towing MERCEDES-BENZ G-CLASS SUV 2012 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MERCEDES-BENZ, Model Year: 2012, Model line: G-CLASS SUV, Model: MERCEDES-BENZ G-CLASS SUV 2012Pages: 357, PDF Size: 8.86 MB
Page 285 of 357
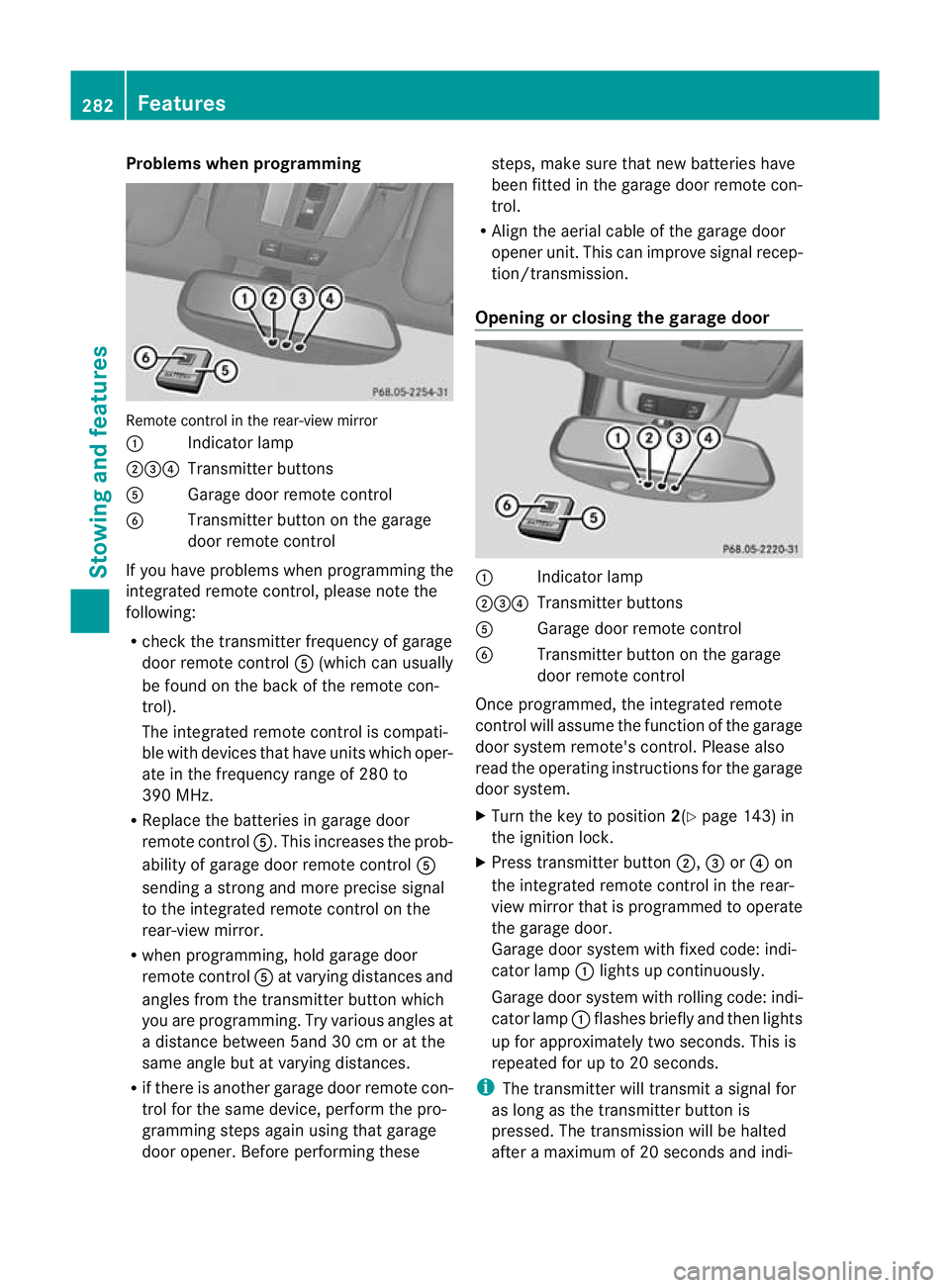
Problems when programming
Remote control in the rear-view mirror
:
Indicator lamp
;=? Transmitter buttons
A Garage door remote control
B Transmitter button on the garage
door remote control
If you have problems when programming the
integrated remote control, please note the
following:
R check the transmitter frequency of garage
door remote control A(which can usually
be found on the back of the remote con-
trol).
The integrated remote control is compati-
ble with devices that have units which oper-
ate in the frequency range of 280 to
390 MHz.
R Replace the batteries in garage door
remote control A.This increases the prob-
ability of garage door remote control A
sending a strong and more precise signal
to the integrated remote control on the
rear-view mirror.
R when programming, hold garage door
remote control Aat varying distances and
angles from the transmitter button which
you are programming. Try various angles at
a distance between 5and 30 cm or at the
same angle but at varying distances.
R if there is another garage door remote con-
trol for the same device, perform the pro-
gramming steps again using that garage
door opener. Before performing these steps, make sure that new batteries have
been fitted in the garage door remote con-
trol.
R Align the aerial cable of the garage door
opener unit. This can improve signal recep-
tion/transmission.
Opening or closing the garage door :
Indicator lamp
;=? Transmitter buttons
A Garage door remote control
B Transmitter button on the garage
door remote control
Once programmed, the integrated remote
control will assume the function of the garage
door system remote's control. Please also
read the operating instructions for the garage
door system.
X Turn the key to position 2(Ypage 143) in
the ignition lock.
X Press transmitter button ;,=or? on
the integrated remote control in the rear-
view mirror that is programmed to operate
the garage door.
Garage door system with fixed code: indi-
cator lamp :lights up continuously.
Garage door system with rolling code: indi-
cator lamp :flashes briefly and then lights
up for approximately two seconds. This is
repeated for up to 20 seconds.
i The transmitter will transmit a signal for
as long as the transmitter button is
pressed. The transmission will be halted
after a maximum of 20 seconds and indi- 282
FeaturesStowing and features
Page 286 of 357
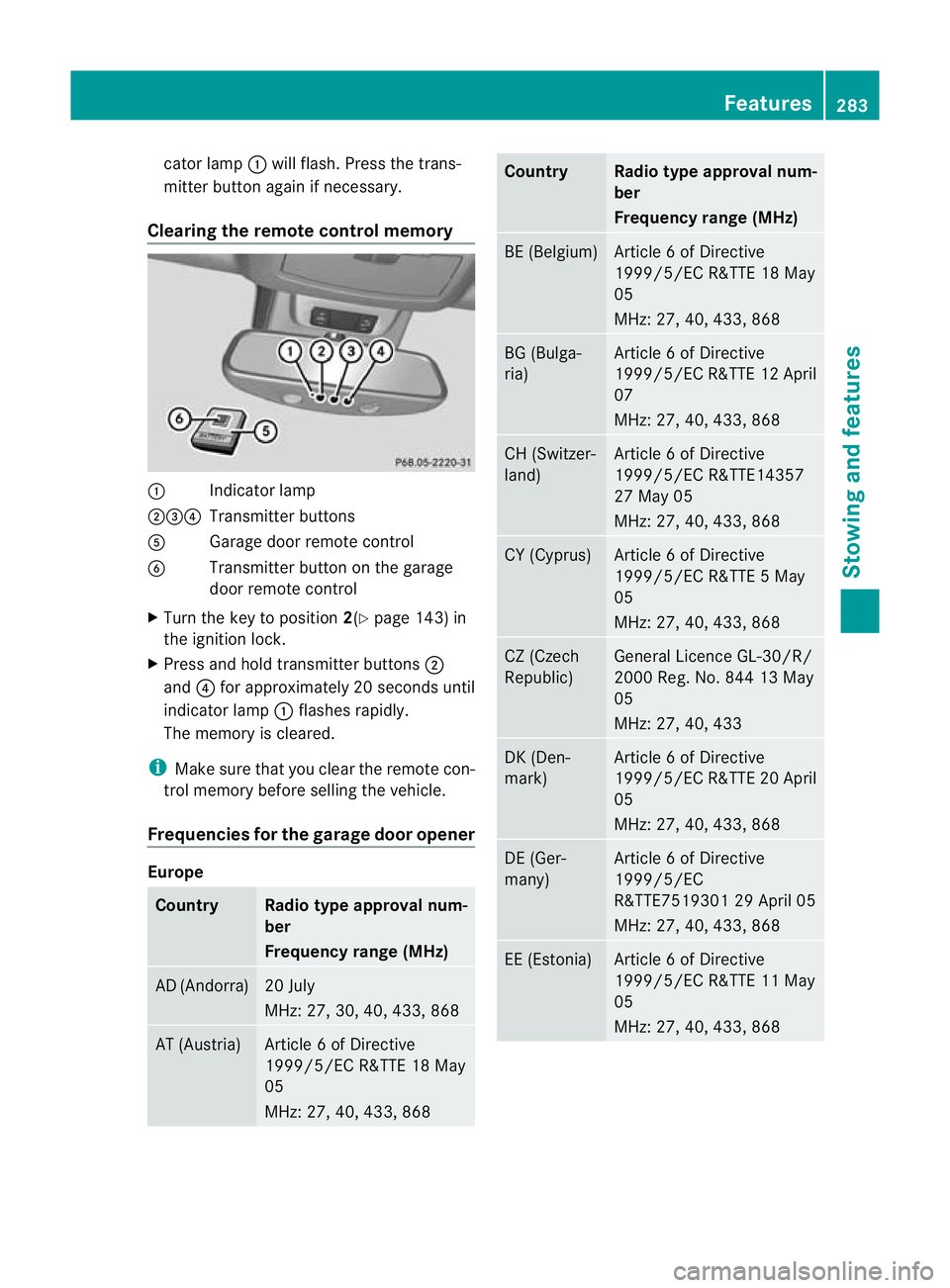
cator lamp
:will flash. Press the trans-
mitter button agai nifnecessary.
Clearing the remote control memory :
Indicator lamp
;=? Transmitter buttons
A Garage door remote control
B Transmitter button on the garage
door remote control
X Turn the key to position 2(Ypage 143) in
the ignition lock.
X Press and hold transmitter buttons ;
and ?for approximately 20 seconds until
indicator lamp :flashes rapidly.
The memory is cleared.
i Make sure that you clear the remote con-
trol memory before selling the vehicle.
Frequencies for the garage door opener Europe
Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
AD (Andorra) 20 July
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 433, 868
AT (Austria) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
BE (Belgium) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
BG (Bulga-
ria) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/ECR
&TTE 12 April
07
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 CH (Switzer-
land) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE14357
27 May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
CY (Cyprus) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 5 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
CZ (Czech
Republic) General Licence GL-30/R/
2000 Reg. No. 844 13 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433
DK (Den-
mark) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 20 April
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
DE (Ger-
many) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC
R&TTE7519301 29 April 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
EE (Estonia) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 11 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 Features
283Stowing and features Z
Page 287 of 357
Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
ES (Spain) 000438/2005,
000439/2005,
000440/2005
000441/2005,
000445/2005,
000446/2005
000447/2005
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 FI (Finland) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE10668
13 May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
FR (France) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE10668
13 May 05
27, 30, 40, 433, 868
GI (Gibraltar) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE13 May
05 (UK)
MHz: 27
,40, 418, 433, 868 GR (Greece) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC
R&TTE11409/18/4/2005
18 May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
HR (Croatia) SDR 224/06
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
HU (Hun-
gary) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
IC (Canary
Islands) 000438/2005,
000439/2005
000440/2005,
000441/2005
000445/2005,
000446/2005
000447/2005, 3rd June
2005
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
IE (Ireland) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
IS (Iceland) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
IT (Italy) DGPGSR/II/347487/
FOR/15347
DGPGSR/II/347487/
FOR/15348
DGPGSR/II/347487/
FOR/15350
DGPGSR/II/347487/
FOR/15357
DGPGSR/II/347487/
FOR/15358
DGPGSR/II/347487/
FOR/15359
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
LI (Liechten-
stein) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 14357
27 May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868284
FeaturesStowing and features
Page 288 of 357
Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
LT (Lithua-
nia) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC
R&TTE27.4-1B-1609 6 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 LU (Luxem-
bourg) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC
R&TTE150405/9538 24
May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 LV (Latvia) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE
27.4-1B-1609 26 April 06
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 MC (Mon-
aco) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE10668
13 May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
MT (Malta) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 NL (Nether-
lands) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 NO (Norway) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC
R&TTE05/02424-SA64
418
May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 PL (Poland) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/ECR
&TTE 21 April
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868 PT (Portugal) ANCOM-S08399/05
27, 40, 433, 868 Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
RO (Roma-
nia) Article 6.4 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 433, 868
RU (Russian
Federation) POCC DE.MJ05.H00015 13
May 05
MHz: 433
SE (Sweden) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
SI (Slovenia) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE
500-1/2005-437 9 May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
SK (Slova-
kia) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE
Slovak
206/11/2005 4 May 05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
UK (United
Kingdom) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 18 May
05
MHz: 27, 40, 418, 433, 868 Features
285Stowing and features Z
Page 289 of 357
Africa
Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
EG (Egypt) W-KLE-17/08 Mar. 06
MHz: 27, 30, 40
,418, 433,
868 RE (Réunion) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 11 July
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
ZA (South
Africa) 11 October 2005
MHz: 27, 40, 433
America
Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
BB (Barba-
dos) Registration not required
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
CL (Chile) 38447/F-23 No.3.3634
MHz: 40, 433
GF (French
Guyana) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE10668
13 May 05
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 433, 868
GP (Guade-
loupe) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE10668
13 May 05
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 433, 868
MQ (Martini-
que) Article 6 of Directive
1999/5/EC R&TTE 11 July
05
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 433, 868
MX (Mexico) MHz: 280 to 390 Asia
Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
AE (United
Arab Emi-
rates) 1623/5/10-2/26/76
MHz: 433
JO (Jordan) TRC/LPD/2005/23
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 433, 868
KW (Kuwait) 5 October 2005
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 418, 433,
868
LB (Leba-
non) 2920/O&M/2006 / 3 July
05
MHz: 27, 40, 433, 868
SA (Saudi
Arabia) 11_02_05/5024-5-6
MHz: 418, 433
SY (Syria) 279/4/14 / 05 March 06
TR (Turkey) National Certification 23
July 07
MHz: 433
Australia
Country Radio type approval num-
ber
Frequency range (MHz)
AU (Aus-
tralia) 28 June
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 433, 868
NZ (New
Zealand) 20 March 06
MHz: 27, 30, 40, 433
Floormat on the driver's side
G
WARNING
Make sure that there is sufficient clearance
around the pedals whe nfloormats are used,
and that the floormats are properly secured. 286
FeaturesStowing and features
Page 290 of 357
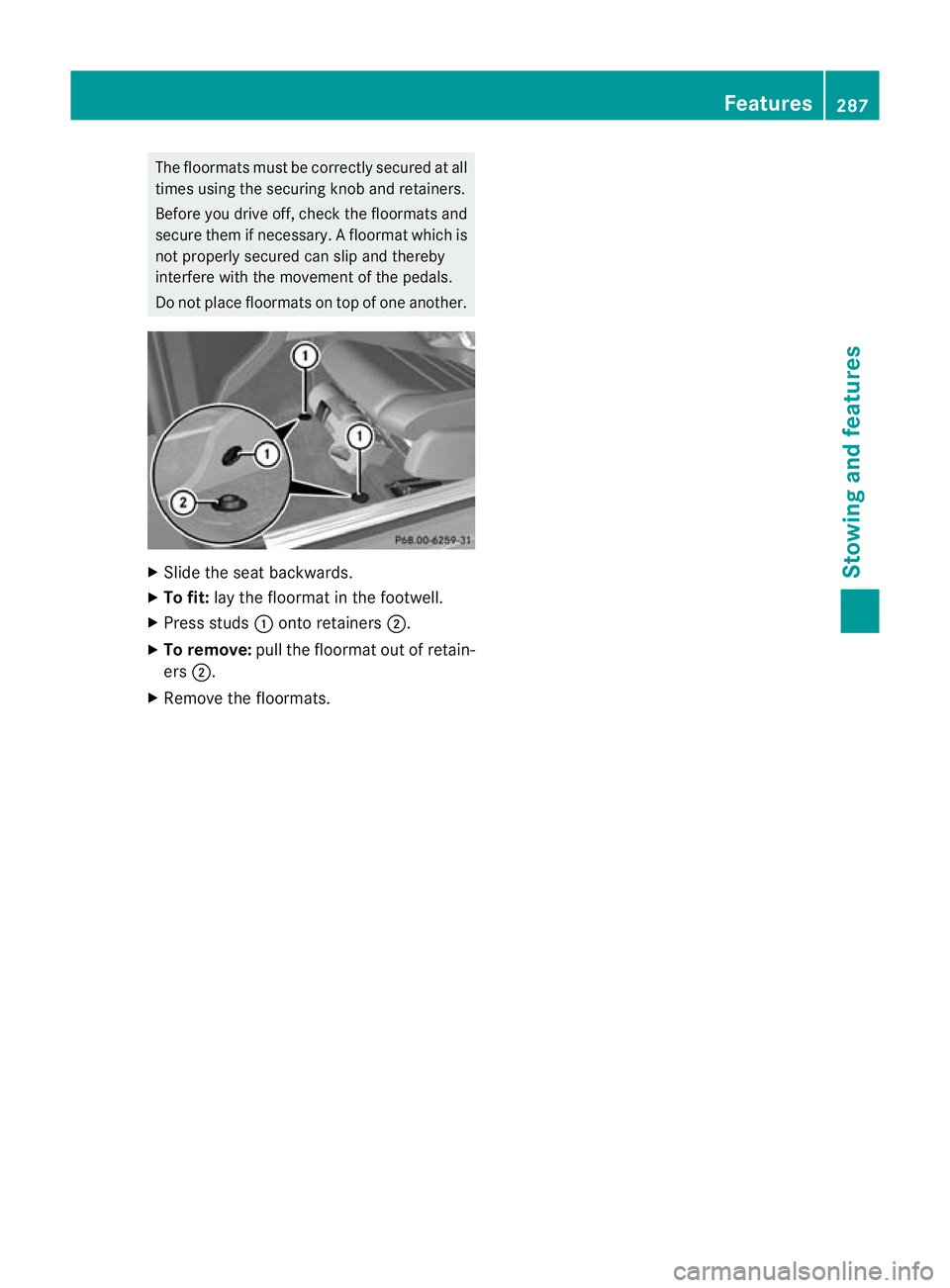
The floormats must be correctly secured at all
times using the securing knob and retainers.
Before you drive off, check the floormats and
secure them if necessary. Afloormat which is
not properly secured can slip and thereby
interfere with the movemen tofthe pedals.
Do not place floormats on top of one another. X
Slide the seat backwards.
X To fit: lay the floormat in the footwell.
X Press studs :onto retainers ;.
X To remove: pull the floormat out of retain-
ers ;.
X Remove the floormats. Features
287Stowing and features Z
Page 306 of 357

Useful information
............................304
Where will I find...? ...........................304
Flat tyre ............................................. 309
Batter y(vehicle) ................................ 309
Jump-starting .................................... 313
Towing and tow-starting ..................315
Electrical fuses ................................. 318 303Breakdown assistance
Page 318 of 357

Position number
Bidentifies the charged battery of the other vehicle or an equivalent jump-
starting device.
The jump-start terminal point consists of terminals ;and ?.
X Lift up cover :of positive terminal ;in the direction of the arrow.
X Connec tpositive terminal ;on your vehicle to positive terminal ?of donor battery B
using the jump lead. Begin with your own battery.
X Start the engine of the donor vehicle and run it at idling speed.
X Connect negative terminal Aof donor battery Bto earth point =of your vehicle using
the jump lead, connectingt he jump lead to donor battery Bfirst.
X Start the engine.
X First, remove the jump lead from earth point =and negative terminal A, then from positive
terminal ;and positive terminal ?, each time disconnecting from the battery on your own
vehicle first.
X Have the battery checked at a qualified specialist workshop.
i Jump-starting is not considered to be a normal operating condition.
i Jump-starting cables and further information regarding jump-starting can be obtained at
any qualified specialist workshop. Towing and tow-starting
Important safety notes
G
WARNING
The vehicle is braked when the HOLD function
or DISTRONIC PLUS is activated. Therefore, deactivate HOLD and DISTRONIC PLUS if the
vehicle is to be towed.
! You may tow the vehicle for a maximum
of 50km. A towing speed of 50 km/h must
not be exceeded. Towing and tow-starting
315Breakdown assistance Z
Page 319 of 357
For towing distances over 50 km, the entire
vehicle mus
tbe lifted up and transported.
! Only secure the tow cable or towing bar
to the towing eyes. You could otherwise
damage the vehicle.
! Do not use the towing eyes for recovery
purposes as this could damage the vehicle.
If in doubt, recover the vehicle with a crane.
! When towing, pull away slowly and
smoothly. If the tractive power is too high,
the vehicles could be damaged.
! Your vehicles is equipped with an auto-
matic transmission .Therefore, you must
not have the vehicle tow-started. The trans-
mission may otherwise be damaged. G
WARNING
If the weight of the vehicle to be towed or tow-
started is greater than the permissible gross
weight of your vehicle:
R the towing eye could detach itself
R the vehicle/trailer combination could over-
turn.
There is a risk of an accident.
When towing or tow-starting another vehicle,
its weight should not be greater than the per-
missible gross weight of your vehicle.
Information on your vehicle's gross vehicle
weight rating can be found on the vehicle
identification plate (Y page 340).
Observe the legal requirements for the rele-
vant countries when towing.
It is better to have the vehicle transported
than to have it towed.
If the transfer case can be shifted into neutral
N, you can tow the vehicle.
If the transfer case cannot be shifted into
neutral N, you can tow the vehicle with one
axle raised. Please bear the following in mind:
R remove the propeller shaft between the
transfer case and the rolling axle.
R turn the key to position 1in the ignition lock
(Y page 143). The battery must be connected and charged.
Otherwise, you:
R
cannot turn the key in the ignition lock to
position 2(Ypage 143)
R cannot shift the automatic transmission to
position N
i Deactivate the automatic locking feature
(Y page 74). You could otherwise be locked
out when pushing or towing the vehicle.
Deactivate tow-away protection before the
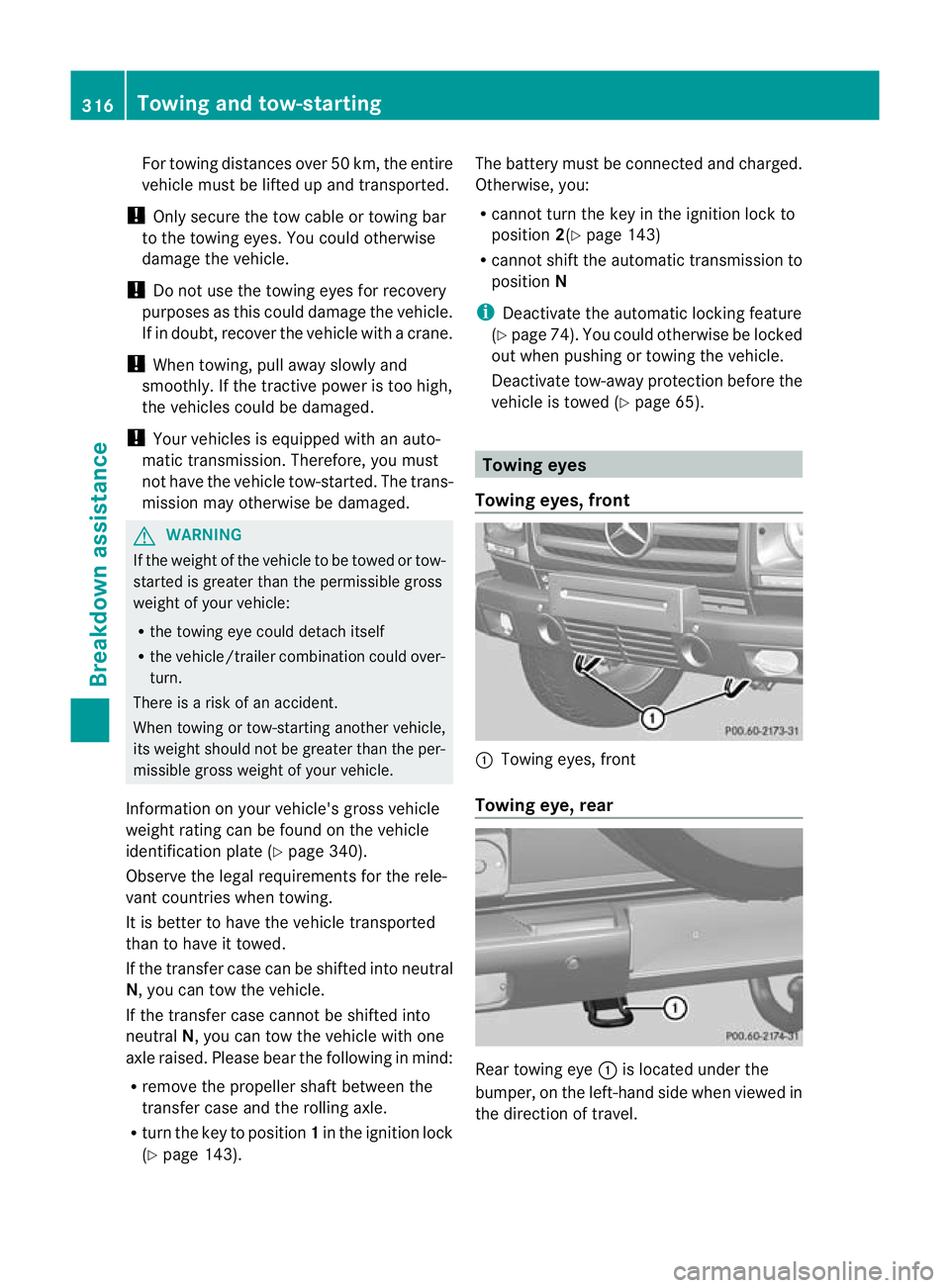
vehicle is towed (Y page 65). Towing eyes
Towing eyes, front :
Towing eyes, front
Towing eye, rear Rear towing eye
:is located under the
bumper, on the left-hand side when viewed in
the direction of travel. 316
Towing and tow-startingBreakdown assistance
Page 320 of 357

Towing the vehicle with both axles on
the ground
It is important tha tyou observe the safety
instructions when towing away your vehicle
(Y page 315).
X Switch on the hazard warning lamps
(Y page 109).
i In order to signal a change of direction
when towing the vehicle with the hazard
warning lamps switched on, use the com-
bination switch as usual.Int his case, only
the turn signals for the desired direction
flash. When you reset the combination
switch, the hazard warning lamps start
flashing again.
X Turn the key to position 2in the ignition
lock (Y page 143).
X When the vehicle is stationary, depress the
brake pedal and keep it depressed.
X Shift the transfer case to neu-
tral(Y page 203).
X Shift the automatic transmission to posi-
tion N.
X Release the brake pedal.
X Release the parking brake (Y page 164).
i The transmission can only change gear
when the battery has sufficient charge.
If you cannot move the selector lever to N,
you must remove the propeller shafts to the
driven axles. Transporting the vehicle
! Only lash the vehicle down by the wheels
or wheel rims, not by parts of the vehicle
such as axle or steering components. Oth-
erwise, the vehicle could be damaged.
Use the towing eyes to pull the vehicle if it
needs to be transported on a trailer or trans-
porter (Y page 316).
X Apply the parking brake.
X Turn the key to position 2in the ignition
lock (Y page 143). X
Move the selector lever to N.
X Shift the transfer case to neu-
tral(Y page 203).
X Secure the towing cable to the towing eyes
(Y page 316).
X Make sure that the vehicle cannot roll
away.
X Release the parking brake.
X Load the vehicle onto the transporter.
As soon as the vehicle is loaded:
X Apply the parking brake.
X Shift the automatic transmission to posi-
tion P.
X Turn the key to position 0in the ignition
lock (Y page 143) and remove it.
X Secure the vehicle. Recovering
avehicle that has become
stuck
! When recovering a trapped vehicle, do not
jerk the vehicle or pull it at an angle. If the
tractive power is too high, the vehicles
could be damaged.
If the drive wheels get trapped on loose or
muddy ground, recover th evehicle with the
utmost care, especially so if the vehicle is
laden.
Never attempt to recover a vehicle with a
trailer attached.
Pull out the vehicle backwards, if possible,
using the tracks it made when it became
stuck. Towing in the event of malfunctions
General notes !
If you are removing the propeller shaft,
use M10 nuts as spacers on the M8 bolts
and secure them with M8 nuts.
New self-locking nuts must be used when
the propeller shafts are refitted. Towing and tow-starting
317Breakdown assistance Z