vin NISSAN TIIDA 2009 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2009, Model line: TIIDA, Model: NISSAN TIIDA 2009Pages: 4331, PDF Size: 58.04 MB
Page 16 of 4331
AT
N
O P
PREPARATION
Special Service Tool INFOID:0000000004305293
The actual shapes of Kent-Moore tools may differ fr om those of special service tools illustrated here.
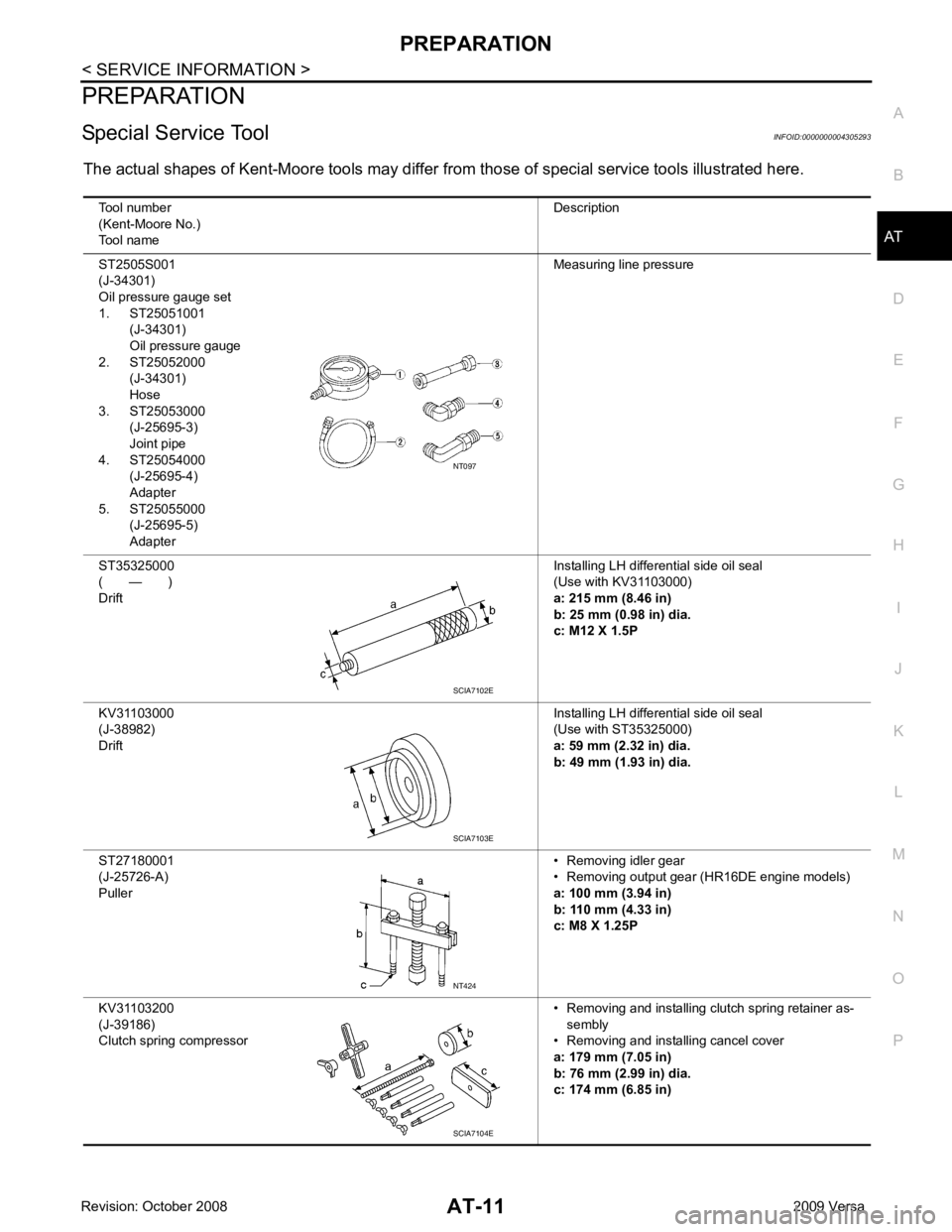
Tool number
(Kent-Moore No.)
Tool name Description
ST2505S001
(J-34301)
Oil pressure gauge set
1. ST25051001 (J-34301)
Oil pressure gauge
2. ST25052000 (J-34301)
Hose
3. ST25053000
(J-25695-3)
Joint pipe
4. ST25054000
(J-25695-4)
Adapter
5. ST25055000
(J-25695-5)
Adapter Measuring line pressure
ST35325000
( — )
Drift Installing LH differential side oil seal
(Use with KV31103000)
a: 215 mm (8.46 in)
b: 25 mm (0.98 in) dia.
c: M12 X 1.5P
KV31103000
(J-38982)
Drift Installing LH differential side oil seal
(Use with ST35325000)
a: 59 mm (2.32 in) dia.
b: 49 mm (1.93 in) dia.
ST27180001
(J-25726-A)
Puller • Removing idler gear
• Removing output gear (HR16DE engine models)
a: 100 mm (3.94 in)
b: 110 mm (4.33 in)
c: M8 X 1.25P
KV31103200
(J-39186)
Clutch spring compressor • Removing and installing clutch spring retainer as-
sembly
• Removing and installing cancel cover
a: 179 mm (7.05 in)
b: 76 mm (2.99 in) dia.
c: 174 mm (6.85 in) SCIA7102E
NT424
SCIA7104E
Page 19 of 4331
AMT153
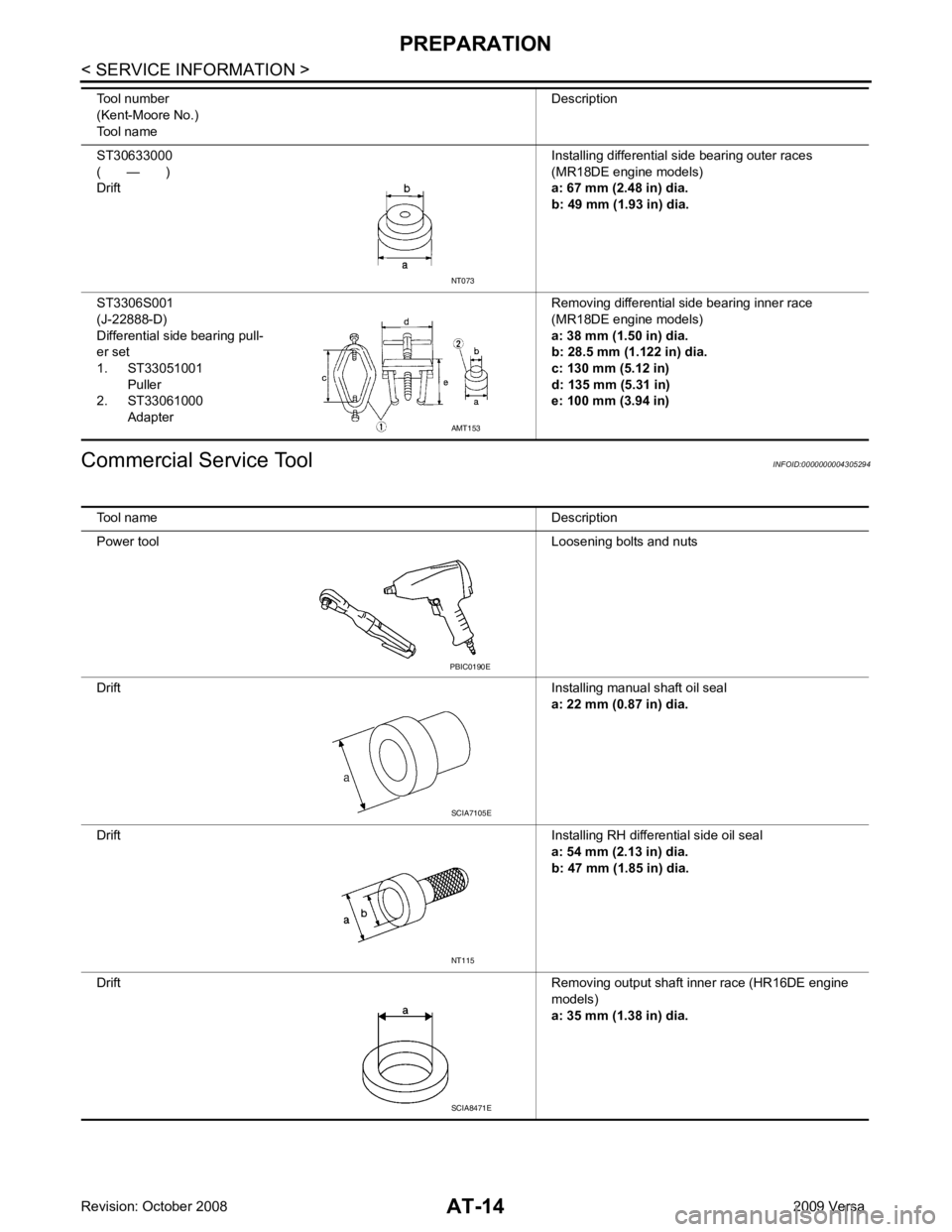
Tool name Description
Power tool Loosening bolts and nuts
Drift Installing manual shaft oil seal
a: 22 mm (0.87 in) dia.
Drift Installing RH differential side oil seal
a: 54 mm (2.13 in) dia.
b: 47 mm (1.85 in) dia.
Drift Removing output shaft inner race (HR16DE engine
models)
a: 35 mm (1.38 in) dia. NT115
SCIA8471E
Page 20 of 4331
AT
N
O P
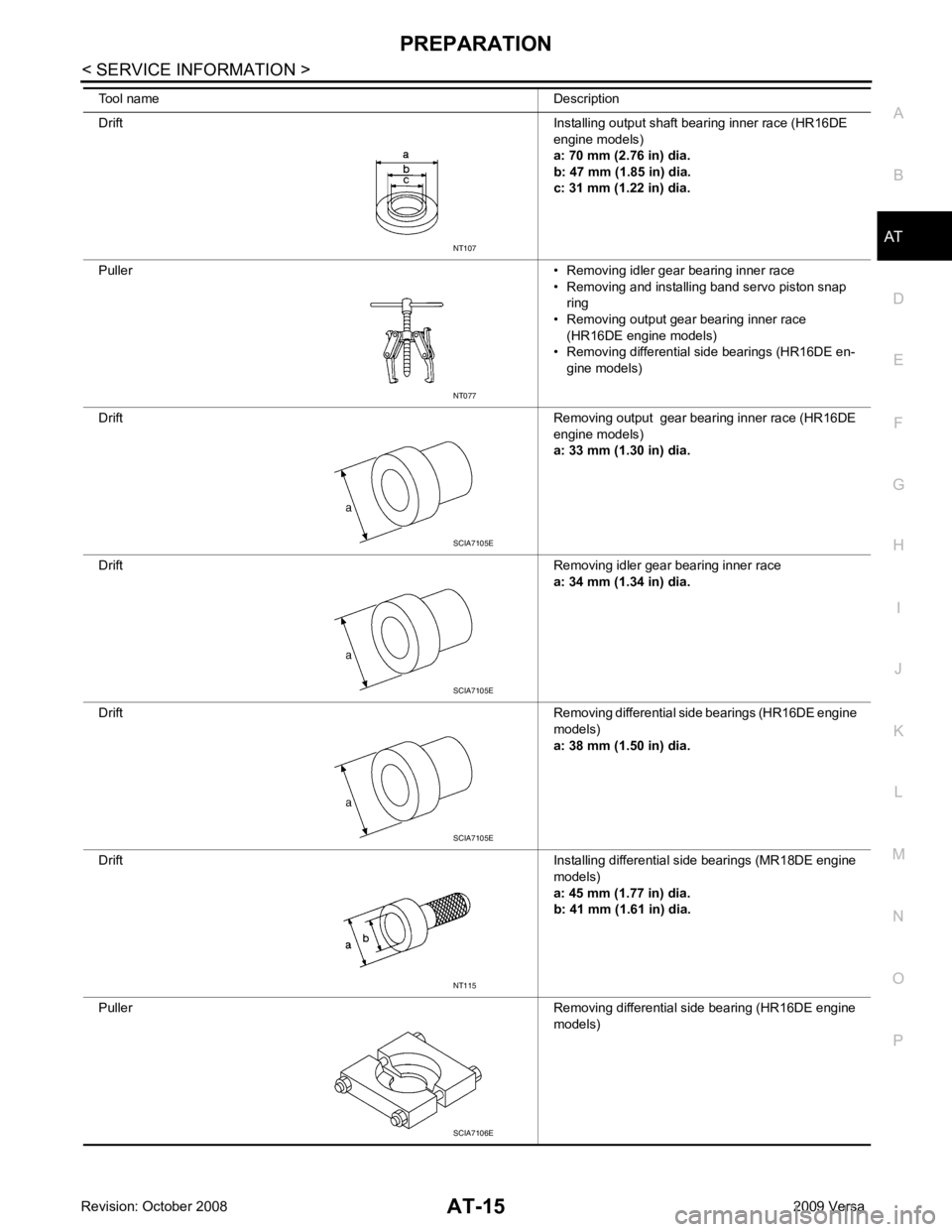
Drift
Installing output shaft bearing inner race (HR16DE
engine models)
a: 70 mm (2.76 in) dia.
b: 47 mm (1.85 in) dia.
c: 31 mm (1.22 in) dia.
Puller • Removing idler gear bearing inner race
• Removing and installing band servo piston snap ring
• Removing output gear bearing inner race (HR16DE engine models)
• Removing differential side bearings (HR16DE en-
gine models)
Drift Removing output gear bearing inner race (HR16DE
engine models)
a: 33 mm (1.30 in) dia.
Drift Removing idler gear bearing inner race
a: 34 mm (1.34 in) dia.
Drift Removing differential side bearings (HR16DE engine
models)
a: 38 mm (1.50 in) dia.
Drift Installing differential side bearings (MR18DE engine
models)
a: 45 mm (1.77 in) dia.
b: 41 mm (1.61 in) dia.
Puller Removing differential side bearing (HR16DE engine
models)
Tool name Description
NT077
SCIA7105E
SCIA7105E
NT115
SCIA7106E
Page 22 of 4331
AT
N
O P
A/T FLUID
Checking A/T Fluid INFOID:0000000004305295
1. Warm up engine.
2. Check for A/T fluid leakage.
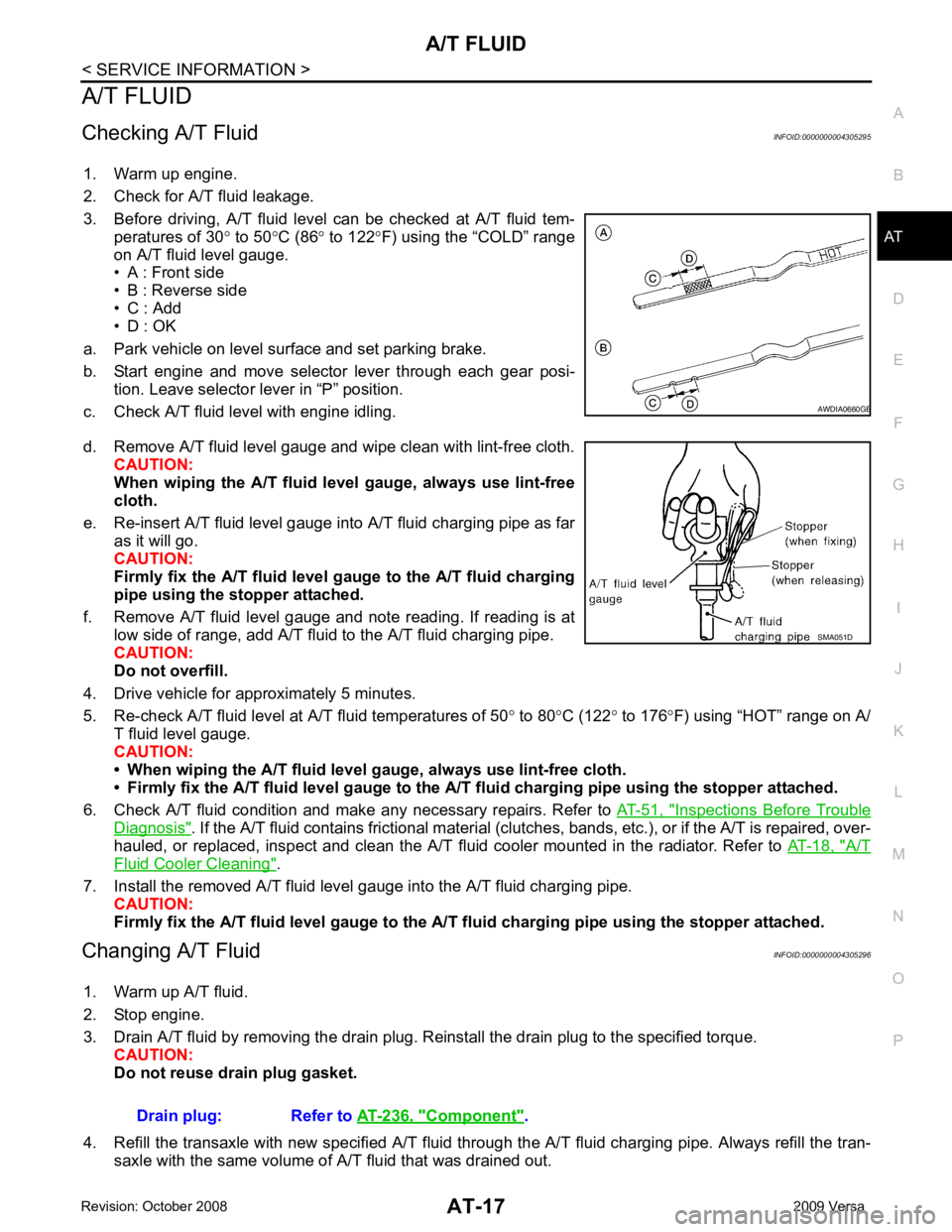
3. Before driving, A/T fluid level can be checked at A/T fluid tem- peratures of 30 ° to 50 °C (86 ° to 122 °F) using the “COLD” range
on A/T fluid level gauge.
• A : Front side
• B : Reverse side
• C : Add
• D : OK
a. Park vehicle on level surface and set parking brake.
b. Start engine and move selector lever through each gear posi- tion. Leave selector lever in “P” position.
c. Check A/T fluid level with engine idling.
d. Remove A/T fluid level gauge and wipe clean with lint-free cloth. CAUTION:
When wiping the A/T fluid l evel gauge, always use lint-free
cloth.
e. Re-insert A/T fluid level gauge into A/T fluid charging pipe as far as it will go.
CAUTION:
Firmly fix the A/T fluid level ga uge to the A/T fluid charging
pipe using the stopper attached.
f. Remove A/T fluid level gauge and note reading. If reading is at low side of range, add A/T fluid to the A/T fluid charging pipe.
CAUTION:
Do not overfill.
4. Drive vehicle for approximately 5 minutes.
5. Re-check A/T fluid level at A/T fluid temperatures of 50° to 80 °C (122 ° to 176 °F) using “HOT” range on A/
T fluid level gauge.
CAUTION:
• When wiping the A/T fluid level gauge, always use lint-free cloth.
• Firmly fix the A/T fluid level ga uge to the A/T fluid charging pipe using the stopper attached.
6. Check A/T fluid condition and make any necessary repairs. Refer to AT-51, " Inspections Before Trouble
Diagnosis " . If the A/T fluid contains frictional material (clu
tches, bands, etc.), or if the A/T is repaired, over-
hauled, or replaced, inspect and clean the A/T fluid cooler mounted in the radiator. Refer to AT-18, " A/T
Fluid Cooler Cleaning " .
7. Install the removed A/T fluid level gauge into the A/T fluid charging pipe. CAUTION:
Firmly fix the A/T fluid level gaug e to the A/T fluid charging pipe using the stopper attached.
Changing A/T Fluid INFOID:0000000004305296
1. Warm up A/T fluid.
2. Stop engine.
3. Drain A/T fluid by removing the drain plug. Re install the drain plug to the specified torque.
CAUTION:
Do not reuse drain plug gasket.
4. Refill the transaxle with new specified A/T fluid th rough the A/T fluid charging pipe. Always refill the tran-
saxle with the same volume of A/T fluid that was drained out. B
Component " .
Page 42 of 4331

AT
N
O P
Control Valve
INFOID:0000000004305307
FUNCTION OF CONTROL VALVES
Centrifugal Cancel Mechanism INFOID:0000000004305308
FUNCTION The centrifugal cancel mechanism is a mechanism to c ancel the centrifugal hydraulic pressure instead of the
conventional check balls. It cancels the centrifugal hy draulic pressure which is generated as high clutch drum
rotates, and it allows for preventing high clutch from dragging and for providing stable high clutch piston press-
ing force in all revolution speeds.
STRUCTURE/OPERATION Valve name Function
Pressure regulator valve, plug and sleeve
plug Regulates oil discharged from the oil pump to provide optimum line pressure for all driving
conditions.
Pressure modifier valve and sleeve Used as a signal supplementary valve to the pressure regulator valve. Regulates pres- sure-modifier pressure (signal pressure) which controls optimum line pressure for all driv-
ing conditions.
Pilot valve Regulates line pressure to maintain a constant pilot pressure level which controls lock-up mechanism, overrun clutch, shift timing.
Accumulator control valve Regulates accumulator back-pressure to pressure suited to driving conditions.
Manual valve Directs line pressure to oil circuits corresponding to select positions. Hydraulic pressure drains when the shift lever is in Neutral.
Shift valve A Simultaneously switches three oil circuits using output pressure of shift solenoid valve A to meet driving conditions (vehicle speed, throttle opening, etc.).
Provides automatic downshifting and upshifting (1st → 2nd → 3rd → 4th gears/4th → 3rd
→ 2nd → 1st gears) in combination with shift valve B.
Shift valve B Simultaneously switches two oil circuits using output pressure of shift solenoid valve B in relation to driving conditions (vehicle speed, throttle opening, etc.).
Provides automatic downshifting and upshifting (1st → 2nd → 3rd → 4th gears/4th → 3rd
→ 2nd → 1st gears) in combination with shift valve A.
Overrun clutch control valve Switches hydraulic circuits to prevent engagement of the overrun clutch simultaneously with application of the brake band in D4. (Interlocking occurs if the overrun clutch engages
during D 4.)
1st reducing valve Reduces low & reverse brake pressure to dampen engine-brake shock when downshift- ing from the 1st position 12 to 1 1.
Overrun clutch reducing valve Reduces oil pressure directed to the overrun clutch and prevents engine-brake shock. In the 1st and 2nd positions, line pressure acts on the overrun clutch reducing valve to
increase the pressure-regulating point, with resultant engine brake capability.
Torque converter relief valve Prevents an excessive rise in torque converter pressure.
Torque converter clutch control valve, plug
and sleeve Activates or inactivates the lock-up function.
Also provides smooth lock-up through transient application and release of the lock-up
system.
1-2 accumulator valve and piston Lessens the shock find when the 2nd gear band servo contracts, and provides smooth shifting.
3-2 timing valve Switches the pace that oil pressure is released depending on vehicle speed; maximizes the high clutch release timing, and allows for soft downshifting.
Shuttle valve Determines if the overrun clutch solenoid valve should control the 3-2 timing valve or the overrun clutch control valve and switches between the two.
Cooler check valve At low speeds and with a small load when a little heat is generated, saves the volume of cooler flow, and stores the oil pressure for lock-up.
Page 44 of 4331

AT
N
O P
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
Introduction INFOID:0000000004305309
A/T system has two self-diagnostic systems.
The first is emission-related on boar d diagnostic system (OBD-II) performed by the TCM in combination with
the ECM. The malfunction is indicated by the MIL (malf unction indicator lamp) and is stored as a DTC in the
ECM memory but not the TCM memory.
The second is the TCM original self-diagnosis indicated by the OD OFF indicator lamp. The malfunction is
stored in the TCM memory. The detected items are ov erlapped with OBD-II self-diagnostic items. For detail,
refer to AT-79, " CONSULT-III Function (TRANSMISSION) " .
OBD-II Function for A/T System INFOID:0000000004305310
The ECM provides emission-related on board diagnostic (O BD-II) functions for the A/T system. One function
is to receive a signal from the TCM used with OBD-rela ted parts of the A/T system. The signal is sent to the
ECM when a malfunction occurs in the corresponding OBD-re lated part. The other function is to indicate a
diagnostic result by means of the MIL (malfunction indica tor lamp) on the instrument panel. Sensors, switches
and solenoid valves are used as sensing elements.
The MIL automatically illuminates in One or Two Trip Detection Logic when a malfunction is sensed in relation
to A/T system parts.
One or Two Trip Detection Logic of OBD-II INFOID:0000000004305311
ONE TRIP DETECTION LOGIC If a malfunction is sensed during the first test drive, the MIL will illuminate and the malfunction will be stored in
the ECM memory as a DTC. The TCM is not provided with such a memory function.
TWO TRIP DETECTION LOGIC When a malfunction is sensed during the first test drive, it is stored in the ECM memory as a 1st trip DTC
(diagnostic trouble code) or 1st trip freeze frame data. At this point, the MIL will not illuminate. — 1st trip
If the same malfunction as that experienced during the fi rst test drive is sensed during the second test drive,
the MIL will illuminate. — 2nd trip
The “trip” in the “One or Two Trip Detection Logic” m eans a driving mode in which self-diagnosis is performed
during vehicle operation.
OBD-II Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) INFOID:0000000004305312
HOW TO READ DTC AND 1ST TRIP DTC DTC and 1st trip DTC can be read by the following methods.
( with CONSULT-III or GST) CONSULT-III or GST (Generic Scan Tool) Examples: P0705, P0720 etc.
These DTC are prescribed by SAE J2012.
(CONSULT-III also displays the malfunctioning component or system.)
• 1st trip DTC No. is the same as DTC No.
• Output of the diagnostic troubl e code indicates that the indicated circuit has a malfunction. How-
ever, in case of the Mode II and GST, they do not indicate whether the malfunction is still occurring or
occurred in the past and returned to normal.
CONSULT-III can identify them as shown below, therefore, CONS ULT-III (if available) is recom-
mended.
DTC or 1st trip DTC of a malfunction is displayed in SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS mode for “ENGINE” with
CONSULT-III. Time data indicates how many times the vehicle was driven after the last detection of a DTC.
If the DTC is being detected curr ently, the time data will be “0”.
If a 1st trip DTC is stored in the ECM, the time data will be “1t”.
Freeze Frame Data and 1st Trip Freeze Frame Data The ECM has a memory function, which stores the driv ing condition such as fuel system status, calculated
load value, engine coolant temperature, short term f uel trim, long term fuel trim, engine speed and vehicle
speed at the moment the ECM detects a malfunction.
Page 47 of 4331

.
Fail-Safe INFOID:0000000004305315
The TCM has an electronic Fail-safe mode. This allows t he vehicle to be driven even if a major electrical input/
output device circuit is damaged.
Under Fail-Safe, the vehicle always runs in third gear, even with a shift lever position of “1”, “2” or “D”. The cus-
tomer may complain of sluggish or poor acceleration.
Always follow the “ AT-43, " How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate Repair " ”.
The SELF-DIAGNOSIS results will be as follows:
• The first SELF-DIAGNOSIS will indicate damage to t he vehicle speed sensor or the revolution sensor.
• During the next SELF-DIAGNOSIS, performed after checking the sensor, no damages will be indicated.
FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION
The following fail-safe functions allow vehicles to be driven even when sensor, switch or solenoid malfunction
occurs.
Vehicle Speed Sensor·A/T (Revolution Sensor)
Vehicle speed sensor·MTR signal is input from combination meter.
Accelerator Pedal Position Signal and Throttle Position Signal
TCM controls the throttle opening angle to a predetermi ned fixed position to enable driving if a malfunctioning
signal is input to TCM.
PNP Switch
When the multiple PNP switch signals are input to TCM, the priority of selector lever position becomes “D”,
“N”, “R”, “2” and “1” in order by internal TCM determination.
The use of 4th gear is inhibited unt il normal operation resumes. Because t he hydraulic circuit of the control
valve is switched by manual valve according to the sele ctor lever position, however, actual operating condition
of vehicle becomes as follows.
Shift Solenoid Valve A and B
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, use of certain gears is limited. Refer to chart shown below.
Priority Detected items
1 CAN communication line
2 Except above Actual lever position PNP switch input signal Running status
“P” “P” position and other position signals P
“R” “R” position and other position signals R
“N” “N” position and other position signals N
“D” “D” position and other position signals D 1
⇔ D2 ⇔ D3 ⇔ D4
“2” “2” position and other position signals (Except “1” position) 2
1 ⇔ 22 ⇔ 23
“2” position and “1” position signals 2 1 ⇔ 22
“1” “1” position and other position signals (Except “2” position) 1
1
⇔ 12 ⇔ 13
“1” position and “2” position signals 1 1 ⇔ 12
Page 75 of 4331

2. Shift solenoid valve A
AT-139 3. Control valve assembly
AT-221 4. Vehicle speed sensor·A/T (Revolution sensor)
and vehicle speed sensor·MTR AT-101 ,
AT-154 5. Accelerator pedal position sensor
EC-412
(HR16DE), EC- 959 (MR Type 1)
or EC-1481 (MR
Type 2)
OFF vehicle 6. Brake band AT-330Failure to change
gear from D 2 to D 3 . ON vehicle 1. Control cable adjustment
AT-216 2. Shift solenoid valve B
AT-144 3. Control valve assembly
AT-221 4. Vehicle speed sensor·A/T (Revolution sensor)
and vehicle speed sensor·MTR AT-101 ,
AT-154 5. Accelerator pedal position sensor
EC-412
(HR16DE), EC- 959 (MR Type 1)
or EC-1481 (MR
Type 2)
OFF vehicle 6. High clutch
AT-301 7. Brake band
AT-330Failure to change
gear from D 3 to D 4 . ON vehicle 1. PNP switch adjustment
AT-224 2. Overdrive control switch
AT-172 3. Control cable adjustment
AT-216 4. Shift solenoid valve A
AT-139 5. Vehicle speed sensor·A/T (Revolution sensor)
and vehicle speed sensor·MTR AT-101 ,
AT-154 6. A/T fluid temperature sensor
AT-96 OFF vehicle 7. Brake band
AT-330A/T does not shift to
D 4 when driving with
OD ON. (OD OFF in-
dicator lamp is off.) ON vehicle1. Accelerator pedal position sensor
EC-412
(HR16DE), EC- 959 (MR Type 1)
or EC-1481 (MR
Type 2)
2. PNP switch adjustment AT-224 3. Overdrive control switch
AT-172 4. Vehicle speed sensor·A/T (Revolution sensor)
and vehicle speed sensor·MTR AT-101 ,
AT-154 5. Shift solenoid valve A
AT-139 6. Overrun clutch solenoid valve
AT-149 7. Control valve assembly
AT-221 8. A/T fluid temperature sensor
AT-96 9. Line pressure solenoid valve
AT-134 OFF vehicle
10. Brake band
AT-330 11. Overrun clutch
AT-306Items Symptom Condition Diagnostic item Reference page
Page 83 of 4331
.)
Battery voltage
When overrun clutch solenoid valve
does not operate. (When overrun clutch
engaged. Refer to AT-22 .)
0 V
25 B Ground Always 0 V
26 Y PNP switch “1” position
and When setting selector lever to “1” posi-
tion. Battery voltage
When setting selector lever to other po-
sitions. 0 V
27 G PNP switch “2” position When setting selector lever to “2” posi-
tion. Battery voltage
When setting selector lever to other po-
sitions. 0 V
28 GR Power supply
(memory back-up) Always Battery voltage
29 V Revolution sensor When driving at 20 km/h (12 MPH) 150 Hz
30 *1
BR CONSULT- III (RX) — —
31 *1
Y CONSULT- III (TX) — —
34 LG PNP switch “D” position
and When setting selector lever to “D” posi-
tion. Battery voltage
When setting selector lever to other po-
sitions. 0 V
35 SB PNP switch “R” position When setting selector lever to “R” posi-
tion. Battery voltage
When setting selector lever to other po-
sitions. 0 V
36 R PNP switch “N” or “P”
position When setting selector
lever to “N” or “P”
position. Battery voltage
When setting selector lever to other po-
sitions. 0 V
38 G Turbine revolution sen-
sor (power train revolu-
tion sensor) When driving at 20 km/h (12 MPH) 360 Hz
Terminal
Wire
color Item Condition Judgement stan-
dard (Approx.)
Page 84 of 4331
AT
N
O P
*1
: These terminals are connected to the data link connector.
*2 : These terminals are connected to the ECM.
CONSULT-III Function (TRANSMISSION) INFOID:0000000004305330
CONSULT-III can display each diagnostic item using the diagnostic test models shown following.
FUNCTION
CONSULT-III REFERENCE VALUE NOTICE:
1. The CONSULT-III electrically displays shift timi ng and lock-up timing (that is, operation timing of each
solenoid).
Check for time difference between actual shift timi ng and the CONSULT-III display. If the difference is
noticeable, mechanical parts (except solenoids, sens ors, etc.) may be malfunctioning. Check mechanical
parts using applicable diagnostic procedures.
2. Shift schedule (which implies gear position) display ed on CONSULT-III and that indicated in Service Man-
ual may differ slightly. This occurs because of the following reasons:
- Actual shift schedule has more or less tolerance or allowance,
- Shift schedule indicated in Service Manual re fers to the point where shifts start, and
- Gear position displayed on CONSULT-III indicates the point where shifts are completed.
3. Shift solenoid valve “A” or “B” is displayed on CONSUL T-III at the start of shifting. Gear position is dis-
played upon completion of shifting (which is computed by TCM).
39
*2
L Engine speed signal
and Refer to
EC-461 (HR16DE),
EC-597 (MR Type 1) or
EC- 1109 (MR Type 2).
40 O Vehicle speed sensor When driving vehicle at 2 to 3 km/h (1 to
2 MPH) for 1 m (3 ft) or more. Voltage varies
between less
than 0 V and
more than 4.5 V
42 B Sensor ground Always 0 V
47 BR A/T fluid temperature
sensor and When A/T fluid temperature is 20
°C
(68 °F). 1.5 V
When A/T fluid temperature is 80 °C
(176 °F). 0.5 V
48 B Ground Always 0 V
Terminal
Wire
color Item Condition Judgement stan-
dard (Approx.) Diagnostic test mode Function
Work Support This mode enables a technician to adjust some devices faster and more accuratelyI.
Self Diagnostic Results Retrieve DTC from ECU and display diagnostic items.
Data Monitor Monitor the input/output signal of the control unit in real time.
CAN Diagnosis Support Monitor It monitors the status of CAN communication.
Function Test This mode can show results of self-diagnosis of ECU with either “OK” or “NG”. For engine, more
practical tests regarding sensors/switches and/or actuators are available.
DTC & SRT confirmation The status of system monitoring tests and the self-diagnosis status/result can be confirmed.
ECU Identification Display the ECU identification number (part number etc.) of the selected system. Item name Condition Display value (Approx.)
VHCL/S SE-A/T During driving Approximately matches the speedometer
reading.
VHCL/S SE-MTR
THROTTLE POSI Released accelerator pedal. 0.0/8
Fully depressed accelerator pedal. 8.0/8