engine MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 202 of 909
F2–50
FUEL SYSTEM
NONRETURN VALVE INSPECTIONA6E401242270201
Note
•Nonreturn valve is integrated in the fuel tank. Therefore, before inspecting the nonreturn valve perform the
follwing:
1. Remove the fuel gauge sender unit. (See F2–45 FUEL TANK REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
2. Siphon the fuel from the fuel tank.
Note
•The nonreturn valve is normally closed by the spring force.
3. Verify that the nonreturn valve is closed.
•If it is stuck open, replace the fuel tank.
4. Verify that the nonreturn valve opens when pulled up by a finger.
•If it does not open, replace the nonreturn valve.
End Of Sie
FUEL FILTER COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONA6E4012348022011. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Complete the “BEFORE REPAIR PROCEDURE”. (See F2–45 BEFORE REPAIR PROCEDURE.)
3. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
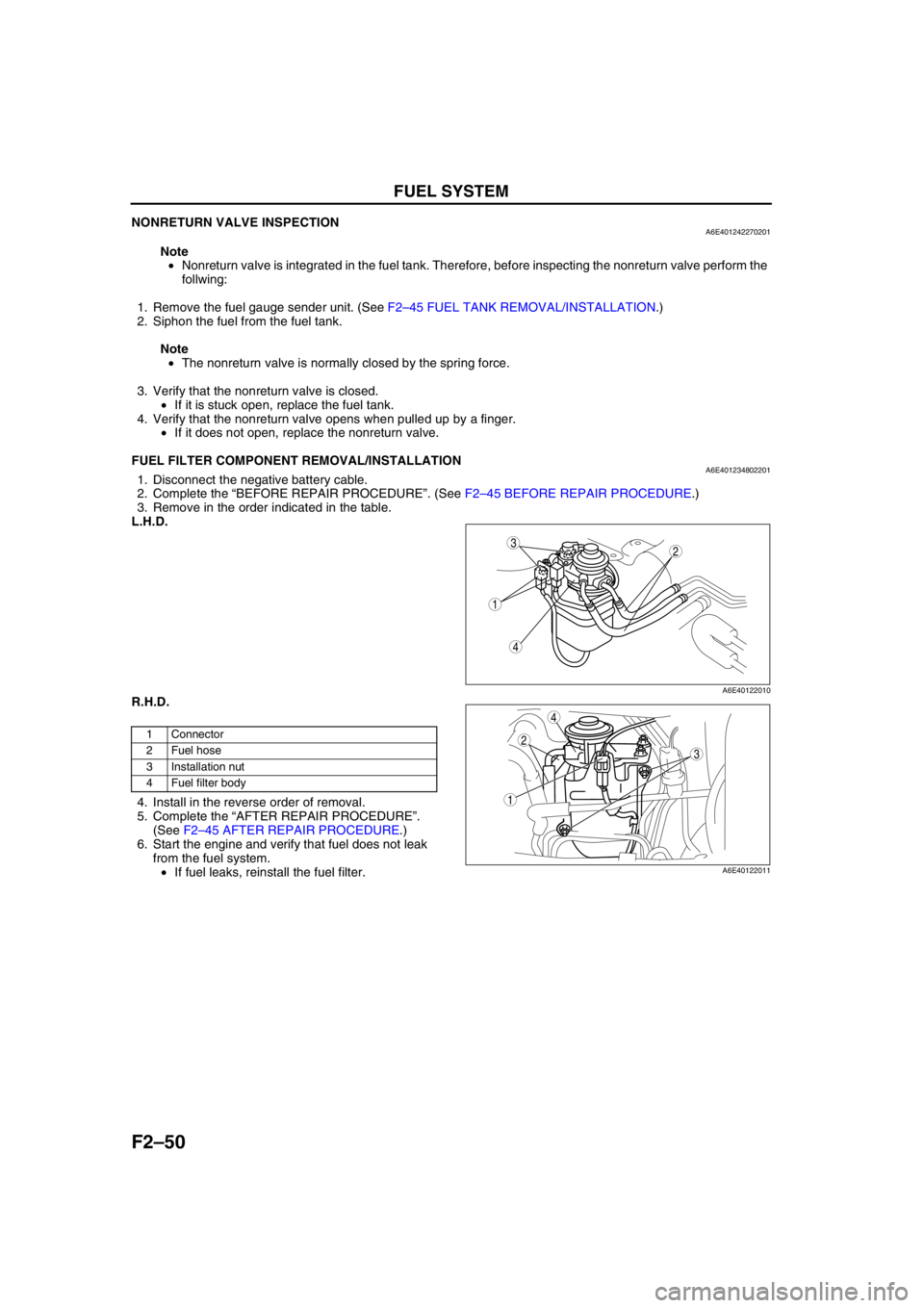
L.H.D.
R.H.D.
.
4. Install in the reverse order of removal.
5. Complete the “AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE”.
(See F2–45 AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE.)
6. Start the engine and verify that fuel does not leak
from the fuel system.
•If fuel leaks, reinstall the fuel filter.
End Of Sie
1
4
23
A6E40122010
1 Connector
2Fuel hose
3 Installation nut
4 Fuel filter body
4
1
2
3
A6E40122011
Page 209 of 909
EXHAUST SYSTEM
F2–57
F2
EXHAUST SYSTEM INSPECTIONA6E4014400002031. Start the engine and inspect each exhaust system component for exhaust gas leakage.
•If leakage is found, repair or replace as necessary.
End Of Sie
EXHAUST SYSTEM REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONA6E401440000204
Warning
•When the engine and exhaust system are hot, they can cause severe burns or injury. Turn off the
engine and wait until they are cool before removing the exhaust system.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
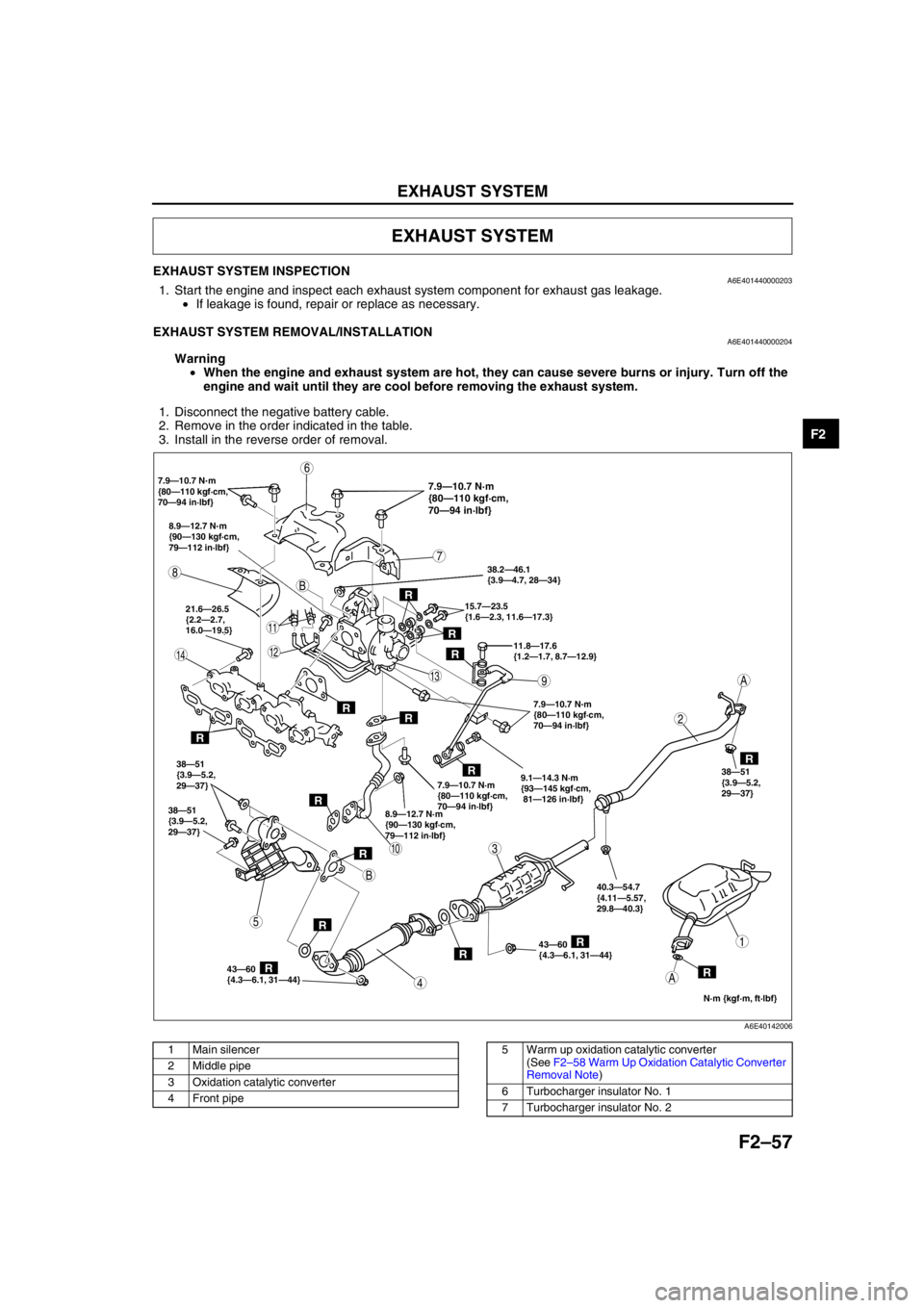
2. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
3. Install in the reverse order of removal.
.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
13
B
B
A
A
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf} 7.9—10.7 N
·m
{80—110 kgf·cm,
70—94 in·lbf}
7.9—10.7 N
·m
{80—110 kgf·cm,
70—94 in·lbf}
38—51
{3.9—5.2,
29—37} 7.9—10.7 N·m
{80—110 kgf·cm,
70—94 in·lbf}
38—51
{3.9—5.2,
29—37} 38—51
{3.9—5.2,
29—37} 21.6—26.5
{2.2—2.7,
16.0—19.5} 8.9—12.7 N
·m
{90—130 kgf·cm,
79—112 in·lbf}
8.9—12.7 N·m
{90—130 kgf·cm,
79—112 in·lbf}
43—60
{4.3—6.1, 31—44} 40.3—54.7
{4.11—5.57,
29.8—40.3}
43—60
{4.3—6.1, 31—44}9.1—14.3 N·m
{93—145 kgf·cm,
81—126 in·lbf} 11.8—17.6
{1.2—1.7, 8.7—12.9} 15.7—23.5
{1.6—2.3, 11.6—17.3}
7.9—10.7 N·m
{80—110 kgf·cm,
70—94 in·lbf}
38.2—46.1
{3.9—4.7, 28—34}
R
R
RR
R
R
R
R
RR
R
R
R
9
8
7
5
4
310
11
12
6
1
2
14
R
R
A6E40142006
1 Main silencer
2 Middle pipe
3 Oxidation catalytic converter
4 Front pipe5 Warm up oxidation catalytic converter
(See F2–58 Warm Up Oxidation Catalytic Converter
Removal Note)
6 Turbocharger insulator No. 1
7 Turbocharger insulator No. 2
Page 210 of 909
F2–58
EXHAUST SYSTEM
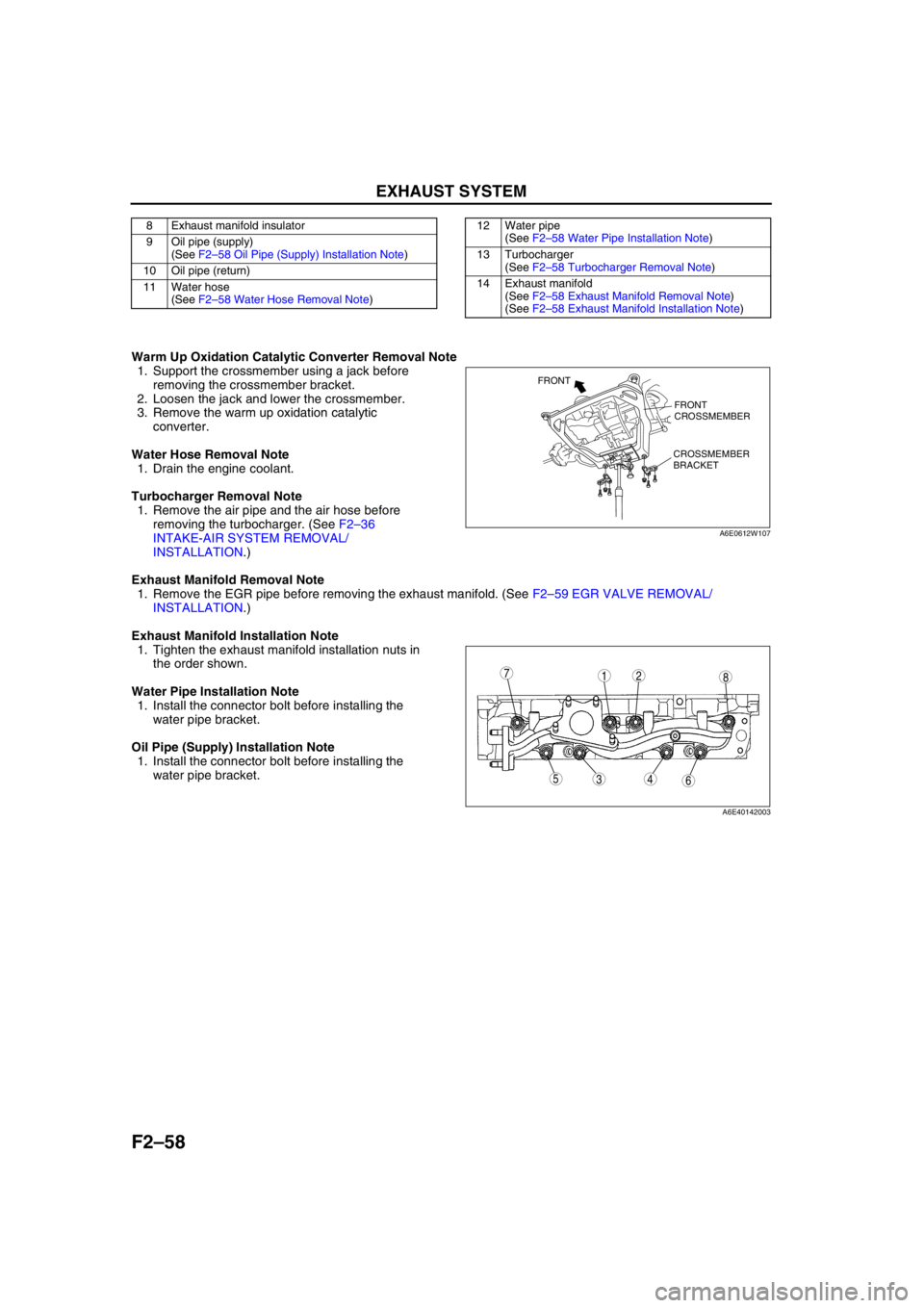
Warm Up Oxidation Catalytic Converter Removal Note
1. Support the crossmember using a jack before
removing the crossmember bracket.
2. Loosen the jack and lower the crossmember.
3. Remove the warm up oxidation catalytic
converter.
Water Hose Removal Note
1. Drain the engine coolant.
Turbocharger Removal Note
1. Remove the air pipe and the air hose before
removing the turbocharger. (See F2–36
INTAKE-AIR SYSTEM REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
Exhaust Manifold Removal Note
1. Remove the EGR pipe before removing the exhaust manifold. (See F2–59 EGR VALVE REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
Exhaust Manifold Installation Note
1. Tighten the exhaust manifold installation nuts in
the order shown.
Water Pipe Installation Note
1. Install the connector bolt before installing the
water pipe bracket.
Oil Pipe (Supply) Installation Note
1. Install the connector bolt before installing the
water pipe bracket.
End Of Sie
8 Exhaust manifold insulator
9 Oil pipe (supply)
(See F2–58 Oil Pipe (Supply) Installation Note)
10 Oil pipe (return)
11 Water hose
(See F2–58 Water Hose Removal Note)12 Water pipe
(See F2–58 Water Pipe Installation Note)
13 Turbocharger
(See F2–58 Turbocharger Removal Note)
14 Exhaust manifold
(See F2–58 Exhaust Manifold Removal Note)
(See F2–58 Exhaust Manifold Installation Note)
FRONT
CROSSMEMBER
CROSSMEMBER
BRACKET FRONT
A6E0612W107
87
5436
12
A6E40142003
Page 217 of 909

CONTROL SYSTEM
F2–65
F2
End Of SiePCM INSPECTIONA6E404018881208Using WDS or Equivalent
Caution
•The PCM terminal voltage vary with change in measuring conditions and vehicle conditions.
Always carry out a total inspection of the input systems, output systems, and PCM to determine
the cause of trouble. Otherwise, diagnosis will be incorrect.
Note
•For replace the PCM, setup the WDS and perform the following.
—“PCM configuration” (See F2–68 PCM CONFIGURATION.)
—“Correction after Parts Installation” (See F2–34 Correction after Parts Installation.)
1. Connect the WDS or equivalent to the DLC-2. (See F2–85 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC TEST.)
2. Turn the engine switch to ON.
3. Measure the PID value.
•If PID value is not within the specification, follow the instructions in ACTION column.
PID Monitor Table
Monitor item (Definition)Unit/
ConditionCondition/Specification
(Reference)ActionPCM
terminal
ACCS
(A/C relay)ON/OFF•A/C operating: ON
•Engine switch is on: OFFInspect A/C relay.
(See T–19 RELAY
INSPECTION)73
ACSW
(A/C switch)ON/OFF•A/C switch is on: ON
•A/C switch is off: OFFInspect A/C switch. 84
APS1
(Accelerator position sensor
No.1 signal voltage)V•Accelerator pedal depressed:
3.35—4.03 V
•Accelerator pedal released: 0.4—
0.7 VInspect accelerator position
sensor.
(See F2–72
ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)10
APS2
(Accelerator position sensor
No.2 signal voltage)V•Accelerator pedal depressed:
3.35—4.03 V
•Accelerator pedal released: 0.4—
0.7 VInspect accelerator position
sensor.
(See F2–72
ACCELERATOR POSITION
SENSOR INSPECTION)88
BARO
(BARO)kPa inHg•Elevation 0—400 m {0—1310 ft}:
100—103 kPa {29.5—30.4 inHg}Replace PCM.
(See F2–64 PCM
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)–
BARO
(BARO signal voltage)V•Elevation 0—400 m {0—1310 ft}:
approx. 4.0 V
BOO
(Brake switch)ON/OFF•Brake pedal depressed: ON
•Brake pedal released: OFFInspect brake switch. 7
CPP
(Clutch switch)ON/OFF•Clutch pedal depressed: ON
•Clutch pedal released: OFFInspect clutch switch.
(See F2–68 CLUTCH
SWITCH INSPECTION)33
CPP/PNP
(neutral switch)Neutral/Drive•Gear is neutral position: Neutral
•Gear is not neutral position: DriveInspect neutral switch.
(See F2–69 NEUTRAL
SWITCH INSPECTION)56
CRUISESW
(Cruise control switch)ON/OFF•Cruise control switch is on: ON
•Cruise control switch is off: OFFInspect cruise control switch. 64
DTCCNT
(DTC count)–•Number of output DTCFollow DTC inspection.
(See F2–87 DTC TABLE)–
ECT
(ECT)°C°F•ECT is 20°C {68°F}: 20°C
{68°F}
•ECT is 85°C {185°F}: 85°C
{185°F}Inspect ECT sensor.
(See F2–76 ENGINE
COOLANT TEMPERATURE
(ECT) SENSOR
INSPECTION)87
ECT
(ECT signal voltage)V•ECT is 20°C {68°F}: 3.0—3.2 V
•ECT is 85°C {185°F}: 0.7—0.9 V
FAN2
(Cooling fan relay No.2)ON/OFF•Engine coolant temperature is
above 100°C {212°F}: ON
•Others: OFFInspect cooling fan relay
No.2.76
FAN3
(Cooling fan relay No.1)ON/OFF•Engine coolant temperature is
above 108°C {226°F}: ON
•A/C switch is on: ON
•Others: OFFInspect cooling fan relay
No.1.102
Page 218 of 909

F2–66
CONTROL SYSTEM
IAT
(IAT)°C°F•IAT is 20°C {68°F}: 20°C {68°F}
•IAT is 30°C {86°F}: 30°C {86°F}Inspect IAT sensor No.1.
(See F2–74 MASS AIR
FLOW (MAF)/INTAKE AIR
TEMPERATURE (IAT)
SENSOR INSPECTION)60
IAT
(IAT signal voltage)V•IAT is 20°C {68°F}: 2.2—2.5 V
•IAT is 30°C {86°F}: 1.7—2.0 V
IMRC
(VSC solenoid valve)ON/OFF•Idle: ON
•Engine speed is above approx.
2,500 rpm: OFFInspect following PIDs:
BARO, ECT, IAT, RPM, VSS101
INGEAR
(In gear)ON/OFF•Gear is not neutral position and
clutch pedal released: ON
•Gear is neutral position: OFF
•Clutch pedal depressed: OFFInspect following PIDs:
CPP, CPP/PNP33, 56
INJ_LRN_DIS
(Distance from the last
injector learning)Km Mile•Distance from the last injector
learning––
MAF
(Mass air flow amount)g/s•Engine switch is on: approx. 0 g/s
•Idle: 6.8—7.4 g/sInspect MAF/IAT sensor.
(See F2–74 MASS AIR
FLOW (MAF)/INTAKE AIR
TEMPERATURE (IAT)
SENSOR INSPECTION)9
MAF
(Mass air flow signal voltage)V•Engine switch is on: 0.0—1.0 V
•Idle: 1.5—2.1 V
MAF_LRN_DIS
(Distance from the last MAF
learning)Km Mile•Distance from the last MAF
learning––
MAINRLY
(PCM control relay)ON/OFF•Engine switch is on: ONInspect PCM control relay.
(See T–19 RELAY
INSPECTION)69
MAP
(MAP)kPa inHg•Engine switch is on: 100—103
kPa {29.5—30.4 inHg}
•Idle: 100—103 kPa {29.5—30.4
inHg}Inspect boost sensor.
(See F2–78 BOOST
SENSOR INSPECTION)36
MAP
(MAP signal voltage)V•Engine switch is on: 2.1—2.5 V
•Idle: 2.1—2.5 V
MIL
(MIL)ON/OFF•Engine switch is on: ON
•DTC output: ON
•Others: OFFInspect instrument cluster.
Inspect CAN system.
(See T–39 MULTIPLEX
COMMUNICATION
SYSTEM)13, 39
NUMKEYS
(Number of keys stored in
module)–•Number of keys stored in module––
RPM
(Engine speed)rpm•Idle: 725—825 rpmInspect CKP sensor.
(See F2–80 CAMSHAFT
POSITION (CMP) SENSOR
INSPECTION)3, 29
VPWR
(Battery positive voltage)V•Engine switch is ON: B+Inspect Battery.
Inspect fuse.4
VSS
(Vehicle speed)km/h mph•Vehicle speed is 20 km/h {12.5
mph}: 20 km/h {12.5 mph}
•Vehicle speed is 40 km/h {25
mph}: 40 km/h {25 mph}Inspect CAN system.
(See T–39 MULTIPLEX
COMMUNICATION
SYSTEM)13, 39 Monitor item (Definition)Unit/
ConditionCondition/Specification
(Reference)ActionPCM
terminal
Page 219 of 909
CONTROL SYSTEM
F2–67
F2
Not Using WDS or Equivalent
Constant voltage terminal inspection
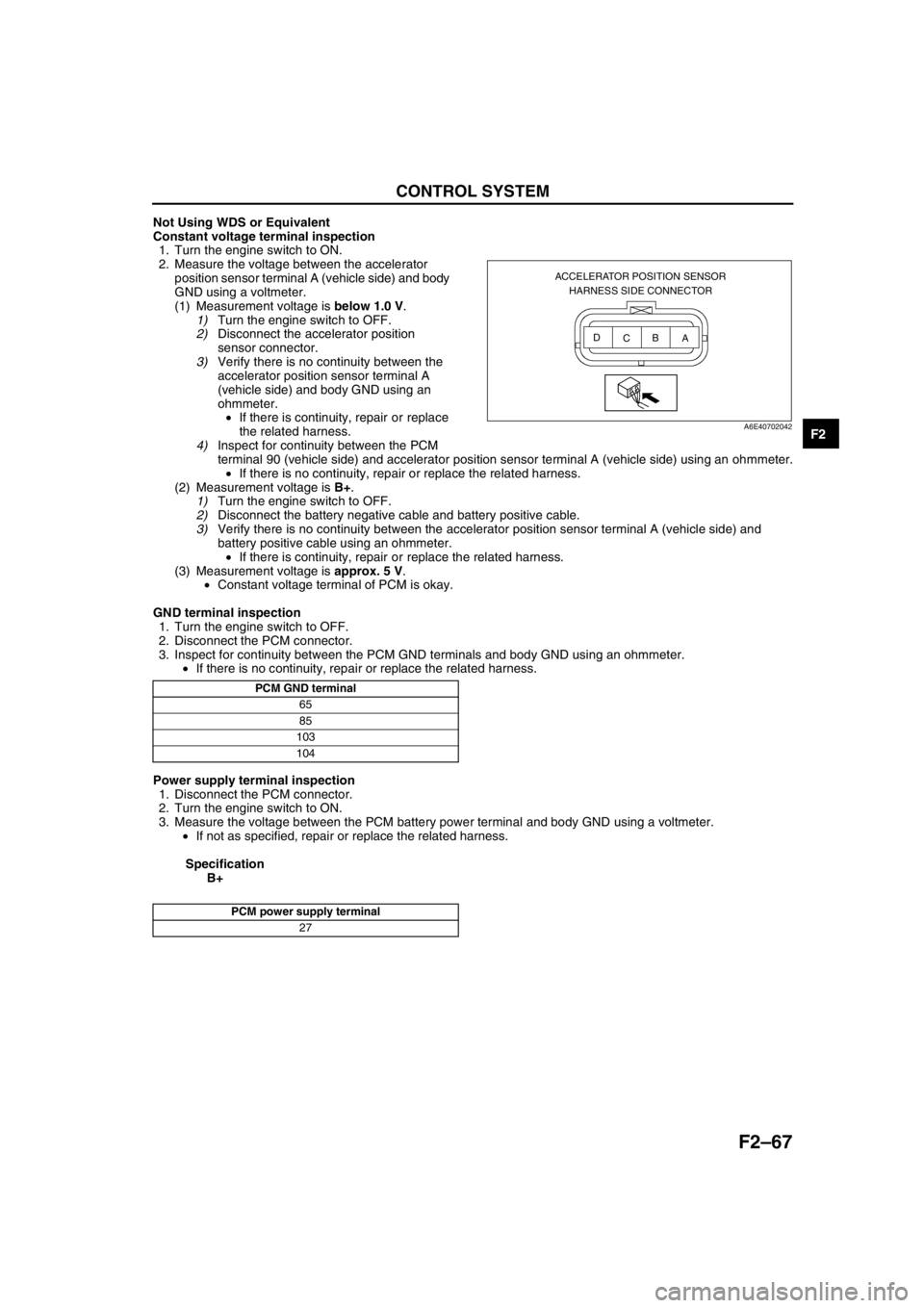
1. Turn the engine switch to ON.
2. Measure the voltage between the accelerator
position sensor terminal A (vehicle side) and body
GND using a voltmeter.
(1) Measurement voltage is below 1.0 V.
1)Turn the engine switch to OFF.
2)Disconnect the accelerator position
sensor connector.
3)Verify there is no continuity between the
accelerator position sensor terminal A
(vehicle side) and body GND using an
ohmmeter.
•If there is continuity, repair or replace
the related harness.
4)Inspect for continuity between the PCM
terminal 90 (vehicle side) and accelerator position sensor terminal A (vehicle side) using an ohmmeter.
•If there is no continuity, repair or replace the related harness.
(2) Measurement voltage is B+.
1)Turn the engine switch to OFF.
2)Disconnect the battery negative cable and battery positive cable.
3)Verify there is no continuity between the accelerator position sensor terminal A (vehicle side) and
battery positive cable using an ohmmeter.
•If there is continuity, repair or replace the related harness.
(3) Measurement voltage is approx. 5 V.
•Constant voltage terminal of PCM is okay.
GND terminal inspection
1. Turn the engine switch to OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM connector.
3. Inspect for continuity between the PCM GND terminals and body GND using an ohmmeter.
•If there is no continuity, repair or replace the related harness.
Power supply terminal inspection
1. Disconnect the PCM connector.
2. Turn the engine switch to ON.
3. Measure the voltage between the PCM battery power terminal and body GND using a voltmeter.
•If not as specified, repair or replace the related harness.
Specification
B+
End Of Sie
ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
A B
C D
A6E40702042
PCM GND terminal
65
85
103
104
PCM power supply terminal
27
Page 223 of 909
CONTROL SYSTEM
F2–71
F2
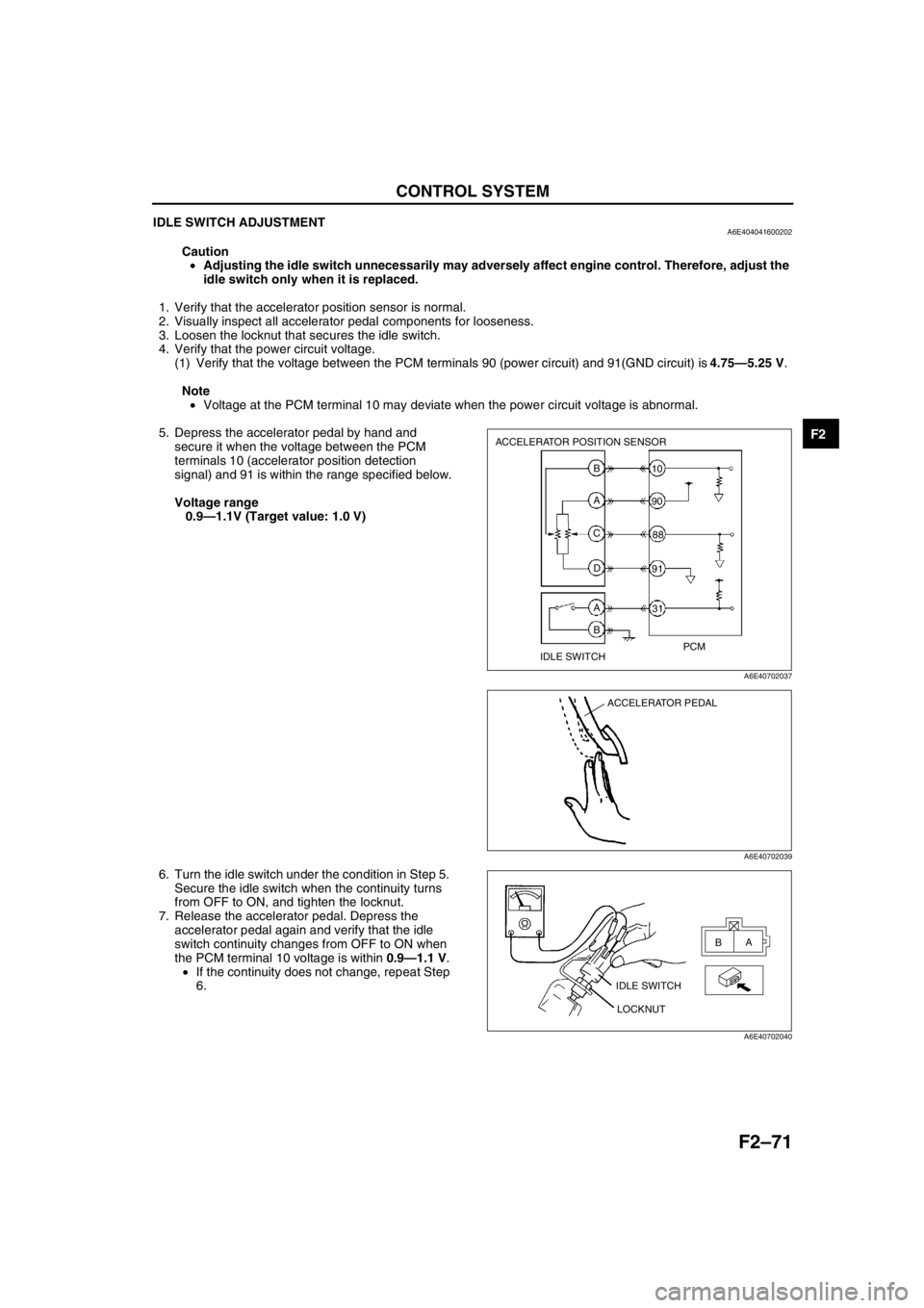
IDLE SWITCH ADJUSTMENTA6E404041600202
Caution
•Adjusting the idle switch unnecessarily may adversely affect engine control. Therefore, adjust the
idle switch only when it is replaced.
1. Verify that the accelerator position sensor is normal.
2. Visually inspect all accelerator pedal components for looseness.
3. Loosen the locknut that secures the idle switch.
4. Verify that the power circuit voltage.
(1) Verify that the voltage between the PCM terminals 90 (power circuit) and 91(GND circuit) is 4.75—5.25 V.
Note
•Voltage at the PCM terminal 10 may deviate when the power circuit voltage is abnormal.
5. Depress the accelerator pedal by hand and
secure it when the voltage between the PCM
terminals 10 (accelerator position detection
signal) and 91 is within the range specified below.
Voltage range
0.9—1.1V (Target value: 1.0 V)
6. Turn the idle switch under the condition in Step 5.
Secure the idle switch when the continuity turns
from OFF to ON, and tighten the locknut.
7. Release the accelerator pedal. Depress the
accelerator pedal again and verify that the idle
switch continuity changes from OFF to ON when
the PCM terminal 10 voltage is within 0.9—1.1 V.
•If the continuity does not change, repeat Step
6.
End Of Sie
ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
IDLE SWITCHPCM B
A
C
D
A
B31 10
90
88
91
A6E40702037
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
A6E40702039
IDLE SWITCH
LOCKNUTA
B
A6E40702040
Page 225 of 909
CONTROL SYSTEM
F2–73
F2
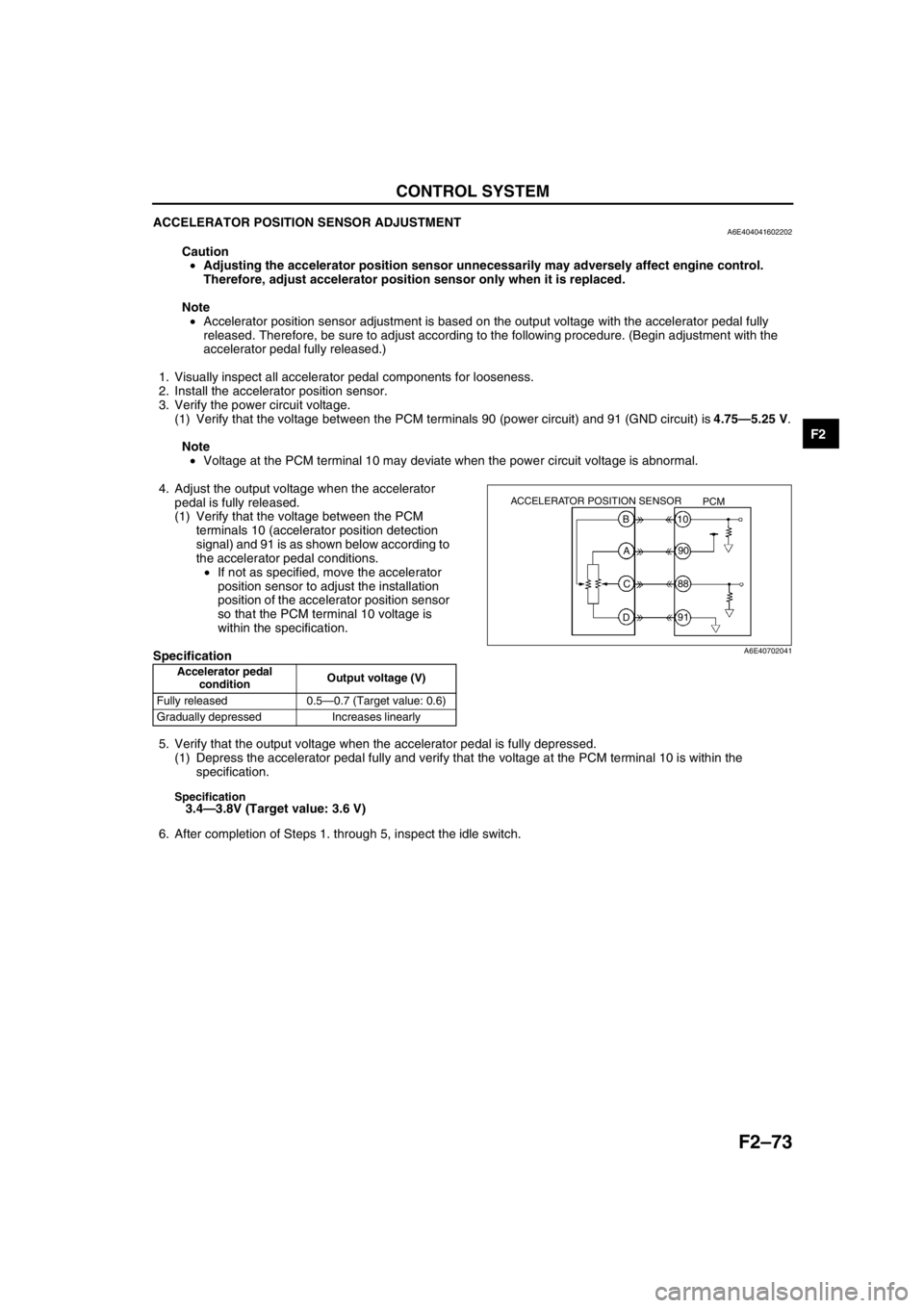
ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR ADJUSTMENTA6E404041602202
Caution
•Adjusting the accelerator position sensor unnecessarily may adversely affect engine control.
Therefore, adjust accelerator position sensor only when it is replaced.
Note
•Accelerator position sensor adjustment is based on the output voltage with the accelerator pedal fully
released. Therefore, be sure to adjust according to the following procedure. (Begin adjustment with the
accelerator pedal fully released.)
1. Visually inspect all accelerator pedal components for looseness.
2. Install the accelerator position sensor.
3. Verify the power circuit voltage.
(1) Verify that the voltage between the PCM terminals 90 (power circuit) and 91 (GND circuit) is 4.75—5.25 V.
Note
•Voltage at the PCM terminal 10 may deviate when the power circuit voltage is abnormal.
4. Adjust the output voltage when the accelerator
pedal is fully released.
(1) Verify that the voltage between the PCM
terminals 10 (accelerator position detection
signal) and 91 is as shown below according to
the accelerator pedal conditions.
•If not as specified, move the accelerator
position sensor to adjust the installation
position of the accelerator position sensor
so that the PCM terminal 10 voltage is
within the specification.
Specification
5. Verify that the output voltage when the accelerator pedal is fully depressed.
(1) Depress the accelerator pedal fully and verify that the voltage at the PCM terminal 10 is within the
specification.
Specification3.4—3.8V (Target value: 3.6 V)
6. After completion of Steps 1. through 5, inspect the idle switch.
End Of SieAccelerator pedal
conditionOutput voltage (V)
Fully released 0.5—0.7 (Target value: 0.6)
Gradually depressed Increases linearly
ACCELERATOR POSITION SENSOR
PCM
B
A
C
D10
90
88
91
A6E40702041
Page 226 of 909
F2–74
CONTROL SYSTEM
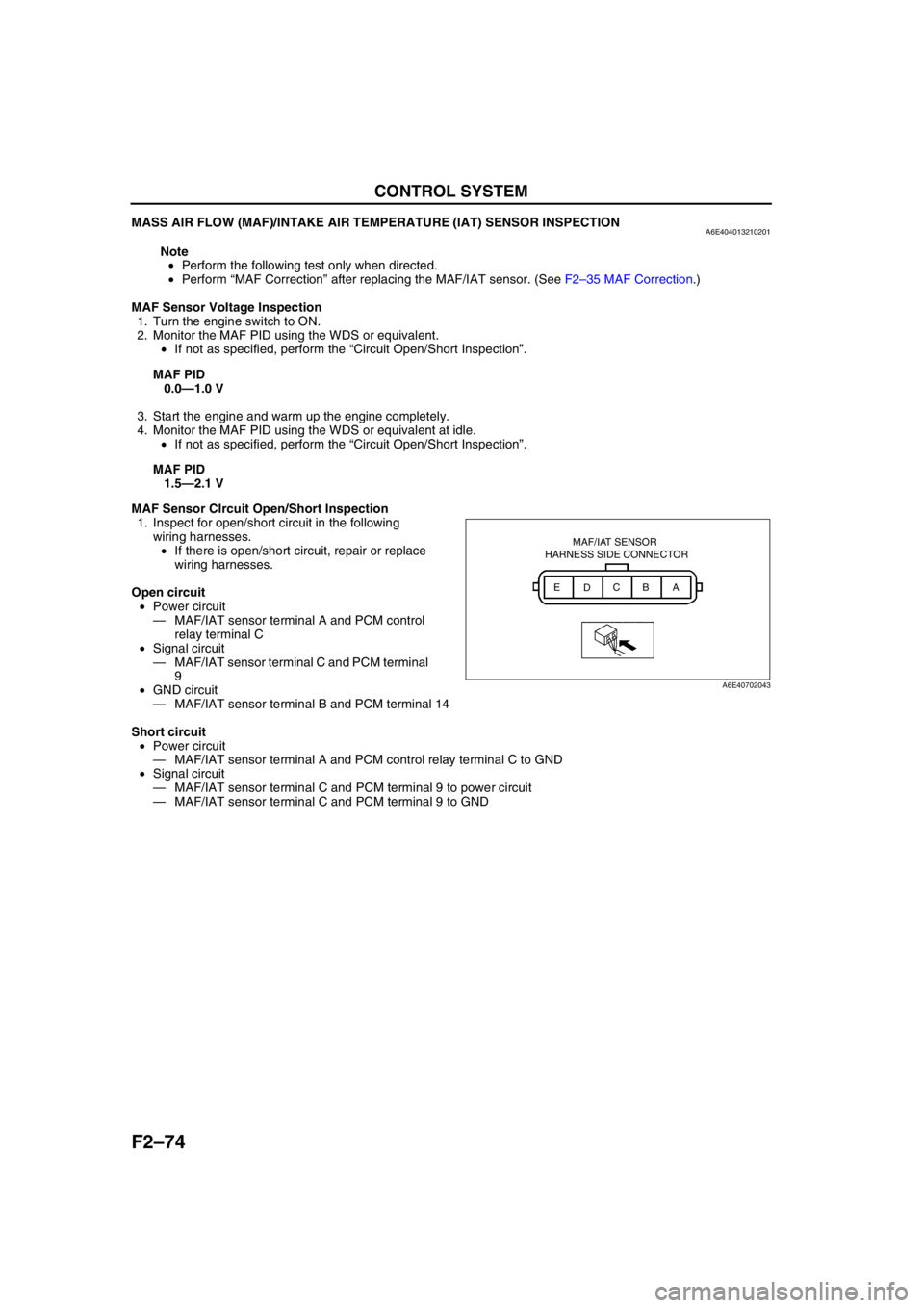
MASS AIR FLOW (MAF)/INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR INSPECTIONA6E404013210201
Note
•Perform the following test only when directed.
•Perform “MAF Correction” after replacing the MAF/IAT sensor. (See F2–35 MAF Correction.)
MAF Sensor Voltage Inspection
1. Turn the engine switch to ON.
2. Monitor the MAF PID using the WDS or equivalent.
•If not as specified, perform the “Circuit Open/Short Inspection”.
MAF PID
0.0—1.0 V
3. Start the engine and warm up the engine completely.
4. Monitor the MAF PID using the WDS or equivalent at idle.
•If not as specified, perform the “Circuit Open/Short Inspection”.
MAF PID
1.5—2.1 V
MAF Sensor CIrcuit Open/Short Inspection
1. Inspect for open/short circuit in the following
wiring harnesses.
•If there is open/short circuit, repair or replace
wiring harnesses.
Open circuit
•Power circuit
—MAF/IAT sensor terminal A and PCM control
relay terminal C
•Signal circuit
—MAF/IAT sensor terminal C and PCM terminal
9
•GND circuit
—MAF/IAT sensor terminal B and PCM terminal 14
Short circuit
•Power circuit
—MAF/IAT sensor terminal A and PCM control relay terminal C to GND
•Signal circuit
—MAF/IAT sensor terminal C and PCM terminal 9 to power circuit
—MAF/IAT sensor terminal C and PCM terminal 9 to GND
MAF/IAT SENSOR
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
A
B
C
D E
A6E40702043
Page 228 of 909
F2–76
CONTROL SYSTEM
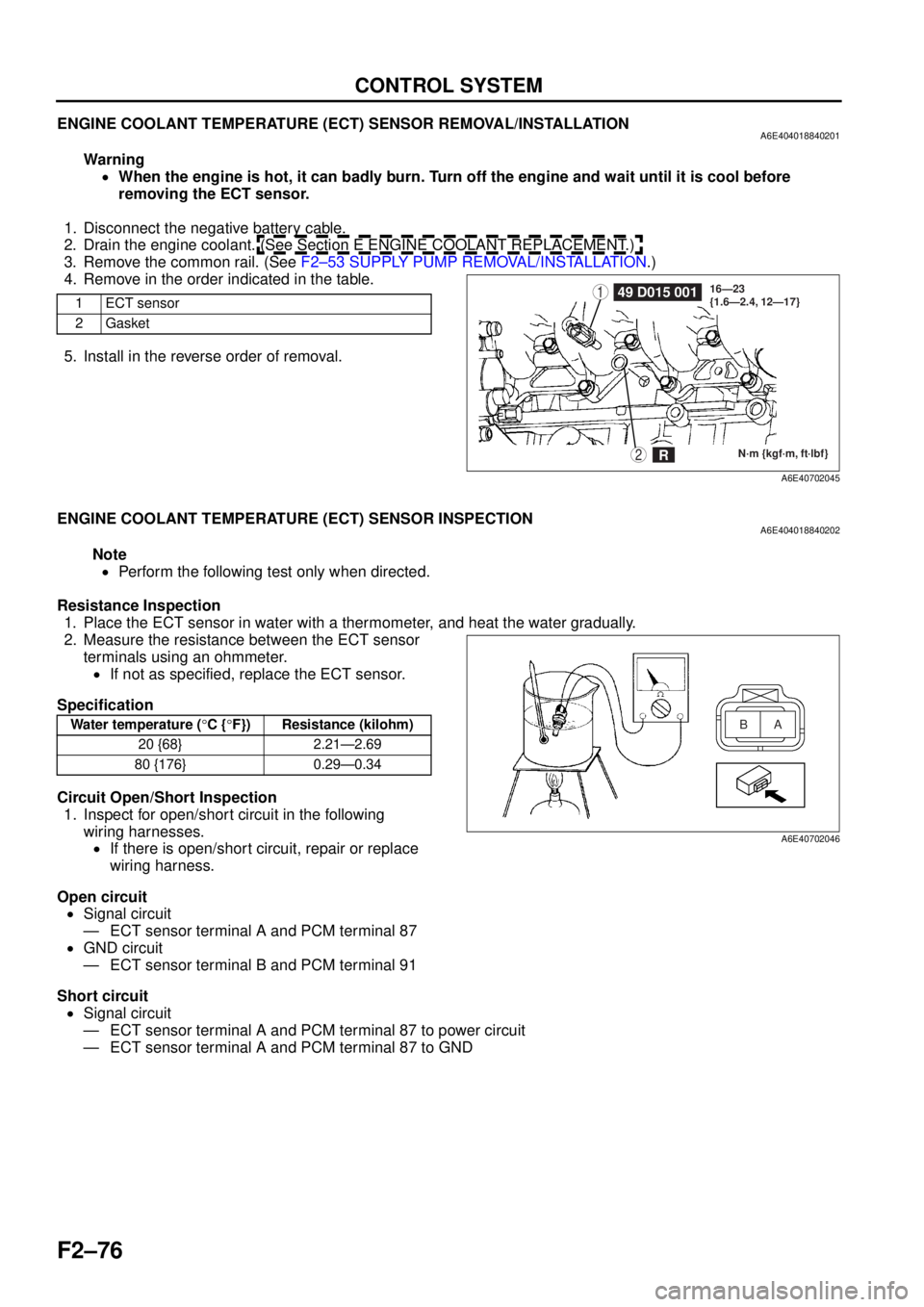
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONA6E404018840201
Warning•When the engine is hot, it can badly burn. Turn off the engine and wait until it is cool before
removing the ECT sensor.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the engine coolant. (See Section E ENGINE COOLANT REPLACEMENT.)
3. Remove the common rail. (See F2–53 SUPPLY PUMP REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .)
4. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
5. Install in the reverse order of removal.
End Of Sie
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR INSPECTIONA6E404018840202
Note
• Perform the following test only when directed.
Resistance Inspection 1. Place the ECT sensor in water with a thermometer, and heat the water gradually.
2. Measure the resistance between the ECT sensor terminals using an ohmmeter.
• If not as specified, replace the ECT sensor.
Specification
Circuit Open/Short Inspection 1. Inspect for open/short circuit in the following
wiring harnesses.• If there is open/short circuit, repair or replace
wiring harness.
Open circuit • Signal circuit
— ECT sensor terminal A and PCM terminal 87
• GND circuit
— ECT sensor terminal B and PCM terminal 91
Short circuit • Signal circuit
— ECT sensor terminal A and PCM terminal 87 to power circuit
— ECT sensor terminal A and PCM terminal 87 to GND
End Of Sie
1ECT sensor
2Gasket149 D015 001
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf}
16—23
{1.6—2.4, 12—17}2R
A6E40702045
Water temperature (
°C { °F}) Resistance (kilohm)
20 {68} 2.21—2.69
80 {176} 0.29—0.34A
B
A6E40702046