check engine OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 4697 of 6000

6E–40
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Common OBD Terms
Diagnostic
When used as a noun, the word diagnostic refers to any
on-board test run by the vehicle’s Diagnostic
Management System. A diagnostic is simply a test run on
a system or component to determine if the system or
component is operating according to specification. There
are many diagnostics, shown in the following list:
Oxygen sensors
Oxygen sensor heaters
EGR
Catalyst monitoring
Enable Criteria
The term “enable criteria” is engineering language for the
conditions necessary for a given diagnostic test to run.
Each diagnostic has a specific list of conditions which
must be met before the diagnostic will run. “Enable
criteria” is another way of saying “conditions required”.
The enable criteria for each diagnostic is listed on the first
page of the DTC description under the heading
“Conditions for Setting the DTC”. Enable criteria varies
with each diagnostic, and typically includes, but is not
limited to the following items:
engine speed
vehicle speed
ECT
MAF/MAP
barometric pressure
IAT
TP
fuel trim
TCC enabled
A/C on
Tr i p
Technically, a trip is a key on-run-key off cycle in which all
the enable criteria for a given diagnostic are met, allowing
the diagnostic to run. Unfortunately, this concept is not
quite that simple. A trip is official when all the enable
criteria for a given diagnostic are met. But because the
enable criteria vary from one diagnostic to another, the
definition of trip varies as well. Some diagnostic are run
when the vehicle is at operating temperature, some when
the vehicle first start up; some require that the vehicle be
cruising at a steady highway speed, some run only when
the vehicle is idle; some diagnostics function with the
TCC disables. Some run only immediately following a
cold engine start-up.
A trip then, is defined as a key on-run-key off cycle in
which the vehicle was operated in such a way as to satisfy
the enables criteria for a given diagnostic, and this
diagnostic will consider this cycle to be one trip. However,
another diagnostic with a different set of enable criteria
(which were not met) during this driving event, would not
consider it a trip. No trip will occur for that particular
diagnostic until the vehicle is driven in such a way as to
meet all the enable criteria.
The Diagnostic Executive
The Diagnostic Executive is a unique segment of
software which is designed to coordinate and prioritize
the diagnostic procedures as well as define the protocol
for recording and displaying their results. The main
responsibilities of the Diagnostic Executive are listed as
following:
Commanding the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) on and
off
DTC logging and clearing
Freeze Frame data for the first emission related DTC
recorded
Non-emission related Service Lamp (future)
Operating conditions Failure Records buffer, (the
number of records will vary)
Current status information on each diagnostic
The Diagnostic Executive records DTCs and turns on the
MIL when emission-related faults occur. It can also turn
off the MIL if the conditions cease which caused the DTC
to set.
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are designed
to locate a faulty circuit or component through a process
of logical decisions. The charts are prepared with the
requirement that the vehicle functioned correctly at the
time of assembly and that there are not multiple faults
present.
There is a continuous self-diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complemented by
the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual. The
language of communicating the source of the malfunction
is a system of diagnostic trouble codes. When a
malfunction is detected by the control module, a
diagnostic trouble code is set and the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) (“Check Engine” lamp) is
illuminated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same as
the MIL you are already familiar with (“Check Engine”
lamp). However, OBD requires that the it illuminate under
a strict set of guide lines.
Basically, the MIL is turned on when the PCM detects a
DTC that will impact the vehicle emissions.
The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic Executive.
The MIL will be turned on if an emissions-related
diagnostic test indicates a malfunction has occurred. It
will stay on until the system or component passes the
same test, for three consecutive trips, with no
emissionsrelated faults.
Extinguishing the MIL
When the MIL is on, the Diagnostic Executive will turn off
the MIL after
three consecutive trips that a “test passed”
has been reported for the diagnostic test that originally
caused the MIL to illuminate.
Although the MIL has been turned off, the DTC will remain
in the PCM memory (both Freeze Frame and Failure
Records) until
forty(40) warm-up cycles after no faults
have been completed.
Page 4698 of 6000

6E–41 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
If the MIL was set by either a fuel trim or misfire-related
DTC, additional requirements must be met. In addition to
the requirements stated in the previous paragraph, these
requirements are as follows:
The diagnostic tests that are passed must occur with
375 RPM of the RPM data stored at the time the last
test failed.
Plus or minus ten (10) percent of the engine load that
was stored at the time the last failed.
Similar engine temperature conditions (warmed up or
warming up ) as those stored at the time the last test
failed.
Meeting these requirements ensures that the fault which
turned on the MIL has been corrected.
The MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) is on the instrument
panel and has the following function:
It informs the driver that a fault affects vehicle emission
levels has occurred and that the vehicle should be
taken for service as soon as possible.
As a bulb and system check, the MIL will come “ON”
with the key “ON” and the engine not running. When
the engine is started, the MIL will turn “OFF.”
When the MIL remains “ON” while the engine is
running, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, a Powertrain
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD ll) System Check must be
performed. The procedures for these checks are given
in On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check. These
checks will expose faults which may not be detected if
other diagnostics are performed first.
DTC Types
Each DTC is directly related to a diagnostic test. The
Diagnostic Management System sets DTC based on the
failure of the tests during a trip or trips. Certain tests must
fail two (2) consecutive trips before the DTC is set. The
following are the four (4) types of DTCs and the
characteristics of those codes:
Ty p e A
Emissions related
Requests illumination of the MIL of the first trip with a
fail
Stores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
Stores a Freeze Frame (if empty)
Stores a Fail Record
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
Ty p e B
Emissions related
“Armed” after one (1) trip with a fail
“Disarmed” after one (1) trip with a pass
Requests illumination of the MIL on the second
consecutive trip
with a fail
Stores a History DTC on the second consecutive trip
with a fail (The DTC will be armed after the first fail)
Stores a Freeze Frame on the second consecutive
trip with a fail (if empty)
Stores a Fail Record when the first test fails (not
dependent on
consecutive trip fails)
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
Type C (if the vehicle is so equipped)
Non-Emissions related
Requests illumination of the Service Lamp or the
service message on the Drive Information Center
(DIC) on the
first trip with a fail
Stores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
Does not store a Freeze Frame
Stores Fail Record when test fails
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
Type D (Ty p e D non-emissions related are not utilized
on certain vehicle applications).
Non-Emissions related
Dose not request illumination of any lamp
Stores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
Does not store a Freeze Frame
Stores Fail Record when test fails
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
IMPORTANT:Only four Fail Records can be stored.
Each Fail Record is for a different DTC. It is possible that
there will not be Fail Records for every DTC if multiple
DTCs are set.
Storing and Erasing Freeze Frame Data and Failure
Records
The data captured is called Freeze Frame data. The
Freeze Frame data is very similar to a single record of
operating conditions. Whenever the MIL is illuminated,
the corresponding record of operating conditions is
recorded to the Freeze Frame buffer.
Data from these faults take precedence over data
associated with any other fault. The Freeze Frame data
will not be erased unless the associated history DTC is
cleared.
Each time a diagnostic test reports a failure, the current
engine operating conditions are recorded in the
Failure
Records
buffer. A subsequent failure will update the
recorded operating conditions. The following operating
conditions for the diagnostic test which failed
typically
include the following parameters:
Air Fuel Ratio
Air Flow Rate
Fuel Trim
Engine Speed
Engine Load
Engine Coolant Temperature
Vehicle Speed
TP Angle
MAP/BARO
Injector Base Pulse Width
Loop Status
Page 4699 of 6000

6E–42
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp
In the case of an “intermittent” fault, the MIL (“Check
Engine” lamp) may illuminate and then (after three trips)
go “OFF”. However, the corresponding diagnostic trouble
code will be stored in the memory. When unexpected
diagnostic trouble codes appear, check for an intermittent
malfunction.
A diagnostic trouble code may reset. Consult the
“Diagnostic Aids” associated with the diagnostic trouble
code. A physical inspection of the applicable sub-system
most often will resolve the problem.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communication with the control module
is the Data Link Connector (DLC). The DLC is used to
connect to Tech 2. Some common uses of Tech 2 are
listed below:
Identifying stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Clearing DTCs.
Performing output control tests.
Reading serial data.
TS24064
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more comprehensive
for vehicles with OBD system diagnostic. Following a
repair, the technician should perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records and/or Freeze
Frame data for the DTC which has been diagnosed
(Freeze Frame data will only be stored for an A or B
type diagnostic and only if the MIL has been
requested).
2. Clear DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail
Records and/or Freeze Frame data.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps are very important in verifying
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using
A Tech 2
The procedure for reading diagnostic trouble code(s) is to
used a diagnostic Tech 2. When reading DTC(s), follow
instructions supplied by Tech 2 manufacturer.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
IMPORTANT:Do not clear DTCs unless directed to do
so by the service information provided for each diagnostic
procedure. When DTCs are cleared, the Freeze Frame
and Failure Record data which may help diagnose an
intermittent fault will also be erased from memory.
If the fault that caused the DTC to be stored into memory
has been corrected, the Diagnostic Executive will begin to
count the “warm-up” cycles with no further faults
detected, the DTC will automatically be cleared from the
PCM memory.
To clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), use the
diagnostic Tech 2 “clear DTCs”. When clearing DTCs
follow instructions supplied by the tool manufacturer.
When Tech 2 is not available, DTCs can also be cleared
by disconnecting
one of the following sources for at least
thirty (30) seconds.
NOTE: To prevent system damage, the ignition key must
be “OFF” when disconnecting or reconnecting battery
power.
The power source to the control module. Examples:
fuse, pigtail at battery PCM connectors etc.
The negative battery cable. (Disconnecting the
negative battery cable will result in the loss of other
on-board memory data, such as preset radio tuning).
Page 4703 of 6000

6E–46
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
060RW223
The following is a brief description of each of the sub
menus in DTC Info and Specific DTC. The order in which
they appear here is alphabetical and not necessarily the
way they will appear on the Tech 2.
DTC Information Mode
Use the DTC info mode to search for a specific type of
stored DTC information. There are seven choices. The
service manual may instruct the technician to test for
DTCs in a certain manner. Always follow published
service procedures.
To get a complete description of any status, press the
“Enter” key before pressing the desired F-key. For
example, pressing “Enter” then an F-key will display a
definition of the abbreviated Tech 2 status.
060RW221
DTC Status
This selection will display any DTCs that have not run
during the current ignition cycle or have reported a test
failure during this ignition up to a maximum of 33 DTCs.
DTC tests which run and pass will cause that DTC
number to be removed from Tech 2 screen.Fail This Ignition
This selection will display all DTCs that have failed during
the present ignition cycle.
History
This selection will display only DTCs that are stored in the
PCM’s history memory. It will not display Type B DTCs
that have not requested the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp). It
will display all type A and B DTCs that have requested the
MIL and have failed within the last 40 warm-up cycles. In
addition, it will display all type C and type D DTCs that
have failed within the last 40 warm-up cycles.
Last Test Failed
This selection will display only DTCs that have failed the
last time the test ran. The last test may have run during a
previous ignition cycle if a type A or type B DTC is
displayed. For type C and type D DTCs, the last failure
must have occurred during the current ignition cycle to
appear as Last Test Fail.
MILSVC or Message Requested
This selection will display only DTCs that are requesting
the MIL. Type C and type D DTCs cannot be displayed
using this option. This selection will report type B DTCs
only after the MIL has been requested.
Not Run Since Code Clear
This option will display up to 33 DTCs that have not run
since the DTCs were last cleared. Since any displayed
DTCs have not run, their condition (passing or failing) is
unknown.
Test Failed Since Code Clear
This selection will display all active and history DTCs that
have reported a test failure since the last time DTCs were
cleared. DTCs that last failed more than 40 warm-up
cycles before this option is selected will not be displayed.
Injector Balance Test
This test is conducted to make it sure that appropriate
electric signals are being sent to injectors Nos. 1–6.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1. Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2. Run the Engine at idle.
Page 4704 of 6000

6E–47 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
3. Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4. Select F7: Injector Balance Test in the Miscellaneous
Te s t .
060RX006
5. Select injector number and push “injector off” of soft
key.
060RW230
6. Make sure of engine speed change.
7. In the engine speed whose change has been
confirmed, the injector electric circuit can be regard
as normal.
As for the engine speed whose change has not been
confirmed, the injector electric circuit or the injector
proper is faulty.
EGR Control Test
This test is conducted check EGR valve for its working.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1. Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2. Run the Engine at idle.
3. Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
Page 4705 of 6000

6E–48
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
4. Select F5: EGR Control Test in the Miscellaneous
Te s t .
060RX008
5. Instruct EGR Valve to check a data list.
060RW234
6. If change in the data list shows a normal valve.
Idle Air Control System Test
This test is conducted check IAC system for its working.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1. Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2. Run the Engine at idle.3. Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4. Select F3: IAC System Test in the Miscellaneous
Te s t .
060RX007
Page 4706 of 6000

6E–49 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
5. Select F1: IAC Control Test.
060RW235
6. Instruct IAC system to check a data list.
060RW233
F0: RPM Control
060RW232
F2: IAC Reset
060RW231
7. If change in the data list shows a normal IAC.
Page 4708 of 6000

6E–51 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
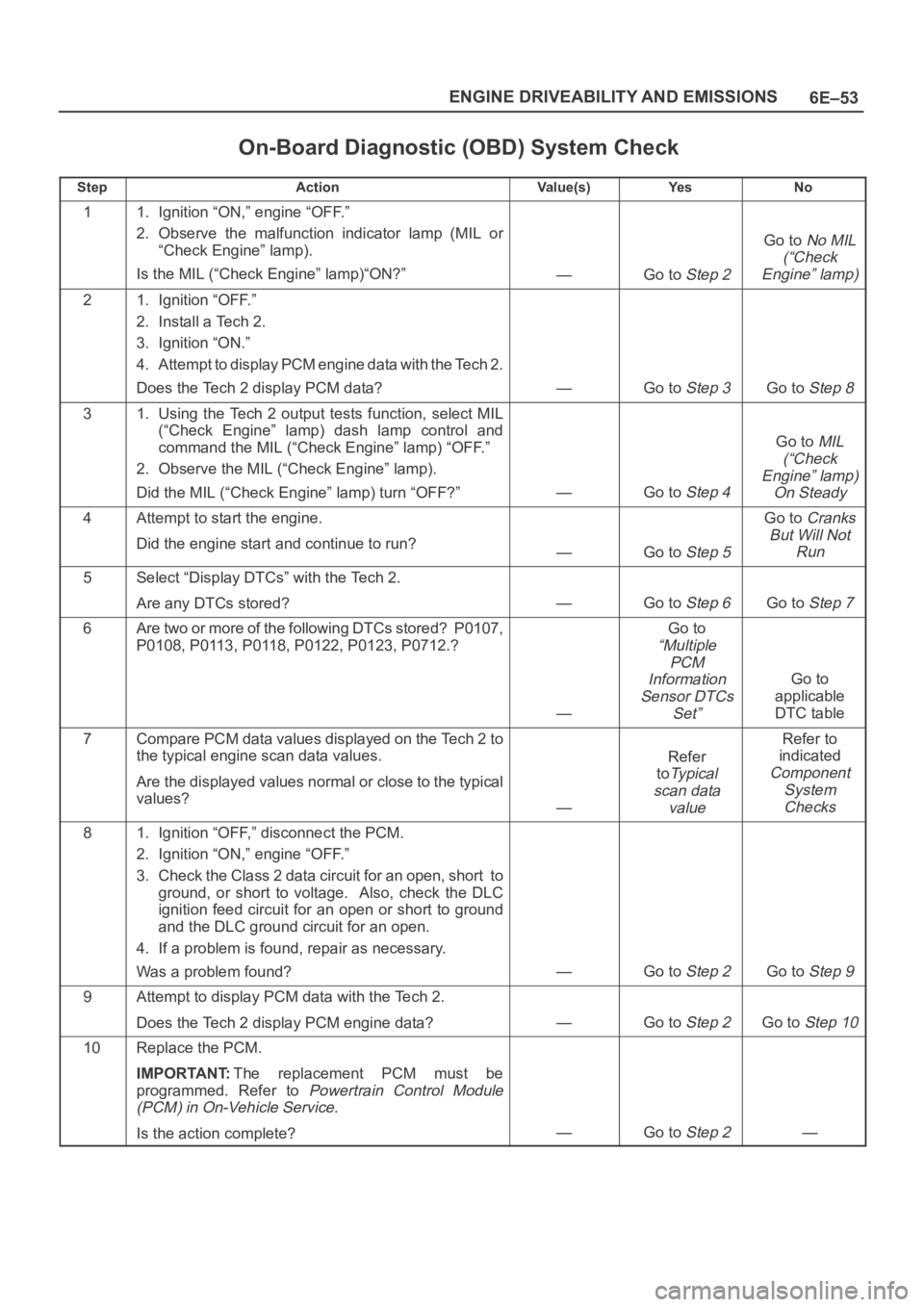
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
TS321119
Circuit Description
The on-board diagnostic system check is the starting
point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. Before
using this procedure, perform a careful visual/physical
check of the PCM and engine grounds for cleanliness and
tightness.
The on-board diagnostic system check is an organized
approach to identifying a problem created by an
electronic engine control system malfunction.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for poor connections or a damaged
harness. Inspect the PCM harness and connector for
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection,
and damaged harness.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1. The MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) should be “ON”
steady with the ignition “ON”/engine “OFF.” If not,
Chart A-1 should be used to isolate the malfunction.
2. Checks the Class 2 data circuit and ensures that the
PCM is able to transmit serial data.
3. This test ensures that the PCM is capable of
controlling the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) and the
MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) driver circuit is not
shorted to ground.
4. If the engine will not start, the
Cranks But Will Not
Run
chart should be used to diagnose the condition.
7. A Tech 2 parameter which is not within the typical
range may help to isolate the area which is causing
the problem.
Page 4710 of 6000
6E–53 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
11. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. Observe the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL or
“Check Engine” lamp).
Is the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp)“ON?”
—Go to Step 2
Go to No MIL
(“Check
Engine” lamp)
21. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Install a Tech 2.
3. Ignition “ON.”
4. Attempt to display PCM engine data with the Tech 2.
Does the Tech 2 display PCM data?
—Go to Step 3Go to Step 8
31. Using the Tech 2 output tests function, select MIL
(“Check Engine” lamp) dash lamp control and
command the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) “OFF.”
2. Observe the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp).
Did the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) turn “OFF?”
—Go to Step 4
Go to MIL
(“Check
Engine” lamp)
On Steady
4Attempt to start the engine.
Did the engine start and continue to run?
—Go to Step 5
Go to Cranks
But Will Not
Run
5Select “Display DTCs” with the Tech 2.
Are any DTCs stored?
—Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
6Are two or more of the following DTCs stored? P0107,
P0108, P0113, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0712.?
—
Go to
“Multiple
PCM
Information
Sensor DTCs
Set”
Go to
applicable
DTC table
7Compare PCM data values displayed on the Tech 2 to
the typical engine scan data values.
Are the displayed values normal or close to the typical
values?
—
Refer
to
Ty p i c a l
scan data
value
Refer to
indicated
Component
System
Checks
81. Ignition “OFF,” disconnect the PCM.
2. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
3. Check the Class 2 data circuit for an open, short to
ground, or short to voltage. Also, check the DLC
ignition feed circuit for an open or short to ground
and the DLC ground circuit for an open.
4. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Go to Step 2Go to Step 9
9Attempt to display PCM data with the Tech 2.
Does the Tech 2 display PCM engine data?
—Go to Step 2Go to Step 10
10Replace the PCM.
IMPORTANT:The replacement PCM must be
programmed. Refer to
Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) in On-Vehicle Service.
Is the action complete?—Go to Step 2—
Page 4711 of 6000

6E–54
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis
D06RW085
Circuit Description
When air conditioning and blower fan are selected, and if
the system has a sufficient refrigerant charge, a 12-volt
signal is supplied to the A/C request input of the
powertrain control module (PCM). The A/C request
signal may be temporarily canceled during system
operation by the electronic thermostat in the evaporator
case. The electronic thermostat may intermittently
remove the control circuit ground for the A/C thermostat
relay to prevent the evaporator from forming ice. When
the A/C request signal is received by the PCM, the PCM
supplies a ground from the compressor clutch relay if the
engine operating conditions are within acceptable
ranges. With the A/C compressor relay energized,
voltage is supplied to the compressor clutch coil.
The PCM will enable the compressor clutch to engage
whenever A/C has been selected with the engine running,
unless any of the following conditions are present:
The throttle is greater than 90%.
The ignition voltage is below 10.5 volts.
The engine speed is greater than 4500 RPM for 5
seconds or 5400 RPM.
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is greater than
125
C (257 F).
The intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 5C
(41
F).
The power steering pressure switch signals a cramped
position.
Diagnostic Aids
To diagnose an the intermittent fault, check for the
following conditions:
Poor connection at the PCM–Inspect connections for
backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.