steering MITSUBISHI MONTERO 2000 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: MONTERO, Model: MITSUBISHI MONTERO 2000Pages: 1839, PDF Size: 29.19 MB
Page 414 of 1839
Page 420 of 1839
Page 464 of 1839

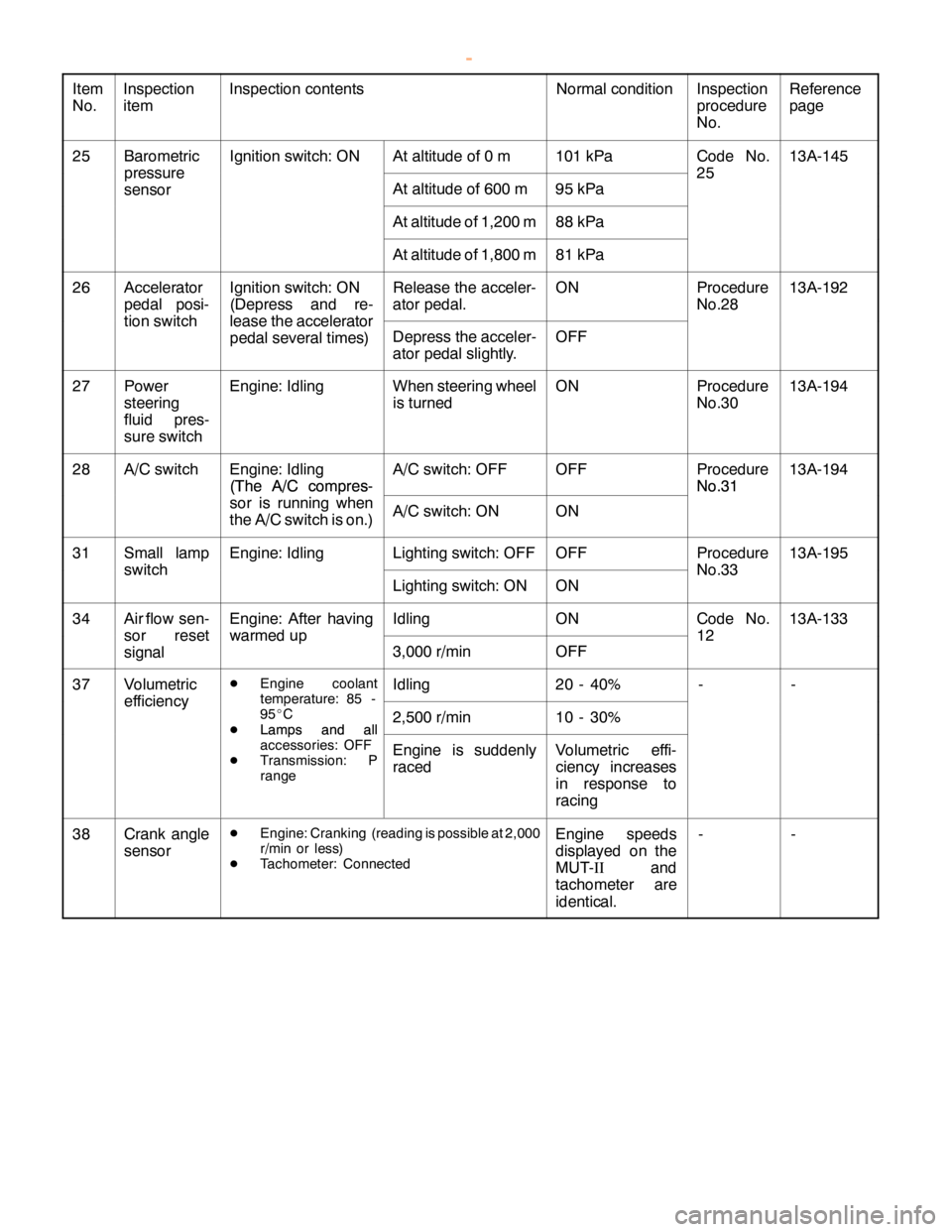
15
DRIVE CYCLE
Performing the running test of the car using the following five drive cycle patterns makes it possible to
monitor all the diagnosis codes that are required for operation of the car in order to determine if the
applicable system is operating properly or not.
In other words, doing such a drive allows to regenerate any kind of trouble which involves illuminating the
Engine Warning Lamp (Check Engine Lamp) and to verify the repair procedure has eliminated the trouble
[the Engine Warning Lamp (Check Engine Lamp) is no longer illuminated].
Caution
Two technicians should always be in the vehicle when carrying out a test drive.
NOTE
Check that the diagnosis code is not output before traveling in the Drive cycle pattern. Erase the diagnosis
code if it has been output.
DRIVE CYCLE PATTERN LIST
PROCEDURE MONITOR ITEM DIAGNOSIS CODE
Catalytic converter monitor P04201
Heated oxygen sensor
2 Fuel trim monitor P0170
3 Feed back monitor P0125
4 Other monitor P0136, P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205,
P0206, P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304,
P0305, P0306, P0325
NOTE
The vehicle speed sensor (P0500) and the power steering fluid pressure switch (P0551) are used to
determine if the system is operating properly or not through use of the Data List function of the MUT-II.
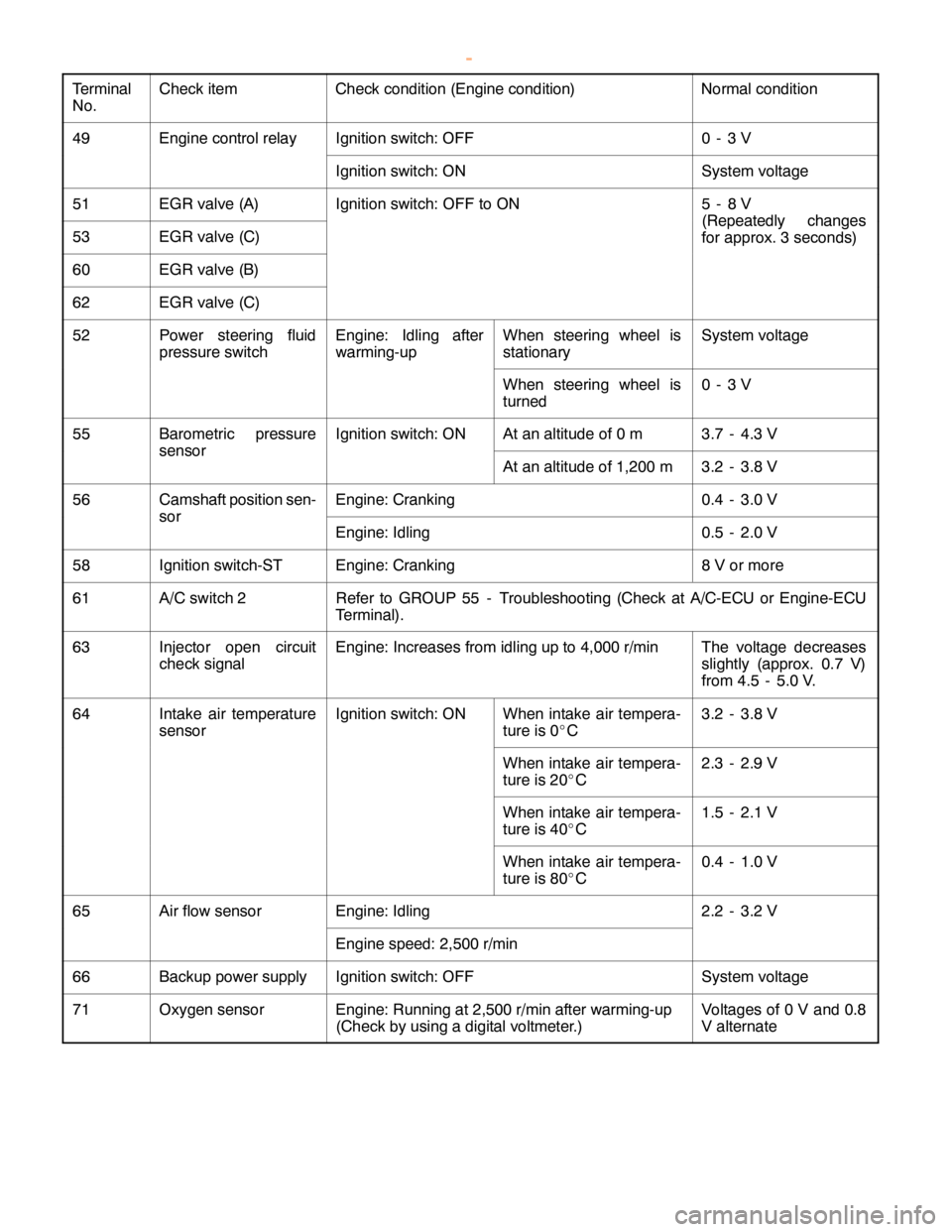
2001 PAJERO/MONTERO WAGON Workshop Manual 6G74
GDI - Troubleshooting
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 527 of 1839
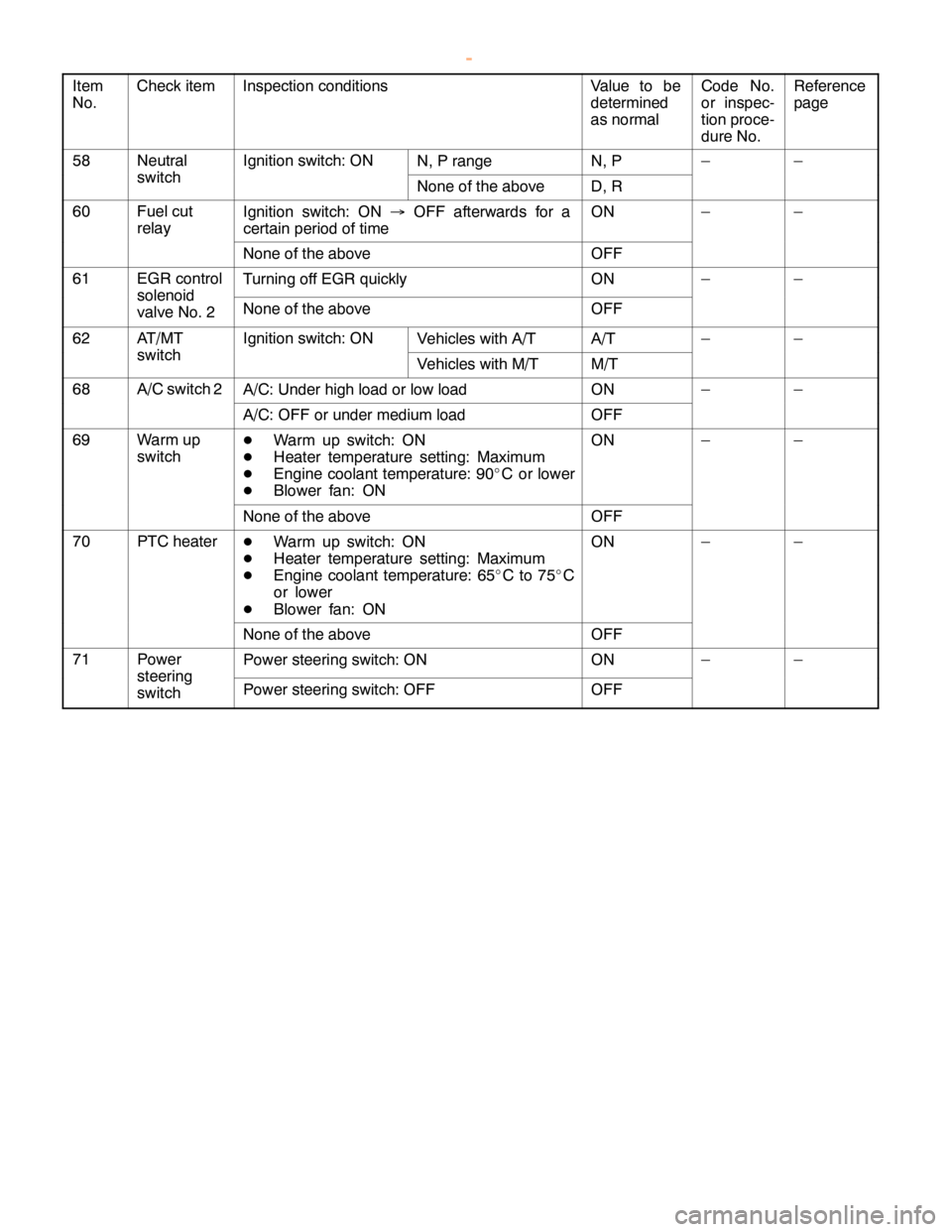
DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -Troubleshooting13C-36
Item
No.Reference
page Code No.
or inspec-
tion proce-
dure No. Value to be
determined
as normal Inspection conditions Check item
58NeutralIgnition switch: ONN, P rangeN, P––
switchNone of the aboveD, R
60Fuel cut
relayIgnition switch: ON®OFF afterwards for a
certain period of timeON––
None of the aboveOFF
61EGR controlTurning off EGR quicklyON––
solenoid
valve No. 2None of the aboveOFF
62AT/MTIgnition switch: ONVehicles with A/TA/T––
switchVehicles with M/TM/T
68A/C switch 2A/C: Under high load or low loadON––
A/C: OFF or under medium loadOFF
69Warm up
switchDWarm up switch: ON
DHeater temperature setting: Maximum
DEngine coolant temperature: 90_C or lower
DBlower fan: ONON––
None of the aboveOFF
70PTC heaterDWarm up switch: ON
DHeater temperature setting: Maximum
DEngine coolant temperature: 65_Cto75_C
or lower
DBlower fan: ONON––
None of the aboveOFF
71PowerPower steering switch: ONON––
steering
switchPower steering switch: OFFOFF
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1165 of 1839

POWER PLANT MOUNT - No.1 Crossmember32-7
No.1 CROSSMEMBER
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Caution
1. Before removing the steering wheel and airbag module assembly, always refer to GROUP 52B
- Service Precautions, Airbag Module and Clock Spring. Also, set the front wheels so that
they are facing straight forward, and remove the ignition key. If you fail to do this, the SRS
clock spring will be damaged, causing the SRS airbag to be inoperative and serious injury.
2. *: Indicates parts which should be initially tightened, and then fully tightened after placing
the vehicle horizontally and loading the full weight of the engine on the vehicle body.
Pre-removal Operation
DUnder Cover Removal
DDrive Shaft Removal
(Refer to GROUP 26.)
DDifferential Carrier and No.2 Crossmember
Assembly Removal (Refer to GROUP 26 -
Freewheel Assembly and Differential Carrier.)
DUpper Arm Removal
(Refer to GROUP 33A.)
DLower Arm Removal
(Refer to GROUP 33A.)
DStabilizer Bar Removal
(Refer to GROUP 33A.)
DEngine Oil Cooler Removal<6G7>
(Refer to GROUP 12.)
DAir Cleaner Removal<4M4>
(Refer to GROUP 15.)
DIntercooler Removal<4M4>
(Refer to GROUP 15.)
DEngine Cover Removal
(Refer to GROUP 11A - Timing Belt.)
DRadiator Removal
(Refer to GROUP 14.)
DPower Steering Fluid Draining
(Refer to GROUP 37A - On - vehicle Service.)Post - installation Operations
DDifferential Carrier and No.2 Crossmember
Assembly Installation (Refer to GROUP 26 -
Freewheel Assembly and Differential Carrier.)
DDrive Shaft Installation
(Refer to GROUP 26.)
DLower Arm Installation
(Refer to GROUP 33A.)
DUpper Arm Installation
(Refer to GROUP 33A.)
DStabilizer Bar Installation
(Refer to GROUP 33A.)
DAir Cleaner Installation<4M4>
(Refer to GROUP 15.)
DIntercooler Installation<4M4>
(Refer to GROUP 15.)
DRadiator Installation
(Refer to GROUP 14.)
DEngine Oil Cooler Installation
(Refer to GROUP 12.)
DPower Steering Fluid Supplying
(Refer to GROUP 37A - On - vehicle Service.)
DPower Steering Fluid Line Bleeding
(Refer to GROUP 37A - On - vehicle Service.)
DPress the dust cover with a finger tocheck whether
the dust cover is cracked or damaged.
DChecking Steering Wheel Position with Wheels
StraightAhead
DFront Wheel AlignmentCheck and Adjustment
(Refer to GROUP 37A - On - vehicle Service.)
DUnder Cover Installation
DEngine Cover Installation
(Refer to GROUP 11A - Timing Belt.)
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1265 of 1839

ABS <4WD> -General Information35B-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
ABS has been adopted as standard equipment
in all vehicles to maintain directional stability and
steering performance during sudden braking.
The ABS control method used is a 4-sensor,
4-channel method (previous models: 4-sensor,
3- channel method
)which allows the brake
pressures for all four wheels to be controlled
independently of each other. The system has the
following features.
DEBD
*(Electronic Brake force Distribution
system) control has been added to provide the
ideal braking force for the rear wheels.DThe hydraulic unit function has been integrated
with the hydraulic brake booster (HBB).
DSelect solenoid valves (two valves for FL and
FR) have been adopted in order to reduce the
pedal kickback and improve the operation
feeling when the ABS is operating.
DIndependent 4-wheel control is carried out wile
the vehicle is turning in order to increase the
braking force.
NOTE
*EBD: Electronic Brake-force Distribution
EBD CONTROL
In ABS, electronic control method is used whereby
the rear wheel brake hydraulic pressure during
braking is regulated by rear wheel control solenoid
valves in accordance with the vehicle’s rate of
deceleration and the front and rear wheel slippage
which are calculated from the signals received from
the various wheel sensors. EBD control is a control
system which provides a high level of control for
both vehicle braking force and vehicle stability. The
system has the following features.
DBecause the system provides the optimum rear
wheel braking force regardless of the vehicle
laden condition and the condition of the road
surface, the system reduces the required pedal
depression force, particularly when the vehicle
is heavily laden or driving on road surfaces
with high frictional coefficients.DBecause the duty placed on the front brakes
has been reduced, the increases in pad
temperature can be controlled during front
brakes applying to improve the wear resistance
characteristics of the pad.
DControl valves such as the proportioning valve
are no longer required.
SPECIFICATIONS
ItemSpecifications
ABS control method4-sensor, 4-channel
No. of ABS rotor teethFront50
Rear50
ABS speed sensorTypeMagnet coil type
Gap between sensor and rotor mm0.9 (non-adjustable type)
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1309 of 1839

STEERING
Click on the applicable bookmark to selected the required model year.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1310 of 1839

37A-1
STEERING
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 2..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 5.................
LUBRICANTS 5..............................
SEALANT AND ADHESIVE 5.................
SPECIAL TOOLS 6..........................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 8.....................
Steering Wheel Free Play Check 8..............
Steering Angle Check 8........................
Tie Rod End Ball Joint Starting Torque Check 8..
Stationary Steering Effort Check 9...............
Steering Wheel Returnability Check 9............
Oil Pump Belt Tension Check <6G7,4D5> 9......Power Steering Fluid Level Check 10............
Power Steering Fluid Replacement 10...........
Power Steering System Bleeding 10.............
Oil Pump Pressure Test 11.....................
Power Steering Oil Pressure Switch Check
<6G7,4M4> 12.................................
Ball Joint Dust Cover Check 12.................
STEERING WHEEL AND SHAFT* 13.........
POWER STEERING GEAR BOX AND
LINKAGE 16................................
POWER STEERING OIL PUMP 30...........
POWER STEERING OIL HOSES 35..........
WARNINGS REGARDING SERVICING OF SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS) EQUIPPED VEHICLES
WARNING!
(1) Improper service or maintenance of any component of the SRS, or any SRS-related component, can lead to personal
injury or death to service personnel (from inadvertent firing of the air bag) or to the driver and passenger (from rendering
the SRS inoperative).
(2) Service or maintenance of any SRS component or SRS-related component must be performed only at an authorized
MITSUBISHI dealer.
(3) MITSUBISHI dealer personnel must thoroughly review this manual, and especially its GROUP 52B - Supplemental
Restraint System (SRS) before beginning any service or maintenance of any component of the SRS or any SRS-related
component.
NOTE
The SRS includes the following components: SRS-ECU, SRS warning lamp, air bag module, clock spring and interconnecting
wiring. Other SRS-related components (that mayhave to be removed/installed in connectionwith SRS service or maintenance) are
indicated in the table of contents by an asterisk(*).
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1314 of 1839
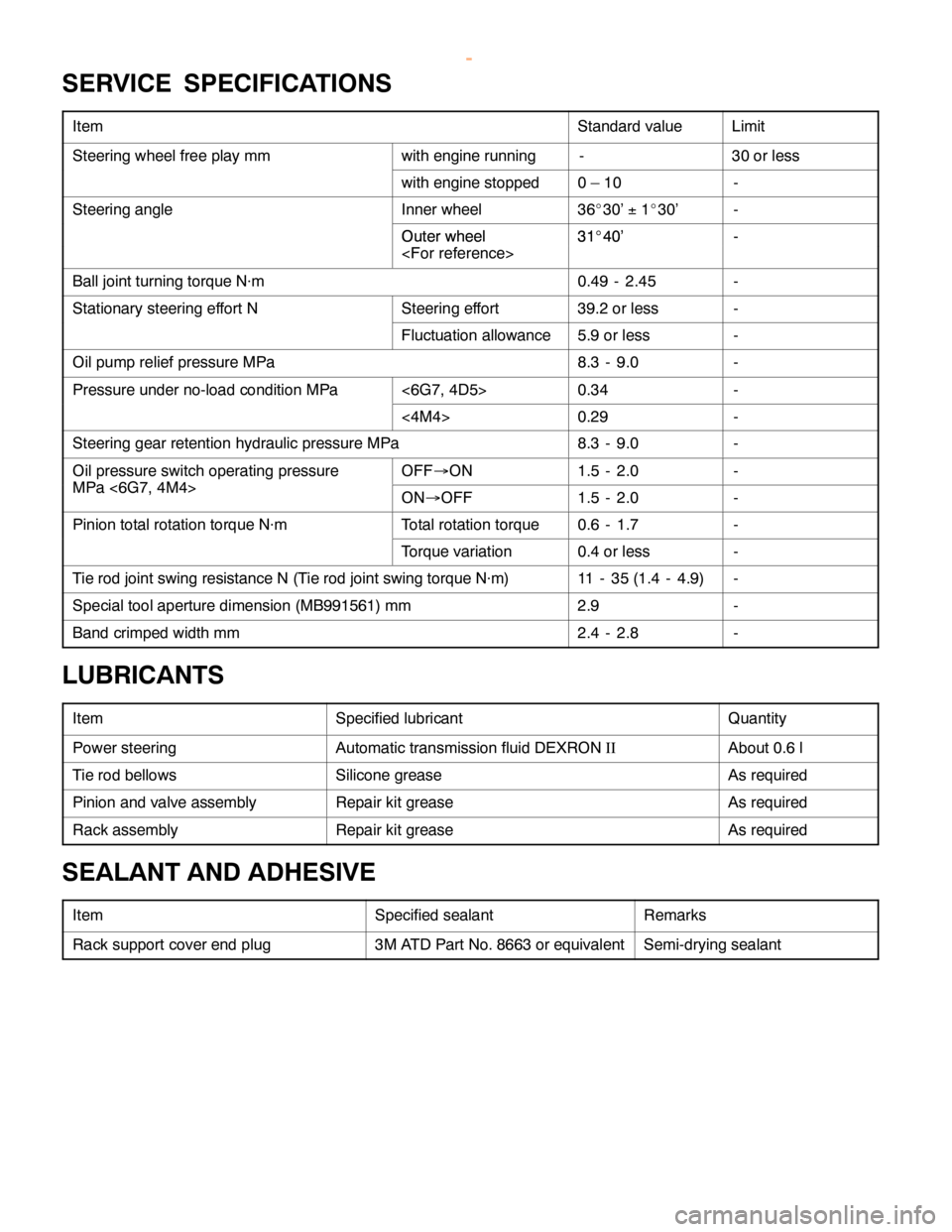
STEERING -Service Specifications/Lubricants/Sealant and Adhesive37A-5
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemStandard valueLimit
Steering wheel free play mmwith engine running-30 or less
with engine stopped0–10-
Steering angleInner wheel36_30’±1_30’-
Outer wheel31_40’-Outer wheel
Ball joint turning torque N×m0.49 - 2.45-
Stationary steering effort NSteering effort39.2 or less-
Fluctuation allowance5.9 or less-
Oil pump relief pressure MPa8.3 - 9.0-
Pressure under no-load condition MPa<6G7, 4D5>0.34-
<4M4>0.29-
Steering gear retention hydraulic pressure MPa8.3 - 9.0-
Oil pressure switch operating pressureOFF®ON1.5 - 2.0-
MPa <6G7, 4M4>ON®OFF1.5 - 2.0-
Pinion total rotation torque N×mTotal rotation torque0.6 - 1.7-
Torque variation0.4 or less-
Tie rod joint swing resistance N (Tie rod joint swing torque N×m)11 - 35 (1.4 - 4.9)-
Special tool aperture dimension (MB991561) mm2.9-
Band crimped width mm2.4 - 2.8-
LUBRICANTS
ItemSpecified lubricantQuantity
Power steeringAutomatic transmission fluid DEXRONIIAbout 0.6 l
Tie rod bellowsSilicone greaseAs required
Pinion and valve assemblyRepair kit greaseAs required
Rack assemblyRepair kit greaseAs required
SEALANT AND ADHESIVE
ItemSpecified sealantRemarks
Rack support cover end plug3M ATD Part No. 8663 or equivalentSemi-drying sealant
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1523 of 1839

SRS -Post-collision Diagnosis52B-23
POST-COLLISION DIAGNOSIS
Whether or not the air bags have deployed, check and service
the vehicle after collision as follows:
SRS-ECU MEMORY CHECK
1. Connect the MUT-
IIto the diagnosis connector. (Refer
to GROUP 00 – How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection
Service Points.)
Caution
Refer to that the ignition switch is LOCK(OFF) when
connecting or disconnecting MUT-II
.
2. Read (and write down) all displayed diagnosis codes.
(Refer to P.52B-7.)
NOTE
If battery power supply has been shut down by the
collision, the MUT-
IIcannot communicate with the
SRS-ECU. Check and, repair if necessary, the instrument
panel wiring harness before the next job.
3. Use the the MUT-
IIto read the data list (how long trouble(s)
have continued and how often memory have been
erased).
Data list
NoService Data ItemApplicability
92Number indication how often the memory is cleared.Maximum time to be stored: 250
93How long problem have lasted (How long it takes
from the occurrence of the problem till the first air bag
squib igniting signal)Maximum time to be stored: 9999 minutes
(approximately 7 days)
94How long problem(s) have lasted (How long it takes
from the first air bag squib igniting signal till now.)
4. Erase the diagnosis codes and after waiting 5 seconds
or more read (and write down) all displayed diagnosis
codes. (Refer to P.52B-7.)
REPAIR PROCEDURE
DEPLOYED DRIVER’S AND FRONT PASSENGER’S AIR
BAGS
1. Replace the following parts with new ones.
DSRS-ECU (Refer to P.52B-30.)
DDriver’s air bag module (Refer to P.52B-32.)
DFront passenger’s air bag module (Refer to P.52B-32.)
2. Check the following parts and replace if malfunction is
found:
DClock spring (Refer to P.52B-32.)
DSteering wheel, steering column and intermediate
joint
(1) Check the wiring harness (built into steering
wheel) and connectors for damage, and terminals
for deformation.
(2) Check the driver’s air bag module for proper
installation to the steering wheel.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk