jacking points NISSAN PULSAR 1987 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1987, Model line: PULSAR, Model: NISSAN PULSAR 1987Pages: 238, PDF Size: 28.91 MB
Page 10 of 238

10 General Information
If tools are to be stored for any length of time, it is
good policy to wipe them with an oily cloth.
Bladed screwdrivers should be checked for dam-
age to the tip. If necessary, the tip can be returned to
its original profile by careful grinding. Do not grind
screwdriver tips to a sharp point.
Hammer heads should be secure on their handles
and should be regularly checked for cracking or other
damage.
Chisels and punches should be checked for dam-
age or 'mushrooming' of the head. Any faults should
be rectified by grinding.
Hydraulic jacks should be regularly checked for
fluid leaks. Chassis stands and car ramps should be
checked for damage and cracks. Any equipment that
is suspect should not be used.
STORES
For routine maintenance, stores of automotive
oils, greases and additives should be kept on hand.
The following is a suggested list.
Engine oil.
Brake fluid.
Manual transmission or automatic transmission
oil — automatic transmission oil is also used in
the power steering system.
Rear axle oil.
Cooling system corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze.
Chassis grease.
High melting point grease, for hub bearings etc.
Penetrating oil or spray.
Kerosene or similar cleaning solvent.
Methylated spirits.
Oils and greases are available in handy pack size for
do-it-yourself lube jobs.
2. SAFETY
PERSONAL SAFETY
Safety when working on a motor vehicle is basical-
ly a matter of commonsense. Some safety precautions
to prevent personal in juries are as follows.
Raising a Vehicle
Always jack a vehicle on firm, level ground and at
the specified jacking points . Ensure that the wheels
remaining on the ground are fully chocked.
After raising the vehicle, place chassis stands
underneath and allow the weight of the vehicle to rest
on them. Do not use bricks, blocks of wood or similar
material.
NOTE: Never work under a vehicle which is
only supported by a jack.
Electrical System
Always disconnect the negative battery terminal
when working on any electrical components. Avoid
wearing metal watches, rings and chains which may
short across live terminals.
As battery gases are explosive, keep naked flames
and sparks clear of the work area. When connecting
and disconnecting jumper leads, use extreme caution
to avoid sparking.
Electronic Ignition Systems
Electronic ignition systems produce dangerous
high tension voltages in bo th the primary and second-
ary circuits which can be fatal. Exercise extreme
caution when working on or near any ignition system
components. Do not disconnect high tension leads
while the engine is running.
Work Area
Do not run the engine in a confined space. Ensure
that the work area is adequately ventilated.
Spilt oil or water should be cleaned immediately
to avoid the possibility of slipping.
Fuel System
Always disconnect the negative battery terminal
when working on any fuel components. Do not smoke.
Keep naked flames and sparks clear of the work area.
Do not siphon fuel using the mouth. Use a hand
pump or suitable siphon.
Do not attempt to repair a fuel tank by welding it.
This is an extremely hazardous procedure and should
be entrusted to a specialist.
Cooling System
To avoid scalding, use caution when releasing the
radiator cap on an engine wh ich is at normal operating
temperature. Turn the cap anti-clockwise to the first
stop and allow any pressure in the system to release.
When the pressure is released, remove the cap from
the radiator.
Brakes
As asbestos is used in some brake lining material,
avoid inhaling brake dust. Do not use compressed air
to remove the dust. Gentle brushing with a small
brush or using a vacuum cleaner with a hose attach-
ment are the safest methods of cleaning the brakes.
The above precautions also apply to the clutch plate
lining material.
Page 14 of 238

14
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
SPECIFICATIONS
CAPACITY AND GRADE
Engine:
Lubricant........................................... 15W-50 SF
Sump capacity including filter ........... 3.3 liters
Cooling system capacity............................ 6.0 liters
Manual transaxle:
Lubricant....................................... 80W-90 GL-4
Capacity ............................................... 2.7 liters
Automatic transaxle:
Lubricant.............................................. Dexron II
Capacity ............................................... 6.0 liters
Power steering:
Lubricant.............................................. Dexron II
Capacity ............................................... 1.0 liters
Manual steering lubricant ........ Castrol EPLl grease
Brake fluid type ................................................ Dot 4
1. HOW TO GREASE AND OIL CHANGE
(1) Run the front of the vehicle onto car ramps
and stop the engine. Chock the front wheels. (2) Raise the rear of the vehicle and place
chassis stands under the rear jacking points.
NOTE: It is best if the vehicle is kept as level
as possible to avoi d false readings when
checking the lubricant levels.
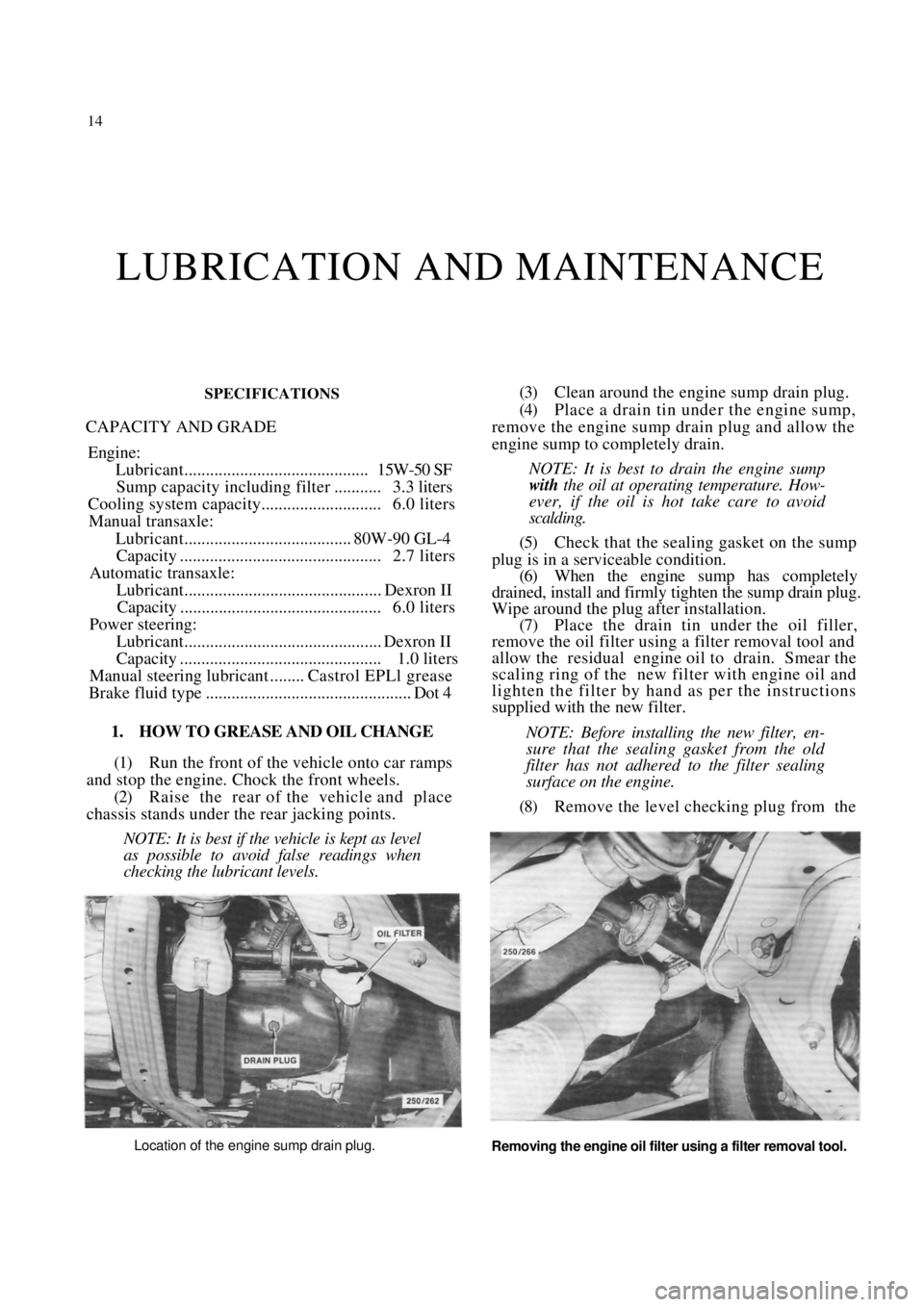
(3) Clean around the engine sump drain plug.
(4) Place a drain tin under the engine sump,
remove the engine sump drain plug and allow the
engine sump to completely drain.
NOTE: It is best to drain the engine sump
with the oil at operating temperature. How-
ever, if the oil is hot take care to avoid
scalding.
(5) Check that the sealing gasket on the sump
plug is in a serviceable condition. (6) When the engine sump has completely
drained, install and firmly tighten the sump drain plug.
Wipe around the plug after installation. (7) Place the drain tin under the oil filler,
remove the oil filter using a filter removal tool and
allow the residual engine oil to drain. Smear the
scaling ring of the new filter with engine oil and
lighten the filter by hand as per the instructions
supplied with the new filter.
NOTE: Before installing the new filter, en-
sure that the sealing gasket from the old
filter has not adhered to the filter sealing
surface on the engine.
(8) Remove the level checking plug from the
Location of the engine sump drain plug.
Removing the engine oil filter using a filter removal tool.
Page 21 of 238
WHEELS AND TYRES
SPECIFICATIONS
TYRES PRESSURES
Front:
Normal load ............................................ 200 kPa
Heavy load or high speed ......................230 kPa
Rear:
Normal load............................................ 180 kPa
Heavy load or high speed ...................... 210 kPa
NOTE: The above pressures are measured
cold and are meant as a guide only. Always
refer to the tire placard positioned on the
inside of the glove compartment lid and the
tire manufacturers recommendations first.
TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
Wheel nut torque .............................................98 Nm
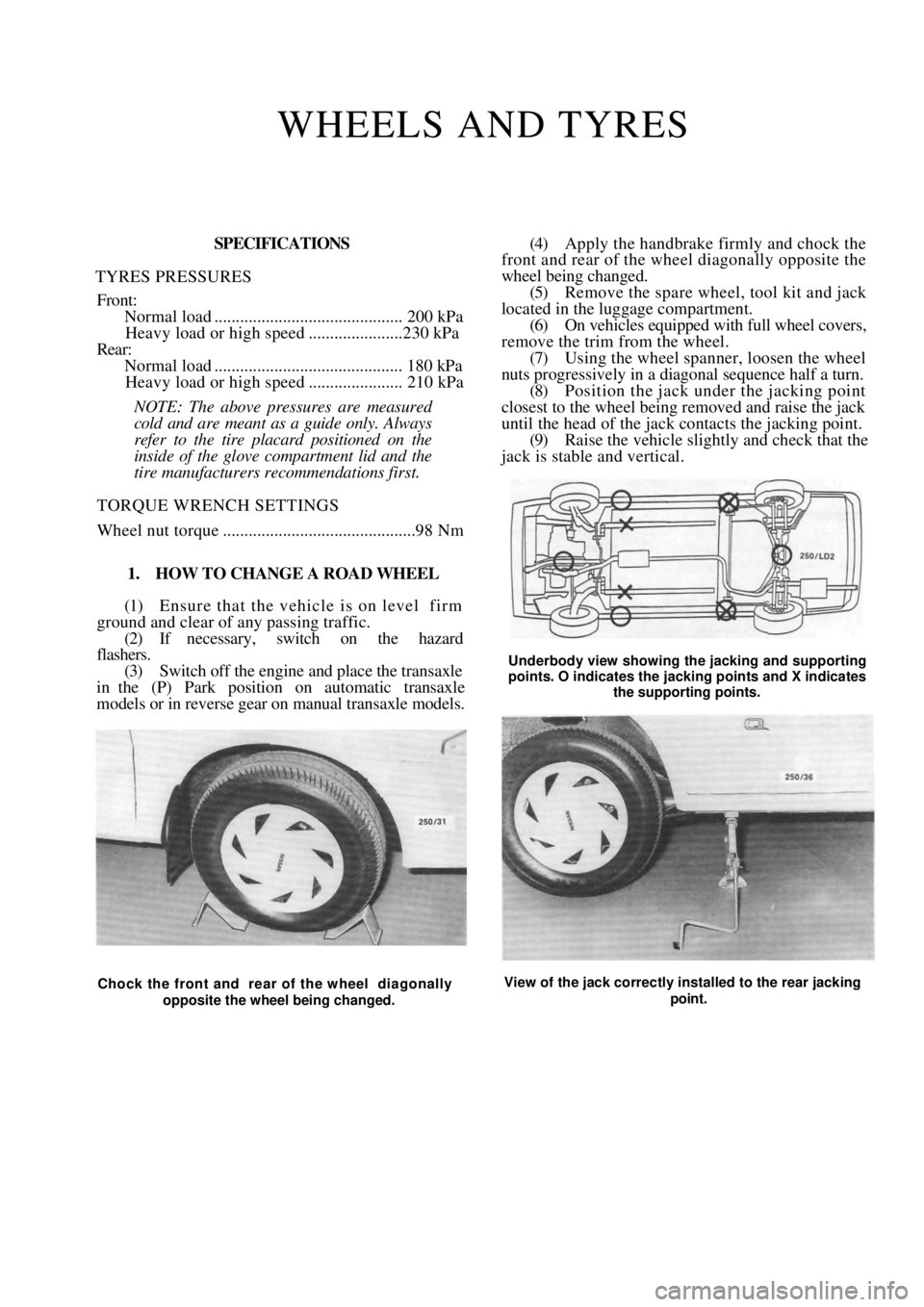
1. HOW TO CHANGE A ROAD WHEEL
(1) Ensure that the vehicle is on level firm
ground and clear of any passing traffic. (2) If necessary, switch on the hazard
flashers.
(3) Switch off the engine a nd place the transaxle
in the (P) Park position on automatic transaxle
models or in reverse gear on manual transaxle models.
(4) Apply the handbrake firmly and chock the
front and rear of the wheel diagonally opposite the
wheel being changed.
(5) Remove the spare wheel, tool kit and jack
located in the luggage compartment. (6) On vehicles equipped with full wheel covers,
remove the trim from the wheel. (7) Using the wheel spanner, loosen the wheel
nuts progressively in a diagonal sequence half a turn.
(8) Position the jack und er the jacking point
closest to the wheel being removed and raise the jack
until the head of the jack contacts the jacking point.
(9) Raise the vehicle slightly and check that the
jack is stable and vertical.
Underbody view showing the jacking and supporting
points. O indicates the jacking points and X indicates
the supporting points.
Chock the front and rear of the wheel diagonally
opposite the wheel being changed. View of the jack correctly installed to the rear jacking
point.
Page 137 of 238
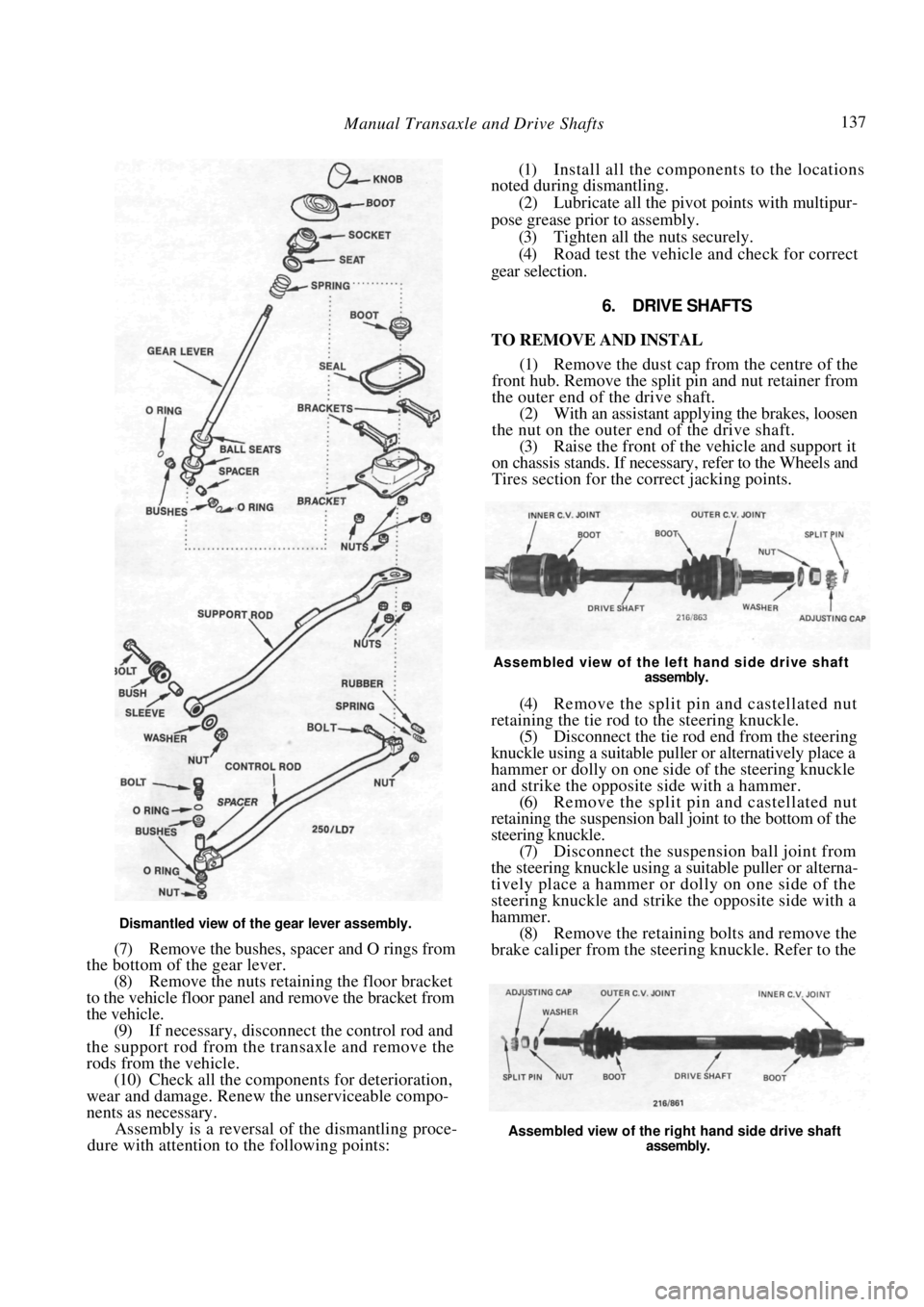
Manual Transaxle and Drive Shafts 137
Dismantled view of the gear lever assembly.
(7) Remove the bushes, spacer and O rings from
the bottom of the gear lever.
(8) Remove the nuts retaining the floor bracket
to the vehicle floor panel and remove the bracket from
the vehicle. (9) If necessary, disconnect the control rod and
the support rod from the transaxle and remove the
rods from the vehicle. (10) Check all the components for deterioration,
wear and damage. Renew the unserviceable compo-
nents as necessary. Assembly is a reversal of the dismantling proce-
dure with attention to the following points:
(1) Install all the components to the locations
noted during dismantling.
(2) Lubricate all the pivot points with multipur-
pose grease prior to assembly. (3) Tighten all the nuts securely.
(4) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
gear selection.
6. DRIVE SHAFTS
TO REMOVE AND INSTAL
(1) Remove the dust cap from the centre of the
front hub. Remove the split pin and nut retainer from
the outer end of the drive shaft. (2) With an assistant applying the brakes, loosen
the nut on the outer end of the drive shaft.
(3) Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
on chassis stands. If necessary, refer to the Wheels and
Tires section for the correct jacking points.
Assembled view of the left hand side drive shaft
assembly.
(4) Remove the split pin and castellated nut
retaining the tie rod to the steering knuckle. (5) Disconnect the tie rod end from the steering
knuckle using a suitable puller or alternatively place a
hammer or dolly on one side of the steering knuckle
and strike the opposite side with a hammer.
(6) Remove the split pin and castellated nut
retaining the suspension ball joint to the bottom of the
steering knuckle. (7) Disconnect the suspension ball joint from
the steering knuckle using a suitable puller or alterna-
tively place a hammer or dolly on one side of the
steering knuckle and strike the opposite side with a
hammer. (8) Remove the retaining bolts and remove the
brake caliper from the stee ring knuckle. Refer to the
Assembled view of the right hand side drive shaft
assembly.