system NISSAN TIIDA 2011 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2011, Model line: TIIDA, Model: NISSAN TIIDA 2011Pages: 3787, PDF Size: 78.35 MB
Page 2711 of 3787

HOW TO USE THIS MANUALGI-7
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O PHOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
DescriptionINFOID:0000000005929718
This volume explains “Removal, Disassembly, Inst allation, Inspection and Adjustment” and “Trouble Diag-
noses”.
Te r m sINFOID:0000000005929719
• The captions WARNING and CAUTION warn you of steps that must be followed to prevent personal injury
and/or damage to some part of the vehicle.
WARNING indicates the possibility of personal injury if instructions are not followed.
CAUTION indicates the possibility of component damage if instructions are not followed.
BOLD TYPED STATEMENTS except WARNING and CAUTION give you helpful information.
Standard value:Tolerance at inspection and adjustment.
Limit value:The maximum or minimum limit value t hat should not be exceeded at inspection and adjustment.
UnitsINFOID:0000000005929720
• The UNITS given in this manual are primarily expressed as the SI UNIT (International System of Unit), and
alternatively expressed in the metric system and in the yard/pound system.
Also with regard to tightening torque of bolts and nuts, there are descriptions both about range and about the
standard tightening torque.
“Example”
Range
Standard
ContentsINFOID:0000000005929721
• A QUICK REFERENCE INDEX , a black tab (e.g. ) is provided on the first page. You can quickly find the
first page of each section by matching it to the section's black tab.
• THE CONTENTS are listed on the first page of each section.
• THE TITLE is indicated on the upper portion of each page and shows the part or system.
• THE PAGE NUMBER of each section consists of two or three letters which designate the particular section
and a number (e.g. “BR-5”).
• THE SMALL ILLUSTRATIONS show the important steps such as ins pection, use of special tools, knacks of
work and hidden or tricky steps which are not shown in the previous large illustrations.
Assembly, inspection and adjustment procedures for the complicated units such as the automatic transaxle
or transmission, etc. are presented in a step-by-step format where necessary. Outer Socket Lock Nut : 59 - 78 N·m (6.0 - 8.0 kg-m, 43 - 58 ft-lb)
Drive Shaft Installation Bolt : 44.3 N·m (4.5 kg-m, 33 ft-lb)
Revision: May 2010
2011 Versa
Page 2714 of 3787

GI-10
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
3.Refer to Component Parts and Harness Connector Location for the Systems described in each
section for identifi cation/location of componen ts and harness connectors.
4. Refer to the Circuit Diagram for quick pinpoint check.
If you need to check circuit continuity between harness connectors in more detail, such as when a
sub-harness is used, refer to Wiring Diagram in each individual section and Harness Layout in PG
section for identificatio n of harness connectors.
5. When checking circuit continuity, ignition switch should be OFF.
6. Before checking voltage at co nnectors, check battery voltage.
7. After accomplishing the Diagnostic Procedures an d Electrical Components Inspection, make sure
that all harness connectors ar e reconnected as they were.
HOW TO FOLLOW TEST GROUPS IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
1.Work and diagnostic procedure
Start to diagnose a problem using procedures indicated in enclosed test groups.
2. Questions and required results
Questions and required results are indicated in bold type in test group.
The meaning of are as follows:
3. Symbol used in illustration
Symbols included in illustrations refer to measurements or procedures. Before diagnosing a problem,
familiarize yourself with each symbol. Refer to "Connector Symbols" in GI Section and "KEY TO SYM-
BOLS SIGNIFYING MEASUREME NTS OR PROCEDURES" below.
4. Action items
Next action for each test group is indicated based on result of each question. Test group number is shown
in the left upper portion of each test group.
HARNESS WIRE COLOR AND CONNECTOR NUMBER INDICATION
There are two types of harness wire color and connector number indication.
TYPE 1: Harness Wire Color and Connector Number are Shown in Illustration
SAIA0256E
a. Battery voltage → 11 - 14V or approximately 12V
b. Voltage : Approximately 0V → Less than 1V
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 2718 of 3787
GI-14
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
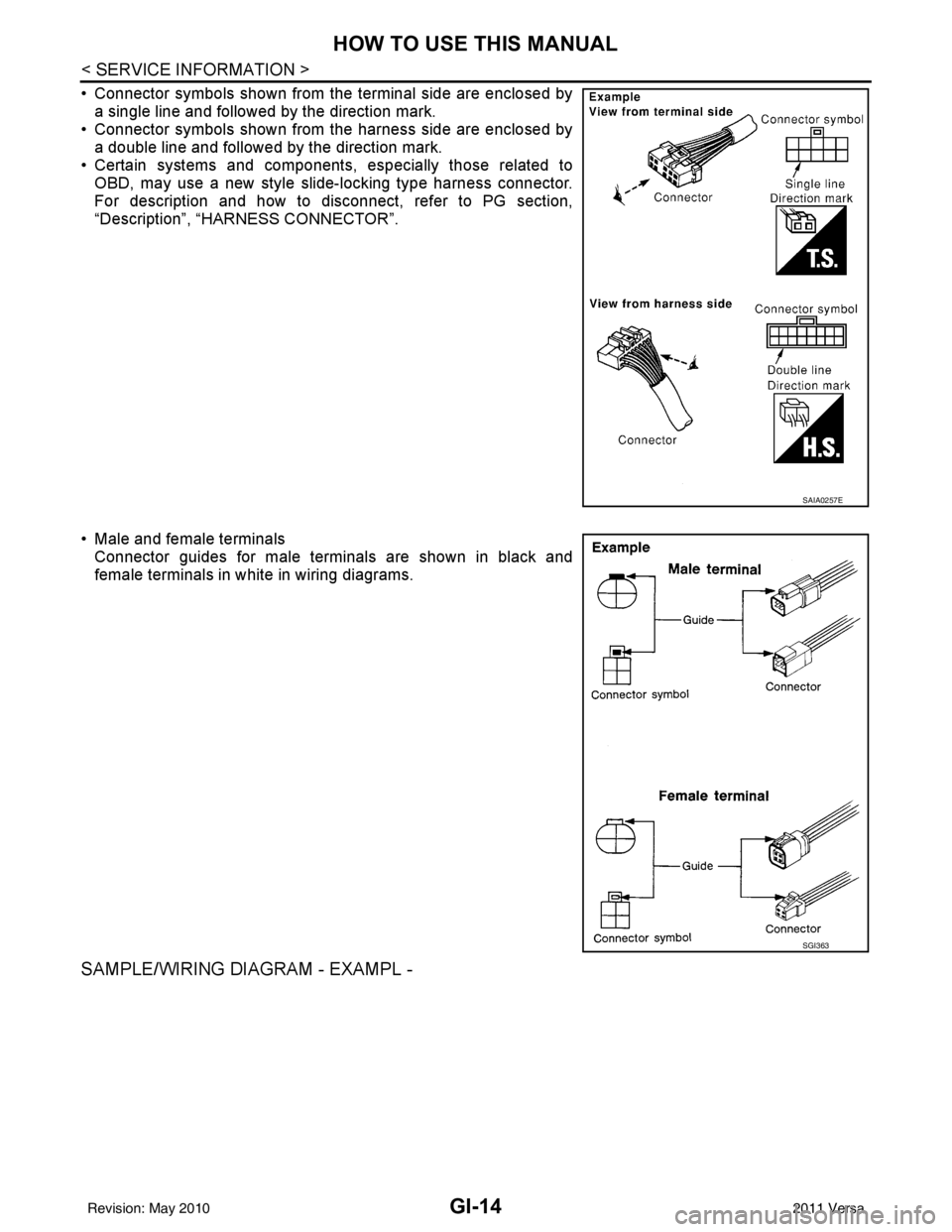
• Connector symbols shown from the terminal side are enclosed bya single line and followed by the direction mark.
• Connector symbols shown from the harness side are enclosed by
a double line and followed by the direction mark.
• Certain systems and components, especially those related to OBD, may use a new style slide-locking type harness connector.
For description and how to disconnect, refer to PG section,
“Description”, “HARNESS CONNECTOR”.
• Male and female terminals Connector guides for male terminals are shown in black and
female terminals in white in wiring diagrams.
SAMPLE/WIRING DIAGRAM - EXAMPL -
SAIA0257E
SGI363
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 2720 of 3787
GI-16
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
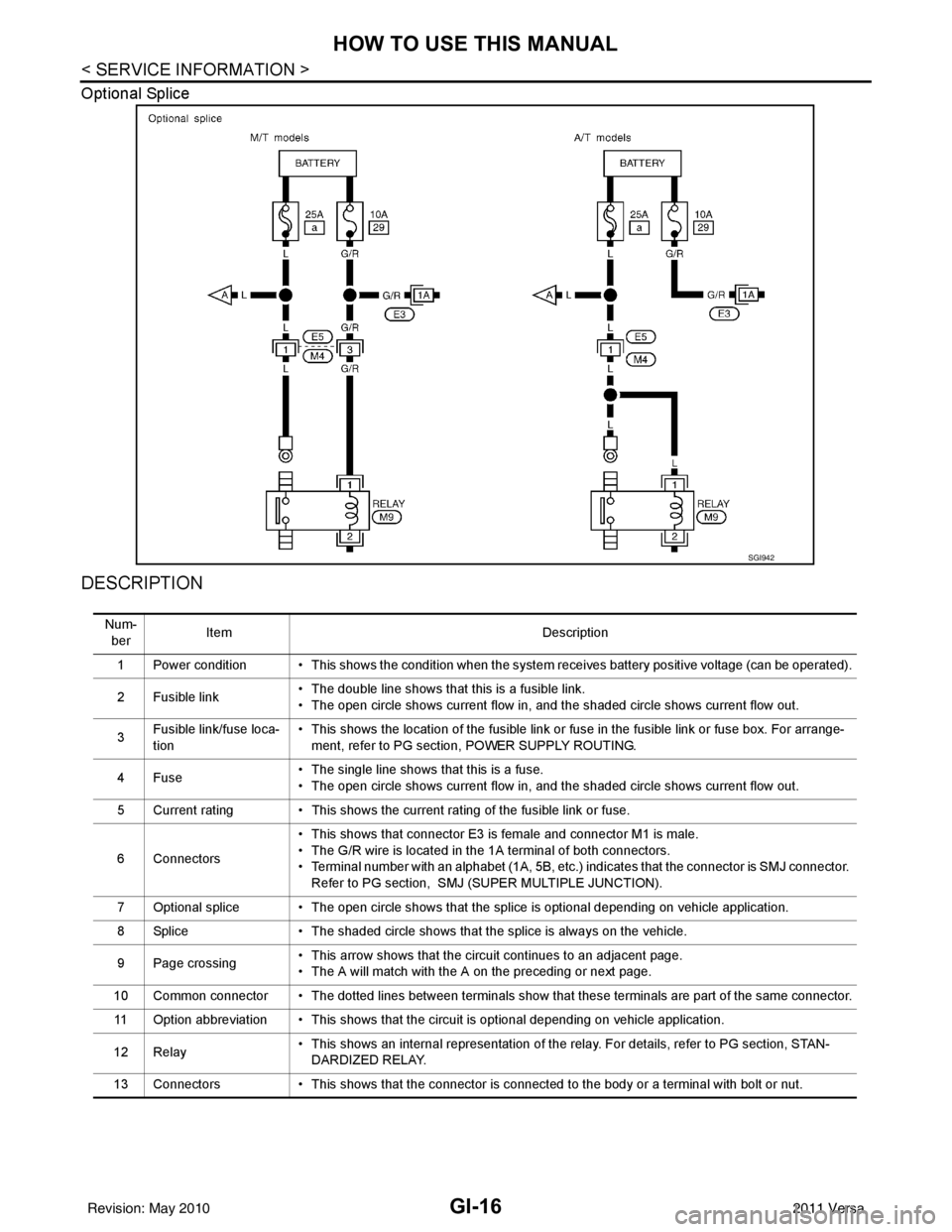
Optional Splice
DESCRIPTION
SGI942
Num-ber Item
Description
1 Power condition • This shows the condition when the system receives battery positive voltage (can be operated).
2 Fusible link • The double line shows that this is a fusible link.
• The open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
3 Fusible link/fuse loca-
tion • This shows the location of the fusible link or fuse in the fusible link or fuse box. For arrange-
ment, refer to PG section, POWER SUPPLY ROUTING.
4Fuse • The single line shows that this is a fuse.
• The open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
5 Current rating • This shows the current rating of the fusible link or fuse.
6 Connectors • This shows that connector E3 is female and connector M1 is male.
• The G/R wire is located in the 1A terminal of both connectors.
• Terminal number with an alphabet (1A, 5B, etc.) indicates that the connector is SMJ connector.
Refer to PG section, SMJ (SUPER MULTIPLE JUNCTION).
7 Optional splice • The open circle shows that the splice is optional depending on vehicle application.
8 Splice • The shaded circle shows that the splice is always on the vehicle.
9 Page crossing • This arrow shows that the circuit continues to an adjacent page.
• The A will match with the A on the preceding or next page.
10 Common connector • The dotted lines between terminals show that these terminals are part of the same connector. 11 Option abbreviation • This shows that the circuit is optional depending on vehicle application.
12 Relay • This shows an internal representation of the relay. For details, refer to PG section, STAN-
DARDIZED RELAY.
13 Connectors • This shows that the connector is connected to the body or a terminal with bolt or nut.
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 2721 of 3787

HOW TO USE THIS MANUALGI-17
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
Harness Indication
14 Wire color • This shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light Green BR = Brown
OR or O = Orange
P = Pink
PU or V (Violet) = Purple
GY or GR = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as shown
below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
15 Option description • This shows a description of the option abbreviation used on the page.
16 Switch • This shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switch is in the A posi-
tion. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is in the B position.
17 Assembly parts • Connector terminal in component shows that it is a harness incorporated assembly.
18 Cell code • This identifies each page of the wiring diagram by section, system and wiring diagram page
number.
19 Current flow arrow • Arrow indicates electric current flow, especially where the direction of standard flow (vertically
downward or horizontally from left to right) is difficult to follow.
• A double arrow “ ” shows that current can flow in either direction depending on circuit operation.
20 System branch • This shows that the system branches to another system identified by cell code (section and
system).
21 Page crossing • This arrow shows that the circuit continues to another page identified by cell code.
• The C will match with the C on another page within the system other than the next or preceding
pages.
22 Shielded line • The line enclosed by broken line circle shows shield wire.
23 Component box in
wave line • This shows that another part of the component is also shown on another page (indicated by
wave line) within the system.
24 Component name • This shows the name of a component.
25 Connector number • This shows the connector number.
• The letter shows which harness the connector is located in.
•Example:
M: main harness. For detail and to locate the connector, refer to PG section "Main
Harness", “Harness Layout”. A coordinate grid is included for complex harnesses to aid in lo-
cating connectors.
26 Ground (GND) • The line spliced and grounded under wire color shows that ground line is spliced at the ground-
ed connector.
27 Ground (GND) • This shows the ground connection. For detailed ground distribution information, refer to
"Ground Distribution" in PG section.
28 Connector views • This area shows the connector faces of the components in the wiring diagram on the page.
29 Common component • Connectors enclosed in broken line show that these connectors belong to the same compo-
nent.
30 Connector color • This shows a code for the color of the connector. For code meaning, refer to wire color codes,
Number 14 of this chart.
31 Fusible link and fuse
box • This shows the arrangement of fusible link(s) and fuse(s), used for connector views of "POW-
ER SUPPLY ROUTING" in PG section.
The open square shows current flow in, and the shaded square shows current flow out.
32 Reference area • This shows that more information on the Super Multiple Junction (SMJ) and Joint Connectors
(J/C) exists on the PG section. Refer to "Reference Area" for details.
Num-
ber Item
Description
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 2723 of 3787
HOW TO USE THIS MANUALGI-19
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
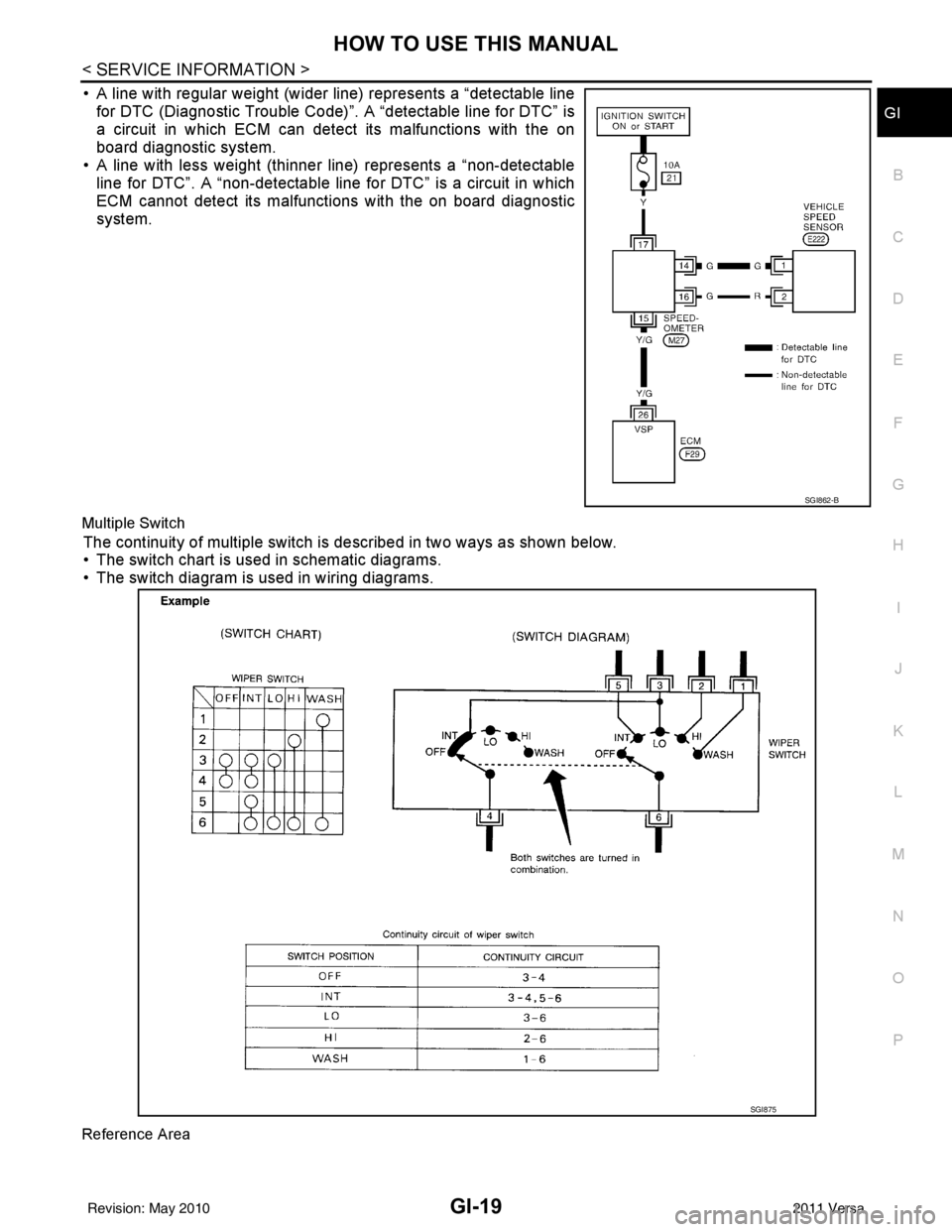
• A line with regular weight (wider line) represents a “detectable line for DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code)”. A “detectable line for DTC” is
a circuit in which ECM can detect its malfunctions with the on
board diagnostic system.
• A line with less weight (thinner line) represents a “non-detectable line for DTC”. A “non-detectable line for DTC” is a circuit in which
ECM cannot detect its malfunctions with the on board diagnostic
system.
Multiple Switch
The continuity of multiple switch is described in two ways as shown below.
• The switch chart is used in schematic diagrams.
• The switch diagram is used in wiring diagrams.
Reference Area
SGI862-B
SGI875
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 2729 of 3787

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENTGI-25
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
How to Perform Efficient Diagnos is for an Electrical IncidentINFOID:0000000005929728
WORK FLOW
INCIDENT SIMULATION TESTS
Introduction
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doi ng so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The fol-
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the c onditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
• Vehicle vibration
• Heat sensitive
• Freezing
• Water intrusion
• Electrical load
SGI838
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1 Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHAT
Vehicle Model, Engine, Transmission/Transaxle and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHEN Date, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERE Road Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOW System Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2 Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem cannot be duplicated, refer to “Incident Simulation Tests”.
STEP 3 Get the proper diagnosis materials together including:
• Power Supply Routing
• System Operation Descriptions
• Applicable Service Manual Sections
• Check for any Service Bulletins
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the customer comments.
STEP 4 Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing and Harness Lay-
outs.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6 Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you have not inad-
vertently created a new incident during your diagnosis or repair steps.
Revision: May 2010
2011 Versa
Page 2730 of 3787
GI-26
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
• Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of the
problem.
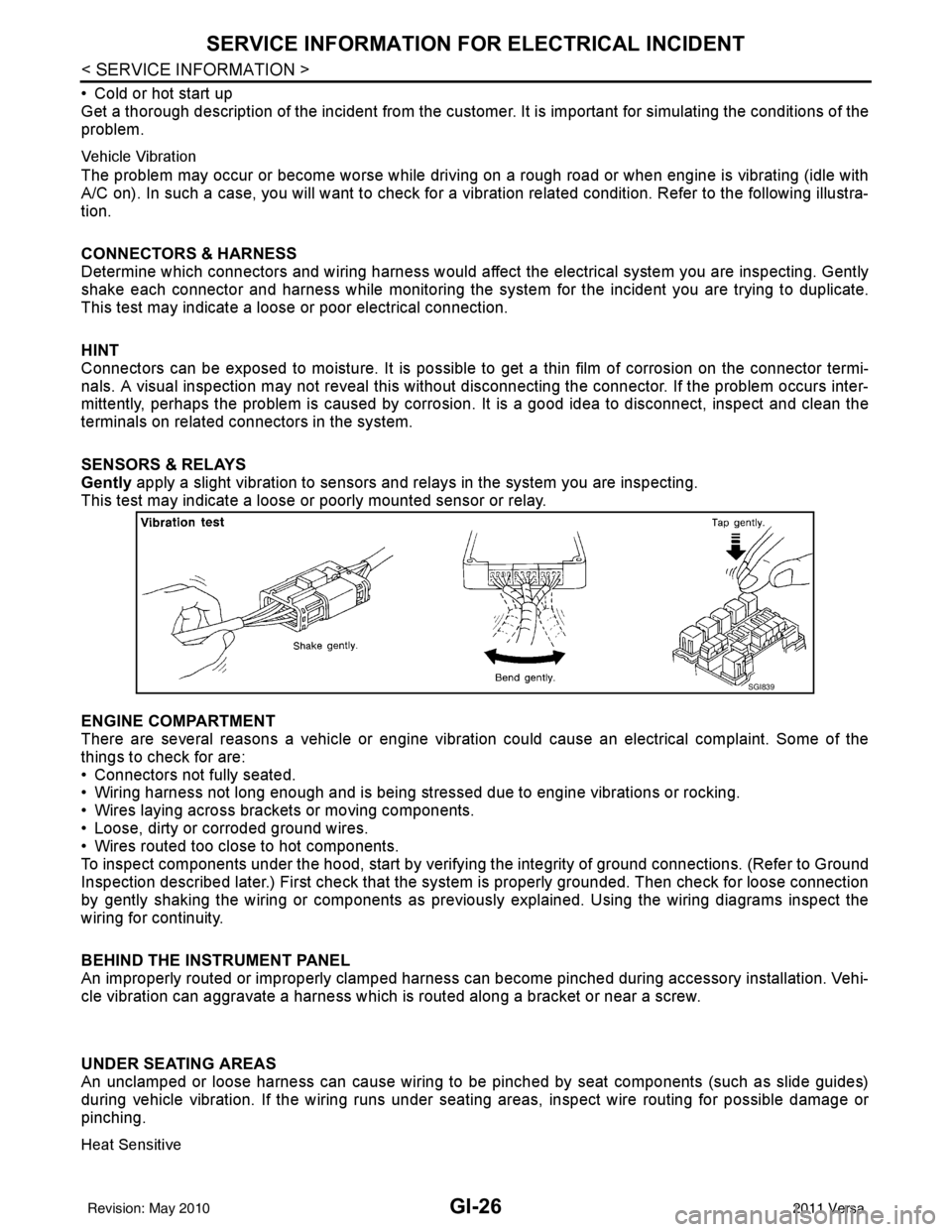
Vehicle Vibration
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the following illustra-
tion.
CONNECTORS & HARNESS
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting. Gently
shake each connector and harness while monitoring the sy stem for the incident you are trying to duplicate.
This test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
HINT
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin film of corrosion on the connector termi-
nals. A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs inter-
mittently, perhaps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
SENSORS & RELAYS
Gently apply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
ENGINE COMPARTMENT
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could cause an e\
lectrical complaint. Some of the
things to check for are:
• Connectors not fully seated.
• Wiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to engine vibrations or rocking.
• Wires laying across brackets or moving components.
• Loose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
• Wires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifyi ng the integrity of ground connections. (Refer to Ground
Inspection described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded. Then check for loose connection
by gently shaking the wiring or components as previous ly explained. Using the wiring diagrams inspect the
wiring for continuity.
BEHIND THE INSTRUMENT PANEL
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become pinched during accessory installation. Vehi-
cle vibration can aggravate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
UNDER SEATING AREAS
An unclamped or loose harness can cause wiring to be pinched by seat components (such as slide guides)
during vehicle vibration. If the wiring runs under s eating areas, inspect wire routing for possible damage or
pinching.
Heat Sensitive
SGI839
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 2731 of 3787
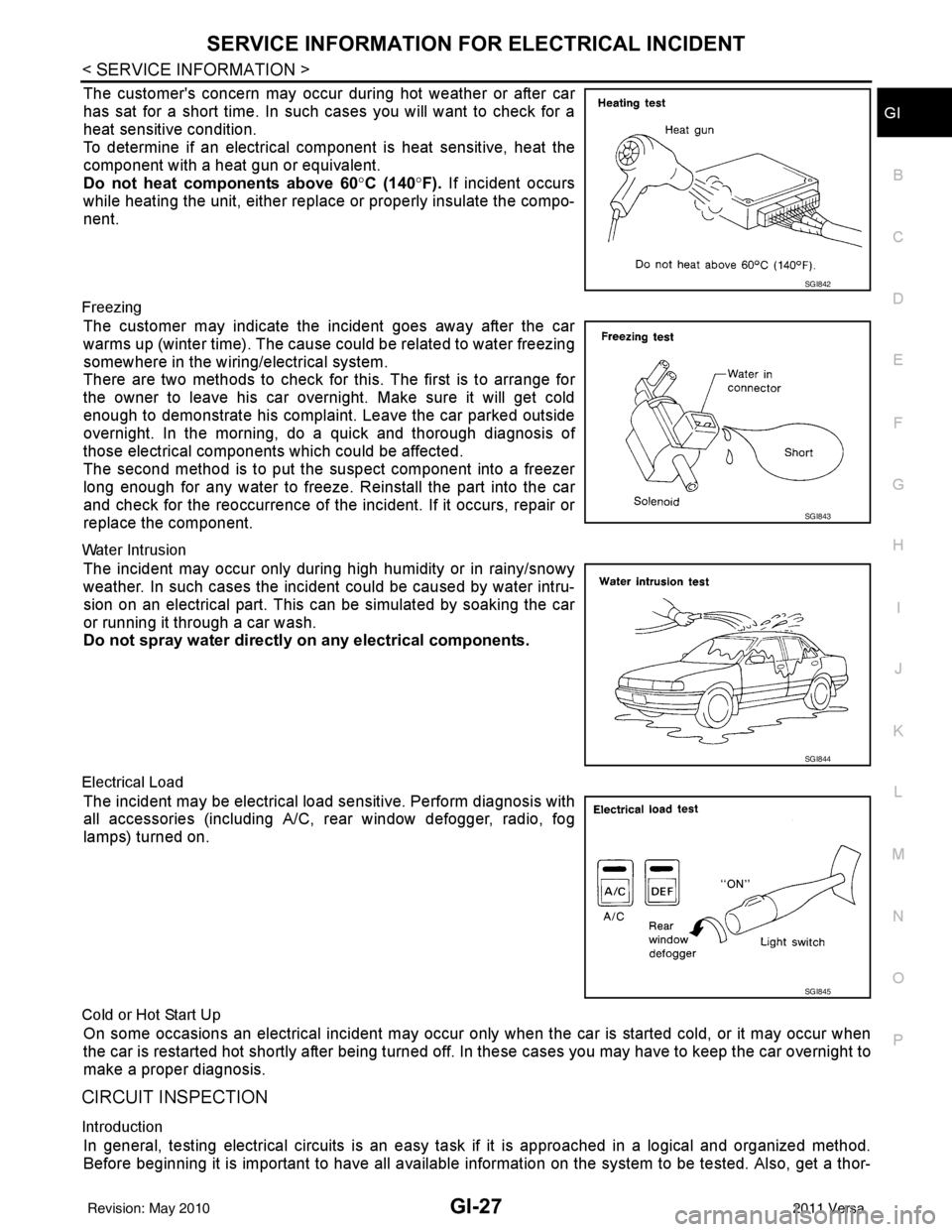
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENTGI-27
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
The customer's concern may occur during hot weather or after car
has sat for a short time. In such cases you will want to check for a
heat sensitive condition.
To determine if an electrical com ponent is heat sensitive, heat the
component with a heat gun or equivalent.
Do not heat components above 60 °C (140° F). If incident occurs
while heating the unit, either replace or properly insulate the compo-
nent.
Freezing
The customer may indicate the incident goes away after the car
warms up (winter time). The cause could be related to water freezing
somewhere in the wiring/electrical system.
There are two methods to check for this. The first is to arrange for
the owner to leave his car overnight. Make sure it will get cold
enough to demonstrate his complaint. Leave the car parked outside
overnight. In the morning, do a quick and thorough diagnosis of
those electrical components which could be affected.
The second method is to put the suspect component into a freezer
long enough for any water to freeze. Reinstall the part into the car
and check for the reoccurrence of the incident. If it occurs, repair or
replace the component.
Water Intrusion
The incident may occur only during high humidity or in rainy/snowy
weather. In such cases the incident could be caused by water intru-
sion on an electrical part. This c an be simulated by soaking the car
or running it through a car wash.
Do not spray water directly on any electrical components.
Electrical Load
The incident may be electrical load sensitive. Perform diagnosis with
all accessories (including A/C, rear window defogger, radio, fog
lamps) turned on.
Cold or Hot Start Up
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the car is started cold, or it may occur when
the car is restarted hot shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep the car overnight to
make a proper diagnosis.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
Introduction
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy ta sk if it is approached in a logical and organized method.
Before beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thor-
SGI842
SGI843
SGI844
SGI845
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa
Page 2732 of 3787
GI-28
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
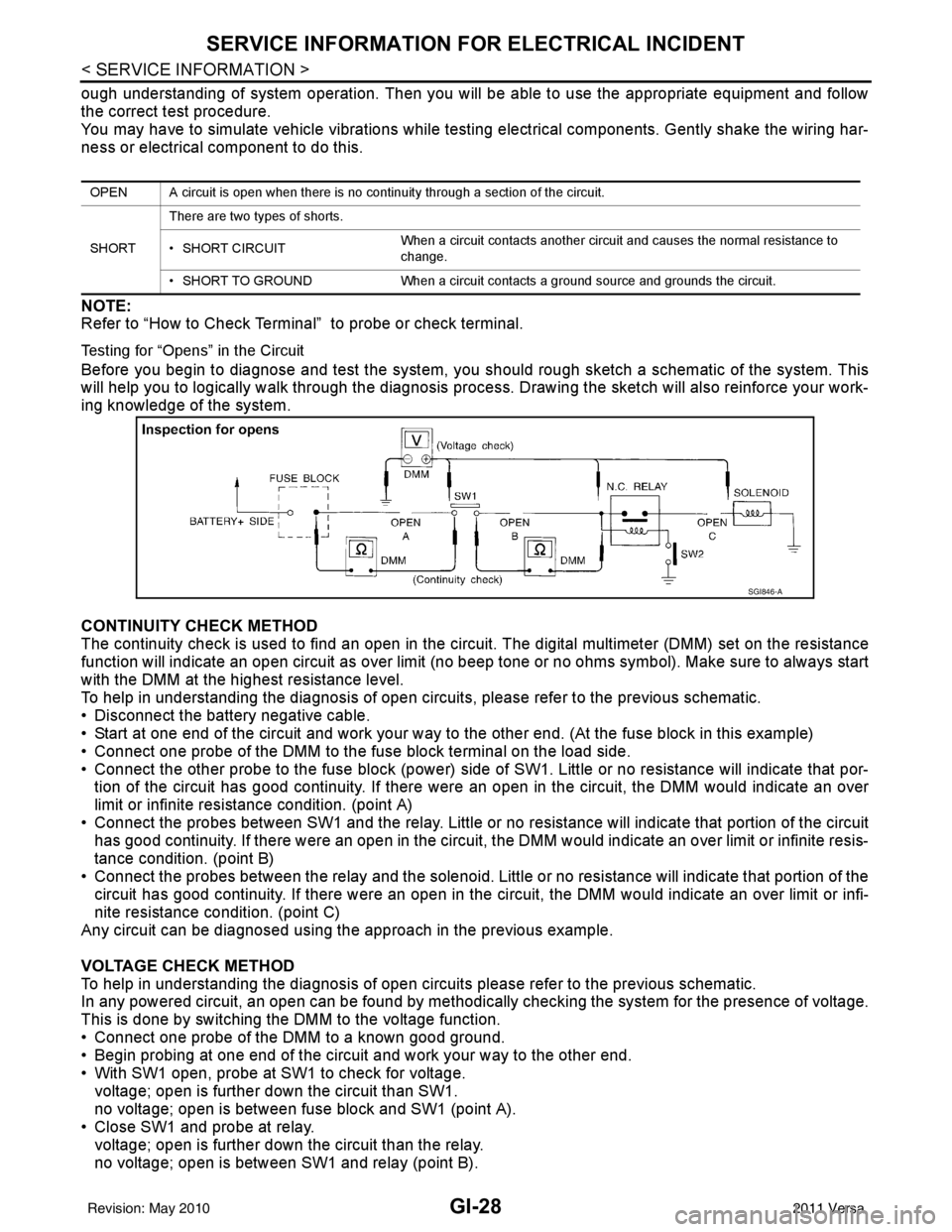
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbo\
l). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circui ts, please refer to the previous schematic.
• Disconnect the battery negative cable.
• Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
• Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
• Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that por-
tion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over
limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
• Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit
has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, t he DMM would indicate an over limit or infinite resis-
tance condition. (point B)
• Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the ci rcuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circui ts please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodica lly checking the system for the presence of voltage.
This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
• Connect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
• Begin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
• With SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage. voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
• Close SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORT There are two types of shorts.
• SHORT CIRCUIT
When a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
• SHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A
Revision: May 2010 2011 Versa