Oil pressure MITSUBISHI MONTERO 1987 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1987, Model line: MONTERO, Model: MITSUBISHI MONTERO 1987 1.GPages: 284, PDF Size: 14.74 MB
Page 266 of 284

24-30 AIR-CONDITIONING -Service Adjustunent Procedures
(4) If the sight glass shows foam or bubbles, the systpm could be low on charge. Occasional foam or bubbles are
normal when the ambient temperature is above 43”C(110”F) or below 21”C(7O”F).
Adjust the engine speed to 1,500 rpm. Block the airflow through the condenser to increase the compressor
discharge pressure to 1,422 to 1,520 kPa (20$ to 220 dsi). If sight glass still shows bubbles or foam, system charge
level is low.
The refrigerant system will not be low on charge unless there is a leak. Find and repair the leak. If the leak can be
repaired without discharging the system an oil level check is not necessary. Use the procedure for correcting low
refrigerant level found in the Refrigerant Sy$em Service Procedure Section.
FUSIBLE PLUG
When ambient temperature of the fusible plug reach& 105~221~F), the fusible plug melts and the refrigerant in
the system is released.
Once the fusible plug is operated, it cannot be used again.
SO, it is necessary to install new one and charge the refrigerant in the system.
Low pressure
switch , LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
The Low Pressure Switch, located on the liquid line, is wired in
series with the magnetic clutch. It cuts off the electrical power
supply to the clutch when refrigerant pressure drops below the
cont$ol point of the switch. Whenever the system is inactivated by
the low pressure switch due to refrigerant loss, the refrigerant oil
may have been lost. Therefore, to prevent damage to the com-
pressor due to operation without sufficient lubrication, the leak
must be repaired and the compressor oil level checked before final
charge of the system. The switch is a sealed, factory calibrated
unit. No attempt should be made to adjust or otherwise repair it.
If it is found to be faulty it must be replaced.
To Test the Low Pressure Switch (Engine Off)
(1) Jump the wire leads.
(2) Press the air conditioner switch and blower switch on.
(3) Momentarily turn the ignition switch on (do not crank the en-
gine), listen for the compressor clutch engaging.
(4) If the clutch does not engage, the fin thermostat, water tem-
perature switch or fuse may be faulty.
(5) If clutch engages, connect the manifold gauge set and
read pressure. At pressure of 210 kPa (30 psi) or above,
switch must actuate the clutch.
If the pressure is below 210 kPa (30 psi), the refrigerant
system is low in charge. For corrective action refer to
refrigerant leak repair procedure.
(6) Reconnect boot on switch and perform step number 3.
If the clutch does not engage, discharge the system, replace
the switch, and recharge the system.
[
STB Revision
Page 272 of 284
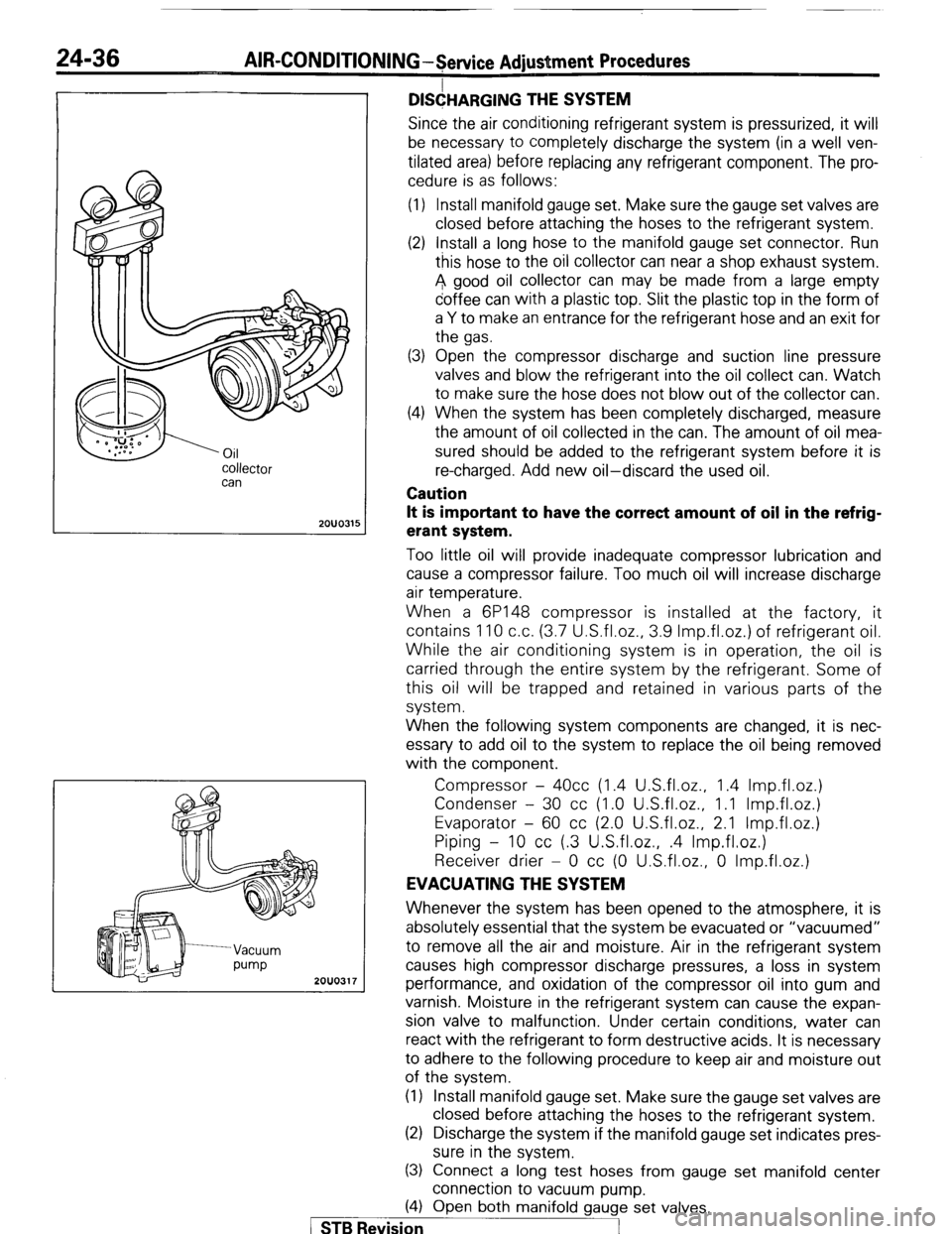
COllector
can
2OUO315
24-36 AIR-CONDITIONING-Service Adjustment Procedures
D&ARG,NG THE SYSTEM
Since the air conditioning refrigerant system is pressurized, it will
be necessary to completely discharge the system (in a well ven-
tilated area) before replacing any refrigerant component. The pro-
cedure is as follows:
(1) Install manifold gauge set. Make sure the gauge set valves are
closed before attaching the hoses to the refrigerant system.
(2) Install a long hose to the manifold gauge set connector. Run
this hose to the oil collector can near a shop exhaust system.
A good oil collector can may be made from a large empty
coffee can with a plastic top. Slit the plastic top in the form of
a Y to make an entrance for the refrigerant hose and an exit for
the gas.
(3) Open the compressor discharge and suction line pressure
valves and blow the refrigerant into the oil collect can. Watch
to make sure the hose does not blow out of the collector can.
(4) When the system has been completely discharged, measure
the amount of oil collected in the can. The amount of oil mea-
sured should be added to the refrigerant system before it is
re-charged. Add new oil-discard the used oil.
Caution
It is important to have the correct amount of oil in the refrig-
erant system.
Too little oil will provide inadequate compressor lubrication and
cause a compressor failure. Too much oil will increase discharge
air temperature.
When a 6P148 compressor is installed at the factory, it
contains 110 c.c. (3.7 U.S.fl.oz., 3.9 Imp.fl.oz.) of refrigerant oil.
While the air conditioning system is in operation, the oil is
carried through the entire system by the refrigerant. Some of
this oil will be trapped and retained in various parts of the
system.
When the following system components are changed, it is nec-
essary to add oil to the system to replace the oil being removed
with the component.
Compressor - 4Occ (1.4 U.S.fl.oz., 1.4 Imp.fl.oz.)
Condenser - 30 cc (1.0 U.S.fl.oz., 1.1 Imp.fl.oz.)
Evaporator - 60 cc (2.0 U.S.fl.oz., 2.1 Imp.fl.oz.)
Piping - 10 cc (.3 U.S.fl.oz., .4 Imp.fl.oz.)
Receiver drier - 0 cc (0 U.S.fl.oz., 0 Imp.fl.oz.)
EVACUATING THE SYSTEM
2OUO31
Whenever the system has been opened to the atmosphere, it is
absolutely essential that the system be evacuated or “vacuumed”
to remove all the air and moisture. Air in the refrigerant system
causes high compressor discharge pressures, a loss in system
performance, and oxidation of the compressor oil into gum and
varnish. Moisture in the refrigerant system can cause the expan-
sion valve to malfunction. Under certain conditions, water can
react with the refrigerant to form destructive acids. It is necessary
to adhere to the following procedure to keep air and moisture out
of the system.
(1) Install manifold gauge set. Make sure the gauge set valves are
closed before attaching the hoses to the refrigerant system.
(2) Discharge the system if the manifold gauge set indicates pres-
sure in the system.
(3) Connect a long test hoses from gauge set manifold center
connection to vacuum pump.
(4) Open both manifold gauge set valves.
/
/vision I
Page 277 of 284

AIR-CONDITIONING -Service Adjustment Procedures 24-41
COMPRESSOR NOISE NWLM
When investigating an air conditioning related noise, you must first know the conditions when the noise occurs.
These conditions are: weather, vehicle speed, in gear or neutral, engine temperature or any other special
conditions.
Noises that develop during air- conditioning operation can often be misleading. For example: what sounds like a
failed front bearing or connecting rod, may be caused by loose bolts, nuts, mounting brackets, or a loose clutch
assembly. Verify accessory drive belt tension (power
steering, alternator or air pump). Improper accessory drive belt
tension can cause a misleading noise when the compressor is engaged and little or no noise when the compressor
is disengaged.
Drive belts are speed sensitive. That is, at different engine speeds, and depending upon belt tension, belts can
develop unusual noises that are often mistaken for mechanical problems within the compressor.
Adjustment Procedures
(1) Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate conditions as much as possible. Switch compressor on and off several
times to clearly identify compressor noise.
To duplicate high ambient conditions (high head pressure), restrict air-flow through
condenser. Install
manifold gauge set to make sure discharge pressure does not exceed 2,070 kPa (300 psi).
(2) Tighten all compressor mounting bolts, clutch mounting bolt, and compressor drive belt. Check to assure clutch
coil is tight (no rotation or wobble).
(3) Check refrigerant hoses for rubbing or interference that can cause unusual noises.
(4) Check refrigerant charge (See “Charging the System”).
(5) Recheck compressor noise as in Step 1.
(6) If noise still exists, loosen compressor mounting bolts and retorque. Repeat Step 1.
(7) If noise continues, replace compressor and repeat Step 1.
1 STB Revision
Page 284 of 284
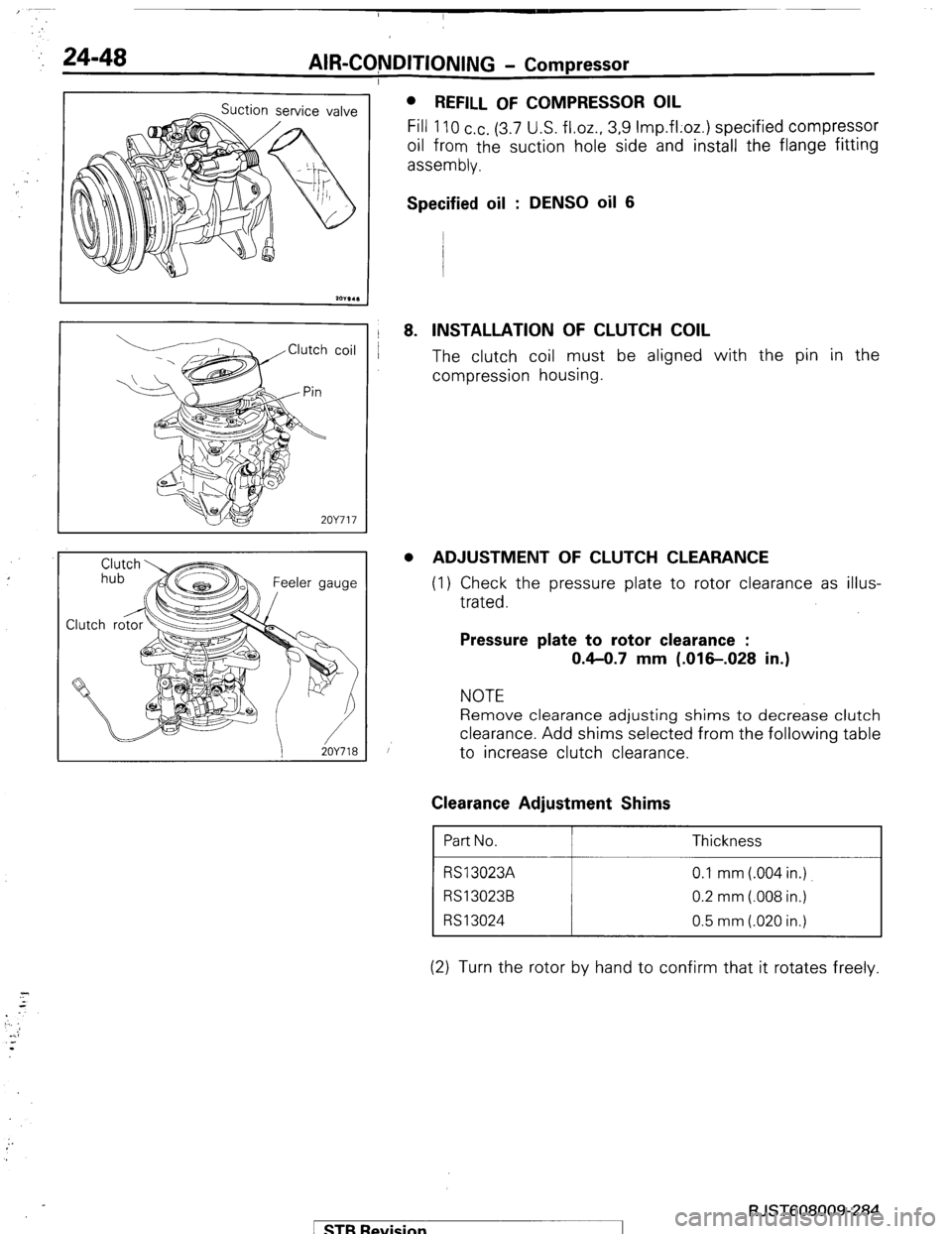
,: 24-48 AIR-CQNDITIONING - Compressor
I
2OY717
1 iOY718 l
REFILL OF COMPRESSOR OIL
Fill 110 cc. (3.7 U.S. fl.oz., 3.9 Imp.fl;oz.) specified compressor
oil from the suction hole side and install the flange fitting
assembly.
Specified oil : DENS0 oil 6
8. INSTALLATION OF CLUTCH COIL
The clutch coil must be aligned with the pin in the
compression housing.
. ADJUSTMENT OF CLUTCH CLEARANCE
(1) Check the pressure plate to rotor clearance as illus-
trated.
Pressure plate to rotor clearance :
0.4-0.7 mm (.016-.028 in.)
NOTE
Remove clearance adjusting shims to decrease clutch
clearance. Add shims selected from the following table
to increase clutch clearance.
Clearance Adjustment Shims
Part No. Thickness
RSI 3023A 0.1 mm (.004 in.).
RSI 3023B 0.2 mm (.008 in.)
RSI 3024 0.5 mm (.020 in.)
(2) Turn the rotor by hand to confirm that it rotates freely.
:.
RJST608009-284
1 STB Revision
-1