engine coolant MAZDA MX-5 1994 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 1994, Model line: MX-5, Model: MAZDA MX-5 1994Pages: 1708, PDF Size: 82.34 MB
Page 235 of 1708
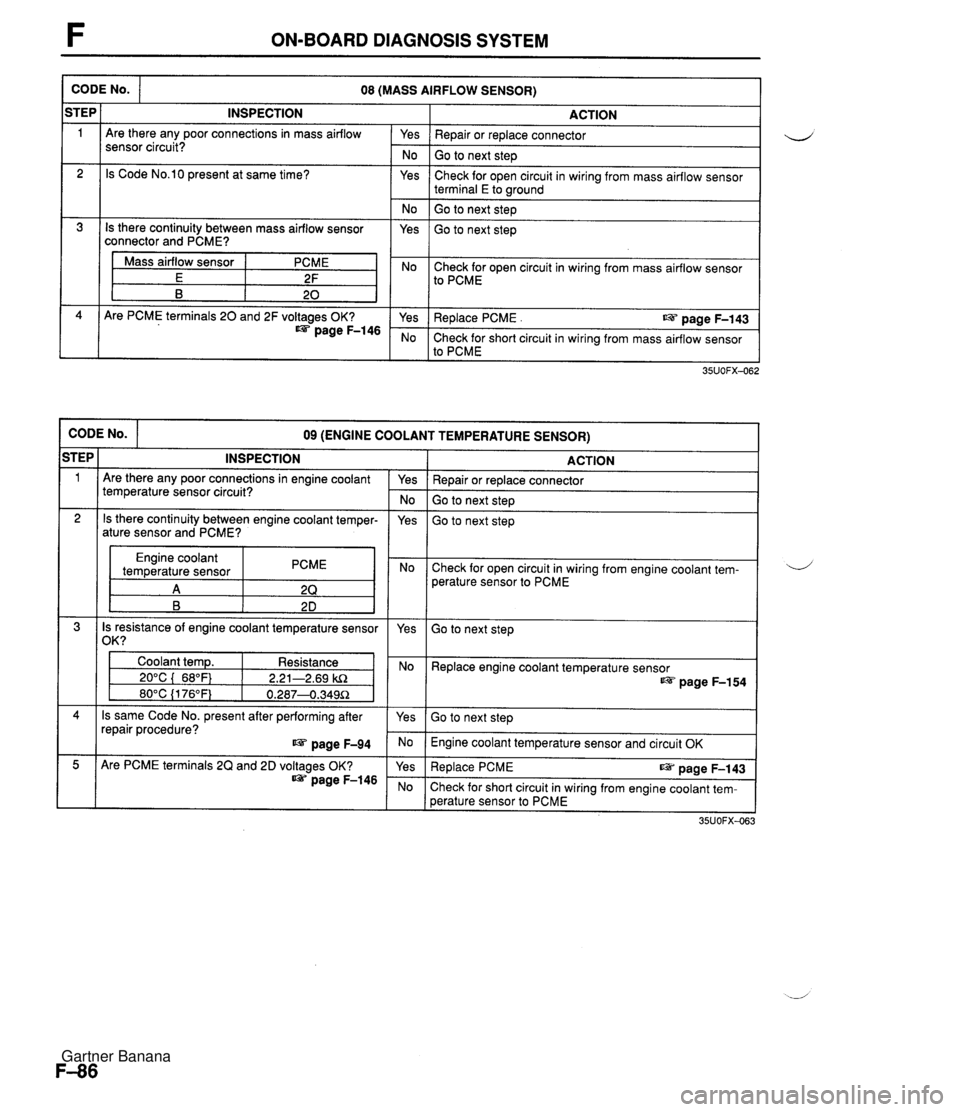
F ON-BOARD DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM CODE No. ACTION Yes I Repair or replace connector 08 (MASS AIRFLOW SENSOR) iTEP 1 No I Go to next step INSPECTION Are there any poor connections in mass airflow sensor circuit? Yes 2 Check for open circuit in wiring from mass airflow sensor terminal E to wound Is Code No.10 present at same time? No ( Go to next step 1 Is there continuity between mass airflow sensor connector and PCME? Yes Go to next step Mass airflow sensor E B I Yes I Replace PCME . us page F-143 PCME 2F 20 No Check for short circuit in wiring from mass airflow sensor to PCME Are PCME terminals 20 and 2F voltages OK? page F-146 Check for open circuit in wiring from mass airflow sensor to PCME CODE No. ACTION 09 (ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR) STEP 1 Repair or replace connector Go to next step INSPECTION Are there any poor connections in engine coolant temperature sensor circuit? Go to next step Yes - No 2 Engine coolant temperature sensor PCME Check for open circuit in wiring from engine coolant tem- perature sensor to PCME Is there continuity between engine coolant temper- ature sensor and PCME? 4 Is resistance of engine coolant temperature sensor 1 /om I yes Yes Go to next step Coolant temp. Resistance 1 I 20°C ( 68°F) 1 2.21-2.69 kR Replace engine coolant temperature sensor page F-154 Is same Code No. present after performing after repair procedure? page F-94 Go to next step Engine coolant temperature sensor and circuit OK Are PCME terminals 2Q and 2D voltages OK? page F-146 Re~lace PCME ~aae F-143 Check for short circuit in wiring from engine coolant tem- perature sensor to PCME Gartner Banana
Page 237 of 1708
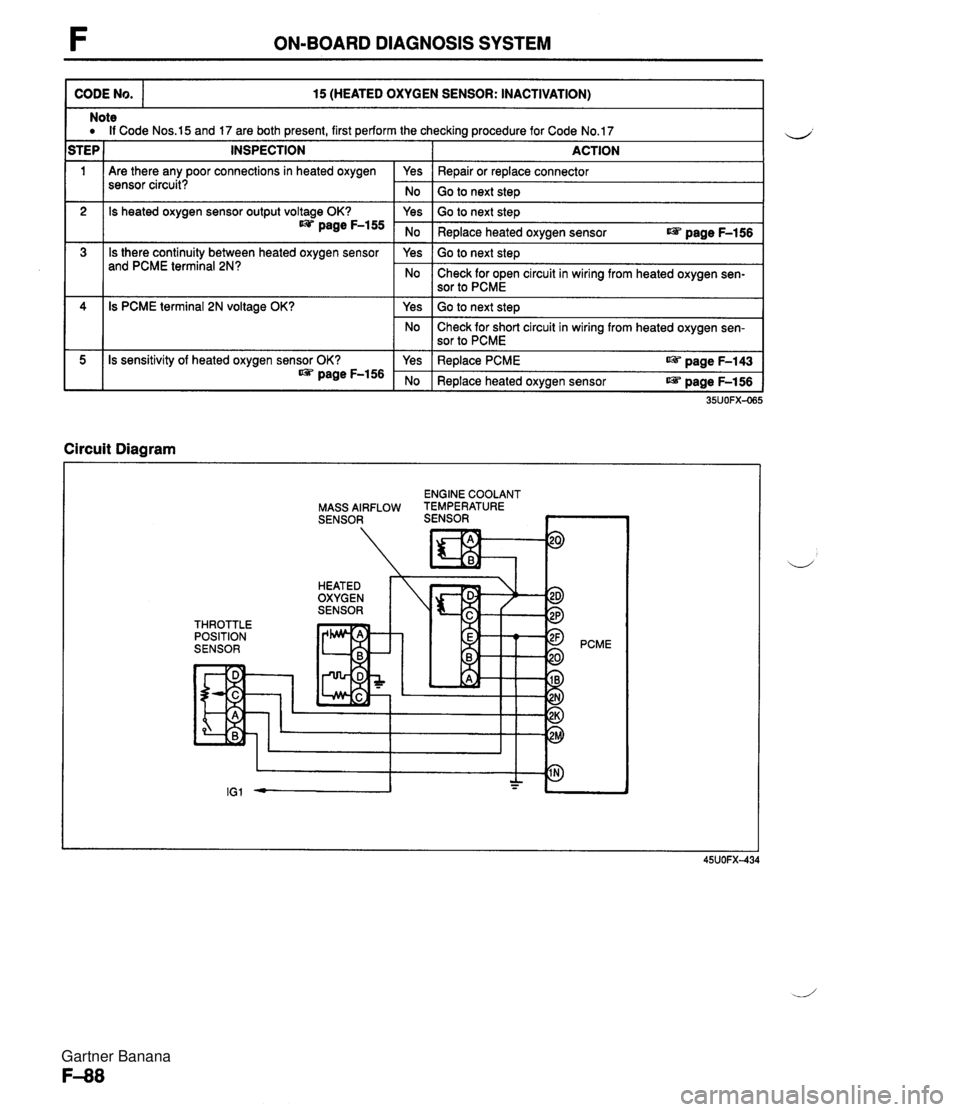
F ON-BOARD DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM CODE No. 15 (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR: INACTIVATION) 111 Are there any poor connections in heated oxygen sensor circuit? Note a If Code Nos.15 and 17 are both present, first perform the checking procedure for Code No.17 STEP 1 INSPECTION I ACTION 2 3 Circuit Diagram I Yes No 4 5 ENGINE COOLANT MASS AIRFLOW TEMPERATURE SENSOR SENSOR ~ Repair or replace connector Go to next steD Is heated oxygen sensor output voltage OK? page F-155 Is there continuity between heated oxygen sensor and PCME terminal 2N? THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR 35UOFX-065 Is PCME terminal 2N voltage OK? Is sensitivity of heated oxygen sensor OK? * page F-156 PCME Yes No Yes No Go to next step Replace heated oxygen sensor r@ page F-156 Go to next step Check for open circuit in wiring from heated oxygen sen- sor to PCME Yes No Yes No Go to next step Check for short circuit in wiring from heated oxygen sen- sor to PCME Replace PCME aPi. page F-143 Replace heated oxygen sensor r@ page F-156 Gartner Banana
Page 247 of 1708

INTAKE AIR SYSTEM INTAKE AIR SYSTEM COMPONENTS Removal 1 Inspection l Installation Warning Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can very easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep sparks and flames away from fuel. Fuel in the fuel system is under high pressure when the engine is not running. Warning Fuel line spills and leaks are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injuries or death and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To prevent this, always complete the follow- ing "Fuel Line Safety Procedures". Fuel Line Safety Procedures A. Release the fuel pressure before disconnecting a fuel line. 1. Start the engine. 2. Remove the fuel pump relay. 3. After the engine stalls, turn the ignition switch to OFF. 4. lnstall the fuel pump relay. B. Avoid leakage. 1. When disconnecting a fuel line hose, wrap a rag around it to protect against fuel leakage. 2. Plug the hose after removal. C. lnstall hose clamps to secure the fuel pressure gauge connections. 1. Drain the engine coolant. (Refer to section E.) 2. Remove in the order shown in the figure. 3. Check the components for damage and repair or replace as necessary. 4. lnstall in the reverse order of removal, using new gaskets. 5. Refill the engine coolant. (Refer to section E.) Gartner Banana
Page 253 of 1708
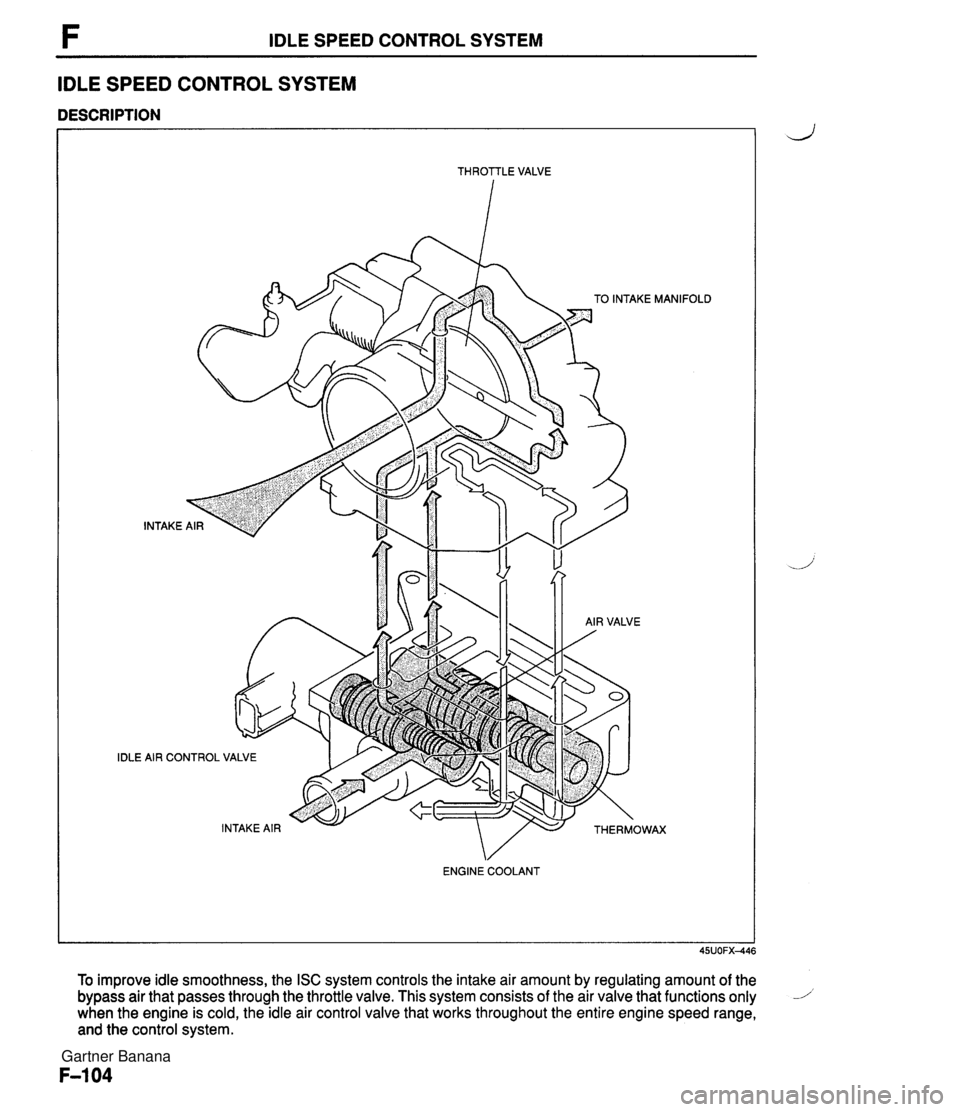
F IDLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM IDLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION - -- - THROTTLE VALVE IDLE TO INTAKE MANlF INTAKE i AIR CONTROL VALVE ENGINE COOLANT To improve idle smoothness, the ISC system controls the intake air amount by regulating amount of the bypass air that passes through the throttle valve. This system consists of the air valve that functions only 1 when the engine is cold, the idle air control valve that works throughout the entire engine speed range, and the control system. Gartner Banana
Page 254 of 1708

IDLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM PREPARATION SST I 'L 49 801 9 9AO For inspection of air System valve Selector BAC VALVE System Operation Air valve - Perform this inspection when the engine is cold. (Engine coolant temperature below 20°C {68OF).) 1. Connect a tachometer to the data link connector terminal IG-. When using an externally powered timing light and/ or tachometer connect it to the power connector (Blue: 1 -pin). Caution Grounding the power connector terminal (Blue: 1-pin) will burn out the 20A wiper fuse. 2. Connect the SST and set the TEST SW to "SELF TEST" or connect data link connector terminals TEN and GND with a jumper wire. 3. Verify that the engine speed gradually decreases as the engine warms up. 4. Remove the SST or the jumper wire. Gartner Banana
Page 271 of 1708

PRESSURE REGULATOR CONTROL SYSTEM PRESSURE REGULATOR CONTROL SYSTEM DATA LINK CONNECTOR - CLUTCH SWITCH (MT) (TEN TERMINAL) PARKINEUTRAL SWITCH (PCMT) (AT) THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR L 1 ,,,, INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE 1 SENSOR (IN MASS AIRFLOW SENSOR) -;- ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR PRC SOLENOID VALVE CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR PRESSURE REGULATOR PCME I Above 90°C {194OF} ( Above 70°C {158'F} I Throttle valve closed throttle position or no load condition I Approx. 150 1 I Operating condition Coolant temperature I Intake air temperature I Engine condition I I To prevent percolation of the fuel during hot restart idle, vacuum to the pressure regulator is momentarily cut, and the fuel injection pressure is increased to slightly more than 284 kPa (2.9 kgf/cm2, 41.2 psi}. Operating time (sec) Gartner Banana
Page 273 of 1708

F EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) PREPARATION SST I 49 9200 162 Engine Signal Monitor 49 GO1 8 904 Sheet DESCRIPTION For inspection of EGR For inspection of EGR 49 GO1 8 903 For inspection of Adapter EGR harness / TO AIR CLEANER HOUSING I THROTTLE POSITION ENGINE COOLANT SENSOR SENSOR TEMPERATURE CRANKSHAFT SENSOR POSITION SENSOR EGR SOLENOID VALVE (VACUUM) EGR SOLENOID VALVE (VENT) / PCME I This ~~st~rn~recirculates a small amount of exhaust gas into the intake manifold to reduce the combus- tion temperature, and reduce the NOx emissions. This system consists of the EGR control valve, EGR function sensor, two solenoid valves, powertrain control module (engine) (PCME) and input devices. Gartner Banana
Page 274 of 1708
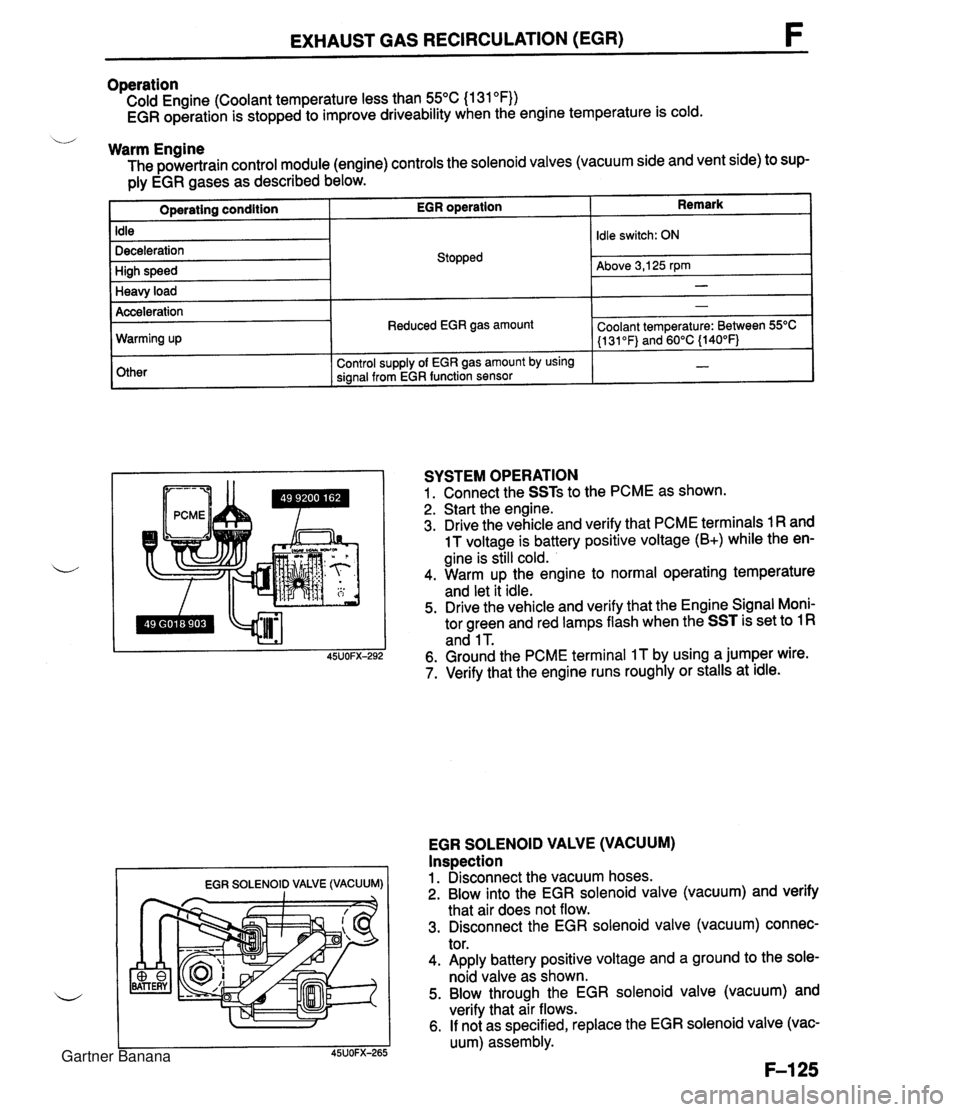
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) Operation Cold Engine (Coolant temperature less than 55°C (1 31 OF)) EGR operation is stopped to improve driveability when the engine temperature is cold. u Warm Engine The powertrain control module (engine) controls the solenoid valves (vacuum side and vent side) to sup- ply EGR gases as described below. Remark Operating condition Idle Deceleration High speed Heavy load EGR SOLENOID VALVE (VACUUM) I I EGR operation Acceleration Warming up Other SYSTEM OPERATION 1. Connect the SSTs to the PCME as shown. 2. Start the engine. 3. Drive the vehicle and verify that PCME terminals 1 R and 1 T voltage is battery positive voltage (B+) while the en- gine is still cold. 4. Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature and let it idle. 5. Drive the vehicle and verify that the Engine Signal Moni- tor green and red lamps flash when the SST is set to 1 R and 1 T. 6. Ground the PCME terminal IT by using a jumper wire. 7. Verify that the engine runs roughly or stalls at idle. Stopped EGR SOLENOID VALVE (VACUUM) Inspection 1. Disconnect the vacuum hoses. 2. Blow into the EGR solenoid valve (vacuum) and verify that air does not flow. 3. Disconnect the EGR solenoid valve (vacuum) connec- tor. 4. Apply battery positive voltage and a ground to the sole- noid valve as shown. 5. Blow through the EGR solenoid valve (vacuum) and verify that air flows. 6. If not as specified, replace the EGR solenoid valve (vac- uum) assembly. Idle switch: ON Above 3,125 rpm - Reduced EGR gas amount Control supply of EGR gas amount by using signal from EGR function sensor - Coolant temperature: Between 55OC (1 31 OF) and 60°C {140°F) - Gartner Banana
Page 280 of 1708

FUEL EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM FUEL EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The fuel evaporative system consists of the fuel vapor valve, the two-way check valve, the charcoal can- ister, the purge solenoid valve, the powertrain control module (engine), and the input devices. The amount of evaporative fumes introduced into the engine and burned is controlled by the solenoid valve in relation to the engine's operating conditions. To maintain the best engine performance, the solenoid valve is controlled by the powertrab control module (engine). THROTTLE 1-1 POSITION SENSOR I1 I I (IDLE SWITCH) 7 BAROMETIC ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR PARWNEUTRAL SWITCH (AT) MASS AIRFLOW SENSOR CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (SGT-SIGNAL) n - DUTY - LOW HIGH (ENGINE) CHARCOAL PURGE SOLENOID VALVE CANISTER HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR ENGINE COOLANT POWERTRAIN TEMPERATURE SENSOR CONTROL MODULE CHECK VALVE # 11 FUEL VAPOR VALVE Operation The purge solenoid valve is controlled by duty signals from the powertrain control module (engine) to per- form purging of the charcoal canister. Purging is done when these conditions are met: i/ 1. After warm-up. 2. Driving in gear. 3. Accelerator pedal depressed (idle switch OFF). 4. Heated oxygen sensor functioning normally. Gartner Banana
Page 286 of 1708

DECHOKE CONTROL SYSTEM DECHOKE CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION To clean out excess fuel in cylinders, as in the case of engine flooding, when the engine is cold, no fuel will be injected when the accelerator is held fully depressed while cranking the engine. CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (NE-SIGNAL) n POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR I (ENGINE) 1 DETERMINA- TION OF FUEL CUT SPEED Gartner Banana