display OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1247 of 6000
6E–130
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
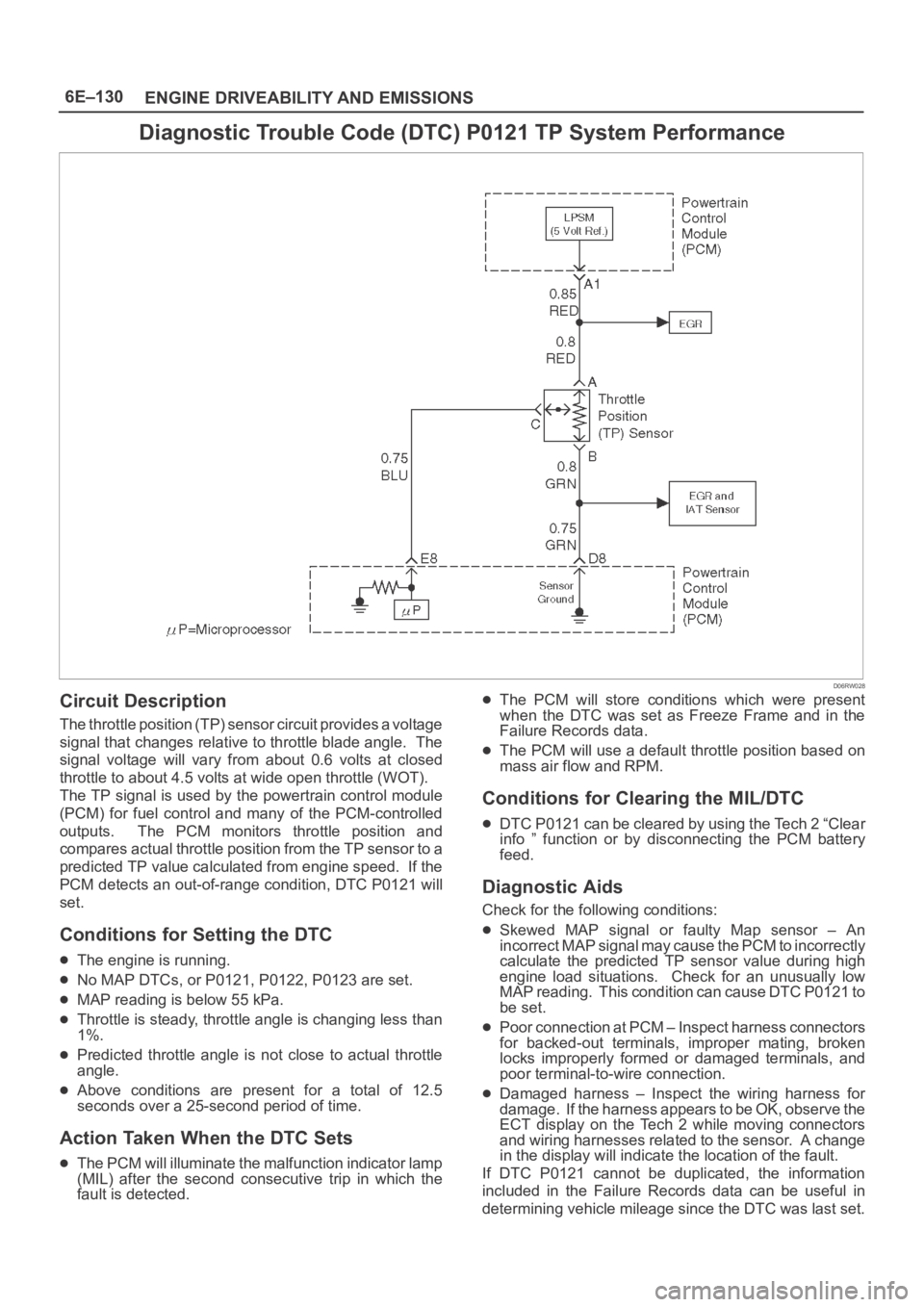
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0121 TP System Performance
D06RW028
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to throttle blade angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about 0.6 volts at closed
throttle to about 4.5 volts at wide open throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is used by the powertrain control module
(PCM) for fuel control and many of the PCM-controlled
outputs. The PCM monitors throttle position and
compares actual throttle position from the TP sensor to a
predicted TP value calculated from engine speed. If the
PCM detects an out-of-range condition, DTC P0121 will
set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The engine is running.
No MAP DTCs, or P0121, P0122, P0123 are set.
MAP reading is below 55 kPa.
Throttle is steady, throttle angle is changing less than
1%.
Predicted throttle angle is not close to actual throttle
angle.
Above conditions are present for a total of 12.5
seconds over a 25-second period of time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
The PCM will use a default throttle position based on
mass air flow and RPM.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0121 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
info ” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Skewed MAP signal or faulty Map sensor – An
incorrect MAP signal may cause the PCM to incorrectly
calculate the predicted TP sensor value during high
engine load situations. Check for an unusually low
MAP reading. This condition can cause DTC P0121 to
be set.
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0121 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Page 1250 of 6000
6E–133 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
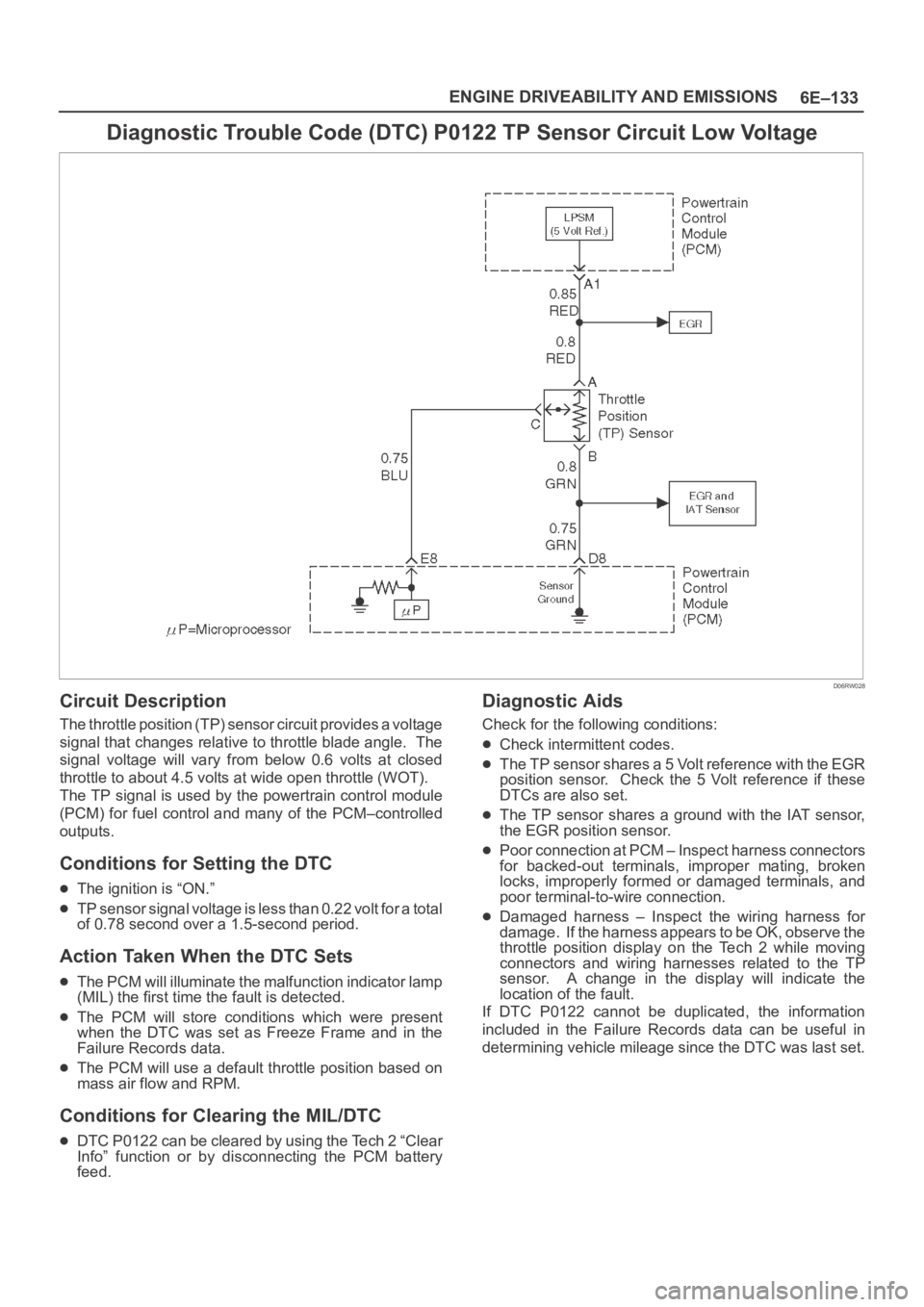
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0122 TP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
D06RW028
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to throttle blade angle. The
signal voltage will vary from below 0.6 volts at closed
throttle to about 4.5 volts at wide open throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is used by the powertrain control module
(PCM) for fuel control and many of the PCM–controlled
outputs.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ignition is “ON.”
TP sensor signal voltage is less than 0.22 volt for a total
of 0.78 second over a 1.5-second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
The PCM will use a default throttle position based on
mass air flow and RPM.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0122 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Check intermittent codes.
The TP sensor shares a 5 Volt reference with the EGR
position sensor. Check the 5 Volt reference if these
DTCs are also set.
The TP sensor shares a ground with the IAT sensor,
the EGR position sensor.
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
throttle position display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the TP
sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
If DTC P0122 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Page 1251 of 6000

6E–134
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DTC P0122 –TP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. With the throttle closed, observe the “TP Sensor”
display on the Tech 2.
Is the “TP Sensor” below the specified value?
0.22 VGo to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor the “DTC” info for DTC
P0122.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0122 failed?
—Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the TP sensor electrical connector.
3. Jumper the 5 volt reference “A” circuit and the TP
signal together at the TP sensor harness connector.
4. Ignition “ON.”
Observe the “TP Sensor” display on the Tech 2.
Is the “TP Sensor” at the specified value?
5 VGo to Step 10Go to Step 5
51. Disconnect jumper.
2. Connect a test light between B+ and the TP sensor
signal circuit at the TP sensor harness connector.
Observe the “TP Sensor” display on the Tech 2.
Is the “TP Sensor” at the specified value?
5 VGo to Step 6Go to Step 8
61. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the PCM and check the 5 volt reference
“A” circuit for an open or short to ground.
3. If the 5 volt reference “A” circuit is open or shorted to
ground, repair it as necessary.
Was the 5 volt reference “A” circuit open or shorted to
ground?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
7Check the 5 volt reference “A” circuit for a poor
connection at the PCM and replace the terminal if
necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
81. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the PCM, and check the TP signal
circuit for an open, short to ground, or short to the
sensor ground circuit.
3. If the TP sensor signal circuit is open or shorted to
ground, repair it as necessary.
Was the TP signal circuit open or shorted to ground?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
9Check the TP sensor signal circuit for a poor
connection at the PCM and replace the terminal if
necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
Page 1253 of 6000
6E–136
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
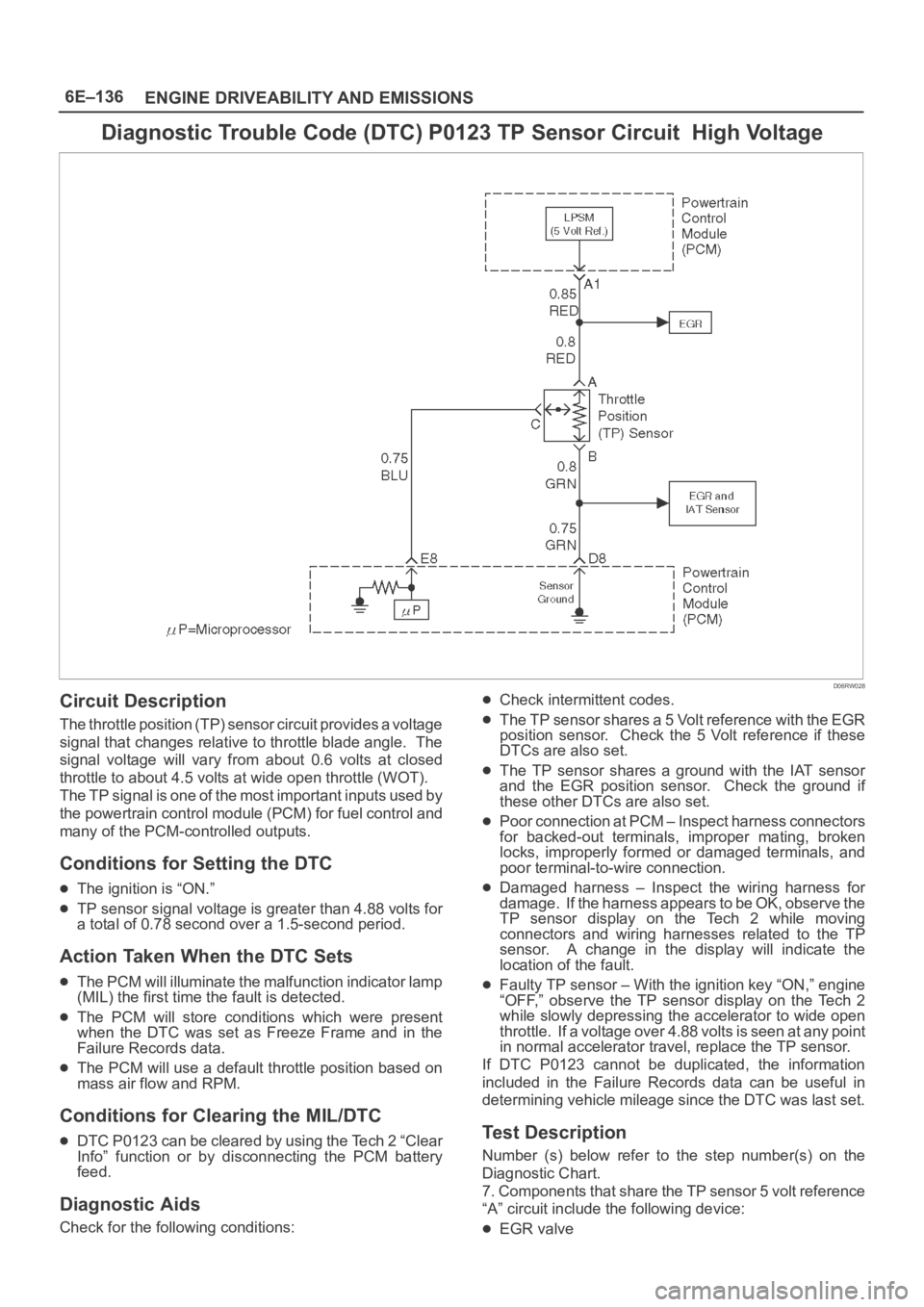
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0123 TP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
D06RW028
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to throttle blade angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about 0.6 volts at closed
throttle to about 4.5 volts at wide open throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is one of the most important inputs used by
the powertrain control module (PCM) for fuel control and
many of the PCM-controlled outputs.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ignition is “ON.”
TP sensor signal voltage is greater than 4.88 volts for
a total of 0.78 second over a 1.5-second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
The PCM will use a default throttle position based on
mass air flow and RPM.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0123 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Check intermittent codes.
The TP sensor shares a 5 Volt reference with the EGR
position sensor. Check the 5 Volt reference if these
DTCs are also set.
The TP sensor shares a ground with the IAT sensor
and the EGR position sensor. Check the ground if
these other DTCs are also set.
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
TP sensor display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the TP
sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Faulty TP sensor – With the ignition key “ON,” engine
“OFF,” observe the TP sensor display on the Tech 2
while slowly depressing the accelerator to wide open
throttle. If a voltage over 4.88 volts is seen at any point
in normal accelerator travel, replace the TP sensor.
If DTC P0123 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Test Description
Number (s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
7. Components that share the TP sensor 5 volt reference
“A” circuit include the following device:
EGR valve
Page 1254 of 6000
6E–137 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Disconnect the component while observing the TP
sensor display on the Tech 2. If the reading
changes drastically when this component isdisconnected, replace the component that affected
the reading.
DTC P0123 – TP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. With the throttle closed, observe the “TP Sensor”
display on the Tech 2.
Is the “TP Sensor” above the specified value?
4.88 VGo to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” info for DTC
P0123.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0123 failed.
—Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Disconnect the TP sensor electrical connector.
2. Observe the “TP Sensor” display on the Tech 2.
Is the “TP Sensor” near the specified value?
0 VGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Probe the sensor ground circuit at the TP sensor
harness connector with a test light connected to B+.
Is the test light “ON?”
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 10
61. Ignition “OFF,” disconnect the PCM.
2. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
3. Check for a short to voltage on the TP sensor signal
circuit.
4. If the TP sensor signal circuit is shorted, repair it as
necessary.
Was the TP sensor signal circuit shorted?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
71. Ignition “ON.”
2. Monitor the “TP Sensor” Tech 2 display while
disconnecting each of the components that share
the 5 volt reference “A” circuit (one at a time).
3. If the “TP Sensor” Tech 2 display changes, replace
the component that caused the display to change
when disconnected.
Does disconnecting any of these components cause
the “TP Sensor” display to change?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Ignition “OFF,” disconnect the PCM.
2. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF.”
3. Check for a short to B+ on the 5 volt reference “A”
circuit.
4. If the 5 volt reference “A” circuit is shorted, repair it
as necessary.
Was the 5 volt reference “A” circuit shorted?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
9Check for poor electrical connections at the TP sensor
and replace terminals if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
Page 1256 of 6000

6E–139 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0131 HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1
Sensor 1
060RW236
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a bias
voltage of about 450 mV between the heated oxygen
sensor (HO2S) signal high and signal low circuits. When
measured with a 10 megaohm digital voltmeter, this may
display as low as 350 mV. The oxygen sensor varies the
voltage within a range of about 1000 mV when the
exhaust is rich, down through about 10 mV when exhaust
is lean. The PCM constantly monitors the HO2S signal
during “closed loop” operation and compensates for a rich
or lean condition by decreasing or increasing injector
pulse width as necessary. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage
remains excessively low for an extended period of time,
DTC P0131 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No related DTCs.
Vehicle is operating in “closed loop.”
Engine coolant temperature is above 60C (140F).
“Closed loop” commanded air/fuel ratio is between
14.5 and 14.8.
Throttle angle is between 3% and 19%.
Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains below 22 mV
during normal “closed loop” operation for a total of 77
seconds over a 90-second period of time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
“Open loop” fuel control will be in effect.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0131 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Heated oxygen sensor wiring – The sensor pigtail may
be routed incorrectly and contacting the exhaust
system.
Poor PCM to engine block grounds.
Fuel pressure – The system will go lean if pressure is
too low. The PCM can compensate for some
decrease. However, If fuel pressure is too low, a DTC
P0131 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis.
Lean injector(s) – Perform “Injector Balance Test.”
Vacuum leaks – Check for disconnected or damaged
vacuum hoses and for vacuum leaks at the intake
manifold, throttle body, EGR system, and PCV system.
Exhaust leaks – An exhaust leak may cause outside air
to be pulled into the exhaust gas stream past the
Page 1259 of 6000

6E–142
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0132 HO2S Circuit High Voltage Bank 1
Sensor 1
060RW236
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a bias
voltage of about 450 mV between the heated oxygen
sensor (HO2S) signal and low circuits. When measured
with a 10 megaohm digital voltmeter, this may display as
low as 320 mV. The oxygen sensor varies the voltage
within a range of about 1000 mV when exhaust is rich,
down through about 10 mV when exhaust is lean. The
PCM constantly monitors the HO2S signal during “closed
loop” operation and compensates for a rich or lean
condition by decreasing or increasing injector pulse width
as necessary. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remains
excessively high for an extended period of time, DTC
P0132 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No related DTCs.
Engine coolant temperature is above 60C (140F)
“Closed loop” commanded air/fuel ratio is between
14.5 and 14.8.
Throttle angle is between 3% and 19%.
Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains above 952 mV
during normal “closed loop” operation for a total of 77
seconds over a 90-second period.
OR
Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains above 500 mV
during “deceleration fuel cutoff mode” operation for 3
seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
“Open loop” fuel control will be in effect.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0132 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check the following items:
Fuel pressure – The system will go rich if pressure is
too high. The PCM can compensate for some
increase. However, if fuel pressure is too high, a DTC
P0132 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis.
Perform “Injector Balance Test” – Refer to Fuel System
Diagnosis.
MAF sensor –The system can go rich if MAF sensor
signal indicates an engine airflow measurement that is
not correct. Disconnect the MAF sensor to see it the
rich condition is corrected. If so, replace the MAF
sensor.
Check for a leak in the fuel pressure regulator
diaphragm by checking the vacuum line to the
regulator for the presence of fuel. There should be no
fuel in the vacuum line.
Page 1260 of 6000

6E–143 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
An intermittent TP sensor output will cause the system
to go rich due to a false indication of the engine
accelerating.
Shorted Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) –If the HO2S
is internally shorted, the HO2S voltage displayed on
the Tech 2 will be over 1 volt. Try disconnecting the
affected HO2S with the key “ON,” engine “OFF.” If the
displayed HO2S voltage changes from over 1000 mV
to around 450 mV, replace the HO2S. Silicon
contamination of the HO2S can also cause a high
HO2S voltage to be indicated. This condition is
indicated by a powdery white deposit on the portion of
the HO2S exposed to the exhaust stream. If
contamination is noticed, replace the affected HO2S.
Open HO2S Signal Circuit or Faulty HO2S–A poor
connection or open in the HO2S signal circuit can
cause the DTC to set during deceleration fuel mode.
A n H O 2 S w h i c h i s f a u l t y a n d n o t a l l o w i n g a f u l l v o l t a g e
swing between the rich and lean thresholds can also
cause this condition. Operate the vehicle by
monitoring the HO2S voltage with a Tech 2. If theHO2S voltage is limited within a range between 300
mV to 600 mV, check the HO2S signal circuit wiring
and associated terminal conditions.
If none of the above conditions are present, replace the
affected HO2S.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
3. DTC P0132 failing during “deceleration fuel cutoff
mode” operation may indicate a condition described
in the “Diagnostic Aids” above. If the DTC P0132
test passes while the Failure Records conditions are
being duplicated, an intermittent condition is
indicated.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0132 – HO2S Circuit High Voltage Bank 1 Sensor 1
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Install the Tech 2.
2. Run the engine at operating temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within parameters specified
under “Conditions for Setting the DTC” included in
Diagnostic Support.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage.
Does the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remain above the
specified value?
952 mV (500
mV in
deceleration
fuel cutoff
mode)
Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Ignition “ON,” review and record Tech 2 Failure
Records data.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” info for DTC
P0132 until the DTC P0132 test runs.
4. Note the test result.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0132 failed this
ignition?
—Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect Bank 1 HO2S 1.
3. Ignition “ON.”
4. At HO2S Bank 1 Sensor 1 connector (PCM side)
use a DVM to measure voltages at the high and low
signal terminals.
Are the voltages in the specified range?
3-4 VGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair short to voltage in signal circuit.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 1262 of 6000

6E–145 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
D i a g n o s t i c Tr o u b l e C o d e ( D T C ) P 0 1 3 4 H O 2 S C i r c u i t I n s u f f i c i e n t Activity Bank 1
Sensor 1
060RW237
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a bias
voltage of about 450 mV between the heated oxygen
s e n s o r ( H O 2 S ) h i g h a n d l o w c i r c u i t s . W h e n m e a s u r e d
with a 10 megaohm digital voltmeter, this may display
as low as 320 mV. The oxygen sensor varies the
voltage within a range of about 1000 mV when the
exhaust is rich, down through about 10 mV when
exhaust is lean. The PCM constantly monitors the
HO2S signal during “closed loop” operation and
compensates for a rich or lean condition by decreasing
or increasing injector pulse width as necessary. If the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remains at or near the 450 mV
bias for an extended period of time, DTC P0134 will be
set, indicating an open sensor signal or sensor low
circuit.
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the
amount of time required for “closed loop” fuel control
operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring.
The oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the
amount of time required for fuel control sensors Bank
1 HO2S 1 and Bank 2 HO2S 1 to become active.
Oxygen sensor heaters are required by post-catalyst
monitor sensors to maintain a sufficiently high
temperature for accurate exhaust oxygen content
readings further from the engine.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No related DTCs.
Battery voltage is above 10 volts.
Engine run time is longer than 40 seconds.
Oxygen sensor heater has been determined to be
functioning properly.
Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains between
400 mV and 500 mV for a total of 77 seconds over a
90-second period of time.
Action Take When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
“Open loop” fuel control will be in effect.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0134 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
harness connectors for backed-out terminals,
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection,
and damaged harness.
Faulty HO2S heater or heater circuit – With the ignition
“ON,” engine “OFF,” after a cool down period, the
HO2S 1 voltage displayed on Tech 2 is normally
455-460 mV. A reading over 1000 mV indicates a
signal line shorted to voltage. A reading under 5 mV
Page 1265 of 6000

6E–148
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0151 HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 2
Sensor 1
060RW190
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a bias
voltage of about 450 mV between the heated oxygen
sensor (HO2S) signal high and signal low circuits. When
measured with a 10 megaohm digital voltmeter, this may
display as low as 320 mV. The oxygen sensor varies the
voltage within a range of about 1000 mV when the
exhaust is rich, down through about 10 mV when exhaust
is lean. The PCM constantly monitors the HO2S signal
during “closed loop” operation and compensates for a rich
or lean condition by decreasing or increasing injector
pulse width as necessary. If the Bank 2 HO2S 1 voltage
remains excessively low for an extended period of time,
DTC P0151 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No related DTCs.
The engine is operating in “closed loop.”
Engine coolant temperature is above 60C (140F).
“Closed loop” commanded air/fuel ratio is between
14.5 and 14.8.
Throttle angle is between 3% and 19%.
Bank 2 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains below 22 mV
during normal “closed loop” operation for a total of 77
seconds over a 90-second period of time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
“Open loop” fuel control will be in effect.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0151 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Heated oxygen sensor wiring – The sensor pigtail may
be mispositioned and contacting the exhaust system.
Poor PCM to engine block grounds.
Fuel pressure – The system will go lean if pressure is
too low. The PCM can compensate for some
decrease. However, if fuel pressure is too low, a DTC
P0151 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis.
Lean injector(s) – Perform “Injector Balance Test.”
Vacuum leaks – Check for disconnected or damaged
vacuum hoses and for vacuum leaks at the intake
manifold, throttle body, EGR system, and PCV system.
Exhaust leaks – An exhaust leak may cause outside air
to be pulled into the exhaust gas stream past the
HO2S, causing the system to appear lean. Check for