engine MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 196 of 1146
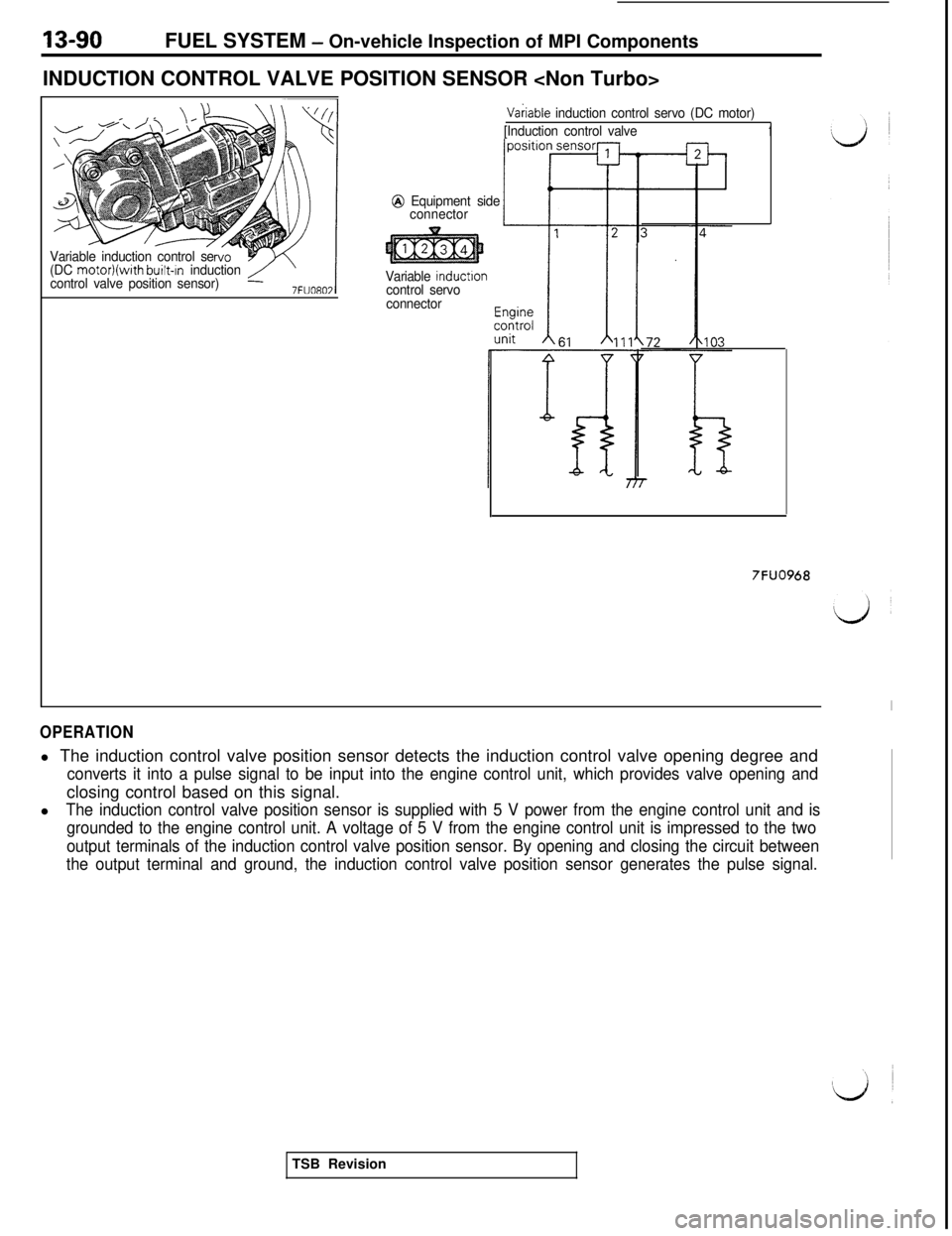
13-90FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
INDUCTION CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR
Variable induction control se
(DC motor)(with built-In induction
control valve position sensor)
Vakiable induction control servo (DC motor)
[Induction control valve
1
@ Equipment side
connector
Variable
inductloncontrol servo
connector
7FUO968
OPERATIONl The induction control valve position sensor detects the induction control valve opening degree and
converts it into a pulse signal to be input into the engine control unit, which provides valve opening andclosing control based on this signal.
l
The induction control valve position sensor is supplied with 5 V power from the engine control unit and is
grounded to the engine control unit. A voltage of 5 V from the engine control unit is impressed to the two
output terminals of the induction control valve position sensor. By opening and closing the circuit between
the output terminal and ground, the induction control valve position sensor generates the pulse signal.TSB Revision
Page 198 of 1146
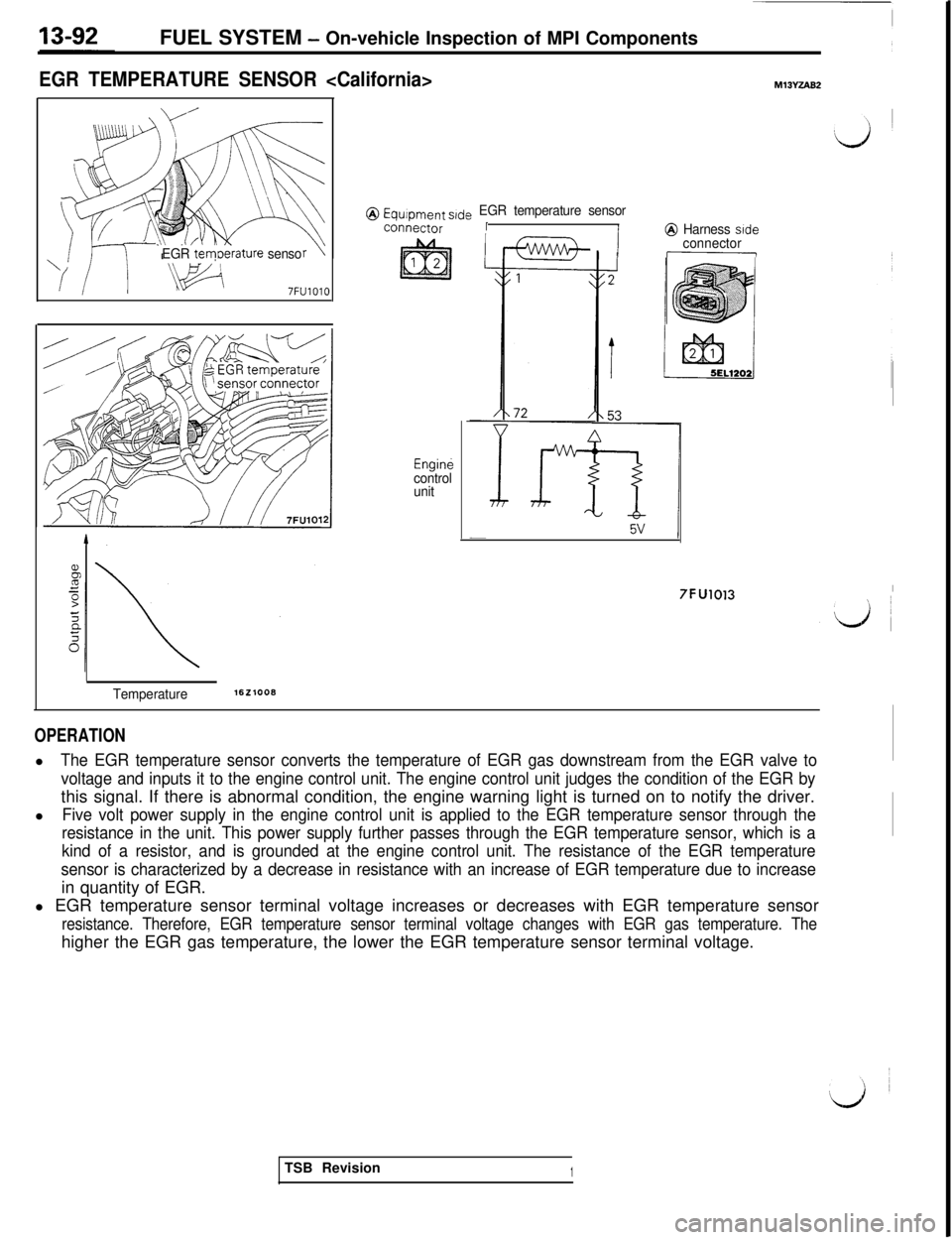
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
EGR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
EGR tem0erature senso
7FUlOlO
@ Equipment s,de EGR temperature sensor
connectorII@ Harness side
Enginecontrol
unit
I Iconnector
7FU1013I
Temperature1621008
OPERATIONl
The EGR temperature sensor converts the temperature of EGR gas downstream from the EGR valve to
voltage and inputs it to the engine control unit. The engine control unit judges the condition of the EGR bythis signal. If there is abnormal condition, the engine warning light is turned on to notify the driver.
l
Five volt power supply in the engine control unit is applied to the EGR temperature sensor through the
resistance in the unit. This power supply further passes through the EGR temperature sensor, which is a
kind of a resistor, and is grounded at the engine control unit. The resistance of the EGR temperature
sensor is characterized by a decrease in resistance with an increase of EGR temperature due to increasein quantity of EGR.
l EGR temperature sensor terminal voltage increases or decreases with EGR temperature sensor
resistance. Therefore, EGR temperature sensor terminal voltage changes with EGR gas temperature. Thehigher the EGR gas temperature, the lower the EGR temperature sensor terminal voltage.
TSB Revision
1
Page 199 of 1146
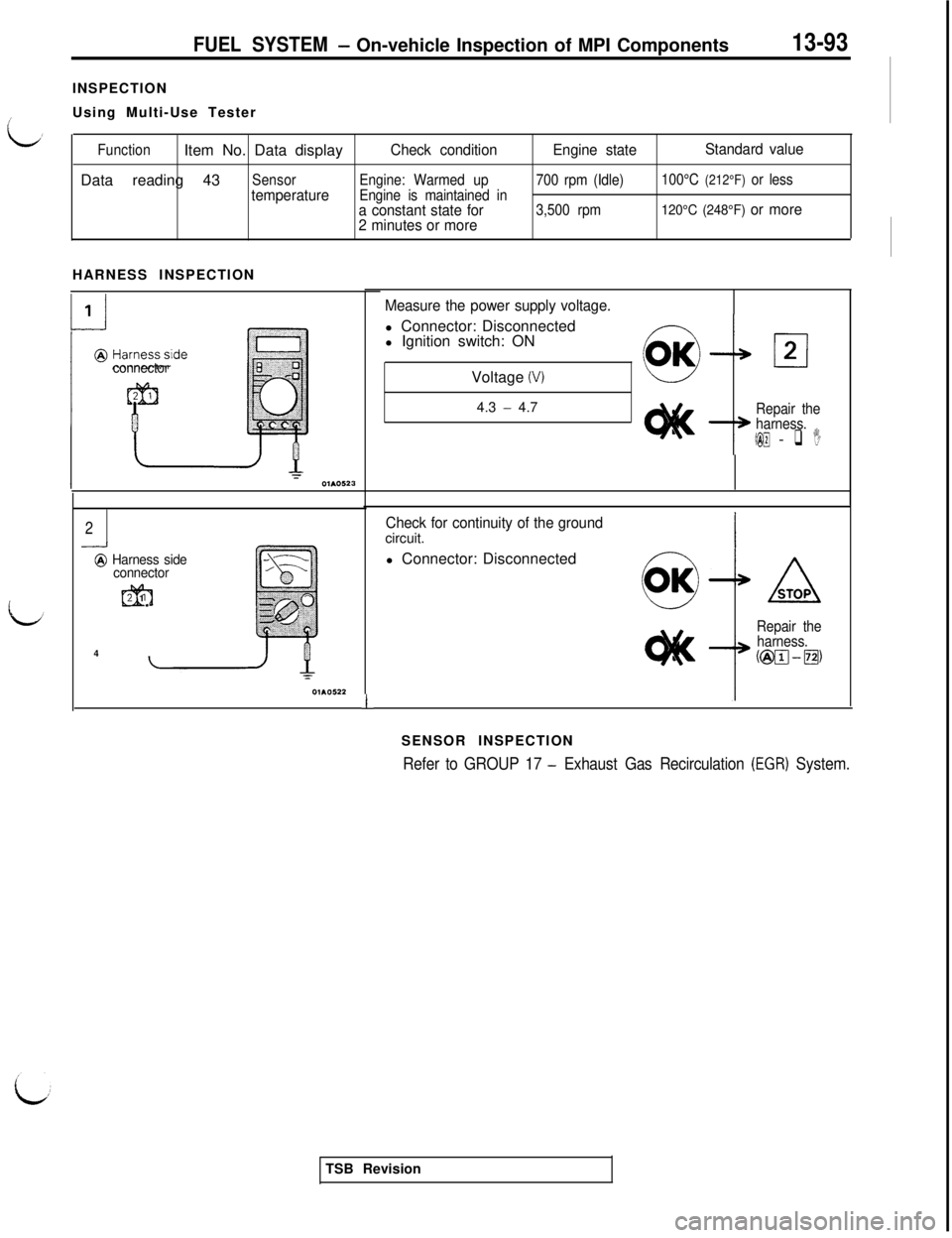
FUEL SYSTEM- On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-93INSPECTION
Using Multi-Use Tester
FunctionItem No. Data displayCheck conditionEngine stateStandard valueData reading 43
SensorEngine: Warmed up700 rpm (Idle)100°C (212°F) or less
temperatureEngine is maintained in-
a constant state for3,500 rpm120°C (248°F) or more
2 minutes or moreHARNESS INSPECTION
connector
2-..-I
@ Harness side
connector
m2 1
4
1
Measure the power supply voltage.l Connector: Disconnected
l Ignition switch: ON
Voltage
(V)4.3
- 4.7Repair the
harness.
(@I@ - q I
Check for continuity of the groundcircuit.
l Connector: Disconnected
I
Repair the
harness.@@J-m,
SENSOR INSPECTION
Refer to GROUP 17 - Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System.TSB Revision
Page 200 of 1146
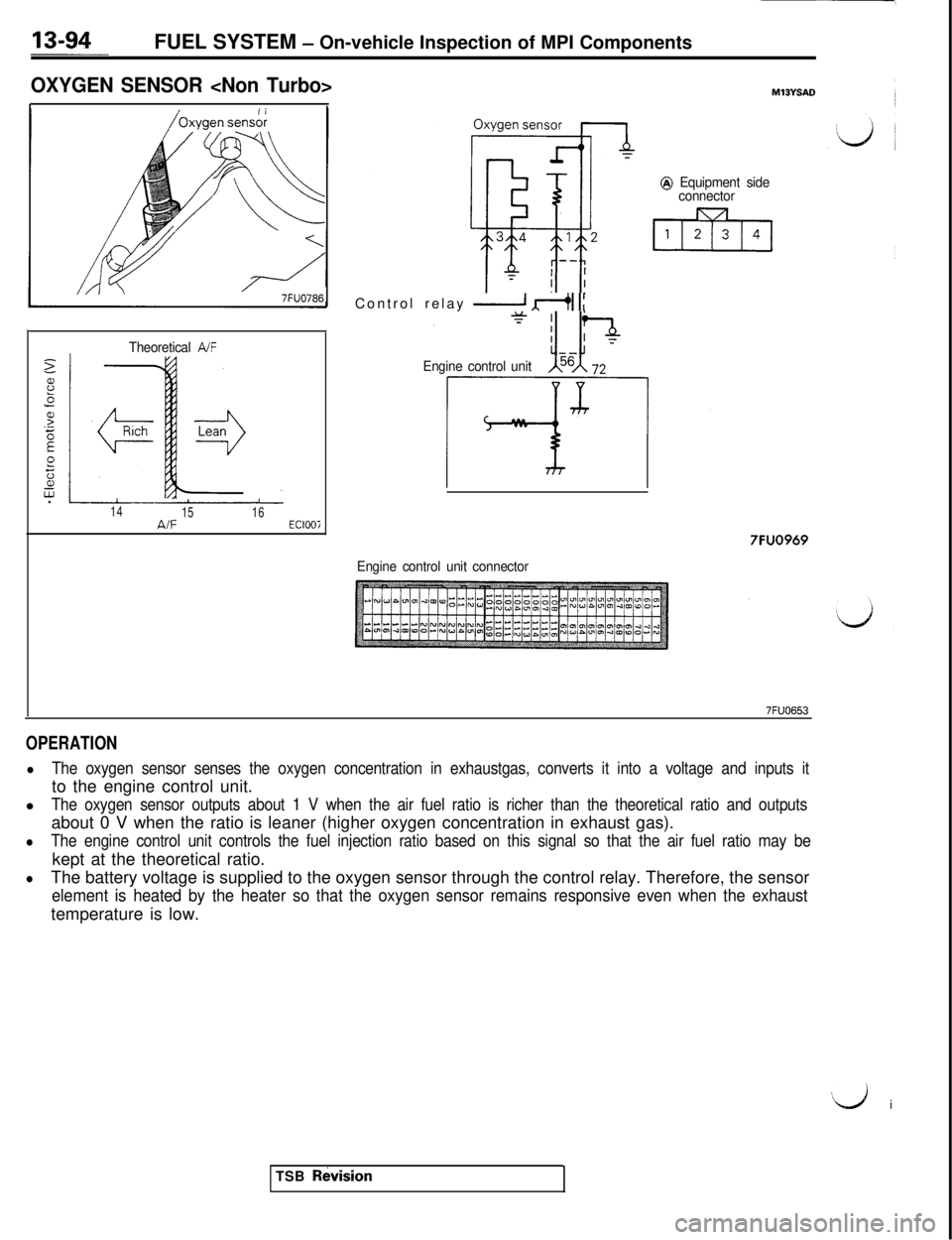
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
OXYGEN SENSOR
7FUO786
Theoretical A/F
14
1516A/FEClOOiControl relay
2 dI 1:
Engine control unit
@ Equipment side
connector
7FUO969
Engine control unit connector
7FUO653
OPERATION
lThe oxygen sensor senses the oxygen concentration in exhaustgas, converts it into a voltage and inputs itto the engine control unit.
l
The oxygen sensor outputs about 1 V when the air fuel ratio is richer than the theoretical ratio and outputsabout 0 V when the ratio is leaner (higher oxygen concentration in exhaust gas).
lThe engine control unit controls the fuel injection ratio based on this signal so that the air fuel ratio may bekept at the theoretical ratio.
lThe battery voltage is supplied to the oxygen sensor through the control relay. Therefore, the sensor
element is heated by the heater so that the oxygen sensor remains responsive even when the exhausttemperature is low.
‘d i
TSB
RtkisionI
Page 201 of 1146
FUEL SYSTEM - 0
n-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-95
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTSHint 1: Poor cleaning of exhaust gas will result if the oxygen sensor fails.
Hint 2:If the oxygen sensor check has resulted normal but the sensor output voltage is out of specification,
troubles of parts related to air fuel ratio control system are suspected.
[Examples]
(1) Faulty injector
(2) Air leaking into the intake manifold through gasket gap, etc.
(3) Faulty air flow sensor, intake air temperature sensor, barometric pressure sensor,’ engine
Data readingcoolant temperature sensor
INSPECTIONUsing Multi-use Tester
FunctionItem No. Data displayCheck conditionEngine stateStandard value
11SensorvoltaceEngine: Warm-upWhen sudden200 mV or lower
(make the mixture leandeceleration from
L
by engine speed reduc-4,000 rpm
tion, and rich by racing)
When engine is600-1,000 mV
suddenly raced
Engine: Warm-up700 rpm (Idle)
400 mV or lower
(using the oxygen sensorsignal, check the air/2,000 rpm,,,5-‘$-$-;3
fuel mixture ratio, and
also check the condition
of control by the engine
control unit)
TSB Revision
Page 203 of 1146
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI ComDonents13-97
,
7FU1014
7FUlOl5
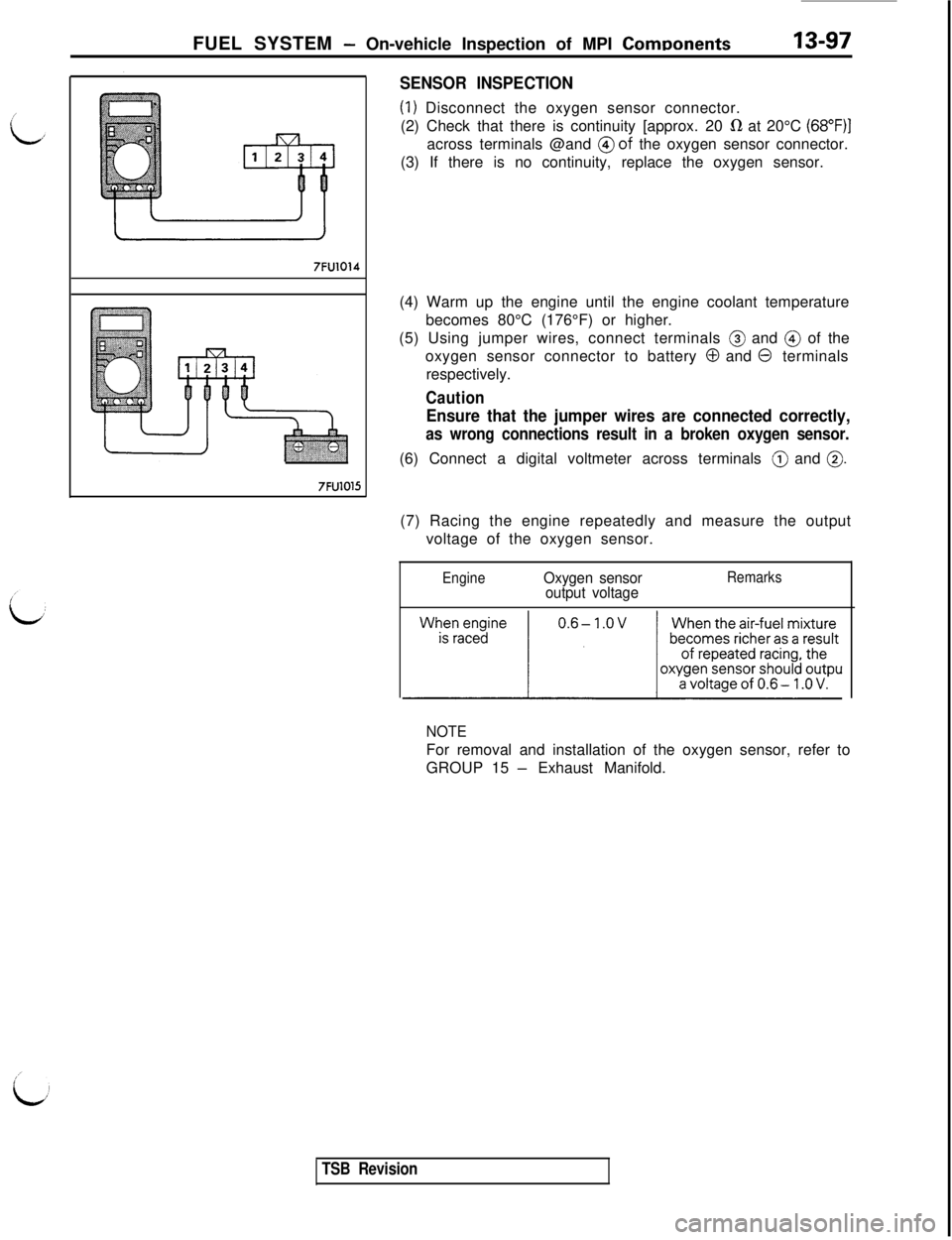
SENSOR INSPECTION
(1) Disconnect the oxygen sensor connector.
(2) Check that there is continuity [approx. 20
IR at 20°C (68”F)jacross terminals @and
@of the oxygen sensor connector.
(3) If there is no continuity, replace the oxygen sensor.
(4) Warm up the engine until the engine coolant temperature
becomes 80°C (176°F) or higher.
(5) Using jumper wires, connect terminals @ and @ of the
oxygen sensor connector to battery
0 and 0 terminals
respectively.
Caution
Ensure that the jumper wires are connected correctly,
as wrong connections result in a broken oxygen sensor.(6) Connect a digital voltmeter across terminals @ and
0.(7) Racing the engine repeatedly and measure the output
voltage of the oxygen sensor.
EngineOxygen sensor
output voltageRemarks
NOTEFor removal and installation of the oxygen sensor, refer to
GROUP 15
- Exhaust Manifold.
TSB Revision
Page 204 of 1146
FUEL SYSTEM - 0
n-vehicleInspection of MPI Components
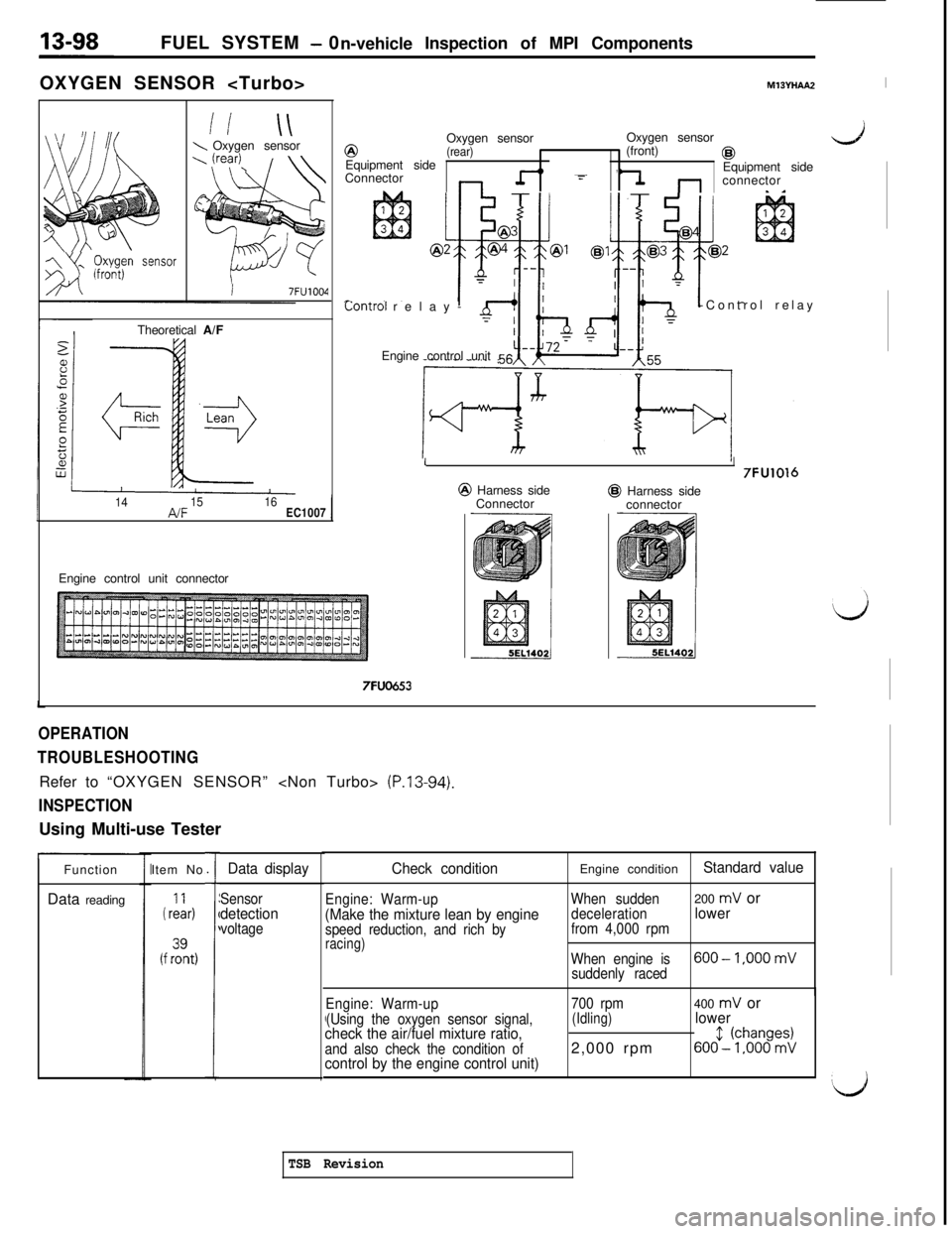
OXYGEN SENSOR
M13YHAA2I
2
2-J
_ Fr;;syn m-wr
li \\\Oxygen sensor
I7FU1004Theoretical A/F@Oxygen sensor
(rear)Oxygen sensor
Equipment side(front)@,ConnectorEquipment side:connectorf-l -1
Lonrrol relay--Control relay
Engine control unit 56
141516PJFEC1007Engine control unit connector
7FUO453
I
I7FU1016@ Harness side@ Harness side
Connector
connector
OPERATION
TROUBLESHOOTINGRefer to “OXYGEN SENSOR”
(P.13-94).
INSPECTIONUsing Multi-use Tester
Function
Data readingItem No.
i rL&
(f fzt,
,
1
Data display
Sensordetectionvoltage
Check condition
Engine: Warm-up(Make the mixture lean by enginespeed reduction, and rich byracing)Engine condition
Standard value
When sudden200 mV or
decelerationlowerfrom 4,000 rpm
When engine is
600-1.000 mV
suddenly raced
./
Engine: Warm-up
(Using the oxygen sensor signal,
check the air/fuel mixture ratio,and also check the condition ofcontrol by the engine control unit)
700 rpm(Idling)2,000 rpm400 mV orlower
6()(f--(~jbaono9~;
‘d
TSB Revision
Page 205 of 1146
1
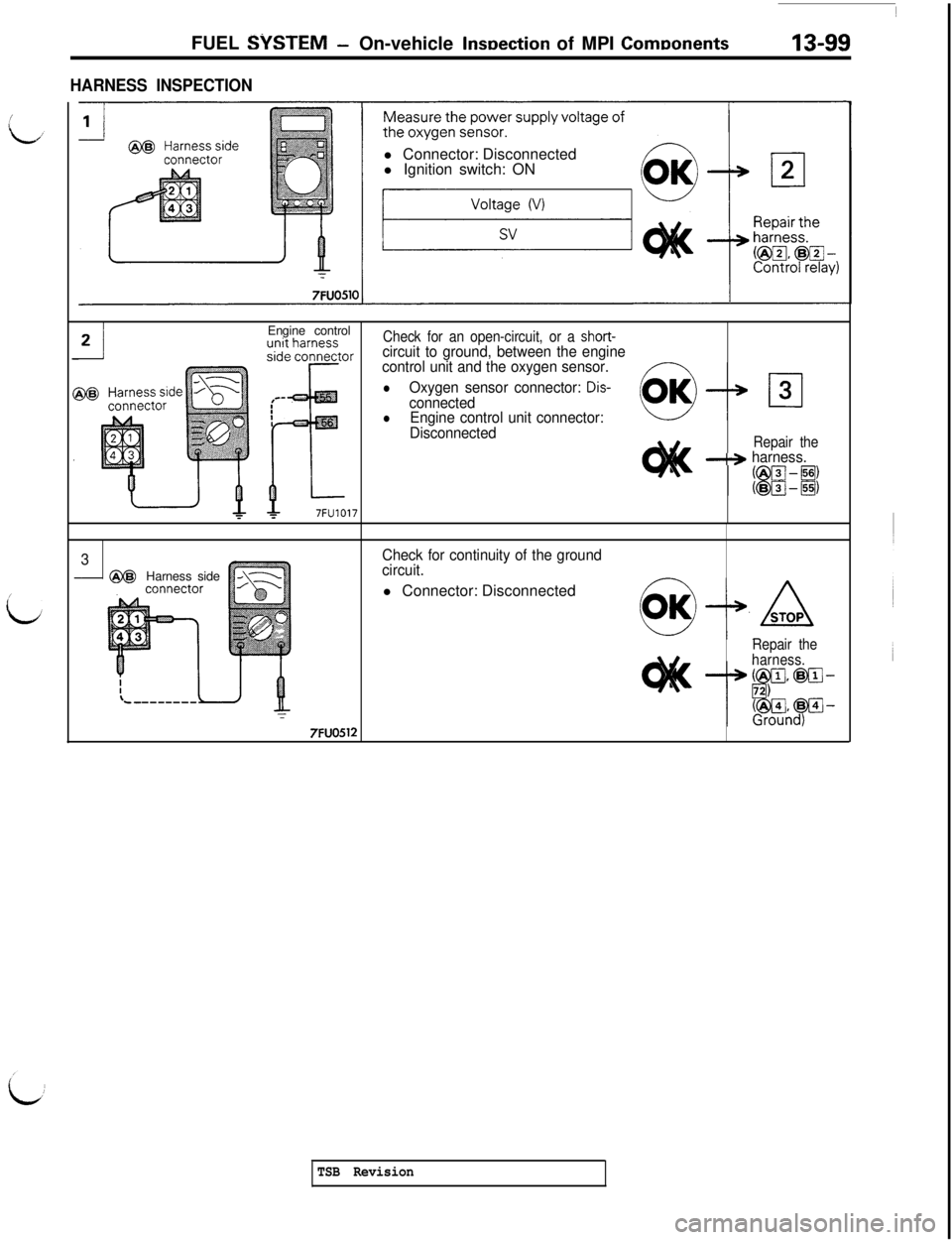
FUEL SYSTEM- On-vehicle InsDection of MPI ComDonents13-99
HARNESS INSPECTIONl Connector: Disconnected
l Ignition switch: ON
Engine control
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-circuit to ground, between the engine
control unit and the oxygen sensor.
lOxygen sensor connector: Dis-connectedlEngine control unit connector:
Disconnected
Repair the-+ harness.
3Check for continuity of the ground
- @@
Harness sidecircuit.l Connector: Disconnected
Repair the
harness.
7FUO512
TSB Revision
Page 206 of 1146
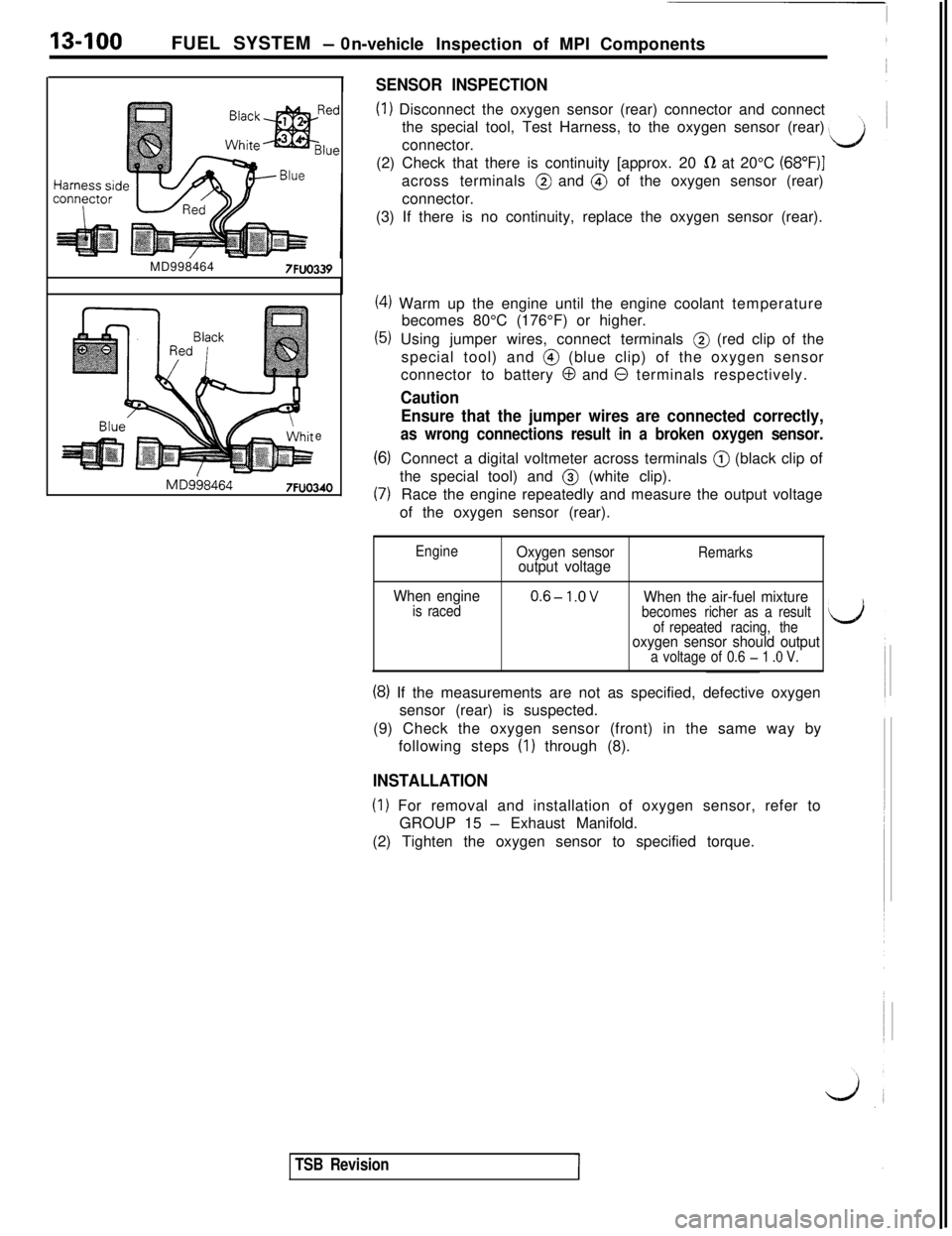
13-100FUEL SYSTEM - 0
n-vehicleInspection of MPI Components
SENSOR INSPECTION
(1) Disconnect the oxygen sensor (rear) connector and connect
the special tool, Test Harness, to the oxygen sensor (rear)
connector.
MD998464
7FUO339
e
MD9584647FUO340(2) Check that there is continuity [approx. 20
R at 20°C (68”F)Iacross terminals @ and @ of the oxygen sensor (rear)
connector.
(3) If there is no continuity, replace the oxygen sensor (rear).
(4) Warm up the engine until the engine coolant temperature
becomes 80°C (176°F) or higher.
(5) Using jumper wires, connect terminals @ (red clip of the
special tool) and @ (blue clip) of the oxygen sensor
connector to battery
0 and 0 terminals respectively.
Caution
Ensure that the jumper wires are connected correctly,
as wrong connections result in a broken oxygen sensor.
(6)Connect a digital voltmeter across terminals @ (black clip of
(7)the special tool) and @ (white clip).
Race the engine repeatedly and measure the output voltage
of the oxygen sensor (rear).
EngineOxygen sensor
output voltageRemarks
When engineis raced0.6-l.OVWhen the air-fuel mixturebecomes richer as a result
of repeated racing, the
oxygen sensor should outputa voltage of 0.6 - 1 .O V.
(8) If the measurements are not as specified, defective oxygen
sensor (rear) is suspected.
(9) Check the oxygen sensor (front) in the same way by
following steps
(I) through (8).
INSTALLATION
(1) For removal and installation of oxygen sensor, refer to
GROUP 15
- Exhaust Manifold.
(2) Tighten the oxygen sensor to specified torque.
TSB Revision
Page 207 of 1146
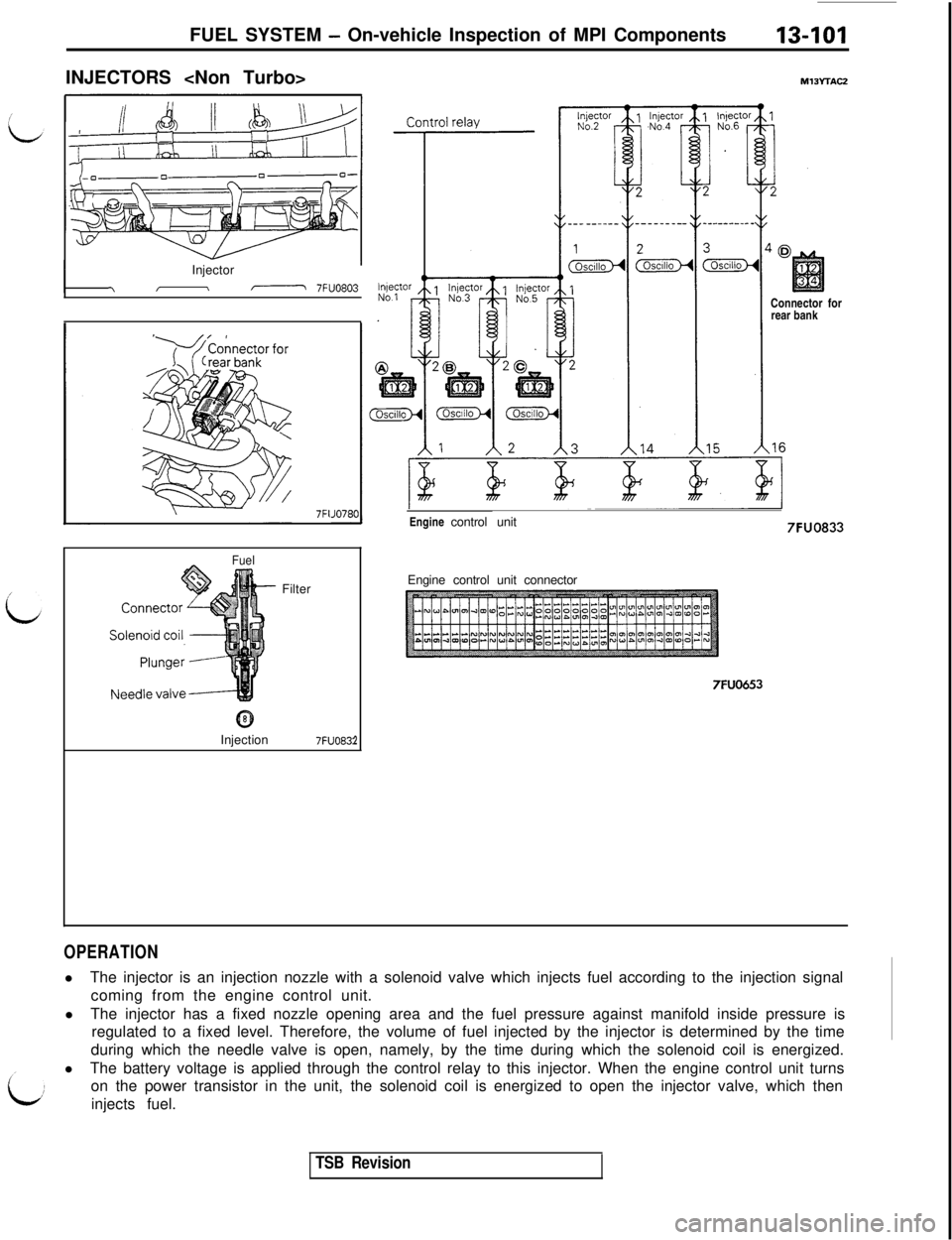
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-101INJECTORS
M13YTAC2
IInjectorII\- 7FUO803
7FI
FuelFilter
@Injection
7FUO83:2Connector for
rear bank
Engine control unit7FUO833
Engine control unit connector
7FUO653
OPERATIONlThe injector is an injection nozzle with a solenoid valve which injects fuel according to the injection signal
coming from the engine control unit.
lThe injector has a fixed nozzle opening area and the fuel pressure against manifold inside pressure is
regulated to a fixed level. Therefore, the volume of fuel injected by the injector is determined by the time
during which the needle valve is open, namely, by the time during which the solenoid coil is energized.
lThe battery voltage is applied through the control relay to this injector. When the engine control unit turns
on the power transistor in the unit, the solenoid coil is energized to open the injector valve, which then
injects fuel.
TSB Revision