automatic transmission MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1900, Model line: DIAMANTE, Model: MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900Pages: 408, PDF Size: 71.03 MB
Page 2 of 408

.
1-2 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
Chitton’s Total Car Care manual for the 199M10
Mitsubishi Mirage, Galant and Diamante is intended
to help you learn more about the inner workings of
your vehicle while saving you money on its upkeep
and operation.
The beginning of the book will likely be referred to
the most, since that is where you will find information
for maintenance and tune-up. The other sections deal
with the more complex systems of your vehicle. Oper-
ating systems from engine through brakes are cov-
ered to the extent that the average do-it-yourselfer be-
comes mechanically involved. This book will not
explain such things as rebuilding a differential for the
simple reason that the expertise required and the in-
vestment in special tools make this task uneconomi-
cal. It will, however, give you detailed instructions to
help you change your own brake pads and shoes, re-
place spark plugs, and perform many more jobs that
can save you money, give you personal satisfaction
and help you avoid expensive problems.
A secondary purpose of this book is a reference for
owners who want to understand their vehicle and/or
their mechanics better. In this case, no tools at all are
required.
Before removing any bolts, read through the entire
procedure. This will give you the overall view of what
tools and supplies will be required. There is nothing
more frustrating than having to walk to the bus stop
on Monday morning because you were short one bolt
on Sunday afternoon. So read ahead and plan ahead.
Each operation should be approached logically and
all procedures thoroughly understood before attempt-
ing any work.
All sections contain adjustments, maintenance, re-
moval and installation procedures, and in some cases,
repair or overhaul procedures. When repair is not con-
sidered practical, we tell you how to remove the part
and then how to install the new or rebuilt replacement.
In this way, you at least save labor costs. “Backyard”
repair of some components is just not practical.
Many procedures in this book require you to “label
and disconnect. . ” a group of lines, hoses or wires.
Don’t be lulled into thinking you can remember where
everything goes-you won’t. If you hook up vacuum
or fuel lines incorrectly, the vehicle may run poorly, if
at all. If you hook up electrical wiring incorrectly, you
may instantly learn a very expensive lesson.
You don’t need to know the official or engineering
name for each hose or line. A piece of masking tape
on the hose and a piece on its fitting will allow you to
assign your own label such as the letter A or a short name. As long as you remember your own code, the
lines can be reconnected by matching similar letters
or names. Do remember that tape will dissolve in
gasolrne or other fluids; if a component is to be
washed or cleaned, use another method of identifica-
tion. A permanent felt-tipped marker or a metal scribe
can be very handy for marking metal parts. Remove
any tape or paper labels after assembly.
It’s necessary to mention the difference between
maintenance and repair Maintenance includes rou-
tine inspections, adjustments, and replacement of
parts which show signs of normal wear Maintenance
compensates for wear or deterioration. Repair implies
that something has broken or is not working. A need
for repair is often caused by lack of maintenance. Ex-
ample, draining and refilling the automatic transaxle
fluid is maintenance recommended by the manufac-
turer at specific mileage intervals. Failure to do this
can shorten the life of the transmission/transaxle, re-
quiring very expensive repairs. While no maintenance
program can prevent items from breaking or wearing
out, a general rule can be stated: MAINTENANCE IS
CHEAPER THAN REPAIR.
Two basic mechanrc’s rules should be mentioned
here. First, whenever the left side of the vehicle or en-
gine is referred to, it is meant to specify the drivers
side. Conversely, the right side of the vehicle means
the passengers side. Second, screws and bolts are
removed by turning counterclockwise, and tightened
by turning clockwrse unless specifically noted.
Safety is always the most important rule. Con-
stantly be aware of the dangers involved in working
on an automobile and take the proper precautions.
See the informatron in this section regarding SER-
VICING YOUR VEHICLE SAFELY and the SAFETY
NOTICE on the acknowledgment page.
Pay attention to the instructions provided. There
are 3 common mistakes in mechanical work:
1. Incorrect order of assembly, disassembly or
adjustment. When taking something apart or putting
it together, performing steps in the wrong order usu-
ally just costs you extra time; however, it CAN break
something. Read the entire procedure before begin-
ning disassembly. Perform everything in the order in
which the instructions say you should, even if you
can’t immedrately see a reason for it. When you’re
taking apart something that is very intricate, you
might want to draw a picture of how it looks when as-
sembled at one point in order to make sure you get everything back in its proper position. We will supply
exploded views whenever possible. When making
adjustments, perform them in the proper order. One
adjustment possibly will affect another.
2. Overtorquing (or undertorquing). While it is
more common for overtorquing to cause damage,
undertorquing may allow a fastener to vibrate loose
causing serious damage. Especially when dealing
with aluminum parts, pay attention to torque specifi-
cations and utilize a torque wrench in assembly. If a
torque figure is not available, remember that if you
are using the right tool to perform the job, you will
probably not have to strain yourself to get a fastener
tight enough. The pitch of most threads is so slight
that the tension you put on the wrench will be multi-
plied many times in actual force on what you are
tightening. A good example of how critical torque is
can be seen in the case of spark plug installation, es-
pecially where you are putting the plug into an alu-
minum cylinder head. Too little torque can fail to
crush the gasket, causing leakage of combustion
gases and consequent overheating of the plug and
engine parts. Too much torque can damage the
threads or distort the plug, changing the spark gap.
There are many commercial products available for
ensuring that fasteners won’t come loose, even if they
are not torqued just right (a very common brand is
Loctite? If you’re worried
about getting something
together tight enough to hold, but loose enough to
avoid mechanical damage during assembly, one of
these products might offer substantial insurance. Be-
fore choosing a threadlocking compound, read the
label on the package and make sure the product is
compatible with the materials, fluids, etc. involved.
3. Crossthreading. This occurs when a part such
as a bolt is screwed into a nut or casting at the wrong
angle and forced. Crossthreading is more likely to
occur if access is difficult. It helps to clean and lubri-
cate fasteners, then to start threading the bolt, spark
plug, etc. with your fingers If you encounter resis-
tance, unscrew the part and start over again at a dif-
ferent angle until it can be inserted and turned several
times without much effort. Keep in mind that many
parts, especially spark plugs, have tapered threads,
so that gentle turning will automatically bring the part
you’re threading to the proper angle. Don’t put a
wrench on the part until its been tightened a couple
of turns by hand. If you suddenly encounter resis-
tance, and the part has not seated fully, don’t force it.
Pull it back out to make sure it’s clean and threading
properly.
Be sure to take your time and be patient, and al-
ways plan ahead. Allow yourself ample time to per-
form repairs and maintenance You may find main-
taining your car a satisfying and enjoyable
experience.
b See Figures 1 thru 15
Naturally, without the proper tools and equipment
it is impossible to properly service your vehicle. It
would also be virtually impossible
to catalog every
tool that you would need to perform all of the opera-
tions in this book. Of course, It would be unwise for
the amateur to rush out and buy an expensive set of
tools on the theory that he/she may need one or more
of them at some time, The best approach is to proceed slowly, gathering savings will
be far outweighed by frustration and
a good quality set of those tools that are used most mangled knuckles.
frequently Don’t be misled by the low cost of bargain Begin accumulating those tools that are used most
tools. It is far better to spend a little more for better frequently: those associated with routine maintenance
quality. Forged wrenches, 6 or 12-point sockets and and tune-up. In addition to the normal assortment of
fine tooth ratchets are by far preferable to their less screwdrivers and pliers, you should have the follow-
expensive counterparts. As any good mechanic can ing tools:
tell you, there are few worse experiences than trying
l Wrenches/sockets and combination open
to work on a vehicle with bad tools. Your monetary end/box end wrenches in sizes from %-% in. or
Page 35 of 408

.
l-36 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
Install the drain plug and tighten to 22 ft. Ibs.
(304Nm)
5. Refill the transaxle to the proper level, as
shown in the Capacities chart, with the appropriate
fluid. The oil level should be at the bottom of the oil
filler hole. I
6. When the oil reaches the orooer level, install
the filler plug and tighten to 22 ft. Ibs. (30 Nm).
FLUID RECOMMENDATIONS
8957i565 Fig, 165 Oil, when at the proper level, will
reach the lower edge of tC=+ frfr*r u*rn -non-
ing Mitsubishi recommends the use of Mercon@auto-
matic transmission fluid.
LEVELCHECK
Fig. 170 The fluid level is OK if it is within
the between the HOT and ADD areas on the
&&i& Do not overfill the transaxle or
-.*".."... -- .*"- problems could o ccur
1. Makesure the vehicle is oarked on a level sur-
face.
2. Remove the filler plug and make sure the oil
level is up to the lower edge of the filler plug hole.
3. Check to be sure that the transaxle oil is not
noticeably dirty and that it has a suitable viscosity. u See Figures 168,169, and 170
fluid is at normal operating temperature, drive the ve- The transaxle dipstick is located behind the air in-
hicle at least 10 miles. let hose, towards the firewall.
1. Park the vehicle on a level surface.
2. The transaxle should be at normal operating
temperature when checking fluid level. To ensure the 5. Pull the dipstick from its tube again. Holding it
horizontally, road the fluid level. The fkrid should be
between the MIN and MAX mark. If the fluid is below
the MIN mark, add fluid through the dipstick tube.
DRAIN & REFILL
6. Insert the dipstick, and check the level again
after adding any fluid. Be careful not to overfill the
transaxle.
3. With the selector lever in P and the parking
DRAIN & REFILL u See Figures 166 and 167
1. Make sure the vehicle is parked on a level sur-
face.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle. Place a brake applied, start the engine.
4. Open the hood and locate the transaxle fluid
dipstick. Pull the dipstick from its tube, wipe it clean,
and reinsert it. Make sure the dipstick is fully in-
serted.
suitable drain pan under the manual transaxle.
3. Remove the filler plug and the drain plug and
allow the oil to drain completely.
Fig. 166 The automatic transaxle dipstick is
typically located under the air cleaner inlet
Fig. 166 Use a box-end wrench to loosen
the manual transaxle drain plug . . . tube. Pull the dipstick up to remove it from
the transaxle
Fig. 169 Wipe the dipstick clean and Insert
/fluid level reading ., it mto the transaxle agam to get the correct
j The fluid should be changed according to the
schedule in the Maintenance Intervals chart. If the car
is normally used in severe service, such as stop and
start driving, trailer towing, or the like, the interval
should be halved. If the car is driven under especially
nasty conditions, such as in heavy city traffic where
the temperature normally reaches 90°F (32%), or in
very hilly or mountainous areas, or in police, taxi, or b See Figures 171 thru 177
1. Raise and support the vehicle safely.
2. Place a suitable drain pan under the transaxle
drain plug.
3. Remove the transaxle pan drain plug. Let the
fluid completely drain out of the transaxle.
4. Install the drain plug and tighten it to 22-25 ft.
lbs. (30-35 Nm).
5. If equipped, remove the drain plug on the dif-
ferential of the transaxle.
6. Install the differential drain plug and tighten ft
to 22-25 ft. Ibs. (30-35 Nm).
7. Remove the drain pan.
8. Lower the vehicle.
9. Fill the transaxle through the dipstick to the
proper level.
10. Place the gear selector lever in P and start the
engine. Run the engine at idle, engage the emergency
brake and hold the brake pedal down. Move the gear
selector lever through all transaxle ranges for approx-
imately 5 minutes.
11. Return the selector lever to P and leave the
engine running at idle.
12. Check the transaxle fluid level. The fluid level
at normal operating temperature should read within
the crosshatched area of the fluid level dipstick.
13. If the fluid level reads below the crosshatched
area, adjust the level by adding fluid in small incre-
ments until the correct fluid level is obtained.
PAN &FILTER SERVICE
b See Figures 178 thru 184
Page 41 of 408
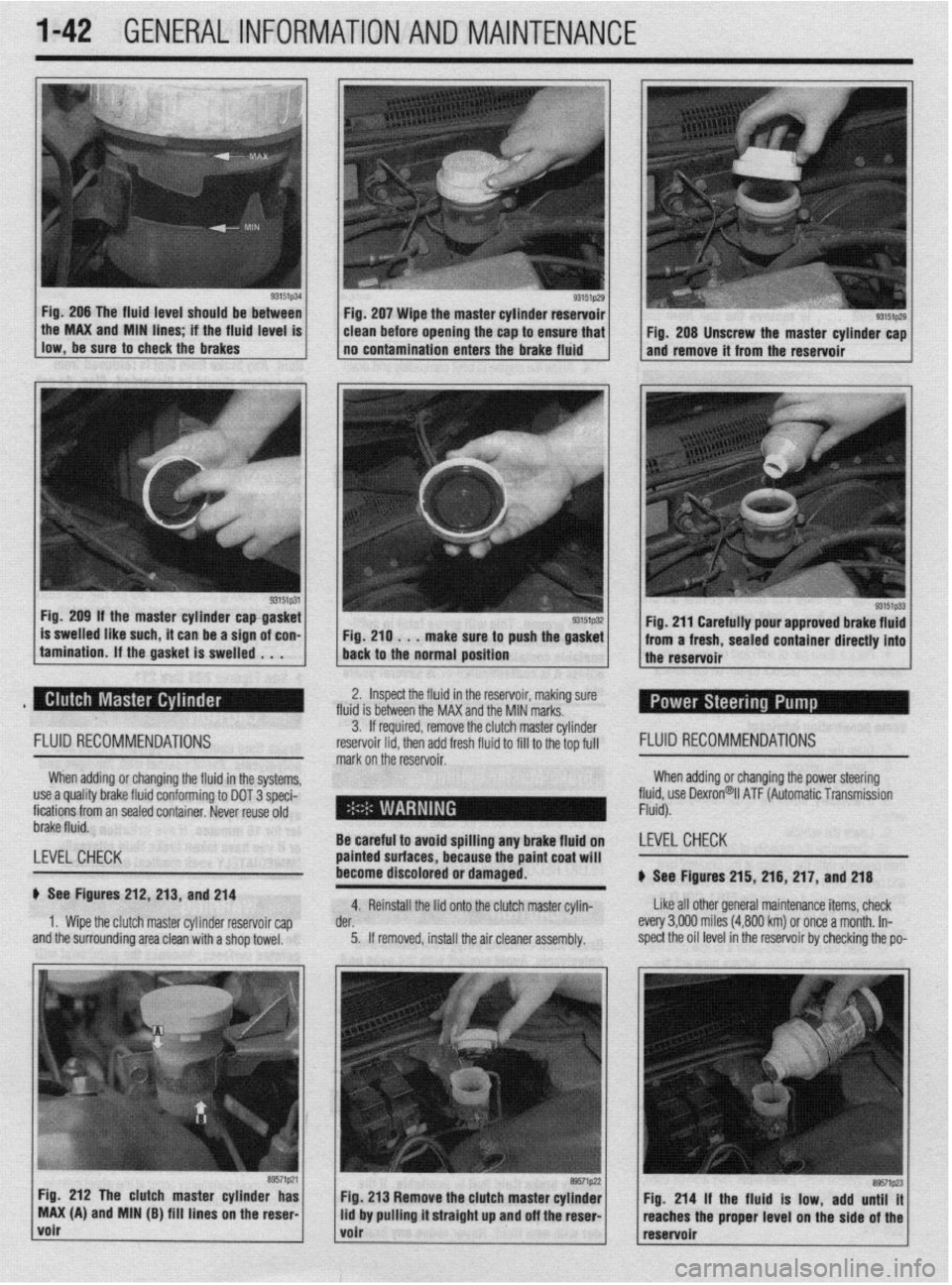
1-42 GENERAL~INFORMATION AND MAINTENANCE
Fig. 206 The fluid level should be between
llow,be*“retoch~ckiebrake~ . the MAX and MIN hnes if the fhud level IS
93151p31 Fig. 209 If the master cylinder capgasket
is swelled like such, it can be a sign of con-
tamination. If the gasket is swelled . . . Fig. 207 Wipe the master cylinder reservoir
clean before opening the cap to ensure that
no contamination enters the brake fluid
Fig. 210 . . .
make sure to push the gasket
back to the normal position
93151p29 I Fig. 208 Unscrew the master cylinder cap
and remove it from the reservoir
Fig. 211 Carefully pour approved brake fluid
from a fresh, sealed container directly into
the reservoir
2. Inspect the fluid in the reservoir, making sure
fluid is between the MAX and the MIN marks.
FLUID RECOMMENDATIONS
When adding or changing the fluid in the systems,
use a quality brake fluid conforming to DOT 3 speci-
fications from an sealed container. Never reuse old
brake fluid.
LEVEL CHECK
b See Figures 212, 213, and 214
1. Wipe the clutch master cylinder reservoir cap
and the surrounding area clean with a shop towel. 3. If required, remove the clut ch master cylinder
reservoir lid. then add fresh fluid I FLUID RECOMMENDATIONS
mark on the’reservoir. to fill to the top full
When adding or changing the power steering
fll$,“” Dexron@il ATF (Automatic Transmission
-
- .
Be careful to avoid sf Billing any brake fluid on LEVELCHECK
painted surfaces, bet
:ause the paint coat will
become discolored or damaged.
b See Figures 215, 216, 217, and 218
4. Reinstall the lid onto the clutch master cylin- Like all other general maintenance items, check
der. every 3,OOfl miles (4,800 km) or once a month. In-
5. If removed, install the air cleaner assembly. spect the oil level in the reservoir by checking the po-
Fig. 212 The clutch master cylinder has
MAX (A) and MIN (B) fill lines on the reser
volr
Page 170 of 408

DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS 4-27
WITHOUTASCANTOOL
8 See Figure 87. 1. Remove the under dash cover, if equipped.
2. Attach an analoa voltmeter between the on-
board diagnostic outpit terminal of the data link con-
nector and the ground terminal
3. Turn the ignition switch ON.
4. Read the on-board diagnostic output pattern
from the voltmeter and record.
5. Diagnose and repair the faulty components as
required.
OBD OUTPUT
[TERMINAL
tic (OBO) output and ground terminal loca-
tions on the data link connector
6. Erase the trouble code.
7. Turn the ignition swatch ON, and read the di-
agnostic trouble codes, checking that a normal code
is output.
*To erase diagnostic trouble codes with a
scan tool, follow the directions given by the
tools manufacturer.
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF. 2. Disconnect the negative battery cable from the
battery for 1 minute or more, then reattach it.
3. Turn ON the ignition switch and read the diag-
nostic trouble codes checking that a normal code is
output.
Code 11 Oxygen sensor Code 12 Air flow sensor Code 13 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Code 14 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Code 15 SC Motor Position Sensor (MPS)
Code 21 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Code 22 Crank angle sensor Code 23 No. 1 cylinder TDC (camshaft position)
Sensor
Code 24 Vehicle speed sensor Code 25 Barometric pressure sensor Code 31 Knock sensor (KS) Code 32 Manifold pressure sensor Code 36 Ignition timmg adjustment signal Code 39 Oxygen sensor (rear - turbocharged) Code 41 Injector Code 42 Fuel pump Code 43 EGR-California Code 44 Ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
1 and No. 4 cvlinders) on 3.OL
Code 62 ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
2 and No. 5 cvlinders) on 3.OL
Code 53 ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
3 and No. 6 cylinders) on 3.OL
Code 55 AC valve position sensor Code 59 Heated oxygen sensor Code 61 Transaxle control unit cable (automatic
transmission)
Code 62 Warm-up control valve position sensor
(non-turbo)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is given
responsibrlity for the operation of the emission con-
trol devices, cooling fans, ignition and advance and
in some cases, automatic transaxle functions. Be-
cause the PCM oversees both the ignition timing and
the fuel injection operation, a precise air/fuel ratio
will be maintained under all operating conditions,
The PCM is a microprocessor, or small computer,
which receives electrical inputs from several sensors,
switches and relays on and around the engine.
Based on combinations of these inputs, the PCM
controls outputs to various devices concerned with
engine operation and emissions. The control module
relies on the signals to form a correct picture of cur-
rent vehicle operation. If any of the input signals is
incorrect, the PCM reacts to whatever picture is
painted for it. For example, if the coolant temperature
sensor is inaccurate and reads too low, the PCM may
see a picture of the engine never warming up. Conse-
quently, the engine settings will be maintained as if
the engine were cold. Because so many inputs can
affect one output, correct diagnostic procedures are
essential on these systems,
One part of the PCM is devoted to monitoring
both input and output functions within the system.
This ability forms the core of the self-diagnostic sys-
tem. If a problem is detected within a circuit, the con-
trol module will recognize the fault, assign it a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC), and store the code in
memory. The stored code(s) may be retrieved during
diagnosis. While the OBD-II system is capable of recognizing
many internal faults, certain faults WIII not be recog-
nized. Because the control module sees only electri-
cal signals, it cannot sense or react to mechanical or
vacuum faults affecting engine operation. Some of
these faults may affect another component which will
set a code. For example, the PCM monitors the out-
put signal to the fuel injectors, but cannot detect a
partially clogged injector. As long as the output dri-
ver responds correctly, the computer will read the
system as functioning correctly. However, the im-
proper flow of fuel may result in a lean mixture. This
would, in turn, be detected by the oxygen sensor and
noticed as a constantly lean signal by the PCM. Once
the signal falls outside the pre-programmed limits,
the control module would notice the fault and set a
trouble code.
Additionally, the OBD-II system employs adaptive
fuel logic. This process is used to compensate for
normal wear and variability within the fuel system.
Once the engine enters steady-state operation, the
control module watches the oxygen sensor signal for
a bias or tendency to run slightly rich or lean. If such
a bias is detected, the adaptive logic corrects the fuel
delivery to bring the air/fuel mixture towards a cen-
tered or 14.7:1 ratio. This compensating shift is
stored In a non-volatile memory which is retained by
battery power even with the ignition switched
OFF. The correction factor is then available the next time
the vehicle is operated.
WITHASCANTOOL
8 See Figures 88, 89, 90, and 91
The Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), under the
left-hand side of the instrument panel, must be lo-
cated to retrieve any OTC’s
Reading the control module memory is on of the
first steps in OBD II system diagnostics. This step
should be initially performed to determine the general
nature of the fault. Subsequent readings will deter-
mine if the fault has been cleared.
Reading codes can be performed by any of the
methods below:
l Read the control module memory with the
Generic Scan Tool (GST)
l Read the control module memory with the ve-
hicle manufacturers specific tester
To read the fault codes, connect the scan tool or
tester according to the manufacturers instructions.
Follow the manufacturers specified procedure for
reading the codes.
WITHOUTASCANTOOL
8 See Figure 92
The Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), under the
left-hand side of the instrument panel, must be lo-
cated to retrieve any DTC’s.
Page 214 of 408
CHASSIS ELECTRICAL 6-11
45. Install the heater hoses under the hood.
46. Install the mstrument panel by reversing its
removal procedure.
47. Install the center console.
48. install the upper and lower steering column
covers.
49. Install the center panel undercover.
50. Install the small column panel.
51. Install the steering wheel.
52. Fill the cooling system.
53. Connect the negative battery cable and check
the entire climate control system for proper operation
and leaks.
Mirage
# See Figures 29, 30, and 31
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the cooling system and disconnect the
heater hoses.
3. Remove the front seats by removing the cov-
ers over the anchor bolts, the underseat tray, the seat
belt guide ring, the seat mounting nuts and bolts and
disconnect the seat belt switch wiring harness from
under the seat. Then lift out the seats
4. Remove the floor console by first taking out
the coin holder and the console box tray. Remove the
remote control mirror switch or cover. All of these
items require only a plastic trim tool to carefully pry
them out.
5. Remove the rear half of the console.
6. Remove the shift lever knob on manual trans-
mission vehicles.
7. Remove the front console box assembly.
8. A number of the instrument panel pieces may
be retamed by pin type fasteners. They may be re-
moved using the following procedure:
a. Press down on the center pin with a suit-
able blunt pointed tool. Press down a little more
than l/re in. (2mm) to release the clip. Pull the
clip outward to remove it.
b. Do not oush the oin inward more than
necessary because it may damage the grommet
or the pin may fall in if pushed in too far. Once
the clips are removed, use a plastic trim stick to
pry the piece loose.
9. Remove both lower cowl trim panels (kick
panels).
10. Remove the ashtray.
11. Remove the center panel around the radio.
12. Remove the sunglass pocket at the upper left
side of panel and the side panel into which it mounts,
13. Remove the drivers side knee protector and
the hood release handle.
14. Remove the steering column top and bottom
covers.
15. Remove the radio.
16. Remove the glove box striker and box assem-
bly.
17. Remove the instrument panel lower cover, 2
small pieces in the center, by pulling forward.
18. Remove the heater control assembly screw.
19. Remove the instrument cluster bezel and pull
out the Qauge assembly.
20. Remove the speedometer adapter by discon-
necting the speedometer cable at the transaxle
pulling the cable Sightly towards the vehicle interior
and giving a Slight twist on the adapter to release it.
21. Insert a small flat-tipped tool to open the tab
on the QauQe cluster connector. Remove the harness
connectors.
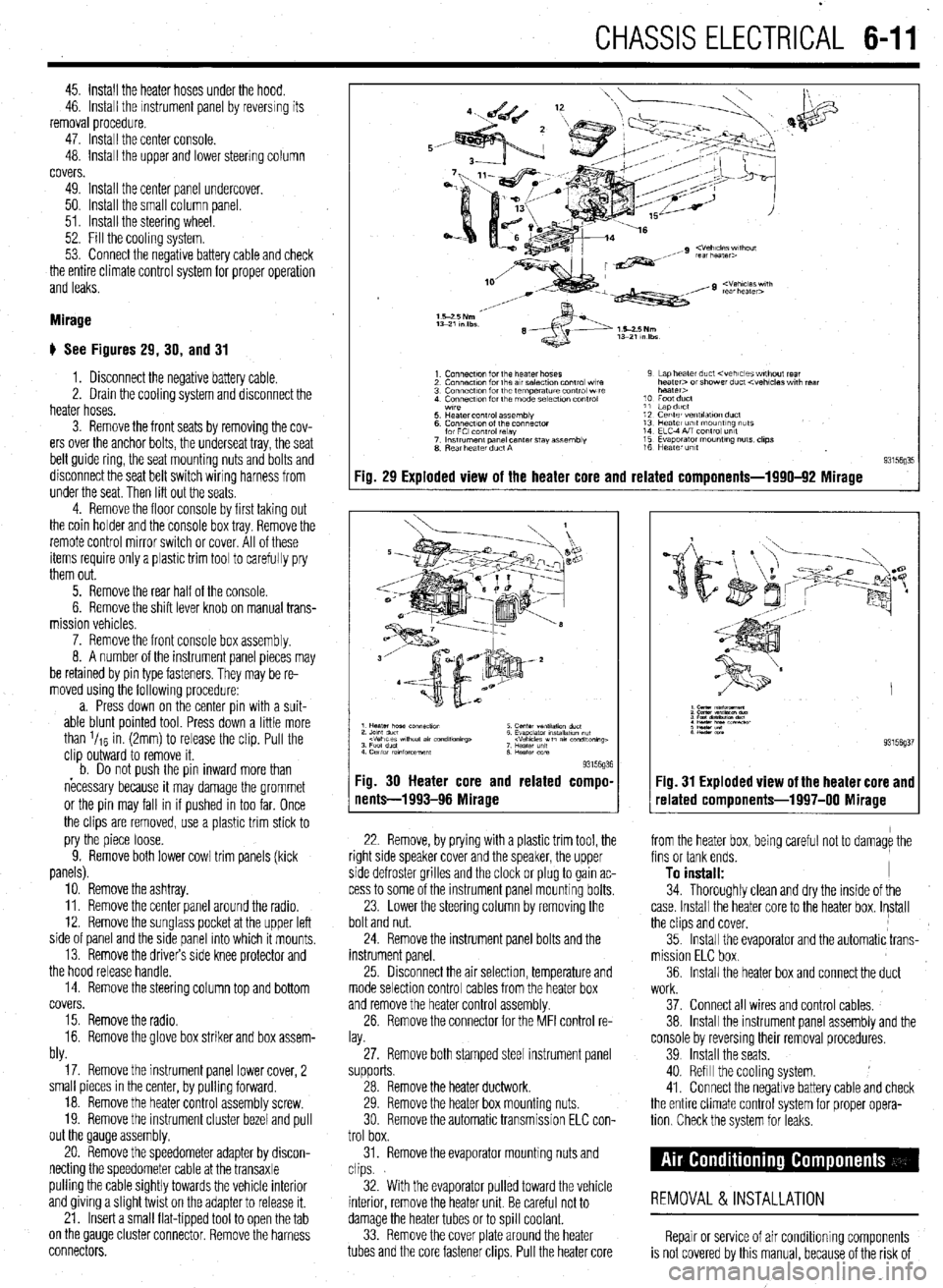
Fig. 29 Exploded view of the heater core and related components-1990-92 Mirage
93l%Q% Fig. 30 Heater core and related compo-
nents-1993-96 Mirage
22. Remove, by prying with a plastic trim tool, the
right side speaker cover and the speaker, the upper
side defroster grilles and the clock or plug to gain ac-
cess to some of the instrument panel mounting bolts.
23. Lower the steering column by removing the
bolt and nut.
24. Remove the instrument panel bolts and the
instrument panel.
25 Drsconnect the air selection, temperature and
mode selection control cables from the heater box
and remove the heater control assembly.
26. Remove the connector for the MFI control re-
lay.
27. Remove both stamped steel instrument panel
supports.
28. Remove the heater ductwork.
29. Remove the heater box mounting nuts.
30 Remove the automatic transmission ELC con-
trol box.
31. Remove the evaporator mounting nuts and
clips.
32. With the evaporator pulled toward the vehicle
interior, remove the heater unit. Be careful not to
damage the heater tubes or to spill coolant.
33. Remove the cover plate around the heater
tubes and the core fastener clips. Pull the heater core 34. Thoroughly clean and dry the inside of the
case. Install the heater core to the heater box. Install
the clips and cover,
35. Install the evaporator and the automatic trans-
mission ELC box.
36. Install the heater box and connect the duct
Fig. 31 Exploded view of the heater core and
related components-1997-00 Mirage
from the heater box, being careful not to damage the
fins or tank ends.
To install: I
work.
37. Connect all wires and control cables,
38. Install the instrument panel assembly and the
console by reversmg their removal procedures.
39 Install the seats.
40. Refill the cooling system.
41. Connect the negative battery cable and check
the entire climate control system for proper opera-
tion Check the system for leaks.
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
Repair or service of air Conditioning components
is not covered by this manual, because of the risk of
Page 253 of 408
1990-93 GALANT CHASSIS SCHEMATIC WI ETACS
ETACS CMfWOL WIT
0
r
mGNT
Et (1 LOCK
I I AcllJAToll
I
w/o Tumo TlBBO 4
FE
!3vzE NOT AT AU TIMES
FUSE
5
I5A
1996-00 GALANT CHASSIS SCHEMA.TIC MANUAL NOT AT AU TIMES TRANSMISSION
16NITIoW
SWITCH
.
i
0
: >
ii
MTTENY - STBRTER
= NOTOR
z
zz
i 3
T
-cLuTcN
FEMA’
Foslnow
~clwcll
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
HOT AT ALL TlHES
DIAGRAM 31 93156815 DIAGIUM 32 93156616
Page 269 of 408
1993 MIRAGE 1.5L CHASSIS SCHEMATIC
MANUAL HOT AT ALL TIHES HOT AT ALL TIMES TRANSMISSION FWSLE FUSISLE
LINK
LINK
s L
LPI
SW
HOT Al ALL rims
HOT1
FUSISLE
LINM
5
LOA . TIHES
AUTOMATIC FUSlSLE
LINK I TRANSMISSION
SOA
1
RABATOR
!ZEHIlLY
i
DIAGRAM 63
93156B42
1994-96 MIRAGE ML CHASSIS SCHEMATIC
IF
I IGNlTi#l
SWITCH
STAR-
L R&
(
I
r 4
1
NAOIATOR
) ZLLY
m
I
RADIATOR
FAN
MOTOR
CONTROL
RELAY
1
CONDENSER FAN
L MOTOR
RELAY
DIAGRAM 64 93WB43
Page 289 of 408

7-10 DRIVETRAIN
The automatic transaxle allows engine torque and
power to be transmitted to the front wheels within a
narrow range of engine operating speeds. It will allow
the engine to turn fast enough to produce plenty of
power and torque at very low speeds, while keeping it
at a sensible rpm at high vehicle speeds (and it does
this job without driver assistance). The transaxle uses
a light fluid as the medium for the transmission of
power. This fluid also works in ths operation of vari-
ous hydraulic control circuits and as a lubricant. Be-
cause the transaxle fluid performs all of these func-
tions, trouble within the unit can easily travel from one
part to another For this reason, and because of the
complexity and unusual operating principles of the
transaxle, a very sound understanding of the basic
principles of operation will simplify troubleshooting
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
Pan removal, fluid and filter
in Section 1 of this manual changes are covered
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
1990-97 Mirage and 1990-93 Galant
# See Figure 44
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the selector cable from the lever
3. Remove the two retaining screws and lift off
the switch.
To install: 4. Mount and position new switch. Do not tighten
the bolts until the switch is adjusted.
5. Connect selector cable and adjust switch.
6. After installation and adjustment make sure the
engine only starts in the
P and N selections. Also check
that the reverse lights operate only in the R selectlon.
1994-00 Galant and 1998-00 Mirage
e See Figure 44
93157pm Fig. 44 Typically, the park/neutral position
switch is located on the top of the transaxle
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the nut attaching the shift control ca-
ble from the transaxle manual shaft lever. Position
the control cable out of the way.
3. Place the manual shaft lever in the Neutral
position, remove the nut and the manual shaft lever.
4. Detach the park/neutral switch electrical con-
nector.
5. Remove the park/neutral switch mounting
bolts and remove the switch from the transaxle man-
ual shaft.
To install: 6. Install the park/neutral switch to the transaxle
manual shaft and install the switch mounting bolts
Do not tighten the mounting bolts unh the switch is
adjusted.
7. Install the manual shaft lever to the park/neu-
tral switch with the nut. Make sure that the shaft lever
is in the Neutral position.
8. Adjust the switch in the following manner:
turn the switch body until the hole in the body of the
switch aligns with the hole in the manual shaft lever.
Insert a drill bit or equivalent into the holes. Tighten
the switch mounting bolts to 8 ft. Ibs. (11 Nm).
9. Attach the electrical connector.
10. Install the control cable to the manual shaft
lever with the nut. Adjust the cable so that there is no
slack in the cable and that the selector lever moves
smoothly
11. Reconnect the negative battery cable Check
for proper starting and proper reverse light operatron.
Diamante
ti See Figure 44
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
Wait at least 90 seconds after the negative
battery cable is disconnected to prevent pos-
sible deployment of the air bag.
2. Disconnect the selector cable from the lever.
3. Remove the two retaining screws and lift off
the switch.
To install: 4. Install the lever, tighten the bolts only hand
tight.
5. Rotate switch body so the manual control lever
0.20 inch (5mm) hole and the switch body 0.20 inch
(5mm) holes are aligned.
6. Tighten the mounting bolts to 7-8 ft. Ibs.
(10-12 Nm).
7. Connect the selector cable to the lever.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
9. After installahon and adjustment make sure the
engine only starts in the
P and N selections. Also
check that the reverse lights operate only in the R se- lection.
ADJUSTMENT
1990-97 Mirage and 1990-93 Galant
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable and lo-
cate the neutral safety switch on the top of the
transaxle.
*Apply parking brake and chock wheels be-
fore placing transaxle into the N position
2. At the transmission, loosen the shift cable ad-
justment nut. Inside the vehicle place the gearshift
selector lever in N
3. Place the manual shift control lever in N.
4. Loosen neutral safety switch mounhng screws
and rotate switch body so the manual control lever
0.20 in. (5mm) hole and the switch body 0.20 in.
(5mm) holes are aligned.
5. Tighten switch body mounting bolts to 7-8 ft.
Ibs. (lo-12 Nm).
6. At the shift cable adjusting nut, gently pull ca-
ble to remove any slack. Tighten locknut to 8 ft. Ibs.
(12 Nm)
7. Verify that the switch lever moves to positions
corresponding to each position of the selector lever.
Connect the negative battery terminal.
8. Make sure the engine only starts in the
P and
N positions. Also make sure the reverse lights oper-
ate only in
R selection.
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
Diamante
) See Figures 45, 46, 47, and 48
1. Properly disarm the SRS system (air bag).
Refer to Section 6.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
3. Remove the front wheels.
4. Remove the engine side cover and undercov-
ers.
5. Drain the transaxle assembly into a suitable
container.
6. If equipped, remove the front catalytic con-
verter.
7. Remove the exhaust pipe, main muffler and
catalytic converter.
8. Disconnect the tie rod end and ball joint from
the steering knuckle.
9. Unbolt the support bearing for the left side
halfshaft.
10. Remove the halfshafts by inserting a prybar
between the transaxle case and the driveshaft and
prying the shaft from the transaxle.
11. Remove the air cleaner assembly and adjoin-
ing duct work.
12. Detach the engine harness connection.
13. If the vehicle is equipped with Active Elec-
tronlc Controlled Suspension (Active-ECS), remove
the compressor assembly from the transaxle and sus-
pend with wire. Do not allow the compressor to hang
from the air hose.
14. If equipped, remove the roll stopper stay
bracket.
15. Disconnect the speedometer cable from the
transaxle.
16. Remove the clip that secures the shifter and
disconnect the shifter control cable from the
transaxle.
17. Disconnect and plug the oil cooler hoses
from the transaxle.
18. Detach the following:
Page 291 of 408
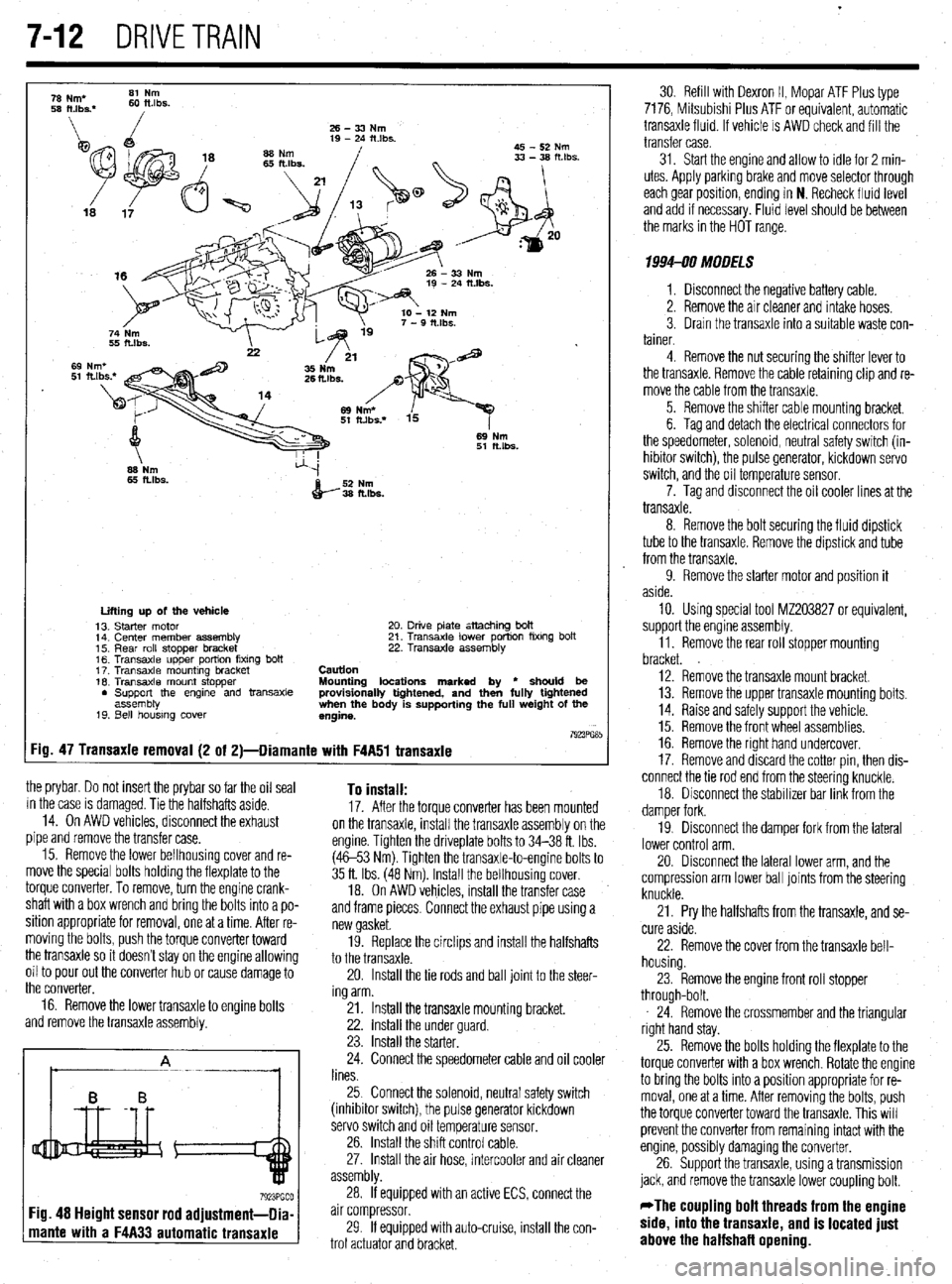
.
7-12 DRIVETRAIN
26-33Nm
19 - 24 itlbs.
45 - 52 Nm
69 Nm
51 ftlbs.
66 Nm
65 ftlbs.
52 Nm
36 fl.lbs.
:ig.
the prybar. Do not insert the prybar so far the oil seal
in the case is damaged. Tie the halfshafts aside.
14. On AWD vehicles, disconnect the exhaust
pipe and remove the transfer case.
15. Remove the lower bellhousing cover and re-
move the special bolts holding the flexplate to the
torque converter. To remove, turn the engine crank-
shaft with a box wrench and bring the bolts into a po-
sition appropriate for removal, one at a time. After re-
moving the bolts, push the torque converter toward
the transaxle so it doesn’t stay on the engine allowing
oil to pour out the converter hub or cause damage to
the converter,
16. Remove the lower transaxle to engine bolts
and remove the transaxle assembly. To install: 17. After the torque converter has been mounted
on the transaxle, install the transaxle assembly on the
engine. Tighten the driveplate bolts to 34-38 ft. Ibs.
(4653 Nm). Tighten the transaxle-to-engine bolts to
35 ft. Ibs. (48 Nm). Install the bellhousing cover.
18. On AWD vehicles, install the transfer case
and frame pieces. Connect the exhaust pipe using a
new gasket.
19. Replace the circlips and install the halfshafts
to the transaxle.
20. Install the tie rods and ball joint to the steer-
ing arm.
21. Install the transaxle mounting bracket.
22. install the under guard.
23. Install the starter.
24. Connect the speedometer cable and oil cooler
lines.
25 Connect the solenoid, neutral safety switch
(inhibitor switch), the pulse generator kickdown
servo switch and oil temperature sensor.
26. Install the shift control cable.
27. Install the air hose, intercooler and air cleaner
assembly.
If equipped with an active ECS, connect the
mante with a F4A33 automatic transaxle
30 Refill with Dexron II, Mopar ATF Plus type
7176, Mitsubishi Plus ATF or equivalent, automatic
transaxle fluid. If vehicle is AWD check and fill the
transfer case.
31. Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 min-
utes. Apply parkrng brake and move selector through
each gear posrtion, ending in N. Recheck fluid level
and add if necessary. Fluid level should be between
the marks in the HOT range.
1994-90 MODELS
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the air cleaner and intake hoses.
3. Drain the transaxle into a suitable waste con-
tainer.
4. Remove the nut securing the shifter lever to
the transaxle. Remove the cable retaining clip and re-
move the cable from the transaxle.
5. Remove the shifter cable mounting bracket,
6. Tag and detach the electrical connectors for
the speedometer, solenoid, neutral safety switch (in-
hibitor switch), the pulse generator, kickdown servo
switch, and the oil temperature sensor.
7. Tag and disconnect the oil cooler lines at the
transaxle.
8. Remove the bolt securing the fluid dipstick
tube to the transaxle. Remove the dipstrck and tube
from the transaxle.
9. Remove the starter motor and position it
aside.
10. Using special tool MZ203827 or equivalent,
support the engine assembly.
11. Remove the rear roll stopper mounting
bracket.
12. Remove the transaxle mount bracket.
13. Remove the upper transaxle mounting bolts.
14. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
15. Remove the front wheel assemblies.
16. Remove the right hand undercover.
17. Remove and discard the cotter pin, then dis-
connect the tie rod end from the steering knuckle,
18. Disconnect the stabilizer bar link from the
damper fork.
19. Disconnect the damper fork from the lateral
lower control arm.
20. Disconnect the lateral lower arm, and the
compression arm lower ball joints from the steering
knuckle.
21. Pry the halfshafts from the transaxle, and se-
cure aside.
22. Remove the cover from the transaxle bell-
housing.
23. Remove the engine front roll stopper
through-bolt.
24. Remove the crossmember and the triangular
right hand stay.
25. Remove the bolts holding the flexplate to the
torque converter with a box wrench Rotate the engine
to bring the bolts into a position appropriate for re-
moval, one at a time. After removing the bolts, push
the torque converter toward the transaxle. This will
prevent the converter from remaining intact with the
engine, possibly damaging the converter,
26. Support the transaxle, using a transmission
jack, and remove the transaxle lower coupling bolt.
*The coupling bolt threads from the engine
side, into the transaxle, and is located just
above the halfshafl opening.
Page 297 of 408

.
8-2 SUSPENSION AND STEERING
b
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
# See Figures 1, 2, 3, and 4
1. Park the vehicle on a level surface.
2. Remove the jack, tire iron and, if necessary,
the spare tire from their storage compartments.
3. Check the owners manual, or refer to Section
1 of this manual for the jacking points on your vehi-
cle. Then, place the jack in the proper position,
4. If equipped with lug nut trim caps, remove
them by either unscrewing or pulling them off the lug
nuts, as appropriate. Consult the owners manual, if
necessary.
5. If equipped with a wheel cover or hub cap,
insert the tapered end of the tire iron in the groove
and pry off the cover.
6. Apply the parking brake and block the diago-
nally opposite wheel with a wheel chock or two.
*Wheel chocks may be purchased at your
local auto parts store, or a block of wood cut
into wedges may be used. If possible, keep
one or two of the chocks in your tire storage
compartment, in case any of the tires has to
be removed on the side of the road. 7. If equipped with an automatic
transmission/transaxle, place the selector lever in P
or Park; with a manual transmission/transaxle, place
the shifter in Reverse.
8. With the tires still on the ground, use the tire
iron/wrench to break the lug nuts loose.
*If a nut is stuck, never use heat to loosen it
or damage to the wheel and bearings may
occur. If the nuts are seized, one or two
heavy hammer blows directly on the end of
the bolt usually loosens the rust. Be careful,
as continued pounding will likely damage the
brake drum or rotor.
9. Using the jack, raise the vehicle until the tire
is clear of the ground. Support the vehicle safely us-
ing jackstands.
10. Remove the lug nuts, then remove the tire
and wheel assembly.
To install:
11. Make sure the wheel and hub mating sur-
faces, as well as the wheel lug studs, are clean and
free of all foreign material. Always remove rust from
the wheel mounting surface and the brake rotor or
drum. Failure to do so may cause the lug nuts to
loosen in service.
12. Install the tire and wheel assembly and hand-
tighten the lug nuts. 13. Using the tire wrench, tighten all the lug nuts,
in a crisscross pattern, until they are snug.
14. Raise the vehicle and withdraw the jackstand,
then lower the vehicle.
15. Using a torque wrench, tighten the lug nuts in
a crisscross pattern to 65-80 ft. lbs. ( 90-l 10 Nm).
Check your owners manual or refer to Section 1 of
this manual for the proper tightening sequence.
Do not overtighten the lug nuts, as this may
cause the wheel studs to stretch or the brake
disc (rotor) to warp.
16. If so equipped, install the wheel cover or hub
cap. Make sure the valve stem protrudes through the
proper opening before tapping the wheel cover into
position.
17. If equipped, install the lug nut trim caps by
pushing them or screwing them on, as applicable.
18. Remove the jack from under the vehicle, and
place the jack and tire iron/wrench in their storage
compartments. Remove the wheel chock(s).
19. If you have removed a flat or damaged tire,
place it in the storage compartment of the vehicle and
take it to your local repair station to have it fixed or
replaced as soon as possible.
Inspect the tires for lacerations, puncture marks,
nails and other sharp objects. Repair or replace as
necessary. Also check the tires for treadwear and air
pressure as outlined in Section 1 of this manual.
Check the wheel assemblies for dents, cracks, rust
and metal fatigue. Repair or replace as necessary.
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
Fig. 3 Place the jackstands under the vehi-
cle to support the vehicle’s weight before