oil temperature MAZDA 6 2002 Suplement Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 489 of 909

K2–74
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Evaluation of line pressure test
Stall Speed Test
1. Perform mechanical system test preparation. (See K2–72 Mechanical System Test Preparation.)
2. Connect a tachometer.
3. Start the engine.
4. Shift the selector lever to D range.
Caution
•Do not maintain WOT in any gear range for more than 5 seconds or transaxle damage will occur.
•If engine speed recorded by the tachometer exceeds maximum specified rpm, release the
accelerator pedal immediately. Clutch or band slippage is indicator.
5. Firmly depress the brake pedal with the left foot, and gently depress the accelerator pedal to the floor (WOT)
with the right.
6. When the engine speed no longer increases, quickly read the engine speed and release the accelerator pedal.
7. Shift the selector the to N position and let the engine idle for 1 minute or more to cool the ATF.
8. Perform stall tests for the remaining ranges and position in the same manner.
•R position
•Mrange (1GR, 2GR)
Engine stall speed
ATF temperature : 60—70 °C {140—158 °F}
Turn off all electrical loads
2,200—2,600 rpm
9. Turn off the engine.
Evaluation of stall test
Condition Possible cause
IdleBelow specificationLow pressure in all rangesWorn oil pump
Poor operation of each solenoid
Fluid leaking from oil strainer, oil pump, pressure regulator
valve, torque converter relief valve, and/or pressure relief valve
Pressure regulator valve or pilot valve sticking
Damaged pressure regulator valve spring or pilot valve spring
Low pressure in D and M
rangeFluid leaking from hydraulic circuit of low clutch
Low pressure in R position
onlyFluid leaking from hydraulic circuit of reverse clutch
Fluid leaking from hydraulic circuit of low and reverse brake
clutch
Above specification High pressure in all rangesThrottle position sensor out of adjustment
TFT sensor malfunction
Poor operation of shift solenoid
Pilot valve sticking
Pressure reducing valve or plug sticking
Stall Below specification Low pressure in all rangesThrottle position sensor out of adjustment
Pressure control solenoid malfunction
Poor operation of shift solenoid
Pilot valve sticking
Pressure reducing valve or plug sticking
Condition Possible cause
Above specificationIn all forward ranges and R
positionInsufficient line pressure
Worm oil pump
Poor operation of low clutch
Poor adjustment or malfunction of TR switch
Oil leaking from oil pump, control valve, and/or transmission
case
Pressure regulator valve or pilot valve sticking
In all forward ranges Low clutch slippage
Low one-way clutch slippage
Reduction one-way clutch slippage
In R positionLow and reverse brake slippage
Reverse clutch slippage
Reduction brake slippage
Below specificationIn all forward ranges and R
positionEngine out of tune
One-way clutch slippage within torque converter
Page 490 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–75
K2
Time Lag Test
1. Perform mechanical system test preparation. (See K2–72 Mechanical System Test Preparation.)
2. Start the engine.
3. Warm up the engine until the ATF temperature reaches 60—70°C {140—158°F}. Shift the selector lever from N
position to D range.
4. Use a stopwatch to measure the time it takes from shifting until engagement is felt. Take three measurements
for each test and average the results using the following formula.
Formula
Average time lag = (Time 1 + Time 2 + Time 3) / 3
5. Perform the test for the following shifts in the same manner.
•N position → P position
Time lag
N → D range ... approx. 0.5—1.0 second
N → R position ... approx. 0.6— 1.0 second
Evaluation of time lag test
End Of SieROAD TESTA6E571401030210Road Test Preparation
1. Inspect the engine coolant. (See Section E.)
2. Inspect the engine oil. (See D–8 ENGINE OIL INSPECTION.)
3. Inspect the ATF levels. (See K2–78 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID (ATF) INSPECTION.)
4. Inspect the idle speed and ignition timing in P position. (See F1–22 IDLE SPEED INSPECTION (4WD).)
5. Bring up the engine and transaxle to normal operating temperature.
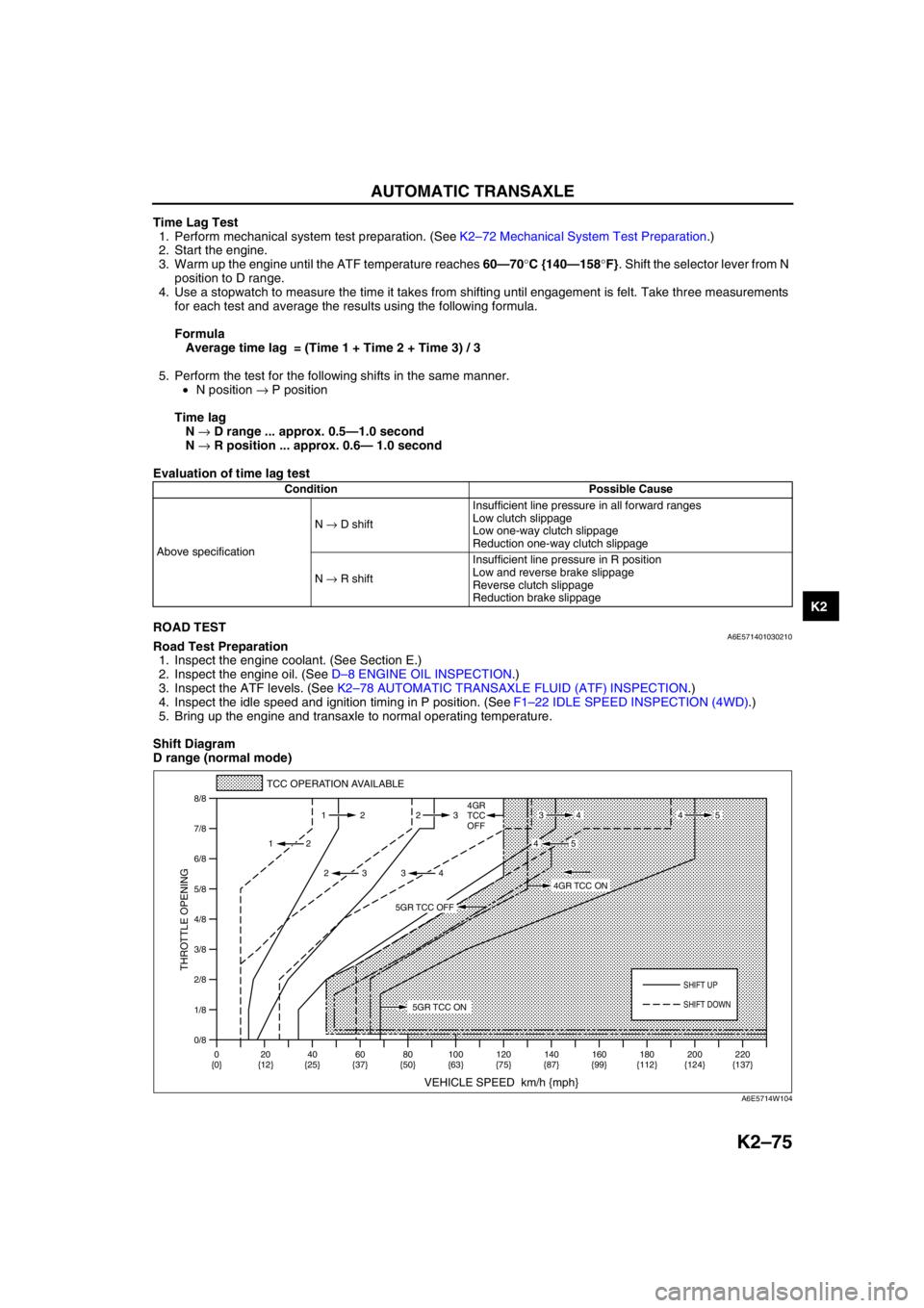
Shift Diagram
D range (normal mode)
Condition Possible Cause
Above specificationN → D shiftInsufficient line pressure in all forward ranges
Low clutch slippage
Low one-way clutch slippage
Reduction one-way clutch slippage
N → R shiftInsufficient line pressure in R position
Low and reverse brake slippage
Reverse clutch slippage
Reduction brake slippage
0/8 1/8
2/8
3/8
4/8
5/8
6/8
7/8
8/8
TCC OPERATION AVAILABLE
VEHICLE SPEED km/h {mph}
THROTTLE OPENING
SHIFT UP
4GR
TCC
OFF
SHIFT DOWN
0
{0}20
{12}40
{25}60
{37}80
{50}100
{63}120
{75}140
{87}160
{99}180
{112}220
{137} 200
{124} 112 23
2
2 232
34
4534
45
5GR TCC ON
4GR TCC ON
5GR TCC OFF
A6E5714W104
Page 494 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–79
K2
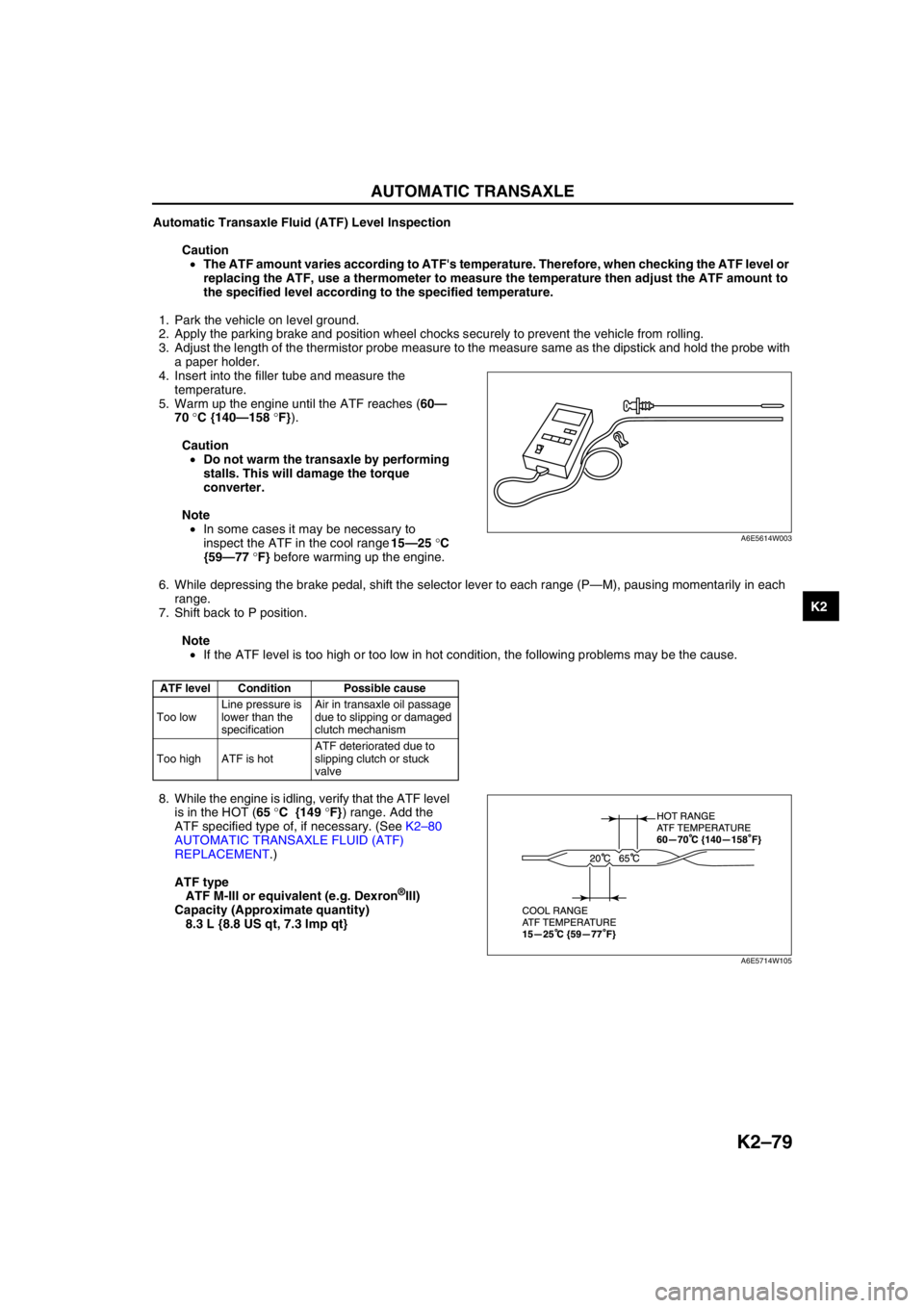
Automatic Transaxle Fluid (ATF) Level Inspection
Caution
•The ATF amount varies according to ATF's temperature. Therefore, when checking the ATF level or
replacing the ATF, use a thermometer to measure the temperature then adjust the ATF amount to
the specified level according to the specified temperature.
1. Park the vehicle on level ground.
2. Apply the parking brake and position wheel chocks securely to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
3. Adjust the length of the thermistor probe measure to the measure same as the dipstick and hold the probe with
a paper holder.
4. Insert into the filler tube and measure the
temperature.
5. Warm up the engine until the ATF reaches (60—
70 °C {140—158 °F}).
Caution
•Do not warm the transaxle by performing
stalls. This will damage the torque
converter.
Note
•In some cases it may be necessary to
inspect the ATF in the cool range 15—25 °C
{59—77 °F} before warming up the engine.
6. While depressing the brake pedal, shift the selector lever to each range (P—M), pausing momentarily in each
range.
7. Shift back to P position.
Note
•If the ATF level is too high or too low in hot condition, the following problems may be the cause.
8. While the engine is idling, verify that the ATF level
is in the HOT (65 °C {149 °F}) range. Add the
ATF specified type of, if necessary. (See K2–80
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID (ATF)
REPLACEMENT.)
ATF type
ATF M-III or equivalent (e.g. Dexron
®III)
Capacity (Approximate quantity)
8.3 L {8.8 US qt, 7.3 Imp qt}
End Of Sie
ATF level Condition Possible cause
Too lowLine pressure is
lower than the
specificationAir in transaxle oil passage
due to slipping or damaged
clutch mechanism
Too high ATF is hotATF deteriorated due to
slipping clutch or stuck
valve
A6E5614W003
A6E5714W105
Page 499 of 909
K2–84
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
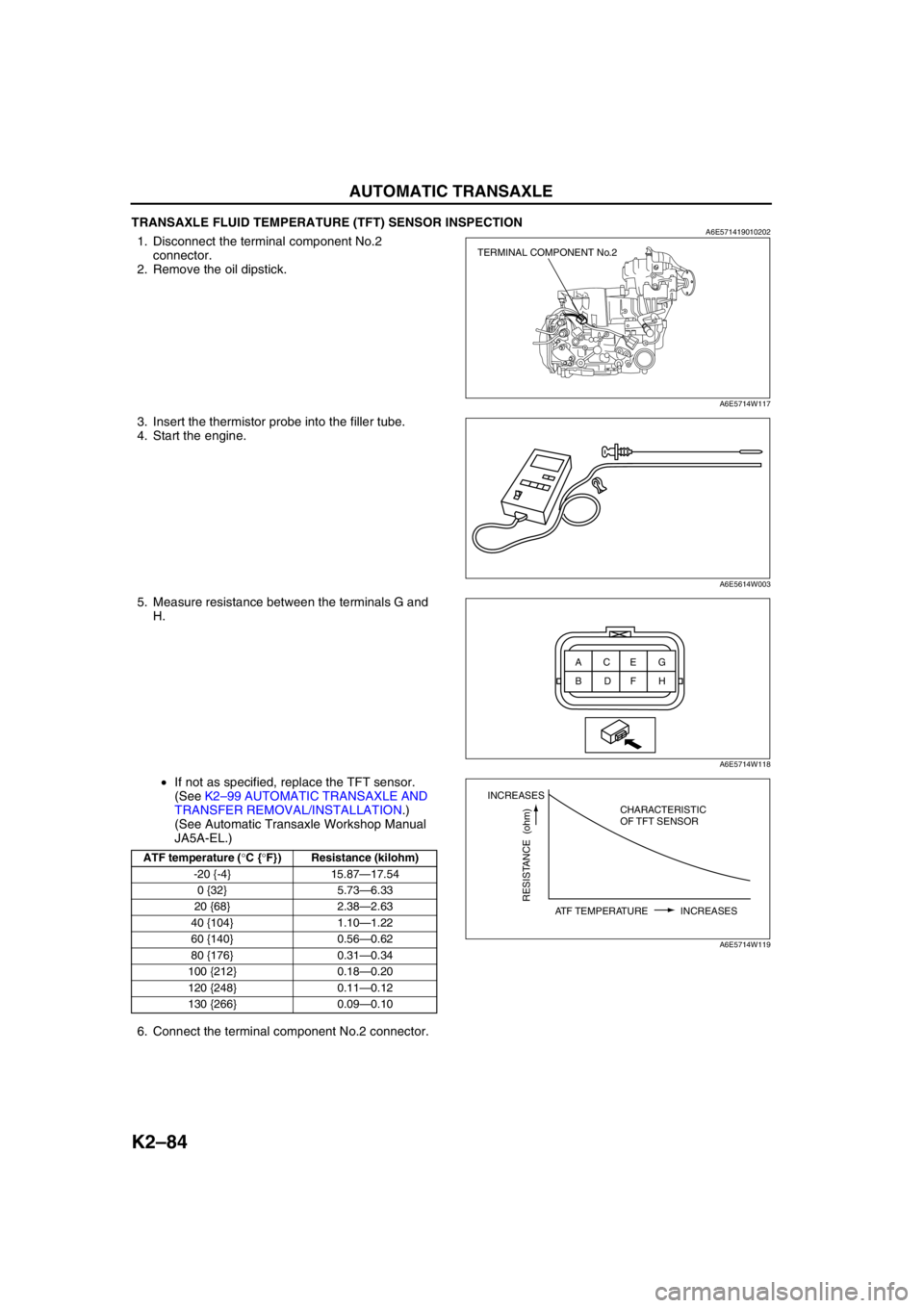
TRANSAXLE FLUID TEMPERATURE (TFT) SENSOR INSPECTIONA6E5714190102021. Disconnect the terminal component No.2
connector.
2. Remove the oil dipstick.
3. Insert the thermistor probe into the filler tube.
4. Start the engine.
5. Measure resistance between the terminals G and
H.
•If not as specified, replace the TFT sensor.
(See K2–99 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE AND
TRANSFER REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
(See Automatic Transaxle Workshop Manual
JA5A-EL.)
6. Connect the terminal component No.2 connector.
End Of Sie
ATF temperature (°C {°F}) Resistance (kilohm)
-20 {-4} 15.87—17.54
0 {32} 5.73—6.33
20 {68} 2.38—2.63
40 {104} 1.10—1.22
60 {140} 0.56—0.62
80 {176} 0.31—0.34
100 {212} 0.18—0.20
120 {248} 0.11—0.12
130 {266} 0.09—0.10
TERMINAL COMPONENT No.2
A6E5714W117
A6E5614W003
ACEG
BDFH
A6E5714W118
INCREASES
RESISTANCE (ohm)
ATF TEMPERATURE INCREASESCHARACTERISTIC
OF TFT SENSOR
A6E5714W119
Page 631 of 909

M–1
M
MFRONT AND REAR AXLES
OUTLINE............................................................... M-2
OUTLINE OF CONSTRUCTION ........................ M-2
FEATURES ......................................................... M-2
SPECIFICATIONS .............................................. M-2
REAR AXLE.......................................................... M-4
REAR AXLE OUTLINE ....................................... M-4
CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW ............................... M-4
DRIVE SHAFT....................................................... M-5
DRIVE SHAFT OUTLINE.................................... M-5
STRUCTURAL VIEW.......................................... M-5
REAR DRIVE SHAFT ......................................... M-5
REAR DIFFERENTIAL.......................................... M-6
REAR DIFFERENTIAL OUTLINE ....................... M-6
CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW ............................... M-6
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM............ M-7
OUTLINE ............................................................ M-7
ELECTRONIC CONTROL COUPLING .............. M-9
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE
SENSOR ........................................................ M-12
4WD WARNING LIGHT .................................... M-12
4WD CONTROL MODURE .............................. M-13
4WD SYSTEM CONTROL................................ M-14
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN) ........ M-15
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC ............................... M-16
OUTLINE............................................................. M-18
SUPPLEMENTAL SERVICE
INFORMATION .............................................. M-18
LOCATION INDEX.............................................. M-19
AXLE/DRIVE SHAFT LOCATION INDEX ......... M-19
REAR DIFFERENTIAL/ELECTRONIC
4WD CONTROL SYSTEM LOCATION
INDEX ............................................................ M-20
GENERAL PROCEDURES................................. M-21
PRECAUTION (FRONT AND REAR AXLE) ..... M-21
REAR AXLE........................................................ M-22
WHEEL HUB BOLT REPL
ACEMENT ..................................................... M-22
WHEEL HUB, KNUCKLE
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-22
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT........................................ M-29
JOINT SHAFT (MZR-CD (RF TURBO))
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-29
JOINT SHAFT (4WD)
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-31
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT
(MZR-CD (RF TURBO))
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-34
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT (4WD)
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-39REAR DRIVE SHAFT.......................................... M-42
REAR DRIVE SHAFT PRE-INSPECTION ........ M-42
REAR DRIVE SHAFT
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-43
REAR DRIVE SHAFT
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-45
REAR DIFFERENTIAL........................................ M-48
DIFFERENTIAL OIL INSPECTION ................... M-48
DIFFERENTIAL OIL REPLACEMENT .............. M-48
OIL SEAL (SIDE GEAR) REPLACEMENT ....... M-49
OIL SEAL (COMPANION FLANGE)
REPLACEMENT ............................................ M-49
REAR DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-51
REAR DIFFERENTIAL DISASSEMBLY ........... M-52
REAR DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY ................. M-56
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM.......... M-65
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE
SENSOR INSPECTION ................................. M-65
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE
SENSOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........... M-65
4WD SOLENOID INSPECTION........................ M-66
4WD CONTROL MODURE INSPECTION ........ M-66
4WD CONTROL MODURE
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-67
COUPLING COMPONENT
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-68
COUPLING COMPONENT
DISASSEMBLY .............................................. M-69
COUPLING COMPONENT ASSEMBLY........... M-72
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC.................................. M-75
WIRING DIAGRAM ........................................... M-75
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSIS ............................... M-76
DTC P1887 ....................................................... M-77
DTC P1888 ....................................................... M-79
DTC U0100 ....................................................... M-80
DTC U0101 ....................................................... M-80
DTC U0121 ....................................................... M-80
TROUBLESHOOTING......................................... M-81
SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAM ........................... M-81
FOREWORD ..................................................... M-82
SYMPTOM TROUBLESHOOTING ................... M-82
NO.1 FREQUENT FRONT WHEEL SLIP ......... M-82
NO.2 TIGHT CORNER BRAKING .................... M-83
NO.3 ABNORMAL NOISE AND/OR
VIBRATION FROM COUPLING
COMPONENT ................................................ M-84 FEATURES
SERVICE
Page 637 of 909
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
M–7
M
OUTLINEA6E632227100201Features
Improved off-road mobility, handling stability, operability, fuel economy and marketability
•An electronic 4WD control system, which automatically optimizes traction distribution to the front and rear
wheels, has been adopted.
Improved serviceability
•A self-diagnostic function has been adopted for the electronic 4WD control system.
Electronic 4WD control system outline
•The newly adopted electronic 4WD control system automatically and optimally controls drive torque distribution
for the front and rear wheels. Due to this off-road mobility, driving stability and fuel economy are improved.
•Based on the input signals from each sensor, the 4WD control modure (4WD CM) determines vehicle driving
and road conditions, and controls output current to the electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid) inside the
rear differential. This control allows for optimal distribution of the drive torque from the engine to the rear
wheels.
•Also, the 4WD CM automatically controls the 4WD, greatly reducing the load on the driver and improving
operability.
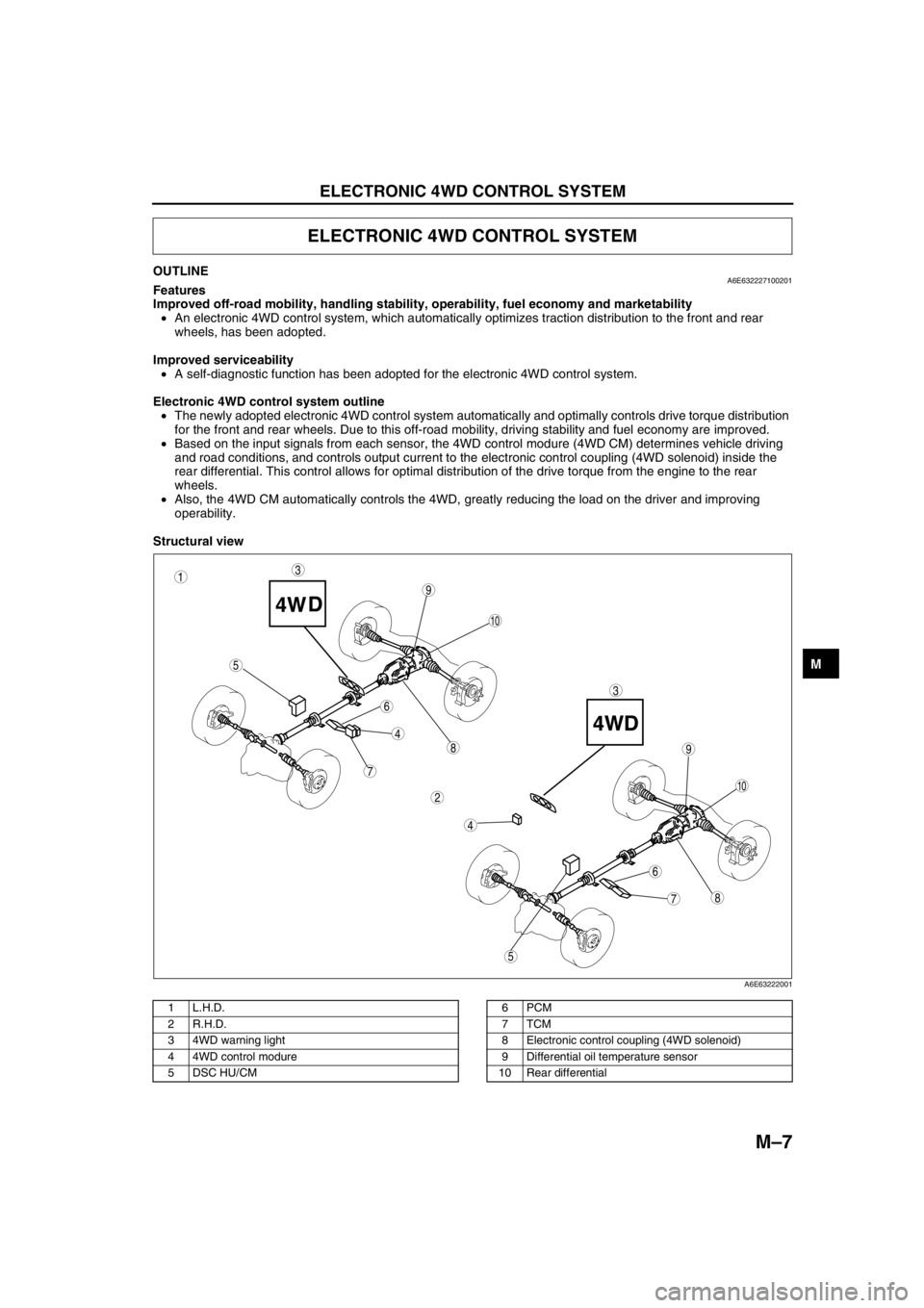
Structural view
.
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
87
5
4
3
6
9
8
7
5
4
3
10
6
1
2
9
10
A6E63222001
1L.H.D.
2 R.H.D.
3 4WD warning light
4 4WD control modure
5 DSC HU/CM6PCM
7TCM
8 Electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid)
9 Differential oil temperature sensor
10 Rear differential
Page 638 of 909
M–8
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
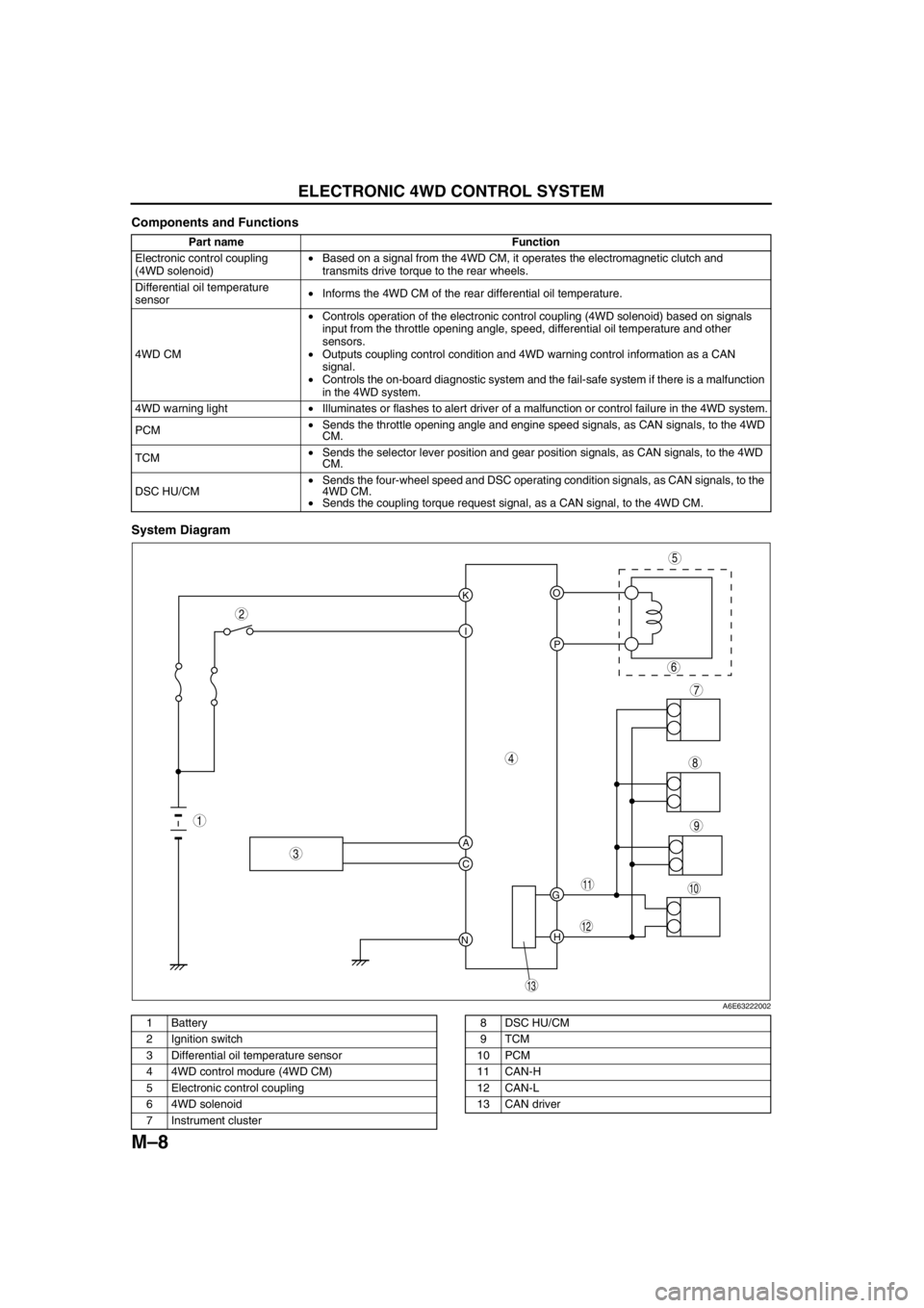
Components and Functions
System Diagram
.
Part name Function
Electronic control coupling
(4WD solenoid)•Based on a signal from the 4WD CM, it operates the electromagnetic clutch and
transmits drive torque to the rear wheels.
Differential oil temperature
sensor•Informs the 4WD CM of the rear differential oil temperature.
4WD CM•Controls operation of the electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid) based on signals
input from the throttle opening angle, speed, differential oil temperature and other
sensors.
•Outputs coupling control condition and 4WD warning control information as a CAN
signal.
•Controls the on-board diagnostic system and the fail-safe system if there is a malfunction
in the 4WD system.
4WD warning light•Illuminates or flashes to alert driver of a malfunction or control failure in the 4WD system.
PCM•Sends the throttle opening angle and engine speed signals, as CAN signals, to the 4WD
CM.
TCM•Sends the selector lever position and gear position signals, as CAN signals, to the 4WD
CM.
DSC HU/CM•Sends the four-wheel speed and DSC operating condition signals, as CAN signals, to the
4WD CM.
•Sends the coupling torque request signal, as a CAN signal, to the 4WD CM.
KO
P I
A
C
NH G
9
8
7
5
4
3
10
13
11
12
6
1
2
A6E63222002
1 Battery
2 Ignition switch
3 Differential oil temperature sensor
4 4WD control modure (4WD CM)
5 Electronic control coupling
6 4WD solenoid
7 Instrument cluster8 DSC HU/CM
9TCM
10 PCM
11 CAN-H
12 CAN-L
13 CAN driver
Page 642 of 909
M–12
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
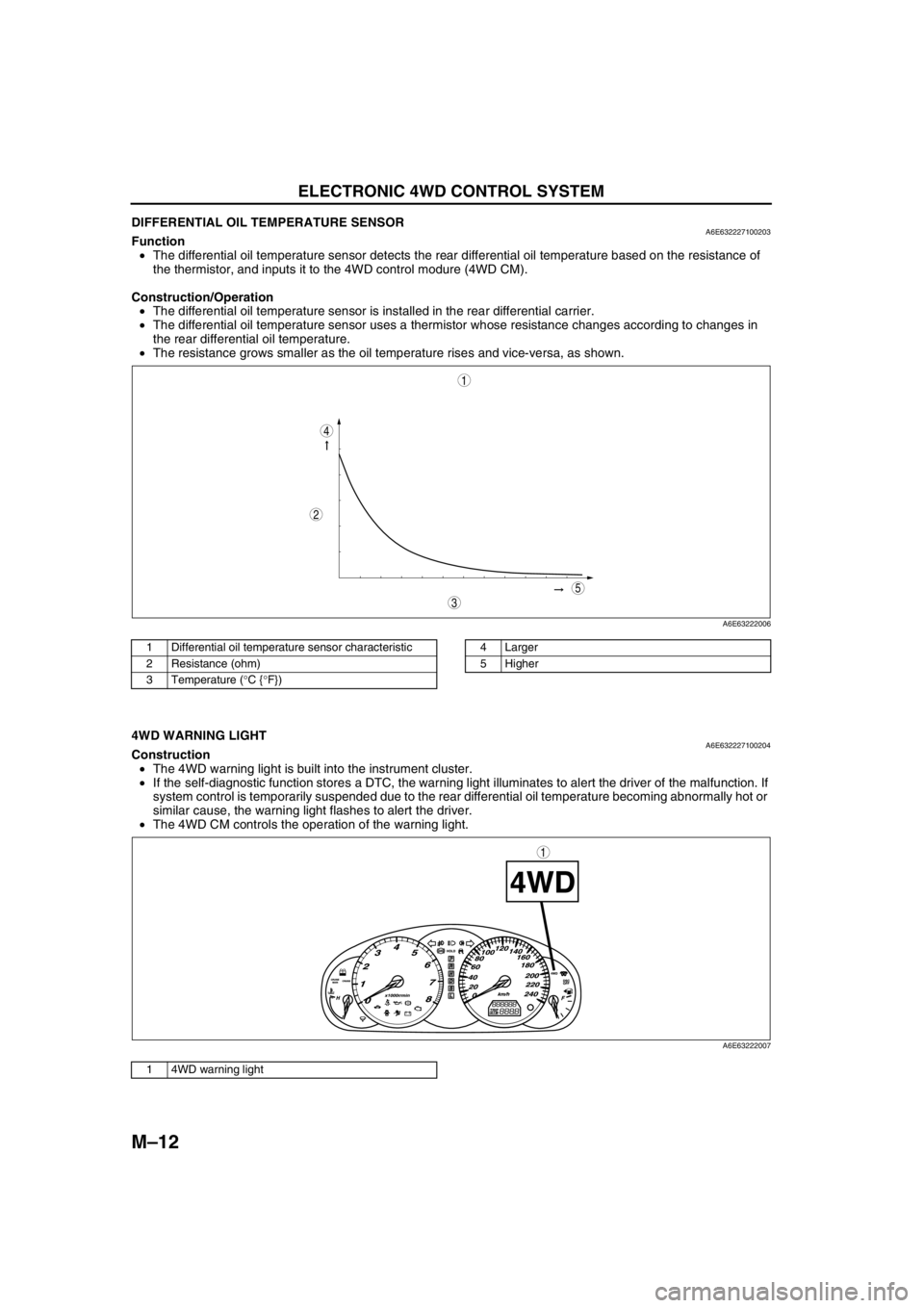
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE SENSORA6E632227100203Function
•The differential oil temperature sensor detects the rear differential oil temperature based on the resistance of
the thermistor, and inputs it to the 4WD control modure (4WD CM).
Construction/Operation
•The differential oil temperature sensor is installed in the rear differential carrier.
•The differential oil temperature sensor uses a thermistor whose resistance changes according to changes in
the rear differential oil temperature.
•The resistance grows smaller as the oil temperature rises and vice-versa, as shown.
.
End Of Sie
4WD WARNING LIGHTA6E632227100204Construction
•The 4WD warning light is built into the instrument cluster.
•If the self-diagnostic function stores a DTC, the warning light illuminates to alert the driver of the malfunction. If
system control is temporarily suspended due to the rear differential oil temperature becoming abnormally hot or
similar cause, the warning light flashes to alert the driver.
•The 4WD CM controls the operation of the warning light.
.
End Of Sie
5
4
3
1
2
A6E63222006
1 Differential oil temperature sensor characteristic
2 Resistance (ohm)
3 Temperature (°C {°F})4 Larger
5 Higher
1
A6E63222007
1 4WD warning light
Page 644 of 909
M–14
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
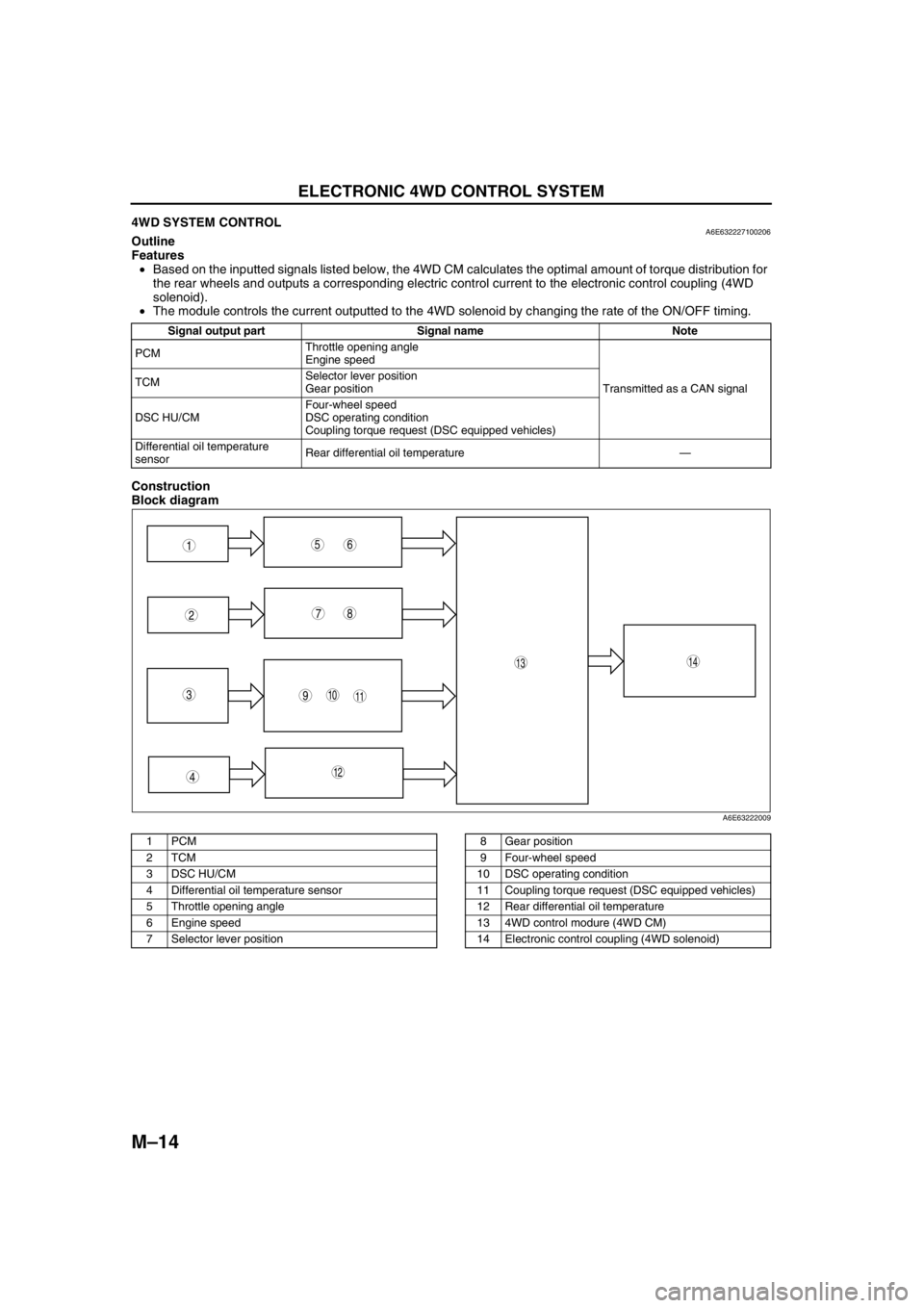
End Of Sie4WD SYSTEM CONTROLA6E632227100206Outline
Features
•Based on the inputted signals listed below, the 4WD CM calculates the optimal amount of torque distribution for
the rear wheels and outputs a corresponding electric control current to the electronic control coupling (4WD
solenoid).
•The module controls the current outputted to the 4WD solenoid by changing the rate of the ON/OFF timing.
Construction
Block diagram
.
Signal output part Signal name Note
PCMThrottle opening angle
Engine speed
Transmitted as a CAN signal TCMSelector lever position
Gear position
DSC HU/CMFour-wheel speed
DSC operating condition
Coupling torque request (DSC equipped vehicles)
Differential oil temperature
sensorRear differential oil temperature—
9
87
5
4
310
1413
11
12
61
2
A6E63222009
1PCM
2TCM
3 DSC HU/CM
4 Differential oil temperature sensor
5 Throttle opening angle
6 Engine speed
7 Selector lever position8 Gear position
9 Four-wheel speed
10 DSC operating condition
11 Coupling torque request (DSC equipped vehicles)
12 Rear differential oil temperature
13 4WD control modure (4WD CM)
14 Electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid)
Page 645 of 909

ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
M–15
M
Operation
Normal control
•When starting off or accelerating during straight-ahead driving, torque transmitted to the rear wheels is
optimally controlled to ensure sufficient acceleration performance. Due to this, standing-start and acceleration
performance is improved.
•Also, in order to improve fuel economy when driving at a stable, consistent speed, torque transmitted to the
rear wheels is damped, and rear-wheel drive is controlled to maintain it close to that of the front wheels.
Tight cornering control
•When the 4WD CM determines, based on the four-wheel speed signal, that the vehicle is in tight cornering, it
reduces the torque transmitted to the rear wheels to avoid tight corner braking characteristics.
Integrated DSC control
•If a signal from the DSC HU/CM input to the 4WD CM indicates that ABS control is activated, the module
controls the torque transmitted to the rear wheels to prevent undue influence on ABS control.
•Also, when a coupling torque request signal is received from the DSC HU/CM, the module controls the torque
transmitted to the rear wheels to match the amount of requested torque.
Other control
•In case the rear differential oil temperature exceeds the specified amount, or when there is an unusually large
variation in the rotation speed of the front and rear wheels (ex. when trying to get unstuck), control is
temporarily suspended in order to protect the 4WD system. When this occurs the 4WD warning light flashes to
indicate the situation to the driver.
End Of Sie
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN)A6E632227100207Outline
•The 4WD CM transmits/receives information using the CAN system. See Section T for detailed information
regarding the CAN system.
Operation
Transmitted information
•Coupling torque
•4WD system operating condition (warning light information)
Received information
•Four-wheel speed
•Throttle opening angle
•Engine speed
•ABS/DSC operating condition
•Gear position
•Selector lever position
•Coupling torque request
End Of Sie