batteries, used vehicle
components. This will prevent any reaction between
different materials and assist in disposal.
Disposal of waste
Disposal of waste materials must only be to waste
carriers who are licensed to carry those particular
waste materials and all the necessary
documentation must be completed. The waste
carrier is responsible for ensuring that the waste is
taken to the correct disposal sites.Dispose of waste in accordance with the following
guidelines:
lFuel, hydraulic fluid, anti-freeze and oil –
keep separate and dispose of to specialist
contractor.
lRefrigerant – collect using specialist
equipment and containers, and reuse.
lDetergents – safe to pour down the foul drain
if diluted.
lPaint, thinners – keep separate and dispose of
to specialist contractor.
lComponents – send back to supplier for
refurbishment, or disassemble and reuse any
suitable parts. Dispose of the remainder in
ordinary waste.
lSmall parts – reuse any suitable parts, dispose
of the remainder in ordinary waste.
lMetals – can be sold if kept separate from
general waste.
lTyres – keep separate and dispose of to
specialist contractor.
lPackaging – compact as much as possible and
dispose of in ordinary waste.
lAsbestos-containing – keep separate and
dispose of to specialist contractor.
lOily and fuel wastes (e.g. rags, used spill kit
material) – keep separate and dispose of to
specialist contractor.
lAir filters – keep separate and dispose of to
specialist contractor.
lRubber/plastics – dispose of in ordinary
waste.
lHoses – dispose of in ordinary waste.
lBatteries – keep separate and dispose of to
specialist contractor.
lAirbags (explosives) – keep separate and
dispose of to specialist contractor.
lElectrical components – send back to
supplier for refurbishment, or disassemble and
reuse any suitable parts. Dispose of the
remainder in ordinary waste.
lElectronic components – send back to
supplier for refurbishment, or disassemble and
reuse any suitable parts. Dispose of the
remainder in ordinary waste.
lCatalysts – can be sold if kept separate from
general waste.
lUsed spill-absorbing material – keep
separate and dispose of to specialist contractor.
lOffice waste – recycle paper and toner/ink
cartridges, dispose of the remainder in ordinary
waste.
Page 38 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-7
General fitting instructions
Precautions against damage
To avoid damage to the vehicle when carrying out
repairs, always adhere to the following:
lAlways fit wing and seat covers before
commencing work. Avoid spilling brake fluid or
battery acid on paintwork; immediately wash off
with water if this occurs.
lDisconnect the battery earth lead before starting
work, see ELECTRICAL PRECAUTIONS.
lAlways use the recommended service tool or a
satisfactory equivalent where specified.
lProtect exposed bearing surfaces, sealing
surfaces and screw threads from damage.
Component removal
Whenever possible, clean components and
surrounding area before removal.
lBlank off openings exposed by component
removal.
lImmediately seal fuel, oil or hydraulic lines when
apertures are exposed; use plastic caps or
plugs to prevent loss of fluid and ingress of dirt.
lClose open ends of oilways exposed by
component removal with tapered hardwood
plugs or conspicuous plastic plugs.
lImmediately a component is removed, place it in
a suitable container; use a separate container
for each component and its associated parts.
lClean bench and provide marking materials,
labels, containers and locking wire before
dismantling a component.
Dismantling
Observe scrupulous cleanliness when dismantling
components, particularly when brake, fuel or
hydraulic system parts are being worked on. A
particle of dirt or a cloth fragment could cause a
serious malfunction if trapped in these systems.Use the following procedures:
lBlow out all tapped holes, crevices, oilways and
fluid passages with an air line. Ensure that any
O-rings used for sealing are correctly replaced
or renewed if disturbed during the process.
lUse marking ink to identify mating parts and
ensure correct reassembly. Do not use a centre
punch or scriber to mark parts, they could
initiate cracks or distortion in marked
components.
lWire together mating parts where necessary to
prevent accidental interchange (e.g. roller
bearing components).
lWire labels on to all parts which are to be
renewed, and to parts requiring further
inspection before being passed for reassembly;
place these parts in separate containers from
those containing parts for rebuild.
lDo not discard a part due for renewal until after
comparing it with a new part to ensure that its
correct replacement has been obtained.
Cleaning components
Always use the recommended cleaning agent or
equivalent. Ensure that adequate ventilation is
provided when volatile degreasing agents are being
used. Do not use degreasing equipment for
components containing items which could be
damaged by the use of this process.
When washing under bonnet, never direct water onto
ECM, as water ingress may occur resulting in
damage to electrical components inside.
General Inspection
All components should be inspected for wear or
damage before being reassembled.
lNever inspect a component for wear or
dimensional check unless it is absolutely clean;
a slight smear of grease can conceal an
incipient failure.
lWhen a component is to be checked
dimensionally against recommended values,
use the appropriate measuring equipment
(surface plates, micrometers, dial gauges etc.).
Ensure the measuring equipment is calibrated
and in good serviceable condition.
lReject a component if its dimensions are
outside the specified tolerances, or if it appears
to be damaged.
lA part may be refitted if its critical dimension is
exactly to its tolerance limit and it appears to be
in satisfactory condition.
lUse 'Plastigauge' 12 Type PG-1 for checking
bearing surface clearances.
Page 39 of 1007
GENERAL INFORMATION
03-8
Ball and roller bearings
General
When removing and installing bearings, ensure that
the following practices are observed to ensure
component serviceability:
lRemove all traces of lubricant from the bearing
under inspection by cleaning with a suitable
degreasant; maintain absolute cleanliness
throughout operations.
lConduct a visual inspection for markings on
rolling elements, raceways, outer surface of
outer rings or inner surface of inner rings. Reject
any bearings found to be marked, since marking
in these areas indicates onset of wear.
lHold inner race of bearing between finger and
thumb of one hand and spin outer race to check
that it revolves absolutely smoothly. Repeat,
holding outer race and spinning inner race.
lRotate outer ring gently with a reciprocating
motion, while holding inner ring; feel for any
check or obstruction to rotation. Reject bearing
if action is not perfectly smooth.
lLubricate bearing with generous amounts of
lubricant appropriate to installation.
lInspect shaft and bearing housing for
discoloration or other markings which indicate
movement between bearing and seatings.
lEnsure that shaft and housing are clean and
free from burrs before fitting bearing.
lIf one bearing of a pair shows an imperfection, it
is advisable to replace both with new bearings;
an exception could be if the faulty bearing had
covered a low mileage, and it can be
established that damage is confined to only one
bearing.
lNever refit a ball or roller bearing without first
ensuring that it is in a fully serviceable condition.
lWhen hub bearings are removed or displaced,
NEW bearings must be fitted; do not attempt to
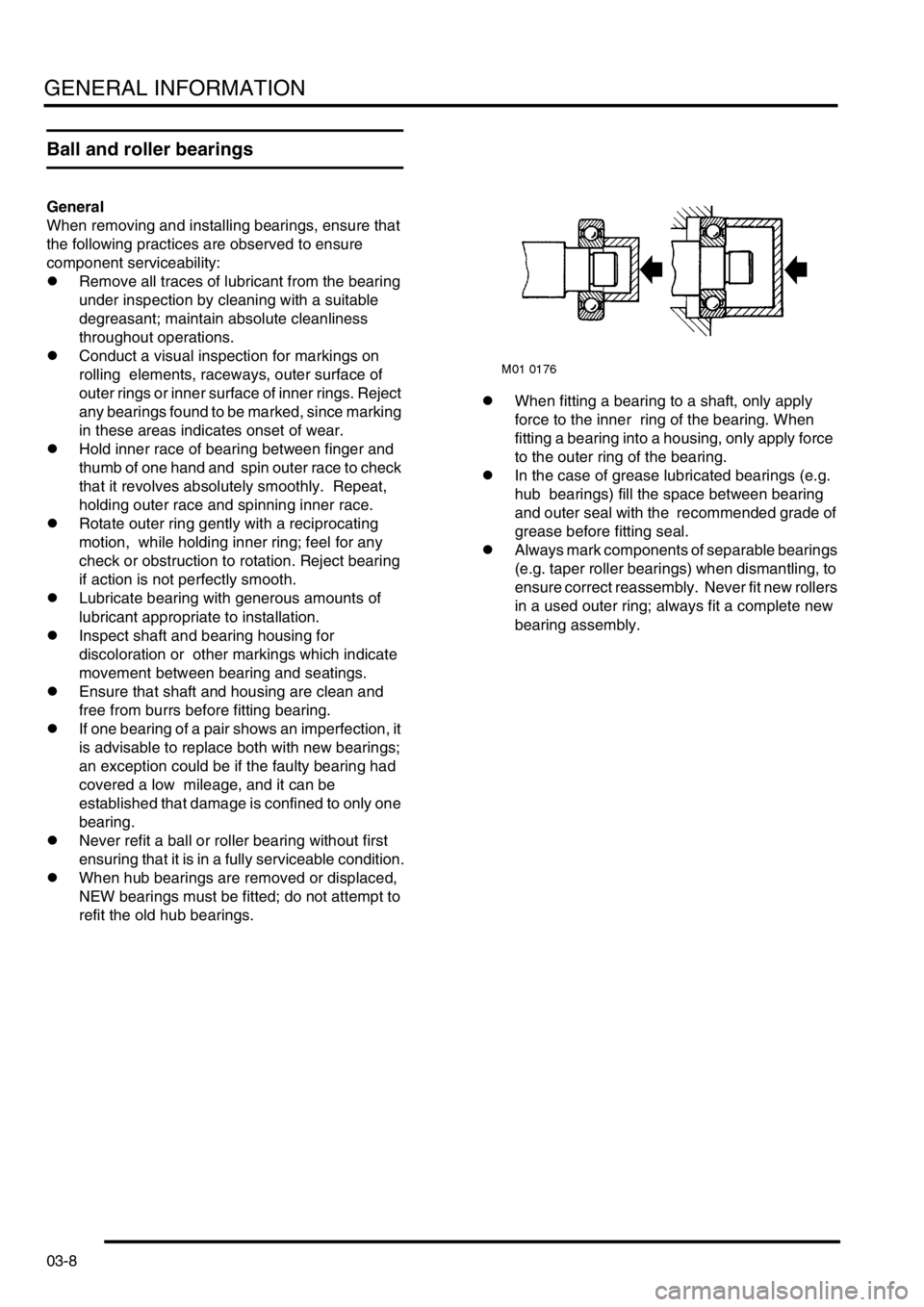
refit the old hub bearings.lWhen fitting a bearing to a shaft, only apply
force to the inner ring of the bearing. When
fitting a bearing into a housing, only apply force
to the outer ring of the bearing.
lIn the case of grease lubricated bearings (e.g.
hub bearings) fill the space between bearing
and outer seal with the recommended grade of
grease before fitting seal.
lAlways mark components of separable bearings
(e.g. taper roller bearings) when dismantling, to
ensure correct reassembly. Never fit new rollers
in a used outer ring; always fit a complete new
bearing assembly.
Page 41 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-10
Joints and joint faces
General
Fit joints dry unless specified otherwise.
lAlways use the correct gaskets as specified.
lWhen joining compound is used, apply in a thin
uniform film to metal surfaces; take care to
prevent joining compound from entering
oilways, pipes or blind tapped holes.
lIf gaskets and/or joining compound is
recommended for use; remove all traces of old
joining material prior to reassembly. Do not use
a tool which will damage the joint faces and
smooth out any scratches or burrs using an oil
stone. Do not allow dirt or joining material to
enter any tapped holes or enclosed parts.
lPrior to reassembly, blow through any pipes,
channels or crevices with compressed air.
Locking devices
General
Always replace locking devices with one of the same
design.
Tab Washers
Always release locking tabs and fit new locking
washers, do not re-use locking tabs. Ensure the new
tab washer is the same design as that replaced.
Locking Nuts
Always use a backing spanner when loosening or
tightening locking nuts, brake and fuel pipe unions.
Roll Pins
Always fit new roll pins of an interference fit in the
hole.
Circlips
Always fit new circlips of the correct size for the
groove.
Locking wire
Always fit locking wire of the correct type. Arrange
wire so that its tension tends to tighten the bolt heads
or nuts to which it is fitted.
Keys and Keyways
Remove burrs from edges of keyways with a fine file
and clean thoroughly before attempting to refit key.
Clean and inspect key closely; keys are suitable for
refitting only if indistinguishable from new, as any
indentation may indicate the onset of wear.