turn signal OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 4679 of 6000

6E–22
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White Connector – Row “D”
(For except EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA)
TS23345
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
D1Injector Cylinder #2GRN/ORNB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
D2Torque Converter Clutch
(TCC)BRN/BLU0.0 V0.0 VOn-Vehicle Service, Torque
Converter Clutch
D3Injector Cylinder #1GRN/WHTB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
D4Serial Data (8192)ORN5.0 V5.0 VChassis Electrical
D5Ignition Control, Cylinder
#5RED/YEL0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Ignition Coil
D6Ignition Control, Cylinder
#3RED/BLUE0.0 V0.0 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Ignition Coil
D7VSS Input / IMOB
ResponseWHT/BLK0.0 V0.1 V
(at rest)Chassis Electrical
D8Sensor Ground 5V
Reference A ReturnGRN0.0 V0.0 VAppropriate Sensor
D9Sensor Ground 5 V
Reference B ReturnGRY0.0 V0.0 VAppropriate Sensor
D10Mass Air Flow (MAF)YEL4.9 V4.2 VGeneral Description, Mass
Air Flow Sensor
D11Camshaft Position SensorWHT5.0 V or less
than 1.0 V4.6 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Camshaft
Position Sensor
D12Not Used————
D13Not Used————
D14Bank 1 HO2S 1 LowGRN0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel HO2S 1
D15Bank 1 HO2S 1 SignalRED0.4 V0.1-0.9 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel HO2S 1
D16Not Used————
Page 4695 of 6000

6E–38
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Service Information
OBD Serviceablity Issues
The list of non-vehicle faults that could affect the
performance of the OBD system has been compiled.
These non-vehicle faults vary from environmental
conditions to the quality of fuel used.
The illumination of the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) due to
a non-vehicle fault could lead to misdiagnosis of the
vehicle, increased warranty expense and customer
dissatisfaction. The following list of non-vehicle faults
does not include every possible fault and may not apply
equally to all product lines.
Fuel Quality
Using fuel with the wrong octane rating for your vehicle
may cause driveability problems. Many of the major fuel
companies advertise that using “premium” gasoline will
improve the performance of your vehicle. Most premium
fuels use alcohol to increase the octane rating of the fuel.
Although alcohol-enhanced fuels may raise the octane
rating, the fuel’s ability to turn into vapor in cold
temperatures deteriorates. This may affect the starting
ability and cold driveability of the engine.
Low fuel levels can lead to fuel starvation, lean engine
operation, and eventually engine misfire.
Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Something as simple as a
high-performance exhaust system that affects exhaust
system back pressure could potentially interfere with the
operation of the EGR valve and thereby turn on the MIL
(“Check Engine” lamp). Small leaks in the exhaust
system near the post catalyst oxygen sensor can also
cause the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) to turn on.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the MIL (“Check
Engine” lamp).
Environment
Temporary environmental conditions, such as localized
flooding, will have an effect on the vehicle ignition system.
If the ignition system is rain-soaked, it can temporarily
cause engine misfire and turn on the MIL (“Check Engine”
lamp).
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the MIL
(“Check Engine” lamp) to turn on if the vehicle is not
maintained properly. Restricted air filters, fuel filters, and
crankcase deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper
oil viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics, vehicle
maintenance schedules must be more closely followed.Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
PCM detects a fault on a related system or component.
One example would be that if the PCM detected a Misfire
fault, the diagnostics on the catalytic converter would be
suspended until Misfire fault was repaired. If the Misfire
fault was severe enough, the catalytic converter could be
damaged due to overheating and would never set a
Catalyst DTC until the Misfire fault was repaired and the
Catalyst diagnostic was allowed to run to completion. If
this happens, the customer may have to make two trips to
the dealership in order to repair the vehicle.
Maintenance Schedule
Refer to the Maintenance Schedule.
Visual / Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any diagnostic
procedure or diagnosing the cause of an emission test
failure. This can often lead to repairing a problem without
further steps. Use the following guidelines when
performing a visual/physical inspection:
Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts,
disconnects, and correct routing.
Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other
components.
Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper
connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched wires,
contact with sharp edges or contact with hot exhaust
manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain when
performing diagnostic procedures could result in an
incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to effec-
tively use this section of the Service Manual.
Serial Data Communications
Class II Serial Data Communications
This vehicle utilizes the “Class II” communication system.
Each bit of information can have one of two lengths: long
or short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by
transmitting and receiving multiple signals over a single
wire. The messages carried on Class II data streams are
also prioritized. If two messages attempt to establish
communications on the data line at the same time, only
the message with higher priority will continue. The device
with the lower priority message must wait. The most
significant result of this regulation is that it provides Tech 2
manufacturers with the capability to access data from any
make or model vehicle that is sold.
Page 4722 of 6000

6E–65 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Knock Sensor Diagnosis
The Tech 2 has two data displays available for diagnosing
the knock sensor (KS) system. The two displays are
described as follows:
“Knock Retard” indicates the number of degrees that
the spark timing is being retarded due to a knock
condition.
“KS Noise Channel” indicates the current voltage level
being monitored on the noise channel.
DTCs P0325 and P0327 are designed to diagnose the KS
module, the knock sensor, and the related wiring. The
problems encountered with the KS system should set a
DTC. However, if no DTC was set but the KS system is
suspect because of a detonation complaint, refer to
Detonation/Spark Knock in Symptoms.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Diagnosis
To read and clear diagnostic trouble codes, use a Tech 2.
IMPORTANT:Use of a Tech 2 is recommended to clear
diagnostic trouble codes from the PCM memory.
Diagnostic trouble codes can also be cleared by turning
the ignition “OFF” and disconnecting the battery power
from the PCM for 30 seconds. Turning off the ignition and
disconnecting the battery power from the PCM will cause
all diagnostic information in the PCM memory to be
cleared. Therefore, all the diagnostic tests will have to be
re-run.
Since the PCM can have a failure which may affect only
one circuit, following the diagnostic procedures in this
section will determine which circuit has a problem and
where it is.
If a diagnostic chart indicates that the PCM connections
or the PCM is the cause of a problem, and the PCM is
replaced, but this does not correct the problem, one of the
following may be the reason:
There is a problem with the PCM terminal connections.
The terminals may have to be removed from the
connector in order to check them properly.
The problem is intermittent. This means that the
problem is not present at the time the system is being
checked. In this case, refer to the
Symptoms p o r t i o n o f
the manual and make a careful physical inspection of
all component and wiring associated with the affected
system.
There is a shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness.
S o l e n o i d s a n d r e l a y s a r e t u r n e d “ O N ” a n d “ O F F ” b y t h e
PCM using internal electronic switches called drivers.
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness will not
damage the PCM but will cause the solenoid or relay to
be inoperative.
Multiple PCM Information Sensor
DTCS Set
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors various
sensors to determine the engine operating conditions.
The PCM controls fuel delivery, spark advance,
transmission operation, and emission control device
operation based on the sensor inputs.The PCM provides a sensor ground to all of the sensors.
The PCM applies 5 volts through a pull-up resistor, and
determines the status of the following sensors by
monitoring the voltage present between the 5-volt supply
and the resistor:
The engine coolant temperature (ETC) sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
The transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
The PCM provides the following sensors with a 5-volt
reference and a sensor ground signal:
The exhaust gas recirculating (EGR) pintle position
sensor
The throttle position (TP) sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
The PCM monitors the separate feedback signals from
these sensors in order to determine their operating
status.
Diagnostic Aids
IMPORTANT:Be sure to inspect PCM and engine
grounds for being secure and clean.
A short to voltage in one of the sensor input circuits may
cause one or more of the following DTCs to be set:
P0108
P0113
P0118
P0123
P0560
P0712
P0406
IMPORTANT:If a sensor input circuit has been shorted
to voltage, ensure that the sensor is not damaged. A
damaged sensor will continue to indicate a high or low
voltage after the affected circuit has been repaired. If the
sensor has been damaged, replace it.
An open in the sensor ground circuit between the PCM
and the splice will cause one or more of the following
DTCs to be set:
P0108
P0113
P0118
P0123
P0712
P0406
A short to ground in the 5-volt reference A or B circuit will
cause one or more of the following DTCs to be set:
P0107
P0122
In the 5-volt reference circuit A, between the PCM and the
splice, will cause one or more of the following DTCs to be
set:
P0122
In the 5-volt reference circuit B, between the PCM and the
splice, will cause one or more of the following DTCs to be
set:
P0107
Check for the following conditions:
Page 4723 of 6000

6E–66
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Poor connection at PCM. Inspect the harness
connectors for backed-out terminals, improper mating,
broken locks, improperly formed or damage terminals,
and a poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness is not damaged, observe an
affected sensor’s displayed value on the Tech 2 with
the ignition “ON” and the engine “OFF” while you move
the connectors and the wiring harnesses related to the
following sensors:
IAT
ECT
TP
MAP
EGR
TFT
Multiple PCM Information Sensor DTCs Set
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Turn the ignition “OFF,” disconnect the PCM.
2. Turn the ignition “ON,” check the 5 volt reference A
circuit for the following conditions:
A poor connection at the PCM.
An open between the PCM connector and the
splice.
A short to ground.
A short to voltage.
Is there an open or short?
—Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3Repair the open or short.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
4Check the sensor ground circuit for the following
conditions:
A poor connection at the PCM or the affected
sensors.
An open between the PCM connector and the
affected sensors.
Is there an open or a poor connection?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair the open or the poor connection.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
6Measure the voltage between the EGR pintle position
sensor signal circuit at the PCM harness connector and
ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value?
0 VGo to Step 7Go to Step 12
7Measure the voltage between the MAP sensor signal
circuit at the PCM harness connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value?
0 VGo to Step 8Go to Step 15
8Measure the voltage between the TP sensor signal
circuit at the PCM harness connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value?
0 VGo to Step 9Go to Step 16
9Measure the voltage between the IAT sensor signal
circuit at the PCM harness connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value?
0 VGo to Step 10Go to Step 17
10Measure the voltage between the ECT sensor signal
circuit at the PCM harness connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value?
0 VGo to Step 11Go to Step 18
Page 4753 of 6000
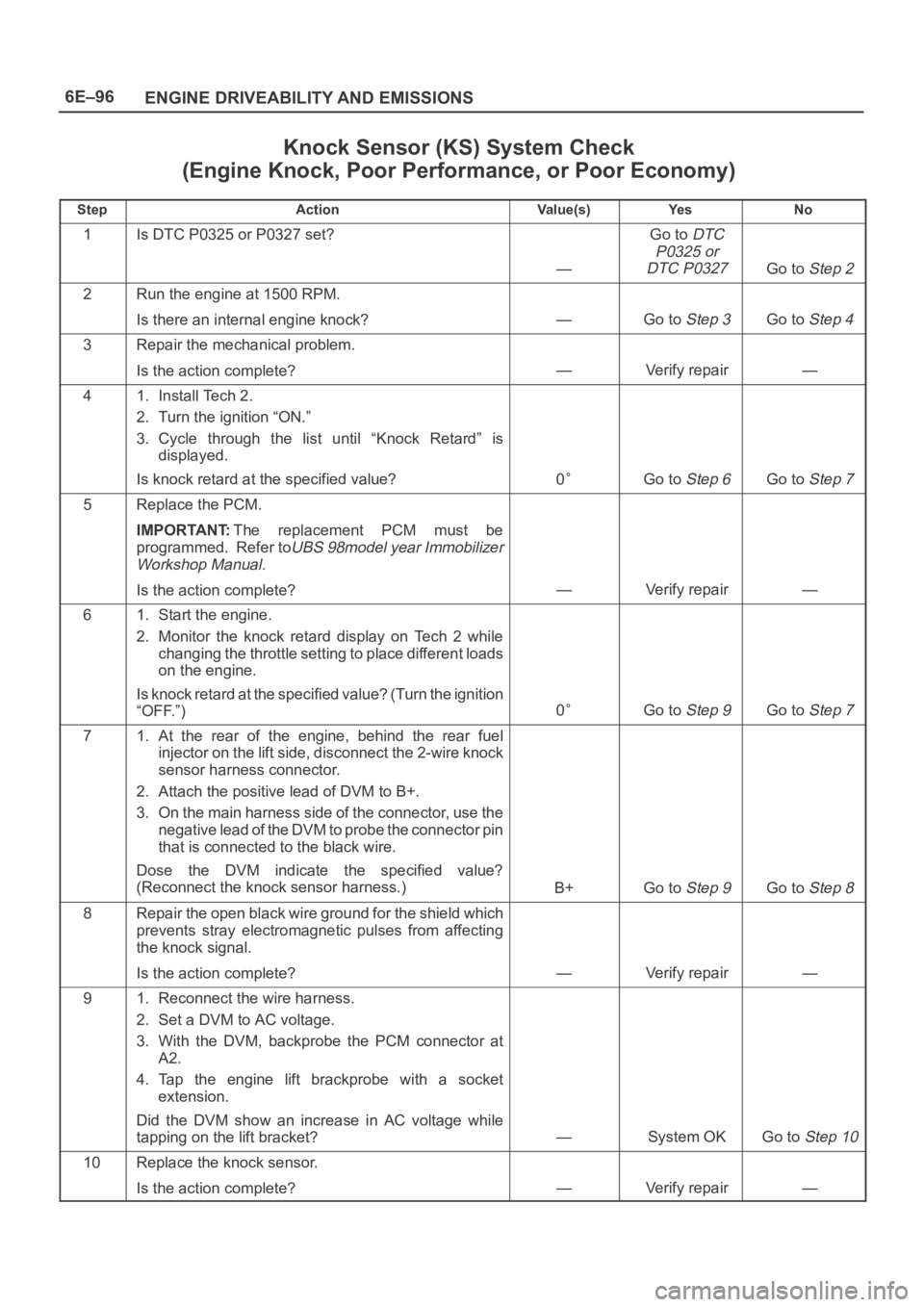
6E–96
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Knock Sensor (KS) System Check
(Engine Knock, Poor Performance, or Poor Economy)
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Is DTC P0325 or P0327 set?
—
Go to DTC
P0325 or
DTC P0327
Go to Step 2
2Run the engine at 1500 RPM.
Is there an internal engine knock?
—Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3Repair the mechanical problem.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
41. Install Tech 2.
2. Turn the ignition “ON.”
3. Cycle through the list until “Knock Retard” is
displayed.
Is knock retard at the specified value?
0Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
5Replace the PCM.
IMPORTANT:The replacement PCM must be
programmed. Refer to
UBS 98model year Immobilizer
Workshop Manual.
Is the action complete?—Verify repair—
61. Start the engine.
2. Monitor the knock retard display on Tech 2 while
changing the throttle setting to place different loads
on the engine.
Is knock retard at the specified value? (Turn the ignition
“OFF.”)
0Go to Step 9Go to Step 7
71. At the rear of the engine, behind the rear fuel
injector on the lift side, disconnect the 2-wire knock
sensor harness connector.
2. Attach the positive lead of DVM to B+.
3. On the m ain harness side of the connector, use th e
negative lead of the DVM to probe the connector pin
that is connected to the black wire.
Dose the DVM indicate the specified value?
(Reconnect the knock sensor harness.)
B+Go to Step 9Go to Step 8
8Repair the open black wire ground for the shield which
prevents stray electromagnetic pulses from affecting
the knock signal.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
91. Reconnect the wire harness.
2. Set a DVM to AC voltage.
3. With the DVM, backprobe the PCM connector at
A2.
4. Tap the engine lift brackprobe with a socket
extension.
Did the DVM show an increase in AC voltage while
tapping on the lift bracket?
—System OKGo to Step 10
10Replace the knock sensor.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4762 of 6000
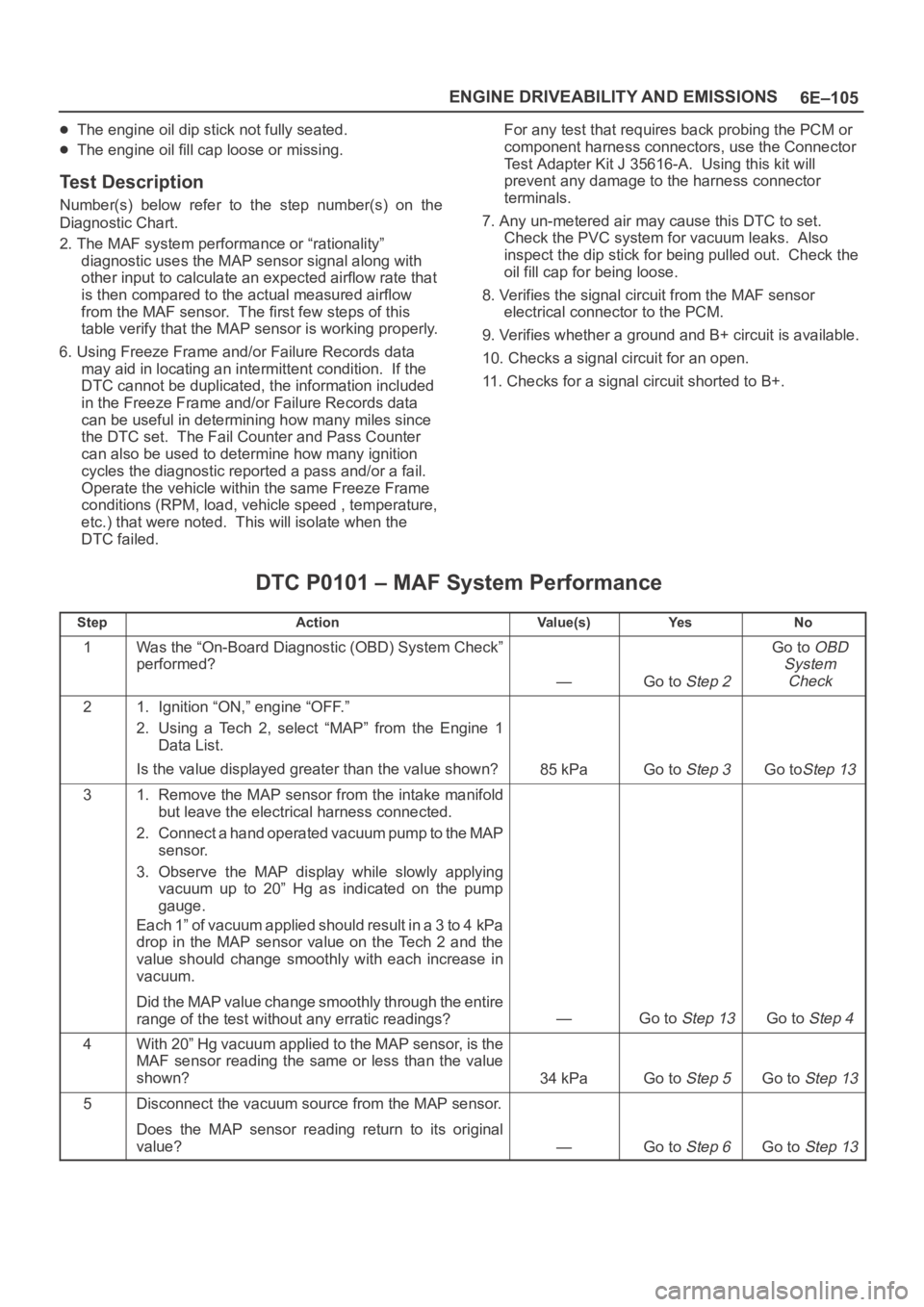
6E–105 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
The engine oil dip stick not fully seated.
The engine oil fill cap loose or missing.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. The MAF system performance or “rationality”
diagnostic uses the MAP sensor signal along with
other input to calculate an expected airflow rate that
is then compared to the actual measured airflow
from the MAF sensor. The first few steps of this
table verify that the MAP sensor is working properly.
6. Using Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data
may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If the
DTC cannot be duplicated, the information included
in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data
can be useful in determining how many miles since
the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter
can also be used to determine how many ignition
cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail.
Operate the vehicle within the same Freeze Frame
conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed , temperature,
etc.) that were noted. This will isolate when the
DTC failed.For any test that requires back probing the PCM or
component harness connectors, use the Connector
Test Adapter Kit J 35616-A. Using this kit will
prevent any damage to the harness connector
terminals.
7. Any un-metered air may cause this DTC to set.
Check the PVC system for vacuum leaks. Also
inspect the dip stick for being pulled out. Check the
oil fill cap for being loose.
8. Verifies the signal circuit from the MAF sensor
electrical connector to the PCM.
9. Verifies whether a ground and B+ circuit is available.
10. Checks a signal circuit for an open.
11. Checks for a signal circuit shorted to B+.
DTC P0101 – MAF System Performance
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. Using a Tech 2, select “MAP” from the Engine 1
Data List.
Is the value displayed greater than the value shown?
85 kPaGo to Step 3Go toStep 13
31. Remove the MAP sensor from the intake manifold
but leave the electrical harness connected.
2. Connect a hand operated vacuum pump to the MAP
sensor.
3. Observe the MAP display while slowly applying
vacuum up to 20” Hg as indicated on the pump
gauge.
Each 1” of vacuum applied should result in a 3 to 4 kPa
drop in the MAP sensor value on the Tech 2 and the
value should change smoothly with each increase in
vacuum.
Did the MAP value change smoothly through the entire
range of the test without any erratic readings?
—Go to Step 13Go to Step 4
4With 20” Hg vacuum applied to the MAP sensor, is the
MAF sensor reading the same or less than the value
shown?
34 kPaGo to Step 5Go to Step 13
5Disconnect the vacuum source from the MAP sensor.
Does the MAP sensor reading return to its original
value?
—Go to Step 6Go to Step 13
Page 4797 of 6000

6E–140
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
HO2S, causing the system to appear lean. Check for
exhaust leaks that may cause a false lean condition to
be indicated.
MAF sensor – The system can go lean if the MAF
sensor signal indicates an engine airfiow
measurement that is not correct. Disconnect the MAF
sensor to see if the lean condition is corrected. If so,
replace the MAF sensor.
Fuel contamination – Water, even in small amounts,
can be delivered to the fuel injectors. The water can
cause a lean exhaust to be indicated. Excessive
alcohol in the fuel can also cause this condition. Refer
to
Fuel System Diagnosis for the procedure to check
for fuel contamination.
If none of the above conditions are present, replace the
affected HO2S.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to step numbers on the diagnostic
chart.
3. DTC P0131 failing during operation may indicate a
condition described in the “Diagnostic Aids” above.
If the DTC P0131 test passes while the Failure
Records conditions are being duplicated, an
intermittent condition is indicated.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0131 –HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1 Sensor 1
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Install the Tech 2.
2. Run the engine at operating temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the parameters specified
under “Conditions for Setting the DTC” criteria
included in Diagnostic Support.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage.
Does the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remain below the
specified value?
22 mVGo to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF,” review and record Tech
2 Failure Records data and note parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” info for DTC
P0131 until the DTC P0131 test runs.
Note test result.
Does Tech 2 indicate DTC P0131 failed this ignition?
—Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Turn the ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the PCM.
3. Check the Bank 1 HO2S 1 high and low circuits for a
short to ground or a short to the heater ground
circuit.
Are the Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal circuits shorted to
ground?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair the Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal circuit.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
61. Turn the ignition “OFF,” HO2S 1 and PCM
disconnected.
2. Check for continuity between the high and low
signal circuits.
Was there continuity between the high and low circuits?
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Repair the short between the high and low circuits.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4803 of 6000

6E–146
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
indicates a signal line shorted to ground or signal lines
shorted together. Disconnect the HO2S and connect
a test light between the HO2S ignition feed and heater
ground circuits. If the test light does not light for 2
seconds when the ignition is turned on, repair the open
ignition feed or sensor ground circuit as necessary. If
the test light lights and the HO2S signal and low circuits
are OK, replace the HO2S.
Intermittent test – With the Ignition “ON,” monitor the
HO2S signal voltage while moving the wiring harness
and related connectors. If the fault is induced, the
HO2S signal voltage will change. This may help isolate
the location of the malfunction.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
3. If the DTC P0134 test passes while the Failure
Records conditions are being duplicated, an
intermittent conditions is indicated.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0134 –HO2S Circuit Insufficient Activity Bank 1 Sensor 1
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Install Tech 2.
2. Run the engine at operating temperature.
3. Operate the engine above 1200 RPM for two
minutes.
Does Tech 2 indicate Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage varying
outside the specified values?
400-500 mVGo to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF,” review and record Tech
2 Failure Records data and note parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” info for DTC
P0134 until the DTC P0134 test runs.
4. Note the test result.
Does Tech 2 indicate DTC P0134 failed this ignition?
—Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
4Check for a damaged harness.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 5
5Check for poor Bank 1 HO2S 1 high and low circuit
terminal connections at the Bank 1 HO2S 1 harness
connector and replace terminal(s) if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
6Check for poor Bank 1 HO2S 1 high and low circuit
terminal connections at the PCM and replace terminals
if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Ignition “OFF.”
2. With the PCM disconnected, check continuity of the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 high circuit.
3. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 high circuit measures over 5.0
ohms, repair open or poor connection as necessary.
Was a Bank 1 HO2S 1 high circuit problem found and
corrected?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
Page 4806 of 6000

6E–149 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
exhaust leaks that may cause a false lean condition to
be indicated.
MAF sensor –The system can go lean if the MAF
sensor signal indicates an engine airflow
measurement that is not correct. Disconnect the MAF
sensor to see if the lean condition is corrected. If so,
replace the MAF sensor.
Fuel contamination – Water, even in small amounts,
can be delivered to the fuel injectors. The water can
cause a lean exhaust to be indicated. Excessive
alcohol in the fuel can also cause this condition. Refer
to
Fuel System Diagnosis for the procedure to check
for fuel contamination.
If none of the above conditions are present, replace the
affected HO2S.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
3. DTC P0151 failing during operation may indicate a
condition described in the “Diagnostic Aids” above.
If the DTC P0151 test passes while the Failure
Records conditions are being duplicated, an
intermittent condition is indicate.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0151 – HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 2 Sensor 1
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Install Tech 2.
2. Run the engine at operating temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the parameters specified
under “Conditions for Setting the DTC” criteria
included in Diagnostic Support.
4. Using Tech 2, monitor Bank 2 HO2S 1 voltage.
Does the Bank 2 HO2S 1 voltage remain below the
specified value?
22 mVGo to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF,” review and record Tech
2 Failure Records data and note parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” info for DTC
P0151 until the DTC P0151 test runs.
4. Note test result.
Does Tech 2 indicate DTC P0151 failed this ignition?
—Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Turn ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the PCM.
3. Check the Bank 2 HO2S 1 high and low signal
circuits for a short to ground or a short to the heater
ground circuit.
Were Bank 2 HO2S 1 signal circuits shorted?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair the Bank 2 HO2S 1 signal circuit.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
61. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Leave the PCM and HO2S 1 disconnected.
3. Check for continuity between the high and low
signal circuits.
Was there continuity between the high and low circuits?
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Repair the short between the high and low circuits.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4827 of 6000

6E–170
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0201 Injector 1 Control Circuit
D06RW034
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) has six individual
injector driver circuits. Each controls an injector. When a
driver circuit is grounded by the PCM, the injector is
activated. The PCM monitors the current in each driver
circuit. The voltage on each driver is monitored to detect
a fault. If the voltage is not what the PCM expects to
m o n i t o r o n t h e c i r c u i t , a D T C i s s e t . T h i s D T C i s a l s o s e t i f
an injector driver is shorted to voltage or if there is an open
circuit.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The battery voltage is more than 9 volts.
The engine is turning, determined by 58X crankshaft
position input signal.
The injector voltage does not equal the ignition voltage
when the injector is commanded “OFF” or the injector
voltage does not equal 0 volts when the injector is
commanded “ON.”
The above conditions are met for 15 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0201 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An injector driver circuit that is open or shorted to voltage
will cause a DTC P0201 to set. It will also cause a misfire
due to an inoperative injector. A misfire DTC will also be
set indicating which cylinder is inoperative.
Long term and short term fuel trims that are excessively
high or low are a good indication that an injector is faulty.
Use Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure to check for faulty
injectors.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
3. This step determines if DTC P0201 is the result of a
hard failure or an intermittent condition.
5. A special injector test connector is provided so that
the injectors can be electrically tested without
removal of the manifold. On the Trooper, the
special 7-way gray connector is located at the front
of the charcoal canister. The test connector can be
identified by the blue connector lock which is
tethered to the wiring harness. If the light for
cylinder 1 is “ON” steady before cranking the engine
as well as while cranking the engine, then the
injector driver circuit is shorted to ground.