wiring NISSAN ALMERA N16 2001 Electronic User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2001, Model line: ALMERA N16, Model: NISSAN ALMERA N16 2001Pages: 2493, PDF Size: 66.97 MB
Page 22 of 2493

manual.
Fuse block Ð Junction box (J/B)
Fuse block Ð Junction box (J/B) connector number is shown in the
Reference Area of the wiring diagram. For connector terminal and
fuse arrangement, refer to the ªFUSE BLOCK Ð Junction Box
(J/B)º electrical reference page at the end of the manual.
Fuse and fusible link box
For fuse arrangement in the fuse and fusible link box, refer to the
ªFUSE AND FUSIBLE LINK BOXº electrical reference page at the
end of the manual.
Electrical units
Electrical unit connector symbols are shown in the Connector Area
of the wiring diagram.
However, when there is not enough space to show the connector
terminal arrangement in the Connector Area of the wiring diagram,
the electrical unit connector number is shown in the Reference
Area of the wiring diagram. For electrical unit connector terminal
arrangement, refer to the ªELECTRICAL UNITSº electrical refer-
ence page at the end of the manual. Most of the electrical unit
connectors on this page are shown from the harness side of the
connector.
Joint connector
Joint connector symbols are shown in the connector area of the
wiring diagram. For connector internal wiring layout and joint con-
nector terminal arrangement, refer to the ªJOINT CONNECTOR
(J/C)º electrical reference page at the end of the manual.
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
Description (Cont'd)
GI-20
Page 23 of 2493

NJGI0005
Work FlowNJGI0005S01
SGI838
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1 Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHATVehicle Model, Engine, Transmission and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHENDate, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERERoad Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOWSystem Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2 Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem can not be duplicated, refer to ªIncident Simulation Testsº next page.
STEP 3 Get the proper diagnoses materials together including:
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
System Operation Descriptions
Applicable Service Manual Sections
Check for any Service Bulletin.
Identify where to begin diagnoses based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the cus-
tomer comments.
STEP 4 Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing
and Harness Layouts.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6 Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you
have not inadvertently created a new incident during your diagnoses or repair steps.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Work Flow
GI-21
Page 24 of 2493

Incident Simulation TestsNJGI0005S02INTRODUCTIONNJGI0005S0201Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought
in for service. If possible, re-create the conditions present at the
time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found
Diagnoses. The following section illustrates ways to simulate the
conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
+Vehicle vibration
+Heat sensitive
+Freezing
+Water intrusion
+Electrical load
+Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is
important for simulating the conditions of the problem.
VEHICLE VIBRATIONNJGI0005S0202The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough
road or when engine is vibrating (idle with A/C on). In such a case,
you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the
illustration below.
Connectors & Harness
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the
electrical system you are inspecting.Gentlyshake each connec-
tor and harness while monitoring the system for the incident you
are trying to duplicate. This test may indicate a loose or poor elec-
trical connection.
Hint
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin
film of corrosion on the connector terminals. A visual inspection
may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the
problem occurs intermittently, perhaps the problem is caused by
corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
Sensors & Relays
Gentlyapply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system
you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
SGI839
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Incident Simulation Tests
GI-22
Page 25 of 2493

Engine Compartment
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could
cause an electrical complaint. Some of the things to check for are:
+Connectors not fully seated.
+Wiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to
engine vibrations or rocking.
+Wires laying across brackets or moving components.
+Loose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
+Wires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifying the integ-
rity of ground connections. (Refer to GROUND INSPECTION
described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded.
Then check for loose connection bygently shakingthe wiring or
components as previously explained. Using the wiring diagrams
inspect the wiring for continuity.
Behind The Instrument Panel
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become
pinched during accessory installation. Vehicle vibration can aggra-
vate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
Under Seating Areas
An unclamped or loose harness can cause wiring to be pinched by
seat components (such as slide guides) during vehicle vibration. If
the wiring runs under seating areas, inspect wire routing for pos-
sible damage or pinching.
SGI842
HEAT SENSITIVENJGI0005S0203The owner's problem may occur during hot weather or after car has
sat for a short time. In such cases you will want to check for a heat
sensitive condition.
To determine if an electrical component is heat sensitive, heat the
component with a heat gun or equivalent.
Do not heat components above 60ÉC (140ÉF).If incident occurs
while heating the unit, either replace or properly insulate the com-
ponent.
SGI843
FREEZINGNJGI0005S0204The customer may indicate the incident goes away after the car
warms up (winter time). The cause could be related to water freez-
ing somewhere in the wiring/electrical system.
There are two methods to check for this. The first is to arrange for
the owner to leave his car overnight. Make sure it will get cold
enough to demonstrate his complaint. Leave the car parked out-
side overnight. In the morning, do a quick and thorough diagnoses
of those electrical components which could be affected.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Incident Simulation Tests (Cont'd)
GI-23
Page 26 of 2493

The second method is to put the suspect component into a freezer
long enough for any water to freeze. Reinstall the part into the car
and check for the reoccurrence of the incident. If it occurs, repair
or replace the component.
SGI844
WATER INTRUSIONNJGI0005S0205The incident may occur only during high humidity or in rainy/snowy
weather. In such cases the incident could be caused by water
intrusion on an electrical part. This can be simulated by soaking the
car or running it through a car wash.
Do not spray water directly on any electrical components.
SGI845
ELECTRICAL LOADNJGI0005S0206The incident may be electrical load sensitive. Perform diagnoses
with all accessories (including A/C, rear window defogger, radio,
fog lamps) turned on.
COLD OR HOT START UPNJGI0005S0207On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the
car is started cold. Or it may occur when the car is restarted hot
shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep
the car overnight to make a proper diagnoses.
Circuit InspectionNJGI0005S03INTRODUCTIONNJGI0005S0301In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is
approached in a logical and organized method. Before beginning
it is important to have all available information on the system to be
tested. Also, get a thorough understanding of system operation.
Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical
components.Gently shakethe wiring harness or electrical com-
ponent to do this.
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of
the circuit.
SHORT There are two types of shorts.
+SHORT CIRCUIT When a circuit contacts another circuit
and causes the normal resistance to
change.
+SHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source
and grounds the circuit.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Incident Simulation Tests (Cont'd)
GI-24
Page 30 of 2493
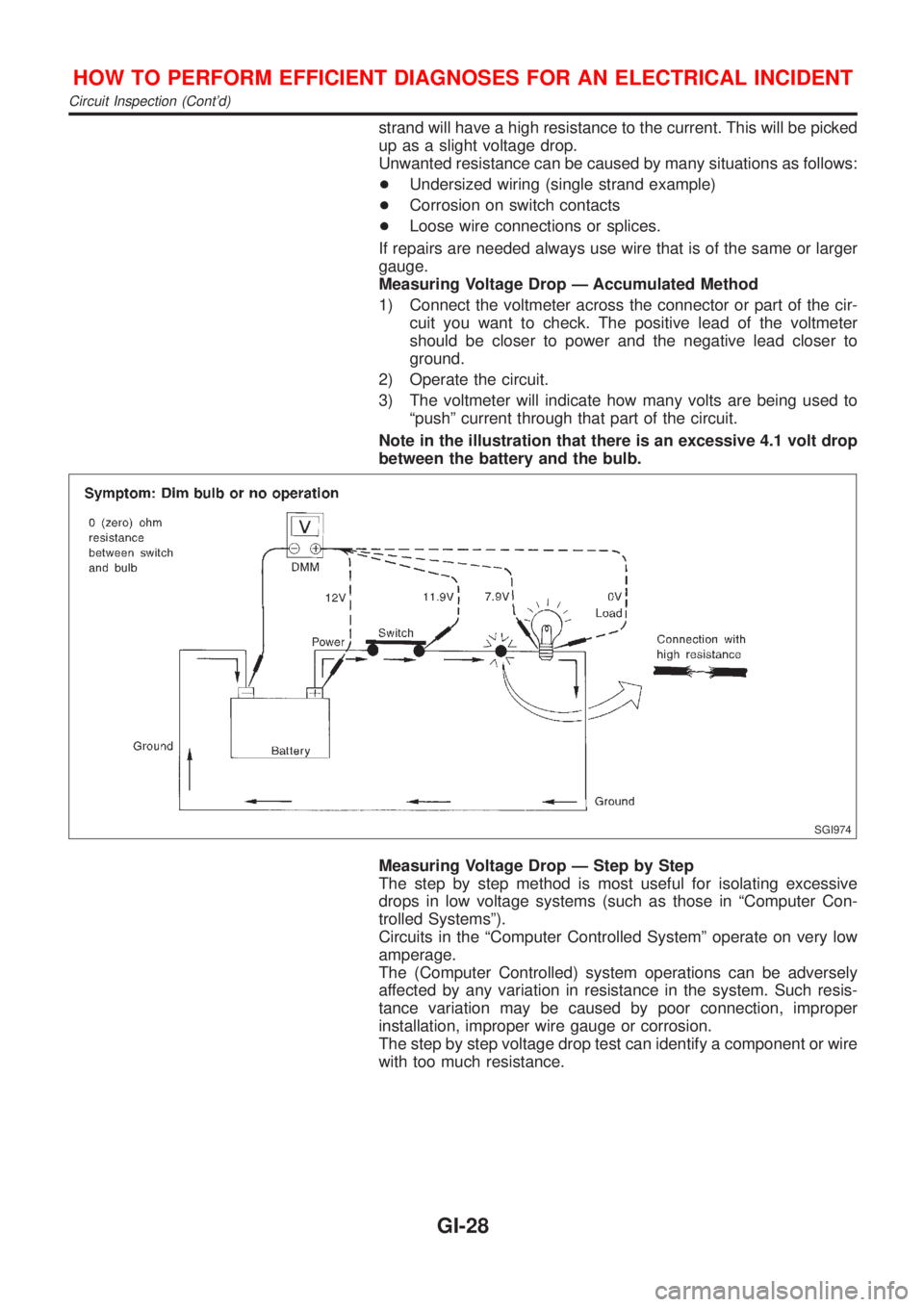
strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
+Undersized wiring (single strand example)
+Corrosion on switch contacts
+Loose wire connections or splices.
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger
gauge.
Measuring Voltage Drop Ð Accumulated Method
1) Connect the voltmeter across the connector or part of the cir-
cuit you want to check. The positive lead of the voltmeter
should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to
ground.
2) Operate the circuit.
3) The voltmeter will indicate how many volts are being used to
ªpushº current through that part of the circuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop
between the battery and the bulb.
SGI974
Measuring Voltage Drop Ð Step by Step
The step by step method is most useful for isolating excessive
drops in low voltage systems (such as those in ªComputer Con-
trolled Systemsº).
Circuits in the ªComputer Controlled Systemº operate on very low
amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely
affected by any variation in resistance in the system. Such resis-
tance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper
installation, improper wire gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire
with too much resistance.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-28
Page 33 of 2493

NJGI0006
NOTICE:
Trouble diagnoses indicate work procedures required to diagnose
problems effectively. Observe the following instructions before
diagnosing.
1)Before performing trouble diagnoses, read the ªPrelimi-
nary Checkº, the ªSymptom Chartº or the ªWork Flowº.
2)After repairs, re-check that the problem has been com-
pletely eliminated.
3)Refer to Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion for the Systems described in each section for
identification/location of components and harness con-
nectors.
4)Refer to the Circuit Diagram for quick pinpoint check.
If you need to check circuit continuity between harness
connectors in more detail, such as when a sub-harness is
used, refer to Wiring Diagram in each individual section
and Harness Layout in EL section for identification of har-
ness connectors.
5)When checking circuit continuity, ignition switch should
be OFF.
6)Before checking voltage at connectors, check battery volt-
age.
7)After accomplishing the Diagnostic Procedures and Elec-
trical Components Inspection, make sure that all harness
connectors are reconnected as they were.
HOW TO FOLLOW TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
GI-31
Page 39 of 2493
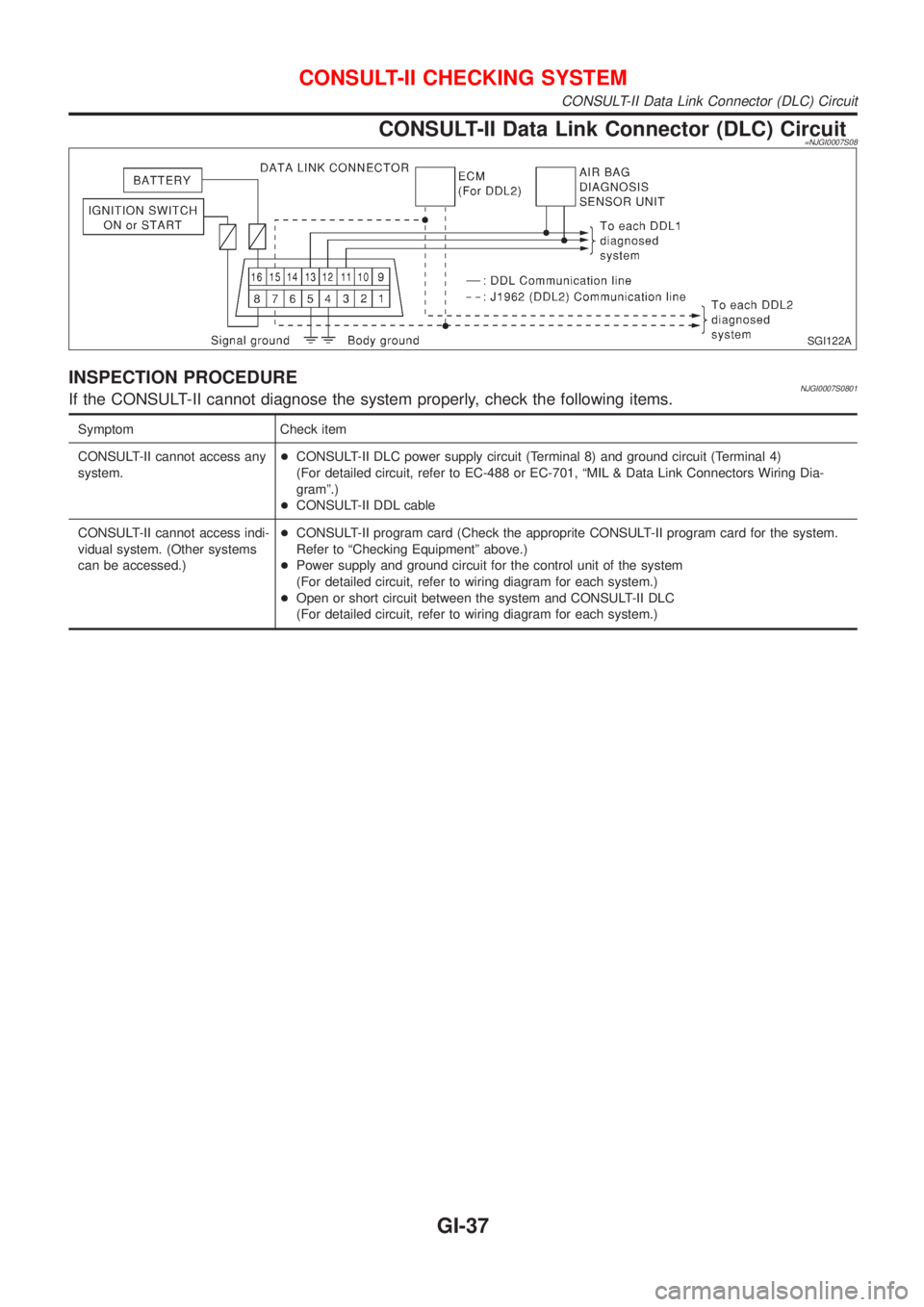
CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit=NJGI0007S08
SGI122A
INSPECTION PROCEDURENJGI0007S0801If the CONSULT-II cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
Symptom Check item
CONSULT-II cannot access any
system.+CONSULT-II DLC power supply circuit (Terminal 8) and ground circuit (Terminal 4)
(For detailed circuit, refer to EC-488 or EC-701, ªMIL & Data Link Connectors Wiring Dia-
gramº.)
+CONSULT-II DDL cable
CONSULT-II cannot access indi-
vidual system. (Other systems
can be accessed.)+CONSULT-II program card (Check the approprite CONSULT-II program card for the system.
Refer to ªChecking Equipmentº above.)
+Power supply and ground circuit for the control unit of the system
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
+Open or short circuit between the system and CONSULT-II DLC
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit
GI-37
Page 189 of 2493
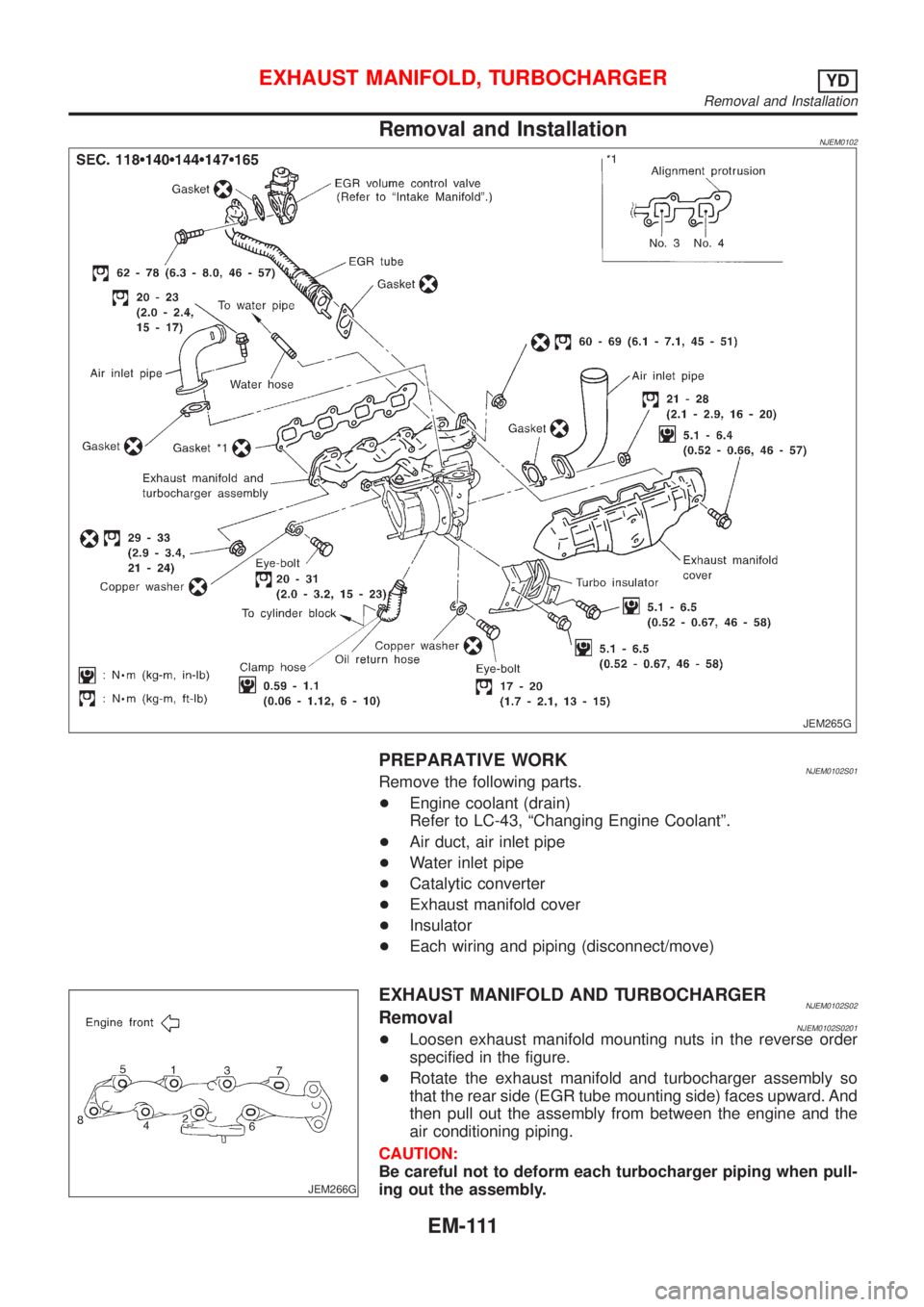
Removal and InstallationNJEM0102
JEM265G
PREPARATIVE WORKNJEM0102S01Remove the following parts.
+Engine coolant (drain)
Refer to LC-43, ªChanging Engine Coolantº.
+Air duct, air inlet pipe
+Water inlet pipe
+Catalytic converter
+Exhaust manifold cover
+Insulator
+Each wiring and piping (disconnect/move)
JEM266G
EXHAUST MANIFOLD AND TURBOCHARGERNJEM0102S02RemovalNJEM0102S0201+Loosen exhaust manifold mounting nuts in the reverse order
specified in the figure.
+Rotate the exhaust manifold and turbocharger assembly so
that the rear side (EGR tube mounting side) faces upward. And
then pull out the assembly from between the engine and the
air conditioning piping.
CAUTION:
Be careful not to deform each turbocharger piping when pull-
ing out the assembly.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD, TURBOCHARGERYD
Removal and Installation
EM-111
Page 297 of 2493
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
SECTION
EC
CONTENTS
QG
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - INDEX..................................10
Alphabetical & P No. Index for DTC .........................10
PRECAUTIONS.............................................................16
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)²AIR
BAG²and²SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER².............16
Precautions for On Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System of Engine and A/T.........................................16
Engine Fuel & Emission Control System ..................17
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnosis ...................19
PREPARATION.............................................................20
Special Service Tools ................................................20
Commercial Service Tools .........................................20
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL
SYSTEM.........................................................................21
Engine Control Component Parts Location ...............21
Circuit Diagram ..........................................................25
System Diagram ........................................................26
Vacuum Hose Drawing ..............................................27
System Chart .............................................................28
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION...............................................29
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System .......................29
Electronic Ignition (EI) System ..................................31
Air Conditioning Cut Control ......................................32
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed) ........................................................................33
Evaporative Emission System ...................................33
Positive Crankcase Ventilation ..................................37
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDURE...................................38
Fuel Pressure Release ..............................................38
Fuel Pressure Check .................................................38
Fuel Pressure Regulator Check ................................39
Injector .......................................................................39
How to Check Idle Speed and Ignition Timing ..........41
Preparation ................................................................42
Inspection Procedure .................................................45
Idle Air Volume Learning ...........................................55ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION...............................................................57
Introduction ................................................................57
Two Trip Detection Logic ...........................................57
Emission-related Diagnostic Information ...................58
NATS (Nissan Anti-theft System) ..............................72
Malfunction Indicator (MI) ..........................................72
OBD System Operation Chart (With Euro-OBD
Models Only)..............................................................76
CONSULT-II ...............................................................81
Generic Scan Tool (GST) ..........................................92
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION..................94
Introduction ................................................................94
Work Flow ..................................................................96
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - BASIC INSPECTION...........98
Basic Inspection.........................................................98
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - GENERAL
DESCRIPTION.............................................................122
DTC Inspection Priority Chart..................................122
Fail-safe Chart .........................................................123
Symptom Matrix Chart .............................................124
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode ........................................................................128
Major Sensor Reference Graph in Data Monitor
Mode ........................................................................130
ECM Terminals and Reference Value .....................132
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - SPECIFICATION VALUE..140
Description ...............................................................140
Testing Condition .....................................................140
Inspection Procedure ...............................................140
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................141
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR INTERMITTENT
INCIDENT.....................................................................144
Description ...............................................................144
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................144
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR POWER SUPPLY........145
Main Power Supply and Ground Circuit ..................145
DTC P0100 MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR (MAFS)......152
Component Description ...........................................152