engine MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER 2005 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MERCEDES-BENZ, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SPRINTER, Model: MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER 2005Pages: 1232, PDF Size: 39.23 MB
Page 126 of 1232

The TCM continuously checks for electrical prob-
lems, mechanical problems, and some hydraulic prob-
lems. When a problem is sensed, the TCM stores a
diagnostic trouble code (DTC). Some of these codes
cause the transmission to go into9Limp-In9or
9default9mode. Some DTCs cause permanent
Limp-In and others cause temporary Limp-In. The
NAG1 defaults in the current gear position if a DTC
is detected, then after a key cycle the transmission
will go into Limp-in, which is mechanical 2nd gear.
Some DTCs may allow the transmission to resume
normal operation (recover) if the detected problem
goes away. A permanent Limp-In DTC will recover
when the key is cycled, but if the same DTC is
detected for three key cycles the system will not
recover and the DTC must be cleared from the TCM
with the DRBIIItscan tool.
TCM SIGNALS
The TCM registers one part of the input signals by
direct inputs, the other part by CAN C bus. In addi-
tion to the direct control of the actuators, the TCM
sends various output signals by CAN C bus to other
control modules.
Selector Lever Position
The TCM monitors the SLA for all shift lever posi-
tions via the CAN bus.
ATF Temperature Sensor
The ATF temperature sensor is a positive temper-
ature co-efficient (PTC) thermistor. It measures the
temperature of the transmission fluid and is a direct
input signal for the TCM. The temperature of the
ATF has an influence on the shifttime and resulting
shift quality. As the temperature rises, resistance
rises, and therefore, the probing voltage is decreas-
ing. Because of its registration, the shifting process
can be optimized in all temperature ranges.
The ATF temperature sensor is wired in series
with the park/neutral contact. The temperature sig-
nal is transmitted to the TCM only when the reed
contact of the park/neutral contact is closed because
the TCM only reads ATF temperature while in any
forward gear, or REVERSE. When the transmission
is in PARK or NEUTRAL, the TCM will substitute
the engine temperature for the ATF temperature.
Starter Interlock
The TCM monitors a contact switch wired in series
with the transmission temperature sensor to deter-
mine PARK and NEUTRAL positions. The contact
switch is open in PARK and NEUTRAL. The TCM
senses transmission temperature as high (switch
supply voltage), confirming switch status as open.
The TCM then broadcasts a message over CAN bus
to confirm switch status. The PCM receives thisinformation and allows operation of the starter cir-
cuit.
N2 and N3 Speed Sensors
The N2 and N3 Input Speed Sensors are two Hall-
effect speed sensors that are mounted internally in
the transmission and are used by the TCM to calcu-
late the transmission's input speed. Since the input
speed cannot be measured directly, two of the drive
elements are measured. Two input speed sensors
were required because both drive elements are not
active in all gears.
CAN C Bus Indirect Input Signals
A 2.5-volt bias (operating voltage) is present on the
CAN C bus any time the ignition switch is in the
RUN position. Both the TCM and the ABS apply this
bias. On this vehicle, the CAN C bus is used for mod-
ule data exchange only. The indirect inputs used on
the NAG1 electronic control system are:
²Wheel Speed Sensors.
²Brake Switch.
²Engine RPM.
²Engine Temperature.
²Cruise Control Status.
²Gear Limit Request.
²Throttle Position - 0% at idle, 100% at WOT. If
open, TCM assumes idle (0% throttle opening).
²Odometer Mileage
²Maximum Effective Torque.
²Engine in Limp-In Mode/Mileage Where DTC
Was Set.
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK (BTSI)
The BTSI solenoid prevents shifting out of the
PARK position until the ignition key is in the RUN
position and the brake pedal is pressed. The TCM
controls the ground while the ignition switch supplies
power to the BTSI solenoid. The PCM monitors the
brake switch and broadcasts brake switch status
messages over the CAN C bus. If the park brake is
depressed and there is power (Run/Start) to SLA, the
BTSI solenoid deactivates.
SHIFT SCHEDULES
The basic shift schedule includes up and down-
shifts for all five gears. The TCM adapts the shift
program according to driving style, accelerator pedal
position and deviation of vehicle speed. Influencing
factors are:
²Road Conditions.
²Incline, Decline and Altitude.
²Trailer Operation, Loading.
²Engine Coolant Temperature.
²Cruise Control Operation.
²Sporty Driving Style.
8E - 6 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESVA
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 127 of 1232

²Low and High ATF Temperature.
Upshift
To :1-2 2-3 3-4 4-5
Activated
By
Solenoid:1-2/4-5 2-3 3-4 1-2/4-5
Shift
Point (at
35.2% of
throttle)17.8
km/h
(11.6
mph)32.1
km/h
(19.95
mph)67.5
km/h
(41.94
mph)73.8
km/h
(45.86
mph)
Downshift
From:5-4 4-3 3-2 2-1
Activated
By
Solenoid:1-2/4-5 3-4 2-3 1-2/4-5
Shift
Point55.7
km/h
(34.61
mph)40.5
km/h
(25.17
mph)24.4
km/h
(15.16
mph)15.1
km/h
(9.38
mph)
DOWNSHIFT SAFETY
Selector lever downshifts are not performed if inad-
missible high engine rpm is sensed.
ADAPTATION
To equalize tolerances and wear, an automatic
adaptation takes place for:
²Shift Time.
²Clutch Filling Time.
²Clutch Filling Pressure.
²Torque Converter Lock-Up Control.
Adaptation data may be stored permanently and to
some extent, can be diagnosed.
Driving Style Adaptation
The shift point is modified in steps based on the
information from the inputs. The control module
looks at inputs such as:
²vehicle acceleration and deceleration (calculated
by the TCM).
²rate of change as well as the position of the
throttle pedal (fuel injection information from the
ECM).
²lateral acceleration (calculated by the TCM).
²gear change frequency (how often the shift
occurs).
Based on how aggressive the driver is, the TCM
moves up the shift so that the present gear is held a
little longer before the next upshift. If the driving
style is still aggressive, the shift point is modified up
to ten steps. If the driving returns to normal, thenthe shift point modification also returns to the base
position.
This adaptation has no memory. The adaptation to
driving style is nothing more than a shift point mod-
ification meant to assist an aggressive driver. The
shift points are adjusted for the moment and return
to base position as soon as the inputs are controlled
in a more rational manner.
Shift Time Adaptation (Shift Overlap Adaptation, Working
Pressure)
Shift time adaptation is the ability of the TCM to
electronically alter the time it takes to go from one
gear to another. Shift time is defined as the time it
takes to disengage one shift member while another is
being applied. Shift time adaptation is divided into
four categories:
33. Accelerating upshift, which is an upshift under
a load. For shift time adaptation for the 1-2 upshift
to take place, the transmission must shift from 1st to
2nd in six different engine load ranges vs. transmis-
sion output speed ranges.
34. Decelerating upshift, which is an upshift under
no load. This shift is a rolling upshift and is accom-
plished by letting the vehicle roll into the next gear.
35. Accelerating downshift, which is a downshift
under load. This shift can be initiated by the throttle,
with or without kickdown. The shift selector can also
be used.
36. Decelerating downshift, which is accomplished
by coasting down. As the speed of the vehicle
decreases, the transmission downshifts.
Fill Pressure Adaptation (Apply Pressure Adaptation,
Modulating Pressure)
Fill pressure adaptation is the ability of the TCM
to modify the pressure used to engage a shift mem-
ber. The value of this pressure determines how firm
the shift will be.
²If too much pressure is used, the shift will be
hard.
²If too little pressure is used, the transmission
may slip.
The pressure adjustment is needed to compensate
for the tolerances of the shift pressure solenoid valve.
The amount the solenoid valve opens as well as how
quickly the valve can move, has an effect on the pres-
sure. The return spring for the shift member pro-
vides a resistance that must be overcome by the
pressure in order for shift member to apply. These
return springs have slightly different values. This
also affects the application pressure and is compen-
sated for by fill pressure adaptation.
Fill Time Adaptation (Engagement Time Adaptation)
Fill time is the time it takes to fill the piston cav-
ity and take up any clearances for a friction element
VAELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 7
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 128 of 1232

(clutch or brake). Fill time adaptation is the ability of
the TCM to modify the time it takes to fill the shift
member by applying a preload pressure.
CONTROLLER MODES OF OPERATION
Permanent Limp-In Mode
When the TCM determines there is a non-recover-
able condition present that does not allow proper
transmission operation, it places the transmission in
permanent Limp-In Mode. When the condition occurs
the TCM turns off all solenoids as well as the sole-
noid supply output circuit. If this occurs while the
vehicle is moving, the transmission remains in the
current gear position until the ignition is turned off
or the shifter is placed in the9P9position. When the
shifter has been placed in9P,9the transmission only
allows 2nd gear operation. If this occurs while the
vehicle is not moving, the transmission only allows
operation in 2nd gear.
Temporary Limp-In Mode
This mode is the same as the permanent Limp-In
Mode except if the condition is no longer present, the
system resumes normal operation.
Under Voltage Limp-In Mode
When the TCM detects that system voltage has
dropped below 8.5 volts, it disables voltage-depen-
dant diagnostics and places the transmission in the
temporary Limp-In Mode. When the TCM senses
that the voltage has risen above 9.0 volts, normal
transmission operation is resumed.
Hardware Error Mode
When the TCM detects a major internal error, the
transmission is placed in the permanent Limp-In
Mode and ceases all communication over the CAN
bus. When the TCM has entered this mode normal
transmission operation does not resume until all
DTCs are cleared from the TCM.
Loss of Drive
If the TCM detects a situation that has resulted or
may result in a catastrophic engine or transmission
problem, the transmission is placed in the neutral
position. Improper Ratio, Input Sensor Overspeed or
Engine Overspeed DTCs cause the loss of drive.
Controlled Limp-in Mode
When a failure does not require the TCM to shut
down the solenoid supply, but the failure is severe
enough that the TCM places the transmission into a
predefined gear, there are several shift performanceconcerns. For instance, if the transmission is slip-
ping, the controller tries to place the transmission
into 3rd gear and maintain 3rd gear for all forward
drive conditions.STANDARD PROCEDURE - TCM ADAPTATION
The adaptation procedure requires the use of the
DRBIIItscan tool. This program allows the elec-
tronic transmission system to re-calibrate itself. This
will provide the proper baseline transmission opera-
tion. The adaptation procedure should be performed
if any of the following procedures are performed:
²Transmission Assembly Replacement
²Transmission Control Module Replacement
²Clutch Plate and/or Seal Replacement
²Electrohydraulic Unit Replacement or Recondi-
tion
(1) With the DRBIIIt, reset the Transmission
adaptives. Resetting the adaptives will set the adap-
tives to factory settings.
NOTE: Perform the Coast Down Adaptations first.
The Transmission Temperature must be greater
than 60ÉC (140ÉF) and less than 70ÉC (158ÉF). Fail-
ure to stay within these temperature ranges will
void the procedure.
(2) Drive the vehicle until the transmission tem-
perature is in the specified range.
(3) Perform 4 to 5 coast downs from 5th to 4th
gear and then 4th to 3rd gear.
NOTE: For Upshift adaptation, the Transmission
temperature must be greater than 60ÉC (140ÉF) and
less than 100ÉC (212ÉF). Failure to stay within these
temperature ranges will void this procedure.
(4) From a stop, moderately accelerate the vehicle
and obtain all forward gear ranges while keeping the
Engine RPM below 1800 RPM. Repeat this procedure
4 to 5 times.
(5) Obtaining 5th gear may be difficult at 1800
RPM. Allow the transmission to shift into 5th gear at
a higher RPM then lower the RPM to 1800 and per-
form manual shifts between 4th and 5th gears using
the shift lever.
(6) The TCM will store the adaptives every 10
minutes. After completion of the adaptation proce-
dure make sure the vehicle stays running for at least
10 minutes.
(7) It is possible to manually store the adaptives
under the 10 minute time frame using the DRBIIIt
Store Adaptives procedure.
8E - 8 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESVA
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 129 of 1232

ENGINE SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY SYSTEM......................... 1
CHARGING SYSTEM....................... 17STARTING SYSTEM....................... 24
BATTERY SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY
SYSTEM.............................2
CLEANING.............................5
INSPECTION...........................6
SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY SYSTEM SPECIAL TOOLS.......6
BATTERY
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY.......7
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BATTERY
CHARGING...........................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OPEN-CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE TEST.......................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - IGNITION-OFF
DRAW TEST.........................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - USING MICRO
420 BATTERY TESTER.................11
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECKING
BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL.........12REMOVAL
UNDER HOOD BATTERY REMOVAL.......12
AUXILIARY BATTERY REMOVAL..........13
INSTALLATION
UNDER HOOD BATTERY INSTALLATION . . . 13
AUXILIARY BATTERY INSTALLATION......13
BATTERY HOLDDOWN
DESCRIPTION.........................14
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
BATTERY CABLES
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY
CABLES............................14
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A single 12-volt battery is standard factory-in-
stalled equipment on this model. Some vehicles are
equipped with a second auxiliary battery for running
additional electrical equipment. The standard battery
is located in the engine compartment, while the aux-
iliary battery (if equipped) is located under the pas-
sengers front seat. The battery system for thisvehicle covers the following related components,
which are covered in further detail later in this sec-
tion of the service manual:
²Battery- The 12v storage battery(s) provides a
reliable means of storing a renewable source of elec-
trical energy within the vehicle.
²Battery Cables- The battery cables connect
the battery terminal posts to the vehicle electrical
system.
VAENGINE SYSTEMS 8F - 1
Page 130 of 1232

²Battery Holddown- The battery holddown
hardware secures the battery in the battery tray in
the engine compartment.
²Battery Tray- The battery tray provides a
secure mounting location in the vehicle for the bat-
tery and an anchor point for the battery holddown
hardware.
For battery system maintenance schedules and
jump starting procedures, see the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box. Optionally, refer to the Lubri-
cation and Maintenance section of this manual for
the recommended battery maintenance schedules and
for the proper battery jump starting procedure. While
battery charging can be considered a maintenance
procedure, the battery charging procedure and
related information are located later in this section of
this service manual. This was done because the bat-
tery must be fully-charged before any battery system
diagnosis or testing procedures can be performed.
OPERATION
The battery system is designed to provide a safe,
efficient, reliable and mobile means of delivering and
storing electrical energy. This electrical energy is
required to operate the engine starting system, as
well as to operate many of the other vehicle acces-
sory systems for limited durations while the engine
and/or the charging system are not operating. The
battery system is also designed to provide a reserve
of electrical energy to supplement the charging sys-
tem for short durations while the engine is running
and the electrical current demands of the vehicle
exceed the output of the charging system. In addition
to delivering, and storing electrical energy for the
vehicle, the battery system serves as a capacitor and
voltage stabilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It
absorbs most abnormal or transient voltages caused
by the switching of any of the electrical components
or circuits in the vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another and must be testedas a complete system. In order for the engine to start
and the battery to maintain its charge properly, all of
the components that are used in these systems must
perform within specifications. It is important that
the battery, starting, and charging systems be thor-
oughly tested and inspected any time a battery needs
to be charged or replaced. The cause of abnormal bat-
tery discharge, overcharging or early battery failure
must be diagnosed and corrected before a battery is
replaced and before a vehicle is returned to service.
The service information for these systems has been
separated within this service manual to make it eas-
ier to locate the specific information you are seeking.
However, when attempting to diagnose any of these
systems, it is important that you keep their interde-
pendency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery,
starting, and charging systems include the most
basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more
sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmme-
ter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load
tester) and a 12-volt test lamp may be required. All
OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
Charging System for the proper charging system on-
board diagnostic test procedures.
MICRO 420 BATTERY TESTER
The Micro 420 automotive battery tester is
designed to help the dealership technicians diagnose
the cause of a defective battery. Follow the instruc-
tion manual supplied with the tester to properly
diagnose a vehicle. If the instruction manual is not
available refer to the standard procedure in this sec-
tion, which includes the directions for using the
Micro 420 battery tester.
8F - 2 BATTERY SYSTEMVA
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 131 of 1232
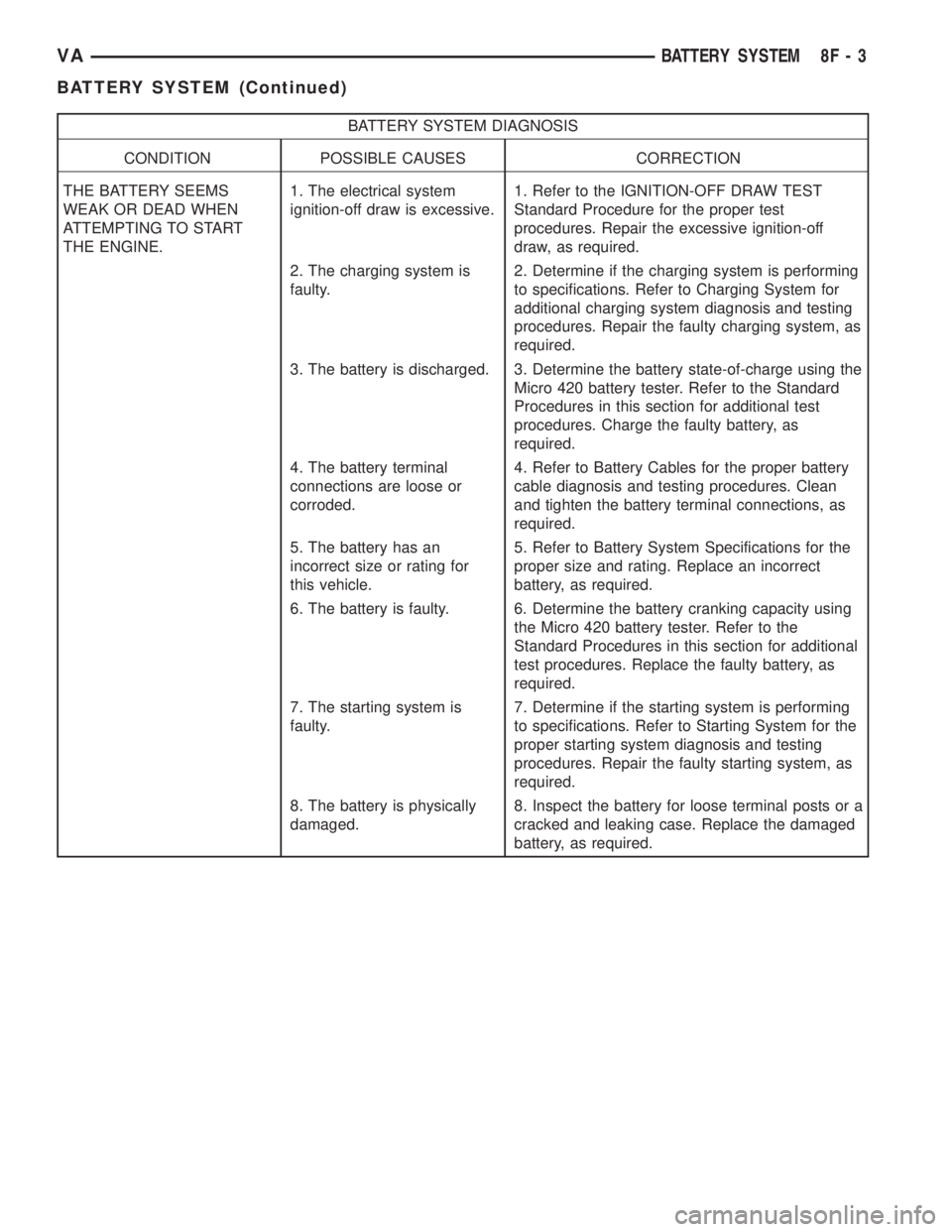
BATTERY SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
THE BATTERY SEEMS
WEAK OR DEAD WHEN
ATTEMPTING TO START
THE ENGINE.1. The electrical system
ignition-off draw is excessive.1. Refer to the IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST
Standard Procedure for the proper test
procedures. Repair the excessive ignition-off
draw, as required.
2. The charging system is
faulty.2. Determine if the charging system is performing
to specifications. Refer to Charging System for
additional charging system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the faulty charging system, as
required.
3. The battery is discharged. 3. Determine the battery state-of-charge using the
Micro 420 battery tester. Refer to the Standard
Procedures in this section for additional test
procedures. Charge the faulty battery, as
required.
4. The battery terminal
connections are loose or
corroded.4. Refer to Battery Cables for the proper battery
cable diagnosis and testing procedures. Clean
and tighten the battery terminal connections, as
required.
5. The battery has an
incorrect size or rating for
this vehicle.5. Refer to Battery System Specifications for the
proper size and rating. Replace an incorrect
battery, as required.
6. The battery is faulty. 6. Determine the battery cranking capacity using
the Micro 420 battery tester. Refer to the
Standard Procedures in this section for additional
test procedures. Replace the faulty battery, as
required.
7. The starting system is
faulty.7. Determine if the starting system is performing
to specifications. Refer to Starting System for the
proper starting system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the faulty starting system, as
required.
8. The battery is physically
damaged.8. Inspect the battery for loose terminal posts or a
cracked and leaking case. Replace the damaged
battery, as required.
VABATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 3
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 134 of 1232

(5) Clean any corrosion from the battery terminal
posts with a wire brush or a post and terminal
cleaner, and a sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and
warm water cleaning solution (Fig. 3).
INSPECTION
The following information details the recommended
inspection procedures for the battery and related
components. In addition to the maintenance sched-
ules found in this service manual and the owner's
manual, it is recommended that these procedures be
performed any time the battery or related compo-
nents must be removed for vehicle service.
(1) Inspect the battery cable terminal clamps for
damage. Replace any battery cable that has a dam-
aged or deformed terminal clamp.
(2) Inspect the battery tray and battery holddown
hardware for damage. Replace any damaged parts.
(3)
Slide the thermal guard off of the battery case, if
equipped. Inspect the battery case for cracks or other
damage that could result in electrolyte leaks. Also, check
the battery terminal posts for looseness. Batteries with
damaged cases or loose terminal posts must be replaced.
(4) Inspect the battery thermal guard for tears,
cracks, deformation or other damage. Replace any
battery thermal guard that has been damaged.
(5) Inspect the battery built-in test indicator sight
glass for an indication of the battery condition. If the
battery is discharged, charge as required. (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY SYSTEM SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY
DESCRIPTION
Large capacity, low-maintenance storage batteries
are standard factory-installed equipment on this
model. The primary battery is located in the engine
compartment on all models. A second auxiliary bat-
tery may be installed under the passengers front seat
for running additional electrical equipment.
Male post type terminals made of a soft lead mate-
rial protrude from the top of the molded plastic bat-
tery case to provide the means for connecting the
battery to the vehicle electrical system. The battery
positive terminal post is physically larger in diameter
than the negative terminal post to ensure proper bat-
tery connection. The lettersPOSandNEGare also
molded into the top of the battery case adjacent to
their respective positive and negative terminal posts
for identification confirmation. Refer to Battery
Cables for more information on the battery cables
that connect the battery to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem.
The battery is made up of six individual cells that
are connected in series. Each cell contains positively
charged plate groups that are connected with lead
straps to the positive terminal post, and negatively
charged plate groups that are connected with lead
straps to the negative terminal post. Each plate con-
sists of a stiff mesh framework or grid coated with
Fig. 3 Clean Battery Terminal Post - Typical
1 - TERMINAL BRUSH
2 - BATTERY CABLE
3 - BATTERY
Micro 420 Battery Tester
8F - 6 BATTERY SYSTEMVA
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 143 of 1232

WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE, USE
FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BATTERY.
PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY
RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS IS IN PLACE AND TIGHT BEFORE
THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SERVICE. PER-
SONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY
RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING CELL CAPS.
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing this
test, be certain that the following procedures are
accomplished:
²The battery is fully-charged and tested. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
²Fully engage the parking brake.
²Place the automatic transmission gearshift selec-
tor lever in the Park position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²Prevent the engine from starting.
(1) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative terminal post. Connect the neg-
ative lead of the voltmeter to the battery negative
cable terminal clamp (Fig. 9). Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct the poor con-
nection between the battery negative cable terminal
clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
(2) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery positive terminal post. Connect the nega-
tive lead of the voltmeter to the battery positive cable
terminal clamp (Fig. 10). Rotate and hold the ignition
switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If
voltage is detected, correct the poor connection
between the battery positive cable terminal clamp
and the battery positive terminal post.
(3) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery positive cable terminal clamp and the starter
solenoid B(+) terminal stud (Fig. 11). Rotate and hold
the ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the
voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2 volt, clean and
tighten the battery positive cable eyelet terminal con-nection at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt,
replace the faulty battery positive cable.
(4) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery negative cable terminal clamp and a good
clean ground on the engine block (Fig. 12). Rotate
and hold the ignition switch in the Start position.
Observe the voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2
volt, clean and tighten the battery negative cable
eyelet terminal connection to the engine block.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt,
replace the faulty battery negative cable.
Fig. 9 Test Battery Negative Connection Resistance
- Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
Fig. 10 Test Battery Positive Connection Resistance
- Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
VABATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 15
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 144 of 1232

REMOVAL
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position. Be
certain that all electrical accessories are turned off.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the remote battery neg-
ative cable terminal.
(3) One at a time, trace and disconnect the battery
cable retaining pushpins, fasteners and routing clips
until the cables are free from the vehicle.
(4)
Feed the battery cable assembly out of the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the battery cable in the vehicle.
(2) One at a time, install the battery cable retain-
ing pushpins, fasteners and routing clips until the
cable is installed exactly in the factory installed loca-
tion in the vehicle. Refer to the Wiring Diagram sec-
tion of the service manual for reference.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable terminal.
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION
The battery is mounted in a stamped steel battery
tray located in the left front corner of the engine
compartment. The battery tray is secured with bolts
to the left front wheelhouse inner steel panel. A hole
in the bottom of the battery tray is fitted with a
formed drain tube. A second hole in the bottom of the
tray is fitted with a battery temperature sensor.
OPERATION
The battery tray provides a mounting location and
support for the vehicle battery. The battery tray sup-
port supports the battery tray and provides an
anchor point for the inboard battery hold down hard-
ware. The battery tray and the battery hold down
hardware combine to secure and stabilize the battery
in the engine compartment, which prevents battery
movement during vehicle operation. Unrestrained
battery movement during vehicle operation could
result in damage to the vehicle, the battery or both.
The battery tray drain tube directs spilled water or
electrolyte from a leaking battery to the ground
through another hole in the front extension of the
left front wheelhouse inner panel.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the battery from the battery tray.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BAT-
TERY - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the battery temperature sensor from
the battery tray. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARG-
ING/BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the bolts that secure the battery tray
to the battery tray support.
(4) Remove the battery tray from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and inspect the battery tray.(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM - CLEANING).
(2) Position the battery tray onto the battery tray
support.
(3) Install and tighten the bolts that secure the
battery tray to the battery tray support. Tighten the
screws to 11.8 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the battery temperature sensor onto the
battery tray. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR - INSTALLA-
TION).
(5) Install the battery onto the battery tray. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 11 Test Battery Positive Cable Resistance - Typical
1 - BATTERY
2 - VOLTMETER
3 - STARTER MOTOR
Fig. 12 Test Ground Circuit Resistance - Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
3 - ENGINE GROUND
8F - 16 BATTERY SYSTEMVA
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 145 of 1232

CHARGING SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING SYSTEM
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE ± 2.7L DIESEL................17
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................17
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GENERATOR
DECOUPLER.........................19
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................23
CHARGING SYSTEM
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE ± 2.7L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
B+ Terminal Nut at Top of Generator 13 - 115
Generator Mounting Bolts/Nut 54 40 -
Rear Generator Support Bracket Bolts (to engine) 28 - 250
Generator Decoupler 110 81 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
GENERATOR DECOUPLER TOOL #8433
GENERATOR DECOUPLER TOOL #8823
VACHARGING SYSTEM 8F - 17