fuel MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007Pages: 1449, PDF Size: 56.82 MB
Page 535 of 1449

MPI -General Information13A-3
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Multipoint Fuel Injection System consists
of sensors which detect the engine conditions,
the engine-ECU which controls the system
based on signals from these sensors, and
actuators which operate under the control of
the engine-ECU. The engine-ECU carries outactivities such as fuel injection control, idle
speed control and ignition timing control. In
addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with
several diagnosis modes which simplify
troubleshooting when a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
The injector drive times and injector timing are
controlled so that the optimum air/fuel mixture
is supplied to the engine to correspond to the
continually-changing engine operation condi-
tions.
A single injector is mounted at the intake port
of each cylinder. Fuel is sent under pressure
from the fuel tank by the fuel pump, with the
pressure being regulated by the fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel thus regulated is distributed
to each of the injectors.
Fuel injection is normally carried out once for
each cylinder for every two rotations of the
crankshaft. The firing order is 1-3-4-2. This iscalled sequential fuel injection. The
engine-ECU provides a richer air/fuel mixture
by carrying out “open-loop” control when the
engine is cold or operating under high load
conditions in order to maintain engine
performance. In addition, when the engine is
warm or operating under normal conditions,
the engine-ECU controls the air/fuel mixture
by using the oxygen sensor signal to carry out
“closed-loop” control in order to obtain the
theoretical air/fuel mixture ratio that provides
the maximum cleaning performance from the
three way catalyst.
IDLE AIR CONTROL
The idle speed is kept at the optimum speed
by controlling the amount of air that bypasses
the throttle valve in accordance with changes
in idling conditions and engine load during
idling. The engine-ECU drives the idle speed
control motor to keep the engine running at
the pre-set idle target speed in accordance
with the engine coolant temperature and airconditioner load. In addition, when the air
conditioner switch is turned off and on while
the engine is idling, the idle speed control motor
operates to adjust the throttle valve bypass
air amount in accordance with the engine load
conditions in order to avoid fluctuations in the
engine speed.
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL
The power transistor located in the ignition
primary circuit turns ON and OFF to control
the primary current flow to the ignition coil. This
controls the ignition timing in order to provide
the optimum ignition timing with respect to theengine operating conditions. The ignition timing
is determined by the engine-ECU from the
engine speed, intake air volume, engine coolant
temperature and barometric pressure.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators related to
emission control, the engine warning lamp
(check engine lamp) illuminates as a
warning to the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis
code corresponding to the abnormality is
output.DThe RAM data inside the engine-ECU that
is related to the sensors and actuators can
be read by means of the MUT-II. In addition,
the actuators can be force-driven under
certain circumstances.
Page 536 of 1449
MPI -General Information13A-4
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Fuel Pump Control
Turns the fuel pump relay ON so that current
is supplied to the fuel pump while the engine
is cranking or running.
2. A/C Relay Control
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C
ON and OFF.3. Fan Motor Control
The revolutions of the radiator fan and
condenser fan are controlled in response to
the engine coolant temperature and vehicle
speed.
4. Purge Control Solenoid Valve Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
5. EGR Control Solenoid Valve Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsSpecifications
Throttle bodyThrottle bore mm60
Throttle position sensorVariable resistor type
Idle speed control servoStepper motor type
(Stepper motor type by-pass air control system with the
air volume limiter)
Engine-ECUIdentification No.E6T34874
SensorsAir flow sensorKarman vortex type
Barometric pressure sensorSemiconductor type
Intake air temperature sensorThermistor type
Engine coolant temperature sensorThermistor type
Oxygen sensorZirconia type
Vehicle speed sensorMagnetic resistive element type
Camshaft position sensorHall element type
Crank angle sensorHall element type
Detonation sensorPiezoelectric type
Power steering fluid pressure switchContact switch type
ActuatorsEngine control relay typeContact switch type
Fuel pump relay typeContact switch type
Injector type and numberElectromagnetic type, 4
Injector identification markMDL560
EGR control solenoid valveDuty cycle type solenoid valve
Purge control solenoid valveDuty cycle type solenoid valve
Fuel pressure control solenoid valveON/OFF type solenoid valve
Waste gate solenoid valveDuty cycle type solenoid valve
Secondary air control solenoid valveON/OFF type solenoid valve
Fuel pressure
regulatorRegulator pressure kPa294
Page 537 of 1449
MPI -General Information13A-5
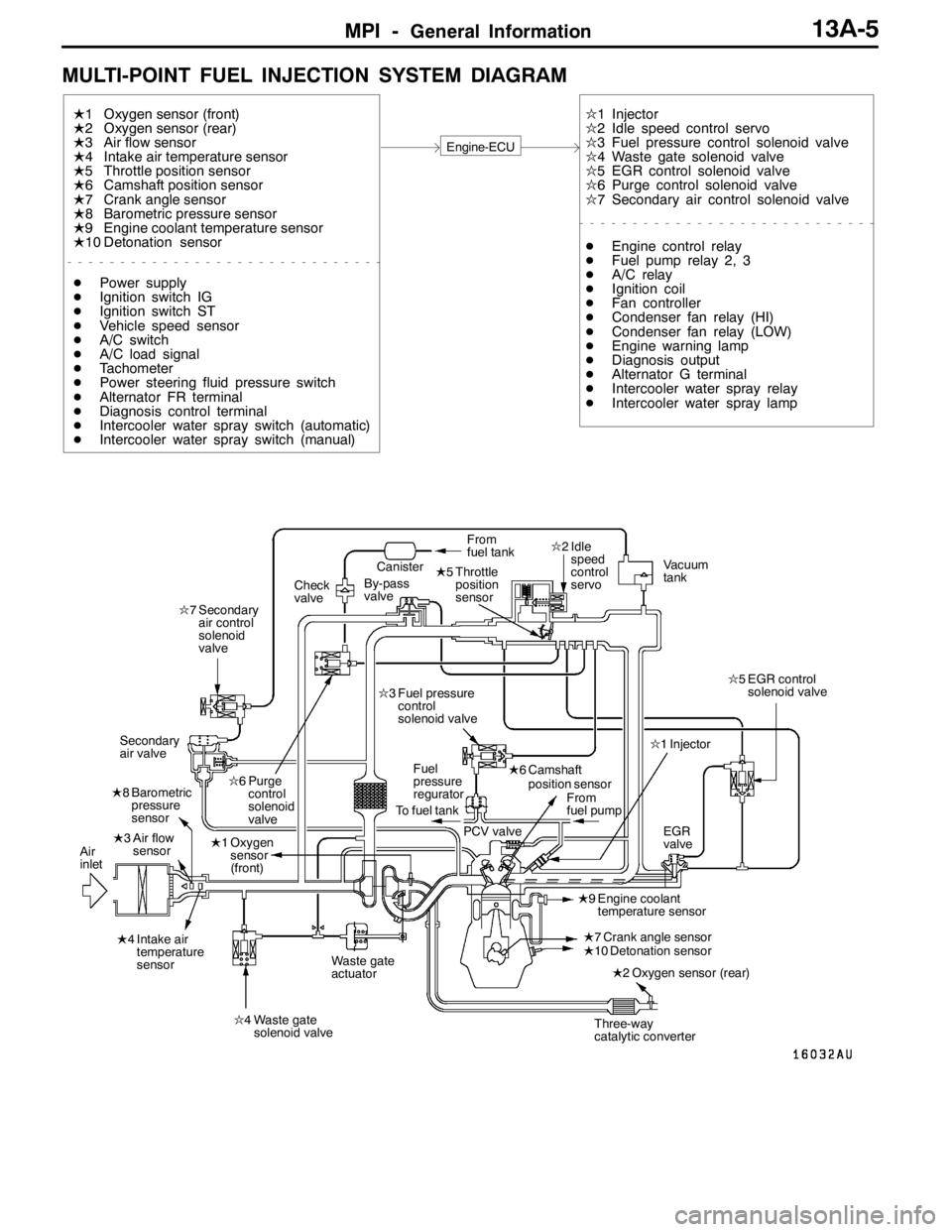
MULTI-POINT FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM DIAGRAM
L1 Oxygen sensor (front)
L2 Oxygen sensor (rear)
L3 Air flow sensor
L4 Intake air temperature sensor
L5 Throttle position sensor
L6 Camshaft position sensor
L7 Crank angle sensor
L8 Barometric pressure sensor
L9 Engine coolant temperature sensor
L10 Detonation sensor
Engine-ECU
l1 Injector
l2 Idle speed control servo
l3 Fuel pressure control solenoid valve
l4 Waste gate solenoid valve
l5 EGR control solenoid valve
l6 Purge control solenoid valve
l7 Secondary air control solenoid valve
DPower supply
DIgnition switch IG
DIgnition switch ST
DVehicle speed sensor
DA/C switch
DA/C load signal
DTachometer
DPower steering fluid pressure switch
DAlternator FR terminal
DDiagnosis control terminal
DIntercooler water spray switch (automatic)
DIntercooler water spray switch (manual)DEngine control relay
DFuel pump relay 2, 3
DA/C relay
DIgnition coil
DFan controller
DCondenser fan relay (HI)
DCondenser fan relay (LOW)
DEngine warning lamp
DDiagnosis output
DAlternator G terminal
DIntercooler water spray relay
DIntercooler water spray lamp
L1 Oxygen
sensor
(front)
L4 Intake air
temperature
sensorL5 Throttle
position
sensor
L6 Camshaft
position sensorl1 Injector l2 Idle
speed
control
servo
l6 Purge
control
solenoid
valve
Three-way
catalytic converter Canister
Air
inletVacuum
tank
Fuel
pressure
reguratorFrom
fuel tank
To fuel tank
PCV valveFrom
fuel pump
Waste gate
actuatorL2 Oxygen sensor (rear) Check
valveBy-pass
valve
l5 EGR control
solenoid valve
l4 Waste gate
solenoid valve L8 Barometric
pressure
sensor
L3 Air flow
sensorl7 Secondary
air control
solenoid
valve
Secondary
air valvel3 Fuel pressure
control
solenoid valve
EGR
valve
L9 Engine coolant
temperature sensor
L7 Crank angle sensor
L10 Detonation sensor
Page 538 of 1449
MPI -Service Specifications/Sealant13A-6
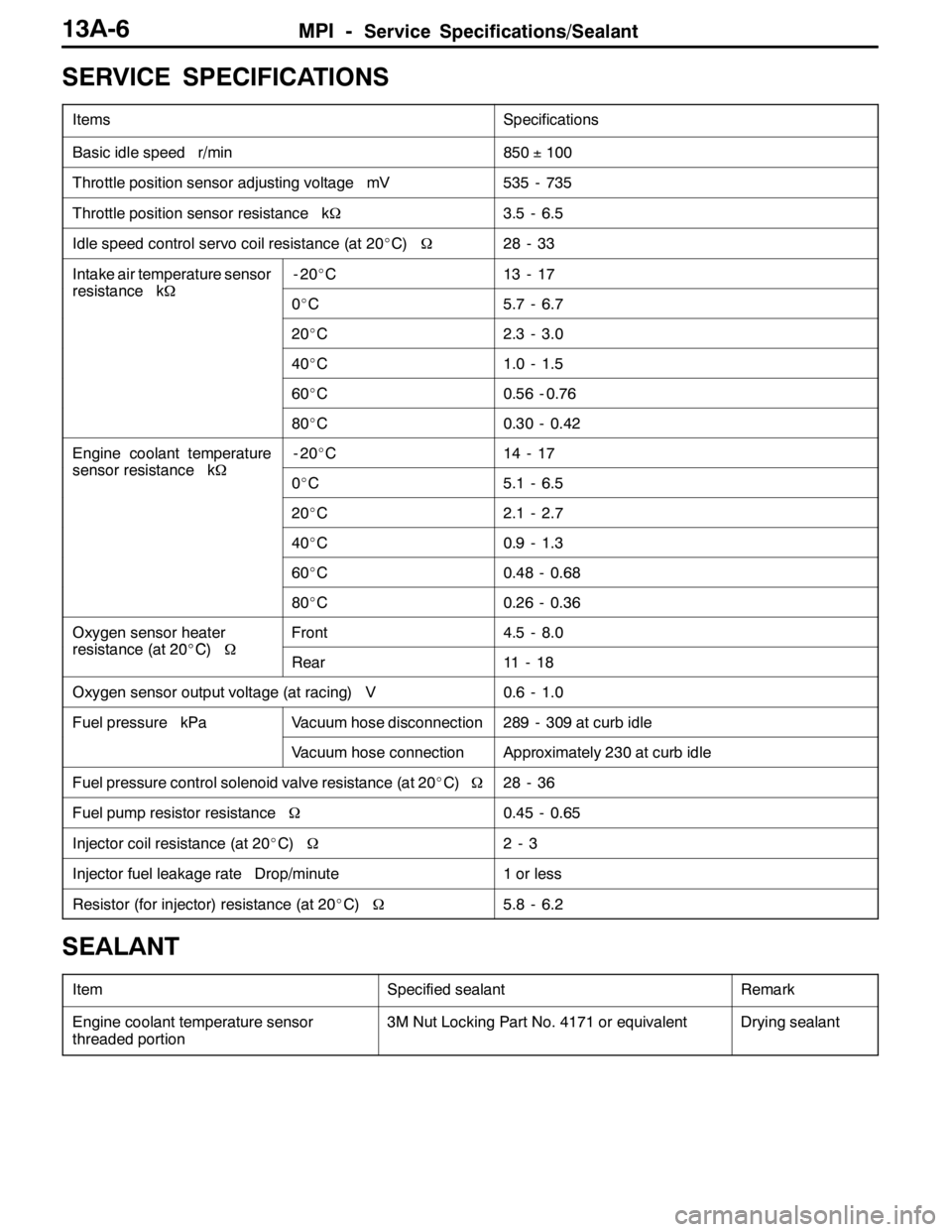
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsSpecifications
Basic idle speed r/min850±100
Throttle position sensor adjusting voltage mV535 - 735
Throttle position sensor resistance kΩ3.5 - 6.5
Idle speed control servo coil resistance (at 20_C)Ω28 - 33
Intake air temperature sensor
resistancekΩ
-20_C13 - 17
resistance kΩ0_C5.7 - 6.7
20_C2.3 - 3.0
40_C1.0 - 1.5
60_C0.56 - 0.76
80_C0.30 - 0.42
Engine coolant temperature
sensorresistancekΩ
-20_C14 - 17
sensor resistance kΩ0_C5.1 - 6.5
20_C2.1 - 2.7
40_C0.9 - 1.3
60_C0.48 - 0.68
80_C0.26 - 0.36
Oxygen sensor heater
resistance(at20_C)Ω
Front4.5 - 8.0
resistance (at 20_C)ΩRear11 - 1 8
Oxygen sensor output voltage (at racing) V0.6 - 1.0
Fuel pressure kPaVacuum hose disconnection289 - 309 at curb idle
Vacuum hose connectionApproximately 230 at curb idle
Fuel pressure control solenoid valve resistance (at 20_C)Ω28 - 36
Fuel pump resistor resistanceΩ0.45 - 0.65
Injector coil resistance (at 20_C)Ω2-3
Injector fuel leakage rate Drop/minute1 or less
Resistor (for injector) resistance (at 20_C)Ω5.8 - 6.2
SEALANT
ItemSpecified sealantRemark
Engine coolant temperature sensor
threaded portion3M Nut Locking Part No. 4171 or equivalentDrying sealant
Page 540 of 1449
MPI -Special Tools13A-8
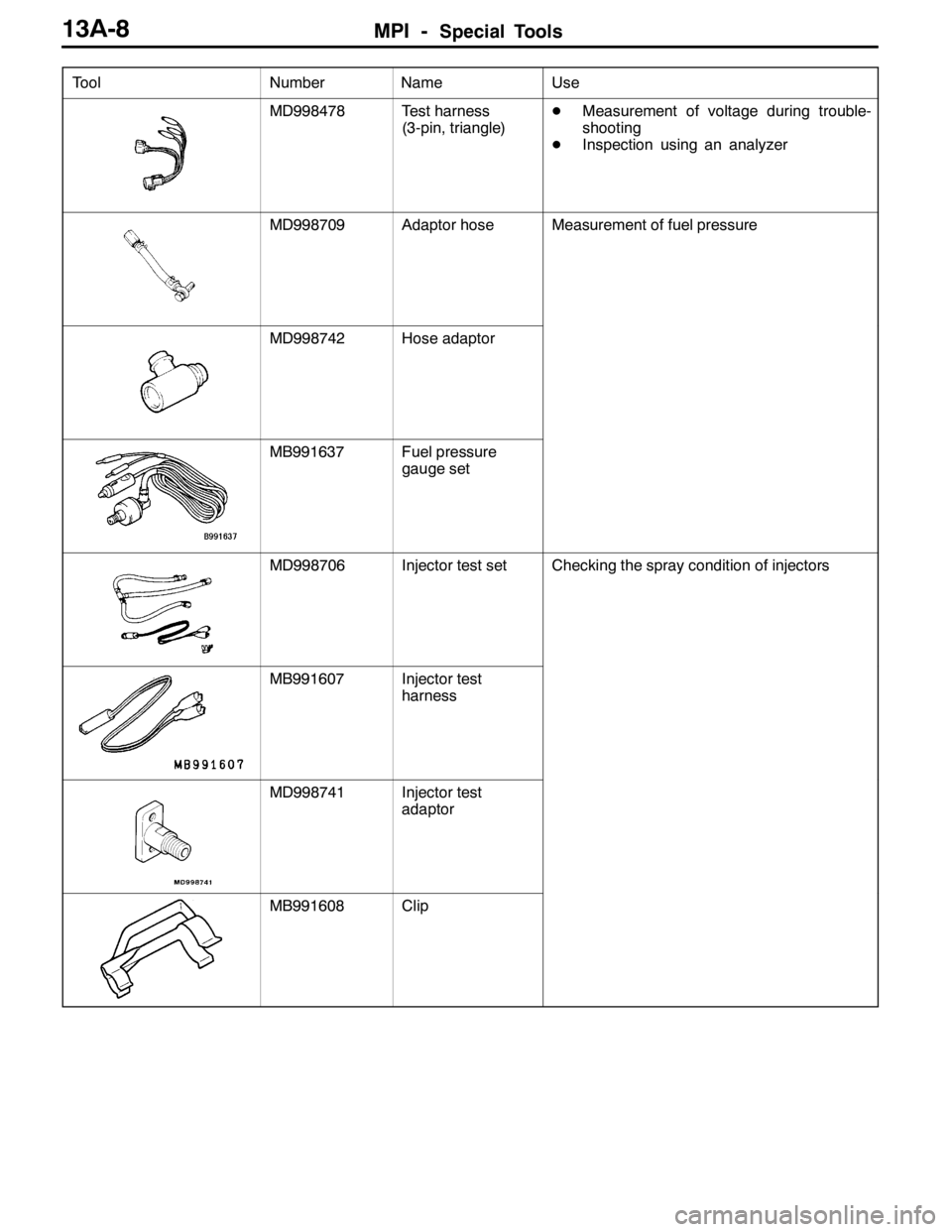
Tool UseName Number
MD998478Test harness
(3-pin, triangle)DMeasurement of voltage during trouble-
shooting
DInspection using an analyzer
MD998709Adaptor hoseMeasurement of fuel pressure
MD998742Hose adaptor
MB991637Fuel pressure
gauge set
MD998706Injector test setChecking the spray condition of injectors
MB991607Injector test
harness
MD998741Injector test
adaptor
MB991608Clip
Page 542 of 1449

MPI -TroubleshootingMPI -Troubleshooting13A-10
Code No. Diagnosis item
P0443Purge control solenoid valve system
P0500Vehicle speed sensor system
P0505Idle speed control system
P0551Power steering fluid pressure switch
P1104Waste gate solenoid valve system
P1105Fuel pressure control solenoid valve system
NOTE
If the engine warning lamp illuminates because of a malfunction of the engine-ECU, communication between
MUT-IIand the engine-ECU is impossible. In this case, the diagnosis code cannot be read.
METHOD OF READING AND ERASING DIAGNOSIS
CODES
Refer to GROUP 00 - How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection
Service Points.
INSPECTION USING MUT-IIDATA LIST AND ACTUATOR
TESTING
1. Carry out inspection by means of the data list and the
actuator test function. If there is an abnormality, check
and repair the chassis harnesses and components.
2. After repairing, re-check using the MUT-IIand check that
the abnormal input and output have returned to normal
as a result of the repairs.
3. Erase the diagnosis code memory.
4. Remove the MUT-II, and then start the engine again and
carry out a road test to confirm that the problem has
disappeared.
Page 543 of 1449
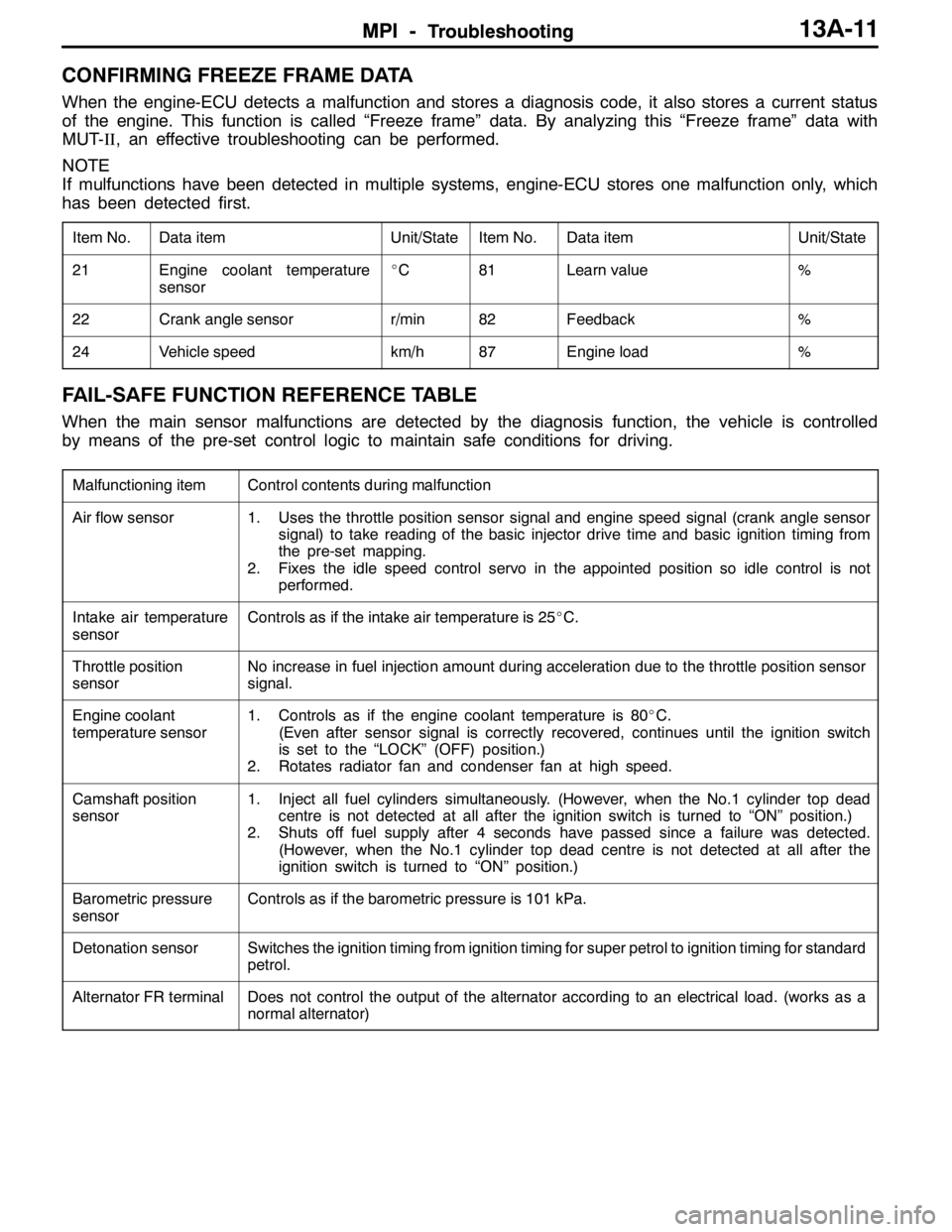
MPI -TroubleshootingMPI -Troubleshooting13A-11
CONFIRMING FREEZE FRAME DATA
When the engine-ECU detects a malfunction and stores a diagnosis code, it also stores a current status
of the engine. This function is called “Freeze frame” data. By analyzing this “Freeze frame” data with
MUT-II, an effective troubleshooting can be performed.
NOTE
If mulfunctions have been detected in multiple systems, engine-ECU stores one malfunction only, which
has been detected first.
Item No.Data itemUnit/StateItem No.Data itemUnit/State
21Engine coolant temperature
sensor_C81Learn value%
22Crank angle sensorr/min82Feedback%
24Vehicle speedkm/h87Engine load%
FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE
When the main sensor malfunctions are detected by the diagnosis function, the vehicle is controlled
by means of the pre-set control logic to maintain safe conditions for driving.
Malfunctioning itemControl contents during malfunction
Air flow sensor1. Uses the throttle position sensor signal and engine speed signal (crank angle sensor
signal) to take reading of the basic injector drive time and basic ignition timing from
the pre-set mapping.
2. Fixes the idle speed control servo in the appointed position so idle control is not
performed.
Intake air temperature
sensorControls as if the intake air temperature is 25_C.
Throttle position
sensorNo increase in fuel injection amount during acceleration due to the throttle position sensor
signal.
Engine coolant
temperature sensor1. Controls as if the engine coolant temperature is 80_C.
(Even after sensor signal is correctly recovered, continues until the ignition switch
is set to the “LOCK” (OFF) position.)
2. Rotates radiator fan and condenser fan at high speed.
Camshaft position
sensor1. Inject all fuel cylinders simultaneously. (However, when the No.1 cylinder top dead
centre is not detected at all after the ignition switch is turned to “ON” position.)
2. Shuts off fuel supply after 4 seconds have passed since a failure was detected.
(However, when the No.1 cylinder top dead centre is not detected at all after the
ignition switch is turned to “ON” position.)
Barometric pressure
sensorControls as if the barometric pressure is 101 kPa.
Detonation sensorSwitches the ignition timing from ignition timing for super petrol to ignition timing for standard
petrol.
Alternator FR terminalDoes not control the output of the alternator according to an electrical load. (works as a
normal alternator)
Page 544 of 1449
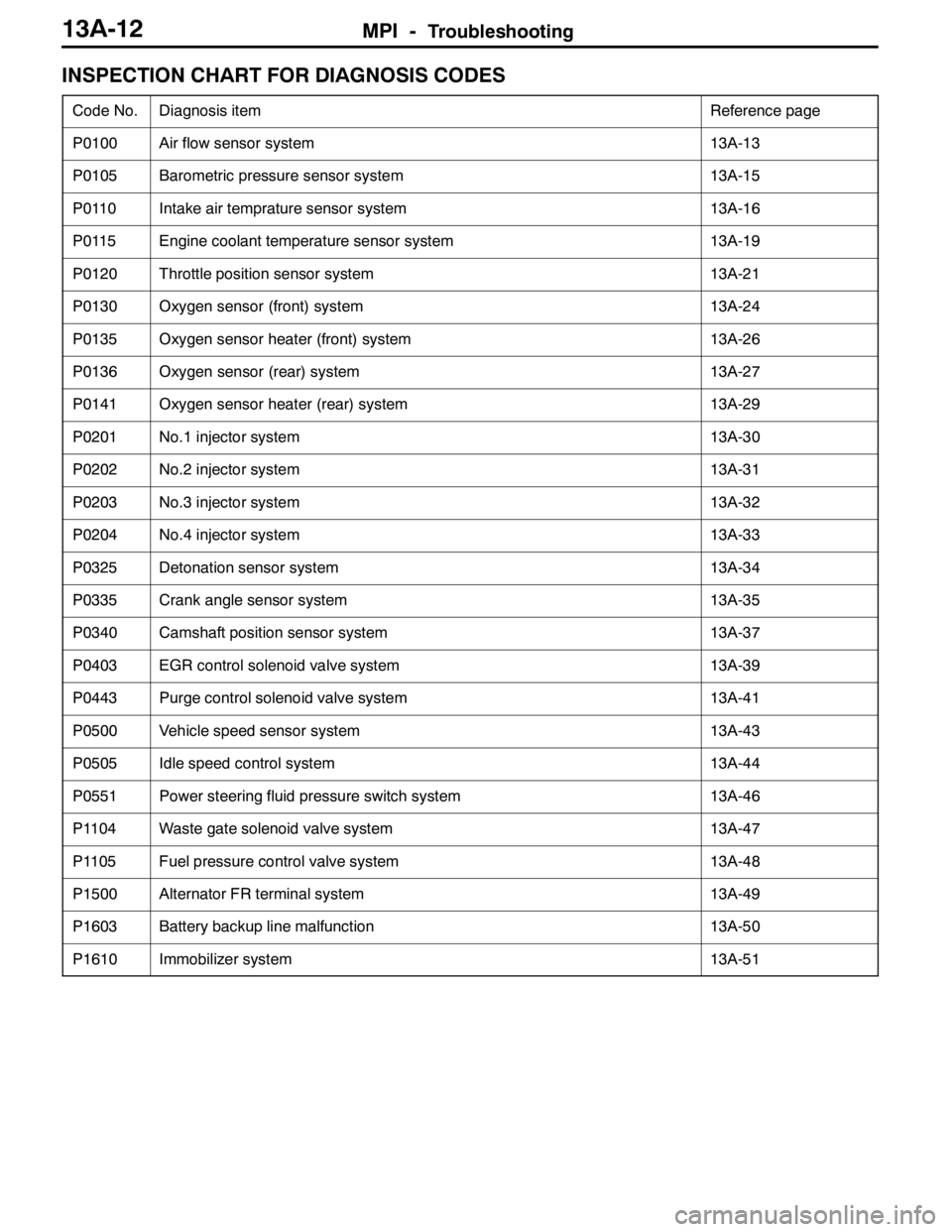
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-12
INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSIS CODES
Code No.Diagnosis itemReference page
P0100Air flow sensor system13A-13
P0105Barometric pressure sensor system13A-15
P0110Intake air temprature sensor system13A-16
P0115Engine coolant temperature sensor system13A-19
P0120Throttle position sensor system13A-21
P0130Oxygen sensor (front) system13A-24
P0135Oxygen sensor heater (front) system13A-26
P0136Oxygen sensor (rear) system13A-27
P0141Oxygen sensor heater (rear) system13A-29
P0201No.1 injector system13A-30
P0202No.2 injector system13A-31
P0203No.3 injector system13A-32
P0204No.4 injector system13A-33
P0325Detonation sensor system13A-34
P0335Crank angle sensor system13A-35
P0340Camshaft position sensor system13A-37
P0403EGR control solenoid valve system13A-39
P0443Purge control solenoid valve system13A-41
P0500Vehicle speed sensor system13A-43
P0505Idle speed control system13A-44
P0551Power steering fluid pressure switch system13A-46
P1104Waste gate solenoid valve system13A-47
P1105Fuel pressure control valve system13A-48
P1500Alternator FR terminal system13A-49
P1603Battery backup line malfunction13A-50
P1610Immobilizer system13A-51
Page 580 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-48
Code No. P1105 Fuel pressure control solenoid valve
systemProbable cause
Inspection Range
DBattery voltage is more than 10 V.
Evaluation Conditions
DSolenoid coil’s surge voltage (battery voltage +2 V) is not detected when the
fuel pressure control solenoid valve turned from ON to OFF.DFuel pressure control solenoid valve malfunction
DEngine-ECU malfunction
OK
NG
Replace the engine-ECU.
OKIntermittent malfunction (Refer to
GROUP 00 - Points to Note for
Intermittent Malfunctions.)MUT-IIActuator Test
DNo. 09: Fuel pressure control
solenoid valve
OK:Operation sound is heard,
and there is vibration.OKNG
Repair
OK
NG
Intermittent malfunction (Refer to
GROUP 00 - Points to Note for
Intermittent Malfunctions.)
OK
Check the following connector:B-37
MUT-IIActuator Test
DNo. 08: Purge control solenoid
valve
OK:Operation sound is heard,
and there is vibration.
NG
Repair
NGNG
Repair
OK
OK
Check and repair the harness
between the fuel pressure control
solenoid valve and engine-ECU.
DCheck for disconnection and
short-circuit of the output cable.
Check the following connector:
C-126
OK
Check the following connector:C-126
Measure at the C-126 engine-ECU
connector.
DDisconnect the connector to
measure at the harness side.
DIgnition switch: ON
DVoltage between terminal No. 3
and earth
OK:System voltageNG
Replace the fuel pressure control
solenoid valve.Measure at the B-37 fuel pressure
control solenoid valve connector.
DDisconnect the connector to
measure at the solenoid valve
side.
DResistance between terminal No.
1 and terminal No. 2
OK:29 - 35Ω(at 20_C)
OK
NG
Measure at the B-37 fuel pressure
control solenoid valve connector.
DDisconnect the connector to
measure at the harness side.
DIgnition switch: ON
DVoltage between terminal No. 1
and earth
OK:System voltage
OKNG
Repair
OK
OKCheck and repair the harness between
the fuel pressure control solenoid valve
and engine control relay.
DCheck for disconnection and
short-circuit of the power cable.
Check the following connector:
B-11X
NG
RepairCheck the harness between the fuel
pressure control solenoid valve and
engine control relay.
DCheck for damage of the power
cable.NG
Repair
OK
Check the harness between the fuel
pressure control solenoid valve and
engine-ECU.
DCheck for damage of the output
cable.
Page 584 of 1449
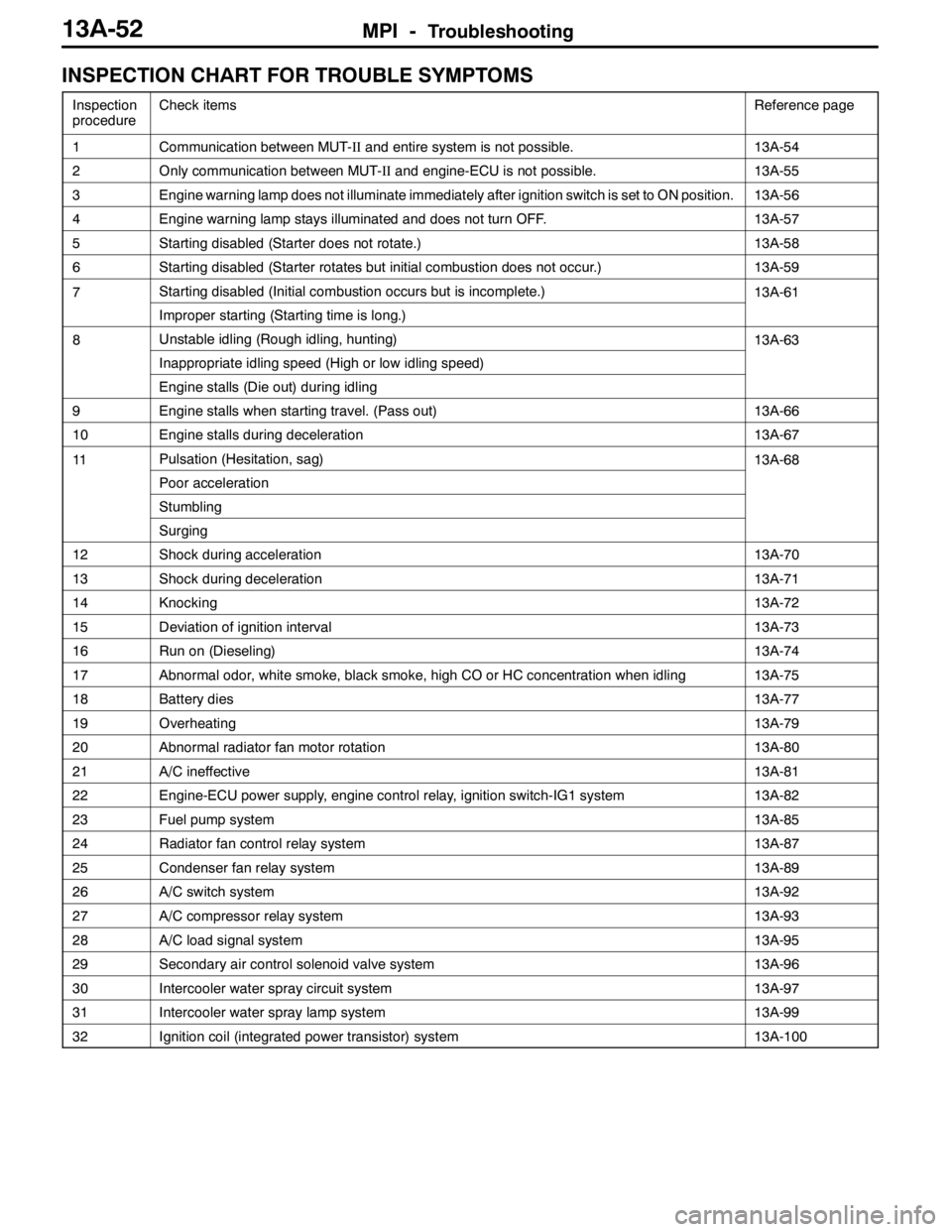
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-52
INSPECTION CHART FOR TROUBLE SYMPTOMS
Inspection
procedureCheck itemsReference page
1Communication between MUT-IIand entire system is not possible.13A-54
2Only communication between MUT-IIand engine-ECU is not possible.13A-55
3Engine warning lamp does not illuminate immediately after ignition switch is set to ON position.13A-56
4Engine warning lamp stays illuminated and does not turn OFF.13A-57
5Starting disabled (Starter does not rotate.)13A-58
6Starting disabled (Starter rotates but initial combustion does not occur.)13A-59
7Starting disabled (Initial combustion occurs but is incomplete.)13A-61
Improper starting (Starting time is long.)
8Unstable idling (Rough idling, hunting)13A-63
Inappropriate idling speed (High or low idling speed)
Engine stalls (Die out) during idling
9Engine stalls when starting travel. (Pass out)13A-66
10Engine stalls during deceleration13A-67
11Pulsation (Hesitation, sag)13A-68
Poor acceleration
Stumbling
Surging
12Shock during acceleration13A-70
13Shock during deceleration13A-71
14Knocking13A-72
15Deviation of ignition interval13A-73
16Run on (Dieseling)13A-74
17Abnormal odor, white smoke, black smoke, high CO or HC concentration when idling13A-75
18Battery dies13A-77
19Overheating13A-79
20Abnormal radiator fan motor rotation13A-80
21A/C ineffective13A-81
22Engine-ECU power supply, engine control relay, ignition switch-IG1 system13A-82
23Fuel pump system13A-85
24Radiator fan control relay system13A-87
25Condenser fan relay system13A-89
26A/C switch system13A-92
27A/C compressor relay system13A-93
28A/C load signal system13A-95
29Secondary air control solenoid valve system13A-96
30Intercooler water spray circuit system13A-97
31Intercooler water spray lamp system13A-99
32Ignition coil (integrated power transistor) system13A-100