change time MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 123 of 1146
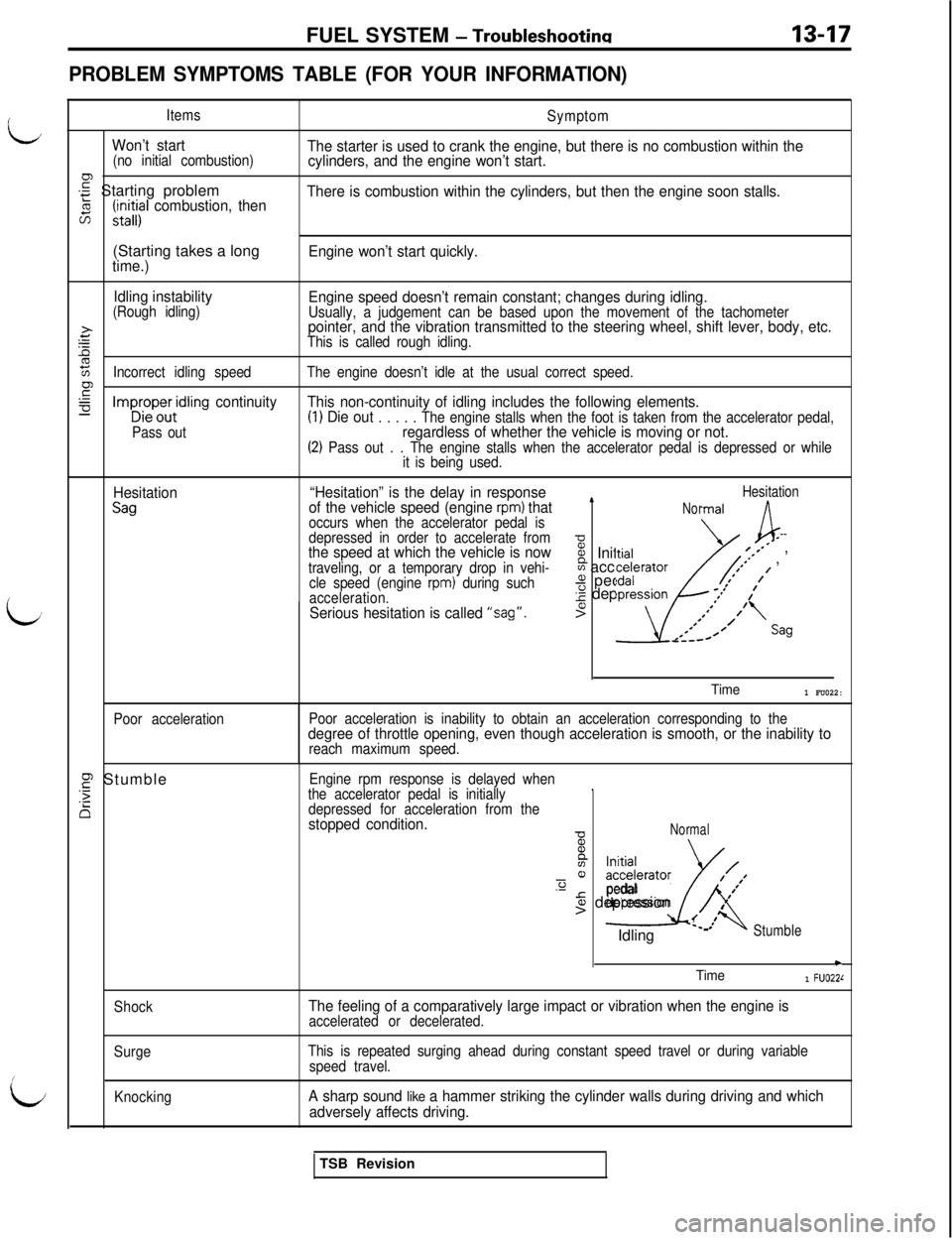
FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshootina13-17
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE (FOR YOUR INFORMATION)
I;
L
/
L/
Items
Won’t start(no initial combustion)-g Starting problem
2(i;il;i combustion, then
Symptom
The starter is used to crank the engine, but there is no combustion within the
cylinders, and the engine won’t start.
There is combustion within the cylinders, but then the engine soon stalls.(Starting takes a long
time.)Engine won’t start quickly.
Idling instability
(Rough idling)Engine speed doesn’t remain constant; changes during idling.Usually, a judgement can be based upon the movement of the tachometer
>.rpointer, and the vibration transmitted to the steering wheel, shift lever, body, etc.
EThis is called rough idling.
s0
Incorrect idling speedThe engine doesn’t idle at the usual correct speed.
F.-=e-ImpDr;p;ertidling continuityThis non-continuity of idling includes the following elements.(1) Die outPass out. . . . . The engine stalls when the foot is taken from the accelerator pedal,regardless of whether the vehicle is moving or not.(2) Pass out . . The engine stalls when the accelerator pedal is depressed or while
it is being used.
Hesitation
Sag
“Hesitation” is the delay in responseHesitation
of the vehicle speed (engine rpm) thatLNormaloccurs when the accelerator pedal is
depressed in order to accelerate from---
the speed at which the vehicle is nowx\a,r- ,
traveling, or a temporary drop in vehi-g Initialv) accelerator**’ ,8’ /cle speed (engine rpm) during such+ pedal/,’ /
’
acceleration.2 depression
Serious hesitation is called “sag”.2
1“*’.’
/’ ,’I&L-e**’Ii Sag
Poor acceleration
Time1 FU022:
Poor acceleration is inability to obtain an acceleration corresponding to thedegree of throttle opening, even though acceleration is smooth, or the inability toreach maximum speed.
0, Stumble.F
‘iIn
Engine rpm response is delayed when
the accelerator pedal is initially.
depressed for acceleration from thestopped condition.
$Normal
x
:Initial
3acceleratorI//
c
-7
pedal2 depression,#’,
4,/Idling *--’Stumble
Shock
cTime1 FUO22L
The feeling of a comparatively large impact or vibration when the engine isaccelerated or decelerated.
SurgeThis is repeated surging ahead during constant speed travel or during variable
speed travel.
Knocking
A sharp sound like a hammer striking the cylinder walls during driving and which
adversely affects driving.TSB Revision
Page 208 of 1146

13-102FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTSHint 1: If the engine is hard to start when hot, check fuel pressure and check the injector for leaks.
Hint 2:If the injector does not when the engine that is hard to start is cranked, the following as well as the
Iinjector itself may be responsible.
(1) Faulty power supply circuit to the engine control unit, faulty ground circuit
\-J
-(2) Faulty control relay
Hint 3:(3) Faulty crank angle sensor, top dead center sensor
If there is any cylinder whose idle state remains unchanged when the fuel injection of injectors is cut
one after another during idling, make following checks about such cylinder.
(1) Injector and harness check
(2) Ignition plug and high tension cable check
(3) Compression pressure check
Hint 4: If the injector harness and individual part checks have resulted normal but the injector drive time is
out of specification, the following troubles are suspected.
(1)Poor combustion in the cylinder (faulty ignition plug, ignition coil, compression pressure, etc.)
(2) Loose EGR valve seating
(3) High engine resistance
INSPECTIONUsing Multi-use Tester
FunctionItem No. Data displayCheck conditionCoolant temperatureStandard valueData reading 41
Drive time”’Engine: Cranking0°C (32”F)*zApprox. 17 ms
20°C (68°F)Approx. 46 ms
8O"C(176"F)Approx. 11 ms
Function
Data readingItem No.Data display
41Drive time*3l Engine coolant tem-perature: 80 to 95°C700 rpm (Idle)2.4-3.0 ms
(176 to 205°F)2,000 rpm2.0-2.6
msl Lamps, electric coolingfan, accessory units:When sharp racing isTo increaseAll OFF
madel Transaxle: Neutral
(P range for vehicle
with A/T)l Steering wheel: Neutral
Check conditionEngine stateStandard value ,
.---NOTE“I : The injector drive time refers to when the supply voltage is 11 V and the cranking speed is less than 250 rpm.*2: When coolant temperature is lower than 0°C (32°F). injection ismade by four-cylinders.---simultaneously.
“3: When the vehicle is new [within initial operation of about 500 km (300 miles)], the injector drive time may be about
10% longer.
Function
Actuator testItem No.
Drive content
Check conditionNormal state
01No. 1 injector shut offEngine: Idling afterIdle state to change
02No. 2 injector shut offwarm-up
(Shut off the injectorsfurther (becoming less
in sequence during afterstable or stalling)
03
No. 3 injector shut offengine warm-up, check
04No. 4 injector shut offthe idling condition)
05No. 5 injector shut off
06No. 6 injector shut off
TSB Revision
Page 212 of 1146

13-106FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
INSPECTION
Using Multi-use Tester
FunctionItem No.Data displayCheck conditionCoolant temperatureStandard value‘L,,,J
DataDrive time*’0°C (32’F)*’readingiRea:bankiEngine: CrankingApprox. 53 ms
(FronT7bank)20°C (68°F)
Approx. 29 ms
80°C (176°F)Approx. 7 ms
FunctionItem No.
Data displayCheck conditionEngine stateStandard value
Datareading(Reaebank)Drive time*3l Engine coolant tem-700 rpm (Idle)1.9 - 2.5 ms
perature: 80 to 95°C
(Front7banki(176 to 205°F)2,000 rpm1.6 - 2.2 ms
l Lamps, electric coolingfan, accessory units:To increase
All OFFWhen sharp racing is
made
l Transaxle: Neutral(P range for vehicle
with A/T)
l Steering wheel: Neutral
NOTE“I : The injector drive time refers to when the supply voltage is 11 V and the cranking speed is less than 250 rpm.
“2: When coolant temperature is lower than 0°C (32°F). injection is made by four cylinders simultaneously.
“3: When the vehicle is new [within initial operation of about 500 km (300 miles)], the injector drive time may be about
10% longer.
Function
Actuator testItem No.
Drive contentCheck conditionNormal state
01No. 1 injector shut offEngine: Idling afterIdle state to changewarm-upfurther (becoming less
02No. 2 injector shut off(Shut off the injectorsstable or stalling)
03in sequence during afterNo. 3 injector shut offengine warm-up, checkthe idling condition)
04No. 4 injector shut off
05
No. 5 injector shut off
06
No. 6 injector shut off
\,iUsing
OscillqscopeI(1) Run the engine at idle speed.
(2) Connect the probe to the oscilloscope pick-up point as
shown in the circuit diagram, and check the waveform at
the drive side of each injector.~
-
LJ
4 AL A: InjectorNormal waveformdrive time03A0209
TSB Revision
Page 245 of 1146

FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of Mql Components13439(10)Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure
regulator, and then measure the fuel pressure while using a
finger to plug the end of the hose.
Standard value:
- 350 kPa (47 - 50 psi) at curb idle
295 - 315 kPa (43 - 45 psi) at curb idle(11
)Check to be sure that the fuel pressure during idling does
not decrease even after the engine is raced a few times.
(12)Use a finger to gently press the fuel return hose while
repeatedly racing the engine, and check to be sure that
there is fuel pressure in the return hose also.
NOTEThere will be no fuel pressure in the return hose if there is
insufficient fuel flow.
(13)lf the fuel pressure measured in steps (9) to (12) deviates
from the standard value range, check for the probable
cause by referring to the table below, and. then make the
appropriate repair.
IConditionProbable cause1 RemedyI
l Fuel pressure is too low.l Fuel pressure drops duringracing.l No fuel pressure in fuel returnhose.
Malfunction of the valve seat withinthe fuel pressure regulator, or fuel
leakage to return, side caused byReplace the fuel filter.
Replace the fuel pressure regulator.
Fuel pump low discharge pressure.Replace the fuel pump.
Fuel pressure is too high.
The valve within the fuel pressureregulator is sticking.Replace the fuel pressure regulator.
Clogging of the fuel return hose and/Clean or replace the hose
and/oror the pipe.pipe.
No change of the fuel pressureDamaged vacuum hose or nippleReplace the vacuum hose, or clean
when the vacuum hose is connected clogging.the nipple.
and when not connected.
Malfunction of the fuel pressure controlChecking the fuel pressure controlsystem
1 TSB Revision
Page 364 of 1146
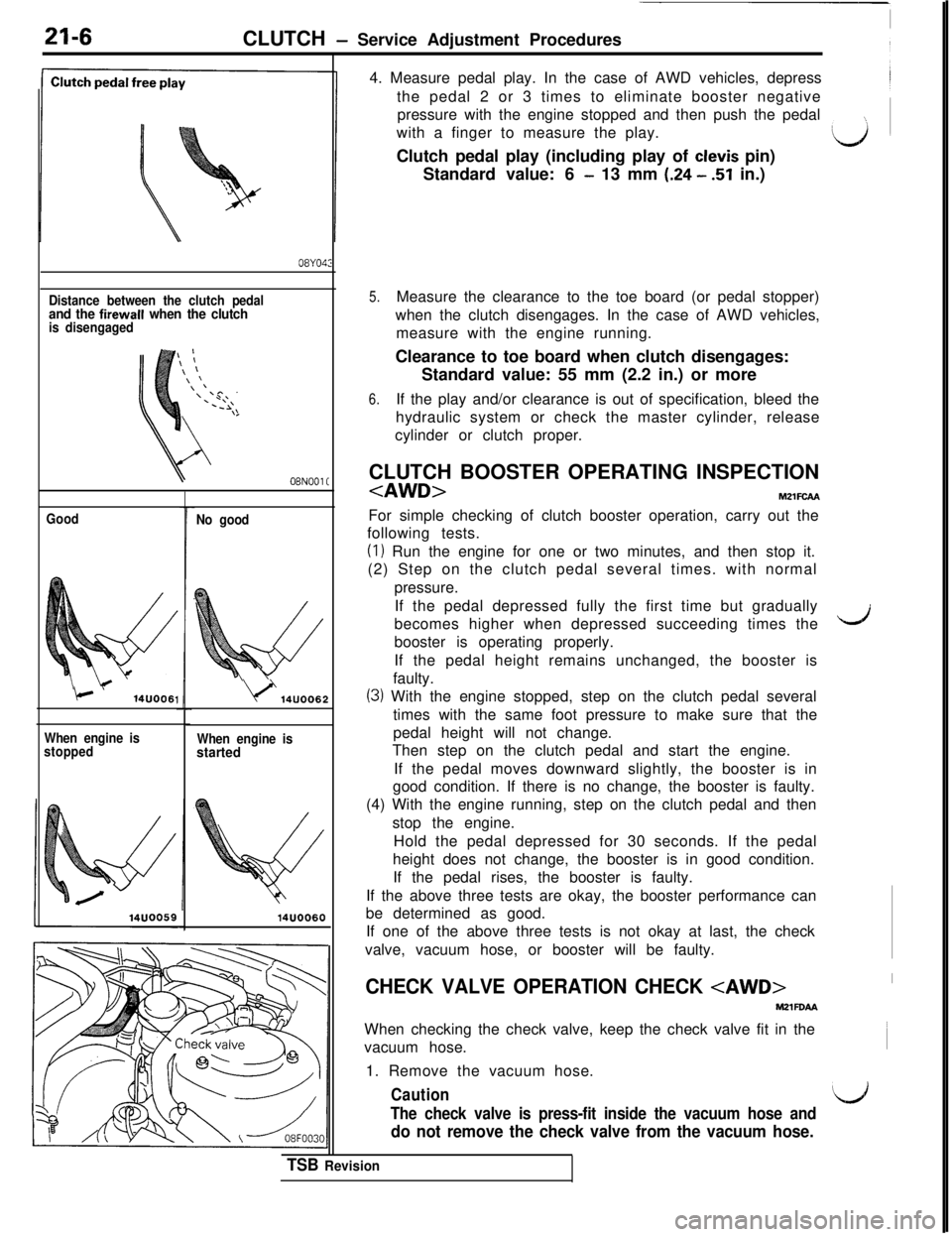
21-6CLUTCH - Service Adjustment Procedures
08YO4Z
Distance between the clutch pedaland the firewall when the clutchis disengaged
08NOOl C
Good
c1‘14UOO61
When engine is
stoppedNo good
\)‘14UOO6:
When engine isstarted
14UOO604. Measure pedal play. In the case of AWD vehicles, depress~
the pedal 2 or 3 times to eliminate booster negative
pressure with the engine stopped and then push the pedal
with a finger to measure the play.
LJClutch pedal play (including play of clevis pin)
Standard value: 6
- 13 mm (.24 - 51 in.)
2
CHECK VALVE OPERATION CHECK
MZlFOAAWhen checking the check valve, keep the check valve fit in the
vacuum hose.
1. Remove the vacuum hose.
CautionL’The check valve is press-fit inside the vacuum hose and
do not remove the check valve from the vacuum hose.
5.Measure the clearance to the toe board (or pedal stopper)
when the clutch disengages. In the case of AWD vehicles,
measure with the engine running.
Clearance to toe board when clutch disengages:
Standard value: 55 mm (2.2 in.) or more
6.If the play and/or clearance is out of specification, bleed the
hydraulic system or check the master cylinder, release
cylinder or clutch proper.
CLUTCH BOOSTER OPERATING INSPECTION
following tests.
(I) Run the engine for one or two minutes, and then stop it.
(2) Step on the clutch pedal several times. with normal
pressure.
If the pedal depressed fully the first time but gradually
becomes higher when depressed succeeding times the
dbooster is operating properly.
If the pedal height remains unchanged, the booster is
faulty.
(3) With the engine stopped, step on the clutch pedal several
times with the same foot pressure to make sure that the
pedal height will not change.
Then step on the clutch pedal and start the engine.
If the pedal moves downward slightly, the booster is in
good condition. If there is no change, the booster is faulty.
(4) With the engine running, step on the clutch pedal and then
stop the engine.
Hold the pedal depressed for 30 seconds. If the pedal
height does not change, the booster is in good condition.
If the pedal rises, the booster is faulty.
If the above three tests are okay, the booster performance can
be determined as good.
If one of the above three tests is not okay at last, the check
valve, vacuum hose, or booster will be faulty.
TSB Revision
Page 674 of 1146
33B-12ELECTRONIC CONTROL SUSPENSION (EC9 - i?:~~u:‘?s*men*
12FOOOESERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
I
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTIONIM33FHAD1. WARNING INDICATION BY ECS INDICATOR LIGHT
If a problem associated with the following items occurs, theECS indicator light (Tour Sport) in the combination light
flashes at intervals of 0.5 sec. At the same time, the
self-diagnosis code associated with the problem is outputto the diagnosis connector.
Warning Indication Items
l G sensor
l Steering angular velocity sensor
l Vehicle speed sensor
lDamping force changeover actuator (including position
detection switch)
2. SELF-DIAGNOSIS OUTPUT CHECK
(I) Check the self-diagnosis code.
(2) After the defective portion has been repaired, erase theself-diagnosis code. (If the defective portion is not
completely repaired, it may be impossible to erase the’self-diagnosis code by the MUT.)d
(3) Perform self-diagnosis output check again and checkthat the self-diagnosis code is good.
(1) Set the ignition switch to OFF.
(2) Connect the positive (+) terminal of the voltmeter to
the No. 3 terminal of the diagnosis connector beside the
junction block and connect the negative (--) terminal ofthe voltmeter to the No. 12 terminal.
(3) Set the ignition switch to ON.
(4) Read the self-diagnosis code on the basis of the
deflection of the pointer of the voltmeter.
(5) Based on the self-diagnosis code, repair the associated
defective portion.(6) Set the ignition switch to OFF.
(7) Disconnect the battery cables from the battery termi-
nals and reconnect them more than
10 seconds
thereafter.(8) Set the ignition switch to ON, perform self-diagnosis
check again, and check that the self-diagnosis code is
good.
TSB Revision
Page 679 of 1146

ELECTRONIC CONTROL SUSPENSION (ECS) - :;:~u:~men*33B17(4) Check that when the accelerator
dedal is operated, the
indications of service data items No. 61 through 64 on theMUT change as shown in the following table.
(5) With the simulated vehicle speed at 60 km/h (37’ mph) and
90 km/h (56 mph), similarly operate the accelerator pedaland check that the MUT indications change over.
Accelerator operating condition
EnE~~esismp~~ed ~;zz-KzxJ130km/h(19mph)
1HARDIMEDllJMI
1 60 km/h (37 mph)1MEDIUMIMEDllJMI
1 90 km/h (56 mph)1SOFTIMEDLJMI(6) Check that when the accelerator pedal is released, the
original damping force (SOFT) is restored in less than a
second.5-4. High Speed Sensitive Control Function
Chleck(I) Select the Tour mode by the ECS switch.
(2) Check that when the entered simulated vehicle speed is
changed by the MUT, the indications of service data itemsNo. 61 through 64 change.
(If the simulated vehicle speed is continuously cihanged by
the
Q and .!J keys of the MUT, however, the indications of
service data items No. 61 through 64 do not change duringthe period the
0 or a key is pressed.)
Changing entered simulated
vehicle speedMUT indication
Acceleration 129 km/h (80 mph)to 130 km/h (81 mph)SOFT + MEDIUM
Deceleration 120 km/h (75 mph)
to 119 km/h (74 mph)MEDIUM +, SOFT
5-5. Pitching and Bouncing Control Function Check
(1) Select the Tour mode by the ECS switch.
(2) Using the MUT, check the indications of service data itemsNo. 61 through 64.
MUT indication: SOFT
(3) Remove the G sensor, slowly shake it up and down througha space of about 5 cm (1.9 in.) with the connector
connected, and check that the indications of service dataitems No. 61 through 64 change.
G sensor status
IMUT indicationI
Shake up and down at a speed of arou.nd trip in a second.HARD(4) Check that when the G sensor is held stationary, the
original damping force indication (SOFT) is restored.
TSB Revision
Page 680 of 1146
33B-18ELECTRONIC CONTROL SUSPENSION (EC9 - ~::::u:?‘s*men*
\/I
I(Front)(Rear)I
12FOOG
6. ACTUATOR OPERATION CHECKM33FJAA
6-1. Actuator Operating Sound Check
(I) Set the ignition switch to ON.
(2) Bring your ear near the top of the shock absorber.dNOTE
In the case of the rear shock absorbers, remove the trim
cover at the top of the shock absorber before bringing your
ear near the shock absorber.
(3) Check that the operating sound of the actuator in the shockabsorber can be heard each time the control modes are
changed by pressing the ECS switch.
6-2. Damping Force Check(1) Set the ignition switch to ON.
(ECS indicator Tour ON, damping force SOFT)
(2) Check the damping force SOFT state by shaking the top
mounting points of the front shock absorbers or the top ofthe rear end panels of the rear shock absorbers up and
down.
(3) Press the ECS switch to change the control mode to Sport.(ECS indicator Sport ON, damping force HARD)
(4) Shake the vehicle up and down to check that the dampingforce is harder than in the SOFT state.
TSB Revision
Page 768 of 1146
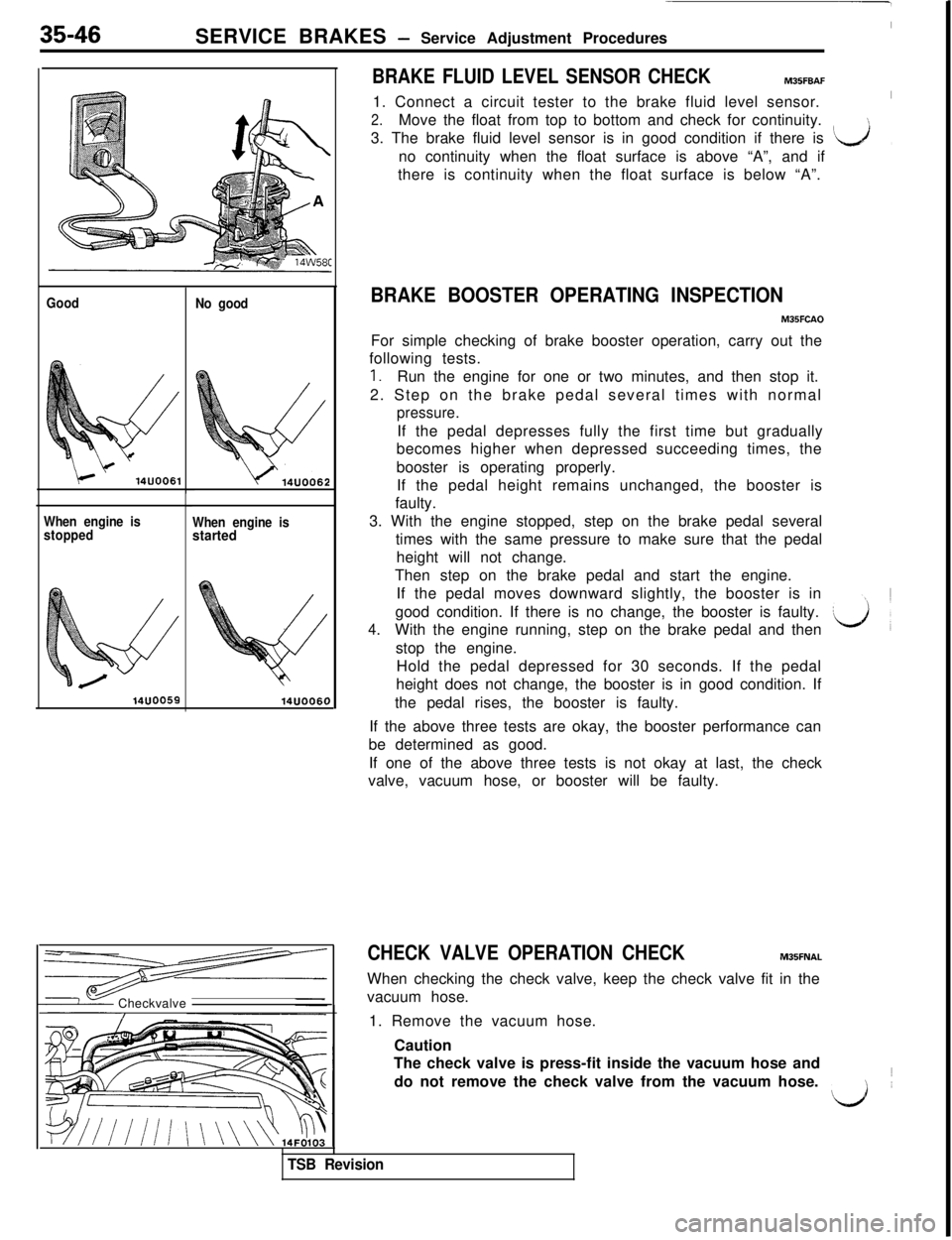
35-46SERVICE BRAKES - Service Adjustment Procedures
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SENSOR CHECK
I
MBSFBAF
Good
k‘14UOO61
When engine is
stoppedNo good
When engine isstarted
14UOO6C)Checkvalve/1. Connect a circuit tester to the brake fluid level sensor.
I
2.Move the float from top to bottom and check for continuity.
3. The brake fluid level sensor is in good condition if there is
‘k&Jno continuity when the float surface is above “A”, and if,there is continuity when the float surface is below “A”.
BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATING INSPECTION
M35FCAOFor simple checking of brake booster operation, carry out the
following tests.
1.Run the engine for one or two minutes, and then stop it.
2. Step on the brake pedal several times with normal
pressure.If the pedal depresses fully the first time but gradually
becomes higher when depressed succeeding times, the
booster is operating properly.
If the pedal height remains unchanged, the booster is
faulty.
3. With the engine stopped, step on the brake pedal several
times with the same pressure to make sure that the pedal
height will not change.
Then step on the brake pedal and start the engine.
If the pedal moves downward slightly, the booster is in
good condition. If there is no change, the booster is faulty.
4.With the engine running, step on the brake pedal and then
stop the engine.
Hold the pedal depressed for 30 seconds. If the pedal
height does not change, the booster is in good condition. If
the pedal rises, the booster is faulty.
If the above three tests are okay, the booster performance can
be determined as good.
If one of the above three tests is not okay at last, the check
valve, vacuum hose, or booster will be faulty.
CHECK VALVE OPERATION CHECKM35FNALWhen checking the check valve, keep the check valve fit in the
vacuum hose.
1. Remove the vacuum hose.
Caution
The check valve is press-fit inside the vacuum hose and
do not remove the check valve from the vacuum hose.1
d~
TSB Revision
Page 775 of 1146
L.
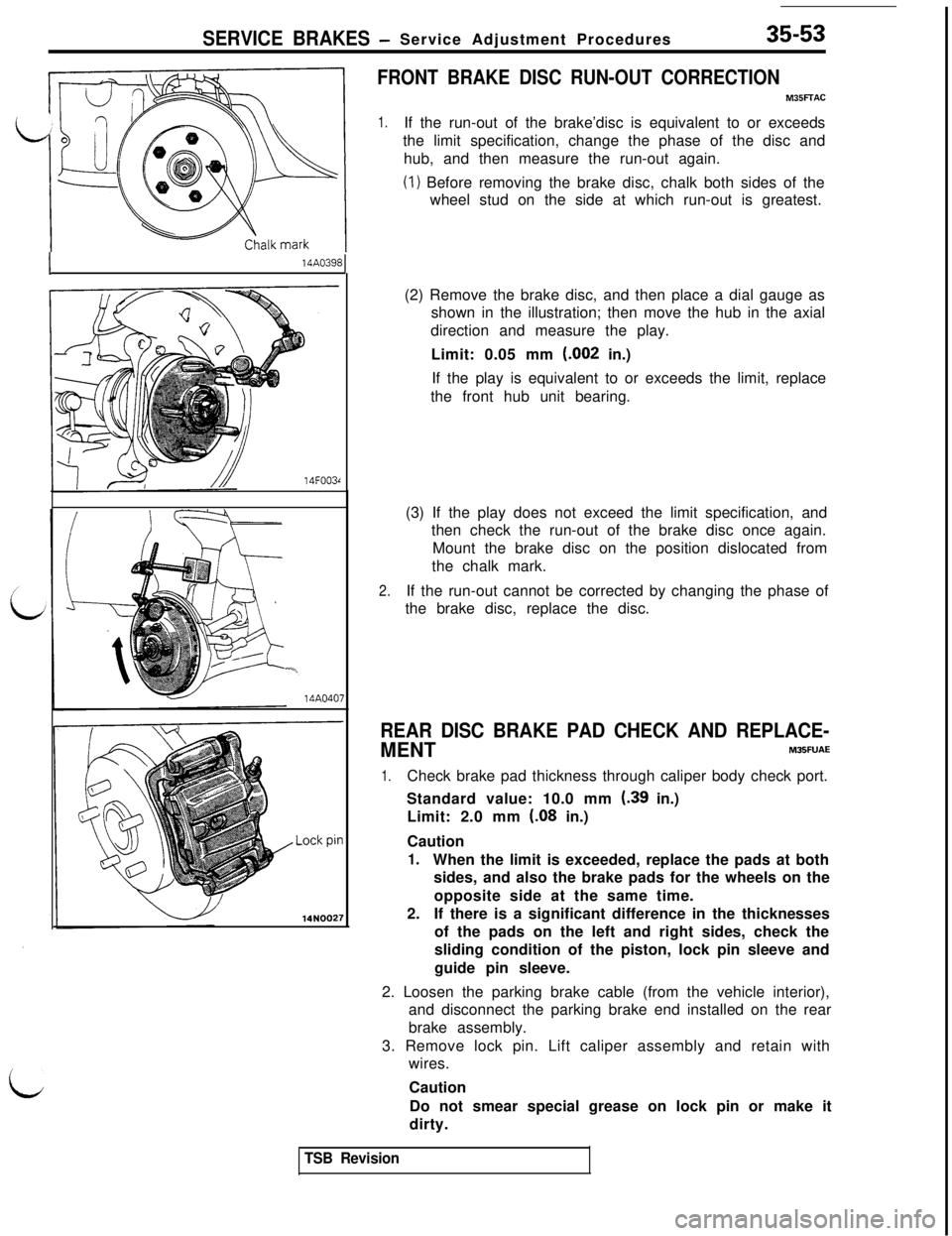
SERVICE BRAKES -Service Adjustment Procedures35-53
I14A0398
14F003r
i14A04014NOO27
7
FRONT BRAKE DISC RUN-OUT CORRECTION
M35FFAC
1.If the run-out of the brake’disc is equivalent to or exceeds
the limit specification, change the phase of the disc and
hub, and then measure the run-out again.
(1) Before removing the brake disc, chalk both sides of the
wheel stud on the side at which run-out is greatest.
(2) Remove the brake disc, and then place a dial gauge as
shown in the illustration; then move the hub in the axial
direction and measure the play.
Limit: 0.05 mm (.002 in.)
If the play is equivalent to or exceeds the limit, replace
the front hub unit bearing.
(3) If the play does not exceed the limit specification, and
then check the run-out of the brake disc once again.
Mount the brake disc on the position dislocated from
the chalk mark.
2.If the run-out cannot be corrected by changing the phase of
the brake disc, replace the disc.
REAR DISC BRAKE PAD CHECK AND REPLACE-
MENTM35FUAE
1.Check brake pad thickness through caliper body check port.
Standard value: 10.0 mm
(39 in.)
Limit: 2.0 mm
(08 in.)
Caution
1.When the limit is exceeded, replace the pads at both
sides, and also the brake pads for the wheels on the
opposite side at the same time.
2.If there is a significant difference in the thicknesses
of the pads on the left and right sides, check the
sliding condition of the piston, lock pin sleeve and
guide pin sleeve.
2. Loosen the parking brake cable (from the vehicle interior),
and disconnect the parking brake end installed on the rear
brake assembly.
3. Remove lock pin. Lift caliper assembly and retain with
wires.
Caution
Do not smear special grease on lock pin or make it
dirty.
TSB Revision