NISSAN TIIDA 2008 Service Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2008, Model line: TIIDA, Model: NISSAN TIIDA 2008Pages: 2771, PDF Size: 60.61 MB
Page 51 of 2771
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
AT-39
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
N
O
P
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
DTC Inspection Priority ChartINFOID:0000000001703177
If some DTCs are displayed at the same time, perform inspections one by one based on the following priority
chart.
NOTE:
If DTC “CAN COMM CIRCUIT” is displayed with other DTCs, first perform the trouble diagnosis for
DTC “CAN COMM CIRCUIT”. Refer to AT- 8 3
.
Fail-SafeINFOID:0000000001703178
The TCM has an electronic Fail-safe mode. This allows the vehicle to be driven even if a major electrical input/
output device circuit is damaged.
Under Fail-Safe, the vehicle always runs in third gear, even with a shift lever position of “1”, “2” or “D”. The cus-
tomer may complain of sluggish or poor acceleration.
Always follow the “AT-40, "
How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate Repair" ”.
The SELF-DIAGNOSIS results will be as follows:
• The first SELF-DIAGNOSIS will indicate damage to the vehicle speed sensor or the revolution sensor.
• During the next SELF-DIAGNOSIS, performed after checking the sensor, no damages will be indicated.
FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION
The following fail-safe functions allow vehicles to be driven even when sensor, switch or solenoid malfunction
occurs.
Vehicle Speed Sensor·A/T (Revolution Sensor)
Vehicle speed sensor·MTR signal is input from combination meter.
Accelerator Pedal Position Signal and Throttle Position Signal
TCM controls the throttle opening angle to a predetermined fixed position to enable driving if a malfunctioning
signal is input to TCM.
PNP Switch
When the multiple PNP switch signals are input to TCM, the priority of selector lever position becomes “D”,
“N”, “R”, “2” and “1” in order by internal TCM determination.
The use of 4th gear is inhibited until normal operation resumes. Because the hydraulic circuit of the control
valve is switched by manual valve according to the selector lever position, however, actual operating condition
of vehicle becomes as follows.
Shift Solenoid Valve A and B
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, use of certain gears is limited. Refer to chart shown below.
Priority Detected items
1 CAN communication line
2 Except above
Actual lever position PNP switch input signal Running status
“P” “P” position and other position signals P
“R” “R” position and other position signals R
“N” “N” position and other position signals N
“D” “D” position and other position signals D
1 ⇔D2 ⇔D3 ⇔D4
“2”“2” position and other position signals (Except “1” position) 21 ⇔22 ⇔23
“2” position and “1” position signals 21 ⇔22
“1”“1” position and other position signals (Except “2” position) 11 ⇔12 ⇔13
“1” position and “2” position signals 11 ⇔12
Page 52 of 2771
AT-40
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
●: Solenoid ON
×: Solenoid OFF
–: Non-standard condition
Line Pressure Solenoid Valve
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, line pressure solenoid valve is turned OFF to achieve maxi-
mum oil pressure.
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, torque converter clutch solenoid valve is turned OFF to release
lock-up.
Overrun Clutch Solenoid Valve
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, overrun clutch solenoid valve is turned OFF to engage overrun
clutch. This will result in more effective engine brake during deceleration.
How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate RepairINFOID:0000000001703179
INTRODUCTION
The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, accelera-
tor pedal position sensor or PNP switch and provides shift control or
lock-up control via A/T solenoid valves.
The TCM also communicates with the ECM by means of a signal
sent from sensing elements used with the OBD-related parts of the
A/T system for malfunction-diagnostic purposes. The TCM is capa-
ble of diagnosing malfunctioning parts while the ECM can store mal-
functions in its memory.
Input and output signals must always be correct and stable in the
operation of the A/T system. The A/T system must be in good oper-
ating condition and be free of valve seizure, solenoid valve malfunc-
tion, etc.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a malfunction that occurs intermittently rather than continuously. Most
intermittent malfunctions are caused by poor electric connections or improper wiring. In this case, careful
checking of suspected circuits may help prevent the replacement of good parts.
Shift positionNormalMalfunction in solenoid
valve AMalfunction in solenoid
valve BMalfunction in solenoid
valves A and B
A B Gear A B Gear A B Gear A B Gear
“D” position●●1st –●→×
3rd ●→×–
3rd ––
3rd ×●2nd –●→× ×–––
××3rd – x×–––
●×4th – x●→×–––
“2” position●●1st –●→×●→×–––
×●2nd –●→× ×–––
××3rd – x×–––
“1” position●●1st –●→×●→×–––
×●2nd –●→× ×–––
××3rd – x×–––
SAT631IA
Page 53 of 2771

TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
AT-41
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
N
O
P
A visual check only, may not find the cause of the malfunctions. A
road test with CONSULT-III or a circuit tester connected should be
performed. Follow the "WORK FLOW" .
Before undertaking actual checks, take a few minutes to talk with a
customer who approaches with a driveability complaint. The cus-
tomer can supply good information about such malfunctions, espe-
cially intermittent ones. Find out what symptoms are present and
under what conditions they occur. A “DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET”
like the example ("DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET" ) should be used.
Start your diagnosis by looking for “conventional” malfunctions first.
This will help troubleshoot driveability malfunctions on an electroni-
cally controlled engine vehicle.
Also check related Service bulletins for information.
WORK FLOW
A good understanding of the malfunction conditions can make troubleshooting faster and more accurate. In
general, each customer feels differently about a malfunction. It is important to fully understand the symptoms
or conditions for a customer complaint.
Make good use of the two sheets provided, "Information from customer" and "Diagnostic Worksheet Chart" ,
to perform the best troubleshooting possible.
Work Flow Chart
SAT632I
SEF234G
Page 54 of 2771

AT-42
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET
Information from Customer
KEY POINTS
•WHAT..... Vehicle & A/T model
•WHEN..... Date, Frequencies
•WHERE..... Road conditions
•HOW..... Operating conditions, Symptoms
*1 "Information from customer" *2 "Diagnostic Worksheet Chart" *3AT- 3 9
*4AT- 4 8*5AT- 4 8, AT- 4 8*6AT- 5 2
*7AT- 7 3*8AT- 3 6*9AT- 3 9
*10AT- 9 6*11AT- 1 6 3*12AT- 1 7 3
*13AT- 6 1*14AT- 3 6*15AT- 8 3
*16AT- 1 6 3*17EC-47
SCIA7146E
Page 55 of 2771

TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
AT-43
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
N
O
P Diagnostic Worksheet Chart
Customer name MR./MS Model & Year VIN
Trans. model Engine Mileage
Incident Date Manuf. Date In Service Date
Frequency❏ Continuous❏ Intermittent ( times a day)
Symptoms❏ Vehicle does not move. (❏ Any position❏ Particular position)
❏ No up-shift (❏ 1st → 2nd❏ 2nd → 3rd❏ 3rd → 4th)
❏ No down-shift (❏ 4th → 3rd❏ 3rd → 2nd❏ 2nd → 1st)
❏ Lock-up malfunction
❏ Shift point too high or too low.
❏ Shift shock or slip (❏ N → D❏ Lock-up❏ Any drive position)
❏ Noise or vibration
❏ No kick down
❏ No pattern select
❏ Others
()
Malfunction indicator lamp (MIL)❏ Continuously lit❏ Not lit
1.❏ Read the Fail-safe and listen to customer complaints.AT- 3 9,
"Information
from custom-
er"
2.❏ Check A/T fluidMA-22
❏ Leakage (Follow specified procedure)
❏ Fluid condition
❏ Fluid level
3.❏ Perform “STALL TEST” and “LINE PRESSURE TEST”.AT- 4 8
,
AT- 4 8
❏“STALL TEST”— Mark possible damaged components/others.
❏ Torque converter one-way clutch
❏ Reverse clutch
❏ Forward clutch
❏ Overrun clutch
❏ Forward one-way clutch❏ Low & reverse brake
❏ Low one-way clutch
❏ Engine
❏ Line pressure is low
❏ Clutches and brakes except high clutch and
brake band are OK
❏“LINE PRESSURE TEST”— Suspected parts:
Page 56 of 2771

AT-44
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
4.❏ Perform “Road Test”.AT- 5 2
4-1. “Check Before Engine is Started”AT- 5 3
❏AT- 1 7 6 , "OD OFF Indicator Lamp Does Not Come On"
❏ Perform self-diagnosis. Enter checks for detected items. AT- 7 3 , AT- 7 8 .
❏AT- 8 3
.
❏AT- 8 6
.
❏AT- 9 1
.
❏AT- 9 6
.
❏AT- 1 0 1
.
❏AT- 1 0 5
❏AT- 1 0 8 .
❏AT- 111
.
❏AT- 11 4
.
❏AT- 11 9
.
❏AT- 1 2 4
.
❏AT- 1 2 9
.
❏AT- 1 3 4
.
❏AT- 1 3 9
.
❏AT- 1 4 4
.
❏AT- 1 4 9
.
❏AT- 1 5 2
.
❏AT- 1 5 8
.
❏AT- 1 6 3
.
❏AT- 1 6 4
.
4-2. “Check at Idle”AT- 5 3
❏AT- 1 7 8 , "Engine Cannot Be Started in "P" and "N" Position" .
❏AT- 1 7 9 , "
In "P" Position, Vehicle Moves Forward or Backward When Pushed" .
❏AT- 1 7 9 , "
In "N" Position, Vehicle Moves" .
❏AT- 1 8 0 , "
Large Shock "N" → "R" Position" .
❏AT- 1 8 1 , "
Vehicle Does Not Creep Backward in "R" Position" .
❏AT- 1 8 2 , "
Vehicle Does Not Creep Forward in "D", "2" or "1" Position" .
Page 57 of 2771

TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
AT-45
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
N
O
P
4. 4-3. “Cruise Test”AT- 5 5
Part 1
❏AT- 1 8 3 , "
Vehicle Cannot Be Started from D1" .
❏AT- 1 8 5 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D1→ D2or Does Not Kickdown: D4→ D2" .
❏AT- 1 8 6 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D2→ D3" .
❏AT- 1 8 8 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D3→ D4" .
❏AT- 1 8 9 , "
A/T Does Not Perform Lock-up" .
❏AT- 1 9 0 , "
A/T Does Not Hold Lock-up Condition" .
❏AT- 1 9 1 , "
Lock-up Is Not Released" .
❏AT- 1 9 2 , "
Engine Speed Does Not Return to Idle (Light Braking D4→ D3)" .
Part 2AT- 5 8
❏AT- 1 8 3 , "Vehicle Cannot Be Started from D1" .
❏AT- 1 8 5 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D1→ D2or Does Not Kickdown: D4→ D2" .
❏AT- 1 8 6 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D2→ D3" .
❏AT- 1 8 8 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D3→ D4" .
Part 3AT- 5 9
❏AT- 1 9 3 , "A/T Does Not Shift: D4→ D3, When OD OFF" .
❏AT- 1 9 4 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: D3→ 22, When Selector Lever "D" → "2" Position" .
❏AT- 1 9 5 , "
A/T Does Not Shift: 22→ 11, When Selector Lever "2" → "1" Position" .
❏AT- 1 9 7 , "
Vehicle Does Not Decelerate by Engine Brake" .
❏ Perform self-diagnosis. Enter checks for detected items. AT- 7 3
, AT- 7 8 .
❏AT- 8 3
.
❏AT- 8 6
.
❏AT- 9 1
.
❏AT- 9 6
.
❏AT- 1 0 1
.
❏AT- 1 0 5
❏AT- 1 0 8 .
❏AT- 111
.
❏AT- 11 4
.
❏AT- 11 9
.
❏AT- 1 2 4
.
❏AT- 1 2 9
.
❏AT- 1 3 4
.
❏AT- 1 3 9
.
❏AT- 1 4 4
.
❏AT- 1 4 9
.
❏AT- 1 5 2
.
❏AT- 1 5 8
.
❏AT- 1 6 3
.
❏AT- 1 6 4
.
5.❏ For self-diagnosis NG items, inspect each component. Repair or replace the damaged parts.AT- 7 3
,
AT- 7 8
6.❏ Perform “Road Test”.AT- 5 2
7.❏ Perform the Diagnostic Procedures for all remaining items marked NG. Repair or replace the damaged parts.
Refer to the Symptom Chart when you perform the procedures. (The chart also shows some other possible symp-
toms and the component inspection orders.)AT- 6 1
8.❏ Erase DTC from TCM and ECM memories.AT- 3 6,
AT- 7 8
Page 58 of 2771
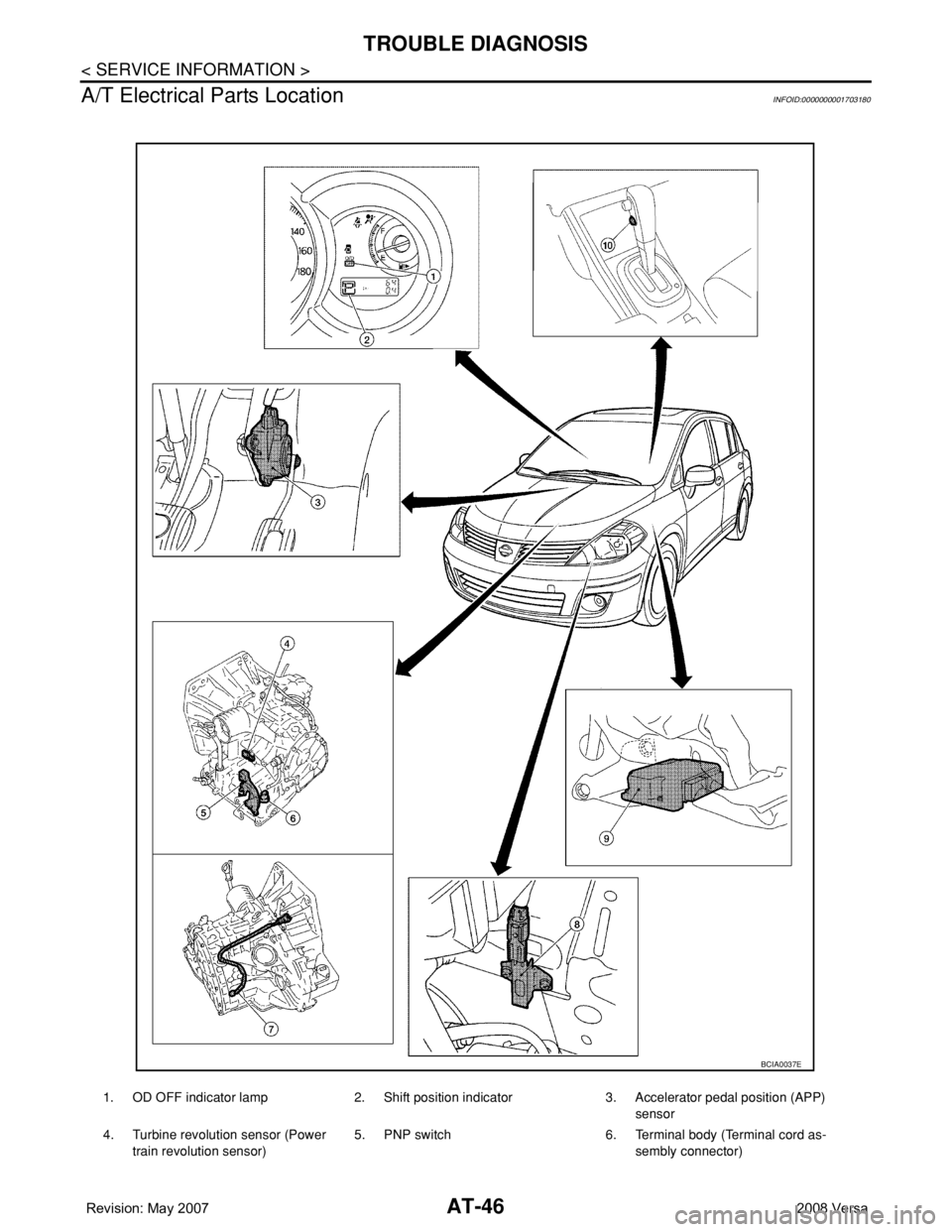
AT-46
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
A/T Electrical Parts Location
INFOID:0000000001703180
1. OD OFF indicator lamp 2. Shift position indicator 3. Accelerator pedal position (APP)
sensor
4. Turbine revolution sensor (Power
train revolution sensor)5. PNP switch 6. Terminal body (Terminal cord as-
sembly connector)
BCIA0037E
Page 59 of 2771
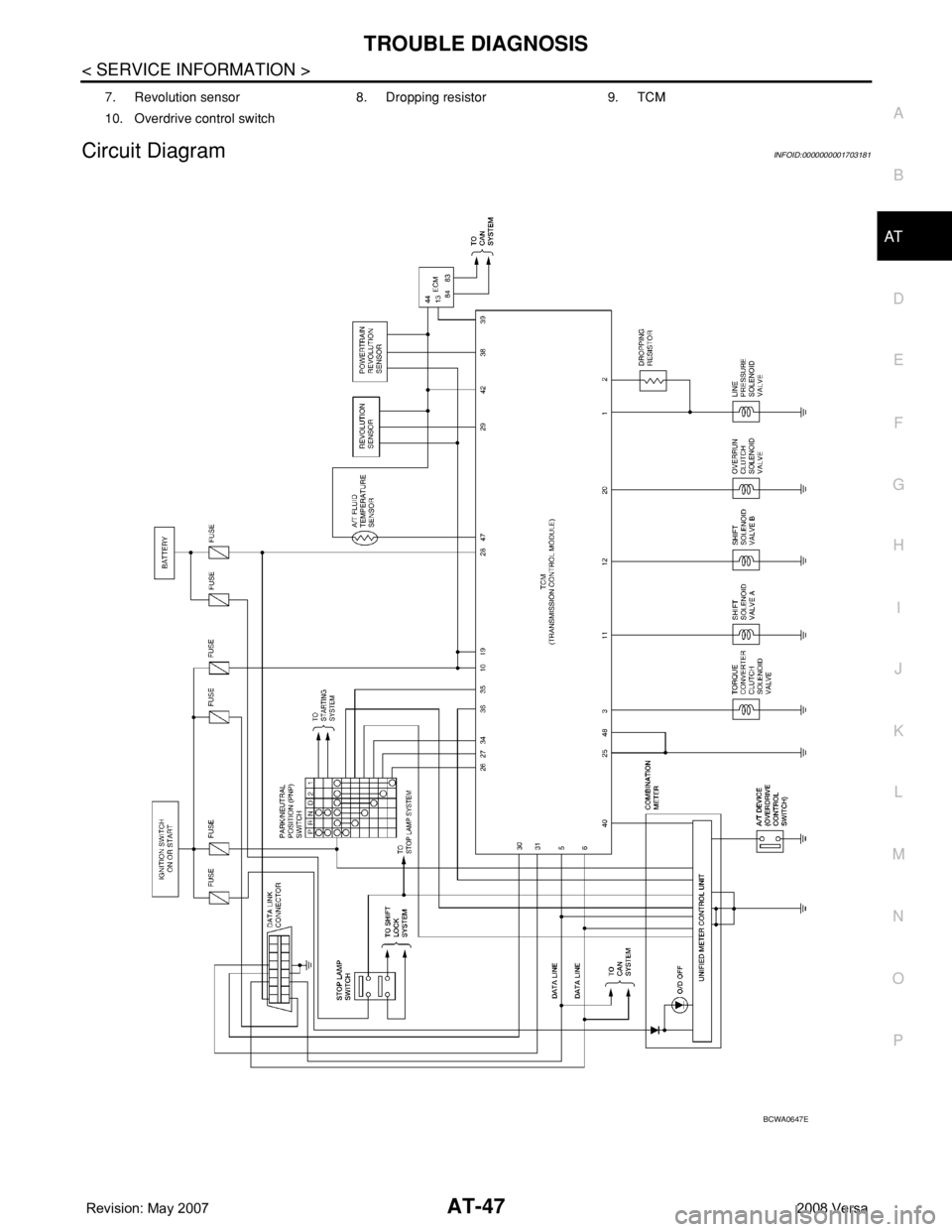
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
AT-47
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
N
O
P
Circuit DiagramINFOID:0000000001703181
7. Revolution sensor 8. Dropping resistor 9. TCM
10. Overdrive control switch
BCWA0647E
Page 60 of 2771
AT-48
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Inspections Before Trouble Diagnosis
INFOID:0000000001703182
A/T FLUID CHECK
Fluid Leakage and Fluid Level Check
Check fluid leakage and check the fluid level. Refer to MA-22, "Checking A/T Fluid".
Fluid Condition Check
Check the A/T fluid condition.
STALL TEST
Stall Test Procedure
1. Check ATF and engine oil levels. If necessary, add ATF and
engine oil.
2. Drive vehicle for approximately 10 minutes or until ATF and
engine oil reach operating temperature.
3. Set parking brake and block wheels.
4. Install a tachometer where it can be seen by driver during test.
•It is good practice to mark the point of specified engine
rpm on indicator.
5. Start engine, apply foot brake, and place selector lever in “D”
position.
Fluid status Conceivable Cause Required Operation
Varnished (viscous
varnish state)Clutch, brake
scorchedReplace the ATF and check the A/T
main unit and the vehicle for mal-
functions (wire harnesses, cooler
pipes, etc.)
Milky white or
cloudyWater in the ATFReplace the ATF and check for plac-
es where water is getting in.
Large amount of
metal powder mixed
inUnusual wear of
sliding parts within
A/TReplace the ATF and check for im-
proper operation of the A/T.
SAT638A
ATF operating temperature: 50 - 80°C (122 - 176°F)
SAT647B
SAT513G
SAT775B