check engine OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1898 of 6000

6E–5 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–159. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–159. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1562
(Flash DTC 35) System Voltage Too Low
at Cranking 6E–160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–160. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–160. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1587
(Flash DTC 25) Brake SW Malfunction 6E–161. . . .
Circuit Description 6E–161. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–161. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–161. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–161. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1588
(Flash DTC 25) Brake SW Malfunction 6E–163. . . .
Circuit Description 6E–163. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–163. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–163. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–163. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0601
(Flash DTC 55) ECM Checksum Error 6E–165. . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–165. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–165. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–165. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0650
(Flash DTC 77) Check Engine Lam Circuit
Open/Short 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–166. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–166. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0654
(Flash DTC 27) Tachometer Circuit
Open/Short 6E–168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–168. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–168. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1655
(Flash DTC 17) Thermo Relay Circuit
Open/Short 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–170. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–170. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1657
(Flash DTC 76) ECM Main Relay Circuit
Open/Short 6E–172. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–172. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–172. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–172. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–172. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1589
(Flash DTC 47) Transmission SW Circuit
Open/Short 6E–174. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Description 6E–174. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When the DTC Sets 6E–174. . . . . . .
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC 6E–174. . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 6E–174. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 6E–176. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Default Matrix Table 6E–199. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On–Vehicle Service Camshaft Position
(CMP) Sensor 6E–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection Procedure 6E–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–202. . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–202. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–202. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E–203.
Removal Procedure 6E–203. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–203. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 6E–203. . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–203. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–204. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E–204.
Removal Procedure 6E–204. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–205. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Temperature (OT) Sensor 6E–205. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–205. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–206. . . . . . . . . .
Removal and Installation Procedure 6E–206. . . . . .
Engine Control Module (ECM) 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . .
Service Precaution 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Damage 6E–206. . .
Removal Procedure 6E–207. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EEPROM 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Check 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Throttle Position (ITP) Sensor 6E–208. . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–208. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Function Check 6E–209. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–209. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) 6E–210. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–210. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection Procedure 6E–210. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–210. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Air Cleaner/Air Filter 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accel Position (AP) Sensor 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removal Procedure 6E–211. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedure 6E–212. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Pedal Replacement 6E–212. . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1912 of 6000
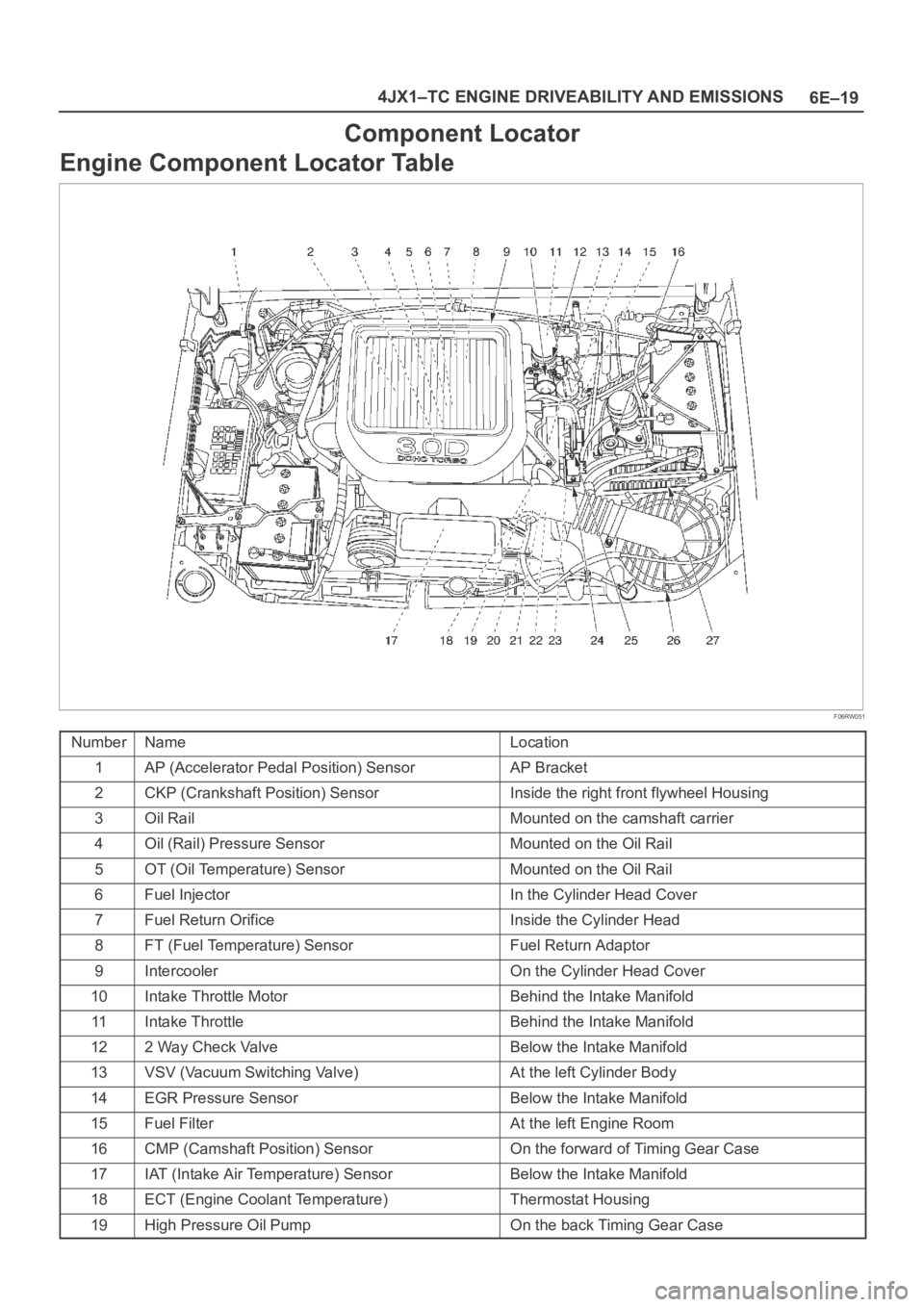
6E–19 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Component Locator
Engine Component Locator Table
F06RW051
NumberNameLocation
1AP (Accelerator Pedal Position) SensorAP Bracket
2CKP (Crankshaft Position) SensorInside the right front flywheel Housing
3Oil RailMounted on the camshaft carrier
4Oil (Rail) Pressure SensorMounted on the Oil Rail
5OT (Oil Temperature) SensorMounted on the Oil Rail
6Fuel InjectorIn the Cylinder Head Cover
7Fuel Return OrificeInside the Cylinder Head
8FT (Fuel Temperature) SensorFuel Return Adaptor
9IntercoolerOn the Cylinder Head Cover
10Intake Throttle MotorBehind the Intake Manifold
11Intake ThrottleBehind the Intake Manifold
122 Way Check ValveBelow the Intake Manifold
13VSV (Vacuum Switching Valve)At the left Cylinder Body
14EGR Pressure SensorBelow the Intake Manifold
15Fuel FilterAt the left Engine Room
16CMP (Camshaft Position) SensorOn the forward of Timing Gear Case
17IAT (Intake Air Temperature) SensorBelow the Intake Manifold
18ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature)Thermostat Housing
19High Pressure Oil PumpOn the back Timing Gear Case
Page 1917 of 6000

6E–24
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnosis
Strategy-Based Diagnostics
Strategy-Based Diagnostics
The strategy-based diagnostic is a uniform approach to
repair all Electrical/Electronic (E/E) systems. The
diagnostic flow can always be used to resolve an E/E
system problem and is a starting point when repairs are
necessary. The following steps will instruct the technician
how to proceed with a diagnosis:
1. Verify the customer complaint.
To verify the customer complaint, the technician
should know the normal operation of the system.
2. Perform preliminary checks.
Conduct a thorough visual inspection.
Review the service history.
Detect unusual sounds or odors.
Gather diagnostic trouble code information to
achieve an effective repair.
3. Check bulletins and other service information.
This includes videos, newsletters, etc.
4. Refer to service information (manual) system
check(s).
“System checks” contain information on a system
that may not be supported by one or more DTCs.
System checks verify proper operation of the
system. This will lead the technician in an
organized approach to diagnostics.
5. Refer to service diagnostics.
DTC Stored
Follow the designated DTC chart exactly to make an
effective repair.
No DTC
Select the symptom from the symptom tables. Follow the
diagnostic paths or suggestions to complete the repair.
You may refer to the applicable component/system check
in the system checks.
No Matching Symptom
1. Analyze the complaint.
2. Develop a plan for diagnostics.
3. Utilize the wiring diagrams and the theory of
operation.
Call technical assistance for similar cases where repair
history may be available. Combine technician knowledge
with efficient use of the available service information.
Intermittents
Conditions that are not always present are called
intermittents. To resolve intermittents, perform the
following steps:
1. Observe history DTCs, DTC modes, and freezeframe
data.2. Evaluate the symptoms and the conditions described
by the customer.
3. Use a check sheet or other method to identify the
circuit or electrical system component.
4. Follow the suggestions for intermittent diagnosis
found in the service documentation.
Most scan tools, such as the Tech 2 and the DVM, have
data-capturing capabilities that can assist in detecting
intermittents.
No Trouble Found
This condition exists when the vehicle is found to operate
normally. The condition described by the customer may
be normal. Verify the customer complaint against another
vehicle that is operating normally. The condition may be
intermittent. Verify the complaint under the conditions
described by the customer before releasing the vehicle.
1. Re-examine the complaint.
When the complaint cannot be successfully found or
isolated, a re-evaluation is necessary. The complaint
should be re-verified and could be intermittent as
defined in
Intermittents, or could be normal.
2. Repair and verify.
After isolating the cause, the repairs should be made.
Validate for proper operation and verify that the
symptom has been corrected. This may involve road
testing or other methods to verify that the complaint
has been resolved under the following conditions:
Conditions noted by the customer.
If a DTC was diagnosed, verify a repair by
duplicating conditions present when the DTC was
set as noted in the Failure Records or Freeze
Frame data.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of the vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with OBD system
diagnostics. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
IMPORTANT:Follow the steps below when you verify
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
1. Review and record the Failure Records and the
Freeze Frame data for the DTC which has been
diagnosed (Freeze Frame data will only be stored for
the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) has been requested).
2. Clear the DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the
Failure Records and Freeze Frame data.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Page 1918 of 6000

6E–25 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Service Information
Serviceability Issues
Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Accordingly, if commercially sold sensor
or switch is installed, it makes a wrong diagnosis and turn
on the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp).
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the MIL (“Check
Engine” lamp).
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the MIL
(“Check Engine” lamp) to turn on if the vehicle is not
maintained properly. Restricted oil filters, fuel filters, and
crankcase deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper
oil viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics, vehicle
maintenance schedules must be more closely followed.
Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
ECM detects a fault on a related system or component.
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any diagnostic
procedure or diagnosing the cause of an emission test
failure. This can often lead to repairing a problem without
further steps. Use the following guidelines when
performing a visual/physical inspection:
Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts,
disconnects, and correct routing.
Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other
components.
Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper
connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched wires,
contact with sharp edges or contact with hot exhaust
manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain when
performing diagnostic procedures could result in an
incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to effec-
tively use this section of the Service Manual.
Serial Data Communications
Class II Serial Data Communications
This vehicle utilizes the “Class II” communication system.
Each bit of information can have one of two lengths: longor short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by
transmitting and receiving multiple signals over a single
wire. The messages carried on Class II data streams are
also prioritized. If two messages attempt to establish
communications on the data line at the same time, only
the message with higher priority will continue. The device
with the lower priority message must wait.
On this vehicle the Tech 2 displays the actual values for
vehicle parameters. It will not be necessary to perform
any conversions from coded values to actual values.
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
On-Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which is
a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive. When
a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
The diagnostic test has been completed since the last
ignition cycle.
The diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not
currently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
The diagnostic test has been completed since the last
ignition cycle.
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is currently
active.
The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
Comprehensive Component Monitor
Diagnostic Operation
Comprehensive component monitoring diagnostics are
required to operate engine properly.
Input Components:
Input components are monitored for circuit continuity and
out-of-range values. This includes rationality checking.
Rationality checking refers to indicating a fault when the
signal from a sensor does not seem reasonable. Accel
Position (AP) sensor that indicates high throttle position
at low engine loads or MAP voltage. Input components
may include, but are not limited to the following sensors:
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
Intake throttle Position (ITP) Sensor
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Manifold absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Accel Position Sensor
Fuel Temp Sensor
Rail Pressure Sensor
Oil Temp Sensor
EGR Pressure Sensor
Vehicle Speed Sensor
Page 1919 of 6000

6E–26
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Output Components:
Output components are diagnosed for proper response to
control module commands. Components where
functional monitoring is not feasible will be monitored for
circuit continuity and out-of-range values if applicable.
Output components to be monitored include, but are not
limited to, the following circuit:
EGR VSV
EGR EVRV
Electronic Transmission controls
Injector
Intake throttle
Glow plug
MIL control
Refer to ECM and Sensors in General Descriptions.
Passive and Active Diagnostic Tests
A passive test is a diagnostic test which simply monitors a
vehicle system or component. Conversely, an active test,
actually takes some sort of action when performing
diagnostic functions, often in response to a failed passive
test.
Intrusive Diagnostic Tests
This is any on-board test run by the Diagnostic
Management System which may have an effect on
vehicle performance or emission levels.
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means that engine at temperature must
reach a minimum of 70
C (160F) and rise at least 22C
(40
F) over the course of a trip.
Freeze Frame
Freeze Frame is an element of the Diagnostic
Management System which stores various vehicle
information at the moment an emissions-related fault is
stored in memory and when the MIL is commanded on.
These data can help to identify the cause of a fault. Refer
to
Storing And Erasing Freeze Fame Data for more
detailed information.
Failure Records
Failure Records data is an enhancement of the OBD
Freeze Frame feature. Failure Records store the same
vehicle information as does Freeze Frame, but it will store
that information for any fault which is stored in on-board
memory, while Freeze Frame stores information only for
emission-related faults that command the MIL on.
Common OBD Terms
Diagnostic
When used as a noun, the word diagnostic refers to any
on-board test run by the vehicle’s Diagnostic
Management System. A diagnostic is simply a test run on
a system or component to determine if the system or
component is operating according to specification. There
are many diagnostics, shown in the following list:
EGR
engine speed
vehicle speed
ECT
MAP
VSV
IAT
ITP
AP
FT (Fuel Temp)
RP (Rail Pressure)
OT (Oil Temp)
EGR EVRV
Idle SW
Brake SW
The Diagnostic Executive
The Diagnostic Executive is a unique segment of
software which is designed to coordinate and prioritize
the diagnostic procedures as well as define the protocol
for recording and displaying their results. The main
responsibilities of the Diagnostic Executive are listed as
follows:
Commanding the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) on and
off
DTC logging and clearing
Freeze Frame data for the first emission related DTC
recorded
Current status information on each diagnostic
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are designed
to locate a faulty circuit or component through a process
of logical decisions. The charts are prepared with the
requirement that the vehicle functioned correctly at the
time of assembly and that there are not multiple faults
present.
There is a continuous self-diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complemented by
the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual. The
language of communicating the source of the malfunction
is a system of diagnostic trouble codes. When a
malfunction is detected by the control module, a
diagnostic trouble code is set and the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) (“Check Engine” lamp) is
illuminated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same as
the MIL you are already familiar with “Check Engine”
lamp.
Basically, the MIL is turned on when the ECM detects a
DTC that will impact the vehicle emissions.
When the MIL remains “ON” while the engine is
running, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, a Powertrain
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check must be
performed. The procedures for these checks are
given in On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check.
These checks will expose faults which may not be
detected if other diagnostics are performed first.
DTC Types
Characteristic of Code
Page 1920 of 6000

6E–27 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Non-Emissions related
Dose not request illumination of any lamp
Stores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
Stores Fail Record when test fails
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic test
fails
Storing and Erasing Freeze Frame Data and Failure
Records
The data captured is called Freeze Frame data. The
Freeze Frame data is very similar to a single record of
operating conditions. Whenever the MIL is illuminated,
the corresponding record of operating conditions is
recorded to the Freeze Frame buffer.
Data from these faults take precedence over data
associated with any other fault. The Freeze Frame data
will not be erased unless the associated history DTC is
cleared.
Each time a diagnostic test reports a failure, the current
engine operating conditions are recorded in the
Failure
Records
buffer. A subsequent failure will update the
recorded operating conditions. The following operating
conditions for the diagnostic test which failed
typically
include the following parameters:
Engine Speed
Engine Load
Engine Coolant Temperature
Vehicle Speed
Intake Throttle Position
MAP
Injector Base Pulse Width
Loop Status
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communication with the contorl module
is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is located at behind
the lower front instrument panel. The DLC is used to
connect to a Tech 2. Some common uses of the Tech 2
are listed below:
Identifying stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Clearing DTCs.
Performing out put control tests.
Reading serial data.
060RW046
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more comprehensive
for vehicles with OBD system diagnostic. Following a
repair, the technician should perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records and/or Freeze
Frame data for the DTC which has been diagnosed.
2. Clear DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail
Records and/or Freeze Frame data.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps are very important in verifying
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
Reading Flash Diagnostic Trouble Codes
The provision for communicating with the Engine Control
Module (ECM) is the Data Link Connector (DLC). The
DLC is located in the front console box. It is used in the
assembly plant to receive information in checking that the
engine is operating properly before it leaves the plant.
The diagnostic trouble code(s) (DTCs) stored in the
ECM’s memory can be read either through a hand-held
diagnostic scanner plugged into the DLC or by counting
the number of flashes of the “Check Engine” Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic test terminal of
the DLC is grounded. The DLC terminal “6” (diagnostic
request) is pulled “Low” (grounded) by jumpering to DLC
terminal “4”, which is a ground wire.
This will signal the ECM that you want to “flash” DTC(s), if
any are present. Once terminals “4” and “6” have been
connected, the ignition switch must be moved to the “ON”
position, with the engine not running.
The “Check Engine”MIL will indicate a DTC three times if
a DTC is present. If more than one DTC has been stored
Page 1924 of 6000

6E–31 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
060RW120
Menu
The following table shows, which functions are used
the available equipment versions.
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Codes
F0: Read DTC Info Ordered By Priority
F1: Read DTC Info As Stored By ECU
F2: Clear DTC Information
F3: Freeze Frame / Failure Records
F1: Data Display
F2: Snapshot
F3: Actuator Tests
F0: Checklight
F1: Glow Time Lamp
F2: EGR Switching Valve
F3: Exhaust Switching Valve 1
F4: Exhaust Switching Valve 2
F4: Miscellaneous Tests
F0: Throttle Motor Control
F1: Rail Pressure Control
F2: EGR Regulating Valve Control
F3: Rail Pressure Control Valve
F4: Injector Balance Test
F5: Programming
F0: Injector Calibration
(F1: Rail Pressure Calibration)
Page 1925 of 6000

6E–32
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DTC Modes
There are three options available in the Tech 2 DTC mode
to display the enhanced information available. A
description of the new modes, DTC Info, follows. After
selecting DTC, the following menu appears:
DTC Info
Clear Info
Read DTC Info Ordered By Priority
The following is a brief description of each of the sub
menus in DTC Info. The order in which they appear here is
alphabetical and not necessarily the way they will appear
on the Tech 2.
DTC Information Mode
Use the DTC info mode to search for a specific type of
stored DTC information.The service manual may instruct
the technician to test for DTCs in a certain manner.
Always follow published service procedures.
Fail This Ignition
This selection will display all DTCs that have failed during
the present ignition cycle.
History
This selection will display only D T C s t h a t a r e s t o r e d i n t h e
ECM’s history memory. It will not display Type B DTCs
that have not requested the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp). It
will display all type A and B DTCs that have requested the
MIL and have failed within the last 40 warm-up cycles. In
addition, it will display all type C and type D DTCs that
have failed within the last 40 warm-up cycles.
MIL SVC or Message Requested
This selection will display only DTCs that are requesting
the MIL. Type C and type D DTCs cannot be displayed
using this option. This selection will report type B DTCs
only after the MIL has been requested.
Test Failed Since Code Cleared
This selection will display all active and history DTCs that
have reported a test failure since the last time DTCs were
cleared.
Injector Test
This test is conducted to make it sure that appropriate
electric signals are being sent to injectors Nos. 1 – 4.
Tech–2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1. Connect Tech–2 to the vehicle DLC.
2. Set Ignition Switch to the “ON” position.
3. Select Control Test.
4. Select Injector Test.
5. Send instructions to each injector(Switch on), making
sure of injector working noise.
NOTE: If injector working noise (Clink) can hardly be
confirmed, remove the engine head cover noise
insulation.
Refer to Section 6A.6. In the injector whose working noise has been
confirmed, its electric circuit can be regarded as
normal.
As for the injector whose working noise has not been
confirmed, its electric circuit or the injector proper is
faulty.
EGR Valve Test
This test is conducted to check EGR valve for its working.
This test needs Tech–2.
Test Procedure
1. Connect Tech–2 to vehicle DLC.
2. Switch on the engine.
3. Select “DIAGNOSIS” from the main menu.
4. Select Miscellaneous Test.
5. Select EGR Valve.
6. Instruct EGR Valve to check a data list.
7. If change in the data list shows a normal valve, the
working of EGR Valve can be judged to be normal.
Rail Pressure Control Valve Test
This test is conducted to check RPC valve for its working.
This test needs Tech–2.
Test Procedure
1. Connect Tech–2 to vehicle DLC.
2. Switch on the engine.
3. Select “DIAGNOSIS” from the main menu.
4. Select Miscellaneous Test.
5. Select Rail Pressure Control Valve.
6. Instruct RPC Valve to check a data list.
7. If change in the data list shows a normal valve, the
working of RPC Valve can be judged to be normal.
Injector Balance Test
This test is conducted to make it sure that appropriate
electric signals are being sent to injectors Nos. 1-4, when
the engine is idling.
This test needs Tech–2.
Test Procedure
1. Connect Tech–2 to vehicle DLC.
2. The engine is running at idling condition.
3. Select “DIAGNOSIS” from the main menu.
4. Select Miscellaneous Test.
5. Select the injector Balance Test.
6. Send instructions to each injector(Switch On),
making sure change of the engine vibration.
7. In the injector whose change of the vibration has been
confirmed, it’s electric circuit can be regarded as
normal.
Data Programming in Case of ECM Change
When replacing ECM, it is necessary to confirm and
record the group sign of injector beforehand. For this
confirmation.
Page 1928 of 6000

6E–35 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Guid to the System
Fuel Injection system is an HEUI (Hydraulically
Actuated, Electronically Controlled, Unit, Injector)
type. In this type of injector system, the oil
pressurized by means of High Pressure Oil Pump
(16) is fed through Rail Pressure Control Valve (10)
and Oil Rail (7) to Injector (29) from which fuel is
injected under this oil pressure.
For diagnosis, therefore, the Rail Pressure as well as
the Electric Circuit must be inspected.
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
A Group
060RW135
Page 1930 of 6000
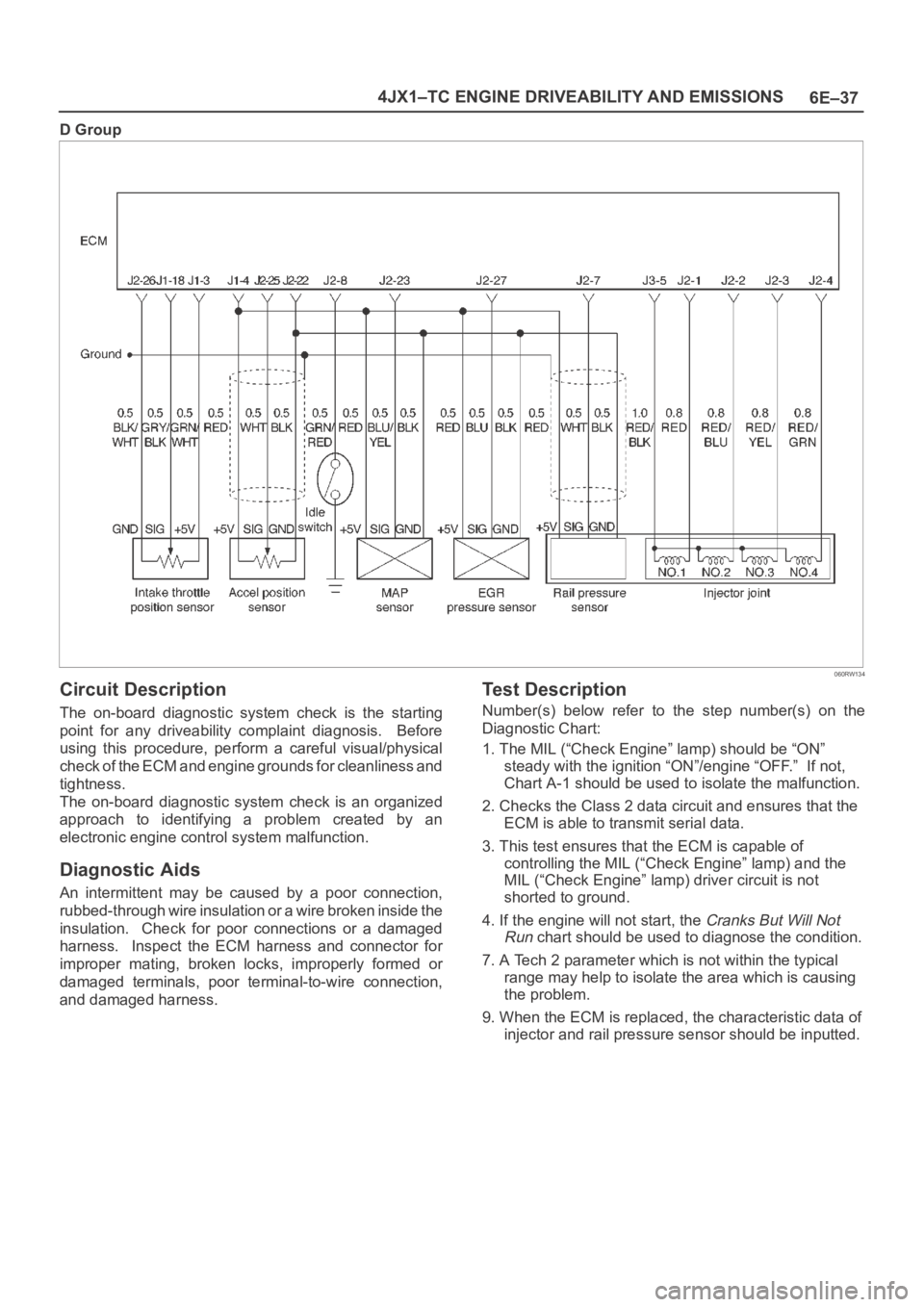
6E–37 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
D Group
060RW134
Circuit Description
The on-board diagnostic system check is the starting
point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. Before
using this procedure, perform a careful visual/physical
check of the ECM and engine grounds for cleanliness and
tightness.
The on-board diagnostic system check is an organized
approach to identifying a problem created by an
electronic engine control system malfunction.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for poor connections or a damaged
harness. Inspect the ECM harness and connector for
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection,
and damaged harness.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1. The MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) should be “ON”
steady with the ignition “ON”/engine “OFF.” If not,
Chart A-1 should be used to isolate the malfunction.
2. Checks the Class 2 data circuit and ensures that the
ECM is able to transmit serial data.
3. This test ensures that the ECM is capable of
controlling the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) and the
MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) driver circuit is not
shorted to ground.
4. If the engine will not start, the
Cranks But Will Not
Run
chart should be used to diagnose the condition.
7. A Tech 2 parameter which is not within the typical
range may help to isolate the area which is causing
the problem.
9. When the ECM is replaced, the characteristic data of
injector and rail pressure sensor should be inputted.