steering MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION X, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008Pages: 241, PDF Size: 8.26 MB
Page 131 of 241
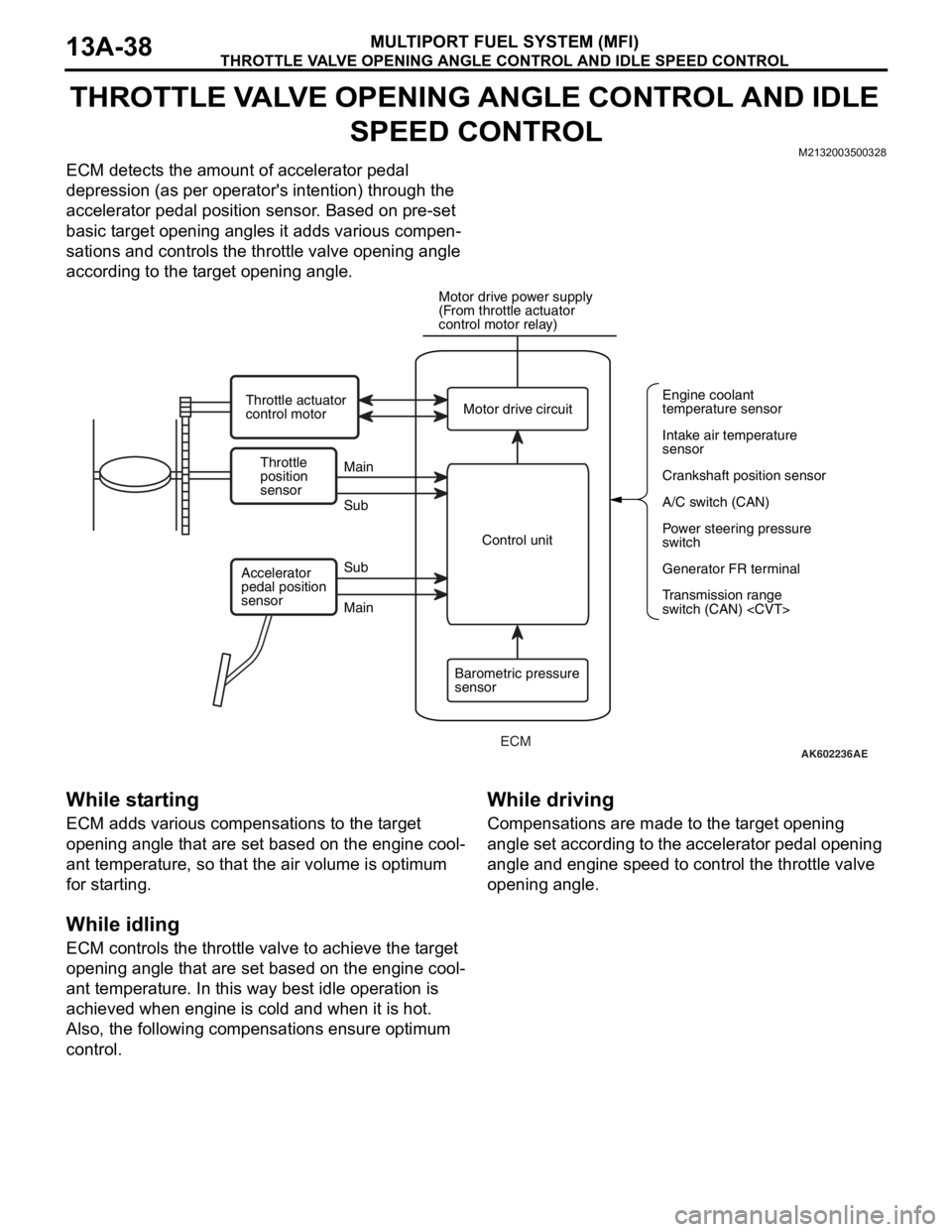
THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL AND IDLE SPEED CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-38
THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL AND IDLE
SPEED CONTROL
M2132003500328
ECM detects the amount of accelerator pedal
depression (as per operator's intention) through the
accelerator pedal position sensor. Based on pre-set
basic target opening angles it adds various compen
-
sations and controls the throttle valve opening angle
according to the target opening angle.
While starting
ECM adds various compensations to the target
opening angle that are set based on the engine cool
-
ant temperature, so that the air volume is optimum
for starting.
While idling
ECM controls the throttle valve to achieve the target
opening angle that are set based on the engine cool
-
ant temperature. In this way best idle operation is
achieved when engine is cold and when it is hot.
Also, the following compensations ensure optimum
control.
While driving
Compensations are made to the target opening
angle set according to the accelerator pedal opening
angle and engine speed to control the throttle valve
opening angle.
AK602236AE
Throttle
position
sensorMain
Main Sub
SubMotor drive circuit
A/C switch (CAN) Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Intake air temperature
sensor
Crankshaft position sensor
Power steering pressure
switch
Generator FR terminal
Transmission range
switch (CAN)
(From throttle actuator
control motor relay)
Throttle actuator
control motor
Control unit
Barometric pressure
sensor Accelerator
pedal position
sensor
ECM
Page 132 of 241
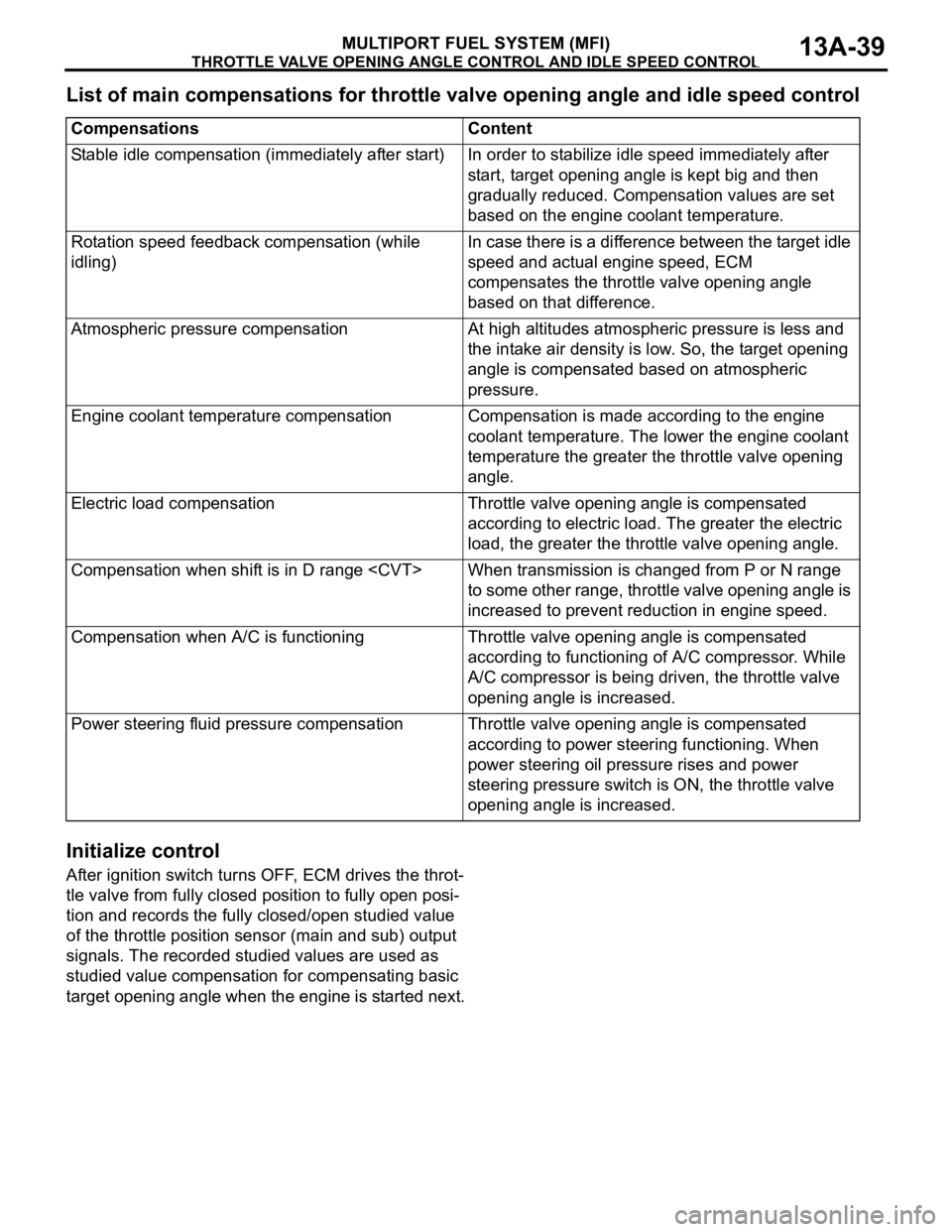
THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL AND IDLE SPEED CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-39
List of main compensations for throttle valve opening angle and idle speed control
Initialize control
After ignition switch turns OFF, ECM drives the throt-
tle valve from fully closed position to fully open posi-
tion and records the fully closed/open studied value
of the throttle position sensor (main and sub) output
signals. The recorded studied values are used as
studied value compensation for compensating basic
target opening angle when the engine is started next.
CompensationsContent
Stable idle compensation (immediately after start)In order to stabilize idle speed immediately after
start, target opening angle is kept big and then
gradually reduced. Compensation values are set
based on the engine coolant temperature.
Rotation speed feedback compensation (while
idling)In case there is a difference between the target idle
speed and actual engine speed, ECM
compensates the throttle valve opening angle
based on that difference.
Atmospheric pressure compensationAt high altitudes atmospheric pressure is less and
the intake air density is low. So, the target opening
angle is compensated based on atmospheric
pressure.
Engine coolant temperature compensationCompensation is made according to the engine
coolant temperature. The lower the engine coolant
temperature the greater the throttle valve opening
angle.
Electric load compensationThrottle valve opening angle is compensated
according to electric load. The greater the electric
load, the greater the throttle valve opening angle.
Compensation when shift is in D range
to some other range, throttle valve opening angle is
increased to prevent reduction in engine speed.
Compensation when A/C is functioningThrottle valve opening angle is compensated
according to functioning of A/C compressor. While
A/C compressor is being driven, the throttle valve
opening angle is increased.
Power steering fluid pressure compensationThrottle valve opening angle is compensated
according to power steering functioning. When
power steering oil pressure rises and power
steering pressure switch is ON, the throttle valve
opening angle is increased.
Page 164 of 241

INSTRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY
TSB Revision
INTERIOR52A-3
CAUTION
•Refer to GROUP 52B-SRS Service Precautions P.52B-24 and Air bag Module and Clock Spring
P.52B-367 before removing the passenger side air bag module.
•Do not subject the SRS-ECU to any shocks when removing or installing the instrument panel.
Pre-removal and Post-installation Operation
•Removal and Installation of Front Pillar Trim (Refer to P.52A-10).
•Removal and Installation of Instrument Under Cover
(Refer to P.52A-10).
•Removal and Installation of Glove Box (Refer to P.52A-10).
•Removal and Installation of Instrument Cover Lower, Air
Outlet Garnish (Refer to P.52A-10).
•Removal and Installation of Audio Unit (Refer to GROUP
54A, Radio with CD Player P.54A-307).
•Removal and Installation of Audio Visual Navigation Unit,
GPS antenna (Refer to GROUP 54A, MMCS P.54A-391).
•Removal and Installation of Steering shaft (Refer to
GROUP 37, Steering Column Shaft P.37-25).
•Removal and Installation of Hands-free Cellular Phone
System (Refer to GROUP 54A, Hands-free Module
P.54A-435).
•Removal and Installation of Sensors (Refer to GROUP
55B, Interior Temperature Sensor
P.55B-25).
Page 223 of 241
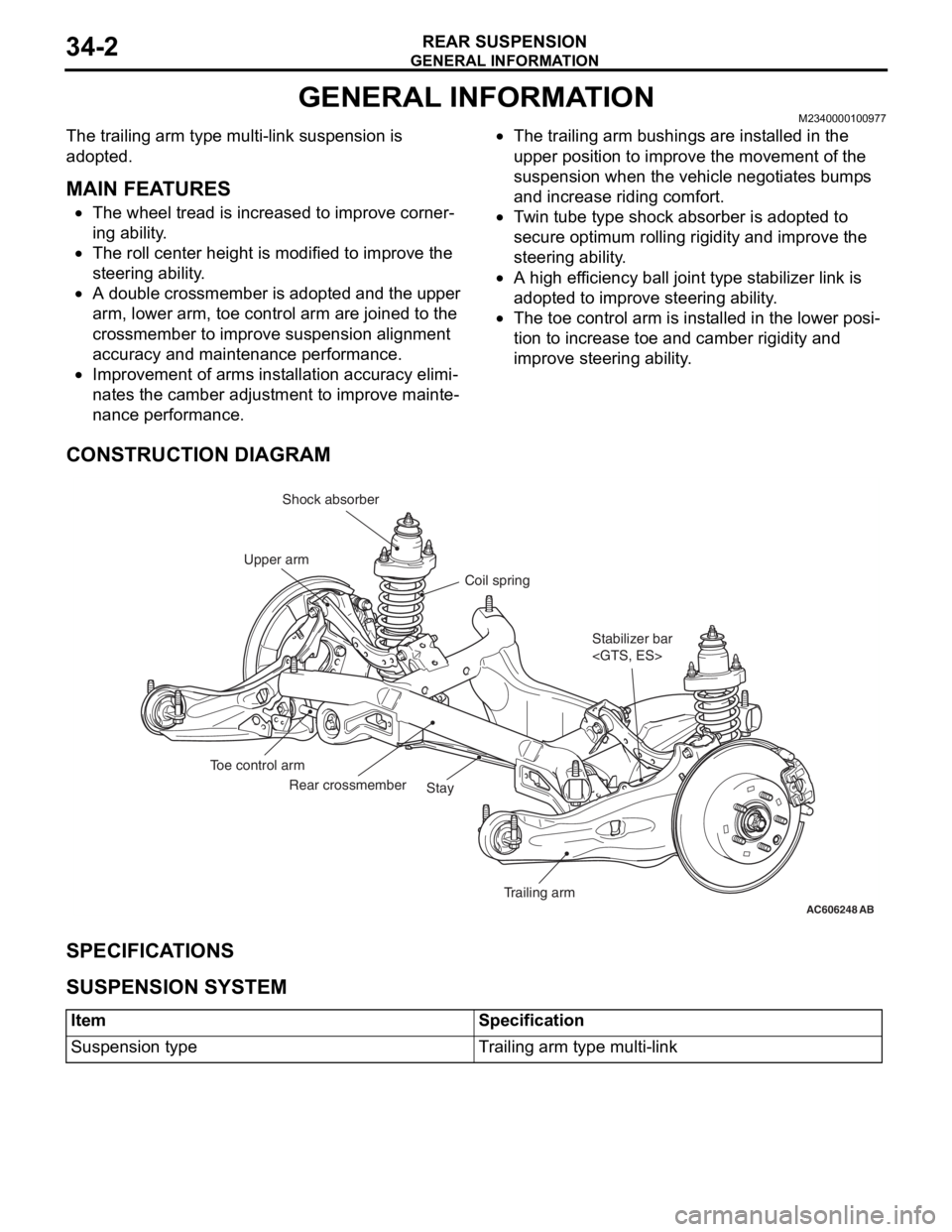
GENERAL INFORMATION
REAR SUSPENSION34-2
GENERAL INFORMATIONM2340000100977
The trailing arm type multi-link suspension is
adopted.
.
MAIN FEATURES
•The wheel tread is increased to improve corner-
ing ability.
•The roll center height is modified to improve the
steering ability.
•A double crossmember is adopted and the upper
arm, lower arm, toe control arm are joined to the
crossmember to improve suspension alignment
accuracy and maintenance performance.
•Improvement of arms installation accuracy elimi-
nates the camber adjustment to improve mainte-
nance performance.
•The trailing arm bushings are installed in the
upper position to improve the movement of the
suspension when the vehicle negotiates bumps
and increase riding comfort.
•Twin tube type shock absorber is adopted to
secure optimum rolling rigidity and improve the
steering ability.
•A high efficiency ball joint type stabilizer link is
adopted to improve steering ability.
•The toe control arm is installed in the lower posi-
tion to increase toe and camber rigidity and
improve steering ability.
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
SPECIFICATIONS
.
SUSPENSION SYSTEM
.
AC606248AB
Stabilizer bar
Trailing arm Stay Rear crossmember Toe control armCoil spring Shock absorber
Upper arm
ItemSpecification
Suspension typeTrailing arm type multi-link
Page 227 of 241
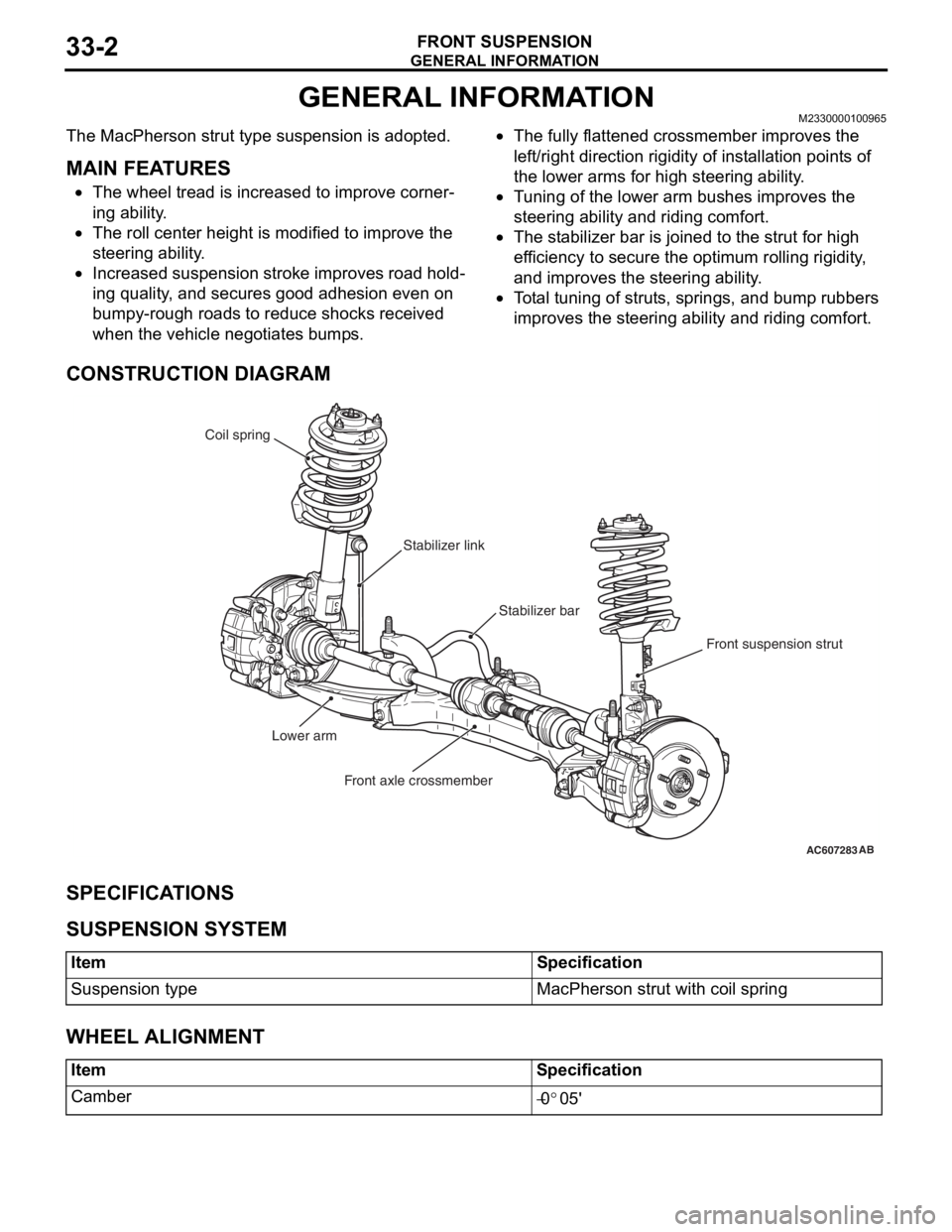
GENERAL INFORMATION
FRONT SUSPENSION33-2
GENERAL INFORMATIONM2330000100965
The MacPherson strut type suspension is adopted..
MAIN FEATURES
•The wheel tread is increased to improve corner-
ing ability.
•The roll center height is modified to improve the
steering ability.
•Increased suspension stroke improves road hold-
ing quality, and secures good adhesion even on
bumpy-rough roads to reduce shocks received
when the vehicle negotiates bumps.
•The fully flattened crossmember improves the
left/right direction rigidity of installation points of
the lower arms for high steering ability.
•Tuning of the lower arm bushes improves the
steering ability and riding comfort.
•The stabilizer bar is joined to the strut for high
efficiency to secure the optimum rolling rigidity,
and improves the steering ability.
•Total tuning of struts, springs, and bump rubbers
improves the steering ability and riding comfort.
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
SPECIFICATIONS
.
SUSPENSION SYSTEM
.
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
AC607283AB
Stabilizer bar Coil spring
Front suspension strut Stabilizer link
Lower arm
Front axle crossmember
ItemSpecification
Suspension typeMacPherson strut with coil spring
ItemSpecification
Camber−0°05'
Page 234 of 241
37-1
GROUP 37
POWER STEERING
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION . . . . . . . .37-2
STEERING WHEEL . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37-3
STEERING SHAFT AND COLUMN . .37-4
OIL PUMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37-6
STEERING GEAR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37-7
OIL RESERVOIR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37-8
Page 235 of 241
GENERAL INFORMATION
POWER STEERING37-2
GENERAL INFORMATIONM2370000101003
FEATURES
A hydraulic power steering system has been adopted
to all models.
This steering system offers the following features:
•The support method of the steering gear to the
crossmember is realised by the left and right
internal bushings with inner cylinders. This sup
-
port method achieves higher rigidity of the steer-
ing gear and improves the steering feeling.
•Configuring the optimum flow characteristics and
gear valve feature improves the handling stability.
•Appropriate application of friction to the steering
gear cuts off the disturbance from the road sur
-
face and improves the stability during the
straight-ahead driving.
•Optimisation of the flexible tube in the high pres-
sure hose reduces the pump noise.
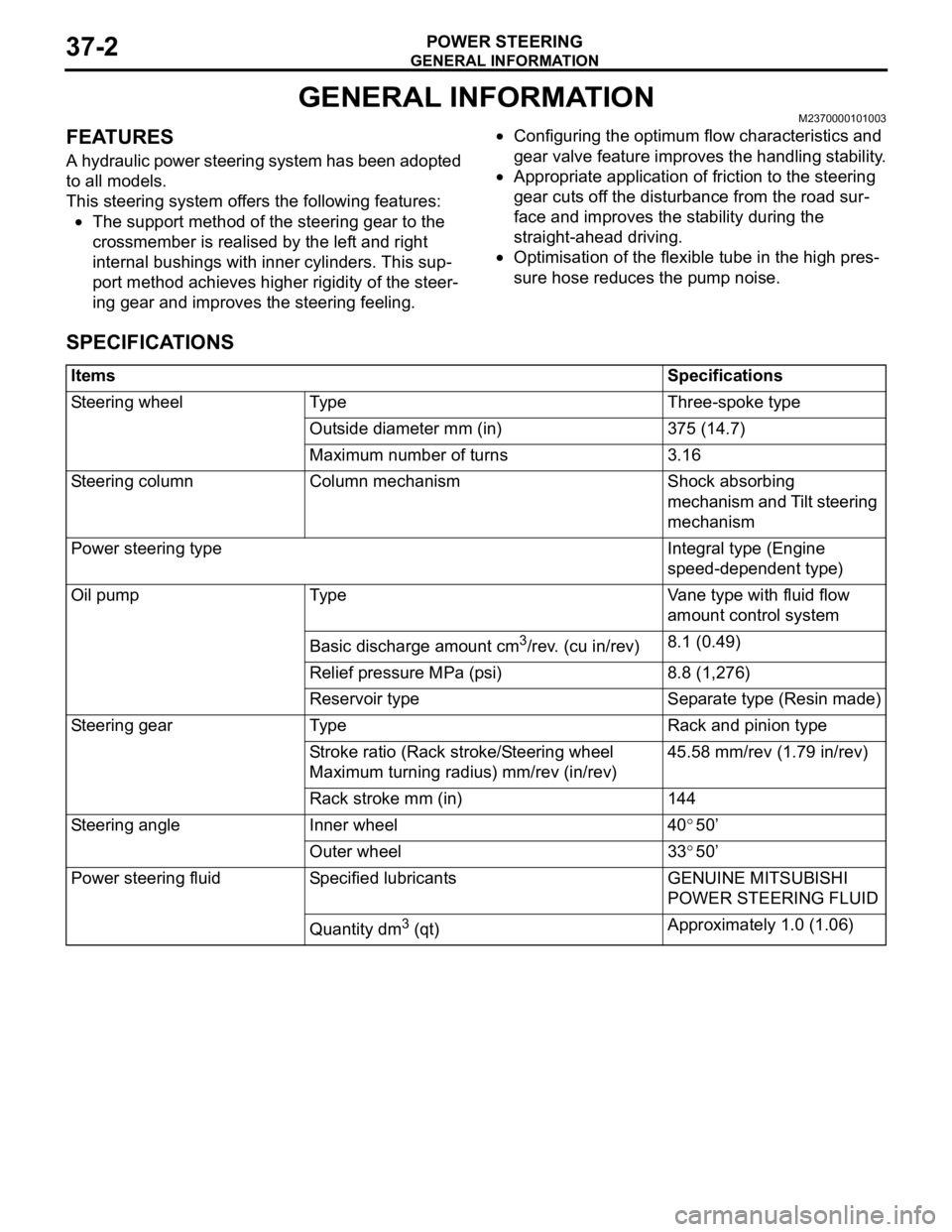
SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsSpecifications
Steering wheelTy p eThree-spoke type
Outside diameter mm (in)375 (14.7)
Maximum number of turns3.16
Steering columnColumn mechanismShock absorbing
mechanism and Tilt steering
mechanism
Power steering typeIntegral type (Engine
speed-dependent type)
Oil pumpTy p eVane type with fluid flow
amount control system
Basic discharge amount cm3/rev. (cu in/rev)8.1 (0.49)
Relief pressure MPa (psi)8.8 (1,276)
Reservoir typeSeparate type (Resin made)
Steering gearTy p eRack and pinion type
Stroke ratio (Rack stroke/Steering wheel
Maximum turning radius) mm/rev (in/rev)45.58 mm/rev (1.79 in/rev)
Rack stroke mm (in)144
Steering angleInner wheel40°50’
Outer wheel33°50’
Power steering fluidSpecified lubricantsGENUINE MITSUBISHI
POWER STEERING FLUID
Quantity dm3 (qt)Approximately 1.0 (1.06)
Page 236 of 241
STEERING WHEEL
POWER STEERING37-3
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
STEERING WHEELM2370001000761
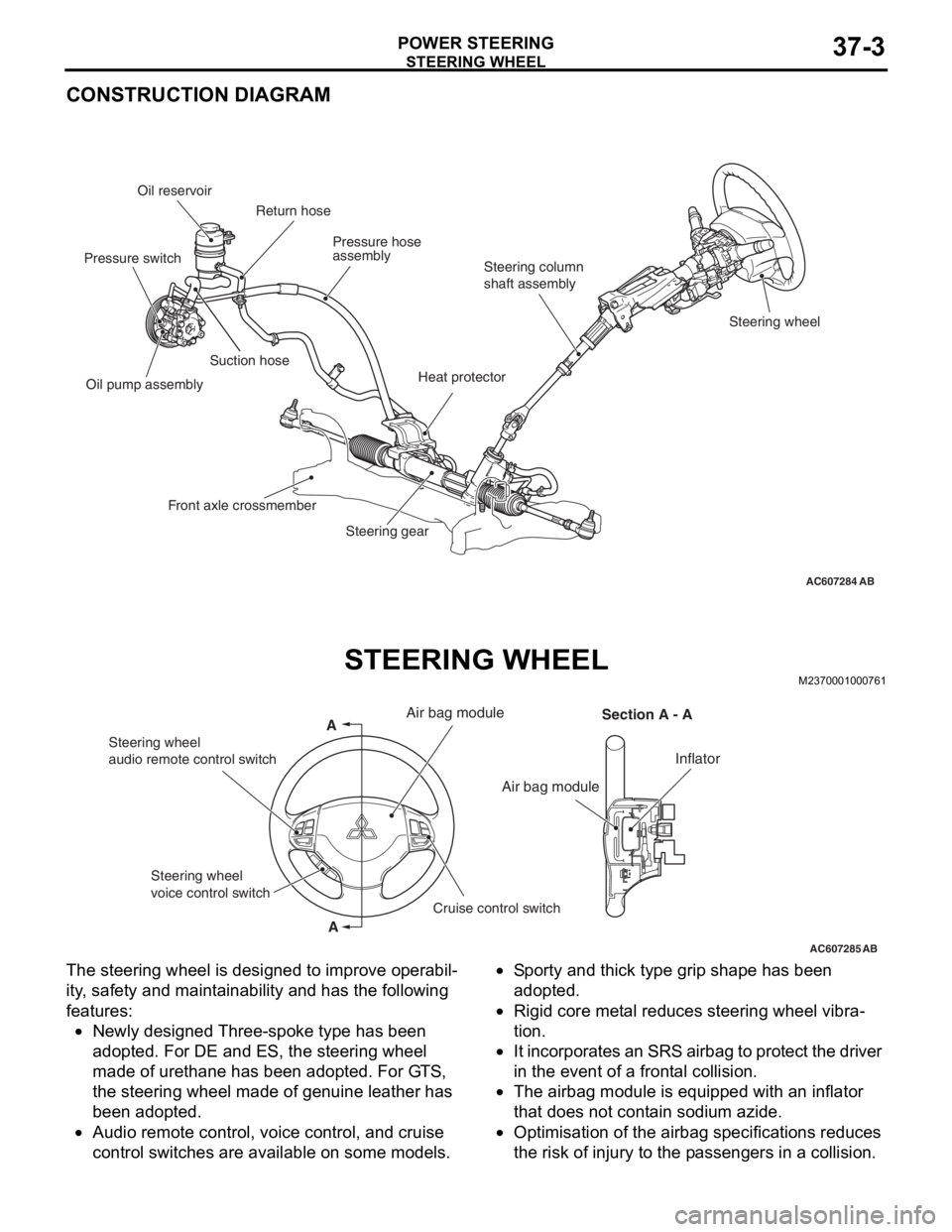
The steering wheel is designed to improve operabil-
ity, safety and maintainability and has the following
features:
•Newly designed Three-spoke type has been
adopted. For DE and ES, the steering wheel
made of urethane has been adopted. For GTS,
the steering wheel made of genuine leather has
been adopted.
•Audio remote control, voice control, and cruise
control switches are available on some models.
•Sporty and thick type grip shape has been
adopted.
•Rigid core metal reduces steering wheel vibra-
tion.
•It incorporates an SRS airbag to protect the driver
in the event of a frontal collision.
•The airbag module is equipped with an inflator
that does not contain sodium azide.
•Optimisation of the airbag specifications reduces
the risk of injury to the passengers in a collision.
AC607284AB
Steering wheel Steering column
shaft assembly Pressure hose
assembly Oil reservoir
Suction hose
Oil pump assembly
Steering gear Return hose
Front axle crossmember
Heat protector
Pressure switch
AC607285
A
AAir bag module
Section A - A
Inflator
Steering wheel
audio remote control switch
Cruise control switch Steering wheel
voice control switch
Air bag module
AB
Page 237 of 241
STEERING SHAFT AND COLUMN
POWER STEERING37-4
STEERING SHAFT AND COLUMNM2370002000667
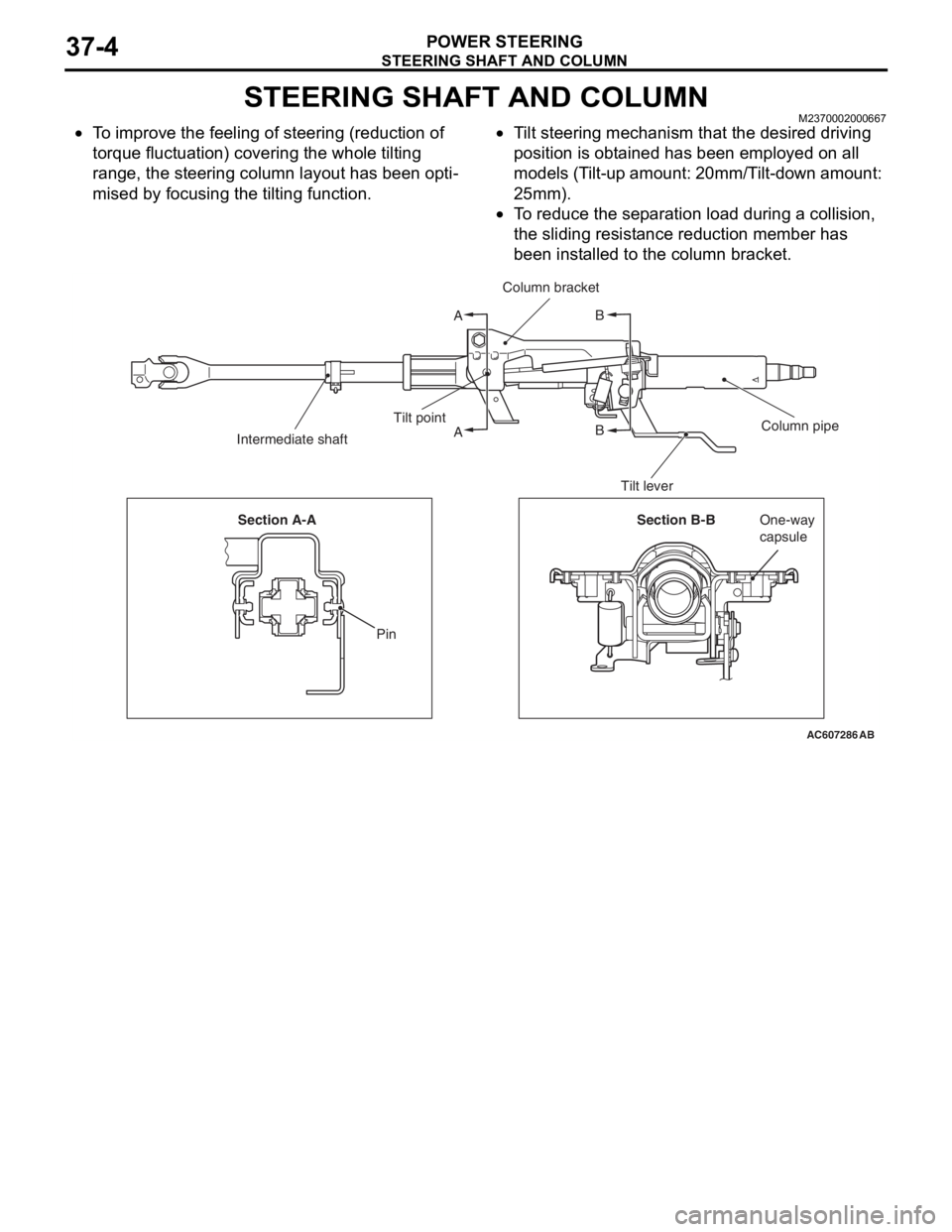
•To improve the feeling of steering (reduction of
torque fluctuation) covering the whole tilting
range, the steering column layout has been opti
-
mised by focusing the tilting function.
•Tilt steering mechanism that the desired driving
position is obtained has been employed on all
models (Tilt-up amount: 20mm/Tilt-down amount:
25mm).
•To reduce the separation load during a collision,
the sliding resistance reduction member has
been installed to the column bracket.
AC607286
A
AB
B
AB
Column bracket
Column pipe Tilt point
Intermediate shaft
Tilt lever
Section B-BOne-way
capsule Section A-A
Pin
Page 238 of 241
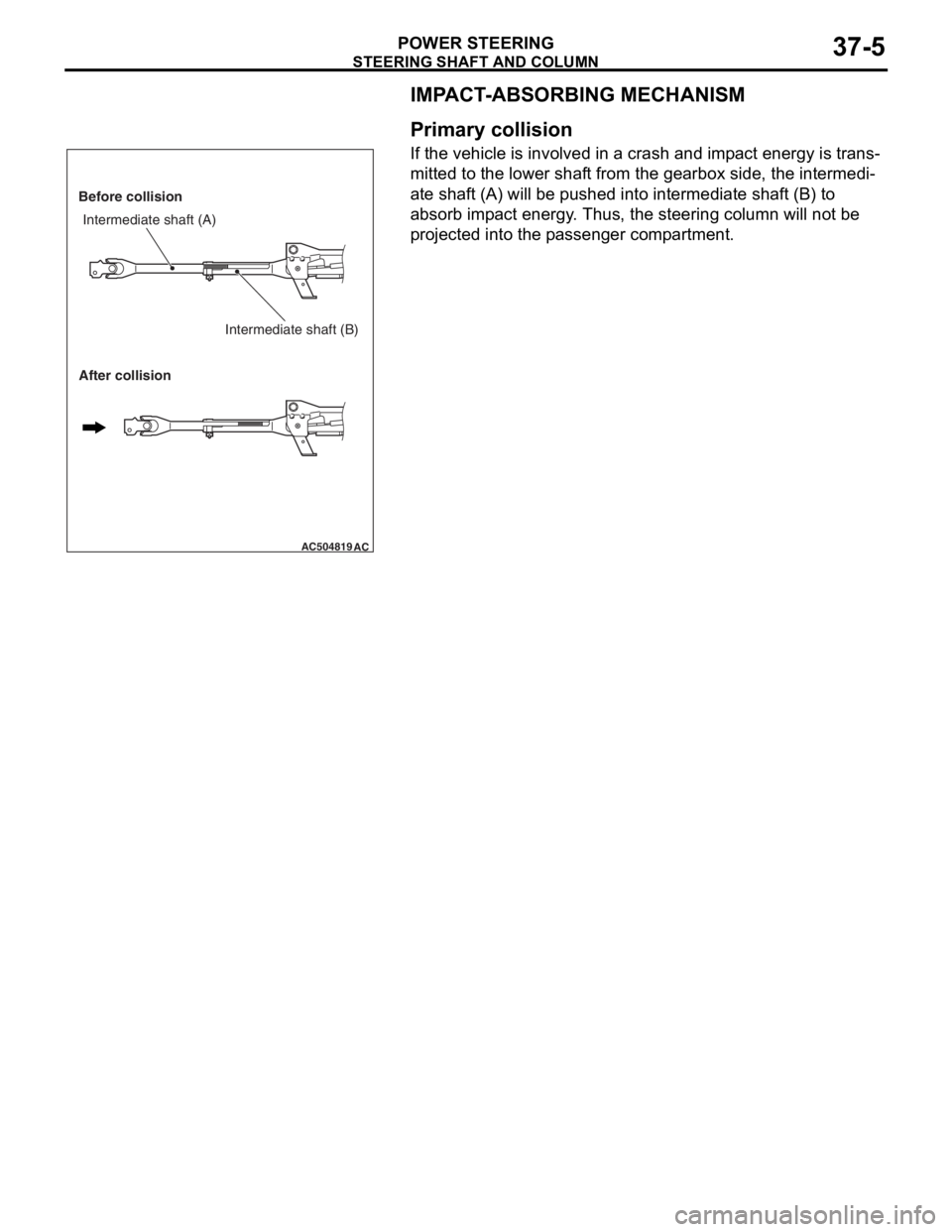
STEERING SHAFT AND COLUMN
POWER STEERING37-5
IMPACT-ABSORBING MECHANISM
.
Primary collision
If the vehicle is involved in a crash and impact energy is trans-
mitted to the lower shaft from the gearbox side, the intermedi-
ate shaft (A) will be pushed into intermediate shaft (B) to
absorb impact energy. Thus, the steering column will not be
projected into the passenger compartment.
.
AC504819AC
Before collision
After collisionIntermediate shaft (A)
Intermediate shaft (B)