remote start OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 2121 of 6000

6E–228
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Description (Air Induction)
Air Induction System
The air induction system filters contaminants from the
outside air, and directs the progress of the air as it is
drawn into the engine. A remote-mounted air cleaner
prevents dirt and debris in the air from entering the
engine. The air duct assembly routes filtered air to the
throttle body. Air enters the engine by to following steps:
1. Through the throttle body.
2. Into the intake manifold.
3. Through the cylinder head intake ports.
4. Into the cylinders.
General Description (Fuel Metering)
Deceleration Mode
The ECM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the Accelerator position.
Fuel Injector
Fuel injector comprises the solenoid, hydraulic line, and
fuel line. Fuel injection is controlled by the continuity time
signal and continuity start timing signal from ECM to the
solenoid
ECM determines the running conditions of engine by
input signals such as engine speed. Accelerator throttle
valve opening, and engine coolant temperature, thereby
to send the solenoid the best suited signal to the engine
status. When current is carried to the solenoid, the
armature opens the poppet valve to alow high pressure oil
to run into the injector. Under the pressure of the oil, the
piston and plunger are depressed to compress the fuel in
the combustion chamber of the plunger. Specifically, the
pressure of the fuel compressed is increased by a piston
top/ plunger bottom area ratio over the pressure of high
pressure oil, thereby lifting the fuel nozzle end needle for
injecting fuel.
Fuel Metering System Components
The fuel metering system is made up of the following
parts:
The fuel injectors.
The intake throttle body.
The Accelerator position (AP) sensor
The ECM.
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
Basic System Operation
Fuel is supplied through fuel filter to the fuel pump.
The fuel pump is installed to the oil pump, and fuel is
forced, through the fuel pump outlet, pipe and cylinder
head inside, into the fuel injector.
An orifice is provided at the rear fuel outlet of cylinder
head to control the pressure of oil.The injector is controlled by ECM which gives
opening/closing commands to the solenoid installed on
the top of the injector. Opening/closing operation of the
pressurized engine oil circuit of the injector controls fuel
injection quantity, fuel injection timing, etc.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the ECM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control head. The ECM uses this to adjust the
idle speed.
Refer to
A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring
diagrams and diagnosis for A/C electrical system.
General Description Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) System
EGR Purpose
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is use to
reduce emission levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx
emission levels are caused by a high combustion
temperature. The EGR system lowers the NOx emission
levels by decreasing the combustion temperature.
The ECM uses information from the following sensors to
control EGR valve boost pressure.
ECT
ITP
Engine Speed
AP sensor
Page 2993 of 6000
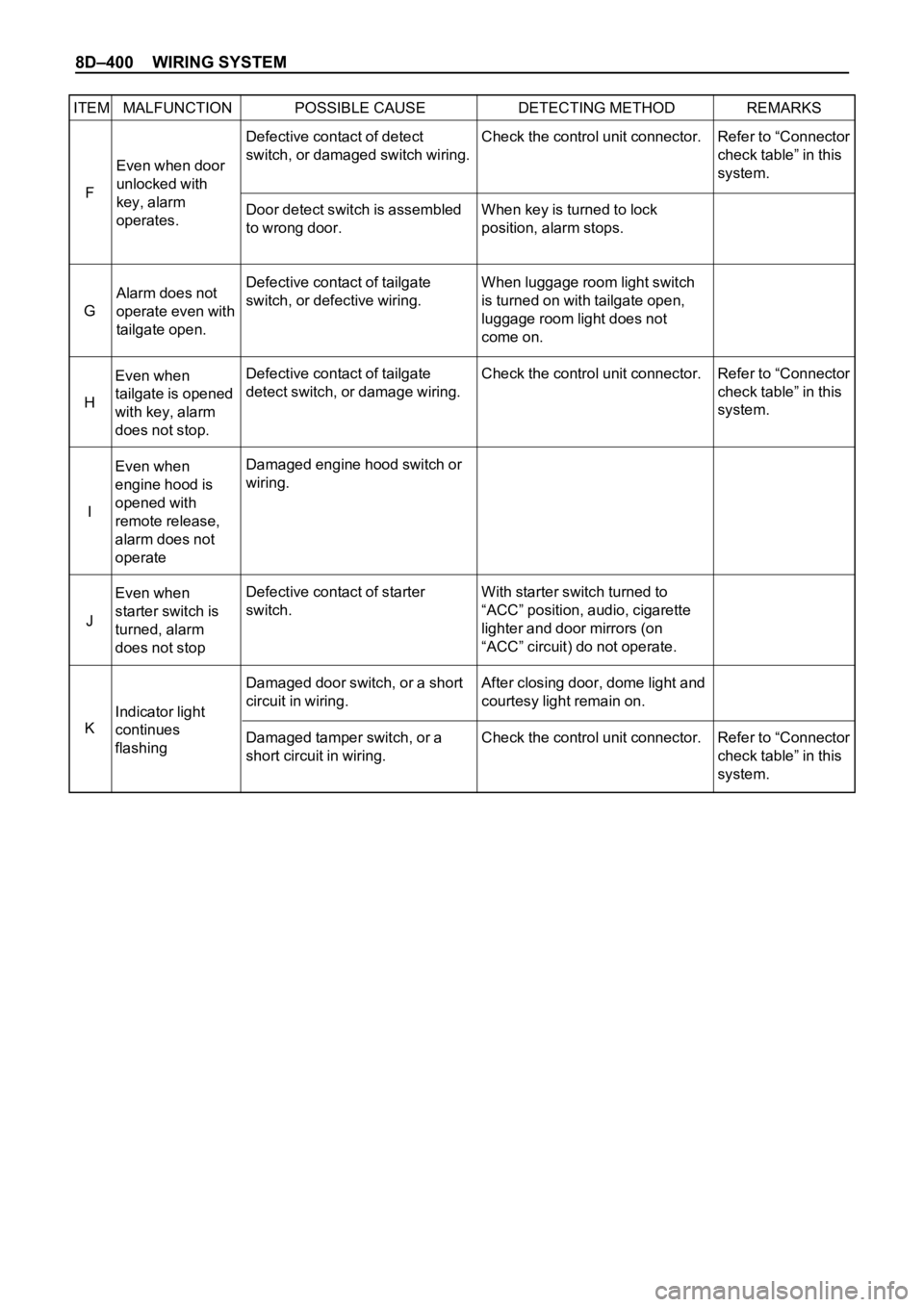
8D–400 WIRING SYSTEM
ITEM MALFUNCTION POSSIBLE CAUSE DETECTING METHOD REMARKS
Even when door
unlocked with
key, alarm
operates.
Alarm does not
operate even with
tailgate open.
Even when
tailgate is opened
with key, alarm
does not stop.
Even when
engine hood is
opened with
remote release,
alarm does not
operate
Even when
starter switch is
turned, alarm
does not stop
Indicator light
continues
flashingRefer to “Connector
check table” in this
system.
Refer to “Connector
check table” in this
system.
Refer to “Connector
check table” in this
system. Defective contact of detect
switch, or damaged switch wiring.
Door detect switch is assembled
to wrong door.
Defective contact of tailgate
switch, or defective wiring.
Defective contact of tailgate
detect switch, or damage wiring.
Damaged engine hood switch or
wiring.
Defective contact of starter
switch.
Damaged door switch, or a short
circuit in wiring.
Damaged tamper switch, or a
short circuit in wiring.Check the control unit connector.
When key is turned to lock
position, alarm stops.
When luggage room light switch
is turned on with tailgate open,
luggage room light does not
come on.
Check the control unit connector.
With starter switch turned to
“ACC” position, audio, cigarette
lighter and door mirrors (on
“ACC” circuit) do not operate.
After closing door, dome light and
courtesy light remain on.
Check the control unit connector. F
G
H
I
J
K
Page 5657 of 6000

6E–228
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Description (Air Induction)
Air Induction System
The air induction system filters contaminants from the
outside air, and directs the progress of the air as it is
drawn into the engine. A remote-mounted air cleaner
prevents dirt and debris in the air from entering the
engine. The air duct assembly routes filtered air to the
throttle body. Air enters the engine by to following steps:
1. Through the throttle body.
2. Into the intake manifold.
3. Through the cylinder head intake ports.
4. Into the cylinders.
General Description (Fuel Metering)
Deceleration Mode
The ECM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the Accelerator position.
Fuel Injector
Fuel injector comprises the solenoid, hydraulic line, and
fuel line. Fuel injection is controlled by the continuity time
signal and continuity start timing signal from ECM to the
solenoid
ECM determines the running conditions of engine by
input signals such as engine speed. Accelerator throttle
valve opening, and engine coolant temperature, thereby
to send the solenoid the best suited signal to the engine
status. When current is carried to the solenoid, the
armature opens the poppet valve to alow high pressure oil
to run into the injector. Under the pressure of the oil, the
piston and plunger are depressed to compress the fuel in
the combustion chamber of the plunger. Specifically, the
pressure of the fuel compressed is increased by a piston
top/ plunger bottom area ratio over the pressure of high
pressure oil, thereby lifting the fuel nozzle end needle for
injecting fuel.
Fuel Metering System Components
The fuel metering system is made up of the following
parts:
The fuel injectors.
The intake throttle body.
The Accelerator position (AP) sensor
The ECM.
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
Basic System Operation
Fuel is supplied through fuel filter to the fuel pump.
The fuel pump is installed to the oil pump, and fuel is
forced, through the fuel pump outlet, pipe and cylinder
head inside, into the fuel injector.
An orifice is provided at the rear fuel outlet of cylinder
head to control the pressure of oil.The injector is controlled by ECM which gives
opening/closing commands to the solenoid installed on
the top of the injector. Opening/closing operation of the
pressurized engine oil circuit of the injector controls fuel
injection quantity, fuel injection timing, etc.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the ECM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control head. The ECM uses this to adjust the
idle speed.
Refer to
A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring
diagrams and diagnosis for A/C electrical system.
General Description Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) System
EGR Purpose
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is use to
reduce emission levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx
emission levels are caused by a high combustion
temperature. The EGR system lowers the NOx emission
levels by decreasing the combustion temperature.
The ECM uses information from the following sensors to
control EGR valve boost pressure.
ECT
ITP
Engine Speed
AP sensor