light MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1990, Model line: SPYDER, Model: MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990Pages: 2103, PDF Size: 68.98 MB
Page 243 of 2103
(Overall)
Intake 111.49-111.99 mm (4.389-4.499 in.) Exhaust
mm in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake 5.934-5.952 mm in.)
Exhaust
mm in.)
Valve Margin
Intake 1.285-1.615 mm in.)
Exhaust
mm in.)
(3) When refacing valve seats, it is important that the correct
size valve guide pilot be used for reseating A
true and complete surface must
Measure the concentricity of valve seat using a va lve
seat dial indicator. Circular
should not exceed.
Limit:
0.05 mm in.) Indicator reading.
(5) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to de termine
where the valve contacts the seat.
To do this, coat valve face LIGHTLY with Prussian b lue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light pressure.
If the blue is transferred to the center of valve f ace, contact
is satisfactory. If the blue is transferred to top edge of
the valve face, lower valve seat with a 15degree stone.
If the blue is transferred to the bottom edge of va lve
face raise valve seat with a 65 degree stone.
Intake valve seat diameter 34.50 mm (1.358 in.)
Exhaust valve seat diameter 29.50 mm (1.161 in.)
Valve seats which are worn or burned can be reworke d
if correct angle and seat width are maintained. Otherwise,
cylinder head must be replaced.
Revision
Page 277 of 2103
On-vehicle Service
A/C COMPRESSOR DRIVE BELT TENSION ADJUSTMENT
1. Loosen tension pulley fixing nut A.
2. Adjust belt tension with adjusting bolt B.
Standard value:
When a new belt isWhen a used belt is
installed installed
Tension
382-411255-333
(Ibs.)
Deflection8.5-7.5
mm (in.)
3. Tighten fixing nut A. Tightening torque: 23-26 Nm
4.Check the belt deflection amount and readjust if ne ces-
sary.
Caution
This check should be carried out after turning the
crankshaft one full rotation or more
the forward
direction (to the right).
IGNITION TIMING CHECK
1.Before inspection and adjustment set vehicle in the follow-
ing condition.
lEngine coolant temperature:
lLights, electric cooling fan and all accessories: OFF
Transaxle: Neutral (P range on vehicles with
2. Turn the ignition switch to OFF and connect the scan
tool to the data link connector.
3. Set up a timing light.
4. Start the engine and run at idle.
5. Select No. 22 of the SCAN TOOL DATA LIST.
6.Check that engine idle speed is within the standard value.
Standard value: 750 100
7. Select No. 17 of the SCAN TOOL ACTUATOR TEST.
Check that basic ignition timing is within the standard
value.
Standard value: BTDC
If the basic ignition timing is outside the standar d value,
inspect the components by referring to GROUP
Troubleshooting.
TSB Revision
Page 278 of 2103

ENGINE O n - v e h i c l e
Press the scan tool clear key (select aforced driving
cancel mode) to release the ACTUATOR TEST
NOTE
If the test is not a forced driving will continue
for 27 minutes. Driving under this condition may damage
the engine.
Check that the actual ignition timing is at the st andard
value.
Standard value: Approx. BTDC
NOTE
Ignition timing is variable within about even under
normal operating.
2. And it is automatically further advanced by abou t
from BTDC at higher altitudes.
CURB IDLE SPEED CHECK
Before inspection and adjustment, set vehicles in the
following condition.
lEngine coolant temperature:
lLights, electric cooling fan and all accessories: OFF
lTransaxle: Neutral (P range on vehicles with A/T)
2. Turn the ignition switch to OFF and connect the scan
tool to the data link connector.
3. Select No. 17 of the SCAN TOOL ACTUATOR TEST
4. Check the basic ignition timing.
Standard value: BTDC
5. Run the engine at idle for 2 minutes.
6. Select No. 22 of the SCAN TOOL DATA LIST.
7. Check the curb idle speed.
Standard value: 750 100
NOTE
The idle speed is controlled automatically by the i dle air
control system.
8. If the idle speed is outside the standard value, check
the components by referring to GROUP Trou-
bleshooting.
IDLE MIXTURE CHECK
Before inspection, set vehicles in the following co ndition:
lEngine coolant temperature:
lLights, electric cooling fan and all accessories: O FF
lTransaxle: Neutral (P range on vehicles with
2. Turn the ignition switch to OFF and connect the scan
tool to the data link connector.
3. Select No. 17 of the SCAN TOOL ACTUATOR TEST.
4.Check that the basic ignition timing is within the standard
value..
Standard value:
TSB Revision
Page 279 of 2103
On-vehicle
Run the engine.
8. Set CO, HC tester.
7. Check the CO contents and the HC contents at idle.
Standard value:
CO contents: 0.5% or less
HC contents: 100 ppm or less
8. the standard value is exceeded, check the following
items:
l Diagnostic output
l Closed-loop control (When the closed-loop control
is carried out normally, the output signal of the heated
oxygen sensor and
at idle.)
l
Injector
lIgnition coil, spark plug
l system the
l Evaporative emission
Compression ,
NOTE,
Replace the three-way CO and
HC contents do not
the value.
(even though the
of the” on
all items.)
PRESSURE CHECK
1.Before inspection, check that the engine oil, start er and
battery are normal. Also, set the vehicle to the fo llowing
condition:
lEngine coolant temperature:
lLights, electric cooling fan and all accessories: O FF
lTransaxle: Neutral (P range on vehicles with
2. Disconnect the spark plug cables.
3. Remove all of the spark plugs.
4. Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor
NOTE
Doing this will prevent the engine control unit fro m carrying
out ignition and fuel injection.
TSB Revision
Page 305 of 2103
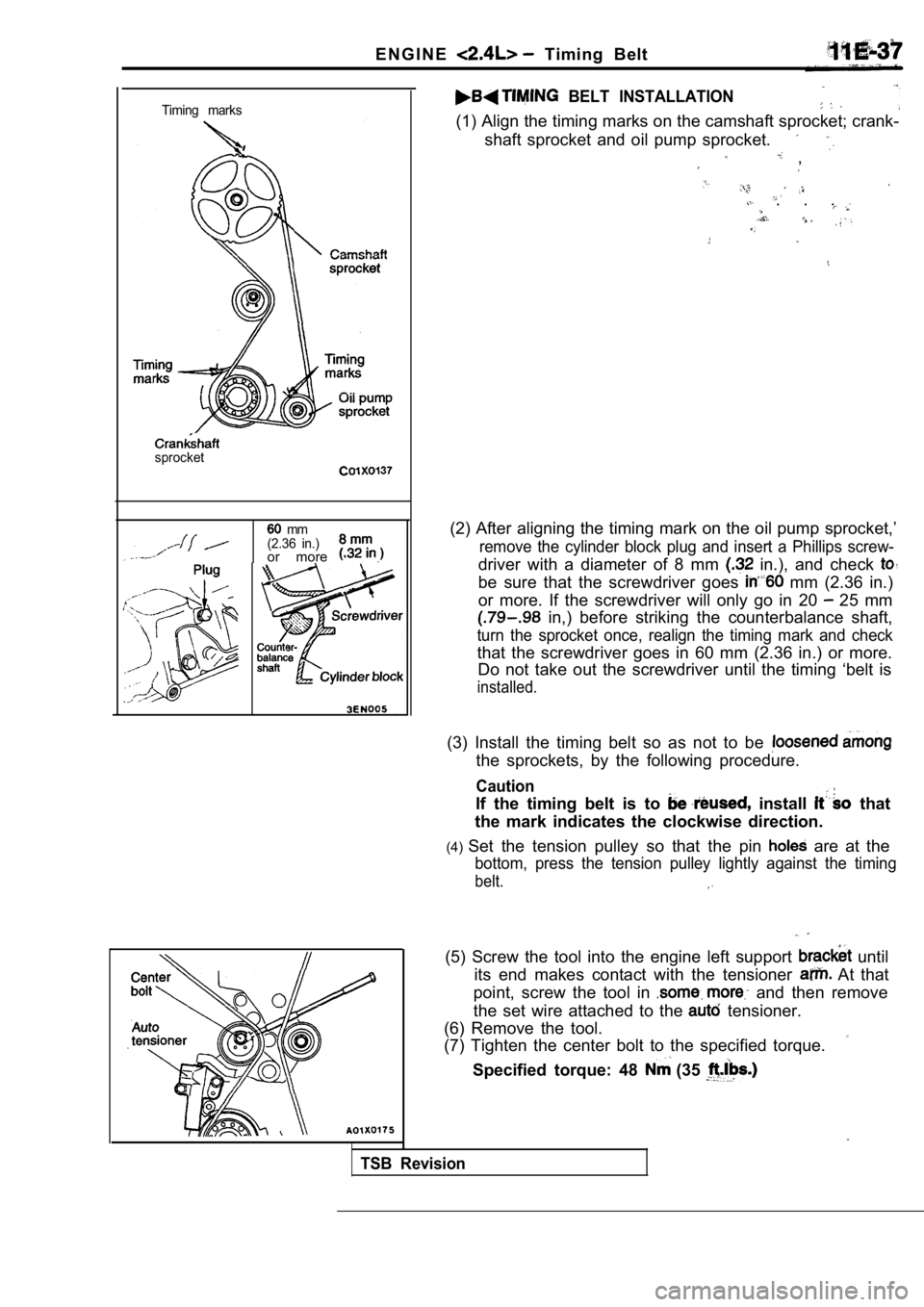
E N G I N E Timing Belt
Timing marks
sprocket
mm
(2.36 in.)
or more .
BELT INSTALLATION
(1) Align the timing marks on the camshaft sprocket ; crank-
shaft sprocket and oil pump sprocket.
,
. . .
(2) After aligning the timing mark on the oil pump sprocket,’
remove the cylinder block plug and insert a Phillips screw-
driver with a diameter of 8 mm in.), and check
be sure that the screwdriver goes mm (2.36 in.)
or more. If the screwdriver will only go in 20
25 mm
in,) before striking the counterbalance shaft,
turn the sprocket once, realign the timing mark and check
that the screwdriver goes in 60 mm (2.36 in.) or mo re.
Do not take out the screwdriver until the timing ‘b elt is
installed.
(3) Install the timing belt so as not to be
the sprockets, by the following procedure.
Caution
If the timing belt is to install that
the mark indicates the clockwise direction.
(4) Set the tension pulley so that the pin
are at the
bottom, press the tension pulley lightly against th e timing
belt.
TSB Revision
(5) Screw the tool into the engine left support until
its end makes contact with the tensioner
At that
point, screw the tool in
and then remove
the set wire attached to the
tensioner.
(6) Remove the tool.
(7) Tighten the center bolt to the specified torque .
Specified torque: 48 (35
Page 340 of 2103
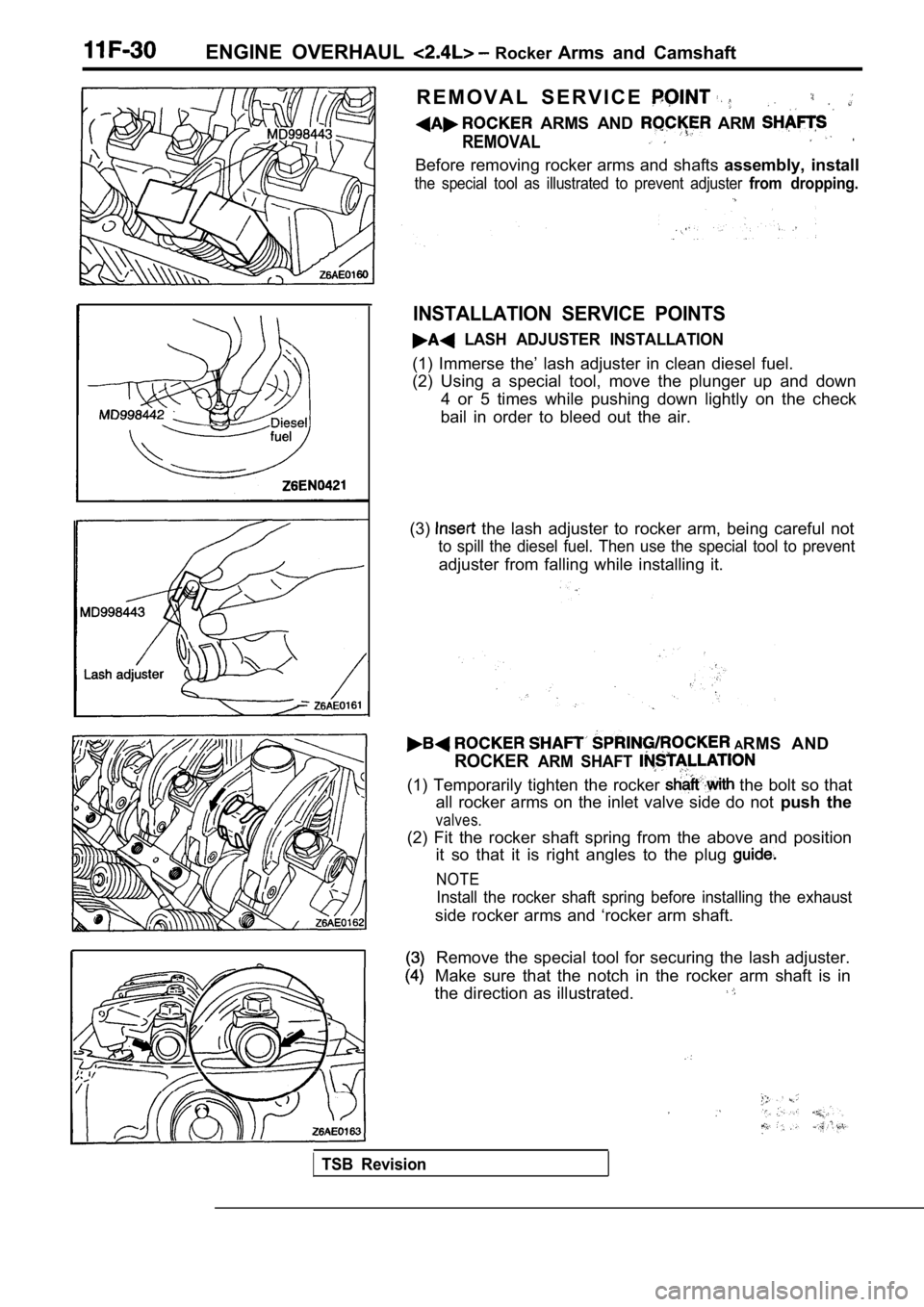
ENGINE OVERHAUL Rocker Arms and Camshaft
R E M O V A L S E R V I C E
ARMS AND ARM
REMOVAL.
Before removing rocker arms and shafts assembly, install
the special tool as illustrated to prevent adjuster from dropping.
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINTS
LASH ADJUSTER INSTALLATION
(1) Immerse the’ lash adjuster in clean diesel fuel .
(2) Using a special tool, move the plunger up and d own
4 or 5 times while pushing down lightly on the chec k
bail in order to bleed out the air.
(3)
the lash adjuster to rocker arm, being careful not
to spill the diesel fuel. Then use the special tool to prevent
adjuster from falling while installing it.
ARMS AND
ROCKERARM SHAFT
(1) Temporarily tighten the rocker the bolt so that
all rocker arms on the inlet valve side do not push the
valves.
(2) Fit the rocker shaft spring from the above and position
it so that it is right angles to the plug
NOTE
Install the rocker shaft spring before installing t he exhaust
side rocker arms and ‘rocker arm shaft.
Remove the special tool for securing the lash adjus ter.
Make sure that the notch in the rocker arm shaft is in
the direction as illustrated.
TSB Revision
Page 342 of 2103
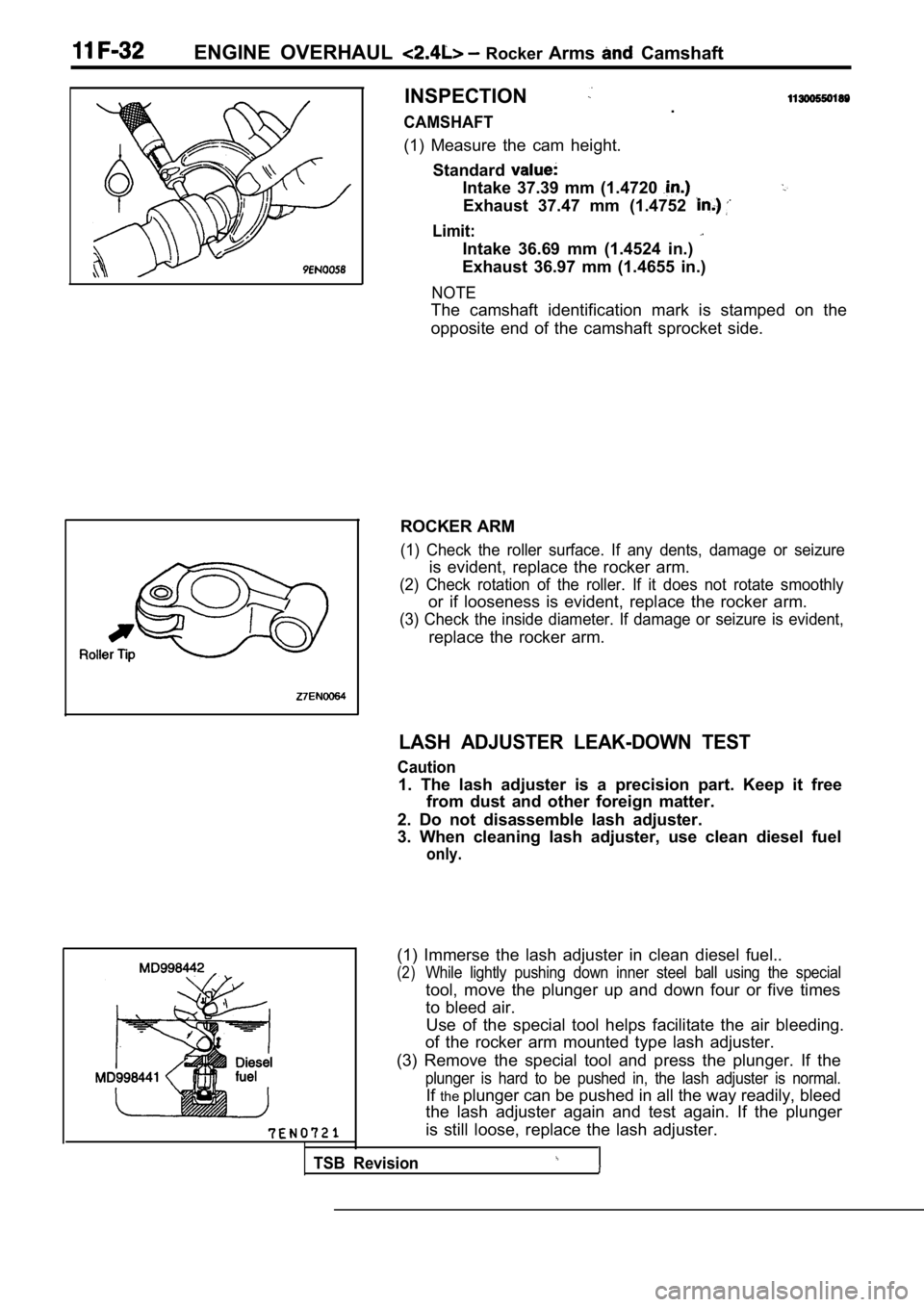
ENGINE OVERHAUL Rocker Arms Camshaft
I
INSPECTION
CAMSHAFT.
(1) Measure the cam height. Standard
Intake 37.39 mm (1.4720
Exhaust 37.47 mm (1.4752
Limit:
Intake 36.69 mm (1.4524 in.)
Exhaust 36.97 mm (1.4655 in.)
NOTE
The camshaft identification mark is stamped on the
opposite end of the camshaft sprocket side.
ROCKER ARM
(1) Check the roller surface. If any dents, damage or seizure
is evident, replace the rocker arm.
(2) Check rotation of the roller. If it does not rotate smoothly
or if looseness is evident, replace the rocker arm.
(3) Check the inside diameter. If damage or seizure is evident,
replace the rocker arm.
LASH ADJUSTER LEAK-DOWN TEST
Caution
1. The lash adjuster is a precision part. Keep it f ree
from dust and other foreign matter.
2. Do not disassemble lash adjuster.
3. When cleaning lash adjuster, use clean diesel fu el
only.
Use of the special tool helps facilitate the air bleeding.
of the rocker arm mounted type lash adjuster.
(3) Remove the special tool and press the plunger. If the
plunger is hard to be pushed in, the lash adjuster is normal.
Ifthe plunger can be pushed in all the way readily, bleed
the lash adjuster again and test again. If the plun ger
is still loose, replace the lash adjuster.
TSB Revision
(1) Immerse the lash adjuster in clean diesel fuel. .
(2)While lightly pushing down inner steel ball using t he special
tool, move the plunger up and down four or five tim es
to bleed air.
Page 385 of 2103
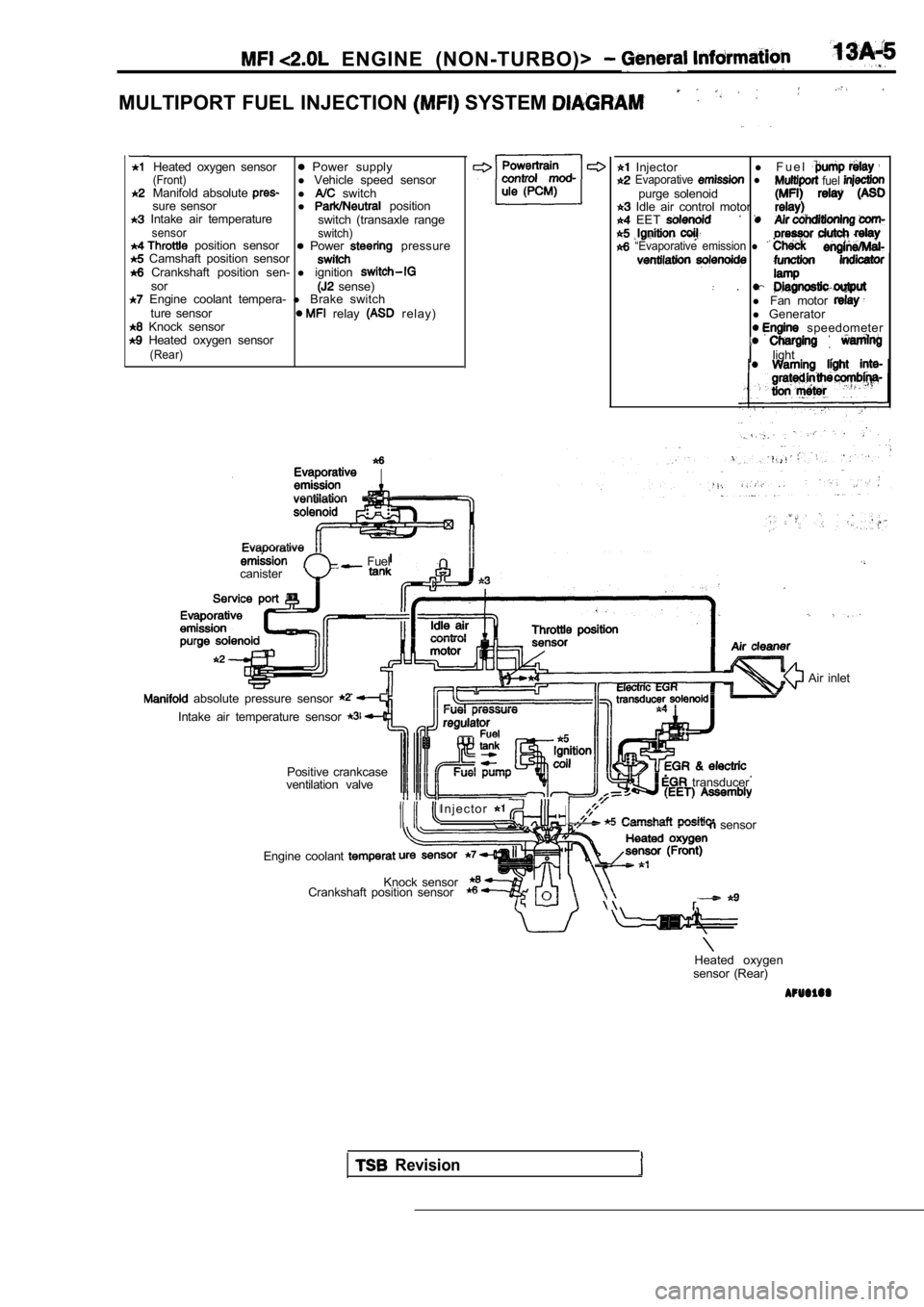
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
Heated oxygen sensor Power supply(Front)l Vehicle speed sensor
Manifold absolute l switch
sure sensor l position Intake air temperature
switch (transaxle rangesensor switch) position sensor Power pressure Camshaft position sensor Crankshaft position sen- l ignitionsor sense) Engine coolant tempera- l Brake switch
ture sensor relay r e l a y ) Knock sensor Heated oxygen sensor(Rear)
Injector l
F u e l Evaporative l fuel purge solenoid Idle air control motor EET
“Evaporative emission l
.l Fan motor l Generator speedometer
light
.
Fuel
canister
absolute pressure sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Positive crankcase
ventilation valve
I n j e c t o r
transducer
sensor
Engine coolant
Knock sensor
Crankshaft position sensor
Air inlet
Heated oxygen
sensor (Rear)
Revision
Page 391 of 2103

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The
Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection syste m.
If the PCM senses a problem with a monitored
circuit often enough to indicate an actual problem,
it stores a diagnostic trouble code in the
memory.
After the PCM first detects a malfunction, a
diagnostic trouble code is recorded when the engine
i s r e s t a r t e d a n d t h e s a m e m a l f u n c t i o n i s
re-defected. However, for items marked with a
a diagnostic trouble code is recorded the
first detection of the malfunction.
After that, if the PCM does not re-detect the
malfunction for 40 drives* (51 engine start for
non-emission related faults), the diagnostic troubl e
code will be erased from the PCM memory.
NOTE
A drive indicates from engine start to stop and
monitors the power train component.
However, for misfiring or a fuel system rich/lean,
the diagnostic trouble codes will be erased under
the following conditions.
lWhen driving conditions (engine speed, engine
coolant temperature, etc.) are similar, to those
when the malfunction was first recorded.
l When the PCM does not re-detect the
malfunction for 80 drives*.
Technicians can display stored diagnostic trouble
codes by two different methods.
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting
The first is to cycle the ignition switch
On-Off-On-Off-On within 5
Then count
the number of times the malfunction indicator lamp
(check engine lamp) on the instrument panel flashes
on and off. The number of flashes represents the
diagnostic trouble code. There is a slight pause
between the flashes representing the first and
second digits of the code. Longer pauses separate
individual trouble codes. The second method of
reading diagnostic trouble codes uses
scan
Connect the scan tool to the
(diagnostic) connector in the vehicle.
FREEZE FRAME DATA
The PCM records the diagnostic trouble code and
also the engine operating conditions the time
the malfunction was detected. are called
“freeze frame” data.
This data indicates the engine operating condition
from when nothing at all is the initial
detection of the
However, misfiring
or fuel trim malfunction data are always. replaced
with the latest data.
This data can be read by using the scan tool, and
can then be used in simulation tests for
troubleshooting.
Data items are as follows.
DataUnit
Engine coolant temperature
Engine speed
Vehicle speed
or
or RPM
km/h or mph
Long-term fuel compensation (Long-term fuel trim)
Short-term fuel compensation (Short-term fuel trim)
Fuel control condition O p e n l o o p
l Closed loop
l Open loop-Drive condition
l Open loop-DTC set
lMalfunction of closed (rear)
Calculated load value
MAP vacuum
(vacuum)
Diagnostic trouble code during data recording
TSB Revision
Page 393 of 2103
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting 3
If scan tool not available
1.Cycle the ignition key On-Off-On-Off-On within seconds.
2.Count the number of times the malfunction indicator lamp
(check engine lamp) on the instrument panel flashes on
and off. The number flashes represents the trouble
code.There is a slight pause between the flashes
representing the first and second digits of the’ co de.
Longer pauses (approx. 4 seconds) separate individu al
,
trouble codes.
3. Repair the malfunction while referring to the in spection
chart for diagnostic trouble codes.
4. After disconnecting the battery cable from the b attery
terminal for a few minutes, reconnect the
5.Start the engine and run it at for about minutes
after the engine has warmed up.
TSB RevisionI