NISSAN PATROL 2004 Electronic Repair Manual
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2004, Model line: PATROL, Model: NISSAN PATROL 2004Pages: 579, PDF Size: 26.61 MB
Page 251 of 579
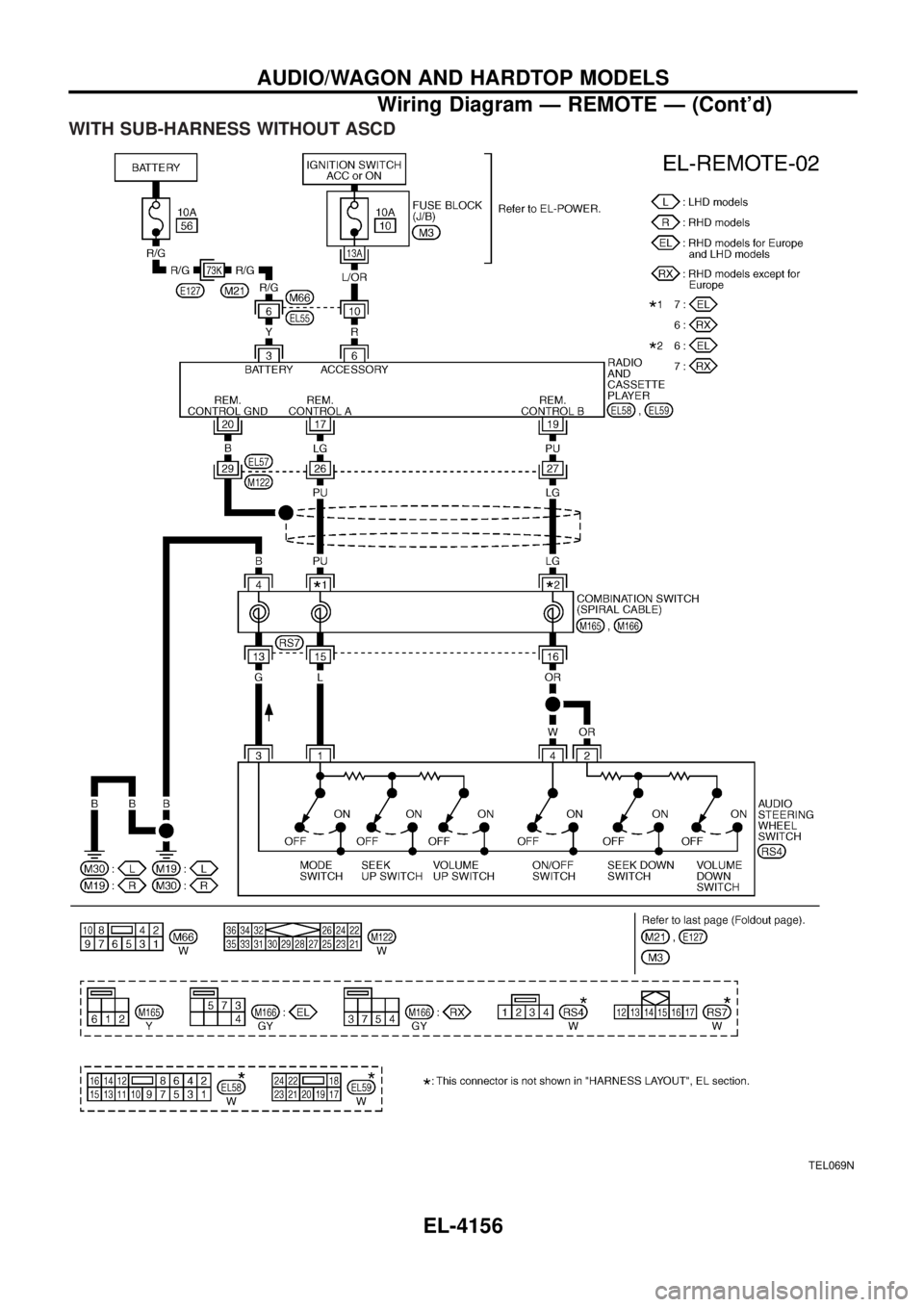
WITH SUB-HARNESS WITHOUT ASCD
TEL069N
AUDIO/WAGON AND HARDTOP MODELS
Wiring Diagram Ð REMOTE Ð (Cont'd)EL-4156
Page 252 of 579
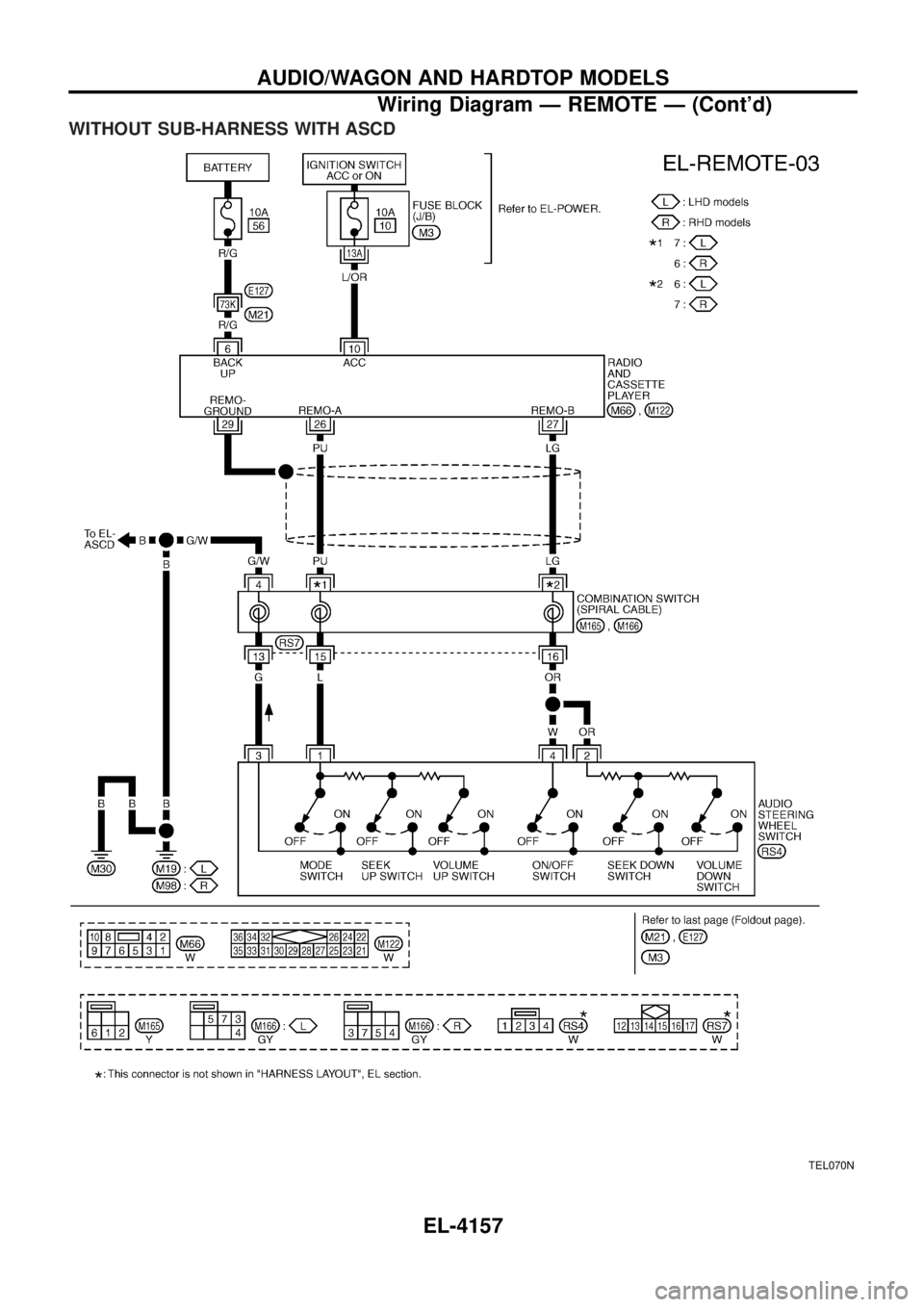
WITHOUT SUB-HARNESS WITH ASCD
TEL070N
AUDIO/WAGON AND HARDTOP MODELS
Wiring Diagram Ð REMOTE Ð (Cont'd)EL-4157
Page 253 of 579
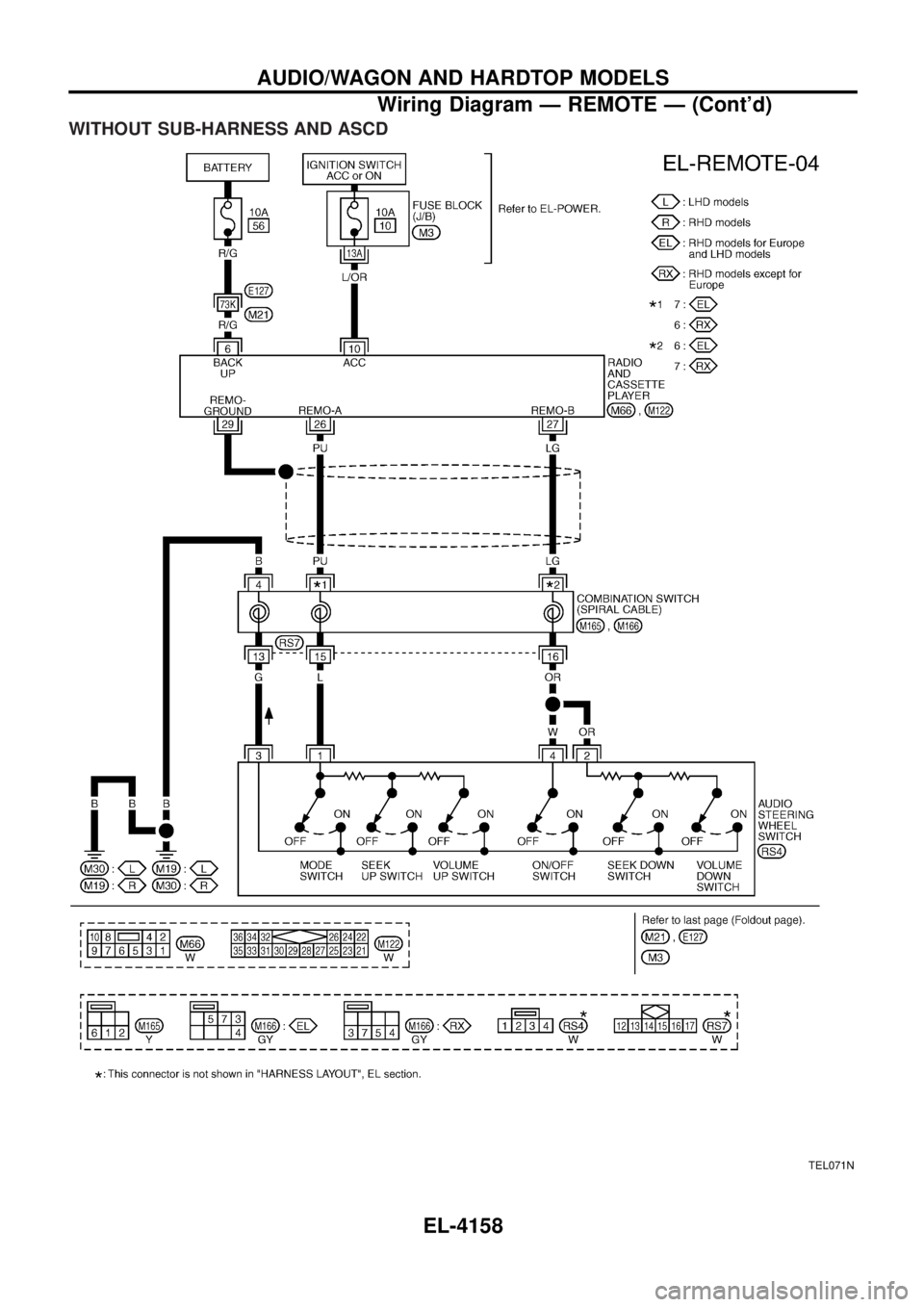
WITHOUT SUB-HARNESS AND ASCD
TEL071N
AUDIO/WAGON AND HARDTOP MODELS
Wiring Diagram Ð REMOTE Ð (Cont'd)EL-4158
Page 254 of 579
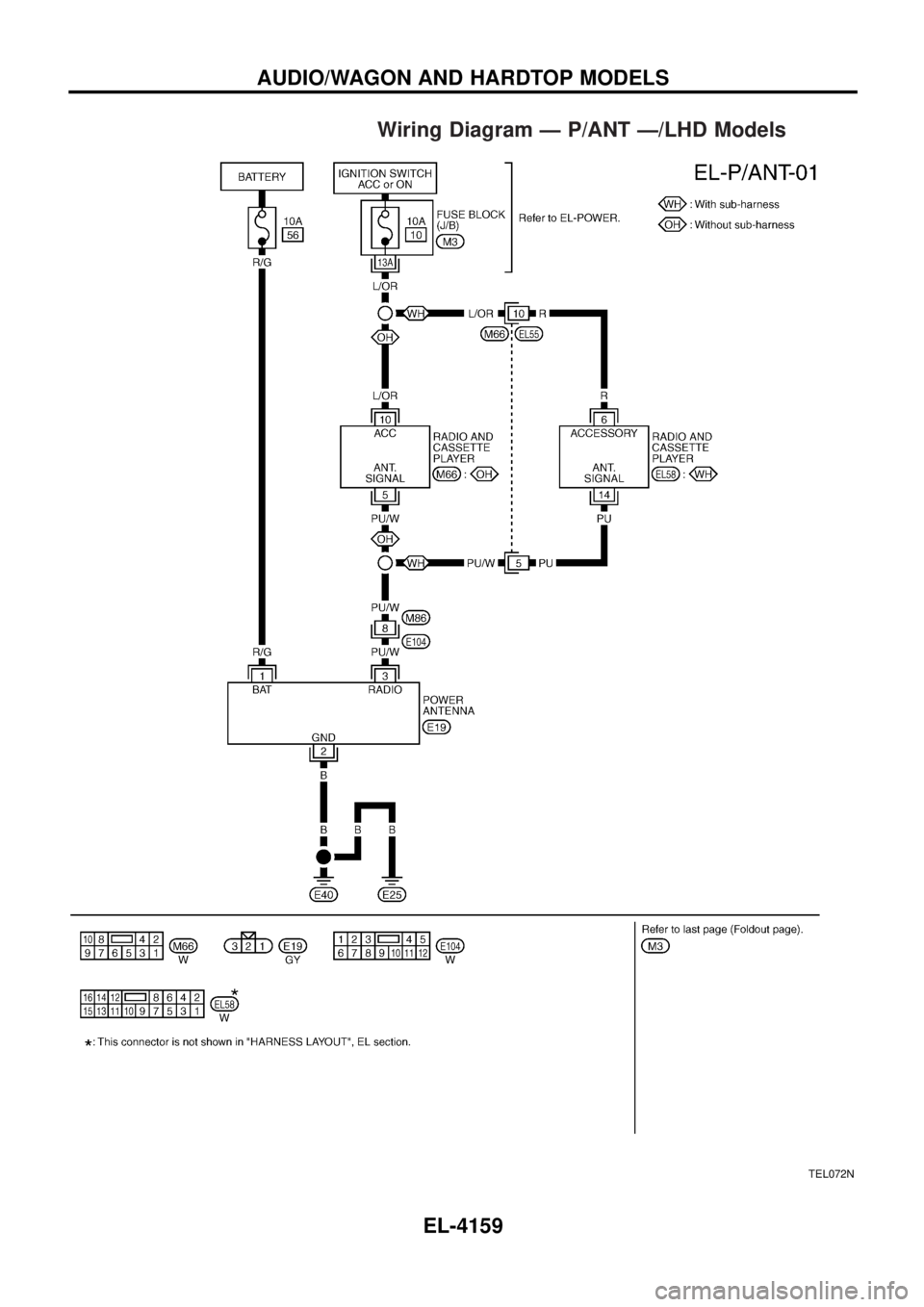
Wiring Diagram Ð P/ANT Ð/LHD Models
TEL072N
AUDIO/WAGON AND HARDTOP MODELS
EL-4159
Page 255 of 579
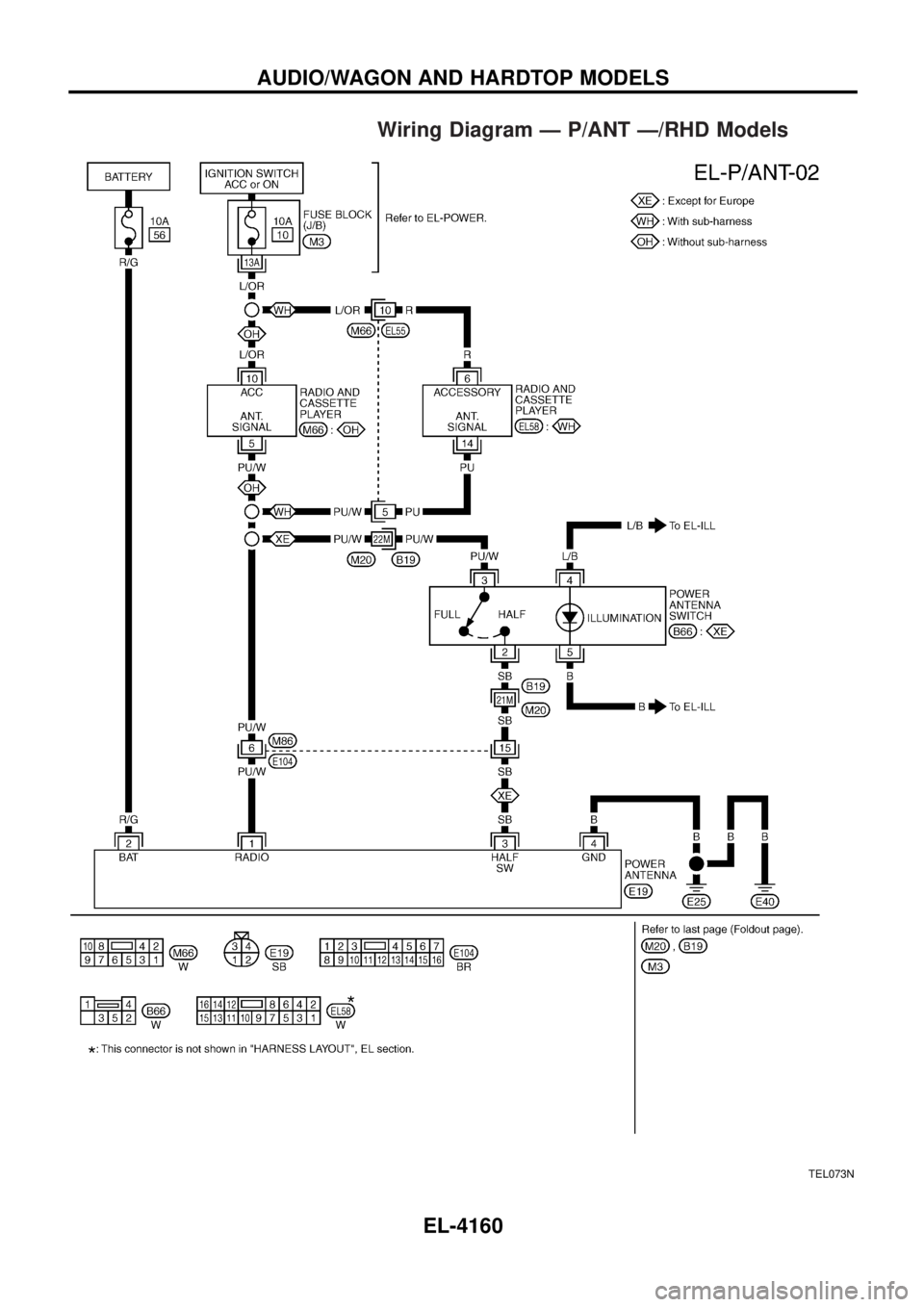
Wiring Diagram Ð P/ANT Ð/RHD Models
TEL073N
AUDIO/WAGON AND HARDTOP MODELS
EL-4160
Page 256 of 579
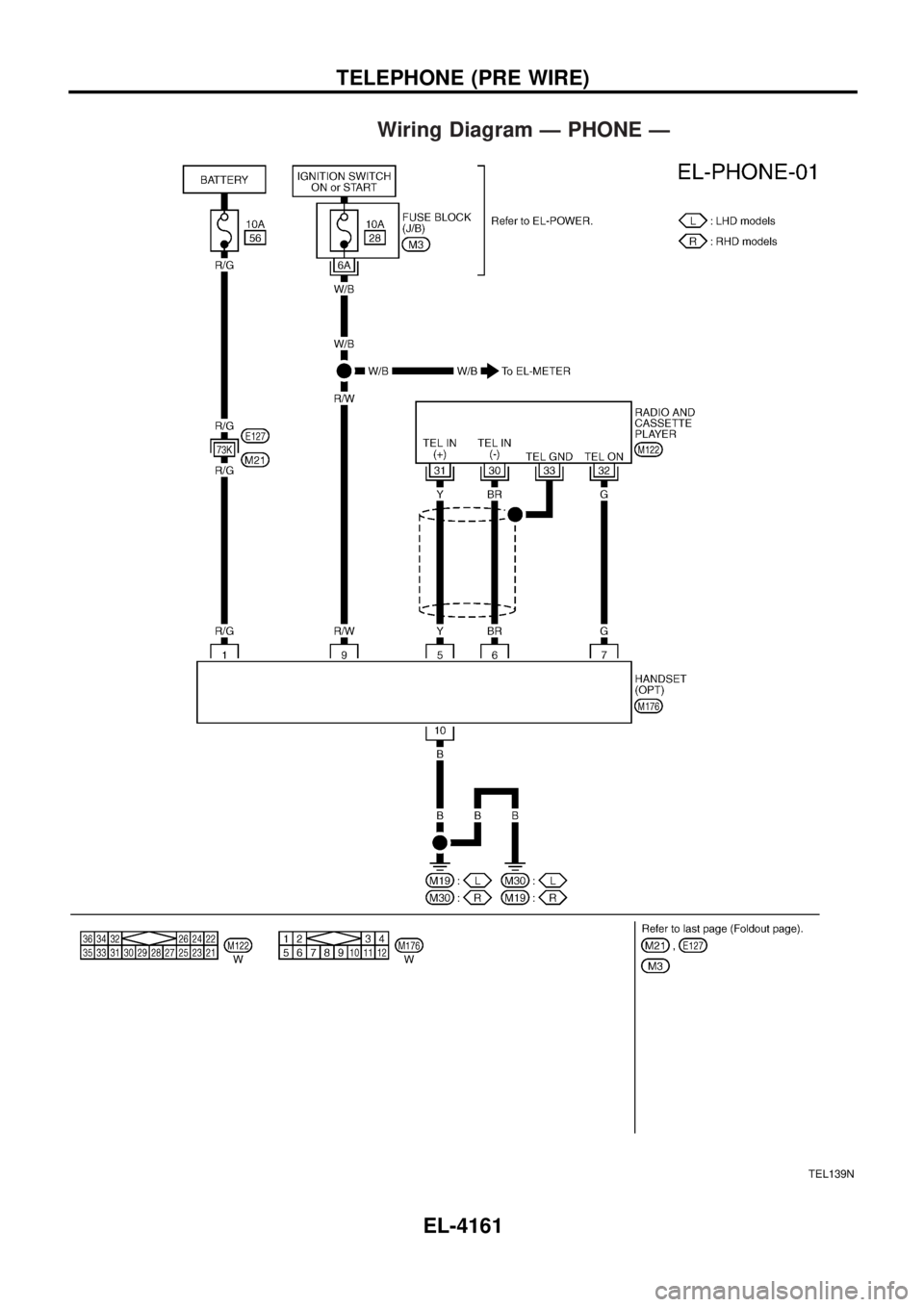
Wiring Diagram Ð PHONE Ð
TEL139N
TELEPHONE (PRE WIRE)
EL-4161
Page 257 of 579

System Description
OUTLINE
The navigation system periodically calculates the vehicle's current
position according to the following three signals: Travel distance of
the vehicle as determined by the vehicle speed sensor, turning
angle of the vehicle as determined by the gyroscope (angular
velocity sensor), and the direction of vehicle travel as determined
by the GPS antenna (GPS information).
The current position of the vehicle is then identi®ed by comparing
the calculated vehicle position with map data read from the map
DVD-ROM, which is stored in the DVD-ROM drive (map-matching),
and indicated on the screen with a current location mark.
By comparing the vehicle position detection results found by the
GPS and by map-matching, more accurate vehicle position data
can be used.
The current vehicle position will be calculated by detecting the dis-
tance the vehicle moved from the previous calculation point and its
direction.
TRAVEL DISTANCE
Travel distance calculations are based on the vehicle speed sen-
sor input signal. Therefore, the calculation may become incorrect
as the tires wear down. To prevent this, an automatic distance ®ne
adjustment function has been adopted.
TRAVEL DIRECTION
Change in the travel direction of the vehicle is calculated by a
gyroscope (angular velocity sensor) and a GPS antenna (GPS
information). As the gyroscope and GPS antenna have both merit
and demerit, input signals from them are prioritized in each situa-
tion. However, this order of priority may change in accordance with
more detailed travel conditions so that the travel direction is
detected more accurately.
Type Advantage Disadvantage
Gyroscope (angular velocity sensor) +
Can detect the vehicle's turning angle
quite accurately. +
Direction errors may accumulate when
the vehicle is driven for long distances
without stopping.
GPS antenna (GPS information) +
Can detect the vehicle's travel direction
(North/South/East/West). +
Correct direction cannot be detected
when the vehicle speed is low.
SKIA0370E
SEL684V
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
EL-4162
Page 258 of 579

MAP-MATCHING
Map-matching is a function that repositions the vehicle on the road
map when a new location is judged to be the most accurate. This
is done by comparing the current vehicle position, calculated by the
method described in the position detection principle, with the road
map data around the vehicle, read from the map DVD-ROM stored
in the DVD-ROM drive.
Therefore, the vehicle position may not be corrected after the
vehicle is driven over a certain distance or time in which GPS
information is hard to receive. In this case, the current location
mark on the display must be corrected manually.
NOTE:
The road map data is based on data stored in the map DVD-ROM.
+In map-matching, alternative routes to reach the destination will
be shown and prioritized, after the road on which the vehicle is
currently driven has been judged and the current location mark
has been repositioned.
If there is an error in distance and/or direction, the alternative
routes will be shown in different order of priority, and the wrong
road can be avoided.
If two roads are running in parallel, they are of the same prior-
ity. Therefore, the current location mark may appear on either
of them alternately, depending on maneuvering of the steering
wheel and con®guration of the road.
+ Map-matching does not function correctly when the road on
which the vehicle is driving is new and not recorded in the map
DVD-ROM, or when the road pattern stored in the map data
and the actual road pattern are different due to repair.
When driving on a road not present in the map, the map-match-
ing function may ®nd another road and position the current
location mark on it. Then, when the correct road is detected, the
current location mark may leap to it.
+ Effective range for comparing the vehicle position and travel
direction calculated by the distance and direction with the road
data read from the map DVD-ROM is limited. Therefore, when
there is an excessive gap between the current vehicle position
and the position on the map, correction by map-matching is not
possible.
SEL685V
SEL686V
SKIA0613E
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
System Description (Cont'd)
EL-4163
Page 259 of 579

GPS (GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM)
GPS (Global Positioning System) has been developed and con-
trolled by the US Department of Defense. The system utilizes GPS
satellite (NAVSTAR), sending out radio waves while ¯ying on an
orbit around the earth at the height of approx. 21,000 km (13,000
miles).
The GPS receiver calculates the vehicle's position in three dimen-
sions (latitude/longitude/altitude) according to the time lag of the
radio waves received from four or more GPS satellites (three-di-
mensional positioning). If radio waves were received only from
three GPS satellites, the GPS receiver calculates the vehicle's
position in two dimensions (latitude/longitude), utilizing the altitude
data calculated previously by using radio waves from four or more
GPS satellites (two-dimensional positioning).
Accuracy of the GPS will deteriorate under the following conditions.
+In two-dimensional positioning, the GPS accuracy will deterio-
rate when the altitude of the vehicle position changes.
+ There may be an error of approximately 10 m (30 ft.) in posi-
tion detected by three-dimensional positioning, which is more
accurate than two-dimensional positioning. The accuracy can
be even lower depending on the arrangement of the GPS sat-
ellites utilized for the positioning.
+ Position detection is not possible when the vehicle is in an area
where radio waves from the GPS satellite do not reach, such
as in a tunnel, parking lot in a building, and under an elevated
highway. Radio waves from the GPS satellites may not be
received when some object is located over the GPS antenna.
+ Position correction by GPS is not available while the vehicle is
stopped.
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
NAVI control unit
+The gyro (angular speed sensor) and the DVD-ROM drive are
built-in units that control the navigation functions.
+ Signals are received from the gyro, the vehicle speed sensor,
and the GPS antenna. Vehicle location is determined by com-
bining this data with the data contained in the DVD-ROM map.
Locational information is shown on liquid crystal display panel.
DVD-ROM drive
Maps, traffic control regulations, and other pertinent information
can be easily read from the DVD-ROM disc.
Map DVD-ROM
+The map DVD-ROM has maps, traffic control regulations, and
other pertinent information.
+ To improve DVD-ROM map matching and route determination
functions, the DVD-ROM uses an exclusive Nissan format.
Therefore, the use of a DVD-ROM provided by other manufac-
turers cannot be used.
SEL526V
PKIA0248E
PKIA0249E
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
System Description (Cont'd)
EL-4164
Page 260 of 579

Gyro (Angular speed sensor)
+The oscillator gyro sensor is used to detect changes in vehicle
steering angle.
+ The gyro is built into the navigation (NAVI) control unit.
BIRDVIEW T
The BIRDVIEW Tprovides a detailed and easily seen display of
road conditions covering the vehicle's immediate to distant area.
+ MAP DISPLAY
+ BIRDVIEW T
Description
+Display area: Trapezoidal representation showing approximate
distances (Wn, D, and Wd).
+ Ten horizontal grid lines indicate display width while six vertical
grid lines indicate display depth and direction.
+ Drawing line area shows open space, depth, and immediate
front area. Each area is to a scale of approximately 5:6:25.
+ Pushing the ªZOOM INº button during operation displays the
scale change and the view point height on the left side of the
screen.
The height of the view point increases or decreases when
ªZOOMº or ªWIDEº is selected.
SKIA1377E
SKIA1378E
SEL691V
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
System Description (Cont'd)
EL-4165