engine oil MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION X, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008Pages: 241, PDF Size: 8.26 MB
Page 99 of 241
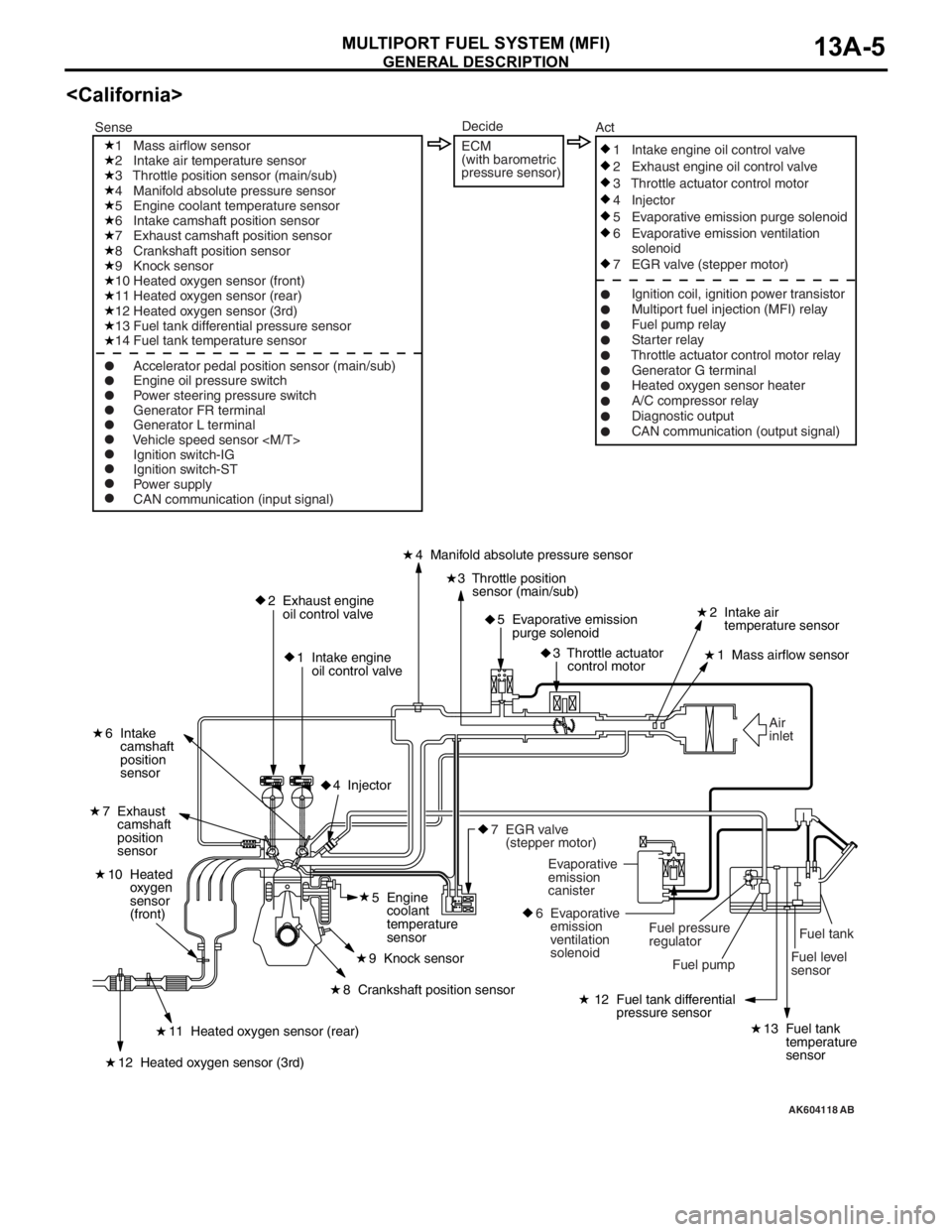
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-5
AK604118
Fuel tank
Fuel level
sensor Air
inlet
2 Exhaust engine
oil control valve
1 Intake engine
oil control valve4 Manifold absolute pressure sensor
2 Intake air
temperature sensor
1 Mass airflow sensor
6 Intake
camshaft
position
sensor
7 Exhaust
camshaft
position
sensor
3 Throttle position
sensor (main/sub)
5 Evaporative emission
purge solenoid
3 Throttle actuator
control motor
12 Fuel tank differential
pressure sensor
13 Fuel tank
temperature
sensor11 Heated oxygen sensor (rear)
10 Heated
oxygen
sensor
(front)
12 Heated oxygen sensor (3rd)
8 Crankshaft position sensor5 Engine
coolant
temperature
sensor
9 Knock sensor
4 Injector
Fuel pump Fuel pressure
regulator Evaporative
emission
canister
6 Evaporative
emission
ventilation
solenoid
7 EGR valve
(stepper motor)
1 Mass airflow sensor
2 Intake air temperature sensor
3 Throttle position sensor (main/sub)
4 Manifold absolute pressure sensor
5 Engine coolant temperature sensor
6 Intake camshaft position sensor
7 Exhaust camshaft position sensor
8 Crankshaft position sensor
9 Knock sensor
10 Heated oxygen sensor (front)
11 Heated oxygen sensor (rear)
12 Heated oxygen sensor (3rd)
13 Fuel tank differential pressure sensor
14 Fuel tank temperature sensor
Ignition switch-IG
Ignition switch-ST
Power supply
CAN communication (input signal)1 Intake engine oil control valve
2 Exhaust engine oil control valve
3 Throttle actuator control motor
4 Injector
5 Evaporative emission purge solenoid
6 Evaporative emission ventilation
solenoid
7 EGR valve (stepper motor)
Ignition coil, ignition power transistor
Multiport fuel injection (MFI) relay
Fuel pump relay
Starter relay
Throttle actuator control motor relay
Generator G terminal
Heated oxygen sensor heater
A/C compressor relay
Diagnostic output
CAN communication (output signal) SenseAct
Engine oil pressure switch
Power steering pressure switch
Generator FR terminal
Generator L terminal
Vehicle speed sensor
Decide
ECM
(with barometric
pressure sensor)
AB
Page 100 of 241
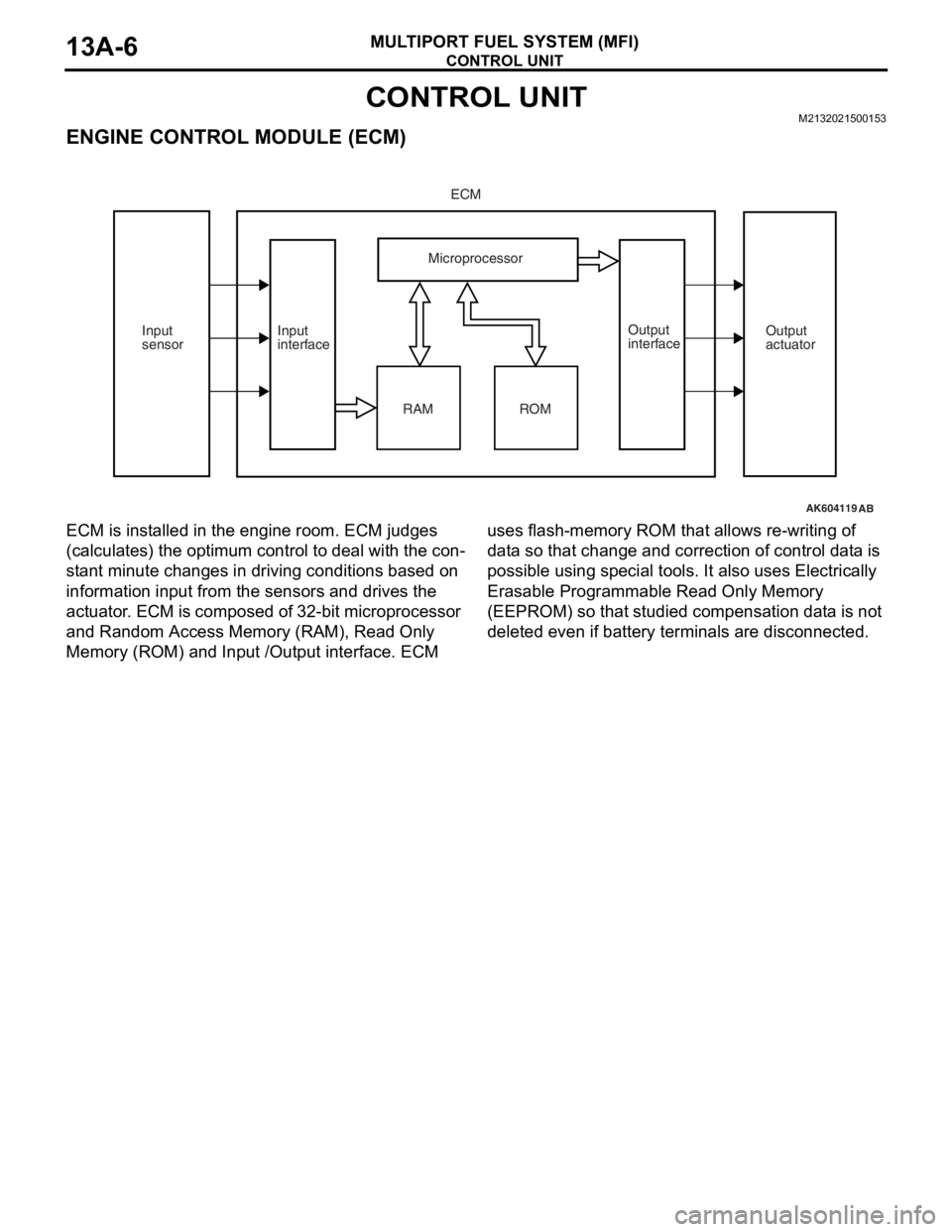
CONTROL UNIT
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-6
CONTROL UNITM2132021500153
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
ECM is installed in the engine room. ECM judges
(calculates) the optimum control to deal with the con
-
stant minute changes in driving conditions based on
information input from the sensors and drives the
actuator. ECM is composed of 32-bit microprocessor
and Random Access Memory (RAM), Read Only
Memory (ROM) and Input /Output interface. ECM uses flash-memory ROM that allows re-writing of
data so that change and correction of control data is
possible using special tools. It also uses Electrically
Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
(EEPROM) so that studied compensation data is not
deleted even if battery terminals are disconnected.
ECM CONNECTOR INPUT/OUTPUT PIN ARRANGEMENT
NOTE: *: California
AK604119
ECM
Microprocessor
RAM Input
interfaceOutput
interface Input
sensorOutput
actuator
AB
ROM
AK602565AC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1213 14 15 16
17 18 19 20 21 91
90
89
87
86
84 85
83 82
88 92 93 94
95 96 97 98 99
109
108
107 106
105
104
103
102
112 113 114 115 116 117 118
100 101
111
110
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33 32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
2260
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49 48
47
46
45
44
43
4263
61 62 6471 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81
1Intake engine oil control valve2No.1 injector
3No.2 injector4Ignition coil No.1 (ignition power transistor)
5Ignition coil No.2 (ignition power transistor)6Starter active signal
7Exhaust camshaft position sensor8Crankshaft position sensor
9Sensor supplied voltage10Throttle position sensor (main)
11Throttle position sensor (sub)12Power supply voltage applied to throttle
position sensor
13Throttle position sensor ground14Intake camshaft position sensor
Page 111 of 241
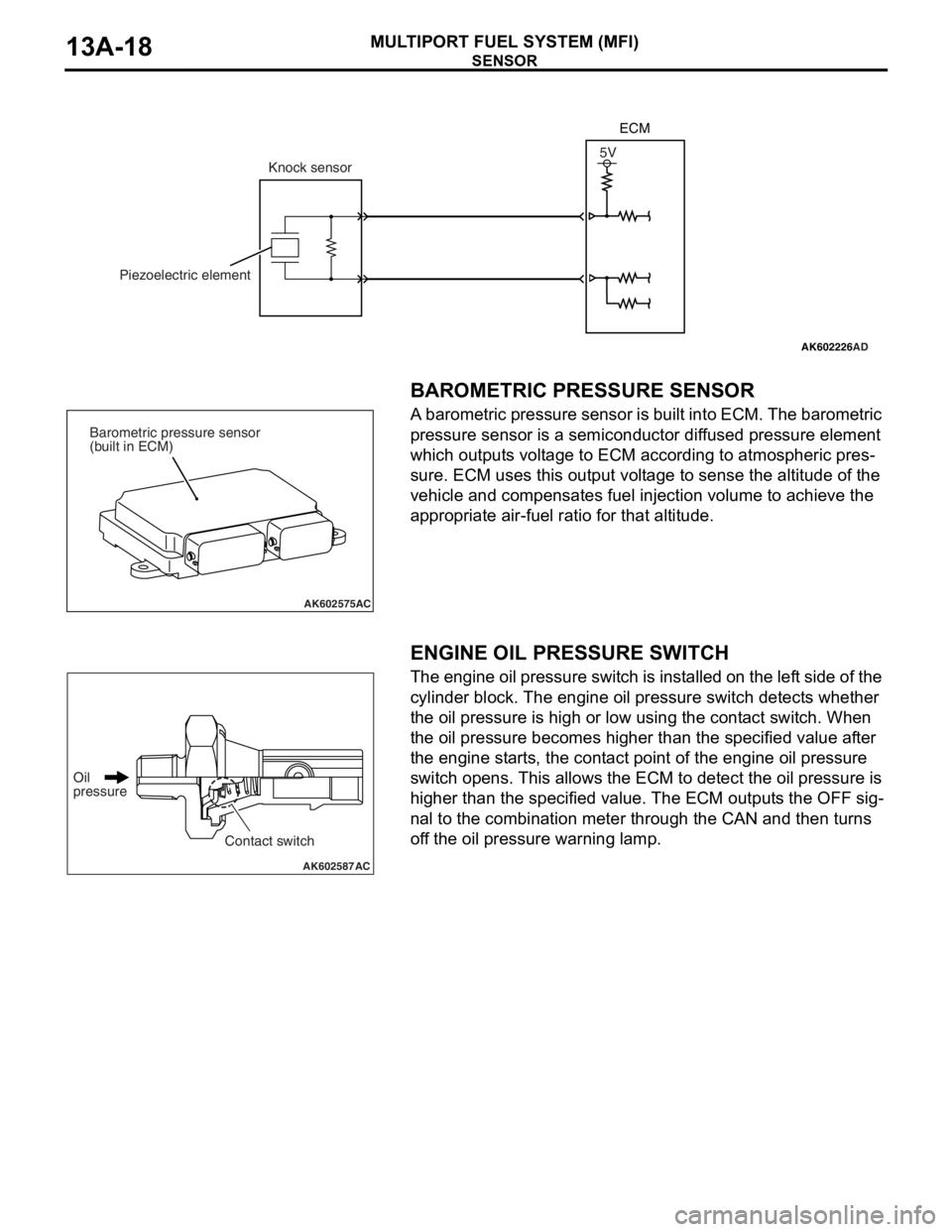
SENSOR
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-18
.
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
A barometric pressure sensor is built into ECM. The barometric
pressure sensor is a semiconductor diffused pressure element
which outputs voltage to ECM according to atmospheric pres
-
sure. ECM uses this output voltage to sense the altitude of the
vehicle and compensates fuel injection volume to achieve the
appropriate air-fuel ratio for that altitude.
.
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
The engine oil pressure switch is installed on the left side of the
cylinder block. The engine oil pressure switch detects whether
the oil pressure is high or low using the contact switch. When
the oil pressure becomes higher than the specified value after
the engine starts, the contact point of the engine oil pressure
switch opens. This allows the ECM to detect the oil pressure is
higher than the specified value. The ECM outputs the OFF sig
-
nal to the combination meter through the CAN and then turns
off the oil pressure warning lamp.
AK602226AD
5V
Knock sensor
Piezoelectric elementECM
AK602575AC
Barometric pressure sensor
(built in ECM)
AK602587AC
Oil
pressure
Contact switch
Page 112 of 241
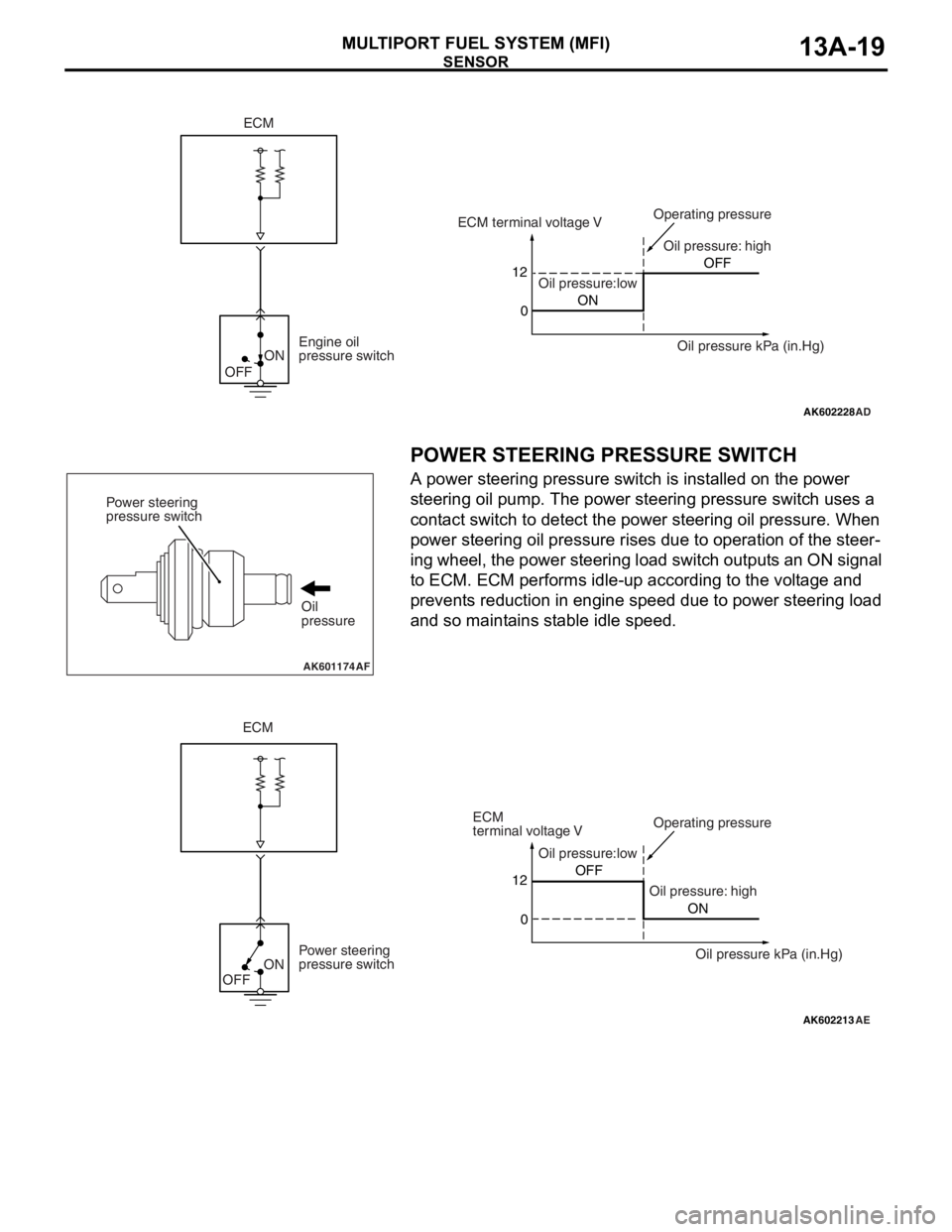
SENSOR
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-19
.
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
A power steering pressure switch is installed on the power
steering oil pump. The power steering pressure switch uses a
contact switch to detect the power steering oil pressure. When
power steering oil pressure rises due to operation of the steer
-
ing wheel, the power steering load switch outputs an ON signal
to ECM. ECM performs idle-up according to the voltage and
prevents reduction in engine speed due to power steering load
and so maintains stable idle speed.
.
AK602228
ON
OFF
AD
12
0ONOFF ECM terminal voltage V
Oil pressure:lowOil pressure: high Operating pressure
Oil pressure kPa (in.Hg) Engine oil
pressure switch
ECM
AK601174AF
Power steering
pressure switch
Oil
pressure
AK602213
ON
OFF
AE
Oil pressure:low
Oil pressure: highOperating pressure
Power steering
pressure switch12
0OFF
ON
ECM
ECM
terminal voltage V
Oil pressure kPa (in.Hg)
Page 118 of 241
ACTUATOR
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-25
IGNITION COIL
Refer to GROUP 16 − Ignition Coil P.16-2.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) VALVE
Refer to GROUP 17 − Emission Control − Exhaust Gas Recircu-
lation (EGR) System P.17-12.
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION PURGE SOLENOID
Refer to GROUP 17 − Emission Control − Evaporative Emission
Control System
P.17-11.
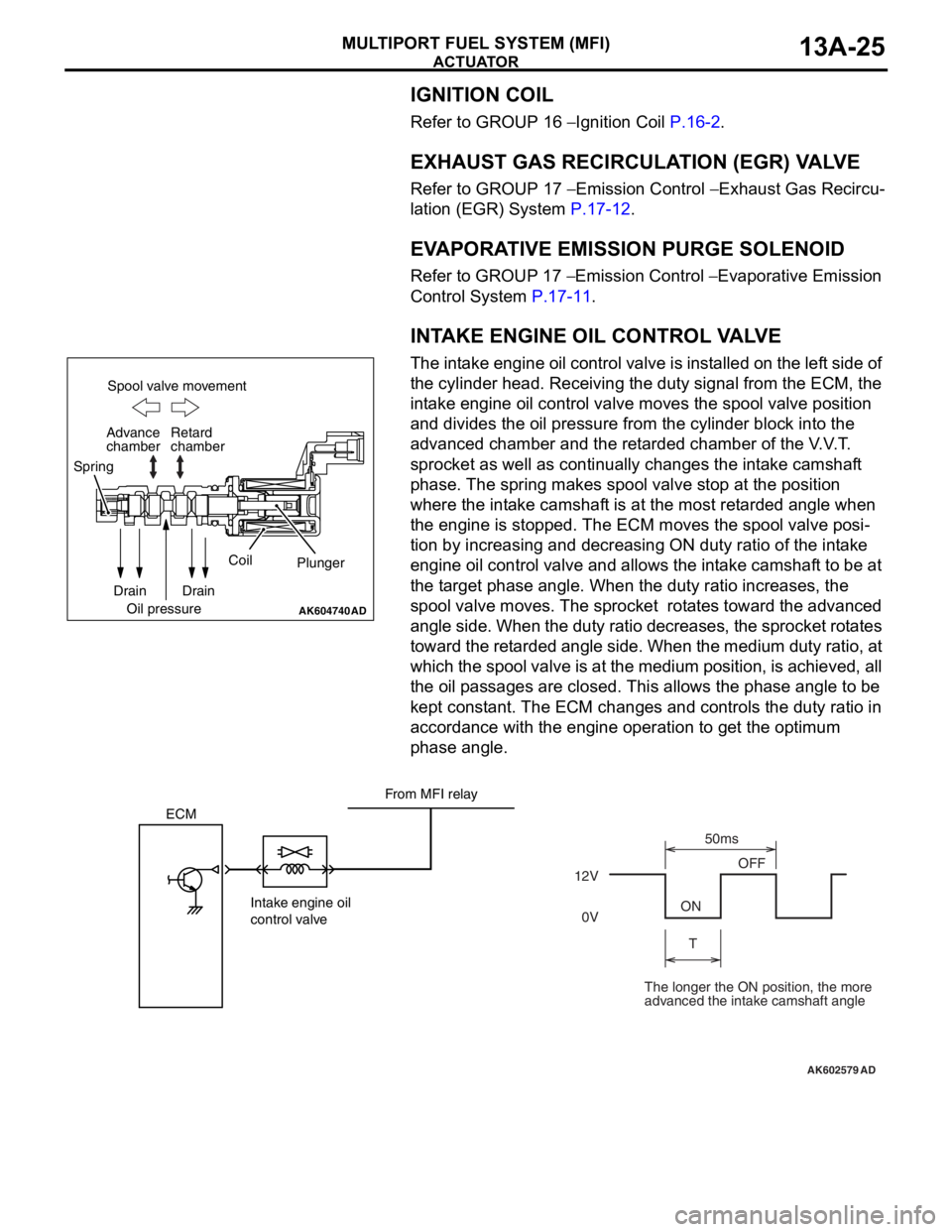
INTAKE ENGINE OIL CONTROL VALVE
The intake engine oil control valve is installed on the left side of
the cylinder head. Receiving the duty signal from the ECM, the
intake engine oil control valve moves the spool valve position
and divides the oil pressure from the cylinder block into the
advanced chamber and the retarded chamber of the V.V.T.
sprocket as well as continually changes the intake camshaft
phase. The spring makes spool valve stop at the position
where the intake camshaft is at the most retarded angle when
the engine is stopped. The ECM moves the spool valve posi
-
tion by increasing and decreasing ON duty ratio of the intake
engine oil control valve and allows the intake camshaft to be at
the target phase angle. When the duty ratio increases, the
spool valve moves. The sprocket rotates toward the advanced
angle side. When the duty ratio decreases, the sprocket rotates
toward the retarded angle side. When the medium duty ratio, at
which the spool valve is at the medium position, is achieved, all
the oil passages are closed. This allows the phase angle to be
kept constant. The ECM changes and controls the duty ratio in
accordance with the engine operation to get the optimum
phase angle.
AK604740AD
Spool valve movement
Retard
chamber
Spring
Drain
Oil pressureCoil
Plunger
Drain Advance
chamber
AK602579
ECM
Intake engine oil
control valve12VOFF
ON
T50ms
0V
AD
From MFI relay
The longer the ON position, the more
advanced the intake camshaft angle
Page 119 of 241
ACTUATOR
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-26
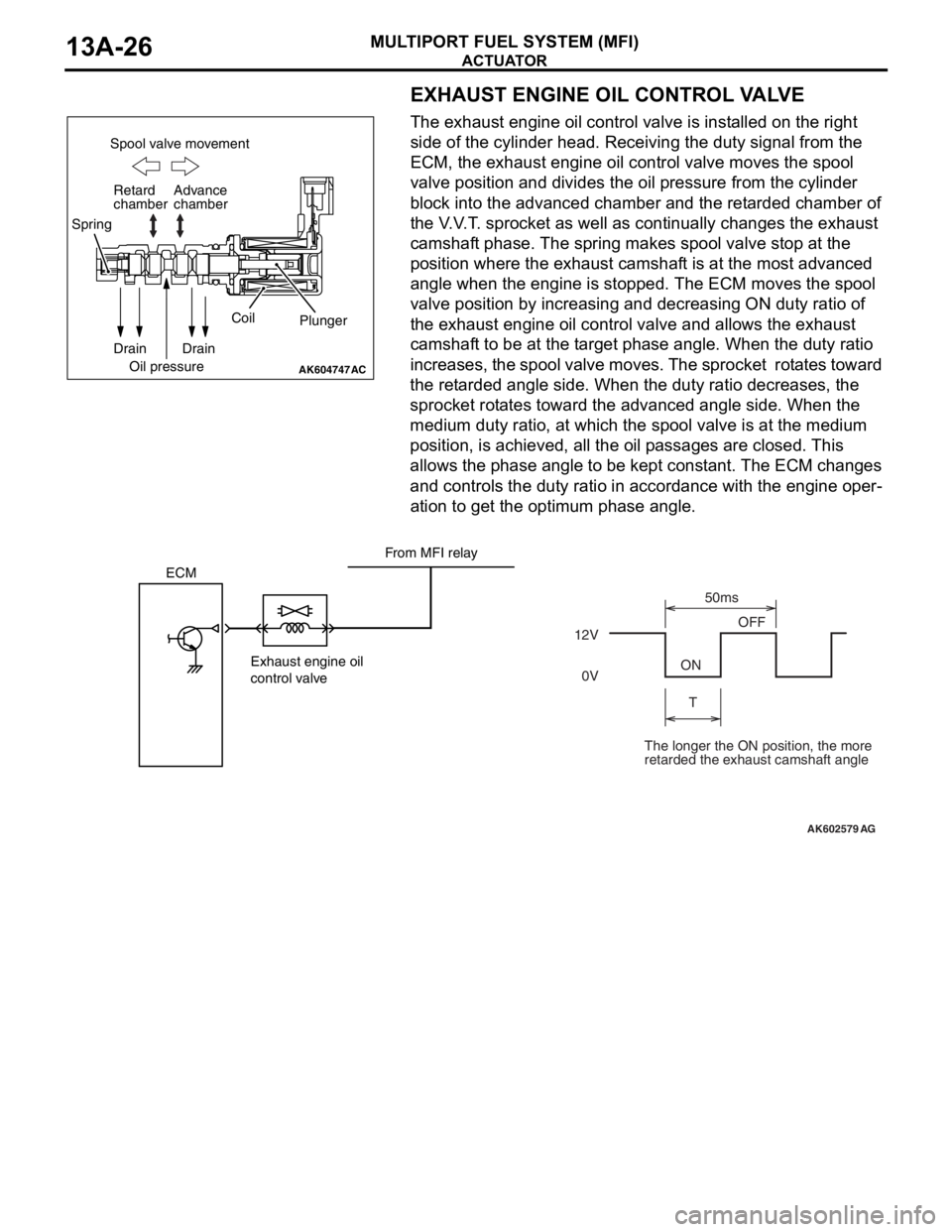
EXHAUST ENGINE OIL CONTROL VALVE
The exhaust engine oil control valve is installed on the right
side of the cylinder head. Receiving the duty signal from the
ECM, the exhaust engine oil control valve moves the spool
valve position and divides the oil pressure from the cylinder
block into the advanced chamber and the retarded chamber of
the V.V.T. sprocket as well as continually changes the exhaust
camshaft phase. The spring makes spool valve stop at the
position where the exhaust camshaft is at the most advanced
angle when the engine is stopped. The ECM moves the spool
valve position by increasing and decreasing ON duty ratio of
the exhaust engine oil control valve and allows the exhaust
camshaft to be at the target phase angle. When the duty ratio
increases, the spool valve moves. The sprocket rotates toward
the retarded angle side. When the duty ratio decreases, the
sprocket rotates toward the advanced angle side. When the
medium duty ratio, at which the spool valve is at the medium
position, is achieved, all the oil passages are closed. This
allows the phase angle to be kept constant. The ECM changes
and controls the duty ratio in accordance with the engine oper
-
ation to get the optimum phase angle.
AK604747
Spool valve movement
Retard
chamber
Spring
Drain
Oil pressureCoil
Plunger
Drain Advance
chamber
AC
AK602579
ECM
Exhaust engine oil
control valve12VOFF
ON
T50ms
0V
AG
From MFI relay
The longer the ON position, the more
retarded the exhaust camshaft angle
Page 120 of 241
ACTUATOR
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-27
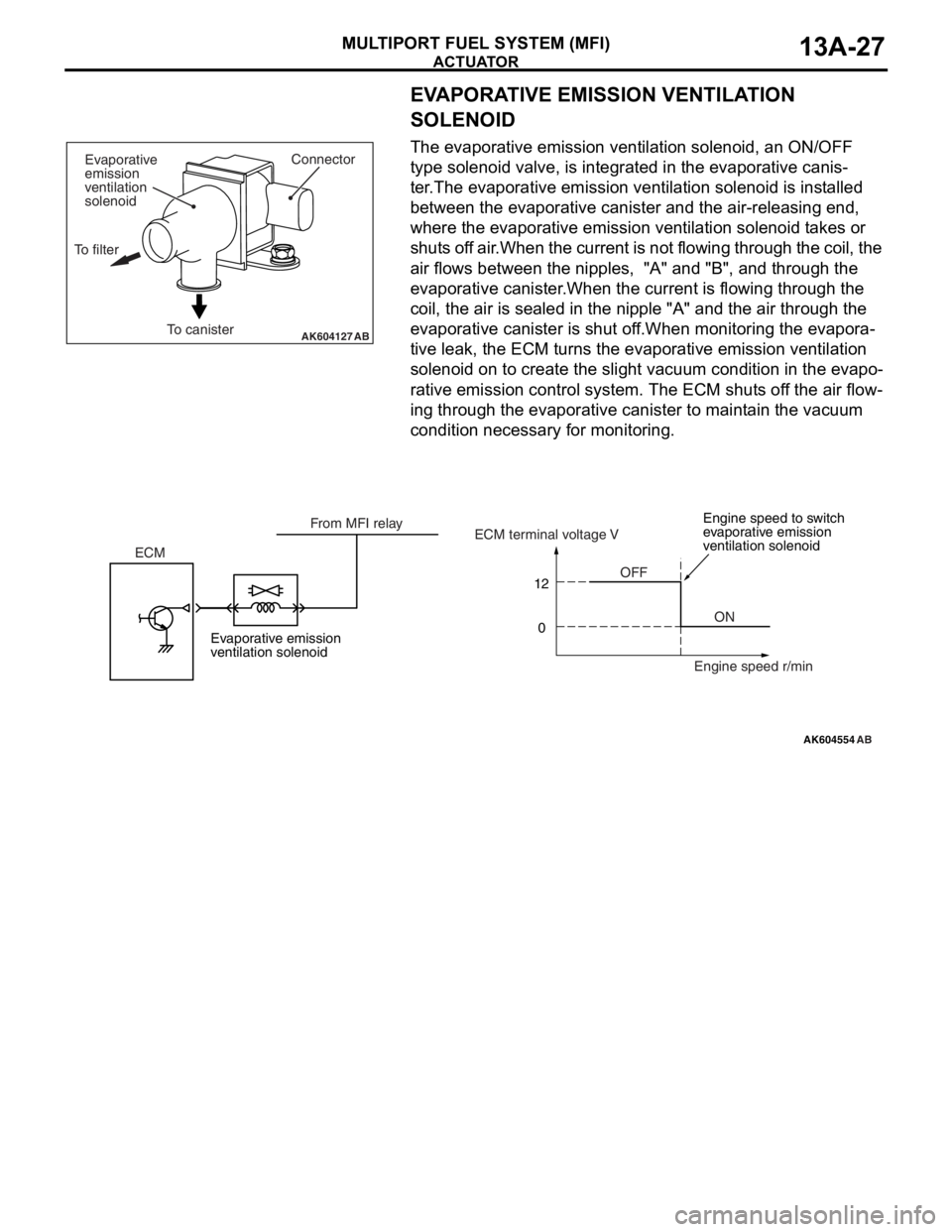
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION VENTILATION
SOLENOID
The evaporative emission ventilation solenoid, an ON/OFF
type solenoid valve, is integrated in the evaporative canis
-
ter.The evaporative emission ventilation solenoid is installed
between the evaporative canister and the air-releasing end,
where the evaporative emission ventilation solenoid takes or
shuts off air.When the current is not flowing through the coil, the
air flows between the nipples, "A" and "B", and through the
evaporative canister.When the current is flowing through the
coil, the air is sealed in the nipple "A" and the air through the
evaporative canister is shut off.When monitoring the evapora
-
tive leak, the ECM turns the evaporative emission ventilation
solenoid on to create the slight vacuum condition in the evapo
-
rative emission control system. The ECM shuts off the air flow-
ing through the evaporative canister to maintain the vacuum
condition necessary for monitoring.
AK604127ABTo canisterConnector
Evaporative
emission
ventilation
solenoid
To filter
AK604554
12
0
AB
OFF
ON ECMECM terminal voltage V
Engine speed r/min From MFI relay
Evaporative emission
ventilation solenoidEngine speed to switch
evaporative emission
ventilation solenoid
Page 128 of 241
IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-35
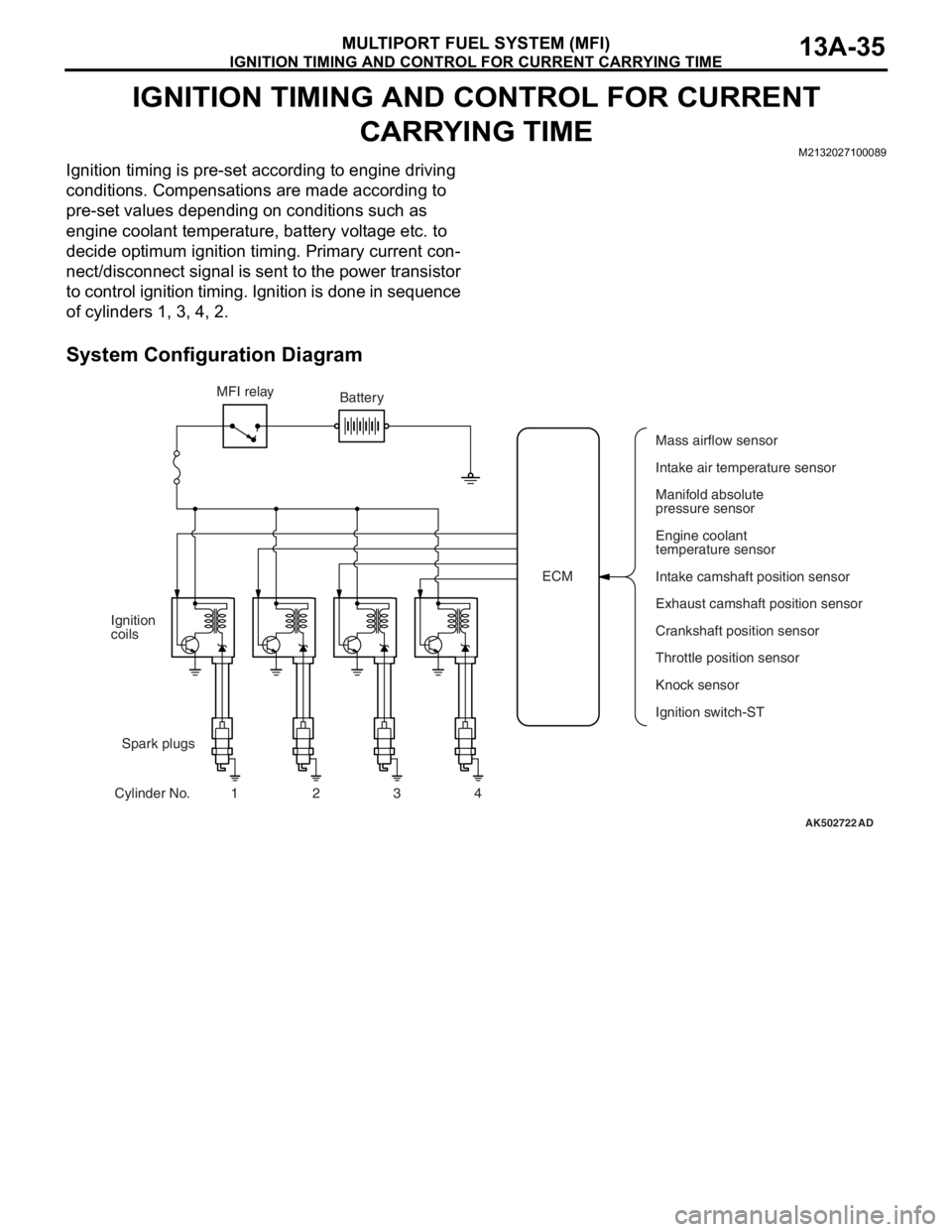
IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT
CARRYING TIME
M2132027100089
Ignition timing is pre-set according to engine driving
conditions. Compensations are made according to
pre-set values depending on conditions such as
engine coolant temperature, battery voltage etc. to
decide optimum ignition timing. Primary current con
-
nect/disconnect signal is sent to the power transistor
to control ignition timing. Ignition is done in sequence
of cylinders 1, 3, 4, 2.
System Configuration Diagram
AK502722AD
ECM MFI relay
Spark plugs Ignition
coils
Cylinder No. 1 2 3 4Battery
Mass airflow sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Manifold absolute
pressure sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Intake camshaft position sensor
Exhaust camshaft position sensor
Crankshaft position sensor
Knock sensor
Ignition switch-ST Throttle position sensor
Page 132 of 241
THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL AND IDLE SPEED CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-39
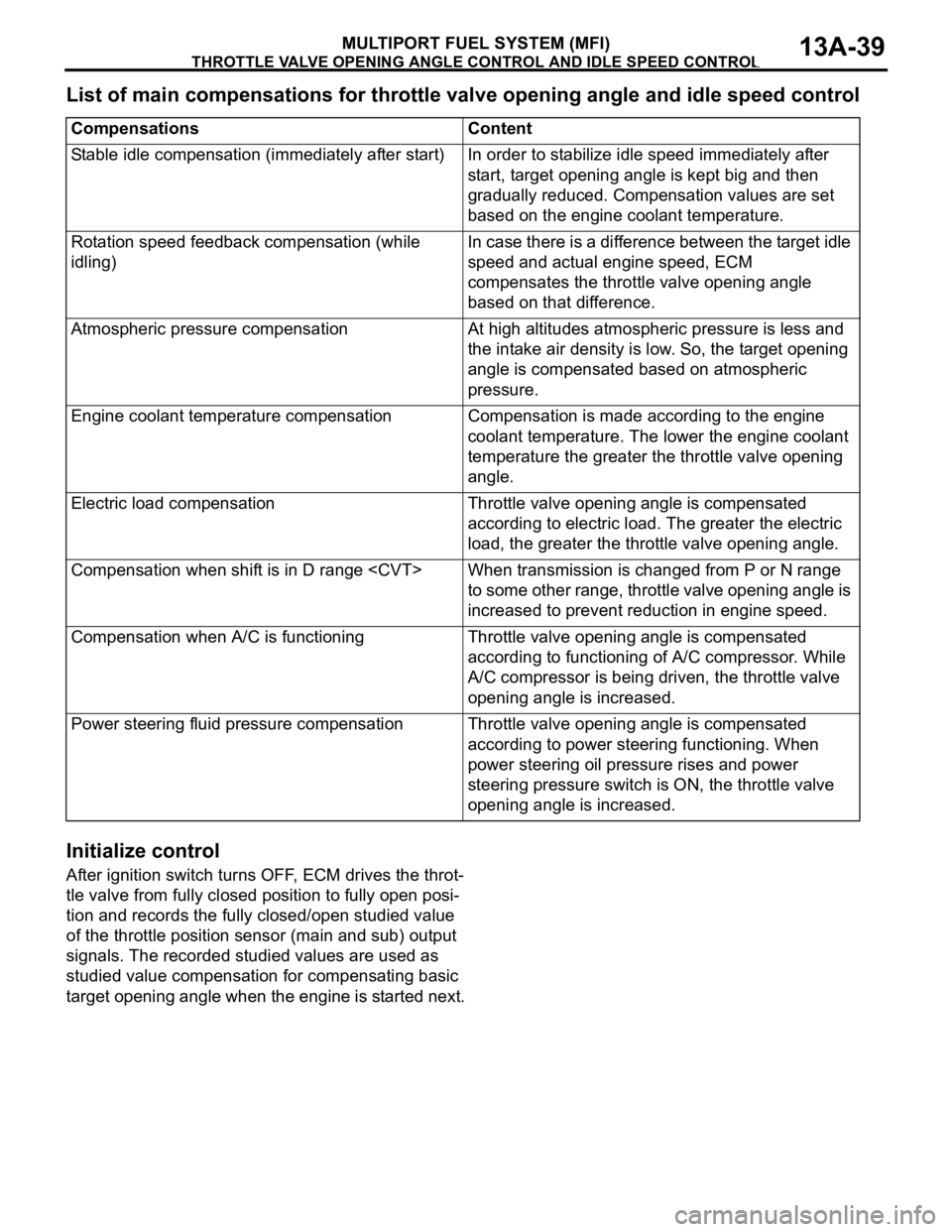
List of main compensations for throttle valve opening angle and idle speed control
Initialize control
After ignition switch turns OFF, ECM drives the throt-
tle valve from fully closed position to fully open posi-
tion and records the fully closed/open studied value
of the throttle position sensor (main and sub) output
signals. The recorded studied values are used as
studied value compensation for compensating basic
target opening angle when the engine is started next.
CompensationsContent
Stable idle compensation (immediately after start)In order to stabilize idle speed immediately after
start, target opening angle is kept big and then
gradually reduced. Compensation values are set
based on the engine coolant temperature.
Rotation speed feedback compensation (while
idling)In case there is a difference between the target idle
speed and actual engine speed, ECM
compensates the throttle valve opening angle
based on that difference.
Atmospheric pressure compensationAt high altitudes atmospheric pressure is less and
the intake air density is low. So, the target opening
angle is compensated based on atmospheric
pressure.
Engine coolant temperature compensationCompensation is made according to the engine
coolant temperature. The lower the engine coolant
temperature the greater the throttle valve opening
angle.
Electric load compensationThrottle valve opening angle is compensated
according to electric load. The greater the electric
load, the greater the throttle valve opening angle.
Compensation when shift is in D range
to some other range, throttle valve opening angle is
increased to prevent reduction in engine speed.
Compensation when A/C is functioningThrottle valve opening angle is compensated
according to functioning of A/C compressor. While
A/C compressor is being driven, the throttle valve
opening angle is increased.
Power steering fluid pressure compensationThrottle valve opening angle is compensated
according to power steering functioning. When
power steering oil pressure rises and power
steering pressure switch is ON, the throttle valve
opening angle is increased.
Page 133 of 241
MIVEC (Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing Electronic Control System)
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-40
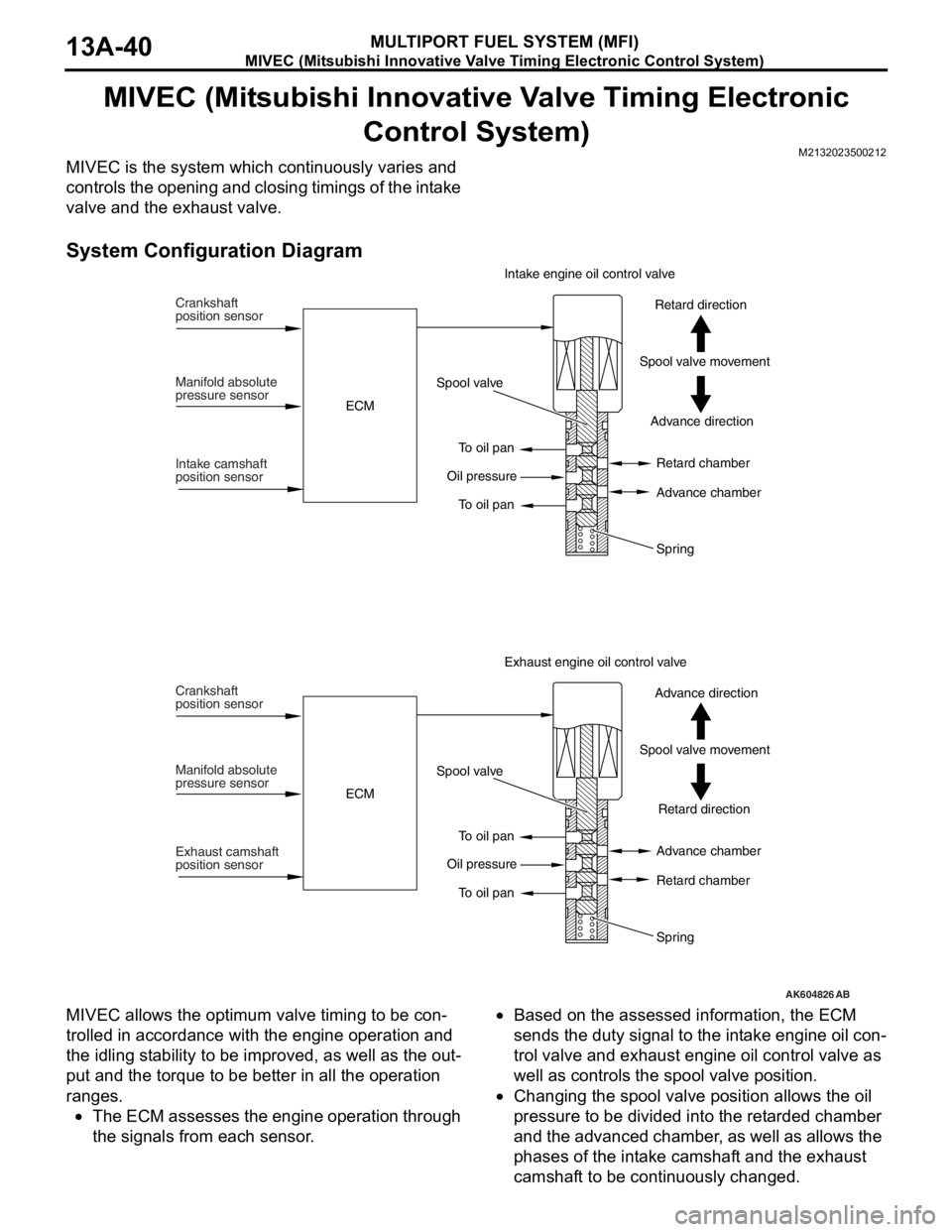
MIVEC (Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing Electronic
Control System)
M2132023500212
MIVEC is the system which continuously varies and
controls the opening and closing timings of the intake
valve and the exhaust valve.
System Configuration Diagram
MIVEC allows the optimum valve timing to be con-
trolled in accordance with the engine operation and
the idling stability to be improved, as well as the out
-
put and the torque to be better in all the operation
ranges.
•The ECM assesses the engine operation through
the signals from each sensor.
•Based on the assessed information, the ECM
sends the duty signal to the intake engine oil con
-
trol valve and exhaust engine oil control valve as
well as controls the spool valve position.
•Changing the spool valve position allows the oil
pressure to be divided into the retarded chamber
and the advanced chamber, as well as allows the
phases of the intake camshaft and the exhaust
camshaft to be continuously changed.
AK604826AB
Crankshaft
position sensor
Manifold absolute
pressure sensor
Intake camshaft
position sensorECMSpool valve
To oil pan
To oil pan Oil pressureAdvance direction Spool valve movementRetard direction Intake engine oil control valve
Retard chamber
Advance chamber
Spring
Crankshaft
position sensor
Manifold absolute
pressure sensor
Exhaust camshaft
position sensorECMSpool valve
To oil pan
To oil pan Oil pressureRetard direction Spool valve movementAdvance direction Exhaust engine oil control valve
Advance chamber
Retard chamber
Spring