distributor NISSAN PRIMERA 1999 Electronic Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1999, Model line: PRIMERA, Model: NISSAN PRIMERA 1999Pages: 2267, PDF Size: 35.74 MB
Page 801 of 2267

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
SECTION
EC
CONTENTS
SR20DE
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - INDEX....................................6
Alphabetical & P No. Index for DTC ...........................6
PRECAUTIONS.............................................................10
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)²AIR
BAG²and²SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER².............10
Precautions for On Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System of Engine and CVT .......................................10
Engine Fuel & Emission Control System .................. 11
Precautions ................................................................12
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnosis ...................13
PREPARATION.............................................................14
Special Service Tools ................................................14
Commercial Service Tool ...........................................14
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL
SYSTEM.........................................................................15
Engine Control Component Parts Location ...............15
Circuit Diagram ..........................................................19
System Diagram ........................................................20
Vacuum Hose Drawing ..............................................21
System Chart .............................................................22
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION...............................................23
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System .......................23
Distributor Ignition (DI) System .................................25
Air Conditioning Cut Control ......................................26
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed) ........................................................................27
Evaporative Emission System ...................................27
Positive Crankcase Ventilation ..................................30
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDURE...................................31
Fuel Pressure Release ..............................................31
Fuel Pressure Check .................................................31
Fuel Pressure Regulator Check ................................32
Injector .......................................................................32
Idle Speed/Ignition Timing/Idle Mixture Ratio
Adjustment .................................................................34Idle Air Volume Learning ...........................................46
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION...............................................................48
Introduction ................................................................48
Two Trip Detection Logic ...........................................48
Emission-related Diagnostic Information ...................49
Malfunction Indicator (MI) ..........................................58
OBD System Operation Chart ...................................63
CONSULT-II ...............................................................68
Generic Scan Tool (GST) ..........................................78
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION..................80
Introduction ................................................................80
Work Flow ..................................................................82
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - BASIC INSPECTION...........84
Basic Inspection.........................................................84
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - GENERAL
DESCRIPTION...............................................................92
DTC Inspection Priority Chart....................................92
Fail-safe Chart ...........................................................93
Symptom Matrix Chart ...............................................94
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode ..........................................................................98
Major Sensor Reference Graph in Data Monitor
Mode ........................................................................100
ECM Terminals and Reference Value .....................103
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - SPECIFICATION VALUE.. 110
Description ............................................................... 110
Testing Condition ..................................................... 110
Inspection Procedure ............................................... 110
Diagnostic Procedure .............................................. 111
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR INTERMITTENT
INCIDENT..................................................................... 114
Description ............................................................... 114
Diagnostic Procedure .............................................. 114
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR POWER SUPPLY........ 115
Main Power Supply and Ground Circuit .................. 115
EC
Page 815 of 2267
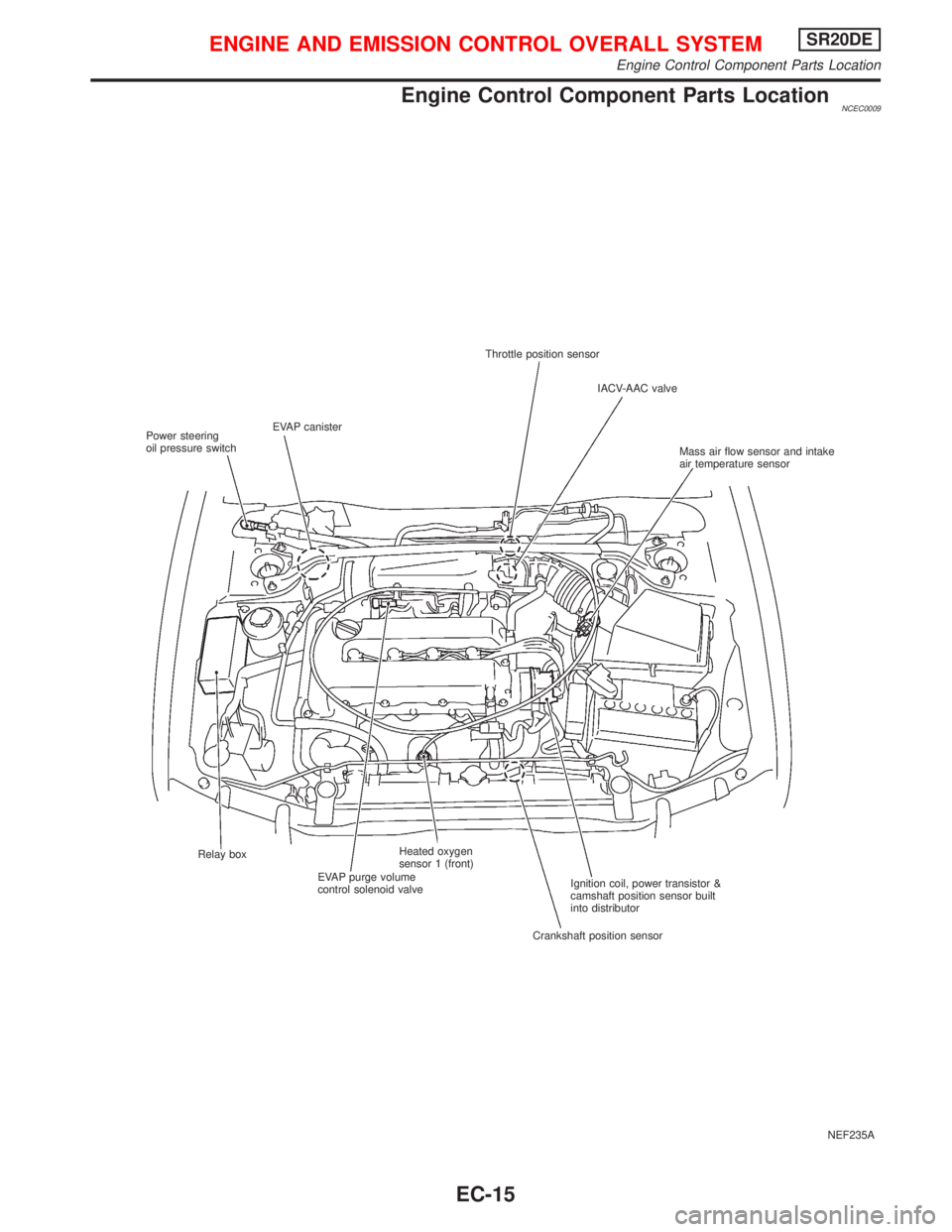
Engine Control Component Parts LocationNCEC0009
NEF235A Throttle position sensor
IACV-AAC valve
Mass air flow sensor and intake
air temperature sensor
Ignition coil, power transistor &
camshaft position sensor built
into distributor
Crankshaft position sensor Relay box
EVAP purge volume
control solenoid valveHeated oxygen
sensor 1 (front) EVAP canister
Power steering
oil pressure switch
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMSR20DE
Engine Control Component Parts Location
EC-15
Page 818 of 2267
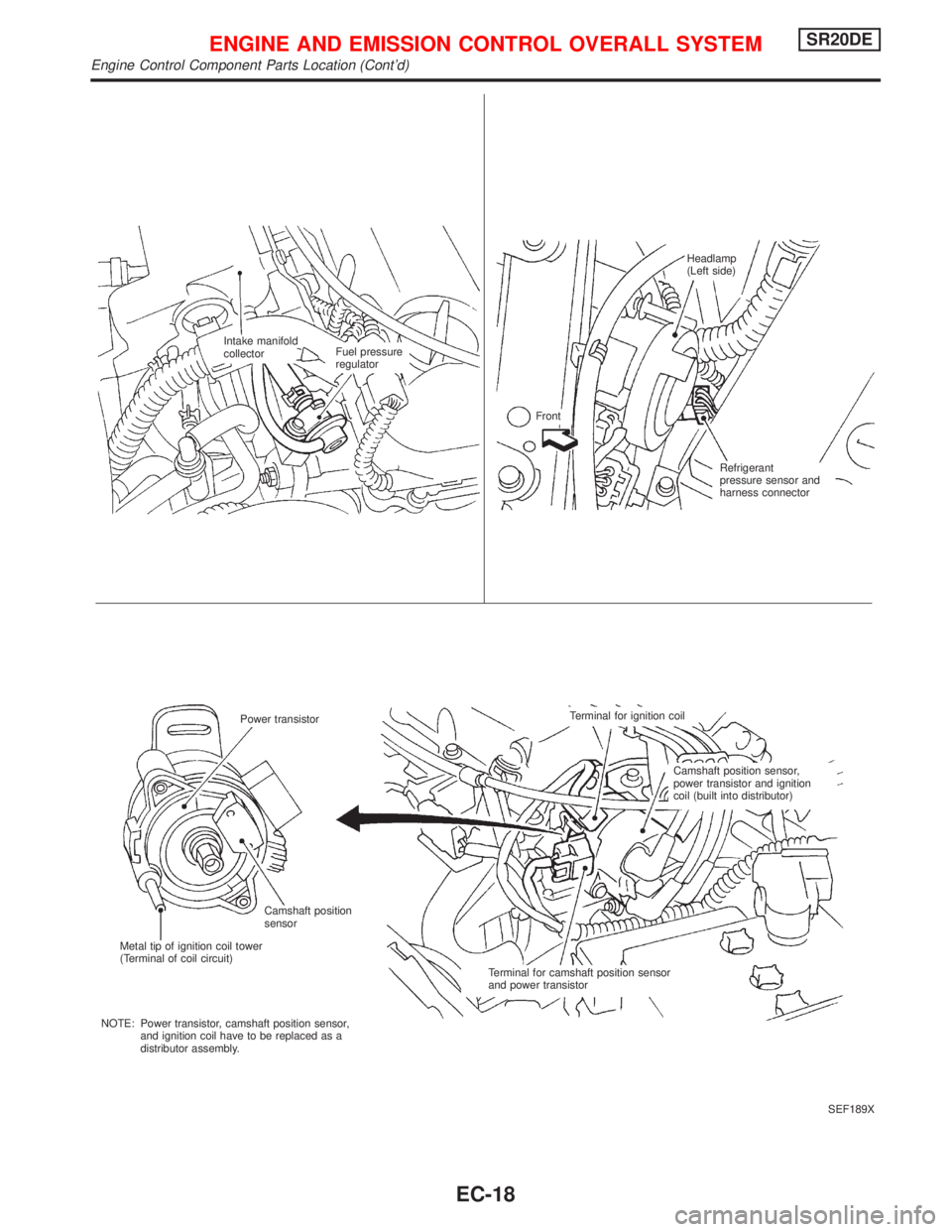
SEF189X Intake manifold
collectorFuel pressure
regulatorHeadlamp
(Left side)
Front
Refrigerant
pressure sensor and
harness connector
Power transistorTerminal for ignition coil
Camshaft position sensor,
power transistor and ignition
coil (built into distributor)
Terminal for camshaft position sensor
and power transistor Camshaft position
sensor
Metal tip of ignition coil tower
(Terminal of coil circuit)
NOTE: Power transistor, camshaft position sensor,
and ignition coil have to be replaced as a
distributor assembly.
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMSR20DE
Engine Control Component Parts Location (Cont'd)
EC-18
Page 822 of 2267
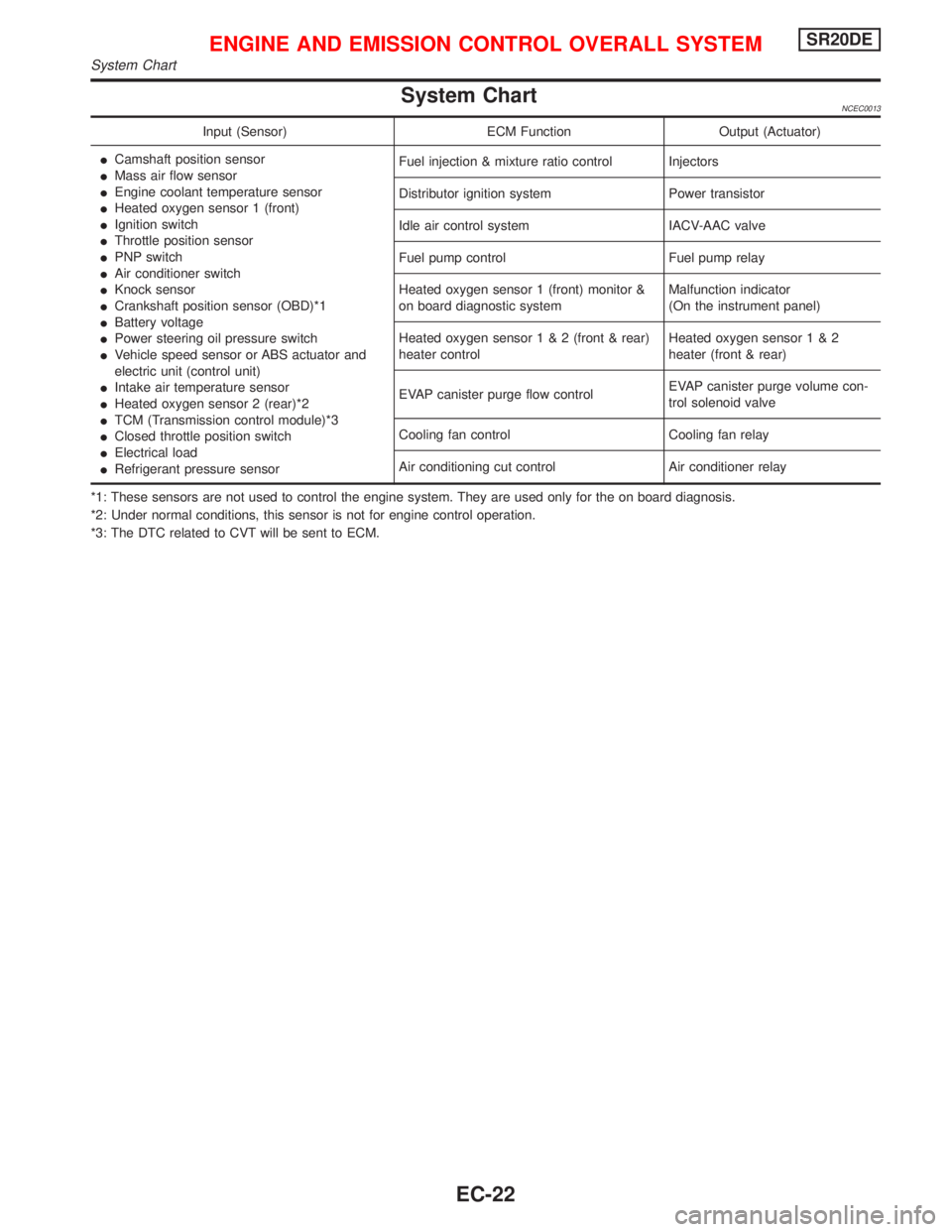
System ChartNCEC0013
Input (Sensor) ECM Function Output (Actuator)
ICamshaft position sensor
IMass air flow sensor
IEngine coolant temperature sensor
IHeated oxygen sensor 1 (front)
IIgnition switch
IThrottle position sensor
IPNP switch
IAir conditioner switch
IKnock sensor
ICrankshaft position sensor (OBD)*1
IBattery voltage
IPower steering oil pressure switch
IVehicle speed sensor or ABS actuator and
electric unit (control unit)
IIntake air temperature sensor
IHeated oxygen sensor 2 (rear)*2
ITCM (Transmission control module)*3
IClosed throttle position switch
IElectrical load
IRefrigerant pressure sensorFuel injection & mixture ratio control Injectors
Distributor ignition system Power transistor
Idle air control system IACV-AAC valve
Fuel pump control Fuel pump relay
Heated oxygen sensor 1 (front) monitor &
on board diagnostic systemMalfunction indicator
(On the instrument panel)
Heated oxygen sensor1&2(front & rear)
heater controlHeated oxygen sensor1&2
heater (front & rear)
EVAP canister purge flow controlEVAP canister purge volume con-
trol solenoid valve
Cooling fan control Cooling fan relay
Air conditioning cut control Air conditioner relay
*1: These sensors are not used to control the engine system. They are used only for the on board diagnosis.
*2: Under normal conditions, this sensor is not for engine control operation.
*3: The DTC related to CVT will be sent to ECM.
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMSR20DE
System Chart
EC-22
Page 825 of 2267

Fuel Injection TimingNCEC0014S07
Two types of systems are used.
Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System
NCEC0014S0701Fuel is injected into each cylinder during each engine cycle according to the firing order. This system is used
when the engine is running.
Simultaneous Multiport Fuel Injection System
NCEC0014S0702Fuel is injected simultaneously into all four cylinders twice each engine cycle. In other words, pulse signals of
the same width are simultaneously transmitted from the ECM.
The four injectors will then receive the signals two times for each engine cycle.
This system is used when the engine is being started and/or if the fail-safe system (CPU) is operating.
Fuel Shut-offNCEC0014S08Fuel to each cylinder is cut off during deceleration or operation of the engine at excessively high speeds.
Distributor Ignition (DI) System
DESCRIPTIONNCEC0015Input/Output Signal ChartNCEC0015S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Camshaft position sensor Engine speed and piston position
Ignition tim-
ing controlPower transistor Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Throttle position sensorThrottle position
Throttle valve idle position
Vehicle speed sensor or ABS actuator and
electric unit (control unit)Vehicle speed
Ignition switch Start signal
Knock sensor Engine knocking
PNP switch Gear position
Battery Battery voltage
SEF337W
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONSR20DE
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System (Cont'd)
EC-25
Page 826 of 2267

System DescriptionNCEC0015S02
The ignition timing is controlled by the ECM to maintain the best air-fuel ratio for every running condition of
the engine. The ignition timing data is stored in the ECM. This data forms the map shown above.
The ECM receives information such as the injection pulse width and camshaft position sensor signal. Com-
puting this information, ignition signals are transmitted to the power transistor.
e.g., N: 1,800 rpm, Tp: 1.50 msec
AÉBTDC
During the following conditions, the ignition timing is revised by the ECM according to the other data stored
in the ECM.
IAt starting
IDuring warm-up
IAt idle
IAt low battery voltage
IDuring acceleration
The knock sensor retard system is designed only for emergencies. The basic ignition timing is programmed
within the anti-knocking zone, if recommended fuel is used under dry conditions. The retard system does not
operate under normal driving conditions.
If engine knocking occurs, the knock sensor monitors the condition. The signal is transmitted to the ECM. The
ECM retards the ignition timing to eliminate the knocking condition.
Air Conditioning Cut Control
DESCRIPTIONNCEC0016Input/Output Signal ChartNCEC0016S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner ªONº signal
Air condi-
tioner cut
controlAir conditioner relay PNP switch Neutral position
Throttle position sensor Throttle valve opening angle
Camshaft position sensor Engine speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Ignition switch Start signal
Refrigerant pressure sensor Refrigerant pressure
Vehicle speed sensor or ABS actuator and
electric unit (control unit)Vehicle speed
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering operation
System DescriptionNCEC0016S02This system improves engine operation when the air conditioner is used.
Under the following conditions, the air conditioner is turned off.
IWhen the accelerator pedal is fully depressed.
IWhen cranking the engine.
SEF742M
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONSR20DE
Distributor Ignition (DI) System (Cont'd)
EC-26
Page 839 of 2267

4 ADJUST IGNITION TIMING
With CONSULT-II
1. Adjust ignition timing to the specified value by turning distributor after loosening bolts which secure distributor.
Without CONSULT-II
1. Adjust ignition timing to the specified value by turning distributor after loosening bolts which secure distributor.
2. Turn off engine and connect throttle position sensor harness connector to throttle position sensor. (CVT models only)
SEF197X
Models with CONSULT-II©GO TO 2.
Models without CONSULT-II©GO TO 3.
5 CHECK TARGET IDLE SPEED
With CONSULT-II
1. Rev engine (2,000 to 3,000 rpm) two or three times under no-load, then run engine at idle speed.
2. Read idle speed in ªDATA MONITORº mode with CONSULT-II.
NEF059A750 50 rpm
(in ªPº or ªNº position for CVT)
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 8.
NG©1. Perform ªIdle air volume learningº. Refer to EC-SR-46.
2. If still NG, GO TO 7.
Throttle position
sensor harness
connector Throttle body
Closed throttle position switch
harness connector (CVT models)
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDURESR20DE
Idle Speed/Ignition Timing/Idle Mixture Ratio Adjustment (Cont'd)
EC-39
Page 1024 of 2267

On Board Diagnosis LogicNCEC0202If a misfire occurs, the engine speed will fluctuate. If the fluctuation is detected by the crankshaft position sen-
sor (OBD), the misfire is diagnosed.
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM function
Crankshaft position sensor (OBD) Engine speed On board diagnosis of misfire
The misfire detection logic consists of the following two conditions.
1. One Trip Detection Logic (Three Way Catalyst Damage)
On the first trip that a misfire condition occurs that can damage the three way catalyst (TWC) due to
overheating, the MI will blink.
When a misfire condition occurs, the ECM monitors the CKP sensor signal every 200 engine revolutions
for a change.
When the misfire condition decreases to a level that will not damage the TWC, the MI will turn off.
If another misfire condition occurs that can damage the TWC on a second trip, the MI will blink.
When the misfire condition decreases to a level that will not damage the TWC, the MI will remain on.
If another misfire condition occurs that can damage the TWC, the MI will begin to blink again.
2. Two Trip Detection Logic (Exhaust quality deterioration)
For misfire conditions that will not damage the TWC (but will affect exhaust vehicle emissions), the MI will
only light when the misfire is detected on a second trip. During this condition, the ECM monitors the CKP
sensor signal every 1,000 engine revolutions.
A misfire malfunction can be detected on any one cylinder or on multiple cylinders.
DTC No. Malfunction is detected when ... Check Items (Possible Cause)
P0300
0300IMultiple cylinders misfire.IImproper spark plug
IInsufficient compression
IIncorrect fuel pressure
IThe injector circuit is open or shorted
IInjectors
IIntake air leak
IThe ignition secondary circuit is open or
shorted
ILack of fuel
IHeated oxygen sensor 1 (front)
IDrive plate/Flywheel
IIncorrect distributor rotor P0301
0301INo. 1 cylinder misfires.
P0302
0302INo. 2 cylinder misfires.
P0303
0303INo. 3 cylinder misfires.
P0304
0304INo. 4 cylinder misfires.
DTC Confirmation ProcedureNCEC0203CAUTION:
Always drive vehicle at a safe speed.
NOTE:
If ªDTC Confirmation Procedureº has been previously conducted,
always turn ignition switch ªOFFº and wait at least 9 seconds
before conducting the next test.
TESTING CONDITION:
IAlways perform at a temperature above þ10ÉC (14ÉF).
With CONSULT-II
1) Turn ignition switch ªONº, and select ªDATA MONITORº mode
with CONSULT-II.
2) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature.
3) Turn ignition switch ªOFFº and wait at least 9 seconds.
4) Start engine again and drive at 1,500 - 3,000 rpm for at least
3 minutes.
Hold the accelerator pedal as steady as possible.
NOTE:
Refer to the freeze frame data for the test driving conditions.
5) If 1st trip DTC is detected, go to ªDiagnostic Procedureº,
EC-SR-225.
With GST
Follow the procedure ªWith CONSULT-IIº above.
NEF068A
DTC P0300 - P0304 NO.4-1CYLINDER MISFIRE,
MULTIPLE CYLINDER MISFIRESR20DE
On Board Diagnosis Logic
EC-224
Page 1026 of 2267

4 CHECK INJECTOR
Does each injector make an operating sound at idle?
MEC703B
YesorNo
Ye s©GO TO 6.
No©Check injector(s) and circuit(s). Refer to EC-SR-304.
5 CHECK IGNITION SPARK
1. Turn Ignition switch ªOFFº.
2. Disconnect ignition wire from spark plug.
3. Connect a known good spark plug to the ignition wire.
4. Place end of spark plug against a suitable ground and crank engine.
5. Check for spark.
SEF282G
OK or NG
OK©GO TO 8.
NG©GO TO 7.
6 CHECK IGNITION WIRES
Refer to ªComponent Inspectionº, EC-SR-229.
OK or NG
OK©Check distributor rotor head for incorrect parts. Check ignition coil, power transistor and
their circuits. Refer to EC-SR-310.
NG©Replace.
Ignition wire
Spark plug
DTC P0300 - P0304 NO.4-1CYLINDER MISFIRE,
MULTIPLE CYLINDER MISFIRESR20DE
Diagnostic Procedure (Cont'd)
EC-226
Page 1029 of 2267

Component InspectionNCEC0576IGNITION WIRESNCEC0576S011. Inspect wires for cracks, damage, burned terminals and for
improper fit.
2. Measure the resistance of wires to their distributor cap termi-
nal. Move each wire while testing to check for intermittent
breaks.
Resistance:
4.5 - 6.7 kW/m (1.37 - 2.04 kW/ft) at 25ÉC (77ÉF)
If the resistance exceeds the above specification, inspect igni-
tion wire to distributor cap connection. Clean connection or
replace the ignition wire with a new one.
16 ERASE THE 1ST TRIP DTC
Some tests may cause a 1st trip DTC to be set.
Erase the 1st trip DTC from the ECM memory after performing the tests. Refer to EC-SR-56.
©GO TO 18.
17 CHECK INTERMITTENT INCIDENT
Perform ªTROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR INTERMITTENT INCIDENTº, EC-SR-114.
©INSPECTION END
SEF174P
DTC P0300 - P0304 NO.4-1CYLINDER MISFIRE,
MULTIPLE CYLINDER MISFIRESR20DE
Component Inspection
EC-229