load capacity OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1084 of 6000

ENGINE ELECTRICAL6D1–5
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Model (JIS)95D31R–MF80D26R–MF75D26R–MF
Voltage (V)121212
Cold Cranking Performance (Amp)622582490
Reserve Capacity (Min)159133123
Load Test (Amp)310290245
Fast Charge Maximum Amperage (Amp)202020
BCI Group No.272424
Page 1737 of 6000
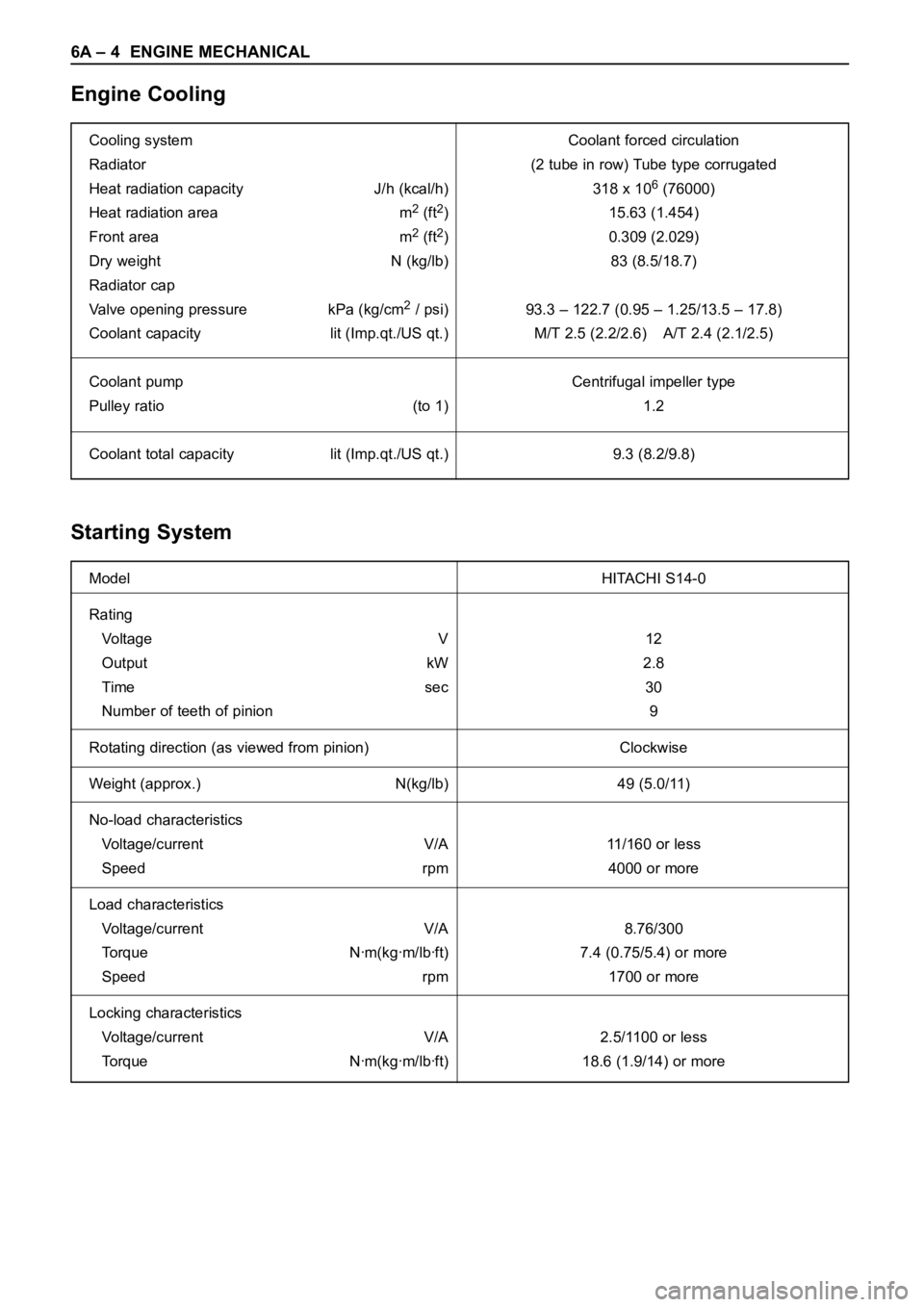
6A – 4 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Engine Cooling
Starting System
Cooling system Coolant forced circulation
Radiator (2 tube in row) Tube type corrugated
Heat radiation capacity J/h (kcal/h) 318 x 10
6(76000)
Heat radiation area m
2(ft2) 15.63 (1.454)
Front area m
2(ft2) 0.309 (2.029)
Dry weight N (kg/lb) 83 (8.5/18.7)
Radiator cap
Valve opening pressure kPa (kg/cm
2/ psi) 93.3 – 122.7 (0.95 – 1.25/13.5 – 17.8)
Coolant capacity lit (Imp.qt./US qt.) M/T 2.5 (2.2/2.6) A/T 2.4 (2.1/2.5)
Coolant pump Centrifugal impeller type
Pulley ratio (to 1) 1.2
Coolant total capacity lit (Imp.qt./US qt.) 9.3 (8.2/9.8)
Model HITACHI S14-0
Rating
Vo l t a ge V 1 2
Output kW 2.8
Time sec 30
Number of teeth of pinion 9
Rotating direction (as viewed from pinion) Clockwise
Weight (approx.) N(kg/lb) 49 (5.0/11)
No-load characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 11/160 or less
Speed rpm 4000 or more
Load characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 8.76/300
Torque Nꞏm(kgꞏm/lbꞏft) 7.4 (0.75/5.4) or more
Speed rpm 1700 or more
Locking characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 2.5/1100 or less
Torque Nꞏm(kgꞏm/lbꞏft) 18.6 (1.9/14) or more
Page 1871 of 6000

6D – 4 ENGINE ELECTRICAL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF THE
BATTERY
REMOVAL
1. Negative cable
2. Positive cable
3. Retainer screw and rods
4. Retainer
5. Battery
INSTALLATION
To install the battery, follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order, noting the following points:
1. Make sure that the rod is hooked on the body side.
065RW029
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
Model (JIS) 80D26R–MF 75D26R–MF
Voltage (V) 12 12
Cold-Cranking Performance (Amp) 582 490
Reserve Capacity (Min) 133 123
Load Test (Amp) 300 300
Fast Charge Maximum Amperage (Amp) 6.5 6.5
Page 2597 of 6000

The chassis electrical system is a 12–volt system with a
negative ground polarity.
Wire size are appropriate to respective circuits, and
classified by color. (The classification of harnesses by
color is shown on the circuit diagram for ease of harness
identification.)
The wire size is determined by load capacity and the
length of wire required.
The vehicle harnesses are: body harness, chassis
harness, engine room harness, instrument harness,
transmission harness, engine ECGI harness, dome light
harness, door harness, rear body harness, tailgate
harness, SRS harness and battery cables.
The harnesses are protected either by tape or corrugated
tube, depending on harness location.
The circuit for each system consists of the power source,
wire, fuse, relay, switch, load parts and ground, all of
which are shown on the circuit diagram.
In this section, each electrical device is classified by
system.
For major parts shown on the circuit based on the circuit
diagram for each system, a summary, diagnosis of
troubles and inspection procedures are detailed.
Notes for Working on Electrical
Items
Disconnecting the Battery Cable
1. All switches should be in the “OFF” position.
2. Disconnect the battery ground cable (2).
3. Disconnect the battery positive cable (1).
CAUTION: It is important that the battery ground
cable be disconnected first. Disconnecting the
battery positive cable first can result in a short circuit.
Connecting the Battery Cable
Follow the disconnecting procedure in the reverse order.CAUTION: Clean the battery terminal and apply a
light coat of grease to prevent terminal corrosion.
Disconnecting the Connector
Some connectors have a tang lock to hold the connectors
together during vehicle operation.
Some tang locks are released by pulling them towards
you (1).
Other tang locks are released by pressing them forward
(2).
Determine which type of tang lock is on the connector
being handled.
Firmly grasp both sides (male and female) of the
connector (3).
Release the tang lock and carefully pull the two halves of
the connector apart.
Never pull on the wires to separate the connectors (4).
2
1
General Description
1
2
3
4
Page 2606 of 6000

Wiring – Wire Size
The size of wire used in a circuit is determined by the
amount of current (amperage), the length of the circuit,
and the voltage drop allowed. The following wire size and
load capacity, shown below, are specified by AWG
(American Wire Gauge). (Nominal size means
approximate cross sectional area (1).)
Wiring – Wire Size Table
Nominal sizeCross sectional Outside diameter Allowable
area (mm2) (mm) current (A)
0.3 0.372 1.5 9
0.5 0.563 1.7 12
0.85 0.885 1.9 16
1.25 1.287 2.2 21
22.0912.728
3 3.296 3.6 37.5
55.2274.453
87.9525.567
15 13.36 7.0 75
20 20.61 8.2 97
1
Page 2609 of 6000

Circuit Breaker
The circuit breaker is a protective device designed to
open the circuit when a current load is in excess of rated
breaker capacity. If there is a short or other type of
overload condition in the circuit, the excessive current will
open the circuit between the circuit breaker terminals.
The reset knob (1) pops out when the circuit is open. Push
the reset knob in place to restore the circuit after repairing
it.
Relay
Battery and load location may require that a switch be
placed some distance from either component. This
means a longer wire and a higher voltage drop (1).
The installation of a relay between the battery and the
load reduces the voltage drop (2).
Because the switch controls the relay, amperage through
the switch can be reduced.
LOAD
12LOAD
RELAY
D08RW404
1
Page 4624 of 6000

ENGINE ELECTRICAL6D1–5
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Model (JIS)95D31R–MF80D26R–MF75D26R–MF
Voltage (V)121212
Cold Cranking Performance (Amp)622582490
Reserve Capacity (Min)159133123
Load Test (Amp)310290245
Fast Charge Maximum Amperage (Amp)202020
BCI Group No.272424
Page 5277 of 6000

6A – 4 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Engine Cooling
Starting System
Cooling system Coolant forced circulation
Radiator (2 tube in row) Tube type corrugated
Heat radiation capacity J/h (kcal/h) 318 x 10
6(76000)
Heat radiation area m
2(ft2) 15.63 (1.454)
Front area m
2(ft2) 0.309 (2.029)
Dry weight N (kg/lb) 83 (8.5/18.7)
Radiator cap
Valve opening pressure kPa (kg/cm
2psi) 93.3 – 122.7 (0.95 – 1.25/13.5 – 17.8)
Coolant capacity lit (Imp.qt./US qt.) M/T 2.5 (2.2/2.6) A/T 2.4 (2.1/2.5)
Coolant pump Centrifugal impeller type
Pulley ratio 1.2
Coolant total capacity lit (Imp.qt./US qt.) 9.3 (8.2/9.8)
Model HITACHI S14-0
Rating
Voltage V 12
Output kW 2.8
Time sec 30
Number of teeth of pinion 9
Rotating direction (as viewed from pinion) Clockwise
Weight (approx.) N(kg/lb) 49 (5.0/11)
No-load characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 11/160 or less
Speed rpm 4000 or more
Load characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 8.76/300
Torque Nꞏm(kgꞏm/lbꞏft) 7.4 (0.75/5.4) or more
Speed rpm 1700 or more
Locking characteristics
Voltage/current V/A 2.5/1100 or less
Torque Nꞏm(kgꞏm/lbꞏft) 18.6 (1.9/14) or more
Page 5407 of 6000

6D – 4 ENGINE ELECTRICAL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF THE
BATTERY
REMOVAL
1. Negative cable
2. Positive cable
3. Retainer screw and rods
4. Retainer
5. Battery
INSTALLATION
To install the battery, follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order, noting the following points:
1. Make sure that the rod is hooked on the body side.
065RW029
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
Model (JIS) 80D26R–MF 75D26R–MF
Voltage (V) 12 12
Cold-Cranking Performance (Amp) 582 490
Reserve Capacity (Min) 133 123
Load Test (Amp) 300 300
Fast Charge Maximum Amperage (Amp) 6.5 6.5