Electrical NISSAN PATROL 2006 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2006, Model line: PATROL, Model: NISSAN PATROL 2006Pages: 1226, PDF Size: 37.18 MB
Page 661 of 1226

Code Section Wiring Diagram Name
STAB RARear Stabilizer Release Device Con-
trol System
START EL Starting System
STOP/L EL Stop Lamp
TAIL/L ELParking, License, Tail and Stop
Lamps
TCV EC Injection Timing Control Valve
TPS EC Throttle Position Sensor
TURN ELTurn Signal and Hazard Warning
Lamps
VSS EC Vehicle Speed Sensor
WARN EL Warning Lamps
WINCH SE Electrical Winch
WINDOW EL Power Window
WIP/R EL Rear Wiper and Washer
WIPER EL Front Wiper and Washer
WIRING DIAGRAM CODES (CELL CODES)
EL-316
Page 666 of 1226
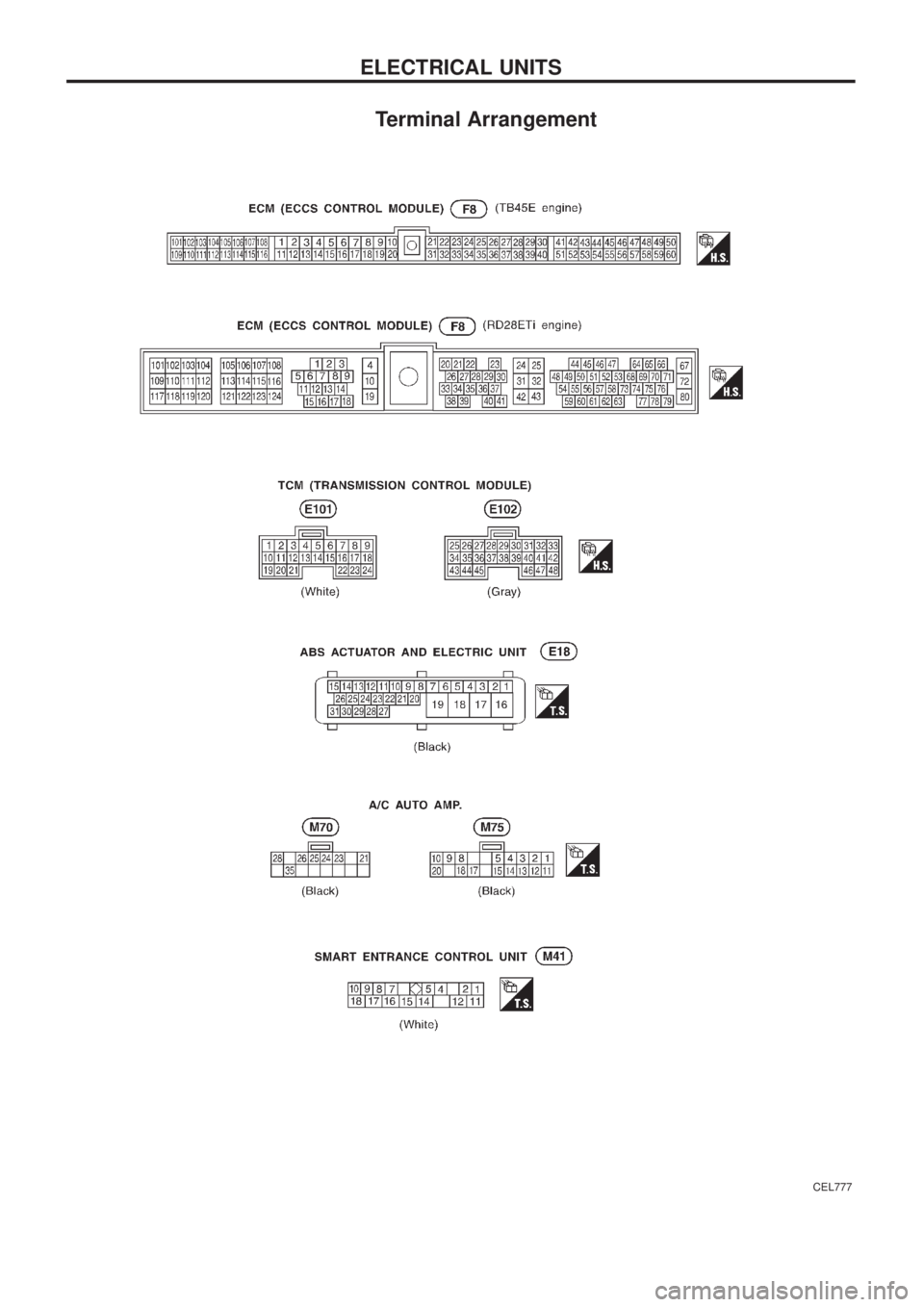
Terminal Arrangement
CEL777
ELECTRICAL UNITS
Page 771 of 1226
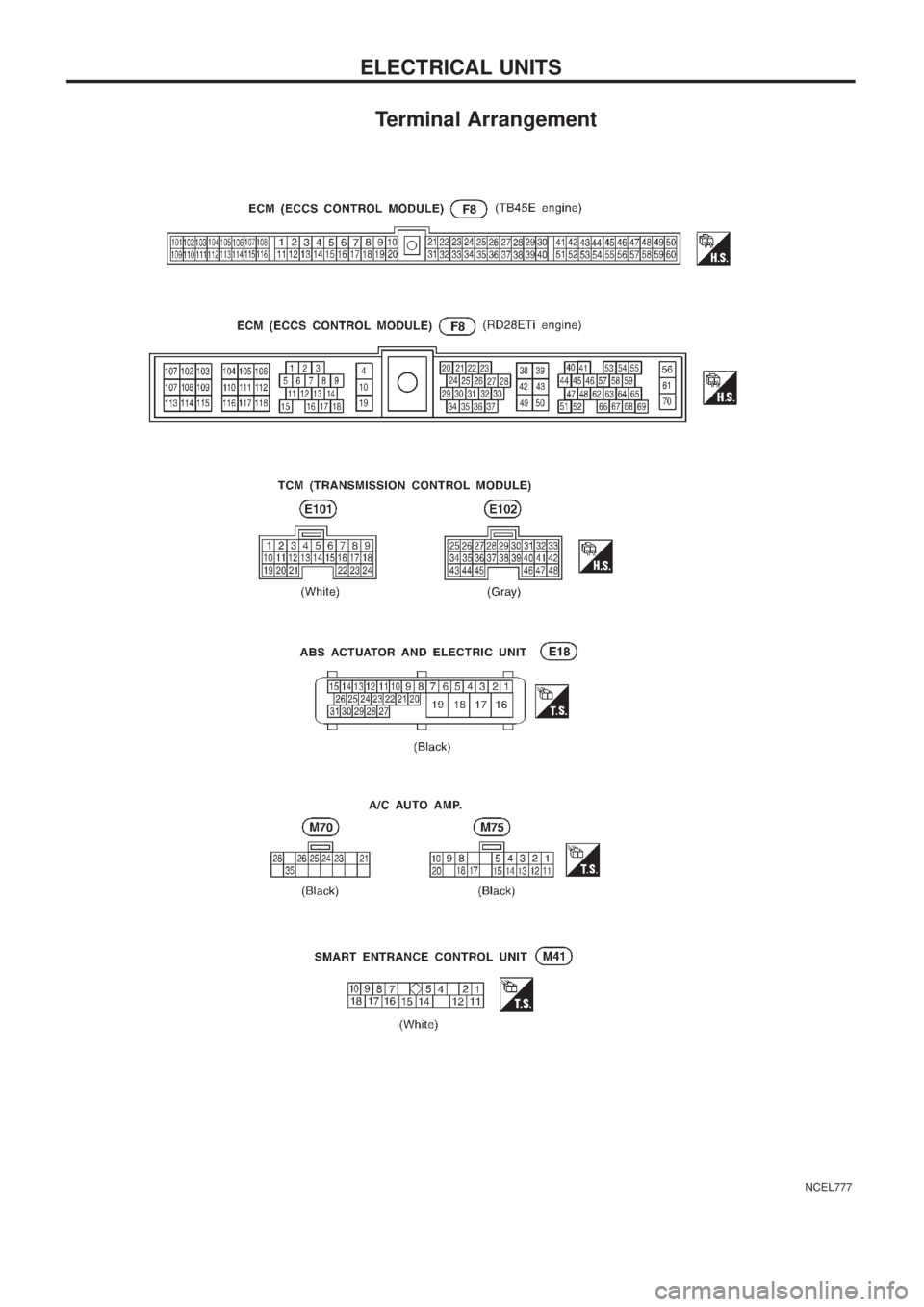
Terminal Arrangement
NCEL777
ELECTRICAL UNITS
Page 773 of 1226

GENERAL INFORMATION
SECTION
GI
CONTENTS
PRECAUTIONS...............................................................1
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) ``AIR BAG'' and ``SEAT BELT
PRE-TENSIONER'' ......................................................1
General Precautions ....................................................2
Precautions for Multiport Fuel Injection System
or ECCS Engine ..........................................................3
Precautions for Three Way Catalyst
(If so equipped)............................................................4
Precautions for Engine Oils .........................................4
Precautions for Fuel ....................................................5
Precautions for Air Conditioning ..................................5
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL........................................6
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS............................8
Sample/Wiring Diagram Ð EXAMPL Ð......................8
Description .................................................................10
HOW TO CHECK TERMINAL.......................................17
How to Probe Connectors .........................................17
How to Check Enlarged Contact Spring of
Terminal .....................................................................18
Waterproof Connector Inspection ..............................19
Terminal Lock Inspection ...........................................19
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR
AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT........................................20Work Flow ..................................................................20
Incident Simulation Tests ...........................................21
Circuit Inspection .......................................................24
HOW TO FOLLOW FLOW CHART IN TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES..................................................................30
How to Follow This Flow Chart .................................31
CONSULT CHECKING SYSTEM..................................33
Function and System Application ..............................33
Lithium Battery Replacement ....................................33
Checking Equipment..................................................33
Loading Procedure ....................................................34
CONSULT Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit..........34
IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION.................................35
Model Variation ..........................................................35
Identi®cation Number .................................................36
Dimensions ................................................................38
Wheels & Tires ..........................................................38
LIFTING POINTS AND TOW TRUCK TOWING...........39
Screw Jack ................................................................39
Garage Jack and Safety Stand .................................39
2-pole Lift ...................................................................40
Tow Truck Towing ......................................................41
SAE J1930 TERMINOLOGY LIST................................43
SAE J1930 Terminology List .....................................43
GI
Page 774 of 1226

Observe the following precautions to ensure safe and proper
servicing. These precautions are not described in each indi-
vidual section.
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) ``AIR BAG'' and ``SEAT BELT
PRE-TENSIONER''
The Supplemental Restraint System such as ``AIR BAG'' and
``SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER'' used along with a seat belt, helps
to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front pas-
senger in a frontal collision. The SRS system composition which is
available to NISSAN MODEL Y61 is as follows (The composition
varies according to the destination.):
Driver air bag module (located in the center of the steering wheel),
front passenger air bag module (located on the instrument panel on
passenger side), seat belt pre-tensioner, a diagnosis sensor unit,
warning lamp, wiring harness and spiral cable.
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in
theRS sectionof this Service Manual.
WARNING:
+To avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could
increase the risk of personal injury or death in the event of
a collision which would result in air bag in¯ation, all main-
tenance must be performed by an authorized NISSAN
dealer.
+Improper maintenance, including incorrect removal and
installation of the SRS, can lead to personal injury caused
by unintentional activation of the system. For removal of
Spiral Cable and Air Bag Module, see the RS section.
+Do not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related
to the SRS unless instructed to in this Service Manual.
Spiral cable and wiring harnesses are covered with yellow
insulation either just before the harness connectors or for
the complete harness are related to the SRS.
SGI646
PRECAUTIONS
GI-1
Page 776 of 1226

+Clean all disassembled parts in the designated liquid or solvent
prior to inspection or assembly.
+Replace oil seals, gaskets, packings, O-rings, locking washers,
cotter pins, self-locking nuts, etc. with new ones.
+Replace inner and outer races of tapered roller bearings and
needle bearings as a set.
+Arrange the disassembled parts in accordance with their
assembled locations and sequence.
+Do not touch the terminals of electrical components which use
microcomputers (such as ECMs).
Static electricity may damage internal electronic components.
+After disconnecting vacuum or air hoses, attach a tag to indi-
cate the proper connection.
+Use only the ¯uids and lubricants speci®ed in this manual.
+Use approved bonding agent, sealants or their equivalents
when required.
+Use tools and recommended special tools where speci®ed for
safe and efficient service repairs.
+When repairing the fuel, oil, water, vacuum or exhaust systems,
check all affected lines for leaks.
+Dispose of drained oil or the solvent used for cleaning parts in
an appropriate manner.
WARNING:
To prevent ECM from storing the diagnostic trouble codes, do
not carelessly disconnect the harness connectors which are
related to the ECCS system and TCM (Transmission Control
Module) system. The connectors should be disconnected only
when working according to the WORK FLOW of TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES in EC and AT sections.
Precautions for Multiport Fuel Injection System
or ECCS Engine
+Before connecting or disconnecting any harness connector for
the multiport fuel injection system or ECM (Engine Control
Module):
Turn ignition switch to ``OFF'' position.
Disconnect negative battery terminal.
Otherwise, there may be damage to ECM.
+
Before disconnecting pressurized fuel line from fuel pump to
injectors, be sure to release fuel pressure.
+Be careful not to jar components such as ECM and mass air
¯ow sensor.SGI787
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions (Cont'd)
GI-3
Page 793 of 1226

Work Flow
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1 Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHATVehicle Model, Engine, Transmission and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHENDate, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERERoad Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOWSystem Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2 Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem can not be duplicated, refer to ``Incident Simulation Tests'' next page.
STEP 3 Get the proper diagnosis materials together including:
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
System Operation Descriptions
Applicable Service Manual Sections
Check for any Service Bulletin.
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the customer comments.
STEP 4 Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing and Harness
Layouts.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6 Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you have not inad-
vertently created a new incident during your diagnosis or repair steps.
SGI838
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-20
Page 794 of 1226

Incident Simulation Tests
INTRODUCTION
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The
following section illustrates ways to simulate the conditions/environment under which the owner experiences
an electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
+Vehicle vibration
+Heat sensitive
+Freezing
+Water intrusion
+Electrical load
+Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of
the problem.
VEHICLE VIBRATION
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the illustration below.
Connectors & harness
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting.Gen-
tlyshake each connector and harness while monitoring the system for the incident you are trying to dupli-
cate. This test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
Hint
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin ®lm of corrosion on the connector termi-
nals. A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs
intermittently, perhaps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean
the terminals on related connectors in the system.
Sensors & relays
Gentlyapply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
SGI839
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-21
Page 795 of 1226

Engine compartment
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could
cause an electrical complaint. Some of the things to check for are:
+Connectors not fully seated.
+Wiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to
engine vibrations or rocking.
+Wires laying across brackets or moving components.
+Loose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
+Wires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifying the integ-
rity of ground connections. (Refer to GROUND INSPECTION
described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded.
Then check for loose connection bygently shakingthe wiring or
components as previously explained. Using the wiring diagrams
inspect the wiring for continuity.
Behind the instrument panel
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become
pinched during accessory installation. Vehicle vibration can aggra-
vate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
Under seating areas
An unclamped or loose harness can cause wiring to be pinched by
seat components (such as slide guides) during vehicle vibration. If
the wiring runs under seating areas, inspect wire routing for pos-
sible damage or pinching.
HEAT SENSITIVE
The owner's problem may occur during hot weather or after car has
sat for a short time. In such cases you will want to check for a heat
sensitive condition.
To determine if an electrical component is heat sensitive, heat the
component with a heat gun or equivalent.
Do not heat components above 60ÉC (140ÉF).If incident occurs
while heating the unit, either replace or properly insulate the com-
ponent.
SGI842
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Incident Simulation Tests (Cont'd)
GI-22
Page 796 of 1226

FREEZING
The customer may indicate the incident goes away after the car
warms up (winter time). The cause could be related to water freez-
ing somewhere in the wiring/electrical system.
There are two methods to check for this. The ®rst is to arrange for
the owner to leave his car overnight. Make sure it will get cold
enough to demonstrate his complaint. Leave the car parked outside
overnight. In the morning, do a quick and thorough diagnosis of
those electrical components which could be affected.
The second method is to put the suspect component into a freezer
long enough for any water to freeze. Reinstall the part into the car
and check for the reoccurrence of the incident. If it occurs, repair
or replace the component.
WATER INTRUSION
The incident may occur only during high humidity or in rainy/snowy
weather. In such cases the incident could be caused by water
intrusion on an electrical part. This can be simulated by soaking the
car or running it through a car wash.
Do not spray water directly on any electrical components.
ELECTRICAL LOAD
The incident may be electrical load sensitive. Perform diagnosis
with all accessories (including A/C, rear window defogger, radio, fog
lamps) turned on.
COLD OR HOT START UP
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the
car is started cold. Or it may occur when the car is restarted hot
shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep
the car overnight to make a proper diagnosis.
SGI843
SGI844
SGI845
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Incident Simulation Tests (Cont'd)
GI-23