sensor MITSUBISHI COLT 2006 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: COLT, Model: MITSUBISHI COLT 2006Pages: 364, PDF Size: 11.65 MB
Page 112 of 364

DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4A9>13A-18
NOTE: Items marked "*" will not appear if a data list is selected in the check mode.
8A*Throttle position sensor (main)%
A1*Oxygen sensor (front)V
A2*Oxygen sensor (rear)V
Item No. Inspection item Unit
Page 116 of 364

GENERAL INFORMATION
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
M2132000101001
Although the control systems are basically the same
as those of the 4G1-Non-Turbo engine used in the
COLT, the following improvements have been added.
ImprovementRemark
A heat-sensing type air flow sensor
is used.•Changed to the intake air flow me asurement system by the air flow
sensor.
•The sensor is basically the same as that of the 4G69-MPI engine
used in the GRANDIS.
Supercharging pressure control
system is used.Controls the boost pressure that affects the waste gate actuator in
response to the signals from the engine-ECU.
Fuel pressure control solenoid valve
is used.Idling stability immediately afte r restarting the engine at high
temperature is maintained.
Dual oxygen sensor is used.Higher reliability of air-fuel ratio control.
Clutch switch is used.The information about whether the clutch pedal is depressed or not is
input into the engine-ECU.
Page 117 of 364
![MITSUBISHI COLT 2006 Service Owners Guide
GENERAL INFORMATION
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-3
SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM
AK600528
Barometric pressure sensorEngine control unitEngine-ECU
[1] Fuel injection control
[2] Throttle valve open MITSUBISHI COLT 2006 Service Owners Guide
GENERAL INFORMATION
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-3
SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM
AK600528
Barometric pressure sensorEngine control unitEngine-ECU
[1] Fuel injection control
[2] Throttle valve open](/img/19/57093/w960_57093-116.png)
GENERAL INFORMATION
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-3
SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM
AK600528
Barometric pressure sensorEngine control unitEngine-ECU
[1] Fuel injection control
[2] Throttle valve opening control
and idle speed control
[3] MIVEC (Mitsubishi Innovative
Valve timing Electronic
control system)
[4] Ignition timing control
[5] Engine control relay control
[6] Throttle valve control servo
relay control
[7] Fuel pump relay control
[8] Oxygen sensor (front) heater
control
[9] Oxygen sensor (rear) heater
control
[10] Fuel pressure control
[11] Waste gate control
[12] Fan relay control
[13] A/C compressor relay
control
[14] Alternator control
[15] Purge control
[16] Diagnostic output
[17] RAM data transmission Throttle valve control unit
Throttle opening feedback control
Engine coolant
temperature sensor Intake air temperature sensor Air flow sensor
Accelerator pedal
position sensor (main) Throttle position sensor (sub)
Camshaft position sensor
Crank angle sensor
Oxygen sensor (front)
Oxygen sensor (rear)
Alternator FR terminal
Clutch switch
Detonation sensor
Ignition switch-IG
Ignition switch-ST
Stop lamp switch
Power supply
Throttle position sensor (main)
Accelerator pedel
position sensor (sub)
Throttle valve control servo No.1 injector
No.2 injector
No.3 injector
No.4 injector
No.1 Ignition coil
No.2 Ignition coil
No.3 Ignition coil
No.4 Ignition coil
Engine control relay
Throttle valve control servo relay
Waste gate solenoid valve
A/C compressor relay
Fuel pump relay
Alternator G terminal
Cooling fan control relay (Hi, Lo)
Purge control solenoid valve
Diagnostic output terminal
Oxygen sensor (front) heater
Oxygen sensor (rear) heater Oil feeder control valve
(for MIVEC)
Fuel pressure control
solenoid valve
AB
Page 118 of 364
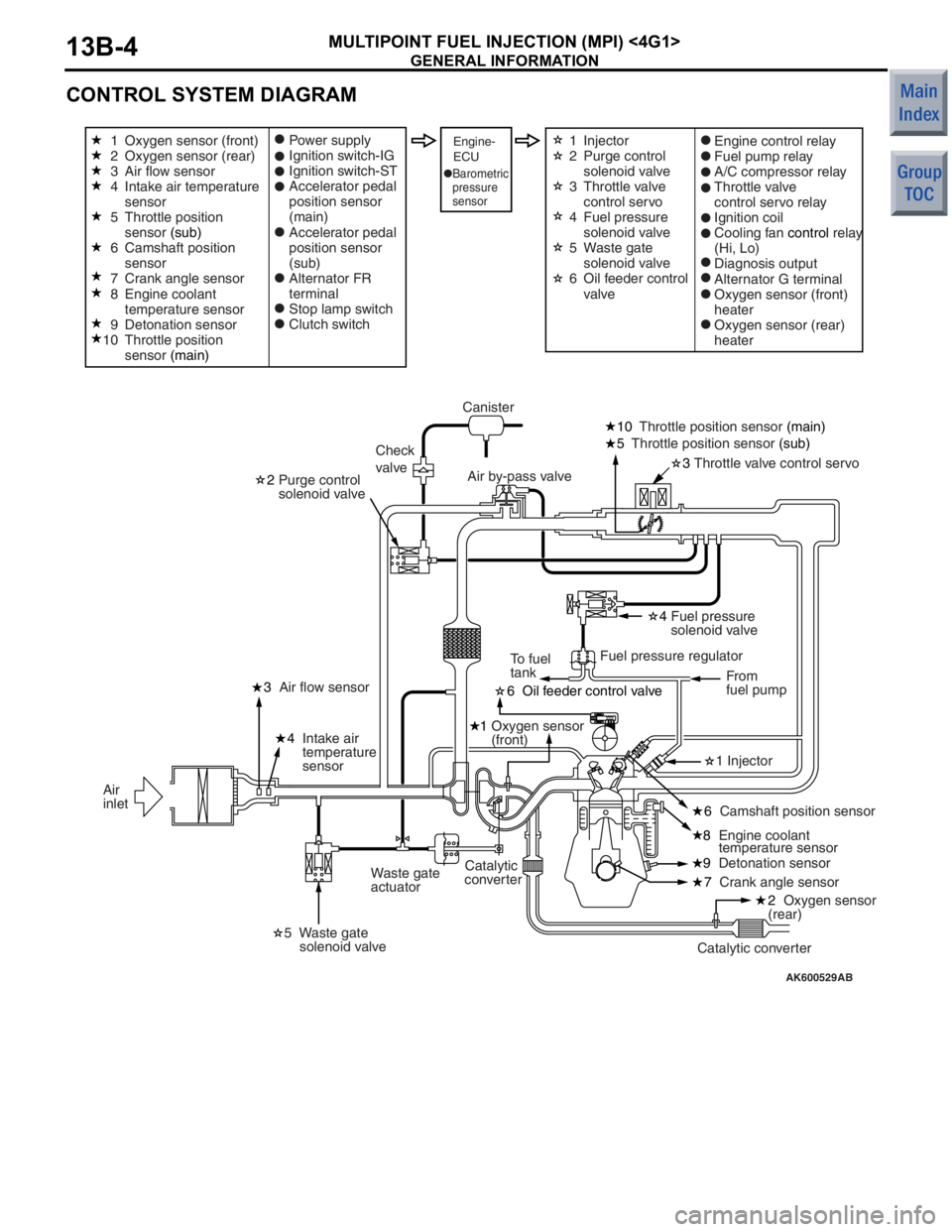
GENERAL INFORMATION
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-4
CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGRAM
AK600529AB
6 Oil feeder control valve
1 Oxygen sensor
(front)
8 Engine coolant
temperature sensor
3
Throttle valve control servo
10
Throttle position sensor (main)
5 Throttle position sensor (sub)
2 Purge control
solenoid valve
4 Fuel pressure
solenoid valve
7 Crank angle sensor
9
Detonation sensor
4
Intake air
temperature
sensor
3
Air flow sensor
Waste gate
actuator Canister
Check
valve Air by-pass valve
Fuel pressure regulatorFrom
fuel pump
To fuel
tank
Catalytic converter
Catalytic
converter
Air
inlet
Oxygen sensor (front)
Oxygen sensor (rear)
Air flow sensor
Intake air temperature
sensor
Throttle position
sensor
(sub)
Camshaft position
sensor
Crank angle sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Detonation sensor
Throttle position
sensor (main) Power supply
Ignition switch-IG
Ignition switch-ST
Accelerator pedal
position sensor
(main)
Accelerator pedal
position sensor
(sub)
Alternator FR
terminal
Stop lamp switch
Clutch switchEngine-
ECUEngine control relay
Fuel pump relay
A/C compressor relay
Throttle valve
control servo relay
Ignition coil
Cooling fan
control relay
(Hi, Lo)
Diagnosis output
Alternator G terminal
Oxygen sensor (front)
heater
Oxygen sensor (rear)
heater
Barometric
pressure
sensor
1 Injector
5 Waste gate
solenoid valve
2 Oxygen sensor
(rear)
6 Camshaft position sensor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 Injector
Purge control
solenoid valve
Throttle valve
control servo
Fuel pressure
solenoid valve
Waste gate
solenoid valve
Oil feeder control
valve
1
2
3
4
5
6
Page 119 of 364

GENERAL INFORMATION
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-5
List of Component Functions
ECU
NameFunction
Engine-ECUThe signals that are input by the sensors enable the
actuators to be controlled in accordance with the
driving conditions.
Sensor
Ignition switch-IGThis signal indicates the ON/OFF condition of the
ignition switch. When this signal is input, the
engine-ECU supplies power to the crank angle
sensor, camshaft position sensor, etc.
Ignition switch-STThis signal indicates that the engine is cranking.
Based on this signal, the engine-ECU controls the
fuel injection, throttle valve position, and the injection
timing that are suited for starting the engine.
Air flow sensor This signal, which indicates the intake air flow rate
(mass), is input into the engine-ECU. Based on the
signals from this sensor, the engine-ECU effects fuel
injection control.
Oxygen sensor
electrodes, detects the level of oxygen concentration
in the exhaust gases. The engine-ECU determines
whether the air-fuel ratio is at the optimal
stoichiometric ratio in accordance with this oxygen
concentration level.
Barometric pressure sensorThis sensor detects the altitude of the vehicle. It
enables the engine-ECU to make fuel injection
volume corrections in order to achieve an appropriate
air-fuel ratio.
Intake air temperature sensorThis sensor, which contains a thermistor, detects the
temperature of the intake air. The engine-ECU
makes fuel injection volume corrections that suit the
intake air temperature, in accordance with the
voltage that is output by this sensor.
Engine coolant temperature sensorThis sensor, which contains a thermistor, detects the
temperature of the engine coolant. The engine-ECU
determines the warm-up condition of the engine in
accordance with the voltage that is output by this
sensor, in order to control the fuel injection volume,
idle speed, and ignition timing.
Throttle position sensor
and inputs it into the engine-ECU. Based on the
voltage that is output by this sensor, the engine-ECU
effects throttle valve feedback control.
Accelerator pedal position sensor
and inputs it into the engine-ECU. Based on the
voltage that is output by this sensor, which
determines the accelerator position (and the intention
of the driver), the engine-ECU effects appropriate
fuel injection and throttle valve position controls.
Page 120 of 364

GENERAL INFORMATION
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-6
Camshaft position sensorThis sensor detects the top-dead-center (TDC) of the
compression stroke of each cylinder.
Crank angle sensorThis sensor detects the crank angle and inputs it into
the engine-ECU. The engine-ECU effects injector
control and other controls in accordance with the
signals received from this sensor.
Detonation sensorThis sensor, which contains a piezoelectric element,
detects the vibration of the cylinder block that results
from knocking. The engine-ECU detects only the
knocking of the engine from these vibrations, in order
to retard the ignition timing in accordance with the
strength of the knocks.
Alternator FR terminalThis terminal is used for detecting the duty cycle ratio
that energizes the alternator field coil.
Stop lamp switchThis is a contact point type switch that detects how
the brake pedal is depressed.
Actuators
Engine control relayThis relay turns ON and OFF the engine-ECU power
circuit.
Throttle valve control servo relayThis relay turns ON and OFF the actuation power
circuit for the throttle valve control servo in the
engine-ECU.
InjectorThe injectors inject fuel in accordance with the
injection signals received from the engine-ECU.
Ignition coil (with power transistor)Applies ignition coil primary current intermittently in
accordance with the ignition signals received from
the engine-ECU, in order to generate high voltage for
ignition.
Fuel pump relayControls the power supplied to the fuel pump in
accordance with the signals received from the
engine-ECU.
A/C compressor relayControls the operation of the A/C compressor in
accordance with the signals received from the
engine-ECU.
Purge control solenoid valveControls the flow rate of the purge air introduced into
the inlet manifold in accordance with the signals
received from the engine-ECU.
Alternator G terminalControls the amount of current generated by the
alternator in accordance with the signals received
from the engine-ECU.
Cooling fan control relayControls the speed of the cooling fan in accordance
with the signals received from the engine-ECU.
Throttle valve control servoControls the throttle valve position in accordance with
the signals received from the engine-ECU.
ECU
Name Function
Page 121 of 364
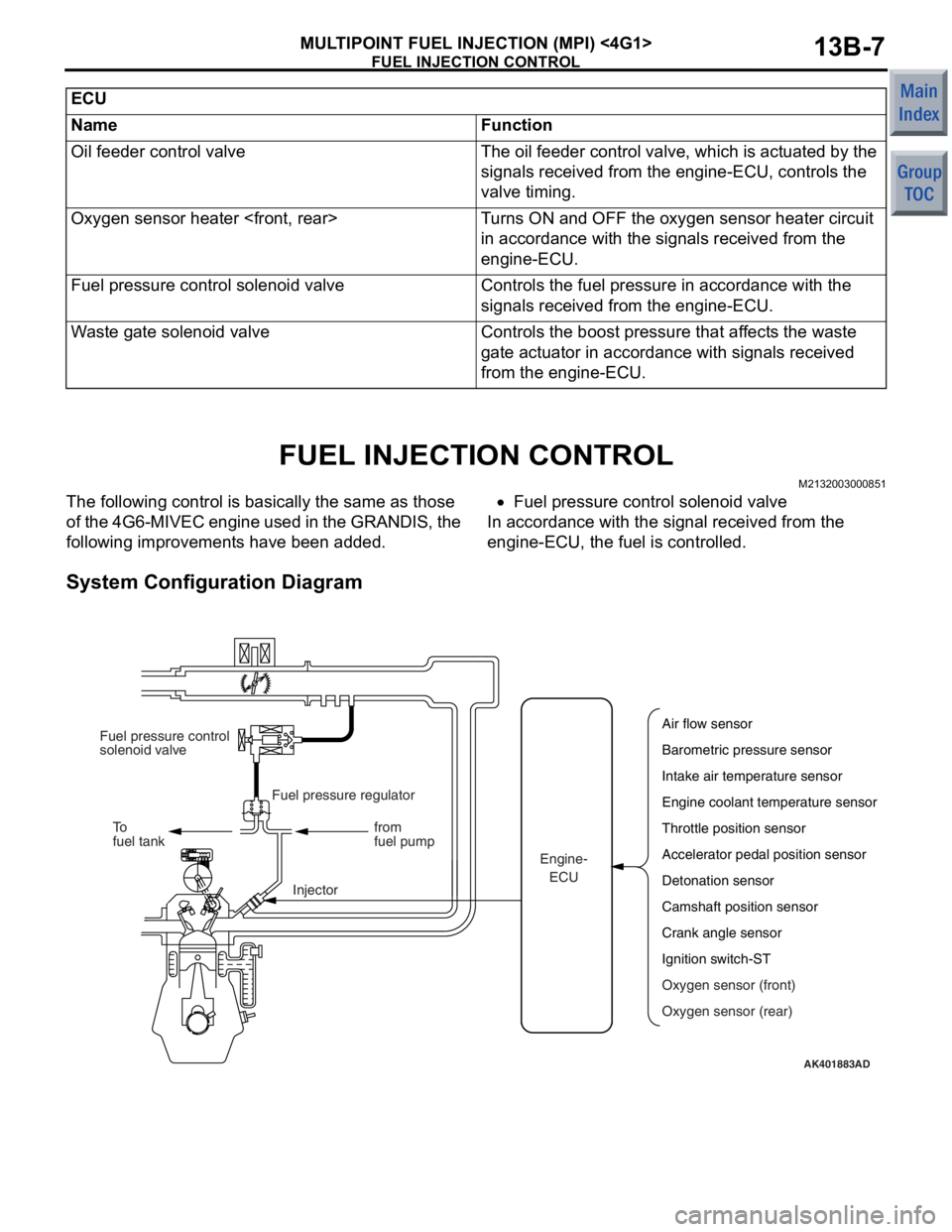
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-7
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
M2132003000851
The following control is basically the same as those
of the 4G6-MIVEC engine used in the GRANDIS, the
following improvements have been added.•Fuel pressure control solenoid valve
In accordance with the signal received from the
engine-ECU, the fuel is controlled.
System Configuration Diagram
AK401883AD
Air flow sensor
Barometric pressure sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Throttle position sensor
Accelerator pedal position sensor
Detonation sensor
Camshaft position sensor
Crank angle sensor
Ignition switch-ST
Oxygen sensor (front)
Oxygen sensor (rear)
Engine-
ECU
Injector from
fuel pump
To
fuel tank Fuel pressure regulator
Fuel pressure control
solenoid valve
Oil feed
er con t rol valveThe oil fee der control va lve , which is actuate d by the
signals re
ceived f r om th e eng ine-ECU, co ntrols the
valve timing.
Oxygen sensor he ater
in
accordan ce wit h the sign als rece ive d from the
en
gine-ECU.
Fuel p r essure control solenoid va lveControls the fue l pressure in a cco rdance with the
signals re
ceived f r om th e eng ine-ECU.
Wa ste g a te solen o id valveControls the boo st pre s sure tha t af fe ct s th e waste
ga
te actuator in accord ance with signals re ceived
from the
engin e -ECU.
ECU
Nam
e Func tion
Page 122 of 364
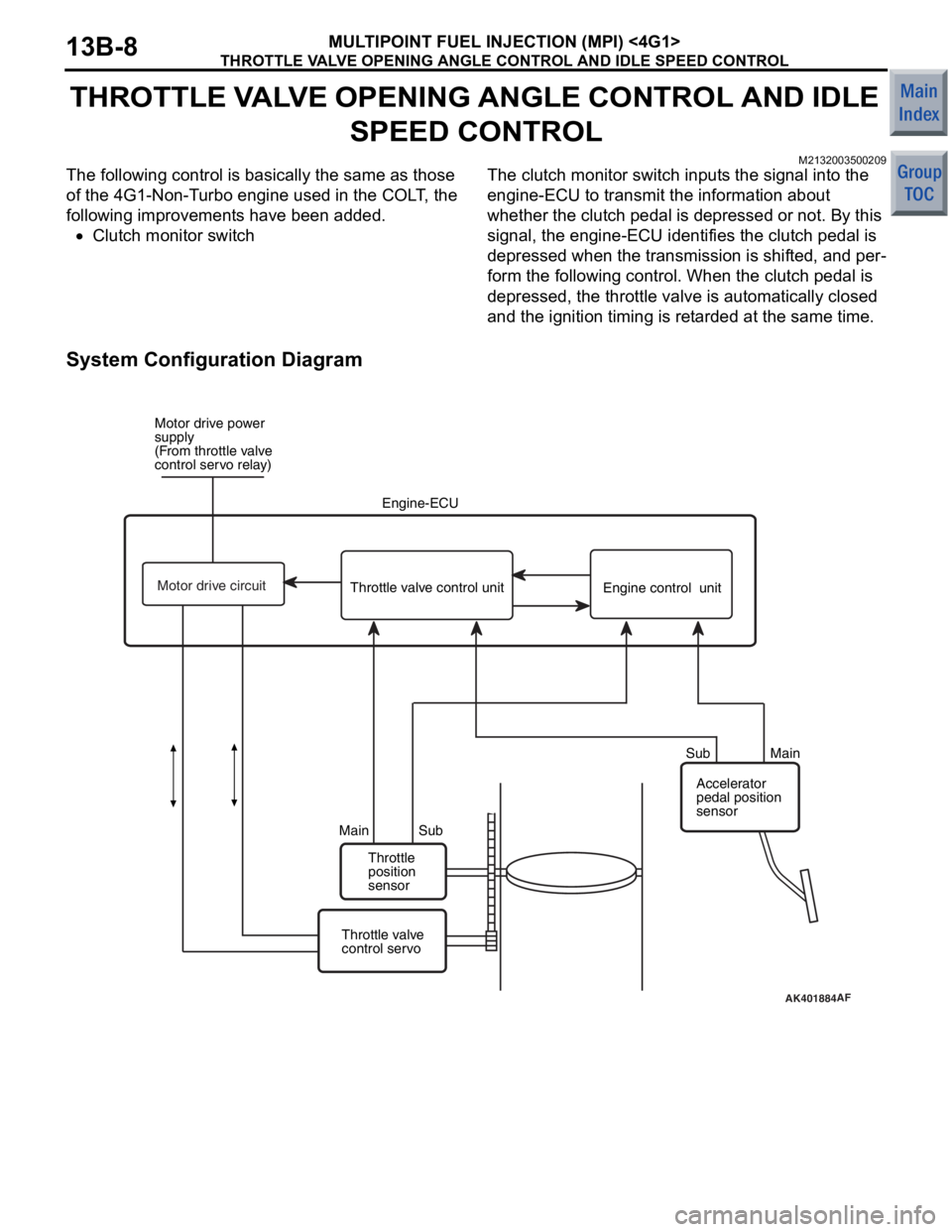
THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL AND IDLE SPEED CONTROL
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-8
THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL AND IDLE
SPEED CONTROL
M2132003500209
The following control is basically the same as those
of the 4G1-Non-Turbo engine used in the COLT, the
following improvements have been added.
•Clutch monitor switch
The clutch monitor switch inputs the signal into the
engine-ECU to transmit the information about
whether the clutch pedal is depressed or not. By this
signal, the engine-ECU identifies the clutch pedal is
depressed when the transmission is shifted, and per
-
form the following control. When the clutch pedal is
depressed, the throttle valve is automatically closed
and the ignition timing is retarded at the same time.
System Configuration Diagram
AK401884AF
Motor drive power
supply
(From throttle valve
control servo relay)
Engine-ECU
Throttle
position
sensor
Main Sub Sub Main
Throttle valve
control servo Accelerator
pedal position
sensor
Throttle valve control unit
Engine control unit
Motor drive circuit
Page 123 of 364
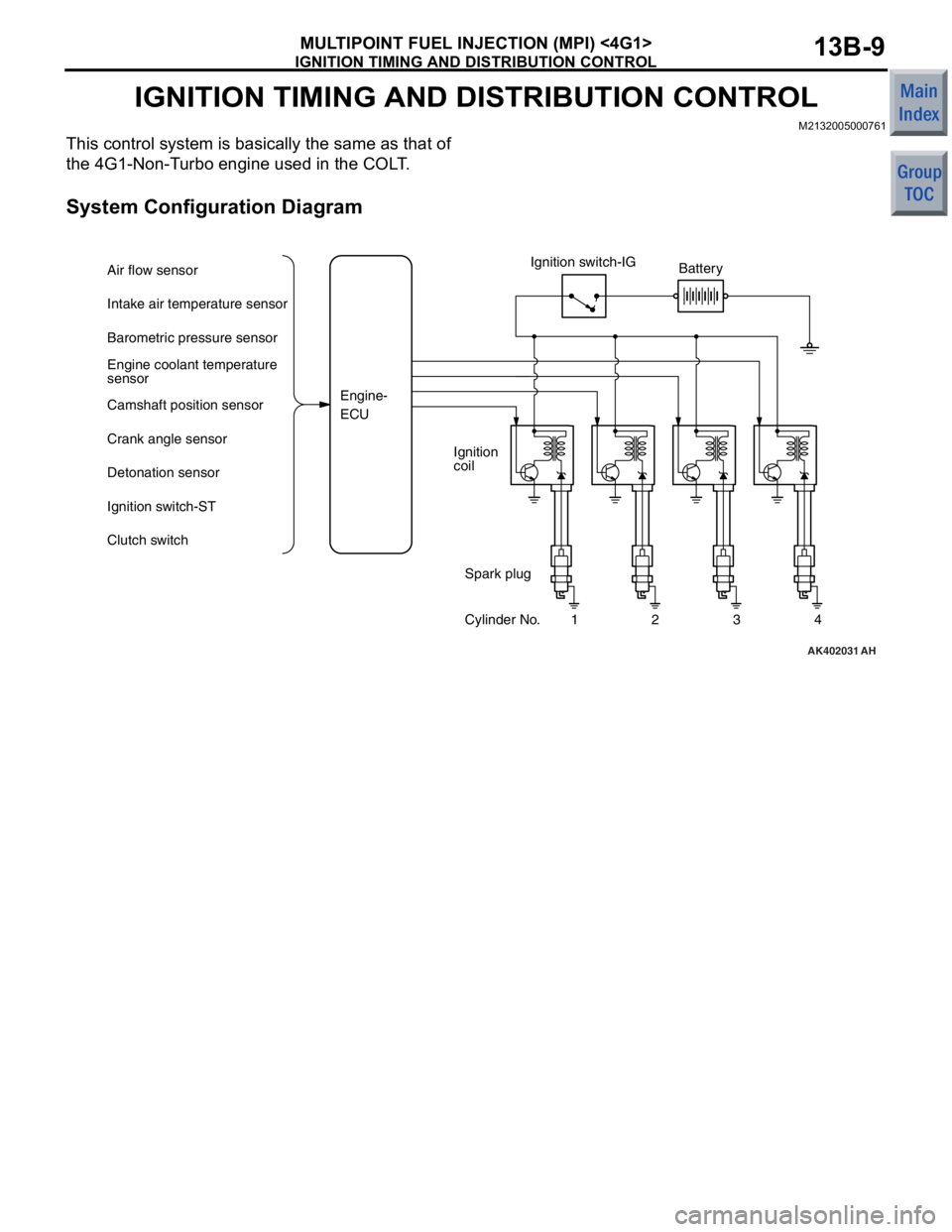
IGNITION TIMING AND DISTRIBUTION CONTROL
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-9
IGNITION TIMING AND DISTRIBUTION CONTROL
M2132005000761
This control system is basically the same as that of
the 4G1-Non-Turbo engine used in the COLT.
System Configuration Diagram
AK402031
Ignition switch-IG
Ignition
coil Battery
Spark plug
Cylinder No. 1 2 3 4
Air flow sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Barometric pressure sensor
Engine coolant temperature
sensor
Camshaft position sensor
Crank angle sensor
Detonation sensor
Ignition switch-ST
Clutch switch
Engine-
ECU
AH
Page 124 of 364
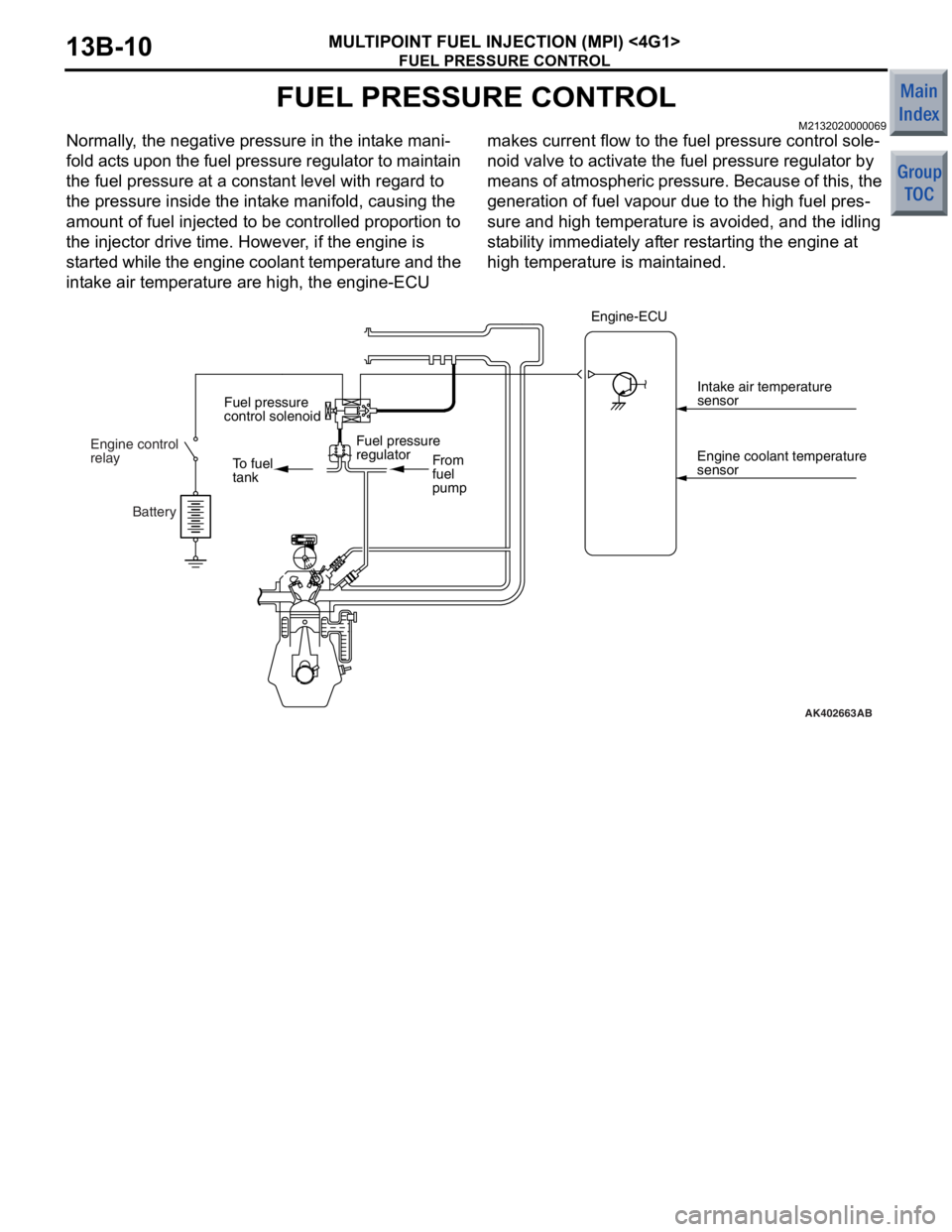
FUEL PRESSURE CONTROL
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G1>13B-10
FUEL PRESSURE CONTROL
M2132020000069
Normally, the negative pressure in the intake mani-
fold acts upon the fuel pressure regulator to maintain
the fuel pressure at a constant level with regard to
the pressure inside the intake manifold, causing the
amount of fuel injected to be controlled proportion to
the injector drive time. However, if the engine is
started while the engine coolant temperature and the
intake air temperature are high, the engine-ECU makes current flow to the fuel pressure control sole
-
noid valve to activate the fuel pressure regulator by
means of atmospheric pressure. Because of this, the
generation of fuel vapour due to the high fuel pres
-
sure and high temperature is avoided, and the idling
stability immediately after restarting the engine at
high temperature is maintained.
AK402663
To fuel
tank
From
fuel
pump
Fuel pressure
regulator
Fuel pressure
control solenoid
AB
Engine control
relay
Engine coolant temperature
sensorIntake air temperature
sensor
Engine-ECU
Battery