relay MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1900, Model line: DIAMANTE, Model: MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900Pages: 408, PDF Size: 71.03 MB
Page 11 of 408
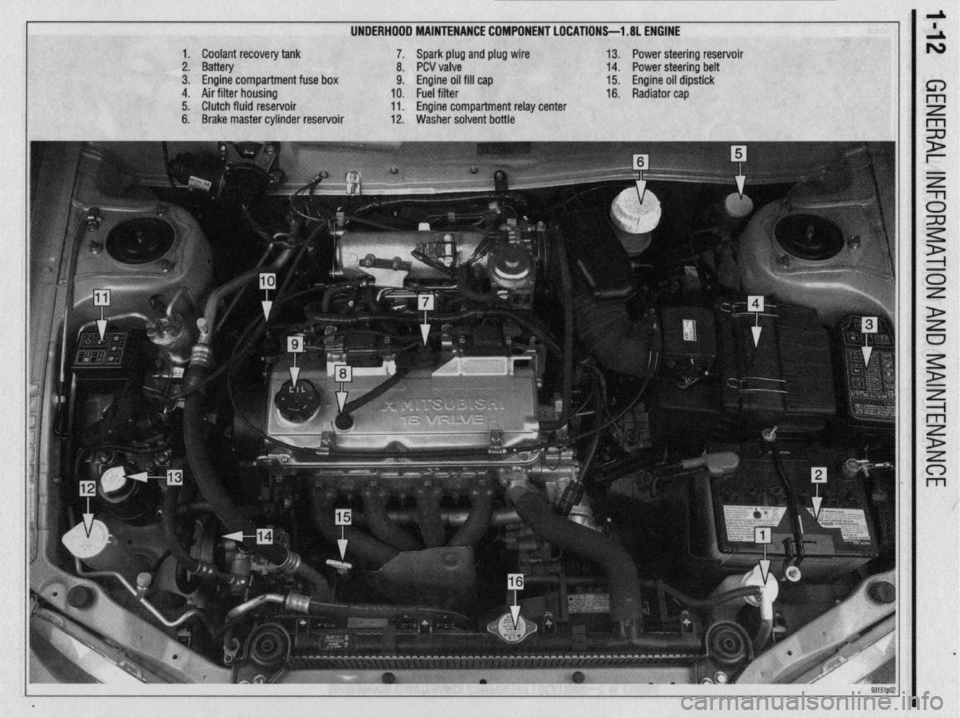
UNDERHOOD MAINTENANCE COMPONENT LOCATIONS-l .8L ENGINE
1. Coolant recovery tank
2. Battery
3. Engine compartment fuse box
4. Air filter housing
5. Clutch fluid reservoir
6. Brake master cylinder reservoir 7. Spark plug and plug wire
8. PCV valve
9. Engine oil fill cap
10. Fuel filter
11. Engine compartment relay center
12. Washer solvent bottle 13. Power steering reservoir
14. Power steering belt
15. Engine oil dipstick
16. Radiator cap
Page 161 of 408
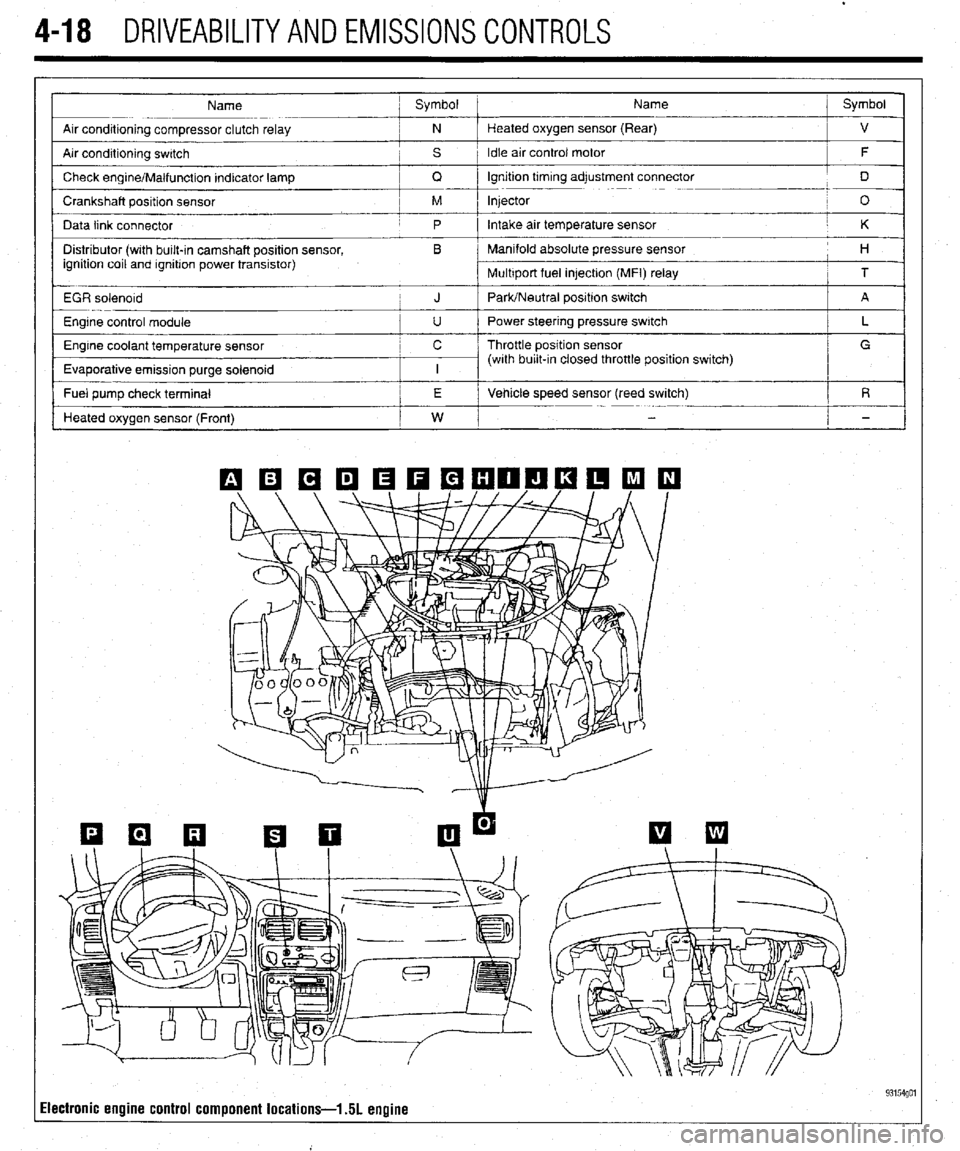
.
4-18 DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS
Name ; Symbol Name j Symbol
I
Arr conditioning compressor clutch relay ; N Heated oxygen sensor (Rear)
j ”
Air condrtioning swatch , s 1 Idle air control motor
/ F
/
Check engrne/Malfunction Indicator lamp
/ Q lgnrtion trmrng adjustment connector
j D
Crankshaft position sensor / M Injector
! O
Data link connector
j p Intake air temperature sensor / K
Distributor (wrth bulk-in camshaft position sensor, , B Manifold absolute pressure sensor
ignition coil and rgnrtron power transistor) I 1 H
Multrport fuel in]ectron (MFI) relay
i T
EGR solenord
i J PaWNeutral positron switch j A
Engine control module
I u I Power steering pressure switch
Engine coolant temperature sensor c / Throttle position sensor
Evaporative emission purge solenoid
I I I (with burl&In closed throttle position switch) / L _
/ G
I
I
- Fuel pump check terminal /
I j E i Vehicle speed sensor (reed switch)
/ R
Heated oxygen sensor (Front)
I w I
i -
Ilectronic engine control component locations-l 51 engine 93154go1
Page 162 of 408
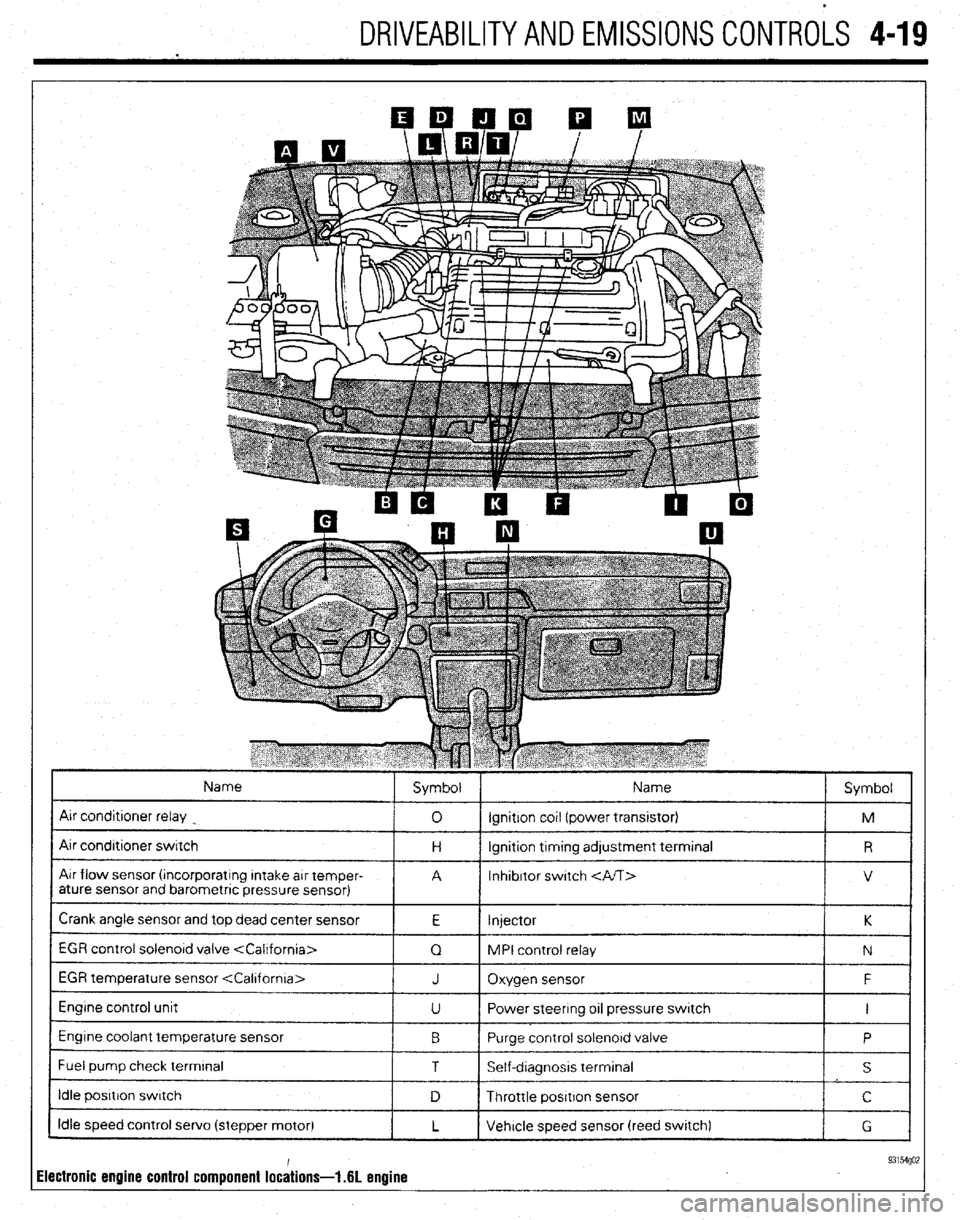
DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS 4-19
Name
Air conditroner relay
Air condrtroner switch
Air flow sensor (rncorporatrng Intake arr temper-
ature sensor and barometric pressure sensor) Symbol Name
Symbol
0 ignition cot1 (power transrstor)
M
H lgnrtion trmtng adjustment terminal
R
A Inhibitor switch
V
Crank angle sensor and top dead center sensor
E Injector K
1 EGR control solenord valve
1 Q 1 MPI control relay
1 N 1
EGR temperature sensor
Engine control unit
Engine coolant temperature sensor
I Fuel pump check terminal J Oxygen sensor F
U Power steering 011 pressure switch I
0 Purge control solenord valve
P
1 T I Self-dragnosis terminal
I s I
I idle posrtron swatch
1 D 1 Throttle positron sensor I c I
Idle speed control servo (stepper motor)
L Vehicle speed sensor (reed swatch)
G
ilectronic engine control component lochions- .6L enuine 93154go;
Page 163 of 408
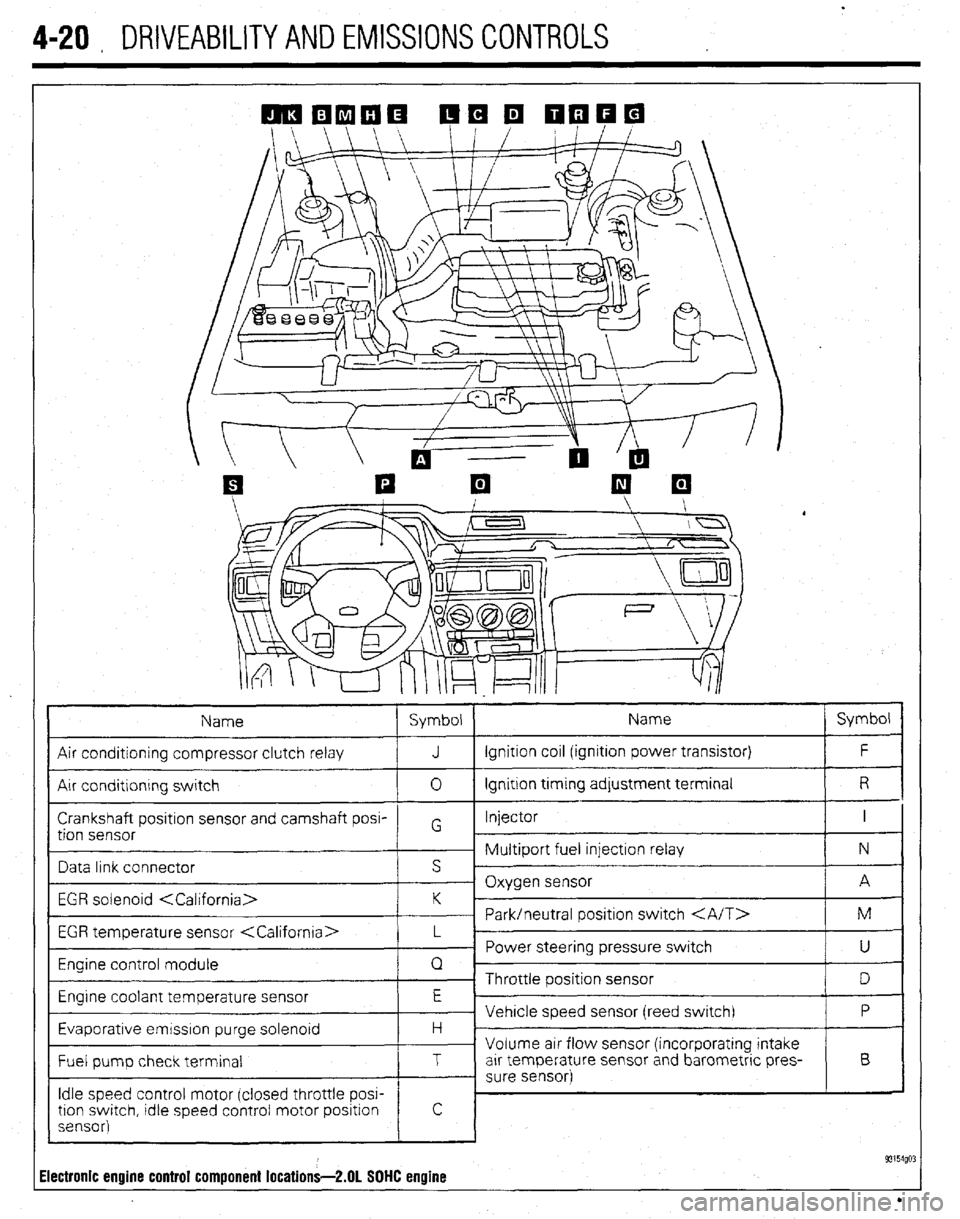
4-20 , DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS
Name Symbol Name Symbol
Air conditioning compressor clutch relay J Ignition coil (ignition power transistor) F
Air conditlonrng switch 0 Ignition trming adjustment terminal R
Crankshaft positron sensor and camshaft posi- Injector I
tion sensor G
~ Multiport fuel injection relay N
Data link connector s ’
- Oxygen sensor A
EGR solenoid
~ Park/neutral positron switch M
EGR temperature sensor
_ Power steering pressure switch
U
Engine control module Q
~ Throttle position sensor
D
Engrne coolant temperature sensor E
Vehicle speed sensor (reed switch) P
Evaporative emrsslon purge solenoid H -
Volume air flow sensor (incorporating intake
Fuel pump check terminal T arr temperature sensor and barometric pres- B
- sure sensor)
Idle speed control motor (closed throttle POW
tron swatch, tdle speed control motor positron
sensor)
! c
93154go: Electronic engine control component locations-2.01 SOHC engine
Page 165 of 408
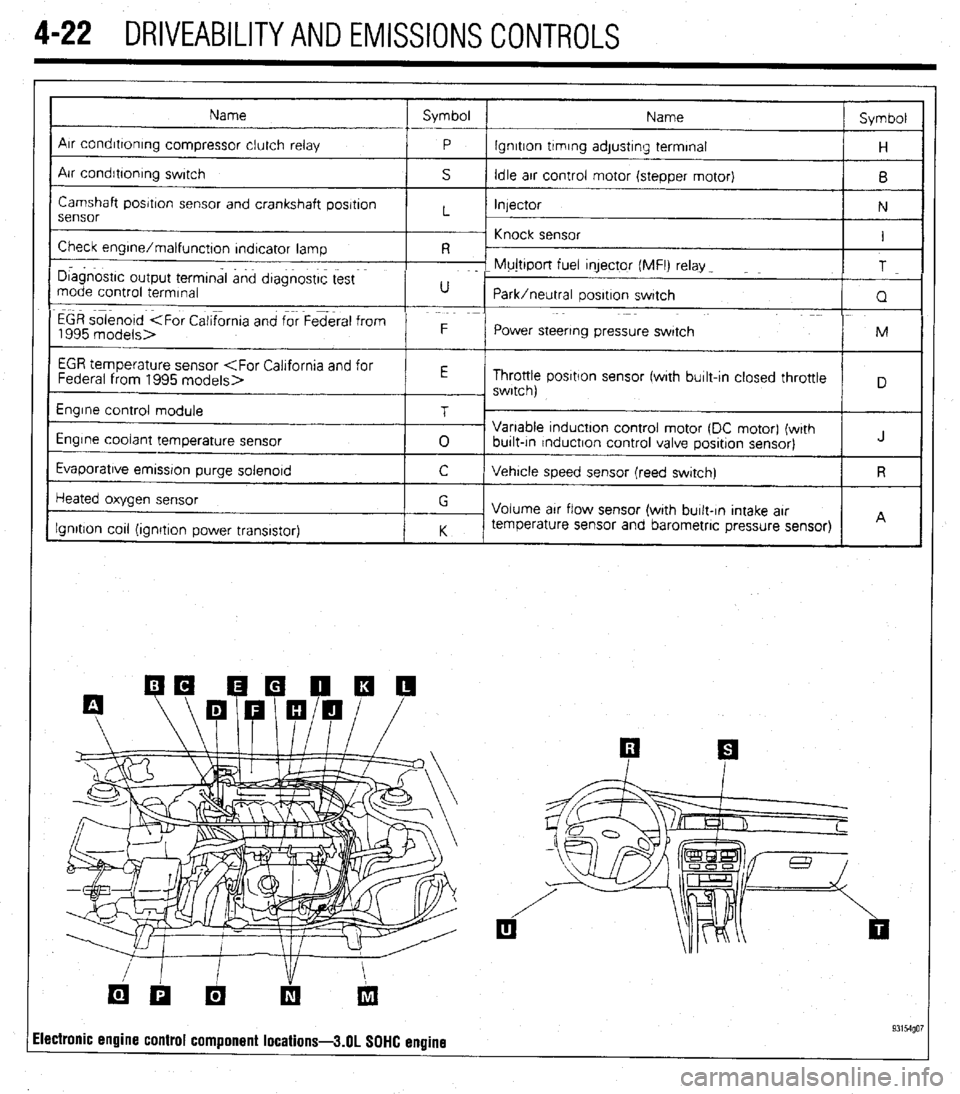
4-22 DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS
Name Symbol
Name Symbol
I
Arr condrttontng compressor clutch relay
P lgnrtton trmrng adjustrng terminal
H
Air condrbonrng swrtch
S Idle arr control motor (stepper motor)
B
Camshaft posrtron sensor and crankshaft posrtron
Injector
N
sensor L
~ Knock sensor
Check engrne/malfunctton rndtcator lamp I
R -
I D~agnostrc output termtnal and dtagnostrc test F- Mujttport fuel qector (MFI) relay _
T
mode control termrnal U
Park/neutral oosrtron swatch
Q
EGR solenoid
1995 models> F
Power steering pressure swatch M
I
EGR temperature sensor
Throttle posrtlon sensor fwrth burlt-In closed throttle
, swrtch)
Engrne control module
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Evaporatrve emrssron purge solenord T
0 Variable tnductton control motor (DC motor) (wrth
burlt-tn rnductron control valve posrtron sensor) J
C Vehrcle speed sensor (reed swatch) R
Heated oxygen sensor
Ignition cot1 (ionrtron Dower transistor) G
Volume arr flow sensor (with burlt-In Intake arr
K temperature sensor and barometric pressure sensor)
I I A
ilectronic engine control component locations-3.01 SOHC engine 93154go7
Page 167 of 408
.
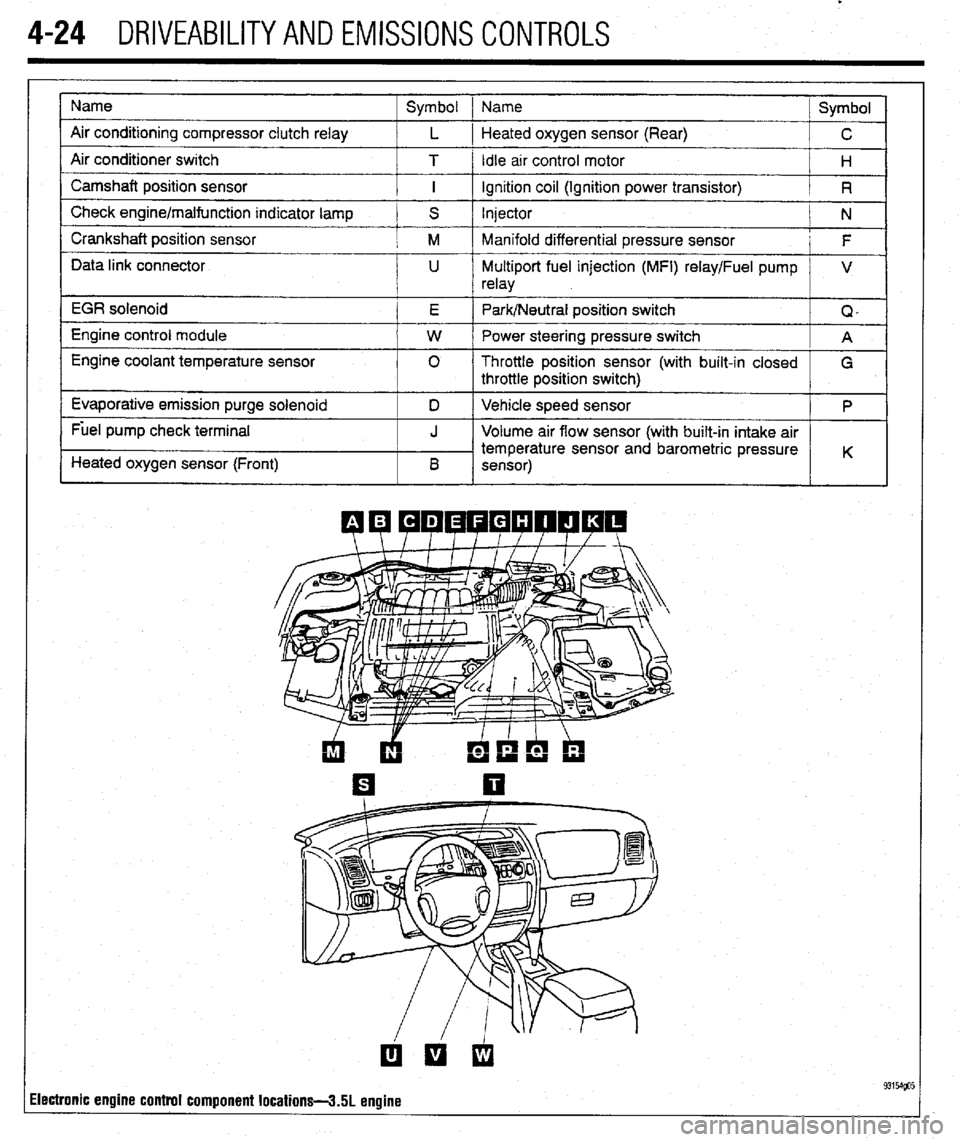
4-24 DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS
Name
Air conditioning compressor clutch relay
Air conditioner switch
Camshaft position sensor
Check engine/malfunction indicator lamp
Crankshaft position sensor
Data link connector
EGR solenoid
Engine control module
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Evaporative emission purge solenoid
Fuel pump check terminal
Heated oxygen sensor (Front) Symbol 1 Name
Symbol
L 1 Heated oxygen sensor (Rear)
C
T / Idle arr control motor
H
I ignition coil (Ignition power transistor)
R
S Injector
N
M Manifold differential pressure sensor
F
U Multiport fuel injection (MFI) relay/Fuel pump V
relay
E Park/Neutral position switch
Q,
W Power steering pressure switch
A
0 Throttle position sensor (with built-in closed
G
throttle position switch)
D Vehicle speed sensor
P
J Volume air flow sensor (with built-in intake air
temperature sensor and barometric pressure
B K
sensor)
ilectronic engine control component locations-3.51 engine
Page 168 of 408
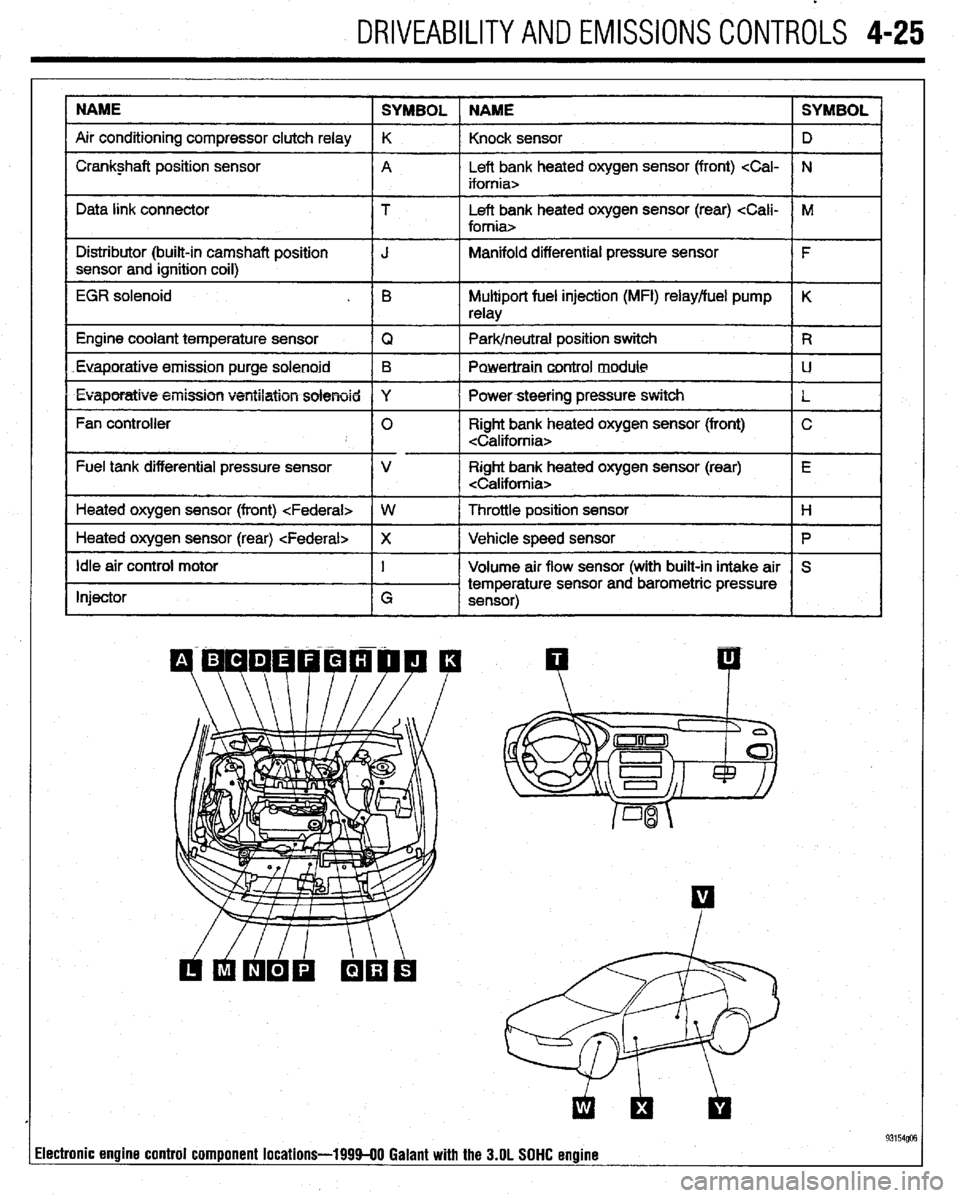
DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS 4-25
NAME
SYMBOL NAME SYMBOL
Air conditioning compressor clutch relay K
Knock sensor D
I Crankshaft position sensor
A Left bank heated oxygen sensor (front)
I I
Data link connector T Left bank heated oxygen sensor (rear)
I Distributor (built-in camshaft position
I J Manifold differential pressure sensor
I F
sensor and ignition coil)
I
EGR solenoid . B Multiport fuel injection (MFI) relay/fuel pump K
relay
1 Engine coolant temperature sensor
IQ 1 Park/neutral position switch IR
Euaporatiue.emission purge solenoid B
Powertraincontrol module LJ
l Evaporatiw5+eiiission ventilation solenoid Y
I Powersteering pressure switch
L
Fan controller 0 Right bank heated oxygen sensor (front) C
Fuel tank differential pressure sensor V Right bank heated oxygen sensor (rear) E
Heated oxygen sensor (front)
I
1 Heated oxygen sensor (rear)
Ip I
Idle air control motor
Injector I
G Volume air flow sensor (with built-in intake air S
temperature sensor and barometric pressure
sensor)
I I
93154@3 lectronic engine control component locations-199940 Galant with the 3.OL SOHC engine
Page 170 of 408

DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS 4-27
WITHOUTASCANTOOL
8 See Figure 87. 1. Remove the under dash cover, if equipped.
2. Attach an analoa voltmeter between the on-
board diagnostic outpit terminal of the data link con-
nector and the ground terminal
3. Turn the ignition switch ON.
4. Read the on-board diagnostic output pattern
from the voltmeter and record.
5. Diagnose and repair the faulty components as
required.
OBD OUTPUT
[TERMINAL
tic (OBO) output and ground terminal loca-
tions on the data link connector
6. Erase the trouble code.
7. Turn the ignition swatch ON, and read the di-
agnostic trouble codes, checking that a normal code
is output.
*To erase diagnostic trouble codes with a
scan tool, follow the directions given by the
tools manufacturer.
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF. 2. Disconnect the negative battery cable from the
battery for 1 minute or more, then reattach it.
3. Turn ON the ignition switch and read the diag-
nostic trouble codes checking that a normal code is
output.
Code 11 Oxygen sensor Code 12 Air flow sensor Code 13 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Code 14 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Code 15 SC Motor Position Sensor (MPS)
Code 21 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Code 22 Crank angle sensor Code 23 No. 1 cylinder TDC (camshaft position)
Sensor
Code 24 Vehicle speed sensor Code 25 Barometric pressure sensor Code 31 Knock sensor (KS) Code 32 Manifold pressure sensor Code 36 Ignition timmg adjustment signal Code 39 Oxygen sensor (rear - turbocharged) Code 41 Injector Code 42 Fuel pump Code 43 EGR-California Code 44 Ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
1 and No. 4 cvlinders) on 3.OL
Code 62 ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
2 and No. 5 cvlinders) on 3.OL
Code 53 ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
3 and No. 6 cylinders) on 3.OL
Code 55 AC valve position sensor Code 59 Heated oxygen sensor Code 61 Transaxle control unit cable (automatic
transmission)
Code 62 Warm-up control valve position sensor
(non-turbo)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is given
responsibrlity for the operation of the emission con-
trol devices, cooling fans, ignition and advance and
in some cases, automatic transaxle functions. Be-
cause the PCM oversees both the ignition timing and
the fuel injection operation, a precise air/fuel ratio
will be maintained under all operating conditions,
The PCM is a microprocessor, or small computer,
which receives electrical inputs from several sensors,
switches and relays on and around the engine.
Based on combinations of these inputs, the PCM
controls outputs to various devices concerned with
engine operation and emissions. The control module
relies on the signals to form a correct picture of cur-
rent vehicle operation. If any of the input signals is
incorrect, the PCM reacts to whatever picture is
painted for it. For example, if the coolant temperature
sensor is inaccurate and reads too low, the PCM may
see a picture of the engine never warming up. Conse-
quently, the engine settings will be maintained as if
the engine were cold. Because so many inputs can
affect one output, correct diagnostic procedures are
essential on these systems,
One part of the PCM is devoted to monitoring
both input and output functions within the system.
This ability forms the core of the self-diagnostic sys-
tem. If a problem is detected within a circuit, the con-
trol module will recognize the fault, assign it a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC), and store the code in
memory. The stored code(s) may be retrieved during
diagnosis. While the OBD-II system is capable of recognizing
many internal faults, certain faults WIII not be recog-
nized. Because the control module sees only electri-
cal signals, it cannot sense or react to mechanical or
vacuum faults affecting engine operation. Some of
these faults may affect another component which will
set a code. For example, the PCM monitors the out-
put signal to the fuel injectors, but cannot detect a
partially clogged injector. As long as the output dri-
ver responds correctly, the computer will read the
system as functioning correctly. However, the im-
proper flow of fuel may result in a lean mixture. This
would, in turn, be detected by the oxygen sensor and
noticed as a constantly lean signal by the PCM. Once
the signal falls outside the pre-programmed limits,
the control module would notice the fault and set a
trouble code.
Additionally, the OBD-II system employs adaptive
fuel logic. This process is used to compensate for
normal wear and variability within the fuel system.
Once the engine enters steady-state operation, the
control module watches the oxygen sensor signal for
a bias or tendency to run slightly rich or lean. If such
a bias is detected, the adaptive logic corrects the fuel
delivery to bring the air/fuel mixture towards a cen-
tered or 14.7:1 ratio. This compensating shift is
stored In a non-volatile memory which is retained by
battery power even with the ignition switched
OFF. The correction factor is then available the next time
the vehicle is operated.
WITHASCANTOOL
8 See Figures 88, 89, 90, and 91
The Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), under the
left-hand side of the instrument panel, must be lo-
cated to retrieve any OTC’s
Reading the control module memory is on of the
first steps in OBD II system diagnostics. This step
should be initially performed to determine the general
nature of the fault. Subsequent readings will deter-
mine if the fault has been cleared.
Reading codes can be performed by any of the
methods below:
l Read the control module memory with the
Generic Scan Tool (GST)
l Read the control module memory with the ve-
hicle manufacturers specific tester
To read the fault codes, connect the scan tool or
tester according to the manufacturers instructions.
Follow the manufacturers specified procedure for
reading the codes.
WITHOUTASCANTOOL
8 See Figure 92
The Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), under the
left-hand side of the instrument panel, must be lo-
cated to retrieve any DTC’s.
Page 173 of 408
.
4-30 DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS
PO275 Cvlinder no. 5 Contribution/Balance Fault
PO276 Cylinder no. 6 Injector Circuit Low
PO277 Cylinder no. 6 lniector Circuit High
PO278 Cylinder no. 6 Contribution/Balance Fault
PO300 Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire De-
tected
PO301 Cylinder no. l-Misfire Detected
PO302 Cvlinder no 2-Misfire Detected
PO303 Cylinder no. 3-Misfire Detected
PO304 Cylinder no. 4-Misfire Detected
PO305 Cylinder no. +-Misfire Detected
PO306 Cylinder no. &-Misfire Detected
PO320 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input
Circuit Malfunction
PO321 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input
Circuit Range/Performance
PO322 Ignibon/Distributor Engine Speed Input
Circuit No Signal
PO323 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input
Circuit Intermittent
PO325 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 1 or Single Sensor)
PO326 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit Range/Per-
formance (Bank no. 1 or Srngle Sensor)
PO327 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit Low Input
(Bank no. 1 or Single Sensor)
PO328 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit High Input
(Bank no. 1 or Single Sensor)
PO329 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit Input Inter-
mittent (Bank no. 1 or Smgle Sensor)
PO330 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 2 )
PO331 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit Range/Per-
formance (Bank no. 2 )
PO332 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit Low Input
(Bank no. 2 )
PO333 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit High Input
(Bank no. 2 )
PO334 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit Input Inter-
mittent (Bank no. 2)
PO335 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit
Malfunction
PO336 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit
Range/Performance
PO337 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit
Low Input
PO338 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit
High Input
PO339 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit In-
termittent
PO340 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Mal-
function
PO341 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
Range/Performance
PO342 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low In-
put
PO343 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit High In-
put
PO344 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Inter-
mittent
PO350 Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary Circuit
Malfunction
PO351 Ignition Coil “A” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO352 Ignition Coil “B” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO353 Ignition Coil “C” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO354 Ignition Coil “D” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO355 Ignition Coil “E” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction PO356 Ignition Coil “F” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO357 Ignition Coil “G” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO358 Ignition Coil ‘Y-l” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunctron
PO359 Ignition Coil “I” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO360 Ignition Coil “J” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO361 Ignition Coil “K” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO362 Ignition Coil “L” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO370 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” Malfunction
PO371 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” Too Many Pulses
PO372 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” Too Few Pulses
PO373 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” Intermittent/Erratic Pulses
PO374 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” No Pulses
PO375 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“B” Malfunction
PO376 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“B” Too Many Pulses
PO377 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
9” Too Few Pulses
PO378 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“B” Intermittent/Erratic Pulses
PO379 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“B” No Pulses
PO385 Crankshaft Position Sensor 9” Circuit
Malfunction
PO386 Crankshaft Position Sensor “B” Circuit
Range/Performance
PO387 Crankshaft Position Sensor ‘9” Circuit
Low Input
PO388 Crankshaft Position Sensor “B” Circuit
High Input
PO389 Crankshaft Position Sensor “B” Circuit In-
termittent
PO400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Malfunc-
tion
PO401 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insuffi-
cient Detected
PO402 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Excessive
Detected
PO403 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Circuit Mal-
function
PO404 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Circuit
Range/Performance
PO405 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor “A” Cir-
cuit Low
PO406 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor “A” Cir-
cuit High
PO407 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor “B” Cir-
cuit Low
PO408 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor “B” Cir-
cuit High
PO410 Secondary Air Injection System Malfunc-
tion
PO411 Secondary Air Injection System Incorrect
Flow Detected
PO412 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “A” Circuit Malfunction
PO413 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “A” Circuit Open
PO414 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “A” Circuit Shorted PO415 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “B” Circuit Malfunction
PO416 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “B” Circuit Open
PO417 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “B” Circuit Shorted
PO418 Secondary Air Injection System Relay “A
Circuit Malfunction
PO419 Secondary Air Injection System Relay “B”
Circuit Malfunction
PO420 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Thresh-
old (Bank no. 1 )
PO421 Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below
Threshold (Bank no. 1 )
PO422 Main Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold
(Bank no. 1 )
PO423 Heated Catalyst Efficiency Below Thresh-
old (Bank no. 1 )
PO424 Heated Catalyst Temperature Below
Threshold (Bank no. 1)
PO430 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Thresh-
old (Bank no. 2 )
PO431 Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below
Threshold (Bank no. 2 )
PO432 Main Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold
(Bank no. 2)
PO433 Heated Catalyst Efficiency Below Thresh-
old (Bank no. 2 )
PO434 Heated Catalvst Temoerature Below
Threshold (Bank no. 2
j ’
PO440 Evaporative Emission Control System
Malfunction
PO441 Evaporative Emission Control System In-
correct Purge Flow
PO442 Evaporative Emission Control System
Leak Detected (Small Leak)
PO443 Evaporative Emission Control System
Purge Control Valve Circuit Malfunction
PO444 Evaporative Emission Control System
Purge Control Valve Circuit Open
PO445 Evaporative Emission Control System
Purge Control Valve Circuit Shorted
PO446 Evaporative Emission Control System
Vent Control Circuit Malfunction
PO447 Evaporative Emission Control System
Vent Control Circuit Open
PO448 Evaporative Emission Control System
Vent Control Circuit Shorted
PO449 Evaporative Emission Control System
Vent Valve/Solenoid Circuit Malfunction
PO450 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor Malfunction
PO451 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor Range/Performance
PO452 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor Low Input
PO453 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor High Input
PO454 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor Intermittent
PO455 Evaporative Emission Control System
Leak Detected (Gross Leak)
PO460 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Malfunction
PO461 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Range/Perfor-
mance
PO462 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Low Input
PO463 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit High Input
PO464 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Intermittent
PO465 Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Malfunction
PO466 Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Range/Perfor-
mance
PO467 Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Low Input
Page 175 of 408
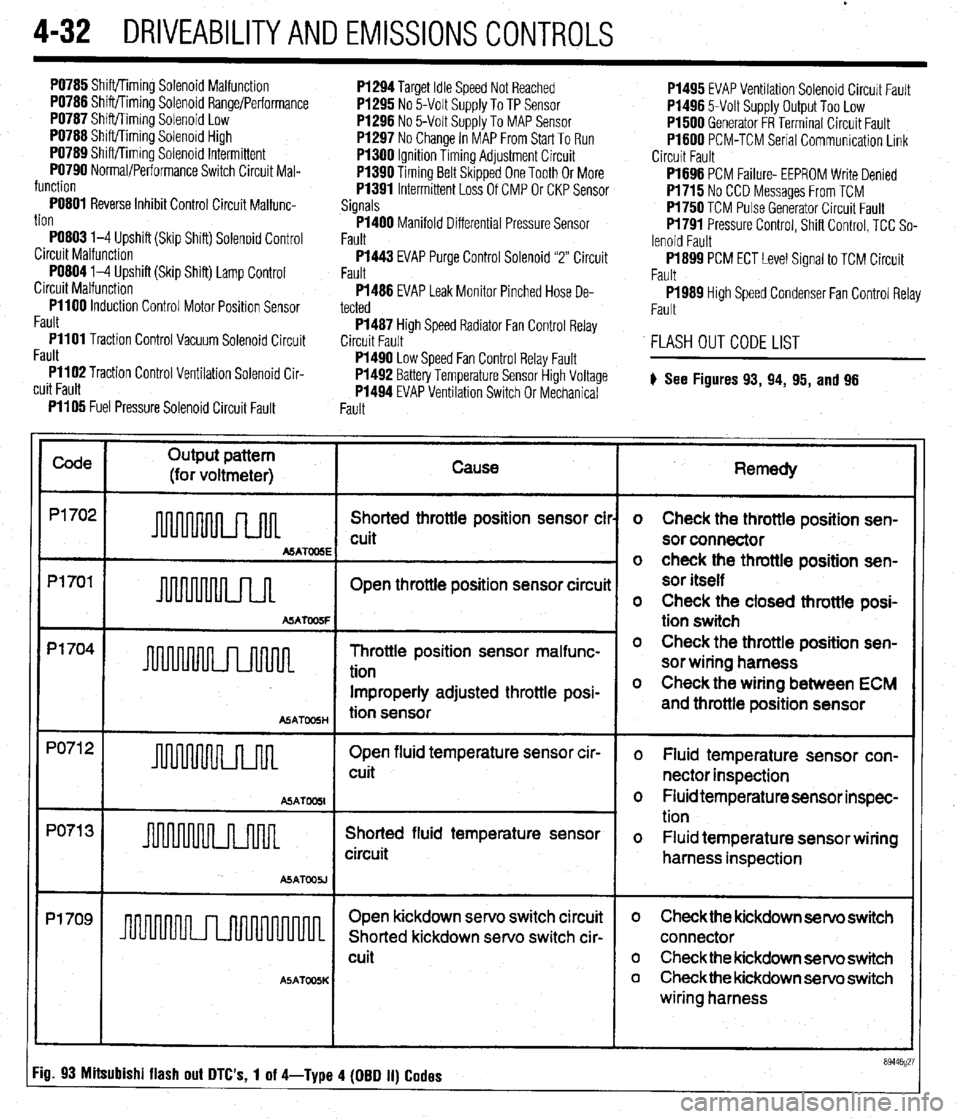
4-32 DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS
PO785 Shift/Timing Solenoid Malfunction
PO786 Shift/Timing Solenoid Range/Performance
PO787 Shift/Timing Solenoid Low
PO788 Shift/Timing Solenord High
PO789 Shift/Timing Solenoid Intermittent
PO790 Normal/Performance Switch Circuit Mal-
function
PO801 Reverse Inhibit Control Circuit Malfunc-
tion
PO803 l-4 Upshift (Skip Shift) Solenoid Control
Circuit Malfunction
PO804 l-4 Upshift (Skip Shift) Lamp Control
Circuit Malfunction
PllOO Induction Control Motor Position Sensor
Fault
PI101 Traction Control Vacuum Solenoid Circuit
Fault
Pl102 Traction Control Ventilation Solenoid Cir-
cuit Fault P1294 Target Idle Speed Not Reached
P1295 No 5-Volt Supply To TP Sensor
P1296 No 5-Volt Supply To MAP Sensor
P1297 No Change In MAP From Start To Run
PI300 Ignition Timing Adjustment Circuit
Pl390 Timing Belt Skipped One Tooth Or More
Pl391 Intermittent Loss Of CMP Or CKP Sensor
Signals P1495 EVAP Ventilation Solenoid Circurt Fault
P1496 5-Volt Supply Output Too Low
Pl500 Generator FR Terminal Circuit Fault
Pl600 PCM-TCM Serial Communication Link
Circuit Fault
Pl400 Manifold Differential Pressure Sensor
Fault P1696 PCM Failure- EEPROM Write Denied
Pl715 No CCD Messages From TCM
Pl750 TCM Pulse Generator Circuit Fault
Pl791 Pressure Control, Shift Control, TCC So-
lenoid Fault
P1443 EVAP Purge Control Solenoid “2” Circuit
Fault P1899 PCM ECT Level Signal to TCM Circuit
Fault
P1486 EVAP Leak Monitor Pinched Hose De-
tected
P1989 High Speed Condenser Fan Control Relay
Fault
P1487 High Speed Radiator Fan Control Relay
Circuit Fault
Pl490 Low Speed Fan Control Relay Fault
P1492 Battery Temperature Sensor High Voltage
P1494 EVAP Ventilation Switch Or Mechanical
FLASH OUT CODE LIST
# See Figures
93, 94, 95, and 96
Fault PI105 Fuel Pressure Solenoid Circuit Fault
Code
Output pattern
(for voltmeter) Cause
P1702
Shorted throttle position sensor cil
cuit
MATOOSE
Pl701
Open throttle position sensor circuii
A!iATW5F
p1704 -
Throttle position sensor malfunc-
tion
Improperly adjusted throttle posi-
ASATmH tion sensor
PO71 2
Open fluid temperature sensor cir-
u 1 cuit
ASAT
PO71 3
Shorted fluid temperature sensor
circuit
ASATOOU
Pl709
I I Open kickdown servo switch circuit
Shorted kickdown servo switch cir-
cuit
A5ATOOSK
Remedy
o Check the throttle position sen-
sor connector
o check the throttle position sen-
sor itself
o Check the closed throttle posi-
tion switch
o Check the throttle position sen-
sor wiring harness
o Check the wiring between ECM
and throttle position sensor
o Fluid temperature sensor con-
nector inspection
o Fluid temperature sensor inspec-
tion
o Fluid temperature sensor wiring
harness inspection
o Check the kickdown servo switch
connector
o Check the kickdown servo switch
o Checkthe kickdown servo switch
wiring harness
Fig. 93 Mitsubishi flash out DTC's, 1 of 4-Type 4 (DBD II) Codes