checking oil NISSAN PULSAR 1987 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1987, Model line: PULSAR, Model: NISSAN PULSAR 1987Pages: 238, PDF Size: 28.91 MB
Page 60 of 238

60 Engine
NOTE: Should the ring end gap be greater
than the specified gap, another ring set
should be obtained and the ring end gaps
checked and compared with the Specifica-
tions.
(3) Treat each ring and cylinder bore individu-
ally and ensure that the rings are assembled to the
respective piston for the cylinder bore in which they
were installed to check the end gap.
(4) Assemble each oil control ring to its respec-
tive piston bottom groove as follows:
(a) Install the oil ring expander to the
piston
groove, ensuring that the ends of the expander are
bulled together and not overlapped. (b) Position one end of the lower side rail in the
groove and peel the ring over the piston and into the
groove. (c) Similarly install the upper side rail.
(5) Install the lower compression ring into
the
lower piston groove.
NOTE: The compression rings should be
installed with the manufacturers mark fac-
ing the top of the piston. To minimize the
possibility of ring breakage the rings can be
immersed in hot water prior to installation.
(6) Install the upper compression ring into
the
upper piston groove.
(7) Space the compression ring gaps 120 degrees
apart, and ensure that the o il ring gaps and the join in
the oil ring expander are not aligned. (8) With the rings correctly installed and
gapped, remove the bearing cap from the connecting
rod. (9) Liberally lubricate the piston assembly and
install the piston ring compressor to number one
piston.
NOTE: When installing the pistons to the
cylinder ensure that the front marking on
the piston is towards the front of the engine.
(10) Turn the crankshaft until number one crank-
pin is at the bottom of its stroke. (11) Install number one piston and connecting
rod
assembly into its bore. Push the assembly down the
bore until the connecting rod can be aligned with
number one crankpin.
NOTE: The bearing shells should be lubri-
cated with engine oil before installation.
(12) Install the connecting rod cap and tighten
the
retaining bolts to the specified torque.
NOTE: If new bearing shells were installed,
check the bearing clearance with Plastigage
as previously described.
(13) With the bearing clearance as specified, in-
stal the remaining pistons in the same manner.
(14) Ensure that the crankshaft turns without
binding.
(15) With all connecting rod bolts tightened to
the specified torque, install the associated
components
by referring to the relevant headings in this section.
11. CRANKSHAFT AND MAIN BEARINGS
Special Equipment Required:
To Inspect — Micrometer, Vee blocks, dial gauge
TO REMOVE
(1) With the engine assembly removed from the
vehicle and the transaxle separated from the engine,
refer to the appropriate headings or sections and
remove the following components: sump, oil pump
pickup pipe, oil pump, and flywheel or drive plate. (2) Remove the crankshaft rear oil seal from the
Using a ring compressor to install the piston.
Checking the crankshaft end float using feeler gauges.
Page 62 of 238
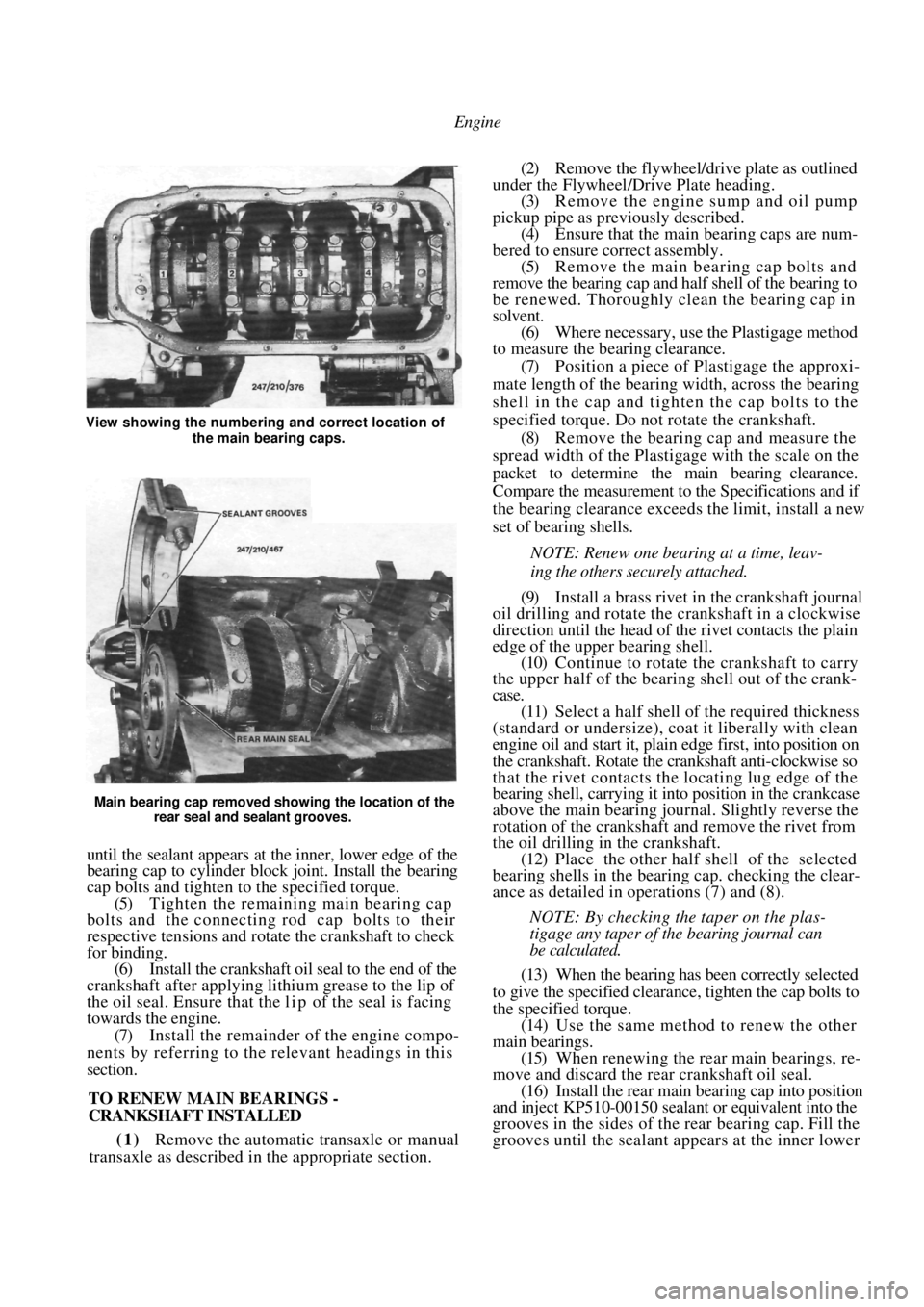
Engine
Main bearing cap removed showing the location of the rear seal and sealant grooves.
until the sealant appears at the inner, lower edge of the
bearing cap to cylinder block joint. Install the bearing
cap bolts and tighten to the specified torque.
(5) Tighten the remaining main bearing cap
bolts and the connecting rod cap bolts to their
respective tensions and rotate the crankshaft to check
for binding. (6) Install the crankshaft oil seal to the end of the
crankshaft after applying lithium grease to the lip of
the oil seal. Ensure that the l i p of the seal is facing
towards the engine.
(7) Install the remainder of the engine compo-
nents by referring to the relevant headings in this
section.
TO RENEW MAIN BEARINGS -
CRANKSHAFT INSTALLED
(1) Remove the automatic transaxle or manual
transaxle as described in the appropriate section.
(2) Remove the flywheel/drive plate as outlined
under the Flywheel/Drive Plate heading. (3) Remove the engine sump and oil pump
pickup pipe as previously described. (4) Ensure that the main bearing caps are num-
bered to ensure correct assembly. (5) Remove the main bearing cap bolts and
remove the bearing cap and half shell of the bearing to
be renewed. Thoroughly clean the bearing cap in
solvent. (6) Where necessary, use the Plastigage method
to measure the bearing clearance.
(7) Position a piece of Plastigage the approxi-
mate length of the bearing width, across the bearing
shell in the cap and tigh ten the cap bolts to the
specified torque. Do not rotate the crankshaft. (8) Remove the bearing cap and measure the
spread width of the Plastigage with the scale on the
packet to determine the main bearing clearance.
Compare the measurement to the Specifications and if
the bearing clearance exceeds the limit, install a new
set of bearing shells.
NOTE: Renew one bearing at a time, leav-
ing the others securely attached.
(9) Install a brass rivet in the crankshaft journal
oil drilling and rotate the crankshaft in a clockwise
direction until the head of the rivet contacts the plain
edge of the upper bearing shell. (10) Continue to rotate the crankshaft to carry
the upper half of the bearing shell out of the crank-
case.
(11) Select a half shell of the required thickness
(standard or undersize), coat it liberally with clean
engine oil and start it, plai n edge first, into position on
the crankshaft. Rotate the crankshaft anti-clockwise so
that the rivet contacts the locating lug edge of the
bearing shell, carrying it into position in the crankcase
above the main bearing journal. Slightly reverse the
rotation of the crankshaft and remove the rivet from
the oil drilling in the crankshaft. (12) Place the other half shell of the selected
bearing shells in the bear ing cap. checking the clear-
ance as detailed in operations (7) and (8).
NOTE: By checking the taper on the plas-
tigage any taper of the bearing journal can
be calculated.
(13) When the bearing has been correctly selected
to give the specified clearance, tighten the cap bolts to
the specified torque. (14) Use the same method to renew the other
main bearings. (15) When renewing the rear main bearings, re-
move and discard the rear crankshaft oil seal. (16) Install the rear main bearing cap into position
and inject KP510-00150 sealant or equivalent into the
grooves in the sides of the rear bearing cap. Fill the
grooves until the sealant a ppears at the inner lower
View showing the numbering and correct location of
the main bearing caps.
Page 68 of 238
68
COOLING AND HEATING SYSTEMS
SPECIFICATIONS
Coolant capacity ........................................ 6.0 liters
Thermostat:
Opening temperature........................... 91 deg
C
Fully open temperature .................... 103 deg
C
Cooling fan:
Fan cut in temperat ure ....................... 100 deg C
Fan cut out temperature ...................... 95 deg C
Radiator cap opening
pressure ................................................... 78 -98 kPa
TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
Water pump retaining bolts .............................25 Nm
Thermostat housing bolts .................................15 Nm
Sender unit .......................................................10 Nm
1. COOLING SYSTEM TROUBLE SHOOTING
COOLANT LEAKAGE - EXTERNAL
(1) Loose hose clips or faulty hoses: Tighten the
hose clips or renew the faulty water hoses.
(2) Leaking radiator core or tanks: Repair or
renew the radiator. (3) Leaking heater core or hoses: Repair or renew the heater core. Check the hose clips and hoses
and renew if necessary.
(4)
Leaks at the thermostat cover and/or water
pump O rings. Renew the O rings. (5) Worn or damaged water pump seal assembly:
Renew the water pump. (6) Worn or damaged water pump bearing as-
sembly: Renew the water pump.
(7) Loose or rusted welch plugs; Renew the
welch plugs. (8) Faulty cylinder head gasket or loose cylinder
head bolts: Renew the cylinder head gasket and
correctly tighten the cylinder head bolts. (9) External crack in the cy linder head or cylin-
der block: Repair or renew the faulty components.
NOTE: Check the system for external leak-
age by running the engine to operating
temperature over a dry floor and checking
for the leak source.
Check the vehicle interior below the
heater core for moisture. If a rusted welch
plug is found, it is a good practice to renew
all the welch plugs.
COOLANT LEAKAGE - INTERNAL
( 1 ) Cylinder head gasket leak due to warped
cylinder head or cylinder block gasket faces: Reface
Checking the radiator hose for deterioration.
Check the engine oil for level and dilution on the
dipstick.
Page 70 of 238

70 Cooling and Heating Systems
Installed view of the heater hoses. 1.6 liter models with the air cleaner removed for clarity
.
When the engine is at normal operating
temperature and the heater valve is open,
both of the heater hoses should feel
warm/hot. If the valve is not allowing the
coolant to flow, one hose will be hot while
the other will be cold.
NO COOLED AIR INSIDE VEHICLE
(1) Compressor drive belt slipping or broken:
Renew and/or adjust the drive belt as described in the
Engine Tune-up section.
(2) Insufficient refrigerant: Check the system for
leaks and charge as necessary. Refer to the Air
Conditioning heading in th is section for information
on checking the refrigerant level. (3) Compressor inoperative: Check for power to
the compressor clutch before removing the compres-
sor for repair by a specialist. (4) Heater system allowing warm air to mix with
cooled air: Check the operation of the heater system.
NOTE: The above trouble shooting proce-
dures are basic checks only. If the air
conditioning system is suspect, it is rec-
ommended that the vehicle be taken to an
authorized dealer for testing and repair.
It is normal for water to be seen drain-
ing under the vehicle from the evaporator
after the vehicle has been operated with
the air conditioning on.
3. DESCRIPTION
The cooling system is of the sealed, pressurized
type with fan and water pump assistance. The system
is pressurized in order to raise the boiling point of the
coolant and so increase the efficiency of the engine.
Provision for pressure a nd vacuum relief of the
system is incorporated in the radiator cap.
The radiator overflow hose is connected to a
reserve tank mounted adjacent to the battery. As the
coolant volume expands due to an increase in tem-
perature, the pressure valve in the radiator cap opens
and allows the excess coolant to flow into the reserve
tank. When the engine is stopped and the temperature
of the coolant falls, the vacuum valve in the radiator
cap opens and allows the excess coolant in the reserve
tank to siphon back into the radiator. Thus the
necessity for frequent topping up of the coolant is
eliminated.
The temperature of the cooling system is con-
trolled by a thermostat located in the thermostat
housing attached to the cylinder head.
The thermostat prevents circulation of coolant
through the radiator by directing coolant through the
by-pass circuit, until the engine has reached operating
temperature. This restricted circulation allows the
engine to reach operating temperature quickly, im-
proving drivability and fuel economy.
Removal of the thermostat to cure overheating is
not recommended because th e by-pass circuit will
remain open reducing the amount of water flowing
through the radiator.
An anti-corrosion inhibitor should always be
added to the coolant to protect the cooling and
heating systems from corrosion.
The water pump is mounted to the front of the
engine and is driven by the camshaft drive belt. It is
equipped with a double row ball bearing and a spring
loaded seal assembly. The water pump is a disposable
unit and cannot be repaired.
The fan is driven by an electric motor which is
actuated by the coolant temperature sensor and the
control unit.
On vehicles equipped with air conditioning, an
additional electric fan is m ounted to the radiator. This
fan is controlled by a sw itch connected to the air
conditioning compressor.
The radiator consists of an aluminum core with
plastic side tanks. Minor damage to the core can be
repaired using Nissan repair agent.
The left hand tank of the radiator houses the
transaxle oil cooler on automatic transaxle models.
To drain the cooling system a drain plug is
provided on the lower radiator pipe outlet.
4. RADIATOR
NOTE: To avoid scalding, use caution when
releasing the radiator cap on an engine
which is at the normal operating tempera-
ture. Turn the cap anti-clockwise to the first
stop and allow any pressure in the system to
release. When the pressure is released turn
the cap past the stop and remove it from the
radiator.
Page 89 of 238

Fuel and Engine Management 89
The procedure for fabricating an LED test lamp is
fully described in the El ectrical System section.
If a conventional test lamp with a filament type
bulb is to be used, ensure that the current draw of the
test lamp does not exceed 0.3 amp to avoid damage to
the electronic components.
To check the current draw connect an accurate
ammeter, such as the multimeter described previ-
ously, in series with the test lamp and a battery.
If the ammeter reads less than 0.3 amp the test
lamp is suitable.
Tachometer
(1) Disconnect the resistor from the tachometer
pick-up wiring connector which is located on the
ignition coil wiring harness, and connect the positive
lead of an accurate tachometer to the brown wire
terminal in the wiring connector. (2) Connect the negative lead to a good earthing
point.
View showing the location of the tachometer pickup
wiring connector with the resistor installed.
Timing Light
(1) Connect the timing light to the engine fol-
lowing the instrument manufacturers instructions.
NOTE: Do not connect or disconnect the
timing light with the engine running as
voltage surges could damage the alternator
or control unit. Do not allow the high
tension leads to open circuit with the engine
running as damage to the engine manage-
ment system could result.
(2) Do not connect the timing light positive lead
to the alternator output terminal. Where possible,
connect the power leads of the timing light to an
external power source to prevent possible transient
voltages damaging the alternator or control unit.
4. SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS AND ADJUSTMENTS
NOTE: Due to the use of complex electronic
components in the engine management sys-
tem, the diagnosis and testing procedures
described in this section should not be
carried out by persons lacking an under-
standing of electronics and the precautions
associated with the servicing of electronic
components. It is rec ommended that should
a fault arise in the system, the vehicle be
referred to an authorized workshop.
The control unit can be damaged by
component faults not indicated by the self
diagnosis codes and the renewal of the
control unit without lo cating the cause of
the failure will result in the failure of the
replacement unit. It is for this reason that
the practice of substituting components to
isolate faults is not recommended.
Prior to performing any of the follow-
ing operations, refer to the Service Pre-
cautions and Procedures heading.
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Prior to performing the Self Diagnosis Test Pro-
cedures, perform the following preliminary checks and
rectify any problems as necessary.
(1) Check for an adequate supply of fuel in the
fuel tank. (2) Check the wiring connectors and earth points
of all engine management components for clean,
secure connections. To prevent damage to the control
unit, disconnect the negative battery terminal before
disconnecting any engine ma nagement wiring connec-
tors. (3) Check the condition of the battery. Refer to
the Electrical System sectio n for checking procedures.
Rectify any faults as necessary. (4) Check the air cleaner element for restriction.
(5) Check for air leaks at the throttle body, inlet
manifold and all related hoses. (6) Check the fuel pump pr essure as described
later in this section. (7) Ensure that the engine is in a satisfactory
mechanical condition and is in tune. Refer to the
Engine and Engine Tune-up sections as necessary.
SELF DIAGNOSIS
This function is very useful in locating system
faults particularly intermittent problems. However,
the self diagnosis mode does not provide comprehen-
sive testing of the engine management system, and
therefore should always be used in conjunction with
the other test procedures described later, in order to
accurately locate system faults.
To Interpret Self Diagnosis Codes
Once the self diagnosis mode is activated, various
fault codes will be displayed as a series of flashes by
the ECM warning lamp on the instrument cluster.
Page 141 of 238

Automatic Transaxle 141
(2) Incorrectly adjusted kickdown cable: Check
and adjust or renew the kickdown cable as required.
NOTE: Check and adjust the throttle cable
before adjusting the kickdown cable.
ENGINE WILL NOT START IN P OR N
RANGE OR WILL START IN ANY RANGE
(1) Neutral safety switch faulty: Adjust or renew
the neutral safety switch. (2) Incorrectly adjusted selector cable: Check
and adjust the selector cable as detailed.
2. DESCRIPTION
The automatic transaxle combines a fluid coup-
ling or torque converter with a fully automatic three
speed epicyclic gear system.
The transaxle provides th ree forward ratios and
one reverse. The hydraulic system consists of a single
pump and valv e arrangement.
The final drive or differential and the transaxle
use a common lubricant. The transaxle oil pan and
final drive drain plug will have to be removed to drain
the transaxle completely. Topping up or refilling is
done through the dipstick tube.
The gear selector lever is floor mounted and
connected to the transaxle by an adjustable cable. The
selector quadrant adjacent to the base of the lever is
marked P, R, N, D, 2, 1.
It is necessary for the selector lever to be in P or
N before the engine can be started. When testing or
tuning the engine, the handbrake must be firmly
applied and the selector lever placed in the P position,
otherwise the vehicle could move forward or back-
wards as the engine speed is increased.
For long distance towing the vehicle should be
towed with the front end raised.
It is not possible to start the engine by either
towing or pushing the vehicle.
The transaxle can be removed from the vehicle
without engine removal.
NOTE: As extensive knowledge and equip-
ment is required to overhaul the automatic
transaxle assembly, it is therefore not a
worthwhile repair proposition for the aver-
age person. However if the transaxle must
be overhauled by a specialist or be replaced
with a reconditioned unit, the removal and
installation procedure is fully described at
the end of this section.
3. TRANSAXLE FLUID
Only use the recommended transaxle fluid speci-
fied by the manufacturer when topping up or changing
the fluid in the system.
TO CHECK AND TOP UP
NOTE: The fluid level should be checked
after approximately 5 minutes driving on
the road when the engine has achieved its
normal operating temperature of approxi-
mately 65 deg C.
(1) Place the vehicle on a level floor and open
the engine bonnet.
NOTE: When working on the automatic
transaxle cleanliness is very important. Do
not reuse transaxle fluid and do not allow
foreign matter to enter the filler opening.
(2) Clean around the top of the dipstick to
ensure that no dirt or foreign matter can enter the
dipstick tube.
(3) Place the selector in the P position and
firmly apply the handbrake. (4) Move the selector thro ugh each gear return-
ing it to the P position.
(5) Check the fluid level with the engine running
at idle. Install the dipstick fully into the dipstick tube.
NOTE: If the vehicle has been driven at high
speed, or has been towing a load, or driven
through heavy city traffic in hot weather, a
period of about 30 minutes should be
allowed to permit the transaxle to cool
before checking the fluid level.
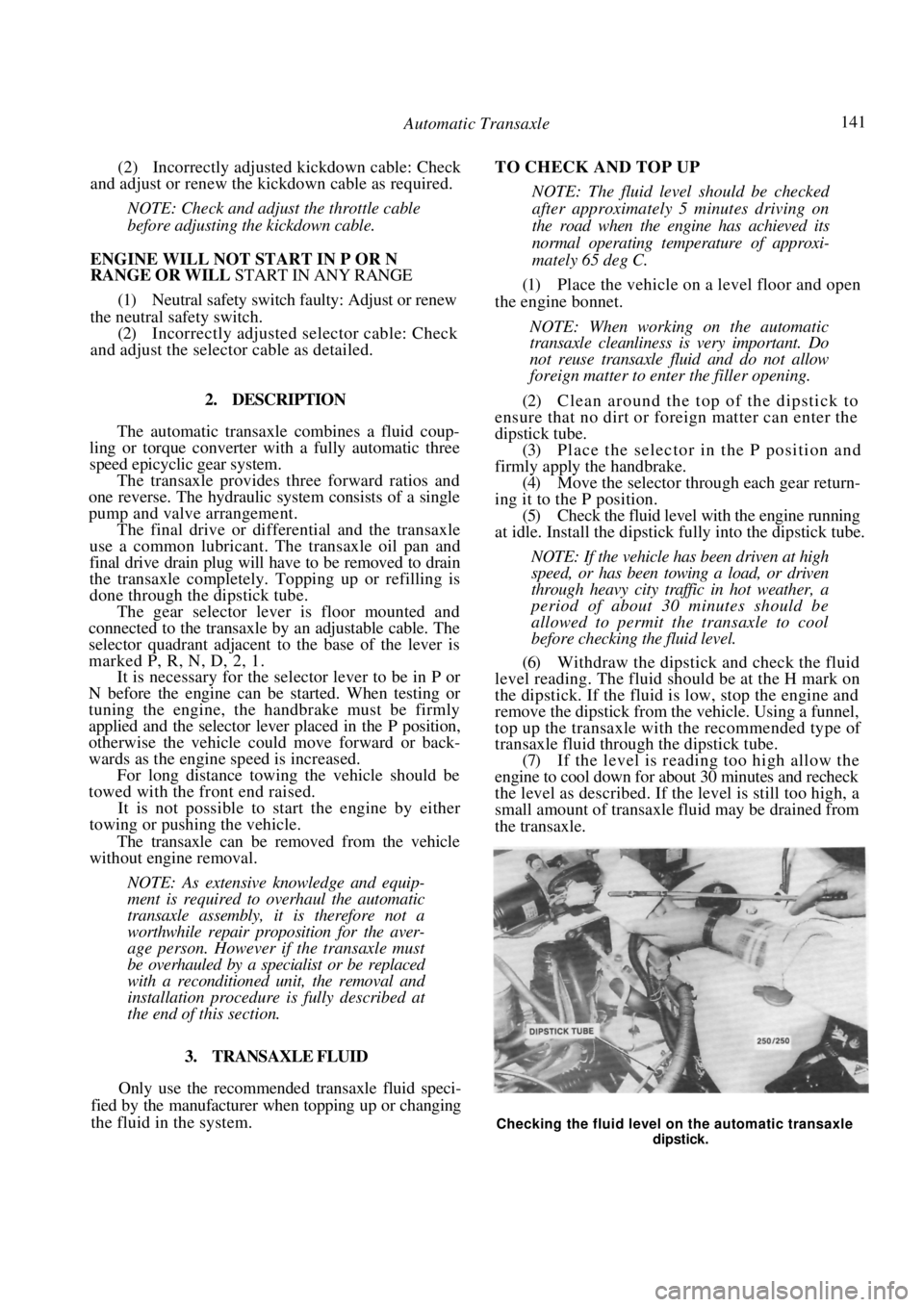
(6) Withdraw the dipstick and check the fluid
level reading. The fluid should be at the H mark on
the dipstick. If the fluid is low, stop the engine and
remove the dipstick from the vehicle. Using a funnel,
top up the transaxle with the recommended type of
transaxle fluid through the dipstick tube. (7) If the level is reading too high allow the
engine to cool down for about 30 minutes and recheck
the level as described. If the level is still too high, a
small amount of transaxle fluid may be drained from
the transaxle.
Checking the fluid level on the automatic transaxle
dipstick.
Page 157 of 238

Front Suspension 157
Check the stabilizer bar links for wear and damage.
(3) Incorrect front end alignment: Check and
adjust the alignment as necessary. (4) Defective stabilizer bar mounting rubbers or
worn link ball joints: Renew component as necessary. (5) Weak or broken front coil spring: Renew
both springs as a matching pair. (6) Broken or weak rear coil spring: Renew both
springs as matching pair. (7) Drive shaft bent or distorted: Check and
renew as necessary. (8) Tie rod end worn or damaged: Check and
renew as necessary.
(9) Control arm ball joint worn or damaged:
Check and renew as necessary.
(10) Control arm mounting bolts loose: Tighten
the control arm bolts. (11) Wheel hub bearing worn: Check and renew
as necessary. NOTE: As a quick guide to suspension unit
condition, bounce the front of the vehicle up
and down (one side at a time), the vehicle
should come to rest in a single movement. If
it bounces two or three times before stop-
ping, the suspension unit should be renewed.
If the from of the vehicle is tower on one
side than the other, remove the coil spring
and check its free length against a new
spring. If the spring is found to be unservice-
able it is good practice to install two new
springs as a matching pair. This also applies
to the springs on the rear of the vehicle.
2. DESCRIPTION
The front suspension is an independent type
comprising two Macpherson strut suspension units
mounted vertically on each side of the vehicle. The
lower end of the suspension unit is bolted to the
steering knuckle, which in turn houses the front hub
bearings. The steering knuckle pivots on the control
arm by means of a ball joint.
The control arm pivots at its inner ends on rubber
bushes.
A stabilizer bar is attached to both ends of the
control arms using ball joint links. The stabilizer bar
is attached to the front underbody by brackets and
mounting rubbers.
Each front suspension unit assembly comprises a
tubular shock absorber type suspension unit, sur-
rounded at the upper end by a coil spring. On top of
the coil spring is the upper mounting which attaches
to the underside of the inner mudguard panel. The
piston rod of the suspensi on unit is attached to the
centre of the upper mounting by a rubber mounted
bearing.
When a suspension unit is found to be defective it
is recommended that both suspension units be re-
newed as a pair.
Camber is adjusted by means of a cam on the
upper steering knuckle to suspension unit mounting
bolt.
The kingpin inclination and caster are set in
production and cannot be adjusted. Any variation in
these angles will be caused by worn or damaged
components.
3. STEERING KNUCKLE
Special Equipment Required:
To Renew Wheel Bearing — Press and press plates
and suitable tubes and mandrels
To Check Hub End Float — Dial gauge
TO REMOVE AND INSTAL
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
on chassis stands. Remove the front wheel.
Checking the control arm bolts for security.
Page 164 of 238
164
REAR SUSPENSION
SPECIFICATIONS
Type........................... Independent MacPherson strut
Shock absorber.................... Oil filled, non-repairable
Maximum hub bearing end float ................. 0.05 mm
Rear wheel alignment:
Toe out ........................................3 mm ± 2 mm
Camber ............................................. - 1 ° ± 4 5 '
TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
Hub retaining nut ......................................... 255 Nm
Suspension unit retaining nuts ....................... 29 Nm
Upper mounting retaining nut ........................ 72 Nm
Suspension unit to knuckle nuts .................. 118 Nm
Control arms to knuckle nut ........................ 118 Nm
Control arms to crossmember nut ............... 118 Nm
Stabiliser bar mounting bracket bolts .......... 108 Nm
Stabiliser bar retaining nut.............................. 83 Nm
Backing plate bolts........................................... 45 Nm
1. REAR SUSPENSION TROUBLE SHOOTING
REAR END NOISE
( 1 ) Defective suspension unit or mounting: Re-
new the faulty components.
(2) Loose or worn control arm bushes or pivot
bolts: Check and tighten or renew the worn compo-
nents. (3) Broken coil spring: Renew the coil spring,
preferably in matching pairs. (4) Worn rear hub bearing: Check and renew the
hub bearing as necessary. (5) Loose or worn stabilizer bar bushes: Check
and tighten or renew the worn components.
NOTE: As a quick guide to suspension unit
condition, bounce the vehicle up and down
(one side at a time) and observe if the vehicle
comes to rest in a single movement If the
vehicle bounces two or three times before
coming to rest the susp ension unit is suspect.
If suspect, remove the suspension unit and
check for fractures and leaks. If the
suspension unit is found to be unserviceable,
it is good practice to install two new
suspension units as a matching pair.
To check the control arm bushes or pivot
bolts, insert a lever between the suspect unit
and its mounting and lever the unit back
and forth checking for excessive movement.
Check the coil springs visually for breaks.
If the spring is found to be unserviceable, it
is good practice to install two new coil
springs as a matching pair.
Rear hub bearing noise can be diagnosed
by raising and supporting the rear of the
vehicle, spinning one wheel at a time and
listening for a rumbling noise.
POOR OR ERRATIC ROAD HOLDING ABILITY
(1) Low or uneven tire pressure: Inflate to the
recommended pressures.
(2) Incorrect rear wheel alignment: Check and
adjust the rear wheel alignment as necessary.
(3) Defective suspension unit: Renew the faulty
suspension unit, preferably in pairs. (4) Loose or broken stabilizer bar: Check and
tighten or renew the faulty components.
Check the stabilizer bar bushes and mounting rubbers
for wear and deterioration.
Page 165 of 238
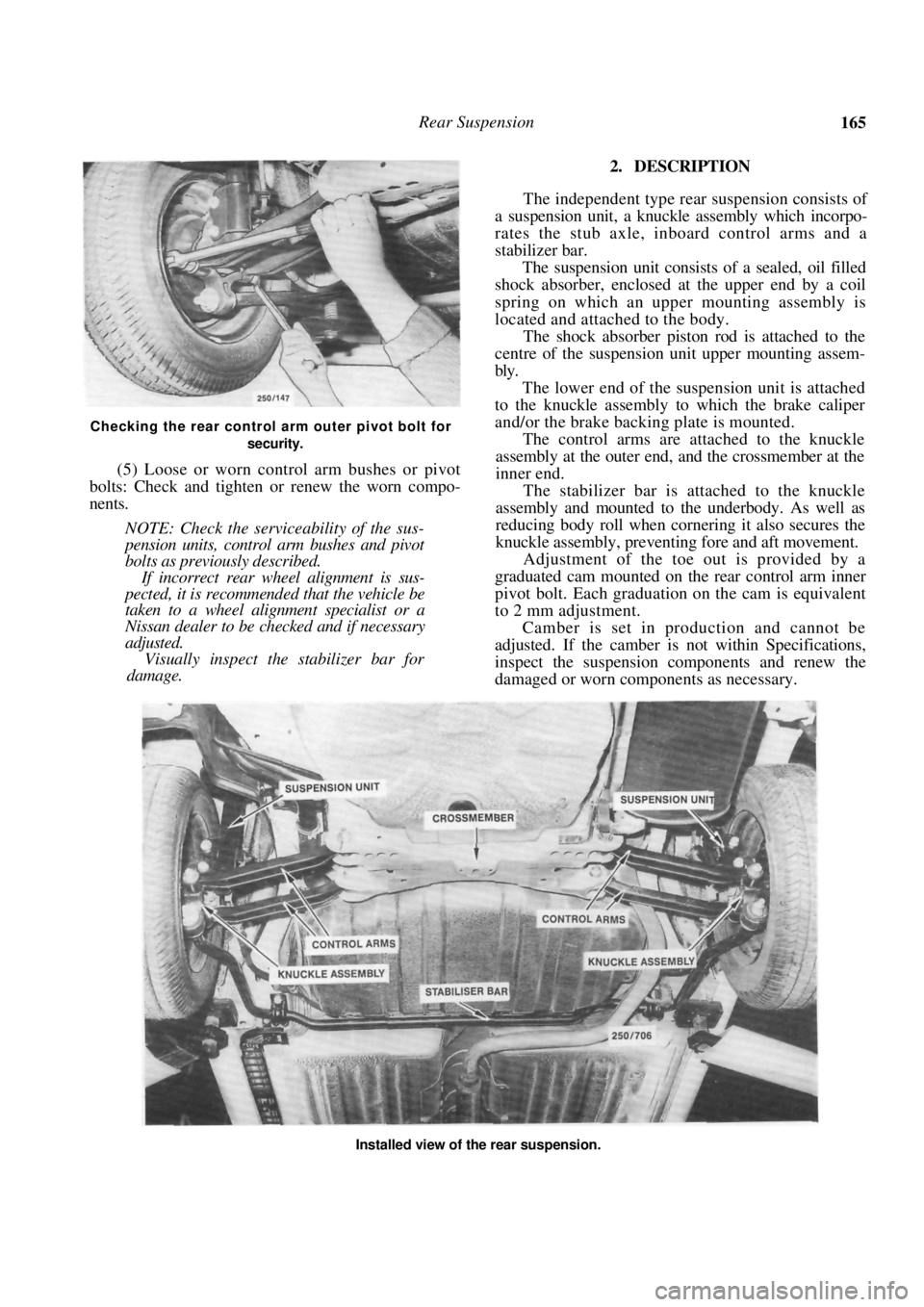
Rear Suspension 165
Checking the rear control arm outer pivot bolt for security.
(5) Loose or worn control arm bushes or pivot
bolts: Check and tighten or renew the worn compo-
nents.
NOTE: Check the service ability of the sus-
pension units, control arm bushes and pivot
bolts as previously described.
If incorrect rear wheel alignment is sus-
pected, it is recommended that the vehicle be
taken to a wheel alignment specialist or a
Nissan dealer to be checked and if necessary
adjusted.
Visually inspect the stabilizer bar for
damage.
2. DESCRIPTION
The independent type rear suspension consists of
a suspension unit, a knuckle assembly which incorpo-
rates the stub axle, inboard control arms and a
stabilizer bar.
The suspension unit consists of a sealed, oil filled
shock absorber, enclosed at the upper end by a coil
spring on which an upper mounting assembly is
located and attached to the body.
The shock absorber piston rod is attached to the
centre of the suspension unit upper mounting assem-
bly.
The lower end of the suspension unit is attached
to the knuckle assembly to which the brake caliper
and/or the brake backing plate is mounted.
The control arms are attached to the knuckle
assembly at the outer end, and the crossmember at the
inner end.
The stabilizer bar is attached to the knuckle
assembly and mounted to the underbody. As well as
reducing body roll when cornering it also secures the
knuckle assembly, preventing fore and aft movement.
Adjustment of the toe out is provided by a
graduated cam mounted on the rear control arm inner
pivot bolt. Each graduation on the cam is equivalent
to 2 mm adjustment.
Camber is set in production and cannot be
adjusted. If the camber is not within Specifications,
inspect the suspension components and renew the
damaged or worn components as necessary.
Installed view of the rear suspension.
Page 199 of 238
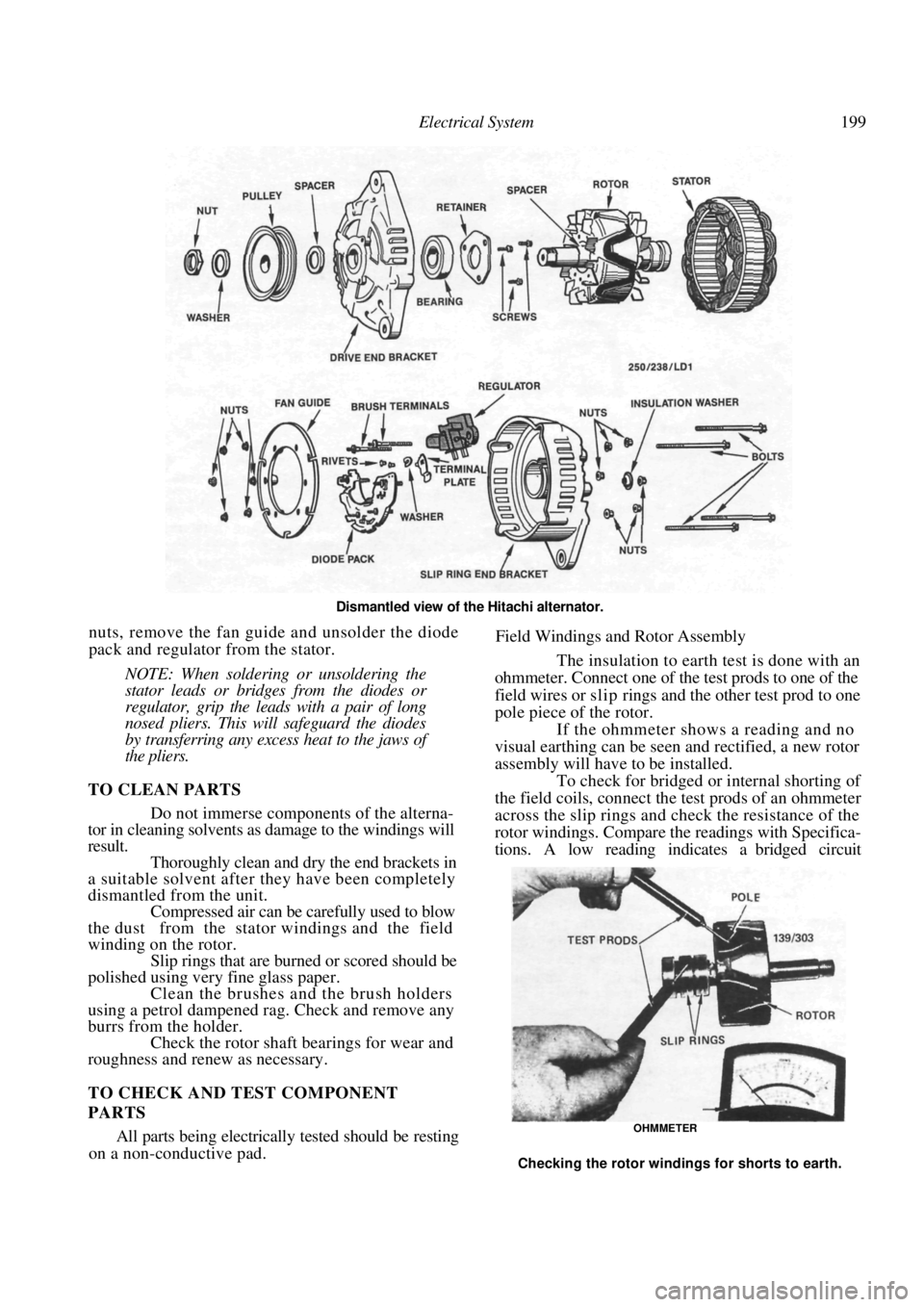
Electrical System 199
Dismantled view of the Hitachi alternator.
nuts, remove the fan guide and unsolder the diode
pack and regulator from the stator.
NOTE: When soldering or unsoldering the
stator leads or bridges from the diodes or
regulator, grip the leads with a pair of long
nosed pliers. This will safeguard the diodes
by transferring any excess heat to the jaws of
the pliers.
TO CLEAN PARTS
Do not immerse components of the alterna-
tor in cleaning solvents as damage to the windings will
result. Thoroughly clean and dry the end brackets in
a suitable solvent after they have been completely
dismantled from the unit. Compressed air can be carefully used to blow
the dust from the stator windings and the field
winding on the rotor. Slip rings that are burned or scored should be
polished using very fine glass paper. Clean the brushes and the brush holders
using a petrol dampened rag. Check and remove any
burrs from the holder. Check the rotor shaft bearings for wear and
roughness and renew as necessary.
TO CHECK AND TEST COMPONENT
PARTS
All parts being electrically tested should be resting
on a non-conductive pad.
Field Windings and Rotor Assembly
The insulation to earth test is done with an
ohmmeter. Connect one of the test prods to one of the
field wires or s l i p rings and the other test prod to one
pole piece of the rotor. If the ohmmeter shows a reading and no
visual earthing can be seen and rectified, a new rotor
assembly will have to be installed. To check for bridged or internal shorting of
the field coils, connect the te st prods of an ohmmeter
across the slip rings and check the resistance of the
rotor windings. Compare the readings with Specifica-
tions. A low reading i ndicates a bridged circuit
OHMMETER
Checking the rotor windings for shorts to earth.