stop start MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1990, Model line: SPYDER, Model: MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990Pages: 2103, PDF Size: 68.98 MB
Page 44 of 2103
GENERALMaintenanceService
Drain
Oil pan side
Engine
Engine (Turbo) and
TSB Revision
Engine (Non-turbo)>
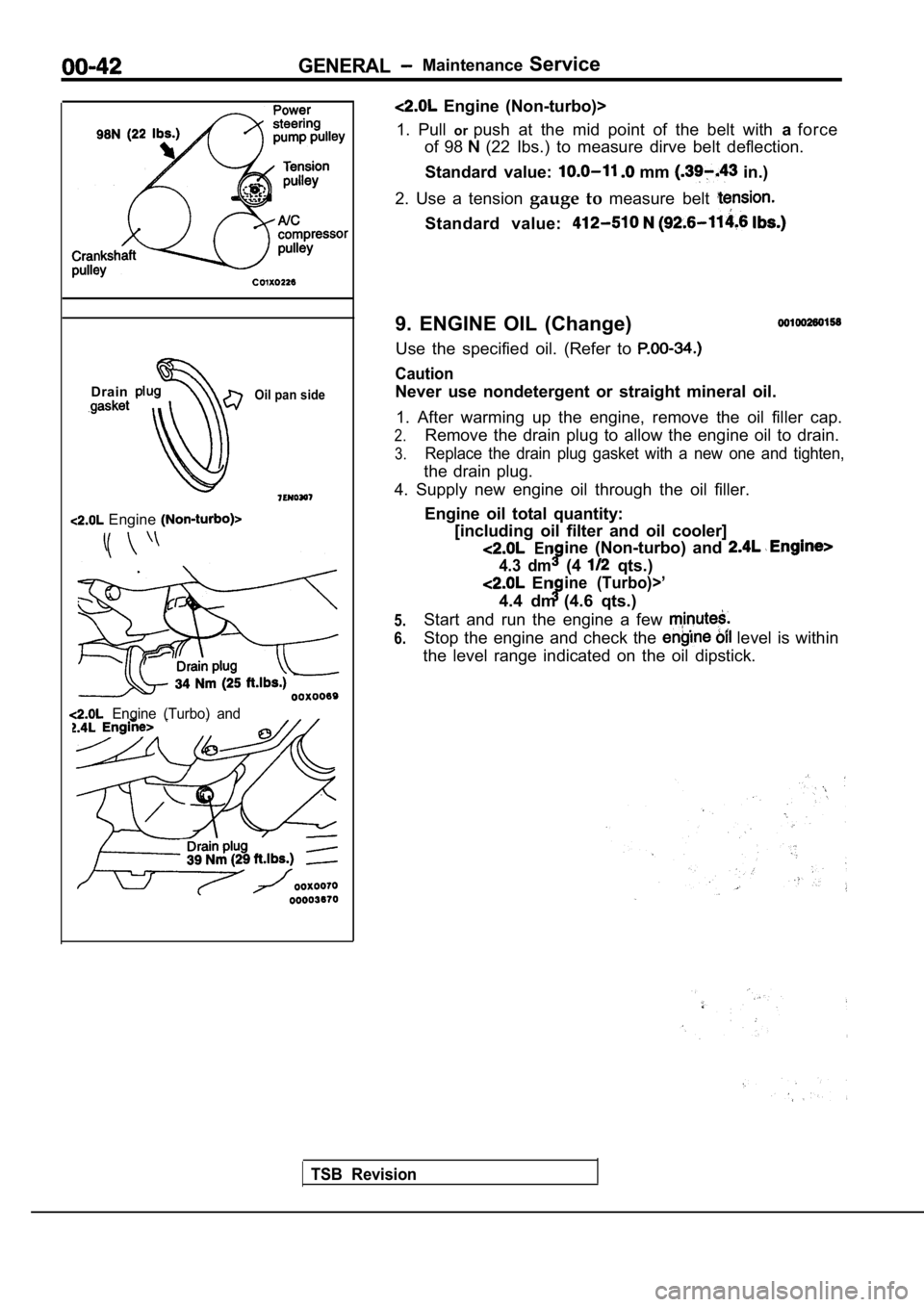
1. Pull orpush at the mid point of the belt with aforce
of 98
(22 Ibs.) to measure dirve belt deflection.
Standard value:
mm in.)
2. Use a tension gauge to measure belt
Standard value:
9. ENGINE OIL (Change)
Use the specified oil. (Refer to
Caution
Never use nondetergent or straight mineral oil.
1. After warming up the engine, remove the oil fill er cap.
2.Remove the drain plug to allow the engine oil to drain.
3.Replace the drain plug gasket with a new one and ti ghten,
the drain plug.
4. Supply new engine oil through the oil filler.
Engine oil total quantity:[including oil filter and oil cooler]
Enine (Non-turbo) and
4.3 dm(4 qts.)
Enine (Turbo)>’
4.4 dm (4.6 qts.)
Start and run the engine a few
Stop the engine and check the level is within
the level range indicated on the oil dipstick.
5.
6.
Page 46 of 2103
GENERAL
Oil level
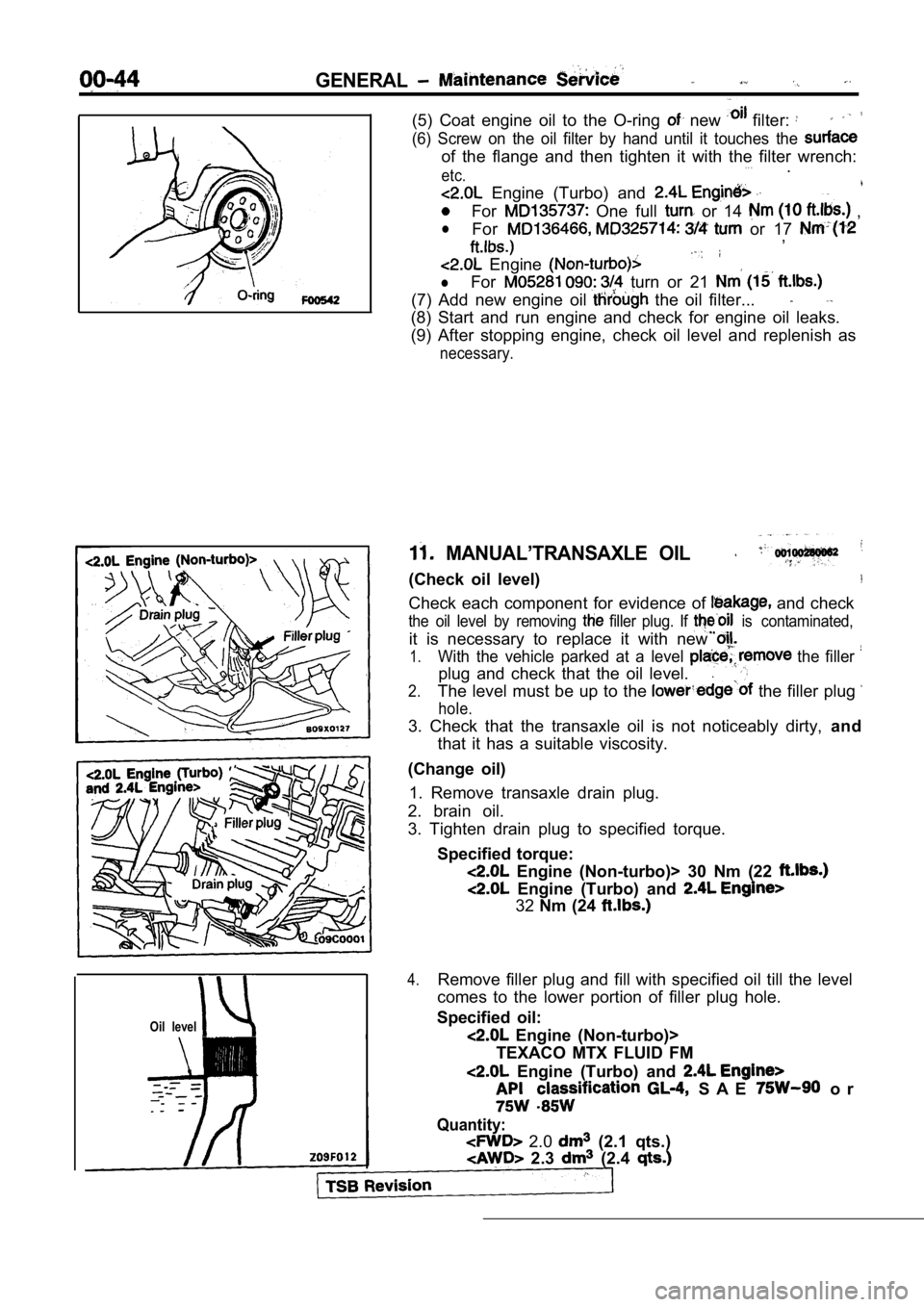
(5) Coat engine oil to the O-ring new filter:
(6) Screw on the oil filter by hand until it touches the
of the flange and then tighten it with the filter w rench:. . .etc..
Engine (Turbo) and
For One full or 14 ,
lFor or 17 ,
Engine
lFor turn or 21
(7) Add new engine oil the oil filter...
(8) Start and run engine and check for engine oil l eaks.
(9) After stopping engine, check oil level and repl enish as
necessary.
MANUAL’TRANSAXLE OIL
(Check oil level)
Check each component for evidence of and check
the oil level by removing filler plug. If is contaminated,
it is necessary to replace it with new
1.With the vehicle parked at a level the filler
plug and check that the oil level..
2.The level must be up to the the filler plug
hole.
3. Check that the transaxle oil is not noticeably d irty, and
that it has a suitable viscosity.
(Change oil) 1. Remove transaxle drain plug.
2. brain oil.
3. Tighten drain plug to specified torque.
Specified torque:
Engine (Non-turbo)> 30 Nm (22
Engine (Turbo) and
32Nm (24
4.Remove filler plug and fill with specified oil till the level
comes to the lower portion of filler plug hole.
Specified oil:
Engine (Non-turbo)>
TEXACO MTX FLUID FM
Engine (Turbo) and
S A E o r
Quantity:
2.0 (2.1 qts.)
2.3 (2.4
Page 51 of 2103
GENERAL Maintenance
a
Engine (Non-turbo)>
in plug
Engine>
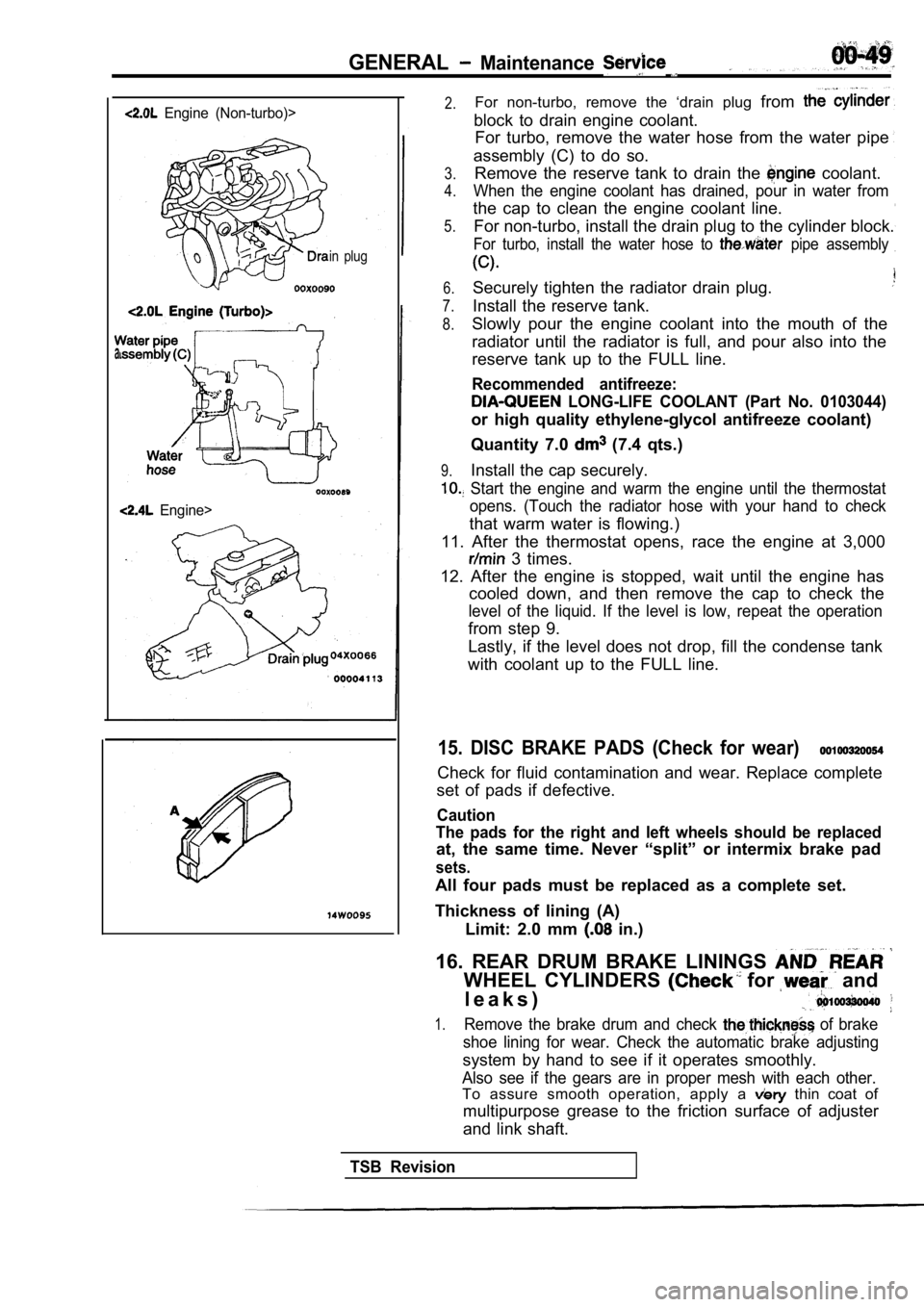
2.For non-turbo, remove the ‘drain plug from
block to drain engine coolant.
For turbo, remove the water hose from the water pip e
assembly (C) to do so.
3.
4.
5.Remove the reserve tank to drain the coolant.
When the engine coolant has drained, pour in water from
the cap to clean the engine coolant line.
For non-turbo, install the drain plug to the cylind er block.
For turbo, install the water hose to pipe assembly
6.
7.
8.
Securely tighten the radiator drain plug.
Install the reserve tank.
9.
Slowly pour the engine coolant into the mouth of th e
radiator until the radiator is full, and pour also into the
reserve tank up to the FULL line.
Recommended antifreeze:
LONG-LIFE COOLANT (Part No. 0103044)
or high quality ethylene-glycol antifreeze coolant)
Quantity 7.0
(7.4 qts.)
Install the cap securely.
Start the engine and warm the engine until the the rmostat
opens. (Touch the radiator hose with your hand to c heck
that warm water is flowing.)
11. After the thermostat opens, race the engine at 3,000
3 times.
12. After the engine is stopped, wait until the eng ine has
cooled down, and then remove the cap to check the
level of the liquid. If the level is low, repeat th e operation
from step 9.
Lastly, if the level does not drop, fill the conden se tank
with coolant up to the FULL line.
15. DISC BRAKE PADS (Check for wear)
Check for fluid contamination and wear. Replace com plete
set of pads if defective.
Caution
The pads for the right and left wheels should be re placed
at, the same time. Never “split” or intermix brake pad
sets.
All four pads must be replaced as a complete set.
Thickness of lining (A) Limit: 2.0 mm
in.)
16. REAR DRUM BRAKE LININGS
WHEEL CYLINDERS for and
l e a k s )
1.Remove the brake drum and check of brake
shoe lining for wear. Check the automatic brake adj usting
system by hand to see if it operates smoothly.
Also see if the gears are in proper mesh with each other.
To assure smooth operation, apply a thin coat of
multipurpose grease to the friction surface of adju ster
and link shaft.
TSB Revision
Page 74 of 2103
ENGINE On-vehicle Service
Timing belt side
.
2.Start the engine and perform gentle racing* several times
(less than times.)
If the abnormal noise stops by racing, the air is b led
from the high pressure chamber of the lash adjusters
and the function of the lash adjusters is normalized.
After raising the engine speed from idling to 3000
gradually (in 30 seconds), drop the
ally (in 30 seconds) to idling.
NOTE
lIf the vehicle is parked on a slope for the oil
in the lash adjusters will be decreased ‘andairmay
enter the high pressure chamber when the
is started.
lAfter the vehicle is parked for long, air may enter
the high pressure chamber because the, oil in the
oil passage will be gone and, it will take a time b efore
the oil is supplied to the lash adjusters.
3.If an abnormal noise does not stop by racing, check the
lash adjusters according to the following procedure s.
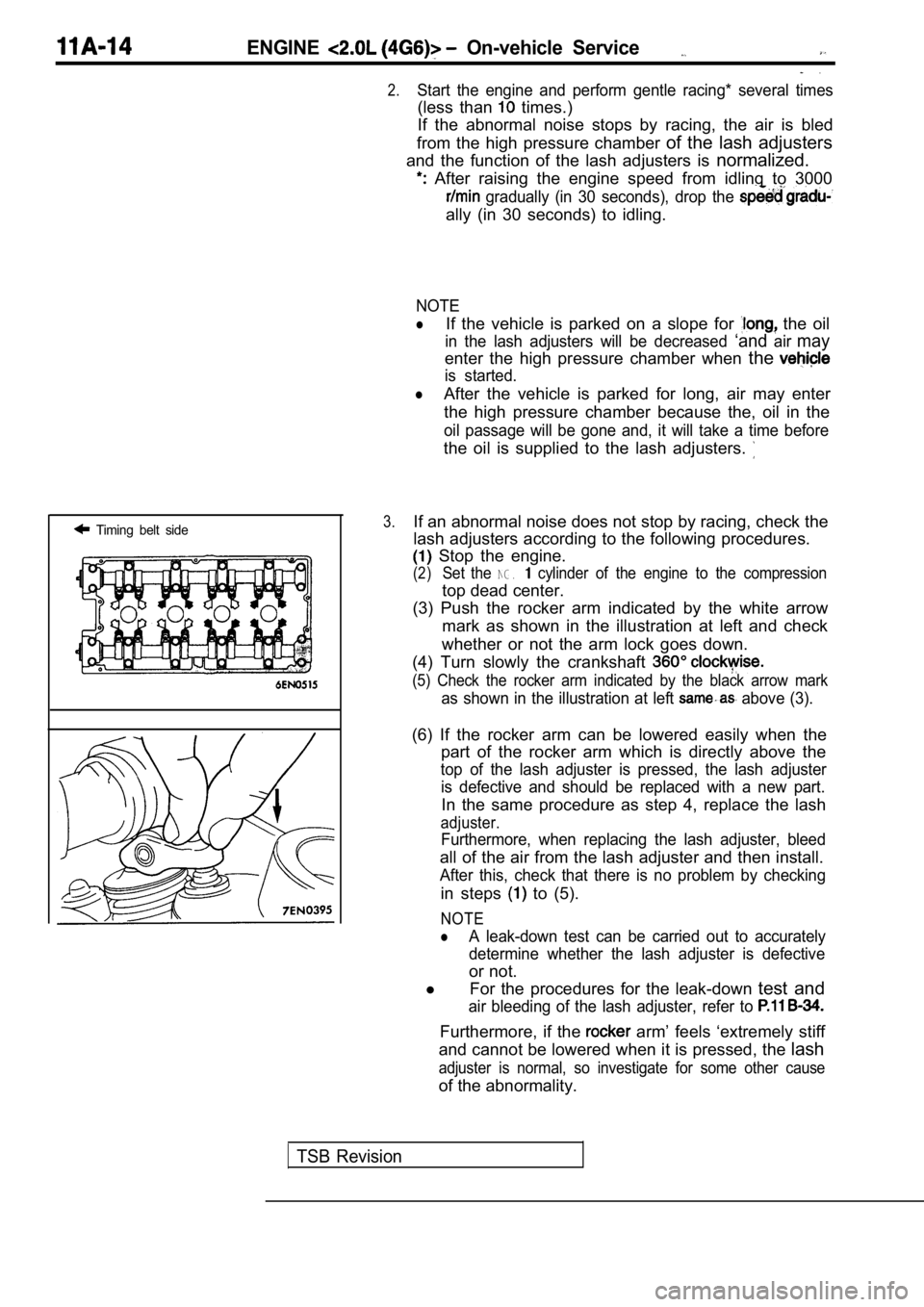
Stop the engine.
(2)Set the NG. cylinder of the engine to the compression
top dead center.
(3) Push the rocker arm indicated by the white arro w
mark as shown in the illustration at left and check
whether or not the arm lock goes down.
(4) Turn slowly the crankshaft
(5) Check the rocker arm indicated by the black arr ow mark
as shown in the illustration at left above (3).
(6) If the rocker arm can be lowered easily when th e
part of the rocker arm which is directly above the
top of the lash adjuster is pressed, the lash adjus ter
is defective and should be replaced with a new part .
In the same procedure as step 4, replace the lash
adjuster.
Furthermore, when replacing the lash adjuster, bleed
all of the air from the lash adjuster and then install.
After this, check that there is no problem by check ing
in steps to (5).
NOTE
lA leak-down test can be carried out to accurately
determine whether the lash adjuster is defective
or not.
l For the procedures for the leak-down test and
air bleeding of the lash adjuster, refer to
Furthermore, if the arm’ feels ‘extremely stiff
and cannot be lowered when it is pressed, the lash
adjuster is normal, so investigate for some other c ause
of the abnormality.
TSB Revision
Page 206 of 2103
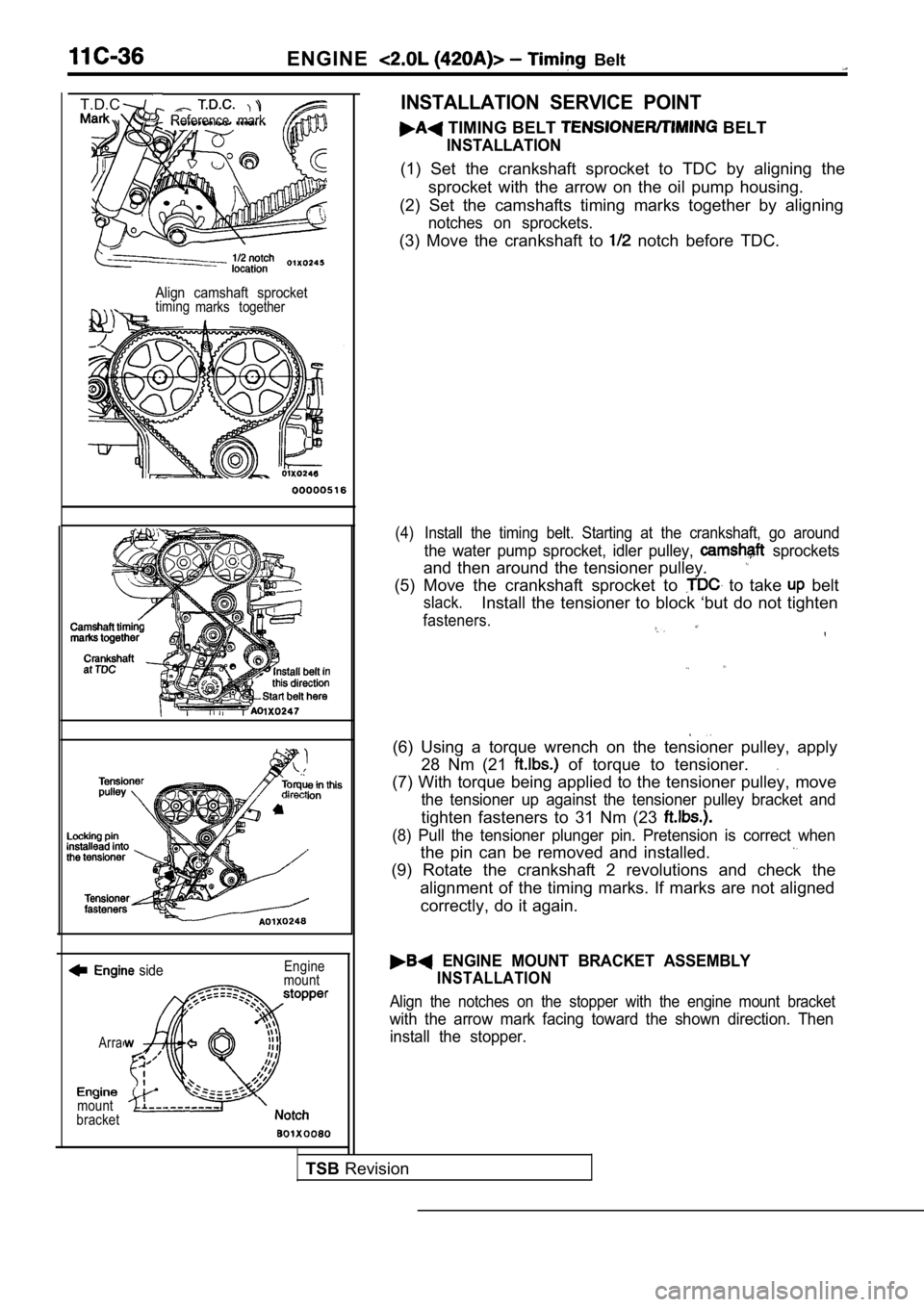
ENGINE Belt
Reference mark
T.D.C.
Align camshaft sprockettimingmarks together
side
Arra
mount
bracket Engine
mount
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINT
TIMING BELT BELT
INSTALLATION
(1) Set the crankshaft sprocket to TDC by aligning the
sprocket with the arrow on the oil pump housing.
(2) Set the camshafts timing marks together by alig ning
notches on sprockets.
(3) Move the crankshaft to notch before TDC.
(4) Install the timing belt. Starting at the crankshaft, go around
the water pump sprocket, idler pulley, sprockets
and then around the tensioner pulley.
(5) Move the crankshaft sprocket to to take belt
slack.Install the tensioner to block ‘but do not tighten
fasteners.
(6) Using a torque wrench on the tensioner pulley, apply
28 Nm (21
of torque to tensioner..
(7) With torque being applied to the tensioner pull ey, move
the tensioner up against the tensioner pulley brack et and
tighten fasteners to 31 Nm (23
(8) Pull the tensioner plunger pin. Pretension is correct when
the pin can be removed and installed.
(9) Rotate the crankshaft 2 revolutions and check t he
alignment of the timing marks. If marks are not ali gned
correctly, do it again.
ENGINE MOUNT BRACKET ASSEMBLY
INSTALLATION
Align the notches on the stopper with the engine mo unt bracket
with the arrow mark facing toward the shown direction. Then
install the stopper.
TSB Revision
Page 281 of 2103
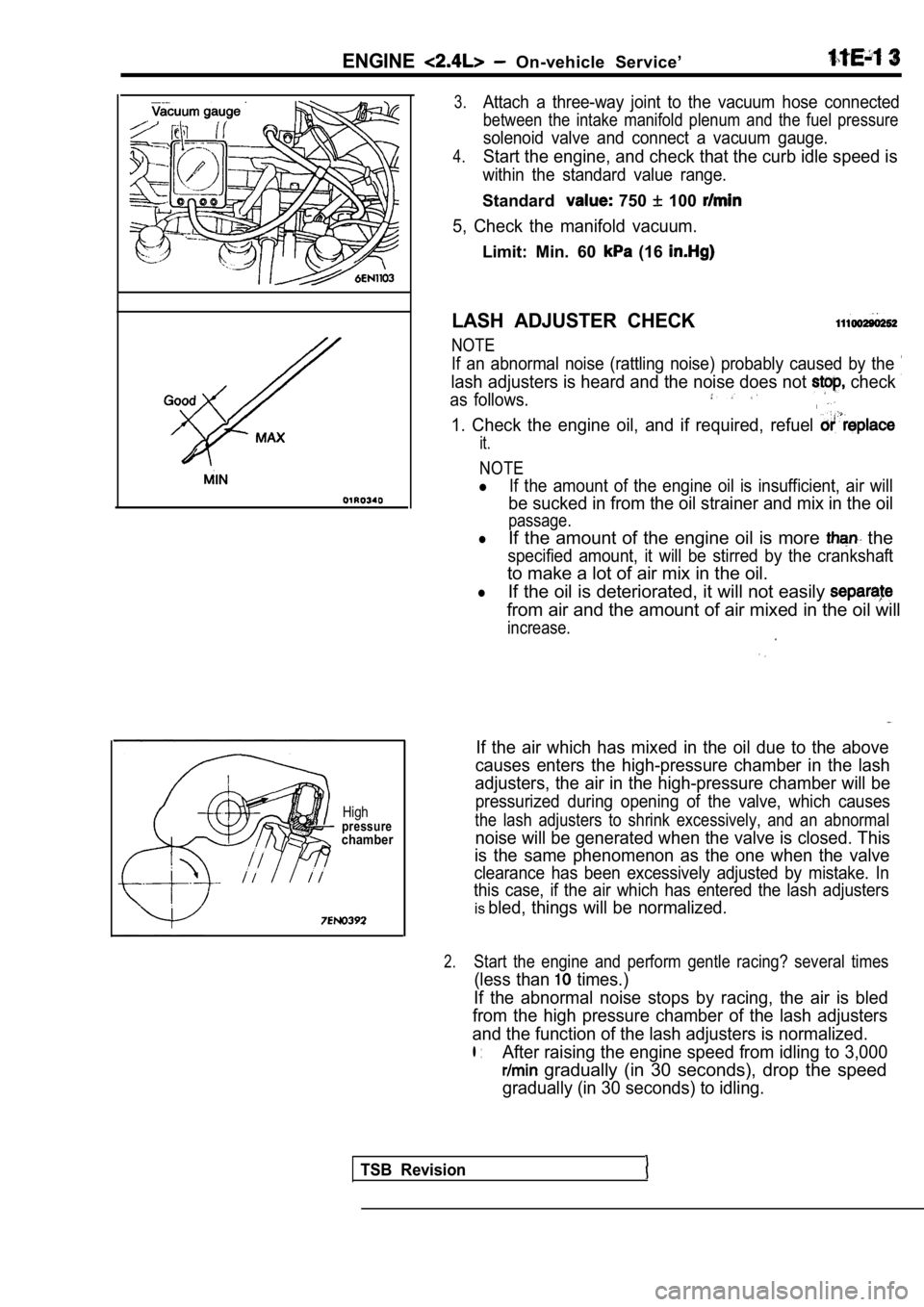
ENGINE On-vehicle Service’
Highpressurechamber
3.Attach a three-way joint to the vacuum hose connected
between the intake manifold plenum and the fuel pressure
solenoid valve and connect a vacuum gauge.
4.Start the engine, and check that the curb idle speed is
within the standard value range.
Standard 750 100
5, Check the manifold vacuum.
Limit: Min. 60 (16
LASH ADJUSTER CHECK
NOTE
If an abnormal noise (rattling noise) probably caus ed by the
lash adjusters is heard and the noise does not check
as follows.
1. Check the engine oil, and if required, refuel
it.
NOTE
lIf the amount of the engine oil is insufficient, air will
be sucked in from the oil strainer and mix in the o il
passage.
lIf the amount of the engine oil is more the
specified amount, it will be stirred by the cranksh aft
to make a lot of air mix in the oil.
lIf the oil is deteriorated, it will not easily
from air and the amount of air mixed in the oil will
increase.
If the air which has mixed in the oil due to the ab ove
causes enters the high-pressure chamber in the lash
adjusters, the air in the high-pressure chamber wil l be
pressurized during opening of the valve, which caus es
the lash adjusters to shrink excessively, and an abnormal
noise will be generated when the valve is closed. This
is the same phenomenon as the one when the valve
clearance has been excessively adjusted by mistake. In
this case, if the air which has entered the lash ad justers
isbled, things will be normalized.
2.Start the engine and perform gentle racing? several times
(less than times.)
If the abnormal noise stops by racing, the air is b led
from the high pressure chamber of the lash adjuster s
and the function of the lash adjusters is normalize d.
l :After raising the engine speed from idling to 3,000
gradually (in 30 seconds), drop the speed
gradually (in 30 seconds) to idling.
TSB Revision
Page 376 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual 12-4 L U B R I C A T I O N
EngineI
Turbo
4. Supply new engine oil through the oil filler.Engine oil total quantity:[including oil filter and oil cooler]
Engine (Non-turbo) arid MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual 12-4 L U B R I C A T I O N
EngineI
Turbo
4. Supply new engine oil through the oil filler.Engine oil total quantity:[including oil filter and oil cooler]
Engine (Non-turbo) arid](/img/19/57345/w960_57345-375.png)
12-4 L U B R I C A T I O N
EngineI
Turbo
4. Supply new engine oil through the oil filler.Engine oil total quantity:[including oil filter and oil cooler]
Engine (Non-turbo) arid
4 . 3 (4 q t s . )
Engine (Turbo)>
4.4
(4.6 qts.)
5. Start and run the engine a
minutes.
6.Stop the engine and check the engine oil level is w ithin
the level range indicated on the oil dipstick.
.
NOTE
may be used for operation in very cold weather
areas where the lowest ambient temperature is below
OIL REPLACEMENT
1. Remove the engine oil filler cap.
2.Remove the engine oil drain plug, and drain out the engine
o i l .
3.Remove the engine oil filter by using the oil filter wrench.
4.Clean the oil filter mounting, surface of the oil f ilter bracket.
5. Coat engine oil to the O-ring of’new filter: .
6.Screw on the oil filter by hand until it touchesthe surface
of the flange and then tighten it with. the filter wrench:
etc.
Engine (Turbo) Engine>
lFor One full turn or 14 Nm
lFor or 17 Nm (12
E n g i n e ( N o n - t u r b o ) >
lFor 090: turn or 21 Nm (15
7. Add new engine oil through the oil filter.
8. Start and run engine and check for engine oil le aks.
9. After stopping engine, check oil level and reple nish as
necessary.
TSB Revision
Page 390 of 2103

ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting
DTC No. ItemsI
107
108
109
110
112
113
114
118
119
126 38)
Cylinder misfire
Cylinder
misfire
Cylinder
misfire
misfire
Catalytic
efficiency failure
EVAP purge flow monitor failure
Park/neutral position switch (transaxle range switc h) failure
Fuel system rich
Fuel system lean
Downstream
shorted to
128Closed loop temperature not reached
129
Downstream at center
132
133
TPS voltage does not agree with MAP
Timing belt skipped 1 tooth or more
135No 5 volts to MAP sensor
136No 5 volts to throttle position sensor
137EATX controller DTC present
138Taraet idle not reached
High speed radiator fan control relay
146 1496)
153
154
155
156
157
160
161
183
5 volts too low
Battery temperature sensor voltage too low
Battery temperature sensor voltage too high
Upstream
voltage grounded
Downstream
voltage grounded
Intermittent loss of CMP or CKP
EVAP leak monitor small leak detected
EVAP leak monitor large leak detected
Evaporative emission ventilation solenoid circuit
Evaporative emission ventilation solenoid switch or mechanical fault
EVAP leak monitor pinched hose found
NOTE
Following a detected malfunction of the Control Module (PCM), the check engine lamp
up the next time the engine is turned on if the mal function is still detected. However, for items
with an asterisk in the table above, the check engine lamp goes on’ the first time a malfundin is
detected.
Once the check engine lamp is lit, any one of the f ollowing
will turn it off.
lWhen the PCMhas found no malfunction after monitoring the power train times time
is from engine start to engine stop).
lA misfire of fuel abnormality when engine speed, coolant temperature, etc. are to those
when the malfunction was first recorded, and the PCM has detected no malfunction.
Caution
If the check engine lamp is turned on by a malfunct ion of the PCM, the scan tool communicate
with the PCM, and the diagnostic trouble code canno t be read.
,
TSB Revision
Page 391 of 2103

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The
Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection syste m.
If the PCM senses a problem with a monitored
circuit often enough to indicate an actual problem,
it stores a diagnostic trouble code in the
memory.
After the PCM first detects a malfunction, a
diagnostic trouble code is recorded when the engine
i s r e s t a r t e d a n d t h e s a m e m a l f u n c t i o n i s
re-defected. However, for items marked with a
a diagnostic trouble code is recorded the
first detection of the malfunction.
After that, if the PCM does not re-detect the
malfunction for 40 drives* (51 engine start for
non-emission related faults), the diagnostic troubl e
code will be erased from the PCM memory.
NOTE
A drive indicates from engine start to stop and
monitors the power train component.
However, for misfiring or a fuel system rich/lean,
the diagnostic trouble codes will be erased under
the following conditions.
lWhen driving conditions (engine speed, engine
coolant temperature, etc.) are similar, to those
when the malfunction was first recorded.
l When the PCM does not re-detect the
malfunction for 80 drives*.
Technicians can display stored diagnostic trouble
codes by two different methods.
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting
The first is to cycle the ignition switch
On-Off-On-Off-On within 5
Then count
the number of times the malfunction indicator lamp
(check engine lamp) on the instrument panel flashes
on and off. The number of flashes represents the
diagnostic trouble code. There is a slight pause
between the flashes representing the first and
second digits of the code. Longer pauses separate
individual trouble codes. The second method of
reading diagnostic trouble codes uses
scan
Connect the scan tool to the
(diagnostic) connector in the vehicle.
FREEZE FRAME DATA
The PCM records the diagnostic trouble code and
also the engine operating conditions the time
the malfunction was detected. are called
“freeze frame” data.
This data indicates the engine operating condition
from when nothing at all is the initial
detection of the
However, misfiring
or fuel trim malfunction data are always. replaced
with the latest data.
This data can be read by using the scan tool, and
can then be used in simulation tests for
troubleshooting.
Data items are as follows.
DataUnit
Engine coolant temperature
Engine speed
Vehicle speed
or
or RPM
km/h or mph
Long-term fuel compensation (Long-term fuel trim)
Short-term fuel compensation (Short-term fuel trim)
Fuel control condition O p e n l o o p
l Closed loop
l Open loop-Drive condition
l Open loop-DTC set
lMalfunction of closed (rear)
Calculated load value
MAP vacuum
(vacuum)
Diagnostic trouble code during data recording
TSB Revision
Page 394 of 2103

ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITOR
Related diagnosis trouble codes (DTC)
l EVAP leak monitor small leak detected
l
EVAP leak monitor large leak detected
l
EVAP leak monitor pinched hose found
Operation
The leak detection assembly incorporates two primar y functions: it must detect a the
system and seal the evaporative system so the leak detection test can be run.. .
The’ primary components within the assembly are: A three port solenoid activates ‘both of the
functions listed above; a pump which contains a swi tch; two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a’
canister vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spr ing loaded vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predetermin ed temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also closes
the vent seal. During non test conditions the vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm assembly
which pushes it open at the full travel position. The vent seal will remain closed while the pump is c ycling
due to the reed switch triggering of the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm assembly from
reaching full travel. After the brief initializatio n period, the solenoid is de-energized allowing atm ospheric
pressure to enter the pump cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the diaphragm which forces air
out of the pump cavity and into the vent system. Wh en the solenoid is energized and de-energized,
the cycle is repeated creating flow in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is controlled in 2 mod es:
Pump Mode: The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten
the overall test length.
Test Mode: The solenoid is energized with a fixed d uration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur
when the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point .
The spring in the pump is set so that the system wi ll achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5”
The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid as the system begins to pump up to this pressure.
As the pressure
the cycle rate starts to drop off. If there is no leak in the system, the pump
would eventually stop pumping at the equalized pres sure. If there is a leak, it will continue to pump
at a rate representative of the flow characteristic of the size of the leak. From this information we can
determine if the leak is larger than the required d etection limit (currently set at
orifice by CARB).
If a leak is revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the test is terminated at the end of the
mode and no further system checks will be performed .
After passing the leak detection phase of the test, system pressure is maintained by turning on the
solenoid until the purge system is activated. Purg e activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases du e to the flow through the purge system, the leak
check portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system afte r completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel positio n.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified b y using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a shi ft in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test i s passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge syst em
is not functioning in some respect. The LDP is agai n turned off and the test is ended.
TSB Revision